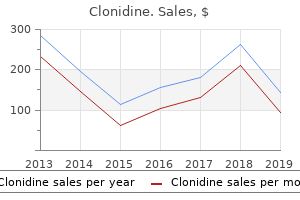
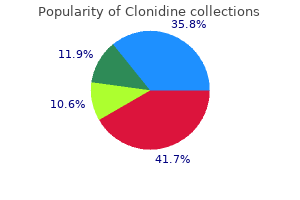
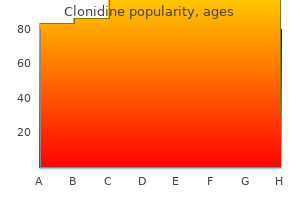
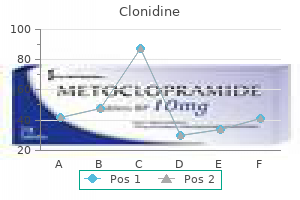
Clonidine
Eloise J. Prijoles, M.D. - Greenwood Genetic Center
- Columbia, South Carolina
Purchase clonidine 0.1 mg lineVirus attachment also involves binding to certainly one of several coreceptors (eg blood pressure normal child cheap clonidine 0.1 mg, members of the immunoglobulin superfamily) blood pressure classification chart purchase clonidine 0.1mg mastercard. Expression of the viral genome is tightly regulated and sequentially ordered in a cascade fashion arteria femoralis profunda purchase clonidine 0.1mg amex. These proteins permit expression of the early set of genes blood pressure ranges in pregnancy buy discount clonidine 0.1mg online, which are translated into proteins. Maturation occurs by budding of nucleocapsids via the altered internal nuclear membrane. Enveloped virus particles are then transported by vesicular motion to the surface of the cell. The number of potential protein-coding open-reading frames in herpesvirus genomes ranges from about 70 to more than 200. The other genes are probably required for viral survival in vivo in natural hosts. Overview of Herpesvirus Diseases A broad number of illnesses are related to infection by herpesviruses. Primary infection and reactivated disease by a given virus could contain completely different cell types and present different clinical photos. Type 1 is classically related to oropharyngeal lesions and causes recurrent assaults of "fever blisters. It causes infectious mononucleosis and can induce human lymphoproliferative problems, particularly in immunocompromised patients. It is often acquired in early infancy and causes exanthem subitum (roseola infantum) as nicely as infections in immunocompromised patients. Herpes B virus of macaque monkeys can infect people upon exposure to stay animals or tissue samples. Such infections are rare, but those that occur often lead to severe neurologic illness and are regularly deadly. Human herpesviruses are incessantly reactivated in the elderly and immunosuppressed sufferers (eg, transplant recipients and cancer patients) and will cause severe illness, similar to pneumonia or lymphomas. They exhibit a broad host range, with the flexibility to replicate in many kinds of cells and to infect many various animals. Their genomes are comparable in group and exhibit substantial sequence homology. The two viruses crossreact serologically, but some distinctive proteins exist for each kind. However, these patterns are becoming much less distinct, and both viruses could cause both presentation. B: Varicella-zoster virus in human kidney cells (hematoxylin and eosin stain, 228�), with multinucleated large cell containing acidophilic intranuclear inclusions (arrow). C: Cytomegalovirus in human fibroblasts (unstained, 35�) with two foci of slowly growing cytopathic impact. D: Cytomegalovirus in human fibroblasts (hematoxylin and eosin stain, 228�), exhibiting giant cells with acidophilic inclusions within the nuclei (small arrow) and cytoplasm (large arrow), the latter being characteristically large and spherical. Glycoprotein C is a complement (C3b)-binding protein, and gE is an Fc receptor, binding to the Fc portion of immunoglobulin G (IgG). Characteristic histopathologic adjustments include ballooning of infected cells, production of Cowdry sort A intranuclear inclusion our bodies, margination of chromatin, and formation of multinucleated large cells. The virus must encounter mucosal surfaces or damaged pores and skin for an infection to be initiated (unbroken skin is resistant). Virus then invades native nerve endings and is transported by retrograde axonal circulate to dorsal root ganglia, where, after additional replication, latency is established. Latent Infection Virus resides in latently infected ganglia in a nonreplicating state; only a only a few viral genes are expressed. Viral persistence in latently contaminated ganglia lasts for the lifetime of the host. No virus may be recovered between recurrences at or near the usual site of recurrent lesions. Provocative stimuli can reactivate virus from the latent state, including axonal injury, fever, physical or emotional stress, and publicity to ultraviolet mild. The virus transits through axons back to the peripheral website, and replication proceeds on the skin or mucous membranes. Many recurrences are asymptomatic, reflected only by viral shedding in secretions. Primary infections happen in persons without antibodies and in most individuals are clinically inapparent but lead to antibody manufacturing and establishment of latent infections in sensory ganglia. The incubation interval is brief (3�5 days, with a variety of 2�12 days), and medical sickness lasts 2�3 weeks. Symptoms include fever, sore throat, vesicular and ulcerative lesions, gingivostomatitis, and malaise. Lesions progress by way of the pustular and crusting stages, and healing without scarring often completes in 8�10 days. Many recurrences of oral shedding are asymptomatic and of short length (24 hours). Recurrent lesions of the eye are common and appear as dendritic keratitis or corneal ulcers or as vesicles on the eyelids. With recurrent keratitis, there may be progressive involvement of the corneal stroma, with everlasting opacification and blindness. Complications embody extragenital lesions (20% of cases) and aseptic