Ciprofloxacin
James W. Albers, M.D., Ph.D. - Department of Neurology
- University of Michigan
- Ann Arbor, MI
Ciprofloxacin 500mg fast deliverySperm cells first enter the short straight tubules after which the rete testis virus quotes generic 250mg ciprofloxacin with visa, which is linked by way of efferent ductules to the head of the epididymis infection lab values order 750mg ciprofloxacin. Efferent ductules join the rete testis with the duct of the epididymis bacteria from bees possible alternative to antibiotics ciprofloxacin 500 mg free shipping, which forms the pinnacle infection in tooth buy ciprofloxacin 500 mg without prescription, physique, and tail of the epididymis. Sperm cells acquire motility, endure further maturation, and are stored within the epididymis earlier than ejaculation. The duct of the epididymis is lined with a pseudostratified columnar epithelium containing stereocilia and is surrounded by a easy muscle coat that gradually will increase in thickness. During ejaculation, sperm cells are forcefully squeezed from the epididymis to the ductus deferens and are propelled into the ejaculatory duct. Erectile tissues contain vascular spaces that enhance in dimension and rigidity by filling with blood during erection. The excretory duct of each seminal vesicle unites with the ampulla of the ductus deferens to form the ejaculatory duct, which pierces the prostate to enter the prostatic urethra. The prostate is a tubuloalveolar gland that lies beneath the bladder and surrounds the prostatic urethra. Parenchyma of the prostate is divided into several distinct anatomical and scientific zones. Glandular epithelium of prostatic alveoli is simple columnar with attribute prostatic concretions which are usually positioned inside the lumen of the glans. Semen contains fluids and sperm cells from the testis and secretory merchandise from the epididymis, ductus deferens, prostate, seminal vesicles, and bulbourethral glands. The features of the testis are the production of sperm and the synthesis and secretion of androgens, especially testosterone. Androgen secretion by the testis begins early in fetal development and is essential for continued regular development of the male fetus. At puberty, androgen secretion resumes and is answerable for initiation and maintenance of sperm production (spermatogenesis), secretion by accessory sex glands. Extending from the very thick capsule are connective tissue septa (S) that divide the organ into compartments. Each compartment incorporates several seminiferous tubules and represents a lobule (L). The seminiferous tubules are convoluted; thus, the profiles they present in a piece are variable in appearance. Not infrequently, the wall of a tubule is sectioned tangentially, thus obscuring the lumen and revealing what appears to be a solid mass of cells (X). Examination at higher magnification, as on this determine, reveals a inhabitants of interstitial cells that happen in small clusters and lie in the space between adjoining tubules. They are readily recognized by virtue of their location and by their small round nucleus and eosinophilic cytoplasm. Macrophages are also discovered, in close affiliation with the Leydig cells, but in lesser number. A layer of intently apposed squamous cells types a sheath-like funding around the tubule epithelium of every seminiferous tubule. The cells of this peritubular investment exhibit myoid options and account for the sluggish peristaltic exercise of the tubules. Peripheral to the myoid layer is a broad lymphatic channel that occupies an extensive house between the tubules. In routine histologic sections, nonetheless, the lymphatic channels are normally collapsed and, thus, unrecognizable. Indeed, under normal circumstances, lymphocytes and other cell varieties associated to the immune system are conspicuously absent. Examination of the tubule epithelium reveals two sorts of cells: a proliferating inhabitants of spermatogenic cells and a nonproliferating population, the sustentacular, or Sertoli, cells. The Sertoli cells are significantly fewer and can be recognized by their elongate, pale-staining nuclei (Sn) and conspicuous nucleolus. The spermatogenic cells encompass successive generations organized in concentric layers. The spermatocytes (Sc), most of which have large round nuclei with a distinctive chromatin sample (because of their chromatin materials being reorganized), come to lie above the spermatogonia. The spermatid inhabitants (Sp) consists of one or two generations and occupies the location closest to the lumen. The tubules on this determine have been identified according to their stage of growth. At this stage, the mature inhabitants of spermatids (identified by their dark blue heads and eosinophilic thread-like flagella protruding into the lumen) are in the process of being released (spermiogenesis). The youthful era of spermatids is composed of spherical cells and reveals spherical nuclei. By inspecting the spermatid inhabitants and assessing the variety of generations current. At puberty, these cords become canalized, and the gonocytes start the multiple divisions that give rise to the spermatogonia that, in flip, will divide and differentiate into the mature sperm. The seminiferous tubules terminate as straight tubules (tubuli recti) which are lined only by Sertoli cells. Instead, the "tubules" are represented by cords of cells in which a lumen is lacking. The seminiferous cords are of considerably smaller diameter than the tubules of the grownup and are composed of two cell types: the gonocyte, or first-generation spermatogonium, derived from the primordial germ cell that migrates from the yolk sac to the creating gonad in the embryo; and a cell that resembles the Sertoli cell of the grownup. The gonocytes (G) are the precursors of the definitive germ cells, or spermatogonia. The cytoplasm takes little stain and normally seems as a light-weight ring around the nucleus. Generally, the gonocytes are found on the periphery of the cord, but many are additionally found more centrally. The gonocytes give rise to spermatogonia that begin to proliferate in males between the ages of 10 and 13 years. The seminiferous epithelium then becomes populated with cells at various stages of spermatogenesis, as seen within the adult. The seminiferous cords are surrounded by one or two layers of cells with long processes and flat nuclei. They resemble fibroblasts at the ultrastructural degree and provides rise to the myoid peritubular cells of the adult. The interstitial cells (of Leydig) are conspicuous within the newborn, a mirrored image of the residual results of maternal hormones. They are ovoid or polygonal and are intently grouped, so that adjacent cells are involved with each other. In the posterior portion of the testis, the connective tissue of the tunica albuginea extends more deeply into the organ. This could be acknowledged within the space delineated by the rectangle, which is shown at greater magnification in figure below. As noted above, the seminiferous tubules are arranged in the form of a loop, with every end becoming a member of the rete testis. Straight tubules are very short and are lined by Sertoli-like cells; no germ cell component is present.
