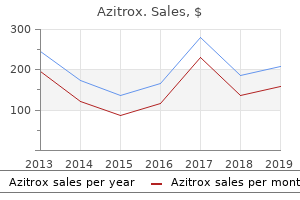
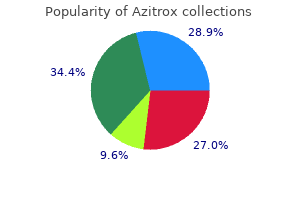
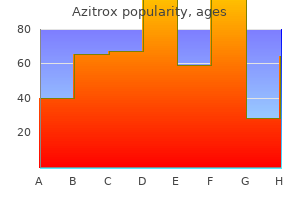
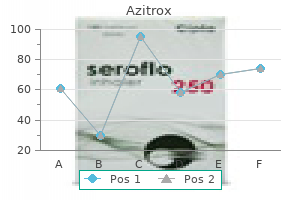
Azitrox
Louanne Hudgins, M.D. - Division of Medical Genetics/Dept. Pediatrics
- Stanford University
- Stanford, California
Generic azitrox 500 mg with mastercardIncrease in luminal mast cell and epithelial harm may account for elevated airway responsiveness after viral infection in canines virus sickens midwest purchase azitrox 100 mg on line. Activation of mast cells by immunoglobulin E-receptor cross-linkage antibiotic eye drops over the counter quality azitrox 100 mg, but not by way of adenosine receptors antibiotic invention order azitrox 250 mg on-line, induces A1 expression and promotes survival bacteria grade 8 purchase 250 mg azitrox with visa. Microenvironmental regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and nitric oxide production in mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells. Atopic and nonatopic eosinophilic oesophagitis are distinguished by immunoglobulin E-bearing intraepithelial mast cells. Cre exercise causes widespread apoptosis and deadly anemia during embryonic development. Identification of semaphorin 4B as a negative regulator of basophil-mediated immune responses. Basophils orchestrate chronic allergic dermatitis and protecting immunity towards helminths. IgE-dependent activation of sphingosine kinases 1 and a pair of and secretion of sphingosine 1-phosphate requires Fyn kinase and contributes to mast cell responses. Requirement of interaction between mast cells and skin dendritic cells to establish contact hypersensitivity. Basophils are required for the induction of Th2 immunity to haptens and peptide antigens. Characterisation of effector mechanisms at the host:parasite interface in the course of the immune response to tissue-dwelling intestinal nematode parasites. Release of mast cell tryptase from human colorectal mucosa in inflammatory bowel illness. Selective ablation of mast cells or basophils reduces peanut-induced anaphylaxis in mice. Exogenous dendritic cell homing to draining lymph nodes may be boosted by mast cell degranulation. Mast cells induce migration of dendritic cells in a murine mannequin of acute allergic airway disease. Mast cell-derived tumour necrosis factor is important for allergic airway disease. Role of mast cells and basophils in IgE responses and in allergic airway hyperresponsiveness. Mouse mast cell protease-4 deteriorates renal perform by contributing to irritation and fibrosis in immune complex-mediated glomerulonephritis. Interferon- regulates growth and controls Fc receptor expression and activation in human intestinal mast cells. Thymic stromal lymphopoietinmediated extramedullary hematopoiesis promotes allergic irritation. Nonspecific B and T cell-stimulatory exercise mediated by mast cells is related to exosomes. Basophils operate as antigen-presenting cells for an allergeninduced T helper type 2 response. Food allergy natural formula 2 safety against peanut anaphylactic reaction is by way of inhibition of mast cells and basophils. Synthetic mast-cell granules as adjuvants to promote and polarize immunity in lymph nodes. Leptin enhances survival and induces migration, degranulation, and cytokine synthesis of human basophils. A key role for mast cell chymase within the activation of pro-matrix metalloprotease-9 and pro-matrix metalloprotease-2. Evidence of pathway-specific basophil anergy induced by peanut oral immunotherapy in peanut-allergic kids. Fc receptors on mast cells: activatory and inhibitory regulation of mediator launch. Basophils preferentially specific mouse Mast Cell Protease 11 among the mast cell tryptase family in contrast to mast cells. Psychological stress and corticotropin-releasing hormone improve intestinal permeability in people by a mast celldependent mechanism. Mast cells are important mediators of vaccine-induced Helicobacter clearance in the mouse mannequin. Selective ablation of basophils in mice reveals their nonredundant role in acquired immunity towards ticks. Mouse mast cell protease 4 is the major chymase in murine airways and has a protecting position in allergic airway inflammation. Allergen-specific basophil suppression related to clinical tolerance in patients with milk allergy. Histochemical and ultrastructural modification of mucosal mast cell granules in parasitized mice lacking the -chymase, mouse mast cell protease-1. Fluorescent willpower of avidin binding and immunofluorescent willpower of chymase, tryptase, and carboxypeptidase content material. Leukotriene B4, an activation product of mast cells, is a chemoattractant for their progenitors. Mast cells can amplify airway reactivity and features of continual inflammation in an bronchial asthma mannequin in mice. IgE-receptor activation induces survival and Bfl-1 expression in human mast cells but not basophils. Protease phenotype of constitutive connective tissue and of induced mucosal mast cells in mice is regulated by the tissue. Therapeutic impact of kakkonto in a mouse mannequin of meals allergy with gastrointestinal symptoms. Role of mast cells in intestinal mucosal function: research in models of hypersensitivity and stress. Signals from kind 1 sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors enhance adult mouse cardiac myocyte survival throughout hypoxia. During wholesome states, eosinophils usually characterize only a small proportion (1�3%) of white blood cells in the bone marrow and blood, and low levels of eosinophils are current in a number of tissues. This early, flora-independent localization strongly contrasts with the homing patterns of many of the other leukocytes (conventional lymphocytes and mast cells) (Ferguson and Parrott, 1972a,b; Watkins et al. Indeed, important studies have elucidated that constitutively expressed chemokines (eotaxins) critically regulate the tissue distribution of eosinophils, offering a molecular mechanism to regulate the tissue distribution of eosinophils. The eosinophil lineage is assumed to be shared with the basophil lineage due to the identification of immature cells that co-express eosinophilic and basophilic staining characteristics, the presence of shared molecules in these cell types. If innate immunity may have an result on eosinophil lineage setup, pathogens and setting would play an important function in eosinophil manufacturing, opening a brand new avenue for antieosinophil pharmaceutical interventions. Therefore, this eosinopoietic deficit renders this line appropriate for eosinophil operate studies, in addition to adoptive switch of eosinophils (Walsh et al. These three development components, also called eosinophilopoietins, bind to a heterodimeric receptor that contains a typical chain (c) and a unique cytokine-specific chain.