meningitis (10% of cases). Some recurrences are asymptomatic with anogenital shedding lasting lower than 24 hours. Primary genital herpes infections could be extreme, with sickness lasting about 3 weeks. Genital herpes is characterised by vesiculoulcerative lesions of the penis of the male or of the cervix, vulva, vagina, and perineum of the feminine. The worst prognosis (80% mortality rate) applies to infants with disseminated infection, many of whom develop encephalitis. The explanation for demise of infants with disseminated illness is normally viral pneumonitis or intravascular coagulopathy. Many survivors of severe infections are left with permanent neurologic impairment. These lesions are seen on the fingers of dentists and hospital personnel (herpetic whitlow) and on the bodies of wrestlers (herpes gladiatorum). Cutaneous infections are often severe and life threatening when they happen in people with disorders of the pores and skin, such as eczema or burns, that permit in depth local viral replication and spread. These embody patients immunosuppressed by disease or remedy (especially those with poor cellular immunity) and individuals with malnutrition. Renal, cardiac, and bone marrow transplant recipients are at explicit threat for extreme herpes infections. Herpes lesions might spread and involve the respiratory tract, esophagus, and intestinal mucosa. Meningitis/Encephalitis A extreme form of meningitis or encephalitis could additionally be produced by herpesvirus.
Clonidine 0.1 mg fast deliveryIt is noteworthy that blood pressure 220120 0.1mg clonidine for sale, regardless of the enzymatic mechanism used for the formation of oxaloacetate hypertension 2006 0.1mg clonidine overnight delivery, acetyl-CoA is required as a optimistic metabolic effector for this process blood pressure medication overdose death effective clonidine 0.1mg. Thus heart attack 21 year old female clonidine 0.1mg amex, the synthesis of oxaloacetate is balanced with the production of acetyl-CoA. Isomerization of the citrate molecule produces isocitrate, which is oxidatively decarboxylated to -ketoglutarate. Succinyl-CoA is a required biosynthetic precursor for the synthesis of porphyrins and other essential compounds. Some organisms form succinyl-CoA by discount of oxaloacetate through malate and fumarate. The ability to use acetate as a net source of carbon, nonetheless, is restricted to comparatively few microorganisms and plants. The general empirical method for carbohydrate phosphate esters, (CnH2nOn)-N-phosphate, is abbreviated (Cn) to emphasize changes in chain length. Growth With Carbon Dioxide: the Calvin Cycle Similar to crops and algae, numerous microbial species can use carbon dioxide as a sole source of carbon. Additional lowered carbon, formed by the reductive assimilation of carbon dioxide, is converted to focal metabolites for biosynthetic pathways. Fermentative organisms obtain this objective by utilizing pyruvate or metabolites derived from pyruvate as oxidants. In one branch, pyruvate is oxidized to acetyl-CoA; in the different, pyruvate is carboxylated to oxaloacetate. This process demands the energy-dependent reduction of 3-phosphoglycerate to the extent of carbohydrate. The sample of depolymerase actions could be useful in the identification of microorganisms. Oxygenases Many compounds within the setting are relatively immune to enzymatic modification, and utilization of those compounds as growth substrates demands a special class of enzymes, oxygenases. These enzymes directly use the potent oxidant molecular oxygen as a substrate in reactions that convert a comparatively intractable compound to a type during which it can be assimilated by thermodynamically favored reactions. Depolymerases Many potential development substrates happen as building blocks inside the structure of biologic polymers. Metabolic divergence at the stage of isocitrate and the motion of two enzymes, isocitrate lyase and malate synthase, modify the tricarboxylic acid cycle in order that it reductively converts two molecules of acetyl-CoA to succinate. Reductive Pathways Some microorganisms reside in extraordinarily lowering environments that favor chemical reactions that might not occur in organisms using oxygen as an electron acceptor. In these organisms, highly effective reductants can be utilized to drive reactions that enable the assimilation of comparatively intractable compounds. An instance is the reductive assimilation of benzoate, a course of during which the aromatic ring is lowered and opened to kind the dicarboxylic acid pimelate. Nitrogenase is a posh of two enzymes-one enzyme (dinitrogenase reductase) incorporates iron and the other (dinitrogenase) accommodates iron and molybdenum. Nitrogen Assimilation the reductive assimilation of molecular nitrogen, additionally referred to as nitrogen fixation, is required for continuation of life on our planet. Additional physiologic demands are placed by the reality that nitrogenase is readily inactivated by oxygen. Aerobic organisms that use nitrogenase have developed elaborate mechanisms to shield the enzyme against inactivation. Some kind specialized cells by which nitrogen fixation takes place, and others have developed elaborate electron transport chains to defend nitrogenase in opposition to inactivation by oxygen. The most vital of those micro organism in agriculture are the Rhizobiaceae, organisms that fix nitrogen symbiotically within the root nodules of