Discount ciprofloxacin 500 mg visaIn this stage bacteria evolution cheap 500mg ciprofloxacin with amex, parasympathetic reflexes working by way of the vagus nerves stimulate gastric secretion at the style antibiotic resistance prevalence 250mg ciprofloxacin, odor antibiotic resistance of bacteria discount ciprofloxacin 500 mg with mastercard, sight antibiotic 100mg discount ciprofloxacin 250 mg visa, or thought of food. The gastric part of gastric secretion, which accounts for a lot of the secretory activity, starts when food enters the stomach. The presence of food and the distension of the stomach wall set off the stomach to launch gastrin, which stimulates manufacturing of more gastric juice. As food enters the abdomen and mixes with gastric juice, the pH of the contents rises, which reinforces gastrin secretion. For the stomach to secrete hydrochloric acid, hydrogen ions are actively transported into the stomach. Negatively charged chloride ions, attracted by the positively charged hydrogen ions, transfer from the blood into the abdomen. Following a meal, the blood focus of bicarbonate ions increases, and the urine excretes excess bicarbonate ions. The intestinal part of gastric secretion begins when meals leaves the abdomen and enters the small gut. When food first contacts the intestinal wall, it stimulates intestinal cells to release a hormone, intestinal gastrin, that briefly enhances gastric gland secretion. His extensive accidents eventually healed, however a hole, known as a fistula, was left, allowing observers to take a look at his abdomen in action. Army surgeon, William beaumont, spent eight years watching meals digesting within the stomach, and famous how the abdomen lining modified within the course of. A colleague who repeated the experiment developed an ulcer and required antibiotics. After a decade of debate, the medical neighborhood lastly concurred that the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which thrives beneath acidic situations, causes many cases of gastritis and peptic ulcers. A quick course of antibiotics and acid-lowering drugs has replaced lifelong treatments. This coating is very important as a end result of pepsin can digest the proteins of stomach tissues, as properly as these in foods. As more meals strikes into the small intestine, a sympathetic reflex triggered by acid in the upper a part of the small intestine inhibits secretion of gastric juice from the abdomen wall. Similarly, fat in the small intestine stimulate intestinal cells to launch intestinal somatostatin, which inhibits launch of gastric juice. Overall, these actions lower gastric secretion and motility as the small gut fills with food. The stomach absorbs only small volumes of water and certain salts, in addition to sure lipid-soluble drugs. Mixing and emptying actions Food stretches the smooth muscle layers of the abdomen wall. The abdomen might enlarge, however its muscle layers keep their tone, and inside strain of the stomach normally is unchanged. When a person eats more than the abdomen can comfortably hold, the internal stress may rise enough to stimulate ache receptors. Following a meal, the blending movements of the stomach wall assist in producing a semifluid paste of meals particles and gastric juice known as chyme (ki m). Peristaltic waves push the chyme � towards the pylorus of the stomach, and as chyme accumulates close to the pyloric sphincter, it begins to loosen up. Stomach contractions push chyme somewhat (5�15 milliliters) at a time into the small intestine. These stomach contraction waves push many of the chyme backward into the abdomen, mixing it additional. The decrease esophageal sphincter prevents reflux of abdomen contents into the esophagus. Food in stomach chemically and mechanically stimulates release of gastrin, which, in turn, stimulates secretion of gastric juice; reflex responses additionally stimulate gastric juice secretion. As meals enters the small intestine, it stimulates intestinal cells to launch intestinal gastrin, which, in turn, briefly promotes the secretion of gastric juice from the stomach wall. A feeling of fullness turns into abdominal ache and then heartburn, as stomach contents back up into the esophagus (gastric reflux). Most antacids include a compound containing sodium, calcium, magnesium, or aluminum. Avoiding gastric reflux and heartburn is a more healthful strategy than gorging and then reaching for medicine. The price at which the stomach empties depends on the fluidity of the chyme and the kind of meals. Fatty meals may stay in the stomach three to six hours; meals excessive in proteins transfer through extra shortly; carbohydrates normally cross by way of more rapidly than either fats or proteins. As chyme fills the duodenum (the proximal portion of the small intestine), internal stress on the organ will increase, stretching the intestinal wall. These actions stimulate sensory receptors within the wall, triggering an enterogastric reflex (en-ter-o-gastrik refleks). The name of this reflex, like these of other digestive reflexes, describes the origin and termination of reflex impulses. That is, the enterogastric reflex begins within the small intestine (entero) and ends within the stomach (gastro). As a result of the enterogastric reflex, fewer parasympathetic impulses arrive on the stomach, decreasing peristalsis, and intestinal filling slows (fig. If chyme coming into the gut is fatty, the intestinal wall releases the hormone cholecystokinin, which additional inhibits peristalsis. Vomiting results from a posh reflex that empties the abdomen in the reverse of the conventional path. Sensory impulses journey from the location of stimulation to the vomiting center in the medulla oblongata. The responses initiated by the vomiting middle embody taking a deep breath, raising the soft palate and thus closing the nasal cavity, closing the opening to the trachea (glottis), stress-free the lower esophageal sphincter, contracting the diaphragm so it presses downward over the abdomen, and contracting the abdominal wall muscle tissue to improve strain contained in the belly cavity. These motor responses squeeze the stomach from all sides, forcing its contents upward and out by way of the open pathway via the esophagus, pharynx, and mouth. It extends horizontally across the posterior stomach wall, with its head in the C-shaped curve of the duodenum (portion of the small intestine) and its tail against the spleen (fig. Pancreatic acinar cells produce pancreatic juice and make up the bulk of the pancreas. The smaller tubes unite to form larger ones, which be part of a pancreatic duct that extends the length of the pancreas and transports pancreatic juice to the small gut. The pancreatic duct normally connects with the duodenum on the same place where the bile duct from the liver and gallbladder joins the duodenum, though divisions and different connections may be current (see figs. The main pancreatic duct and bile duct be part of at a short, dilated tube referred to as the hepatopancreatic ampulla (ampulla of Vater).
Order ciprofloxacin 1000mg with amexIn a condylar joint treatment for k9 uti ciprofloxacin 1000mg generic, or ellipsoidal joint antibiotic resistant urinary tract infection treatment buy 1000mg ciprofloxacin free shipping, the ovoid condyle of 1 bone suits into the elliptical cavity of another bone antibiotic diarrhea treatment cheap ciprofloxacin 500mg with visa, as within the joints between the metacarpals and phalanges (fig antibiotics for acne boils cheap 500mg ciprofloxacin with amex. This kind of joint permits back-and-forth and side-to-side movement in two planes (biaxial movement), but not rotation. The articulating surfaces of aircraft joints, or gliding joints, are practically flat or slightly curved. These joints permit sliding or back-and-forth motion and twisting actions (nonaxial movement). Most of the joints in the wrist and ankle, as properly as those between the articular processes of vertebrae, belong to this group (fig. The sacroiliac joints and the joints fashioned by ribs 2 through 7 connecting with the sternum are additionally airplane joints. In a hinge joint, the convex floor of 1 bone suits into the concave surface of one other, as within the elbow and the joints of the phalanges (fig. Such a joint resembles the hinge menisci separate the articulating surfaces of the femur and tibia. In actuality, articulating cartilages are essentially in contact with one another. In a pivot joint, or trochoid joint, the cylindrical floor of one bone rotates in a ring formed of bone and a ligament. Movement at such a joint is proscribed to rotation around a central axis (uniaxial movement). The joint between the proximal ends of the radius and the ulna, where the pinnacle of the radius rotates in a ring shaped by the radial notch of the ulna and a ligament (anular ligament), is of this kind. Similarly, a pivot joint features in the neck as the top turns from aspect to facet. In this case, the ring fashioned by a ligament (transverse ligament) and the anterior arch of the atlas rotates across the dens of the axis (fig. A saddle joint, or sellar joint, varieties between bones whose articulating surfaces have each concave and convex regions. This bodily relationship permits quite a lot of movements, primarily in two planes (biaxial movement), as in the case of the joint between the carpal (trapezium) and the metacarpal of the thumb (fig. Condylar Joints between metacarpals and phalanges Joints between varied bones of wrist and ankle elbow and joints of phalanges Joint between proximal ends of radius and ulna Joint between carpal and metacarpal of thumb three. Typically, one finish of a muscle is connected to a less movable or relatively fastened part on one facet of a joint, and the other end of the muscle is fixed to a more movable part on the opposite side. When the muscle contracts, its fibers pull its movable finish (insertion) towards its mounted finish (origin), and a movement happens on the joint. The following terms describe actions at joints that occur in numerous instructions and in several planes (figs. Abduction of the top and neck and bending of the trunk to the aspect could additionally be termed lateral flexion. Medial (internal) rotation is the turning of a limb on its longitudinal axis so its anterior surface moves toward the midline, whereas lateral (external) rotation is the turning of a limb on its longitudinal axis in the other way. However, muscle tissue and tendons surround and reinforce the capsule, preserving collectively the articulating parts of the shoulder (fig. Although these joints have much in frequent, each has a unique structure that makes possible its specific operate. The ligaments of the shoulder