Purchase 500mg azitrox fast deliveryFinally antibiotic resistance in agriculture purchase 250 mg azitrox mastercard, there are refined however significant differences in IgA and its receptors between humans and different mammals antibiotics for uti ppt purchase azitrox 250 mg fast delivery, notably mice natural antibiotics for acne treatment azitrox 100mg without prescription, that confound the extrapolation of findings from one species to another antibiotic groups purchase azitrox 250mg fast delivery. Defining the functions of IgA therefore requires defining the context of the query. Adherence-inhibitory intestinal immunoglobulin A antibody response in baboons elicited by use of an artificial intranasal lectin-based amebiasis subunit vaccine. Exposure of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium to a protecting monoclonal IgA triggers exopolysaccharide production through a diguanylate cyclase-dependent pathway. Analysis of the roles of antilipopolysaccharide and anti-cholera toxin immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibodies in proptection towards Vibrio cholerae and cholera toxin by use of monoclonal IgA antibodies in vivo. Neutralization of influenza virus by low concentrations of hemagglutinin-specific polymeric Ig A inhibits viral fusion activity, but activation of the ribonucleoprotein can be inhibited. IgA immunodeficiency leads to insufficient Th cell priming and elevated susceptibility to influenza virus an infection. Protection against influenza virus infection in polymeric Ig receptor knockout mice immunized intranasally with adjuvant-combined vaccines. Heavy-chain isotype patterns of human antibody-secreting cells induced by Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccines in relation to age and preimmunity. Secretory IgA induces antigen-independent eosinophil survival and cytokine manufacturing with out inducing effector capabilities. Allergen-reactive antibodies are present in nasal fluids from sufferers with birch pollen-induced intermittent allergic rhinitis, however not in healthy controls. Passive acquired mucosal immunity to group A streptococci by secretory immunoglobulin A. Translocalized IgA mediates neutralization and stimulates innate immunity inside infected cells. Urease-specific monoclonal antibodies prevent Helicobacter felis infection in mice. IgA is important for clearance and critical for defense from rotavirus an infection. Secretory IgA-mediated neutralization of Shigella flexneri prevents intestinal tissue destruction by down-regulating inflammatory circuits. The medical condition of IgA-deficient sufferers is expounded to the proportion of IgD- and IgM-producing cells of their nasal mucosa. Expression of the high-affinity receptor for IgE on bronchial epithelial cells of asthmatics. Frequency of selective IgA deficiency amongst Brazilian blood donors and healthy pregnant girls. Interference of coronavirus infection by expression of immunoglobulin G (IgG) or IgA virus-neutralizing antibodies. Immunochemical and functional studies of Actinomyces viscosus T14V type 1 fimbriae with monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies directed against the fimbrial subunit. Protective efficacy of major outer membrane protein-specific immunoglobulin A (IgA) and IgG monoclonal antibodies in a murine model of Chlamydia trachomatis genital tract an infection. Role of coproantibody in scientific protection of children during reinfection with rotavirus. Protection of germ-free mice from infection by Helicobacter felis after energetic oral or passive IgA immunization. The excessive lectin-binding capability of human secretory IgA protects nonspecifically mucosae against environmental antigens. Bidirectional FcRndependent IgG transport in a polarized human intestinal epithelial cell line. Antigen binding to secretory immunoglobulin A ends in decreased sensitivity to intestinal proteases and elevated binding to cellular receptors. The use of mouse/human chimaeric antibodies to investigate the roles of different antibody isotypes, including IgA2, within the killing of Schistosoma mansoni schistosomula by eosinophils. The effects of binding mouse IgA to dinitrophenylated Salmonella typhimurium on physicochemical properties and interplay with phagocytic cells. Prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis in low-birth-weight infants by IgA�IgG feeding. Subclass distribution of antigen-specific IgA antibodies in regular donors and people with homozygous C1 or C2 gene deletions. Role of immunoglobulin A monoclonal antibodies in opposition to P23 in controlling murine Cryptosporidium parvum an infection. An in vitro adherence assay reveals that Helicobacter pylori exhibits cell lineage-specific tropism within the human gastric epithelium. Cytofluorographic evaluation of receptors for IgA on human polymorphonuclear cells and monocytes and the correlation of receptor expression with phagocytosis. Impact of the molecular form of immunoglobulin A on practical exercise in protection against Streptococcus pneumoniae. Secretory IgA possesses intrinsic modulatory properties stimulating mucosal and systemic immune responses. Induction of functional secretory IgA responses in breast milk, by pneumococcal capsular polysaccharides. Transient suppression of Shigella flexneri sort 3 secretion by a protective O-antigen-specific monoclonal IgA. Inhibition of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium motility and entry into epithelial cells by a protecting antilipopolysaccharide monoclonal immunoglobulin A antibody. Association of a protecting monoclonal IgA with the O-antigen of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium impacts kind 3 secretion and outer membrane integrity. Decreased expression of mannose-specific adhesins by Escherichia coli within the colonic microflora of immunoglobulin A-deficient people. Increased frequency of intestinal Escherichia coli carrying genes for S fimbriae and haemolysin in IgA-deficient people. Epithelial cell polarization is a determinant within the infectious end result of immunoglobulin A-mediated entry by Epstein-Barr virus. Influence of tumor-necrosis factor- on the expression of Fc IgG and IgA receptors, and different markers by cultured human blood monocytes and U937 cells. SpsA, a novel pneumococcal surface protein with particular binding to secretory immunoglobulin A and secretory component. Amebiasis and mucosal IgA antibody towards the Ent amoeba histolytica adherence lectin in Bangladeshi children. Targeted deletion of the IgA constant area in mice leads to IgA deficiency with alterations in expression of different Ig isotypes. Investigation of in vivo pneumococcal polysaccharide-induced and in vitro mitogen-induced blood B cells by monolayer plaque-forming cell assays. Protective immunoglobulin A and G antibodies bind to overlapping intersubunit epitopes within the head domain of kind 1 reovirus adhesin sigma1. Human immature dendritic cells effectively bind and take up secretory IgA with out induction of maturation. Intestinal IgA responses to Giardia muris in mice depleted of helper T lymphocytes and in immunocompetent mice. Binding of human secretory protease inhibitor in uterine cervical mucus to immunoglobulins: pathophysiology in immunologic infertility and local immune defense.