leguminous crops. The capability to use ammonia as a nitrogen supply is broadly distributed among organisms. The major portal of entry of nitrogen into carbon metabolism is glutamate, which is fashioned by reductive amination of -ketoglutarate. Molecular oxygen participates immediately in the reactions that disrupt the aromaticity of benzoate and catechol. The exercise and synthesis of glutamine synthase are regulated by the ammonia supply and by the availability of metabolites containing nitrogen derived immediately from the amide nitrogen of glutamine. Most of the organic nitrogen in cells is derived from the -amino group of glutamate, and the primary mechanism by which the nitrogen is transferred is transamination. The traditional acceptor in these reactions is an -keto acid, which is remodeled to the corresponding -amino acid. In addition to reductant, the nitrogenase reaction requires a considerable amount of metabolic vitality. Diaminopimelic acid is a part of peptidoglycan in the cell wall, and dipicolinic acid represents a major component of endospores. The peptidoglycan biosynthetic pathway is of particular importance in medication because it supplies a foundation for the selective antibacterial action of several chemotherapeutic agents. Any compound that inhibits any step within the biosynthesis of peptidoglycan causes the wall of the rising bacterial cell to be weakened and the cell to lyse. Synthesis of Reserve Food Granules When nutrients are current in excess of the necessities for progress, micro organism convert sure of them to intracellular reserve food granules. The principal ones are starch, glycogen, poly-hydroxybutyrate, and volutin, which consists mainly of inorganic polyphosphate (see Chapter 2). Note the resemblance to peptidoglycan synthesis: In both instances, a sequence of subunits is assembled on a lipid provider within the membrane and then transferred to open ends of the growing polymer. The latter reaction is energetically unfavorable and should be driven by a transmembrane electrochemical gradient, the proton driving force. In respiration, the electrochemical gradient is created from externally equipped reductant and oxidant. Energy launched by transfer of electrons from the reductant to the oxidant by way of membrane-bound carriers is coupled to the formation of the transmembrane electrochemical gradient. In photosynthesis, mild energy generates membrane-associated reductants and oxidants; the proton driving force is generated as these electron carriers return to the ground state. Synthesis of Extracellular Capsular Polymers the capsular polymers, a few examples of which are listed in Table 2-2, are enzymatically synthesized from activated subunits. The presence of a capsule is often environmentally decided: Dextrans and levans, for instance, can solely be synthesized utilizing the disaccharide sucrose (fructose�glucose) as the supply of the appropriate subunit, and their synthesis thus depends on the presence of sucrose in the development setting. Many compounds can function fermentable development substrates, and tons of pathways for their fermentation have advanced. In the next sections, examples of each of the three phases of fermentation are thought-about. Four substrate phosphorylation reactions accompany the conversion of the triose phosphate to two molecules of pyruvate. The pathway taken is decided by the evolutionary historical past of the organism and, in some microorganisms, by the expansion circumstances. Fermentation of Glucose the variety of fermentative pathways is illustrated by consideration of a number of the mechanisms used by microorganisms to obtain substrate phosphorylation on the expense of glucose. The latter course of is an example of vectorial metabolism, a set of biochemical reactions by which both the construction and the situation of a substrate are altered (see Chapter 2). Why have the choice pathways for glucose fermentation been chosen within the natural environment
Purchase clonidine 0.1 mgWith long-term use blood pressure medication helps acne generic clonidine 0.1 mg online, neurotoxicity (eg blood pressure chart medication discount 0.1 mg clonidine amex, retinal degeneration) arrhythmia bradycardia purchase clonidine 0.1mg fast delivery, hepatic and renal dysfunction pulse pressure 80 mmhg clonidine 0.1mg without prescription, and severe coagulopathies have been reported. Rapid intravenous administration of deferoxamine could cause histamine launch and hypotensive shock. Prussian Blue Prussian blue is a hydrated crystalline compound in which Fe2+ and Fe3+ atoms are coordinated with cyanide groups in a cubic lattice structure. Prussian blue is approved for the therapy of contamination with radioactive cesium (137Cs) and intoxication with thallium salts. A small baby is delivered to a hospital emergency division affected by severe gastrointestinal misery and belly colic. A young woman employed as a dental laboratory technician complains of conjunctivitis, pores and skin irritation, and hair loss. On examination, she has perforation of the nasal septum and a "milk and roses" complexion. These indicators and signs are most probably due to (A) Acute mercury poisoning (B) Chronic inorganic arsenic poisoning (C) Chronic mercury poisoning (D) Excessive use of supplementary iron tablets (E) Lead poisoning 3. A affected person complains of persistent headache, fatigue, loss of appetite, and constipation. Based on the laboratory knowledge