joint, a few of which assist stop displacement of the articulating surfaces, include the next (fig. The coracohumeral (korah-ko-humer-al) ligament is composed of a broad band of connective tissue that connects the coracoid process of the scapula to the larger tubercle of the humerus. The glenohumeral (gleno-humer-al) ligaments include three bands of fibers that appear as thickenings within the ventral wall of the joint capsule. They prolong from the edge of the glenoid cavity to the lesser tubercle and the anatomical neck of the humerus. Shoulder Joint the shoulder joint is a ball-and-socket joint that consists of the rounded head of the humerus and the shallow glenoid cavity of the scapula. The coracoid and acromion processes of the scapula protect these elements, and dense connective tissue and muscle hold them together. The joint capsule of the shoulder is attached along the circumference of the glenoid cavity and the anatomical neck of the humerus. The transverse humeral ligament consists of a slim sheet of connective tissue fibers that runs between the lesser and the larger tubercles of the humerus. Together with the intertubercular sulcus of the humerus, the ligament types a canal (retinaculum) by way of which the long head of the biceps brachii muscle passes. It is connected alongside the margin of the glenoid cavity and types a rim with a skinny, free edge that deepens the cavity. The main ones embrace the subscapular bursa between the joint capsule and the tendon of the subscapularis muscle, the subdeltoid bursa between the joint capsule and the deep floor of the deltoid muscle, the subacromial bursa between the joint capsule and the undersurface of the acromion process of the scapula, and the subcoracoid bursa between the joint capsule and the coracoid means of the scapula (see figs. The shoulder joint is able to a variety of movement, due to the looseness of its attachments and the big articular surface of the humerus in comparability with the shallow depth of the glenoid cavity. These actions include flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, rotation, and circumduction. Motion occurring simultaneously in the joint fashioned between the scapula and the clavicle may also assist such movements. Consequently, the articulating surfaces could become displaced or dislocated easily. Ulnar and radial collateral ligaments thicken the two joints, and fibers from a muscle (brachialis) within the arm reinforce its anterior floor. The ulnar collateral ligament, a thick band of dense connective tissue, is located within the medial wall of the capsule. The anterior portion of this ligament connects the medial epicondyle of the humerus to the medial margin of the coronoid strategy of the ulna. Its posterior part is connected to the medial epicondyle of the humerus and to the olecranon means of the ulna (fig. The radial collateral ligament, which strengthens the lateral wall of the joint capsule, is a fibrous band extending between the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and the anular ligament of the radius. The anular ligament, in flip, attaches to the margin of the trochlear notch of the ulna, and it encircles the top of the radius, maintaining the pinnacle in contact with the radial notch of the ulna (fig. The elbow joint capsule encloses the resulting radioulnar joint so that its perform is closely associated with the elbow. Also, various amounts of adipose tissue form fatty pads between the synovial membrane and the fibrous layer of the joint capsule. The solely actions that may occur at the elbow between the humerus and ulna are hinge-type movements-flexion and extension. Guided by an arthroscope, the surgeon samples a small piece of the synovial membrane and extracts and examines dna for bacterial sequences, such as from the bacterium that causes Lyme illness (Borrelia burgdorferi).
Cheap 250 mg ciprofloxacinThe choroid coat also incorporates plentiful pigment-producing melanocytes that give it a brownish-black appearance antibiotics and wine buy 250 mg ciprofloxacin with visa. The melanin of these cells absorbs extra mild and helps maintain the inside of the eye dark antibiotics for uti at walmart cheap ciprofloxacin 250 mg otc. The ciliary body antimicrobial vinyl order ciprofloxacin 750 mg without prescription, which is the thickest a part of the center tunic antibiotics for acne bad buy 250 mg ciprofloxacin, extends anteriorly and inward from the choroid coat and forms a ring within the front of the attention. In the ciliary body are radiating folds called ciliary processes and teams of smooth muscle cells that represent the ciliary muscular tissues. Many strong but delicate fibers, known as suspensory ligaments (zonular fibers), prolong inward from the ciliary processes and maintain the clear lens in position. The distal ends of these fibers are hooked up along the margin of a thin capsule that surrounds the lens. The physique of the lens, which lacks blood vessels, lies directly behind the iris and pupil and consists of specialised epithelial cells. The cells of the lens originate from a single layer of epithelium beneath the anterior portion of the lens capsule. The cells divide, and the new cells on the floor of the lens capsule differentiate into specialized columnar epithelial cells known as lens fibers, which constitute the substance of the lens. Lens fiber manufacturing continues slowly throughout life, thickening the lens from entrance to back. Simultaneously, the deeper lens fibers are compressed toward the middle of the construction (fig. More than 90% of the proteins in a lens cell are lens crystallins, which combination into the fibers. These proteins, together with the absence of organelles that scatter mild (mitochondria, endoplasmic reticula, and nuclei), provide the transparency of the lens. The lens capsule is a transparent, membranelike structure largely composed of intercellular materials (fig. However, the suspensory ligaments hooked up to the margin of the capsule are additionally under pressure, and so they pull outward, flattening the capsule and the lens. If the tension on the suspensory ligaments relaxes, the elastic capsule rebounds, and the lens floor turns into more convex. This change, referred to as accommodation (ah-komo-dashun), happens in the lens when the attention focuses to view a detailed object. When the circular muscle contracts, the diameter of the ring shaped by the ciliary processes decreases; when the other muscle contracts, the choroid coat is pulled ahead, and the ciliary body shortens. In this thickened state, the lens is concentrated for viewing objects closer than before (fig. To concentrate on a distant object, the ciliary muscular tissues relax, rising tension on the suspensory ligaments. The iris is a thin diaphragm largely composed of connective tissue and easy muscle. The iris extends forward from the periphery of the ciliary body and lies between the cornea and the lens. It divides the space separating these parts, called the anterior cavity, into an anterior chamber (between the cornea and the iris) and a posterior chamber (between the iris and the vitreous humor, occupied by the lens). The epithelium on the inner surface of the ciliary physique constantly secretes a watery uid called aqueous humor into the posterior chamber. The uid circulates from this chamber via the pupil, which is a round opening within the center of the iris, and into the anterior chamber (fig. Aqueous humor fills the area between the cornea and the lens, offering nutrients and sustaining the shape of the front of the attention. It leaves the anterior chamber by way of veins and a special drainage canal, known as the scleral venous sinus (canal of Schlemm), within the wall of the anterior chamber on the junction of the cornea and the sclera (g. The smooth muscle cells of the iris type two groups, a round set and a radial set. The circular set (pupillary constrictor) acts as a sphincter, and when it contracts, the pupil will get smaller and the intensity of the light getting into decreases. When the radial set (pupillary dilator) contracts, the diameter of the pupil will increase and the intensity of the sunshine entering increases. The sizes of the pupils change continuously in response to pupillary reflexes triggered by such elements as light depth, gaze, lodging, and variations in emotional state. For instance, shiny light elicits a re ex, and impulses are carried out along parasympathetic nerve bers to the pupillary constrictors of the irises. Conversely, in dim gentle, impulses are performed on sympathetic nerve bers to the pupillary dilators of the irises, and the pupils dilate (fig. The amount and distribution of melanin in the irises and the density of the tissue in the physique of the iris decide eye shade. When the same distribution of melanin is denser in the body of the iris, eye color is grey. When melanin is inside the physique of the iris as nicely as within the posterior epithelial covering, the iris seems brown. The Inner Tunic the inside tunic of the eye consists of the retina (ret -nah), which i incorporates the visual receptor cells (photoreceptors). This almost transparent sheet of tissue is continuous with the optic nerve in the back of the eye and extends ahead because the internal lining of the eyeball. It has distinct layers, together with retinal pigment epithelium, neurons, nerve bers, and limiting membranes (figs. The nerve bers of three of those groups-the photoreceptors, bipolar neurons, and ganglion cells-provide a direct pathway for impulses triggered within the photoreceptors to the optic nerve and mind. The nerve bers of the opposite two teams of retinal cells, known as horizontal cells and amacrine cells, cross laterally between retinal cells (see g. The horizontal and amacrine cells modify the sample of impulses carried out on the bers of the direct pathway. In the central region of the retina is a yellowish spot referred to as the macula lutea that occupies about 1 sq. millimeter. A depression in its middle, called the fovea centralis, is in the region of the retina that produces the sharpest vision. Here the nerve bers from the retina depart the attention and turn into parts of the optic nerve. These vessels are continuous with capillary networks of the retina, and along with vessels in the underlying choroid coat, they supply blood to the cells of the inner tunic. The light rays should bend to be centered, a phenomenon known as refraction (re-frakshun). Refraction occurs when light rays move at an angle from a medium of one density right into a medium of a unique density. A lens with a convex floor causes gentle waves to converge, and a lens with a concave surface causes light waves to diverge (fig.