Azitrox: 500 mg, 250 mg, 100 mg
Order 500 mg azitrox with mastercardMucosal Immunoglobulins Chapter 17 293 with J chain attaching or bonding each mIgA subunits at cysteine 471 of 1 -chain belonging to each monomer subunit (Bastian et al antibiotic zofran azitrox 500 mg otc. In the absence of relevant crystallographic analyses antibiotic 875125 azitrox 500mg overnight delivery, the precise nature of and J chain interactions remains enigmatic antibiotic justification form discount azitrox 250 mg amex. Models based mostly on answer structures (mentioned above in Physical properties of IgA) and accompanying glycan evaluation (Royle et al quinolone antibiotics for uti azitrox 100mg without prescription. Moreover, in these models, the orientation of J chain has been arbitrarily assigned. Thus, the cleavage of disulfide bonds beneath mildly reducing situations and in the absence of dissociating agents. Presumably, this elevated resistance to proteolysis confers on S-IgA molecules a big useful benefit within the gastrointestinal milieu. Nevertheless, tryptic fragments of S-IgA can be generated by cleavage at increased (50�60�C) temperatures (Zikan et al. Furthermore, particulars of pIgA-pIgR interactions that occur on the surfaces and during the epithelial cell transcytosis are described in Chapter 19. However, IgA shows several necessary structural differences from IgG and IgD, notably the presence of a singular hinge region between the C1 and C2 domains, and the extension of the chain C terminus by 18 amino acid residues not present in the, and chains Table 3). The numbers embrace complex and high-mannose kind N-linked chains within the entire (V and C region) chains. However, there are notable differences in the arrangement of interchain disulfides and the position of N-linked glycans. The two chains are anchored to each other on the high of the C2 domains by disulfide bridges. Three (or four) cysteines on every heavy chain (Cys 242, Cys 299, Cys 301, and possibly Cys 241) are implicated in these linkages. The precise disulfide bond preparations differ within the crystals of IgA1 Fc complexed with the 2 different ligands, consistent with a degree of disulfide interchange (Ramsland et al. The N-linked sugar moieties hooked up to Asn 263 are externally situated, mendacity on the outer surface of the C2 domains with appreciable additional contacts with the C3 domains. Mucosal Immunoglobulins Chapter 17 295 Comparative studies of H chains of all isotypes have indicated a substantial degree of general structural homology between particular person domains; nonetheless, the number of domains throughout the C area and the presence and structure of the hinge area are typical of each isotype Table 3). To maximize alignment, at positions where extra residues happen in some sequences dashes are used in the remaining sequences. Numbering is in accordance with the commonly adopted scheme used for IgA1 Bur (Putnam et al. Because the hinge and C2 domains are encoded in a single exon, the beginning of the C2 was taken as the primary Cys residue encoded by this exon in human IgA1. Fc region of various isotypes display a hanging homology when aligned based on the invariant Cys and Trp residues (Putnam, 1989). In specific, the extremely homologous place of Cys residues that take part within the formation of intradomain disulfide bridges is crucial in sustaining the frequent structural features of all domains, no matter their Ig isotypes. IgA and IgM display the very best diploma of sequence homologies in their Fc areas that, respectively, comprise the C2 and C3 domains and the tailpiece of IgA and the C3 and C4 domains and the tailpiece of IgM (Low et al. This high degree of primary construction homologies between IgA and IgM seems to replicate their close evolutionary origin. Furthermore, IgA and IgM molecules share important structure�function similarities such as the power to type polymers, bind J chain through their penultimate Cys residues in structurally analogous tailpieces (Mestecky et al. Moreover, S-IgM functionally replaces S-IgA in most IgAdeficient individuals (Plebani et al. However, structural homologies of IgA subclasses inside one species are very high. The amino acid sequence of the hinge region in IgA1 is paying homage to that of mucins with multiple Ser, Thr, and Pro residues. The hinge area of the 1 chain is one of a very limited variety of pure substrates for bacterial IgA1 proteases that cleave IgA1 molecules into Fab and Fc fragments with functionally necessary biological consequences (see Chapter 22). It has been postulated that the presence of the prolonged hinge area of IgA1 molecules confers larger segmental flexibility of Fab areas and a extra extended attain between Fab ideas in IgA1 than IgA2 (Pumphrey, 1986; Boehm et al. Structure A occurs in IgA proteins of both subclasses; structure B is current solely in the hinge region of IgA1. Indeed, the hinge region is a source of major heterogeneity in nonhuman primate IgA (Rogers et al. The 1 and 2 chains contain an unusually excessive quantity (17) of Cys residues concerned in the formation of disulfide bridges inside a single chain (intra-chain) and between component chains of mIgA, pIgA, and S-IgA. A probable task of individual Cys residues to numerous intra- or inter- chain disulfides has been proposed (Fallgren-Gebauer et al. The structural significance of a few of these Cys residues has been revealed by sitedirected mutagenesis research. For instance, Cys 133 is essential for the formation of the inter L�1 chain disulfide bridge. In IgA2, this residue is deleted and Cys 220 is probably concerned in L� chain disulfides. However, in IgA2 of the A2m(1) allotype (see beneath, -Chains), a lot of the molecules lack these L� chain bridges; as an alternative, dimerized L chains are present (Jerry and Kunkel, 1974). The lack of formation of L�2 chain disulfides is due to the presence of Pro at position 221 that interferes with the formation of the disulfide bridge between the L chain and Cys Mucosal Immunoglobulins Chapter 17 299 220 (Chintalacharuvu and Morrison, 1996). It is possible to engineer a model by which the L chains are covalently linked to the heavy chains by mutation of Pro 221 to Arg, which allows formation of a disulfide bond between Cys 241 within the chain and Cys 214 in the L chain (Lohse et al. Several investigators addressed the query regarding the structural features of the (and also) chain that facilitate the formation of pIgA and IgM (Atkin et al. The capability of IgA and IgM to form polymers has been related to the presence of the 18-amino-acid C terminal tailpieces on and chains, which embody the penultimate Cys residue to which J chain is hooked up (Mestecky et al. Indeed, the addition of this tailpiece to IgG leads to the formation of pIgG with interesting useful consequences (S�rensen et al. On the other hand, deletion of the chain tailpiece completely prevents formation of pIgA (Atkin et al. Domain swapping experiments between IgA and IgM have suggested a task for the C3 and C4 domains in figuring out polymer size and J chain incorporation (Braathen et al. It is fascinating to note that potential linkage of the tailpiece Cys 471 to Cys 311 was proven to not account for the nonbinding of pIgR by IgA monomers as a outcome of mIgA by which the tailpiece was deleted was discovered to remain incapable of binding pIgR (Lewis et al. The human IgA2 subclass exists in two allotypic forms termed IgA2m(1) and IgA2m(2) (Wang and Fudenberg, 1974; Loghem and Biewenga, 1983). A third variant, IgA2(n), so far described in a single individual, may characterize one other allotype that arose through recombination or gene conversion between the two IgA2 alleles (Chinatalacharuvu and Morrison, 1996; Chintalacharuvu et al. A main structural difference between the IgA2m(1) and IgA2m(2) allotypes considerations the arrangement of inter-�L-chain disulfide bridges (Grey et al. The A2m(2) allotype differs from the A2m(1) allotype and the IgA1 isotype in six positions, two of that are in the C1 area (residues 212 and 221) and 4 of that are situated within the C3 area (residues 411, 428, 458, and 467). The A2m(1) allotype is a hybrid of IgA1 and A2m(2) and will have arisen by a gene conversion event (Tsuzukida et al.