within the desk below, the most cheap prognosis is chronic poisoning caused by (A) Arsenic (B) Hexane (C) Inorganic lead (D) Iron (E) Mercuric chloride Test Hemoglobin Urinary coproporphyrin Urinary aminolevulinic acid Result in Patient <13 g/dL >80 mcg/100 mg creatinine >2 mg/100 mg creatinine Normal >14 g/dL <10 mcg/100 mg creatinine <0. Which of the following drugs ought to be included in the management of this patient A 24-year-old man was employed within the supply division of an organization that manufactures semiconductors. After an accident on the plant, he offered with nausea and vomiting, headache, hypotension, and shivering. Laboratory analyses confirmed hemoglobinuria and a plasma free hemoglobin level larger than 1. This young man was most likely exposed to (A) Arsine (B) Inorganic arsenic (C) Mercury vapor (D) Methylmercury (E) Tetraethyl lead 6. A 2-year-old youngster was dropped at the emergency division 1 h after ingestion of tablets he had managed to get hold of from a bottle on high of the refrigerator. His signs included marked gastrointestinal misery, vomiting (with hematemesis), and epigastric ache. This patient is more than likely to have ingested tablets containing (A) Acetaminophen (B) Aspirin (C) Diphenhydramine (D) Iron (E) Vitamin C Questions 7�10. The matching questions in this part include a list of lettered choices followed by several numbered objects. This toxic compound can be produced in seawater by the action of micro organism and algae. Gingivitis, discolored gums, and free teeth are frequent signs of persistent publicity to this agent. The "milk and roses" complexion, which ends from vasodilation and anemia, is a characteristic of persistent inorganic arsenic poisoning, whereas patients with lead poisoning often have a gray pallor. Other indicators and signs of arsenic poisoning include gastrointestinal misery, hyperpigmentation, and white strains on the nails. Of the agents listed, lead is most probably to cause a lower in heme biosynthesis. Arsine gas binds to hemoglobin and reduces erythrocyte glutathione levels, inflicting membrane fragility and ensuing hemolysis. This question emphasizes that the ingestion of iron tablets is a comparatively common explanation for accidental poisoning in younger children. In a child whose physique weight is 22 lb, the ingestion of 600 mg can cause extreme, maybe lethal, toxicity. Oral and gastrointestinal complaints are widespread in persistent mercury poisoning, and tremor involving the fingers and arms is often present. Regulation of complete physique iron occurs through a tightly regulated system of intestinal absorption. Iron is absorbed and both saved in mucosal cells as ferritin or transported into blood and distributed all through the physique certain to transferrin. Small quantities of iron are eradicated in sweat, saliva, and the exfoliation of skin and mucosal cells. Iron deficiency could be identified from purple blood cell adjustments, including microcytic size and decreased hemoglobin content material, and from measurement of serum and bone marrow iron shops. Iron deficiency anemia is handled by dietary oral ferrous iron supplements or, in severe cases, parenteral administration of a colloid containing a core of iron oxyhydroxide surrounded by a shell of carbohydrate. Identify the clinically helpful chelators and know their indications and their opposed effects. Describe the main scientific features and therapy of acute and chronic lead poisoning. Describe the most important scientific features and treatment of inorganic and organic mercury poisoning. Most chemical compounds are capable of causing poisonous results when given in extreme dosage; even for therapeutic drugs, the difference between a therapeutic motion and a poisonous one is most frequently a matter of dose. Many toxic results of therapeutic brokers have been discussed in previous chapters. Common poisonous syndromes associated with major drug groups are summarized in this chapter. For instance, hypertension and tachycardia are usually seen in overdoses with amphetamines, cocaine, and antimuscarinic medicine. Hypotension with bradycardia occurs with overdoses of calcium channel blockers, blockers, and sedative-hypnotics. Hypotension with tachycardia happens with tricyclic antidepressants, phenothiazines, and theophylline. Hyperthermia is most frequently a results of overdose of medicine with antimuscarinic actions, the salicylates, or sympathomimetics. Increased respiratory rate is commonly a characteristic of overdose with carbon monoxide, salicylates, and other medication that cause metabolic acidosis or cellular asphyxia. Overdoses of brokers that depress the center are more doubtless to affect the capabilities of all organ systems that are critically depending on blood move, including the brain, liver, and kidney. Cause of Death in Intoxicated Patients the most typical causes of dying from drug overdose reflect the drug teams most often selected for abuse or for suicide. Sedativehypnotics and opioids cause respiratory melancholy, coma, aspiration of gastric contents, and other respiratory malfunctions. Tricyclic antidepressants and cardiac glycosides cause harmful and regularly lethal arrhythmias. These include acetaminophen, mushroom poisons of the Amanita phalloides type, sure inhalants, and a few heavy metals (see Chapter 57). Toxicokinetics this time period denotes the disposition of poisons in the physique (ie, their pharmacokinetics).