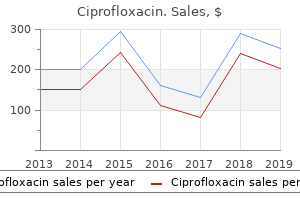
Ciprofloxacin: 1000 mg, 750 mg, 500 mg, 250 mg
Buy ciprofloxacin 250mg visaThese enzymes and others dissolved in the fluid within the mitochondrion antibiotic resistance microbiology cheap ciprofloxacin 500mg with mastercard, called the matrix antibiotic resistant klebsiella uti buy 1000 mg ciprofloxacin amex, control many of the chemical reactions that launch vitality from glucose and other nutrients in a process known as cellular respiration antibiotic resistance prediction buy 250 mg ciprofloxacin with amex. Milk protein Cell membrane Milk protein in Golgi vesicle Sugars 5 Fat droplets pick up a layer of the cell membrane as they exit the cell headphones bacteria 700 times cheap 250 mg ciprofloxacin free shipping. In sure scavenger cells they might engulf and digest complete smaller physique cells that have been broken. An abnormality in just one type of lysosomal enzyme may be devastating to well being (see Clinical Application three. Peroxisomes (pe-roksi-somz) are membranous sacs that resemble lysosomes in measurement and form. They are in all human cells but are most abundant in cells of the liver and kidneys. Peroxisomes contain enzymes, referred to as peroxidases, that catalyze metabolic reactions that launch hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), which is toxic to cells. Peroxisomes additionally comprise an enzyme known as catalase, which decomposes hydrogen peroxide. The outer surface of a peroxisome membrane contains some forty types of enzymes, which catalyze a wide range of biochemical reactions, together with: � synthesis of bile acids utilized in fat digestion � breakdown of lipids known as very-long-chain fatty acids � degradation of uncommon biochemicals � detoxing of alcohol Abnormal peroxisomal enzymes can significantly have an result on health (Clinical Application 3. This abundance is why common symptoms of illnesses affecting mitochondria are exercise intolerance and weak, flaccid muscle tissue. Lysosomes (liso-somz) are the "rubbish disposals" of the � cell, where enzymes dismantle debris. They contain powerful enzymes that break down proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids, including these of international particles that the cell has taken in. Lysosomes are membranous sacs that include enzymes that dismantle debris in a process known as autophagy. Today, remedies for many problems are a direct result of understanding a illness course of on the mobile stage. Following are three examples of how abnormalities in organelles cause whole-body signs. Had he been born at present, he would have been examined for Krabbe illness, together with dozens of other "inborn errors of metabolism," with a few drops of blood from his heel taken shortly after delivery. There are several kinds of these uncommon situations that have an effect on about 10,000 folks worldwide. Treatments use several strategies: replacing the enzyme or gene, utilizing a drug to reduce the biochemical buildup, or utilizing a drug that can unfold and appropriately refold a misfolded enzyme. Blood tests revealed that mother and daughter had elevated ranges of biochemicals (pyruvic acid and lactic acid) that indicated they were unable to extract maximal vitality from nutrients. Mitochondria are inherited only from the mother as a end result of the mitochondria are excluded from the part of a sperm that enters an egg cell. When he grew to become torpid, weak, and dizzy, his academics and fogeys realized that his drawback was not simply temper tantrums. His pores and skin darkened, blood sugar levels plummeted, heart rhythm altered, and the degrees of electrolytes in his physique fluids changed. Without the enzyme, the fatty acid builds up in cells in the mind and spinal twine, stripping these cells of their myelin. Lorenzo lived much longer than his medical doctors expected, to age thirty, either due to the oil or the wonderful supportive care. A centrosome (sentro-som) (central body) is a construction located within the cytoplasm close to the nucleus. Centrioles also produce the interior elements of cell membrane projections called cilia and flagella. Internally, both cilia and flagella include 9 teams of three microtubules with two additional microtubules within the center, forming a definite cylindrical sample. Each cilium is a hairlike construction about 10 �m lengthy, which attaches simply beneath the cell membrane to a modified centriole known as a basal body. They move in a coordinated "to-and-fro"method in order that rows of cilia beat one after the opposite, producing a wave that sweeps throughout the surface. Ciliary action moves an egg toward the uterus, and early in improvement controls movement of cells as they kind organs. Another kind of this organelle, known as a primary or nonmotile cilium, functions as a "mobile antenna," sensing indicators and sending them into cells to management progress and keep tissues. Compared to the various motile cilia that fringe cells, main cilia are shorter and may be one per cell. Cilia and flagella work in the identical means, but in distinction to the sweeping movements caused by cilia, where the cells are fastened in position, the flagellum instead causes the cell to transfer. Microfilaments and microtubules are two kinds of threadlike constructions in the cytoplasm. Microfilaments are tiny rods of the protein actin that type meshworks or bundles and supply sure cellular actions (fig. For example, microfilaments represent myofibrils, which shorten or contract muscle cells. In different cell sorts, microfilaments associated with the internal floor of the cell membrane aid cell motility. Microtubules are long, slender tubes with diameters two or 3 times larger than these of microfilaments. They type centrioles and supply conduits for organelles, just like the tracks of a curler coaster. Unlike the microtubules which are all tubulin protein and the microfilaments which might be all actin protein, intermediate filaments are composed of any of several types of proteins and take the overall type of dimers (protein pairs) entwined into nested, coiled rods. In dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa, skin layers separate because of irregular keratin proteins in intermediate filaments. In large axonal neuropathy, intermediate filaments usually built of a protein known as gigaxonin overfill motor neurons, robbing kids of mobility. Most striking is progeria, in which irregular lamin intermediate filaments trigger extremely rapid getting older. Here they form a strong internal scaffolding that helps the cells connect to kind a barrier. In all cells, intermediate filaments composed of proteins referred to as lamins support the inner floor of the membranous envelope that defines the nucleus. The nucleus is enclosed in a double-layered nuclear envelope, which consists of an internal and an outer lipid bilayer membrane. These two membranes have a slender space between them, however are joined at locations that surround openings referred to as nuclear pores. Nuclear pores enable sure dissolved substances to move between the nucleus and the cytoplasm (fig. The nucleus accommodates a fluid (nucleoplasm) by which other buildings are suspended. When cell division begins, chromatin fibers coil so tightly that the person chromatin fibers become visible, when stained correctly, under the light microscope. The tightness with which chromatin regionally folds varies along the chromosomes, relying upon which genes are being accessed for their data at a particular time. It has no surrounding membrane and is formed in specialized areas of certain chromosomes.
Syndromes - Recent surgery or a history of structural problems in the urinary tract
- Roof of mouth looks red
- Watery diarrhea (often five to 10 times per day)
- Teach your child to watch for cars and ride bikes safely.
- Pregnant women should ask their health care provider if the vaccine is safe for them.
- Cover your mouth with a tissue when coughing and throw it away after use.