Order 100mg azitrox visaHowever virusbarrier purchase azitrox 250 mg, it is essential to bacteria exponential growth order 100 mg azitrox overnight delivery recognize that small molecules can diffuse via mucus and sometimes should in order that mucosal tissues can achieve secretion and absorption infection jobs buy generic azitrox 250mg on-line. Mucus is highly effective at aggregating particulate matter antibiotic for uti pseudomonas order azitrox 500 mg line, and in the respiratory tract the cilia that promote the motion of mucus are necessary for removing of particulate matter (including pathogens) from the lung. In the immune context in the gut, it can be clearly demonstrated that mucus separates the luminal microbes from the epithelial surface (Johansson et al. The reasons for these differences in properties are unknown but are more probably to involve degradation/disruption of the mucin community as it ages and meets the extracellular environment, including microbes. While the traditional microbes within the gut are found only within the outer mucus layer, intestinal pathogens can quickly penetrate mucus (discussed below). Separation of microbes from the mucosal epithelia might be a serious perform of mucus in a number of tissues, though this has not been well illustrated in other tissues largely because the mucus layer in these areas is thinner and thus harder to preserve for evaluation. While a lot of the microbial exclusion properties of mucus may be attributed to its inherent biophysical properties, nonmucin parts of mucus such as antimicrobial molecules and secreted antibodies are prone to be critical in maintaining sterility of the internal mucus layer. The significance of mucus for regular mucosal operate is highlighted by the phenotypes of mice missing individual mucin genes. Mice missing the most important intestinal mucin, Muc2, lose their intestinal mucus barrier and develop early onset progressive intestinal irritation, and on some genetic backgrounds develop adenomas and cancers in the small intestine and colon (Burger-Van Paassen et al. Muc2deficient mice are additionally extra vulnerable to an infection with enteric bacterial pathogens and parasites (Bergstrom et al. Unpublished reviews also point out that mice lacking the Muc5ac and Muc5b mucins in the respiratory tract develop pathophysiology in the lung underneath infectious and inflammatory challenges. Interestingly, Muc5ac-deficient mice have less lung inflammation and pulmonary edema following ventilator-induced lung injury due to decreased pulmonary neutrophil trafficking (Koeppen et al. These mice also develop signs of dry eye disease according to insufficient hydration of or protection of the ocular surface (Floyd et al. Further work is required in multiple tissues to establish the roles of secreted mucins in normal physiology. Altering Ca2+ concentrations quite markedly modulates the viscosity of saliva, although the mechanism of action remains unclear (Raynal et al. One view is that insufficient Cl- transport leads to dehydration of the air�liquid interface leading to mucins being unable to hydrate and broaden on secretion (Boucher, 2007). This is an extreme example in disease, however the host may utilize extra subtle manipulation of the ionic setting to modulate the biophysical properties of secreted mucus. Cell Surface Mucins Whereas the secreted mucins present a physical and chemical barrier to microbes, cell surface mucins seem to be concerned in blocking pathogen adhesion to the apical surface of mucosal epithelial cells, sustaining a wholesome glycocalyx and modulating responses of mucosal epithelial cells to luminal microbes. A recent analysis and modeling of cell floor mucins in bronchial epithelial cells offers necessary insights into the biophysical position of the cell floor mucins and overturns the previous notion that there was a fluid layer (periciliary liquid) between the mucus and the cilia in the lung allowing the movement of mucus (Button et al. Using penetration/diffusion of beads of assorted sizes and mathematical modeling these authors show that the cell floor mucins form a community at the cell surface that stops diffusion of mucus and small particles into the glycocalyx and helps preserve hydration. They suggest that this "gel-on-brush" mannequin explains the flexibility of cilia to move usually hydrated mucus within the lung and the issue in transferring underhydrated mucus. Under this mannequin the massive cell floor mucins are dominant determiners of the biophysical state of the apical floor, which is the point at which many mucosal pathogens contact the host. Exploration of the dynamics of cell floor mucins during an infection and the implications of cell floor mucin deficiency indicate that these mucins provide an essential impediment to pathogens. Mice missing Muc1 develop greater density infection and much stronger inflammation, demonstrating that these effects are essential in vivo (McGuckin et al. All of the cell floor mucins have complicated cytoplasmic domains and it appears that these mucins are involved in modulating sign transduction in mucosal epithelial cells. While many of these research have been conducted in cultured human cancer cells which often overexpress these mucins, these functions are likely to relate to protecting mucosal epithelia from mucosal cytotoxins including toxins made by pathogens to injury epithelial integrity (McAuley et al. Thus, these mucins not solely try and forestall penetration of microbes into the epithelial cells however assist set the tenor of the subsequent wound restore and inflammatory responses. Why are mucosal viruses environment friendly at penetrating mucus and infecting underlying epithelial cells Viruses are small enough to diffuse via the pores in the mucin network in mucus. Many viruses additionally bind to glycans discovered on mucins, and viral-host carbohydrate binding relationships are probably an important determinant of the host species specificities of viruses. For evaluations see Vazquez-Torres and Fang (2000), Siebers and Finlay (1996), and Jones et al. This specialised part of the epithelium lacks secreted mucus and has an altered glycocalyx to aid the first function of M cells in sampling the intestinal microbiota. Many pathogenic bacteria and parasites penetrate mucus and make the most of cues in mucus in upregulated genes involved in pathogenicity, including enzymes which degrade mucus, making penetration simpler. The murine attaching and effacing bacterial pathogen, Citrobacter rodentium, is an fascinating example. However, after several days in this area of interest the micro organism move from this area of interest to the outer mucus layer, which is occupied by a fancy neighborhood of mainly anaerobic micro organism. Interestingly, under germ-free situations the relocation to the outer mucus layer still happens but the Citrobacter prosper in the absence of competing species (Kamada et al. Genetic linkage to mucins in disease is advanced due to the big and polymorphic nature of the mucin genes, including vast repeat domains, and because nonmucin genes are crucial to mucin biosynthesis and, subsequently, might more not directly be involved. Polymorphisms in mucin glycosyltransferases have additionally been linked with susceptibility to mucosal disease. Blood group oligosaccharides decided by inheritance of alleles in glycotransferase genes have an result on mucin glycosylation and, in turn, H. Experimental deficiency of the fucosyltransferase-2 (Fut2) gene in mice increases reproductive tract infection with Candida (Hurd and Domino, 2004), however protects from intestinal norovirus infection (Carlsson et al. Aberrant Mucus Production in Disease Mucus hypersecretion is a feature of many chronic inflammatory illnesses in mucosal tissues, particularly in Mucins and Mucus Chapter 14 245 the respiratory tract. This is unsurprising given the regulation of goblet cell differentiation and secretory mucin gene expression by inflammatory factors, as mentioned earlier within the chapter. There is sweet purpose to imagine that extra mucus manufacturing, typically together with altered properties of the mucus, contributes to pathology and is a rational target for therapy. Mucus hypersecretion combines with bronchoconstriction to scale back the efficient measurement of airways producing the wheezing symptoms of bronchial asthma. While blocking mucin manufacturing appears a beautiful option in some of these diseases, you will want to consider that this could conceivably, in some conditions, lead to exacerbation of pathogen-initiated damage to the mucosa. Photomicrographs of murine cecum stained with Alcian blue to identify stored mucins within the goblet cells. Goblet cell failure is commonly misinterpreted as "exhaustion" because of secretion and loss of the intracellular store of secretory granules. While this could occur within the quick time period, especially following strong secretory stimuli leading to compound exocytosis, during Th2-mediated inflammatory responses, corresponding to those developed towards nematode infections within the gut, individual goblet cells are capable of secreting massive amounts of mucins without depleting their reserves, which is achieved by ramping up charges of mucin biosynthesis. A major contributing issue seems to be protein misfolding and endoplasmic reticulum stress (for reviews on the effect on goblet cells, see McGuckin et al. The isoform Ire1 is ubiquitously expressed and never required for goblet cell operate, however the Ire1 isoform, which is expressed only in intestinal and respiratory goblet cells, is required for growth and mucin production. In the lung, deficiency in Ire1 greatly reduces goblet cell hyperplasia in response to Th2 cytokines (Martino et al. Initially this was a shock as this is a disease that develops within the small airways.