Discount clonidine 0.1 mg visaUpon examination you find swollen lymph nodes and you document a 20-pound weight reduction fetal arrhythmia 32 weeks order clonidine 0.1 mg amex. In a cancer cell blood pressure in psi order clonidine 0.1mg, decreased capacity to phosphorylate pyrimidines may result in resistance to the anticancer action of which of the next A 65-year-old girl with endometrial most cancers comes to pulse pressure of 65 generic clonidine 0.1mg on-line the outpatient cancer remedy heart for her first cycle of platinum-based chemotherapy blood pressure vitamin d buy discount clonidine 0.1mg on-line. To stop chemotherapyinduced nausea and vomiting, this patient is prone to be given which of the next A 20-year-old foreign trade scholar attending school in California is to be handled for pulmonary tuberculosis. Because drug resistance is anticipated, the proposed antibiotic routine consists of ethambutol, isoniazid (with supplementary vitamin B6), pyrazinamide, and rifampin. Provided that his illness responds properly to the drug regimen and that the microbiology laboratory outcomes show sensitivity to the medicine, it would be appropriate after 2 months to (A) Change his drug routine to prophylaxis with isoniazid (B) Discontinue pyrazinamide (C) Establish baseline ocular perform (D) Monitor amylase activity (E) Stop the supplementary vitamin B6 66. An antifungal drug that binds to ergosterol, forming pores that disrupt fungal membrane integrity is (A) Amphotericin B (B) Caspofungin (C) Fluconazole (D) Flucytosine (E) Terbinafine Questions sixty seven and sixty eight. A 20-year-old school student is delivered to the emergency department after taking an overdose of a nonprescription drug. Toxic exposure to which of the next medicine is the most probably trigger of those signs and symptoms In the administration of this patient, it will be most applicable to (A) Administer acetylcysteine (B) Administer fomepizole (C) Administer glucagon (D) Alkalinize the urine (E) Induce vomiting with syrup of ipecac 69. This drug is used prophylactically in meningococcal and staphylococcal provider states. Although the drug eliminates a majority of meningococci from carriers, extremely resistant strains could additionally be chosen out during remedy. Chemoprophylaxis for vacationers to geographic regions the place chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum is endemic is successfully supplied by (A) Doxycycline (B) Malarone (atovaquone-proguanil) (C) Mefloquine (D) None of the medicine listed above (E) Any of the medicine listed above seventy one. A cardiac Purkinje fiber was isolated from an animal heart and placed in a recording chamber. One of the Purkinje cells was impaled with a microelectrode, and action potentials were recorded whereas the preparation was stimulated at 1 stimulus per second. A consultant motion potential obtained on the peak of drug action is proven because the superimposed action potential (blue). Control Drug (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G) (H) (I) (J) Adenosine Amiodarone Diltiazem Flecainide Fluoxetine Lidocaine Nitroglycerin Procainamide Sotalol Verapamil seventy two. A 43-year-old woman was brought to a hospital emergency department by her brother. Visiting the midway home during which she lived, he had discovered her to be lethargic, with slurred speech. The patient had an extended history of treatment for despair, and the brother feared that she might have overdosed on 1 or more of her prescribed drugs. Physical examination reveals hypotension, tachycardia, decreased bowel sounds, dilated pupils, and hyperthermia. If this affected person has taken a drug overdose, the most probably causative agent is (A) Amitriptyline (B) Celecoxib (C) Lithium (D) Ramelteon (E) Zaleplon Examination 1 543 Questions 74 and 75. Other medicine being administered to this patient include ganciclovir, clarithromycin, rifabutin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. None of the drugs being administered to this patient are helpful for prevention or treatment of opportunistic infections attributable to (A) Candida albicans (B) Cytomegalovirus (C) Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare (D) Pneumocystis jirovecii (E) Toxoplasma gondii seventy six. She had been mostly motionless lately because of bone pain and introduced with lethargy, fatigue, muscle weak spot, anorexia, and constipation. Which vasodilator acts on vascular easy muscle to block calcium inflow by way of L-type channels In anesthesia protocols that include succinylcholine, which of the next is a premonitory sign of malignant hyperthermia Diners at a popular seafood restaurant became sick after consuming clams and mussels. Consultation with the native coastal authorities revealed that the world from which the seafood had been harvested had just lately had a serious "red tide. Which of the next medication has each nonselective -blocking and 1-selective blocking motion A 35-year-old girl who has never been pregnant suffers each month from pain, discomfort, and mood melancholy at the time of menses. She may benefit from the usage of this selective inhibitor of the reuptake of serotonin in a type that can be taken once