- Weakness or paralysis that gets slightly better with activity
- Blood vessel disease
- Making certain tendons or ligaments shorter or longer
- Burning in mouth and throat
Purchase ciprofloxacin 250 mg mastercardA gadget referred to as a pacemaker-cardioverter-defibrillator attempts to correct ventricular fibrillation ought to it occur antibiotics for lower uti generic ciprofloxacin 1000 mg with visa. They type a closed circuit of tubes that carries blood from the center to the physique cells and back again antibiotics uti buy ciprofloxacin 1000mg mastercard. The arteries and arterioles conduct blood away from the ventricles of the center and result in bacteria kingdom facts buy 500mg ciprofloxacin mastercard the capillaries antibiotics making me tired buy ciprofloxacin 1000 mg line, the place substances are exchanged between blood and the physique cells. Researchers create substitute blood vessels from cells and their products plus synthetic supplies. One such blood vessel consists of easy muscle cells seeded onto tubes of a biodegradable polymer. The cells secrete collagen and extracellular matrix, which substitute the polymer, and then detergent is utilized to take away the cells. Another strategy makes use of rubber tubing and a nutrient answer that prompts the cells to produce further elastin, which makes the substitute vessels extra versatile. Because development of tissues and organs in the laboratory (part of regenerative medicine) requires a blood provide, tissue engineers are creating cell-lined tubules using 3D printing to function as a part of a semisynthetic, ex vivo ("exterior the physique") cardiovascular system. In normal development, angiogenesis is essential to construct a blood provide to serve a rising physique. New blood vessels deliver nutrients, hormones, and progress elements to tissues and take away wastes. After a heart attack, for instance, new vessels kind within the remaining wholesome cardiac muscle. As is the case for most organic processes, angiogenesis must be extremely managed. Two specific functions are healing hearts and eradicating further capillaries in tumors and in eyes. At the identical time, endothelial cells that are a half of the tumor assemble into sheets, roll into tubules, and snake out of the tumor as new capillaries. Other cancer cells wrap around the capillaries, spreading out on this scaffolding into close by tissues. For a time, possibly even years, these secondary tumors keep small, adhering to the outsides of the blood vessels that delivered them. From the remark by many surgeons that when a major tumor is eliminated, secondary tumors develop, Harvard researcher Judah Folkman hypothesized that the primary tumor secretes antiangiogenesis elements that keep the secondary tumors small. Once components that promote or block angiogenesis have been found within the Eighties, researchers started to research the antiangiogenesis elements that maintain secondary tumors small, to develop them as most cancers therapies. The first antiangiogenesis drug to deal with most cancers became obtainable in 2004, for colorectal most cancers that has spread to other organs. Today antiangiogenesis drugs are also used to deal with age-related macular degeneration, during which extra capillaries prolong into the retina and block central vision. Coronary bypass surgical procedure and angioplasty are therapies that restore blood circulate by circumventing a blockage or opening up an artery, respectively. These vessels subdivide into progressively thinner tubes and finally give rise to the finer, branched arterioles (ar-tere-olz). The wall of an artery consists of three distinct layers, or tunics, proven in figure 15. The innermost tunic, tunica interna (intima), consists of a layer of simple squamous epithelium, referred to as endothelium, that rests on a connective tissue membrane wealthy in elastic and collagen fibers. The endothelial lining of an artery offers a clean floor that enables blood cells and platelets to circulate by way of with out being broken. Additionally, endothelium helps forestall blood clotting by secreting biochemicals that inhibit platelet aggregation (see chapter 14, p. Endothelium also could help regulate native blood circulate by secreting substances that dilate or constrict blood vessels. For example, endothelium releases the gasoline nitric oxide, which relaxes the graceful muscle of the vessel. It includes easy muscle cells, which encircle the tube, and a thick layer of elastic connective tissue. The connective tissue provides the vessel a tough elasticity that enables it to face up to the pressure of blood stress and, at the similar time, to stretch and accommodate the sudden enhance in blood volume that accompanies ventricular contraction. The outer layer, tunica externa (adventitia), is comparatively skinny and chiefly consists of connective tissue with irregular elastic and collagen fibers. It also accommodates tiny vessels (vasa vasorum) that give rise to capillaries and provide blood to the more exterior cells of the artery wall. The sympathetic branches of the autonomic nervous system innervate easy muscle in artery and arteriole walls. Vasomotor fibers stimulate the sleek muscle cells to contract, decreasing the diameter of the vessel. If vasomotor impulses are inhibited, the muscle cells chill out, and the diameter of the vessel increases. Changes within the diameters of arteries and arterioles significantly influence blood flow and blood pressure. The walls of the larger arterioles have three layers similar to those of arteries (fig. The wall of a really small arteriole consists only of an endothelial lining and a few clean muscle cells, surrounded by a small amount of connective tissue (fig. Arterioles, that are microscopic continuations of arteries, give off branches known as metarterioles that, in turn, join capillaries. The arteriole and metarteriole walls are tailored for vasoconstriction and vasodilation in that their clean muscle cells reply to impulses from the autonomic nervous system by contracting or relaxing. Capillaries are extensions of the inner linings of arterioles in that their partitions are endothelium-a single layer of squamous epithelial cells (fig. These skinny walls form the semipermeable layer through which substances in the blood are exchanged for substances in the tissue fluid surrounding physique cells. The openings or intercellular passageways in the capillary walls are skinny slits where endothelial cells overlap (fig. The sizes of these openings, and consequently the permeability of the capillary wall, range from tissue to tissue. Capillaries with the most important openings embrace those of the liver, spleen, and red bone marrow. Discontinuous capillaries permit giant proteins and even intact cells to pass via as they enter or depart the circulation. Muscle and nerve tissues, which use ample oxygen and nutrients, are richly equipped with capillaries. Tissues with slower metabolic charges have fewer capillaries, such as cartilage, or lack them completely, corresponding to within the cornea. Slit Tissue fluid Capillary (a) Nucleus of endothelial cell Endothelial cell cytoplasm Lumen of capillary Cell junction the spatial patterns of capillaries additionally differ in various body elements. For example, some capillaries pass instantly from arterioles to venules, but others result in extremely branched networks (fig.