Purchase 250mg azitroxThe glycosylation and structure of human serum IgA1 antibiotic resistant gonorrhea pictures buy cheap azitrox 100 mg online, Fab and Fc areas and the role of N-glycosylation on Fc receptor interactions virus 2014 adults purchase 250mg azitrox free shipping. Interleukin 2- and interleukin 5-induced modifications in the binding of regulatory elements to the J-chain gene promoter antibiotic resistance peter j collignon purchase azitrox 100 mg otc. Immunoglobulin A (IgA): molecular and cellular interactions concerned in IgA biosynthesis and immune response antibiotics for acne short term 100 mg azitrox overnight delivery. Proportion of human colostral immunoglobulin-A molecules containing the secretory determinant. Parallel synthesis of immunoglobulins and J chain in pokeweed mitogenstimulated regular cells and in lymphoblastid cell lines. Structures of the carbohydrate moieties of secretory part purified from human milk. Cellular origins of human polymeric and monomeric IgA: intracellular and secreted forms of IgA. Human male genital tract secretions: both mucosal and systemic immune compartments contribute to the humoral immunity. High-resolution buildings of the IgM Fc domains reveal ideas of its hexamer formation. Electron microscope examination of free IgA molecules and of their complexes with antigen. Polymer IgM meeting and secretion in lymphoid and nonlymphoid cell lines: evidence that J chain is required for pentamer synthesis. Differential glycosylation of polymeric and monomeric IgA: a potential role in glomerular inflammation in IgA nephropathy. Expression of homing receptors on IgA1 and IgA2 plasmablasts in blood reflects differential distribution of IgA1 and IgA2 in various physique fluids. Heterogeneity of the glycans O-glycosidically linked to the hinge region of secretory immunoglobulins from human milk. IgM and IgD concentrations in the serum and secretions of children with selective IgA deficiency. Streptococcal IgA1 protease digestion, Fab and Fc fragment and the whole amino acid sequence of the 1 heavy chain. J chain synthesis and secretion of hexameric IgM is differentially regulated by lipopolysaccharide and interleukin 5. Direct evidence that J chain regulates the polymeric construction of IgM in antibody-secreting B cells. Determination of aberrant O-glycosylation in the IgA1 hinge area by electron capture dissociation Fourier transform-ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Subtractive hybridization reveals the expression of immunoglobulin-like transcript 7, Eph-B1, granzyme B, and three novel transcripts in human plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Expression of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR) in mucosal tissues of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L. Secretory IgA N- and O-glycans present a link between the innate and adaptive immune systems. IgA-associated renal illnesses: antibodies to environmental antigens in sera and deposition in immunoglobulins and antigens in glomeruli. Intraspecies heterogeneity of immunoglobulin -chain fixed area genes in rhesus macaques. Organization of the constant-region gene family of the mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain. Developmental regulation of IgM secretion: the role of the carboxy-terminal cysteine. Distribution of IgA subclasses in sera and bone marrow plasma cells of 21 normal individuals. Addition of a -tailpiece to IgG results in polymeric antibodies with enhanced effector features including complement-mediated cytolysis by IgG4. Transforming development issue induces IgA manufacturing and acts additively with interleukin 5 for IgA manufacturing. Effect of the IgM and IgA secretory tailpieces on polymerization and secretion of IgM and IgG. Polymerization of IgA and IgM: roles of Cys309/Cys414 and the secretory tailpiece. Discovery of J chain in African lungfish (Protopterus dolloi, Sarcopterygii) using excessive throughput transcriptome sequencing: implications in mucosal immunity. Clustered O-glycans of IgA1: defining macro- and micro-heterogeneity by use of electron capture/transfer dissociation. Human serum IgA1 is substituted with up to six O-glycans as shown by matrix assisted laser desorption ionisation time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Immunization of people with polysaccharide vaccines induces systemic, predominantly polymeric IgA2-subclass antibody responses. Selective elimination of heavy-chain glycosylation sites causes immunoglobulin A degradation and lowered secretion. The differences in carbohydrate composition between the subclasses of IgA immunoglobulins. Microdetermination of monosaccharides in glycoproteins by gas-liquid chromotography. Complete amino acid sequence of the two heavy chain of a human IgA2 immunoglobulin of the A2m(2) allotype. Location and structural significance of the oligosaccharides in human IgA1 and IgA2 immunoglobulins. Mouse IgA heavy chain gene sequence: implications for evolution of immunoglobulin hinge exons. Multiple recombinational events in primate immunoglobulin and genes suggest nearer relationship of human to chimpanzees than to gorillas. Studies on the structural and conformational basis for the relative resistance of serum and secretory immunoglobulin A to proteolysis. Disulfide bonding of secretory element to a single monomer subunit in human secretory IgA. Cloning and structural analysis of two highly divergent IgA isotypes, IgA1 and IgA2 from the duck billed platypus, Ornithorhynchus anatinus. The full map of the immunoglobulin heavy chain fixed gene area reveals evidence for seven IgG isotypes and for IgD within the horse. B cell-specific activator protein prevents two activator elements from binding to the immunoglobulin J chain promoter till the antigen-driven phases of B cell development. A examine of the affiliation of human secretory component with IgA and IgM proteins.
Aspartate Chelated Minerals (Aspartates). Azitrox. - How does Aspartates work?
- Dosing considerations for Aspartates.
- Enhancing athletic performance, liver cirrhosis, and increasing mineral levels.