weekly. Which one of the following medication is considered a first-line remedy for post-traumatic stress disorder A 44-year-old affected person suffering from an alcohol-use dysfunction enters a residential treatment program that emphasizes group therapy and also makes use of pharmacologic agents adjunctively. A 22-year-old lady presents with left lower quadrant abdominal pain and a purulent vaginal discharge that reveals Gram-negative rods. A prognosis is made of pelvic inflammatory disease probably involving each N gonorrhoeae and C trachomatis. A drug or drug combination that provides enough empiric coverage of the organisms involved in this infection is (A) Clarithromycin (B) Ceftriaxone plus doxycycline (C) Metronidazole (D) Norfloxacin plus ampicillin (E) Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole 88. Which of the following is a tyrosine kinase enzyme inhibitor that can be used to deal with this affected person A 17-year-old high school pupil presents with headache, fever, and cough of two days duration. Sputum is scant and nonpurulent, and a Gram stain reveals many white cells but no organisms. Because this in any other case wholesome affected person appears to have a community-acquired pneumonia, you must initiate remedy with (A) Azithromycin (B) Clindamycin (C) Tetracycline (D) Metronidazole (E) Quinupristin-dalfopristin 91. Relative to ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin has improved activity towards (A) Bacteroides fragilis (B) Escherichia coli (C) Haemophilus influenzae (D) Mycoplasma pneumoniae (E) Streptococcus pneumoniae ninety two. Which of the next is the drug of selection for the administration of osteoporosis on this patient A 45-year-old man who acquired an allogenic liver transplant obtained an immunosuppressive regimen containing prednisone, azathioprine, and cyclosporine. Which of the following most accurately describes the mechanism of antiinflammatory activity of cyclosporine An anesthetized topic was given an intravenous bolus dose of a drug (Drug 1) while the systolic and diastolic blood pressures (blue) and the guts fee were recorded, as proven on the left side of the graph below. Blood strain (mm Hg), heart rate (per min) Drug 1 a hundred and twenty 80 Heart rate Drug 2 Drug 1 98.
Clonidine 0.1 mg visaThe antigenic type of the bacteria could additionally be a marker for virulence hypertension recommendations cheap 0.1 mg clonidine, related to the clonal nature of pathogens hypertension x-ray generic 0.1mg clonidine with amex, although it could not actually be the virulence issue (or factors) arteria linguae profunda cheap 0.1 mg clonidine with visa. Only a variety of the group A streptococcal M protein sorts are related to a high incidence of poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis prehypertension ppt 0.1mg clonidine sale. In the examples cited earlier and in different typing techniques that use floor antigens in serologic classification, antigenic varieties for a given isolate of the species stay fixed throughout infection and on subculture of the micro organism. Some bacteria and other microorganisms have the ability to make frequent shifts within the antigenic type of their floor buildings in vitro and presumably in vivo. The gonococcus has three surface-exposed antigens that switch forms at very high charges of about one in every 1000; lipooligosaccharide, 6�8 types; pili, innumerable varieties; and Opa, 10�12 types for each strain. Switching of varieties for every of the three antigens seems to be underneath the management of various genetic mechanisms. Bacterial Secretion Systems Bacterial secretion methods are essential in the pathogenesis of infection and are important for the interplay of bacteria with the eukaryotic cells of the host. The Gram-negative micro organism have cell partitions with cytoplasmic membranes and outer membranes; a thin layer of peptidoglycan is current. Gram-positive bacteria have a cytoplasmic membrane and a really thick layer of peptidoglycan (see Chapter 2). Some Gram-negative micro organism and a few Gram-positive bacteria have capsules as properly. The complexity and rigidity of the cell wall constructions necessitate mechanisms for the translocation of proteins throughout the membranes. These secretion methods are involved in cellular capabilities such as the transport of proteins that make pili or flagella and within the secretion of enzymes or toxins into the extracellular environment. The variations in cell wall structure between Gram-negative and Gram-positive micro organism end in some differences in the secretion systems. The primary mechanisms of the completely different bacterial secretion methods are discussed in Chapter 2. This pathway is concerned within the insertion of a lot of the bacterial membrane proteins and offers the main pathway for proteins crossing the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane. These could be additional characterized as Sec dependent (types 2 and 5) and Sec independent (types 1, three, four, 6). Instead, these methods translocate proteins throughout both the cytoplasmic and outer membranes. The sort 3, which is activated upon contact with a eukaryotic host cell, promotes