Buy 750mg ciprofloxacin overnight deliveryThe Sertoli cells then phagocytose this excess cytoplasm antibiotic nerve damage effective 500mg ciprofloxacin, additionally termed the residual physique antibiotic eye drops for stye buy ciprofloxacin 750 mg online. The two pairs of chromosomes (2n) of maternal and paternal origin are depicted in purple and blue antimicrobial fogger purchase ciprofloxacin 250mg line, respectively antibiotics for sinus infection nz buy ciprofloxacin 1000 mg fast delivery. The mitotic division produces daughter cells which are genetically similar to the parental (2n) cell. The meiotic division, which has two components, a reductional division and an equatorial division, produces a cell that has only half the number of chromosomes (n). In addition, in the course of the chromosome pairing in prophase I of meiosis, chromosome segments are exchanged, crossing-over, creating genetic range. The launch of acrosomal enzymes as the sperm touches the egg is step one in the acrosome response. This advanced course of facilitates sperm penetration and subsequent fertilization and prevents the entry of further sperm into the ovum. The fundamental modifications within the structure of the key organelles of the spermatid are illustrated (see text for detailed explanation). Spermatids are not attached to each other and are launched from the Sertoli cells. Spermatids are launched into the lumen of the seminiferous tubules through the process known as spermiation. Toward the end of maturation section of spermatogenesis, elongated spermatids are launched from Sertoli cells into the lumen of seminiferous tubule. This complicated course of referred to as spermiation includes progressive removing of specialised Sertoli-to-spermatid junctional complexes and disengagement of spermatids from the Sertoli cell. The presence of the 1-integrins within the Sertoli-to-spermatid junctions, as properly as elevated activity of the integrin-linked kinase on the time of spermiation, suggests an enzymatic control of spermatid release. The rate of spermiation within the testis determines the number of sperm cells within the ejaculate of semen. The acrosomal cap that covers the anterior two-thirds of the nucleus accommodates hyaluronidase, neuraminidase, acid phosphatase, and a trypsin-like protease called acrosin. Key structural options of the top (viewed in frontal and sagittal planes), the center piece, and the principal piece of the spermatozoon are illustrated on the proper. The middle piece is approximately 7 m long and contains the mitochondria, helically wrapped around the coarse fibers and the axonemal complex. These mitochondria provide the energy for movement of the tail and thus are answerable for the motility of the sperm. The principal piece is approximately forty m lengthy and accommodates the fibrous sheath external to the coarse fibers and the axonemal advanced. The finish piece, approximately the final 5 m of the flagellum in the mature sperm, incorporates only the axonemal complex. Newly released sperm cells are processed within the epididymis where they purchase motility and endure further maturation. This course of, which includes removal and substitute of glycocalyx elements (glycoconjugates) on the sperm membrane, is known as capacitation. These groupings or associations happen because intercellular bridges are present between the progeny of each pair of type Ap spermatogonia and since the synchronized cells spend specific times in each stage of maturation. Each recognizable grouping, or cell association, is taken into account a stage in a cyclic course of. The series of stages that appears between two successive occurrences of the same cell affiliation sample at any given web site within the seminiferous tubule constitutes a cycle of the seminiferous epithelium. The cycle of the seminiferous epithelium has been most totally studied in rats, in which 14 successive phases occur in linear sequence along the tubule. Male Reproductive System Newly launched sperm cells are nonmotile and are carried from the seminiferous tubules in a fluid secreted by the Sertoli cells. The fluid and sperm move via the seminiferous tubules, facilitated by peristaltic contractions of the peritubular contractile cells of the lamina propria. They then enter the straight tubules, a brief section of the seminiferous tubule where the epithelium consists solely of Sertoli cells. At the mediastinum testis, the fluid and sperm enter the rete testis, an anastomosing system of ducts lined by simple cuboidal epithelium (Plate 87, web page 824). From the rete testis, they transfer into the extratesticular portion of the efferent ductules (ductuli efferentes), the primary a part of the excurrent duct system, and then into the proximal portion of the duct of the epididymis (ductus epididymis). As the sperm cells move through 4 to 5 m of the highly coiled duct of the epididymis, they acquire motility and undergo several maturational adjustments. The surface-associated decapacitation issue is added to inhibit the fertilizing capability of the sperm cells (page 811). These factors regulate flagellar exercise via modifications in protein phosphorylation, ensuing from activities of protein kinases and protein phosphatases. For occasion, pharmacologic stimulation of protein kinase A activity will increase motility of sperm cells, whereas inhibition of protein phosphatase activity may initiate or stimulate such motility. This means that phosphatases have an necessary function in the regulation of sperm kinetic activity. They purchase the ability to fertilize the After injecting a pulse of tritiated thymidine, a particular era of cells could be followed by sequential biopsies of the seminiferous tubules. In this fashion, the time required for the labeled cells to go through the various phases can be determined. Several generations of growing cells may be current within the thickness of the seminiferous epithelium at any given website and at any given time, which produces the attribute cell associations. Autoradiographic research have revealed that the length of the cycle of the seminiferous epithelium is constant, lasting about sixteen days in humans. It would then require roughly 12 days for the spermatozoon to move via the epididymis. The size of the cycle and the time required for spermatogenesis are constant and particular in each species. This diagram shows each of the six recognizable cell associations (stages) that happen within the cycle of the human seminiferous epithelium. These levels of spermatogenesis are artificially defined according to adjustments noticed within the spermatids throughout their various steps of differentiation. In addition, the wave of the seminiferous epithelium describes the distribution of patterns of cellular association (spermatogenic stages) alongside the size of the tubule. In rodents and different mammals which have been studied, including subhuman primates, each stage occupies a big length of the seminiferous tubule, and the levels appear to occur sequentially alongside the size of the tubule. A transverse part through the tubule often reveals just one sample of cell associations. Therefore, a transverse part by way of a human seminiferous tubule could reveal as many as six different phases of the cycle organized in a pie-wedge trend across the circumference of the tubule.
Ciprofloxacin 750mg with amexIn about 40% of circumstances antibiotics medicine ciprofloxacin 500 mg sale, the thyroid gland reveals a pyramidal lobe treatment for sinus infection over the counter effective ciprofloxacin 750 mg, which is a remnant of the thyroglossal duct antibiotic vs antibacterial purchase ciprofloxacin 500mg without a prescription, a developmental reference to the bottom of the tongue antibiotic that starts with r buy ciprofloxacin 250mg visa. The thyroid gland is provided by blood from the superior and inferior thyroid arteries, and blood from the gland is drained by the superior, middle, and inferior thyroid veins. On the posterior (deep) surface of the lateral lobes, there are two pairs of small ovoid constructions which are designated as superior and inferior parathyroid glands. The primordium grows caudally and forms a duct-like invagination often recognized as the thyroglossal duct. The thyroglossal duct descends by way of the tissue of the neck to its ultimate vacation spot in entrance of the trachea, the place it divides into two lobes. During this downward migration, the thyroglossal duct undergoes atrophy, leaving an embryologic remnant, the pyramidal lobe of the thyroid, which is current in about 40% of the inhabitants. About the ninth week of gestation, endodermal cells differentiate into plates of follicular cells that turn into arranged into follicles. By week 14, well-developed follicles lined by the follicular cells contain colloid of their lumen. During week 7, epithelial cells lining the invagination of the fourth pharyngeal (branchial) pouches (sometimes referred to as the fifth pharyngeal pouches), often known as the ultimobranchial bodies, begin their migration towards the developing thyroid gland and become incorporated into the lateral lobes. After fusing with the thyroid, ultimobranchial body cells disperse among the follicles, giving rise to parafollicular cells that turn into integrated into the follicular epithelium. This electron micrograph reveals a single layer of epithelium containing low columnar follicular cells. A slim extracellular connective tissue space separates the follicular cells from the lumen of the capillary. Follicular epithelium contains two forms of cells: follicular and parafollicular cells. Each follicle consists of a single layer of epithelial cells surrounding a central mass of colloid. These cells vary in form and size according to the functional state of the gland. In routine hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) preparations, follicular cells exhibit a barely basophilic basal cytoplasm with spherical nuclei containing one or more prominent nucleoli. Small vesicles present within the apical cytoplasm are morphologically just like vesicles related to the Golgi equipment. Abundant endocytotic vesicles, identified as colloidal resorption droplets, and lysosomes are also present in the apical cytoplasm. A portion of the central mass of colloidal materials (C) in two adjoining follicles could be seen in the left corners of the micrograph. In routine H&E preparations, C cells are pale staining and happen as solitary cells or small clusters of cells. An extensive community of fenestrated capillaries derived from the superior and inferior thyroid arteries surrounds the follicles. Blind-ended lymphatic capillaries are present in the interfollicular connective tissue and may also present a second route for conveying the hormones from the gland. Both hormones regulate cell and tissue basal metabolism and heat production and affect physique progress and