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Aspartates?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96062
Purchase 500mg azitrox free shippingS-IgA is discovered within the bile of teleosts and amphibians antibiotic resistance by area buy 250 mg azitrox otc, although the relative contribution of hepatobiliary transport Phylogeny and Comparative Physiology of Mucosal Immunoglobulins Chapter 18 339 versus native synthesis of IgT and IgX has not systematically been studied antibiotics jobs buy azitrox 250 mg cheap. Studies within the 1970 and Eighties demonstrated unequivocally that pIgR acts as a cell surface receptor for pIgA on hepatocytes in mice antibiotic resistance mechanisms azitrox 500 mg for sale, rats infection walking dead buy azitrox 250mg visa, and rabbits, mediating the transport of pIgA from blood to bile (Jackson et al. To look at species differences in hepatobiliary transport of pIgA, numerous investigators have carried out in vivo experiments during which radiolabeled pIgA from varied species was injected intravenously into recipient animals from the same or completely different species Table 1). The pattern that emerged instructed that the liver of the recipient animal, and never the source of the pIgA, was the first factor regulating hepatobiliary transport. The livers of some rodents (mice, rats, and hamsters), rabbits, and chickens efficiently transported pIgA, in some cases when the pIgA was from a unique species. An intermediate phenotype was noticed in sheep, which effectively transported sheep pIgA from blood to bile, however not pIgA from rat or human. According to this concept, binding of circulating IgM to pIgR on the sinusoidal surface of hepatocytes would lead to its rapid clearance by hepatobiliary transport, a state of affairs that might decrease circulating concentrations of IgM and potentially impair systemic immunity. In most rodents and rabbits, pIgR is expressed on hepatocytes and effectively transports pIgA, however not IgM. In humans and other species by which pIgR binds each pIgA and IgM, hepatobiliary clearance of IgM is prevented by low levels of pIgR expression by hepatocytes (Nagura et al. A molecular basis for differential binding of pIgR to pIgA and pIgM was demonstrated by the finding of specific binding motifs for IgM in the extracellular area of pIgR (R�e et al. Because species during which hepatobiliary transport of pIgA is most lively are coprophagic (rats, rabbits, mice), it may be hypothesized that supply of S-IgA antibodies via bile into the proximal intestinal tract might help to control the load of fecal microorganisms. Some estimates point out that in rats, 90% of intestinal S-IgA is delivered by this mechanism (Lemaitre-Coelho et al. In addition, hepatobiliary clearance of antigen bound to IgA antibody has been demonstrated in rats and mice (Peppard et al. The existence of hepatobiliary transport of pIgA in species as numerous as chickens, rabbits, and Sciurognathic rodents is suggestive of convergent evolution pushed by particular environmental pressures. Future studies of hepatobiliary transport of IgM in cartilaginous fish, IgT in teleosts, and IgX in amphibians may reveal further examples of convergent evolution of this physiological adaptation. The concurrent emergence of IgM and the J chain in cartilaginous fish offered a mechanism for polymerization of IgM, thus offering a mucosal Ig that could balance low affinity and broad antimicrobial cross-reactivity with multivalency and high avidity. Divergence of the tetrapod lineage Phylogeny and Comparative Physiology of Mucosal Immunoglobulins Chapter 18 341 was accompanied by the emergence of IgX in amphibians, which advanced into IgA in birds and mammals (and probably also reptiles). Through specialised immunological capabilities that are distinctive from those of IgA, IgG and IgE also contribute to safety of mucosal surfaces (see Chapter 22). The demonstration of interactions between secreted IgD and basophils in the respiratory tract (Chen et al. Two stages of elevated IgA transfer during lactation in the marsupial, Trichosurus vulpecula (brushtail possum). Evidence for an early look of contemporary post-switch isotypes in mammalian evolution; cloning of IgE, IgG and IgA from the marsupial Monodelphis domestica. Marsupial immunoglobulins: an immunoglobulin molecule resembling eutherian IgA in serum and secretions of Setonix brachyurus (quokka). Immunoglobulin genetics of Ornithorhynchus anatinus (platypus) and Tachyglossus aculeatus (short-beaked echidna). The transport by hepatocytes of immunoglobulin A from blood to bile visualized by autoradiography and electron microscopy. Transfer of passive immunity from mom to younger in a teleost fish: haemagglutinating activity in the serum and eggs of plaice, Pleuronectes platessa L. The secretory immune system of lactating human mammary glands compared with different exocrine organs. Structural and immunologic evaluation of gene triplications within the Ig heavy chain constant area locus. The IgA heavy-chain gene family in rabbit: cloning and sequence analysis of thirteen C genes. Identification of diversified genes that comprise immunoglobulin-like variable areas in a protochordate. Isotype, specificity, and kinetics of systemic and mucosal antibodies to Campylobacter jejuni antigens, including flagellin, throughout experimental oral infections of chickens. Estimation of the intravascular half-lives of normal rhesus monkey IgG, IgA and IgM. Immunoglobulin D enhances immune surveillance by activating antimicrobial, proinflammatory and B cell-stimulating applications in basophils. Cleavage of chimpanzee secretory immunoglobulin A by Haemophilus influenzae IgA1 protease. Secretory part on epithelial cells is a floor receptor for polymeric immunoglobulins. Secretory component-dependent binding of immunoglobulin A within the rat, monkey and human: a comparability of gut and liver. The immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus in zebrafish: identification and expression of a beforehand unknown isotype, immunoglobulin Z. Hepatobiliary transport of plasma IgA within the mouse: contribution to clearance of intravascular IgA. Shark immunity bites back: affinity maturation and memory response in the nurse shark, Ginglymostoma cirratum. Characterization of an IgY-like low molecular weight immunoglobulin class in the Mexican axolotl. Transient developmental expression of IgY and secretory element like protein within the intestine of the axolotl (Ambystoma mexicanum). Origin and evolution of the adaptive immune system: genetic events and selective pressures. Mechanisms of divergence and convergence of the human immunoglobulin alpha 1 and alpha 2 fixed region gene sequences. Local immunological response in the posterior intestinal segment of the rainbow trout after oral administration of macromolecules. Intracellular receptor sorting throughout endocytosis: comparative immunoelectron microscopy of a number of receptors in rat liver. Isolation and characterization of IgG, IgM and IgA in body fluids, eggs and intraocular tissues. A novel "chimeric" antibody class in cartilaginous fish: IgM will not be the primordial immunoglobulin. Phylogeny and Comparative Physiology of Mucosal Immunoglobulins Chapter 18 343 Gyure, L. IgY-like immunoglobulins of birds, reptiles and amphibians, precursors of mammalian IgA. Degree of antigenic relationship between the 7S immunoglobulins of mammals, birds, and lower vertebrates to the turkey IgY. Comparative research on the construction of biliary immunoglobulins of some avian species. Antigenic properties of the biliary immunoglobulins of chicken, turkey, duck and goose. A teleost polymeric Ig receptor exhibiting two Ig-like domains transports tetrameric IgM into the skin.