transport of proteins immediately from inside the bacterium to the within of the host cell utilizing a needlelike construction called an injectosome; when in the host cell cytoplasm, the transported proteins can manipulate host cell operate. Pseudomonas aeruginosa possesses a type 3 secretion system that when expressed could also be associated with more critical illness. Its perform seems to be transport of proteins throughout both the inner and outer membranes. Some different examples of the secretion methods and their roles in pathogenesis are shown in Table 9-5. These examples are a small pattern designed to illustrate the roles of the massive variety of molecular secretion actions used by bacteria to provide vitamins and facilitate their pathogenesis. The Requirement for Iron Iron is an essential nutrient for the growth and metabolism of practically all microorganisms and is an essential cofactor of numerous metabolic and enzymatic processes. The availability of iron in humans for microbial assimilation is limited as a outcome of the iron is sequestered by the high-affinity iron-binding proteins transferrin in serum and lactoferrin on mucosal surfaces. The requirement for iron, how micro organism purchase iron, and bacterial iron metabolism are mentioned in Chapter 5. For example, the gene for diphtheria toxin resides on a lysogenic bacteriophage, and only strains of C. Iron deficiency can have an result on a number of organ systems, including the immune system, and may find yourself in impaired cell-mediated immunity and decreased polymorphonuclear cell function. Providing iron therapy throughout an active infection most likely must be delayed because many pathogenic microorganisms can use the small amounts of supplemental iron, resulting in an increase in virulence. In 1999, Casadevall and Pirofski redefined the ideas of virulence and pathogenicity by introducing the damage-response framework to right the inadequacies which arose as our understanding of microbial pathogens and the host immune response to microbial pathogens developed. In this new paradigm of microbial pathogenesis, the host immune response is given a extra dynamic function within the outcome of an infection. Adoption of this new paradigm requires adopting a brand new lexicon which at first might seen counter-intuitive. For example, an infection is simply defined as aquistion of a microorganism by a host. Infection is mostly followed by multiplication of the microbe within the host surroundings. The two extremes of main an infection are elimination- removing of the microbe from the host by bodily components, an immune response, remedy, or outcompetition by existing microbes; or if the microbe causes enough injury to the host, dying. Damage is defined as the interruption of regular tissue structure and/or function at the cellular, tissue, or organ degree. If the microbe persists inside the host and causes no damage or clinically inapparent damage over time, then the microorganism is taken into account a commensal. Commensals that profit from infecting the host and supply a profit to the host are symbionts. If an infection ends in a continuum of host harm from none to nice, then the host is alleged to be colonized. If host injury increases over time whereas colonized, the host immune response may get rid of or retain the microbe. There have been a quantity of refinements to the injury response framework through the years, with the most recent updates redefining our idea of "host" as our knowledge of microbiomes expands. The Role of Bacterial Biofilms A biofilm is an combination of interactive bacteria hooked up to a stable floor or to each other and encased in an exopolysaccharide matrix. A single species of micro organism may be concerned or multiple species could coaggregate to form a biofilm. After a biofilm is shaped, quorum-sensing molecules produced by the bacteria within the biofilm accumulate, leading to a modification of the metabolic activity of the micro organism. The primary biology of biofilm exopolysaccharide (glycocalyx) is mentioned in Chapter 2; the quorum-sensing molecules are discussed in Chapter 1. This matrix also features as a diffusion barrier for some antimicrobials, however other antimicrobials may bind to it. Biofilms are essential in human infections which are persistent and tough to deal with. Approximately 8 hours later, he developed headache, muscle aches, and belly cramps with diarrhea. He then developed an erythematous rash (resembling sunburn) over much of his body, together with the palms and soles. His liver enzyme exams have been elevated, and there was evidence of reasonable renal failure. A 22-year-old girl who works in a plant nursery presents with a history of fever and cough for two months. The likely means by which the patient acquired her infection is (A) Sexual exercise (B) Ingesting the microorganisms in her meals (C) Holding onto contaminated hand rails when she takes public transportation (D) Handling potting soil (E) Breathing aerosolized droplets containing the microorganism 2. During a pandemic of a well-characterized illness, a bunch of one hundred seventy five airline passengers flew from Lima, Peru, to Los Angeles.