growth. Calcitonin has an necessary role in regulating serum calcium levels in decrease animals; nonetheless, its physiological function in humans remains elusive. Calcitonin lowers blood calcium ranges by suppressing the resorptive motion of osteoclasts and promotes calcium deposition in bones by growing the speed of osteoid calcification. Although calcitonin is used to treat patients with a quantity of problems related to extra bone resorption. The principal component of colloid is thyroglobulin, an inactive storage type of thyroid hormones. Active thyroid hormones are liberated from thyroglobulin and launched into the fenestrated blood capillaries that encompass the follicles solely after further cellular processing. The thyroid is unique amongst endocrine glands because it shops massive amounts of its secretory product extracellularly. From here, iodide ions are transported to the lumen of the follicle by the 86 kDa iodide/chloride transporter called pendrin located in the apical cell membrane. One or two iodine atoms are then added to the specific tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin. The thyroid hormones are fashioned by oxidative coupling reactions of two iodinated tyrosine residues in shut proximity. After endocytosis, thyroglobulin follows a minimum of two completely different intracellular pathways. In the lysosomal pathway, thyroglobulin is internalized and transported inside endocytotic vesicles to early endosomes. Resorption of thyroglobulin at this stage may be confirmed by the presence of large endocytic vesicles referred to as colloidal resorption droplets in the apical area of the follicular cells. In the transepithelial pathway, thyroglobulin is transported intact from the apical to the basolateral surface of follicular cells. This diagram depicts two follicular cells: one in the process of thyroglobulin synthesis (on the left with purple pathways) and the opposite in the means of thyroglobulin resorption (on the proper with blue pathways). Megalin is a transmembrane protein expressed at the apical floor of follicular epithelial cells immediately dealing with colloid. This pathway might scale back the extent of T4 and T3 release by diverting thyroglobulin away from the lysosomal pathway. The majority of T4 and T3 are liberated from thyroglobulin within the lysosomal pathway, and only negligible quantities of T4 and T3 are launched bound to thyroglobulin. Both T4 and T3 cross the basal membrane and enter the blood and lymphatic capillaries. Approximately less than 10% of launched hormones are bound to a nonspecific fraction of albumin, leaving only small quantities (1%) of free circulating hormones which would possibly be metabolically lively. The follicular cells of the thyroid gland predominately produce about 20 occasions more T4 than T3; however, T4 is transformed in the peripheral organs. Approximately 99% of T4 and T3 released from the thyroid gland into circulation bind to specific plasma proteins. The remaining free (unbound) T4 and T3 exert negative suggestions on the system and inhibit further launch of T4 and T3. This inhibition occurs on the level of the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus. After crossing the blood�brain barrier, T4 and T3 are transferred into neighboring astrocytes, where T4 is transformed to T3. T4 and T3 are additionally secreted into the cerebrospinal fluid and are taken up by the tanycytes (specialized ependymal cells) and astrocytes, where T4 is transformed to T3. The feedback system is activated in response to low thyroid hormone levels in the blood or metabolic needs.

Ciprofloxacin 1000mg with mastercardCommon websites of aneurysms embrace the thoracic and stomach aorta and an arterial circle at the base of the mind (circle of Willis) virus yang menguntungkan buy 1000 mg ciprofloxacin with amex. It might happen in association with an injury or an infection or after surgery antibiotics for uti infection symptoms discount 500 mg ciprofloxacin with mastercard, or it might develop for no apparent purpose bacteria have an average generation time cheap 750 mg ciprofloxacin with amex. If irritation is restricted to a superficial vein antibiotic vitamin c 750 mg ciprofloxacin mastercard, such as the higher or lesser saphenous veins, blood circulate may be rechanneled via other vessels. But if it happens in a deep vein, such because the tibial, peroneal, popliteal, or femoral veins, the consequences could be critical, significantly if the blood within the affected vessel clots and blocks normal circulation (see Clinical Application 14. This condition, known as thrombophlebitis, introduces a risk that a blood clot in a vein will detach, move with the venous blood, pass through the heart, and lodge within the pulmonary arterial system in a lung (pulmonary embolism). Varicose veins are abnormal and irregular dilations in superficial veins, notably in the legs. This condition is usually associated with prolonged, increased again strain within the affected vessels as a outcome of gravity, corresponding to when an individual stands. Crossing the legs or sitting in a chair so that its edge presses in opposition to the realm behind the knee can obstruct venous blood move and irritate varicose veins. The valves in these vessels lose their capacity to block the backflow of blood, and blood accumulates within the veins upstream from the valves. The resulting increased venous strain is accompanied by rising pressure in the venules and capillaries that supply the veins. Genetics, being pregnant, obesity, and standing for lengthy durations elevate the chance of developing varicose veins. Elevating the legs above the extent of the guts or placing on help hosiery earlier than arising within the morning can relieve discomfort. Intravenous injection of a substance that destroys veins (a sclerosing agent) or surgical removing of the affected veins may be necessary. The upper number signifies the systolic strain in mm Hg, and the lower quantity indicates the diastolic pressure in mm Hg. The surge of blood entering the arterial system during ventricular systole distends the elastic arterial walls, but the strain begins to drop nearly instantly because the contraction ends, and the arterial partitions recoil. This alternate increasing and recoiling of the arterial wall can be felt as a pulse in an artery that runs near the body floor. The radial pulse rate is equal to the speed at which the left ventricle contracts, and for that reason, it can be used to decide coronary heart fee. The average pressure within the arterial system can additionally be of interest because it represents the average pressure throughout the cardiac cycle driving blood to the tissues. Factors That Influence arterial Blood Pressure Arterial strain is dependent upon a wide range of factors. These include cardiac output, blood quantity, peripheral resistance, and blood viscosity (fig. It is calculated by multiplying the stroke volume by the center rate, expressed in beats per minute. If either the stroke quantity or the heart price will increase, so does the cardiac output, and, blood strain would enhance. Conversely, if the stroke quantity or the heart price decreases, the cardiac output decreases, and blood stress would also lower. Viscosity Viscosity (vis-kosi-te) is the difficulty with which the molecules of a fluid move past one another. However, any situation that alters the concentrations of blood cells or plasma proteins might alter blood viscosity. Blood Volume Blood volume equals the sum of the fashioned parts and plasma volumes within the vascular system. Normally blood pressure is instantly proportional to the volume of the blood in the cardiovascular system. If a transfusion restores regular blood quantity, normal strain may be reestablished. Blood quantity can even fall if the fluid balance is upset, as happens in dehydration. Researchers are investigating drugs that improve these peptides to treat the excess quantity associated with congestive coronary heart failure. Maintenance of regular blood pressure due to this fact requires regulation of these two elements (fig. Cardiac output is proscribed by the quantity of blood returning to the ventricles, referred to as the venous return. Usually, nevertheless, stroke volume could be elevated by sympathetic stimulation, which increases the pressure of ventricular contraction. Because solely about 60% of the end-diastolic quantity is pumped out in a traditional contraction, rising the pressure of ventricular contraction may enhance that fraction and assist maintain stroke quantity if venous return ought to lower. Peripheral resistance Friction between the blood and the partitions of the blood vessels produces a drive called peripheral resistance (pe-rifer-al re-zistans), which impedes blood circulate. Blood pressure must overcome peripheral resistance if the blood is to proceed flowing. For instance, when smooth muscle in arteriolar partitions contracts, this increases the peripheral resistance by constricting these vessels (decreasing the lumen diameter). Blood backs up into the arteries supplying the arterioles, and the arterial stress rises. Dilation of the arterioles (increasing the lumen diameter) has the opposite effect-peripheral resistance decreases, and the arterial blood strain drops in response. Arterial partitions are elastic, so when the ventricles discharge a surge of blood, arteries swell. Almost instantly, the elastic tissues recoil, and the vessel walls press towards the blood inside. This action helps drive the blood onward against the peripheral resistance in arterioles and capillaries. If there were no elasticity in the arterial partitions, blood pressure would fall dramatically between ventricular contractions. Elastic recoil additionally converts the intermittent flow of blood, a results of the cardiac cycle, into a extra continuous movement through the blood vessels. As blood enters the ventricles, myocardial cells within the ventricular walls are mechanically stretched. Within limits, the longer these fibers, the higher the force with which they contract. The more blood that enters the guts from the veins, the greater the ventricular distension, the stronger the contraction, the higher the stroke quantity, and the higher the cardiac output. Conversely, the less blood that returns from the veins, the less the ventricle distends, the weaker the ventricular contraction, and Control center Autonomic nervous system activates effectors Receptors Baroreceptors sense the elevated strain Effectors Peripheral resistance decreases Effectors Heart fee decreases, stroke quantity decreases Cardiac output decreases Stimulus Blood strain rises Response Blood strain returns toward normal too high Normal blood strain lower than 120/80 too low the lesser the stroke volume and cardiac output. This mechanism helps to ensure that the amount of blood discharged from the heart is equal to the quantity coming into its chambers.