Discount azitrox 250 mg without prescriptionIn addition to expressing integrins antibiotics for uti and exercise safe 250mg azitrox, human eosinophils have been demonstrated to selectively categorical a sialic acidbinding immunoglobulin-like lectin designated Siglec-8 (Floyd et al infection near eye discount 100 mg azitrox fast delivery. The ligand for Siglec-8 antibiotic resistance of streptococcus pyogenes effective 100 mg azitrox, as nicely as the murine equal Siglec-F lafee virus cheap azitrox 250 mg with amex, has been recognized as sulfate glycan ligand 6-sulfo-sialyl Lewis X (Tateno et al. Importantly, it was lately confirmed by a number of groups that Siglec8/F cross-linking results in apoptosis in eosinophils (Bochner, 2009). In addition, Siglec-F gene-deficient mice have increased levels of eosinophils and exaggerated responses in models of bronchial asthma (Cho et al. Although the mechanism has to be elucidated, this particular cell dying induction offers a promising foundation for future eosinophil-specific pharmaceutical therapies. It is worthwhile to observe that eosinophil adhesion molecule expression is highly dynamic, with surface expression being bi-directionally regulated by cytokine milieu, tissue context, and pathological standing (Barthel et al. Likewise, some eosinophil features, similar to chemokine and cytokine production, are additionally correlated with floor adhesion molecule expression (Curran and Bertics, 2012). Recently, concerning pathological eosinophil tissue migration, there are lines of evidence indicating a synchronized coordination between eosinophil adhesion and chemotaxis. Eosinophil Chemoattraction the discovering that eosinophils usually account for less than a small share of circulating or tissue-dwelling cells and that their numbers markedly and selectively improve under particular illness states point out the existence of molecular mechanisms that regulate the selective technology and energetic transportation of those leukocytes. The pathological roles and the detrimental effects of eosinophils primarily occur in tissues; subsequently, a serious focus of scientific investigation on eosinophils has been to elucidate the processes involved in eosinophil tissue recruitment. Eotaxin was initially found in guinea pigs utilizing a biological assay designed to determine the molecules responsible for allergen-induced eosinophil accumulation in the lungs (Jose et al. Using an in vivo chemotaxis assay in guinea pig skin, the partial amino acid sequence for the protein responsible for eosinophil chemoattraction within the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in allergen-challenged guinea pigs was determined (Jose et al. Interestingly, this area has been linked to asthma susceptibility, along with some other susceptibility loci (Nickel et al. A number of approaches have been used to decide the organic role of the eotaxin chemokines. In vivo administration studies in guinea pigs and rodents have proven that the eotaxin chemokines are relatively potent and specific eosinophil chemoattractants (Jose et al. In addition to having a chemoattractant position in the respiratory tract, the eotaxin chemokines are involved in regulating eosinophil recruitment in other tissues. Analysis of eotaxin-1�deficient mice have revealed that the constitutive expression of this chemokine is critically involved in regulating the baseline homing of eosinophils, especially in the intestine, the primary reservoir of eosinophils (Matthews et al. These apparently conflicting results may be associated to the sensitization protocol. There is now substantial preclinical proof supporting a role for eotaxin chemokines in human allergic illness (Zimmermann et al. Experimental induction of cutaneous and pulmonary late-phase responses in humans has revealed that the eotaxin chemokines are produced by tissue-resident cells. Following allergen problem, eotaxin-1 is induced early (6 h) and correlates with early eosinophil recruitment; in distinction, eotaxin-2 correlates with eosinophil accumulation at 24 h (Ying et al. A naturally occurring mutation encoding for a change in the last amino acid of the signal peptide (alanine threonine) results in less efficient cellular secretion of eotaxin-1 in vitro and in vivo (Nakamura et al. The activity of eotaxin-1 and eotaxin-2 in humans has been investigated by injection of these chemokines into the pores and skin; each eotaxin-1 and eotaxin-2 had been capable of induce an immediate wheal and flare response associated with mast cell degranulation and subsequent infiltrations by eosinophils, basophils, and neutrophils (Menzies-Gow et al. The infiltration by neutrophils is likely to be mediated indirectly by the mast cell degranulation. These outcomes provide substantial proof that the biological activities attributed to eotaxins in animals are conserved in humans. The degree of eotaxin-3 expression is usually 50- to 100-fold greater than normal, or more, and directly linked to illness severity by method of the density of infiltrating eosinophils. Importantly, like the eosinophil adhesion molecules, the production of human eotaxin-3 is highly orchestrated by the local cytokine milieu. Eosinophils comprise a variety of cytotoxic proteins in their granules, most of which are eosinophilic (basic in nature, readily dyed with eosin staining), hence the name "eosinophils. Interestingly, a recent research also confirmed these proteins in an extragranular compartment in eosinophils (Karawajczyk et al. These proteins elicit potent cytotoxic results, sometimes irritation, on a variety of host tissues at concentrations just like those present in organic fluid from sufferers with eosinophilia. Eosinophils are bilobed granulocytes that reply to numerous stimuli together with allergens, helminths, viral infections, allografts, and nonspecific tissue harm. In addition to releasing their preformed cationic proteins, eosinophils can also release a wide range of cytokines. This determine has been tailored from a prior publication with permission (Rothenberg et al. Finally, eosinophils have the capability to initiate antigenspecific immune responses by appearing as antigen-presenting cells (Mattes et al. Interestingly, experimental adoptive transfer of antigen-pulsed eosinophils induces antigen-specific T-cell responses in vivo (Shi et al. The lowered stage of eosinophils correlated with a larger variety of intact encysted larvae. Thus, though the debate continues, it seems likely that eosinophils participate within the protective immunity against chosen helminths. Consequently, eosinophils are activated, and cytotoxic granule contents are launched onto the focused cells in a "piecemeal" trend by fusion with the eosinophil plasma cell membrane. Notably, this process can additionally be extremely regulated by synchronized cytokines and chemokines, which can be produced by eosinophils (Shamri et al. Several of those eosinophil-produced cytokines and chemokines also can function signaling molecules to "alert" different effector cell types against parasites, such as mast cells, basophils, neutrophils, and endothelial cells (Hogan et al. Therefore, upon helminth infection, eosinophils could serve as either organizers or effectors, or each, to provoke an orchestrated immune response. Immunoregulation Although eosinophils have been thought of as effector cells in parasite infections and allergic reactions, latest studies have indicated that eosinophils are multifaceted immune regulators in addition to effectors. Although most studies have targeted on the function of T cells within the regulation of eosinophils. In addition, the notch ligand constitutively expressed on human eosinophils could regulate naive T-cell polarization (Radke et al. However, it remains to be elucidated whether or not eosinophil antigen presentation has a significant function on this process as in comparison with the conventional presenters. Eosinophils are additionally identified to specific quite so much of cytokines that may induce the proliferation and/or maturation of T cells. Cytokines secreted by eosinophils may be divided into tissue cell targeted and immunocyte targeted. These data counsel that the cytokines produced by eosinophils may be involved in stromal fibrosis and basement hyperplasia. Indeed eosinophil-deficient mice have a marked decrease in secretory IgA (Chu et al.