Cheap 750mg ciprofloxacin with mastercardThe bigger lymphatic vessels lead to zombie infection android cheap ciprofloxacin 750mg with amex lymph nodes and then merge into lymphatic trunks herbal antibiotics for sinus infection buy ciprofloxacin 250mg with visa. Trunks lead to treatment for uti burning ciprofloxacin 500mg on-line two accumulating ducts-the thoracic duct and the best lymphatic duct antibiotic resistance new drugs buy ciprofloxacin 1000 mg cheap. Lymph nodes Lymph nodes are usually bean-shaped, enclosed in connective tissue that extends into the nodes and subdivides them into nodules which include masses of lymphocytes and macrophages and spaces by way of which lymph flows. Locations of lymph nodes (1) Lymph nodes aggregate in teams or chains alongside the paths of bigger lymphatic vessels. It resembles a big lymph node encapsulated and subdivided into lobules by connective tissue. The spleen, which filters international particles and broken red blood cells from the blood, accommodates many macrophages and lymphocytes. Tissue fluid originates from plasma and consists of water and dissolved substances that have handed via the blood capillary wall. Tissue fluid usually lacks massive proteins, however some smaller proteins are filtered out of blood capillaries into interstitial spaces. As the protein concentration of tissue fluid will increase, colloid osmotic stress will increase. Increasing hydrostatic strain in interstitial spaces forces some tissue fluid into lymphatic capillaries. Lymph is underneath comparatively low hydrostatic strain and may not move readily with out exterior aid. Contraction of skeletal muscles, contraction of easy muscle within the partitions of the massive lymphatic trunks, and low strain in the thorax created by respiration movements transfer lymph. The physique has innate (nonspecific) and adaptive (specific) defenses towards infection. Species resistance Each species is resistant to certain ailments that may have an effect on other species but is susceptible to ailments other species could resist. Mechanical limitations (1) Mechanical limitations include the pores and skin and mucous membranes. Inflammation (1) Inflammation is a tissue response to damage, damage, or an infection. Phagocytosis (1) probably the most active phagocytes in blood are neutrophils and monocytes. Monocytes give rise to macrophages, which may be free or mounted in numerous tissues. Antigens (1) Before start, body cells inventory "self " proteins and different giant molecules. Lymphocyte origins (1) Lymphocytes originate in pink bone marrow and are released into the blood. T cells and the mobile immune response (1) T cells are activated when an antigen-presenting cell shows a foreign antigen. Practical classification of immunity (1) A person who encounters a pathogen and has a major immune response develops naturally acquired energetic immunity. Hypersensitivity reactions (1) Hypersensitivity reactions are excessive misdirected immune responses that may injury tissues. The immune system begins to decline early in life, partially as a outcome of the shrinking thymus. Precise mechanisms focusing on specific pathogens present (specific) protection. IgA (1) associated with allergic reactions (2) important in B cell activation, on surfaces B. Why is injecting a substance into the skin like injecting it into the lymphatic system Some dad and mom hold their preschoolers away from different kids to stop them from catching illnesses. Why does vaccination provide long-lasting protection towards illness, whereas gamma globulin (IgG) provides only short-term safety Why is a transplant consisting of fetal tissue less likely to provoke an immune rejection response than tissue from an grownup The surgery was so successful that she was capable of return to aggressive swimming within a yr and made the Olympic staff. However, she was disqualified because of blood take a look at outcomes that found a male Y chromosome in her blood. How can removal of enlarged lymph nodes for microscopic examination help in diagnosing certain illnesses What capabilities of the lymphatic system could be affected in an individual born without a thymus Just as a tunnel via a mountain is crammed with air, not the fabric of the mountain, the within of the digestive tube is actually a half of the outside world, not a half of the interior surroundings. Whereas the pH, electrolyte concentrations, and water quantity of the internal surroundings are tightly regulated, they change from the beginning of the tube to its end, and range with the chemical nature of what we eat. Material that enters the tube is fi rst broken down into its chemical building blocks, corresponding to easy sugars, amino acids, nucleotides, fatty acids, and glycerol, after which absorbed across the wall of the tube, typically by particular transport processes. As long as all of the essential amino acids are present in your food regimen in sufficient quantities, the digestive system will convey them into the internal environment, and your muscles will be in a position to use them to build the proteins that they need. The mucosa (mu-ko sah), or mucous membrane has a surface of epithelium, underlying connective tissue (lamina propria), and a small quantity of smooth muscle (muscularis mucosae). In some areas, the mucosa is folded, with tiny projections that stretch into the passageway, or lumen, of the digestive tube. The mucosa additionally has glands into which the lining cells secrete mucus and digestive enzymes. The mucosa protects the tissues beneath it, secretes into the lumen, and absorbs substances from the food plan. The submucosa (sub mu-ko sah) incorporates considerable unfastened connective tissue in addition to glands, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves. The muscularis externa, or muscularis, which supplies actions of the tube, consists of two layers of easy muscle tissue. Coordinated contractions of both muscle layers cause actions related to digestion and absorption of food. It consists of the visceral peritoneum, which is fashioned of epithelium on the skin and connective tissue beneath. Serous uid permits the organs in the stomach cavity to slide freely against one another. Digestion (di-jest yun) is the mechanical and chemical breakdown of meals into varieties that cell membranes can take in. Mechanical digestion breaks massive pieces into smaller ones without altering their chemical composition.
References - Rasmussen T. Surgical therapy of frontal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 4: 181-198, 1963.
- Su X, Changolkar A, Chacko S, et al: Diabetes decreases rabbit bladder smooth muscle contraction while increasing levels of myosin light chain phosphorylation, Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 287(4):F690nF699, 2004.
- Michelsen LG, Kikura M, Levy JH, et al: Heparinase I (Neutralase) reversal of systemic anticoagulation, Anesthesiology 85:339, 1996.
- Kelly PJ, Rosand J, Kistler JP, et al: Homocysteine, MTHFR 677C>T polymorphism, and risk of ischemic stroke, Neurology 59(4):529-536, 2002.
- Razdan S, Leboeuf L, Meinbach DS, et al: Current practice patterns in the urologic surveillance and management of patients with spinal cord injury, Urology 61(5):893n896, 2003.
- Gasche C, Scholmerich J, Brynskov J, et al: A simple classification of Crohn's disease: Report of the Working Party for the World Congresses of Gastroenterology, Vienna 1998.
- Gebhart, G. F. (1995). Visceral pain. In G. F. Gebhart (Ed.). Progress in pain research and management (Vol. 5). Seattle: IASP Press. Gerhart, K. D., Yezierski, R. P., Fang, Z. R., & Willis, W. D. (1983). Inhibition of primate spinothalamic tract neurons by stimulation in ventral posterior lateral (VPLc) thalamic nucleus: Possible mechanisms. Journal of Neurophysiology, 49, 406n423.
|