Buy 100mg azitrox free shippingThese results prompt future research to explore the risk of using the eosinophil inhibitory receptors to restrict eosinophil-induced damage and remodeling bacterial reproduction generic azitrox 100mg mastercard. The principal elements of this EoE signature include genes coding for proteins involved in epithelial differentiation antibiotic quotes purchase 500 mg azitrox free shipping, tissue remodeling zosyn antimicrobial spectrum discount azitrox 100 mg amex, cell cycle/proliferation antibiotics used to treat acne order azitrox 500mg with visa, and cytokine/chemokine clusters. A majority of research on eosinophils in vivo have concentrated on trafficking and activation of those cells in the lung. Also supporting this notion, it was found that intestinal eosinophils are unique for his or her ultralong turn-over time as in contrast with eosinophils elsewhere (Carlens et al. These outcomes indicate that eosinophil-associated irritation of the massive gut is critically regulated by Th2 cells that particularly home to the colon. Notably, these signs are blocked by anti-IgE remedy or mast cell depletion (Mathias et al. In an effort to perceive the mechanisms and significance of eosinophil accumulation in the esophagus in diseased states, a murine mannequin for antigen-induced esophagitis has been developed (Mishra et al. In the case of EoE and regardless of atopy, elevated B-cell and IgE-bound mast cells levels had been found in EoE tissue sections compared with those of regular controls, suggesting that IgE class switching might occur within the esophageal mucosa (Vicario et al. Therefore, allergic antibody manufacturing could also be dependent on eosoinophils themselves. Similarly, miR-21 remains as a high dysregulated miR in EoE biopsy samples, strongly correlating eosinophil ranges (Lu et al. Most eosinophil-associated ailments are characterised by Th2-associated immune responses, which offer a mechanism to explain eosinophilia. Eosinophils develop in the bone marrow, where they differentiate from hematopoietic progenitor cells into mature eosinophils. Circulating eosinophils subsequently work together with the endothelium by processes involving rolling, adhesion, and diapedesis. Eosinophils are mobilized into the lamina propria in response to a chemotactic gradient primarily established by the chemokine eotaxin-1, liberated from mononuclear cells within the crypts. Regarding eosinophil homing into human esophageal epithelium in eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), current research has identified a quantity of Th2associated molecules listed within the panel, which performs very important roles in eosinophil tissue chemotaxis, centered across the main eosinophil chemokine in EoE, Eotaxin-3. In addition to being associated with Th2 immune responses, eosinophilia can develop as a consequence of aberrant somatic genetic events. In particular, a subset of sufferers with hypereosinophilic syndromes has a chromosome 4 microdeletion that leads to the technology of an activated tyrosine kinase (Cools et al. Importantly, this tyrosine kinase is very delicate to imatinib, an accredited drug for the therapy of chosen malignancies. Regardless of the mechanism of disease induction, activated eosinophils have the capability to take part in a number of features of illness including the promotion of pro-inflammatory damage. Multiple therapeutic approaches are capable of interfering with eosinophils immediately or indirectly. In particular, glucocorticoids promote eosinophil apoptosis and inhibit the production of eosinophil-directed cytokines. We suggest that eosinophils are integral members of the mucosal immune system and are necessary in innate, regulatory, and inflammatory immune responses. Trends in asthma prevalence, health care use, and mortality in the United States, 2001-2010. Beta7 integrin-deficient mice: delayed leukocyte recruitment and attenuated protective immunity within the small intestine throughout enteric helminth an infection. The role of eosinophils in parasitic helminth infections: insights from genetically modified mice. Eotaxin-3 but not eotaxin gene expression is upregulated in asthmatics 24 hours after allergen problem. Interleukin 5 modifies histamine launch and leukotriene era by human basophils in response to various agonists. The authors wish to thank the numerous colleagues and trainees which have contributed to the work introduced on this chapter. Siglec-8 on human eosinophils and mast cells, and Siglec-F on murine eosinophils, are functionally associated inhibitory receptors. Differentiation in vitro of hybrid eosinophil/basophil granulocytes: autocrine operate of an eosinophil developmental intermediate. The alpha4bbeta7integrin is dynamically expressed on murine eosinophils and involved in eosinophil trafficking to the gut. Intraepithelial eosinophils in endoscopic biopsies of adults with reflux esophagitis. Temporal function of chemokines in a murine model of cockroach allergeninduced airway hyperreactivity and eosinophilia. Common gamma-chain-dependent signals confer selective survival of eosinophils within the murine small intestine. Reslizumab for poorly controlled, eosinophilic asthma: a randomized, placebo-controlled examine. Eosinophils promote generation and upkeep of immunoglobulin-A-expressing plasma cells and contribute to intestine immune homeostasis. Cooperation between interleukin-5 and the chemokine eotaxin to induce eosinophil accumulation in vivo. The remodeling development elements beta in development and practical differentiation of the mouse mammary gland. Cloning, expression, and characterization of the human eosinophil eotaxin receptor. Interleukin 3, granulocyte-macrophage colonystimulating issue, and interleukin 5 in eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Kinetics of bone marrow eosinophilopoiesis and related cytokines after allergen inhalation. Migration and accumulation of eosinophils toward regional lymph nodes after airway allergen problem. Ultrastructural identification of exocytosis of granules from human gut eosinophils in vivo. Functionally competent eosinophils differentiated ex vivo in excessive purity from normal mouse bone marrow. Pretreatment with antibody to eosinophil main basic protein prevents hyperresponsiveness by defending neuronal M2 muscarinic receptors in antigen-challenged guinea pigs. The impact of antigen deprivation on thymus-dependent and thymus-independent lymphocytes within the small intestine of the mouse. Interleukin 5 deficiency abolishes eosinophilia, airways hyperreactivity, and lung damage in a mouse bronchial asthma model. Cytotoxic results of the guinea pig eosinophil main primary protein on tracheal epithelium. Human eotaxin is a selected chemoattractant for eosinophil cells and supplies a brand new mechanism to clarify tissue eosinophilia.
References - David KDE, Freud J, Laquer E: Crystalline male hormone from the testes (Testosterone) is more effective than androsterone derived from urine or cholesterin, Hoppe-Seyleris Z Physiol Chem 233:281n282, 1935.
- Bhatt A, Nandipati K, Dhar N, et al: Neurovascular preservation in orthotopic cystectomy: impact on female sexual function, Urology 67:742n745, 2006.
- Hemal, A.K., Kolla, S.B., Wadhwa, P. Robotic reconstruction for recurrent supratrigonal vesicovaginal fistulas. J Urol 2008;180:981-985.
- Zheng RQ, Zhang B, Kudo M, et al. Imaging findings of biliary hamartomas. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:6354-6359.
- Narchi H: Risk of hypertension with multicystic kidney disease, Arch Dis Child 90:921, 2005. Narchi H: Risk of Wilmsi tumour with multicystic kidney disease, Arch Dis Child 90:147, 2005. Nauli S, Alenghat FJ, Luo Y, et al: Polycystins 1 and 2 mediate mechanosensation in the primary cilium of kidney cells, Nat Genet 33:129n137, 2003.
|