Order clonidine 0.1 mg mastercardRifampin can additionally be used for eradication of staphylococci and meningococci in carriers heart attack band 0.1 mg clonidine amex. They are selectively toxic to fungi as a result of they work together with or inhibit the synthesis of ergosterol hypertension 2014 guidelines clonidine 0.1mg without prescription, a sterol distinctive to fungal cell membranes arteria 3d medieval village order clonidine 0.1mg overnight delivery. Drugs appearing on fungi Block nucleic acid synthesis Disrupt microtubule features Flucytosine Griseofulvin Fungal infections are tough to deal with blood pressure app for iphone clonidine 0.1mg overnight delivery, significantly in the immunocompromised or neutropenic patient. Most fungi are immune to conventional antimicrobial brokers, and relatively few drugs are available for the treatment of systemic fungal illnesses. Amphotericin B Amphotericin B continues to be an important drug for the treatment of systemic fungal infections. However, several azoles and echinocandins are proving to be simply as effective in some systemic mycoses with less risk of poisonous effects. Classification and pharmacokinetics-Amphotericin B is a polyene antibiotic associated to nystatin. Amphotericin is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is often administered intravenously as a nonlipid colloidal suspension, as a lipid complicated, or in a liposomal formulation. Elimination is especially via gradual hepatic metabolism; the half-life is approximately 2 weeks. A small fraction of the drug is excreted within the urine; dosage modification is critical only in extreme renal dysfunction. Mechanism of action-The fungicidal motion of amphotericin B is as a outcome of of its results on the permeability and transport properties of fungal membranes. Resistance, though uncommon, can occur via a decreased stage of or a structural change in membrane ergosterol. Clinical uses-Amphotericin B is doubtless one of the most essential medicine out there for the treatment of systemic mycoses and is often used for preliminary induction regimens earlier than follow-up treatment with an azole. It has the widest antifungal spectrum of any agent and stays the drug of alternative, or codrug of alternative, for many systemic infections attributable to Aspergillus, Blastomyces, Candida albicans, Cryptococcus, Histoplasma, and Mucor. Amphotericin B is normally given by sluggish intravenous infusion, but in fungal meningitis intrathecal administration, though harmful, has been used. Except for flucytosine (and presumably griseofulvin, not shown), all out there antifungal medication target the fungal cell membrane or cell wall. Infusion related-Adverse results related to intravenous infusion generally embrace fever, chills, muscle spasms, vomiting, and a shock-like fall in blood strain. These results could also be attenuated by a slow infusion price and by premedication with antihistamines, antipyretics, meperidine, or glucocorticoids. Dose limiting-Amphotericin B decreases the glomerular filtration price and causes renal tubular acidosis with magnesium and potassium wasting. Although concomitant saline infusion might reduce renal damage, the nephrotoxic effects of the drug are dose-limiting. Dose reduction (with lowered toxicity) is possible in some infections when amphotericin B is used with flucytosine. Liposomal formulations of amphotericin B have decreased nephrotoxic effects, presumably due to decreased binding of the drug to renal cells. Neurotoxicity-Intrathecal administration of amphotericin B might cause seizures and neurologic damage. The drug is eradicated intact within the urine, and the dose have to be lowered in patients with renal impairment. Selective toxicity occurs as a end result of mammalian cells have low levels of permease and deaminase. Resistance can occur quickly if flucytosine is used alone and involves decreased activity of the fungal permeases or deaminases. Toxicity-Prolonged high plasma levels of flucytosine trigger reversible bone marrow despair, alopecia, and liver dysfunction. Fluconazole, posaconazole, isavuconazole, and voriconazole are extra reliably absorbed through the oral route than the other azoles. Liver metabolism is responsible for the elimination of ketoconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole, and voriconazole. Inducers of drugmetabolizing enzymes (eg, rifampin) lower the bioavailability of itraconazole. Isavuconazole-Isavuconazole is a triazole with an antifungal spectrum just like posaconazole. Toxicity-Adverse results of the azoles embody vomiting, diarrhea, rash, and typically hepatotoxicity, particularly in patients with preexisting liver dysfunction. Ketoconazole is a infamous inhibitor of hepatic cytochrome P450 isozymes and may enhance the plasma levels of many different drugs, together with cyclosporine, oral hypoglycemics, phenytoin, and warfarin. Inhibition of cytochrome P450 isoforms by ketoconazole interferes with the synthesis of adrenal and gonadal steroids and will result in gynecomastia, menstrual irregularities, and infertility. Voriconazole causes instant however transient visible disturbances including blurring of imaginative and prescient of unknown cause in additional than 30% of sufferers. Based on animal research voriconazole is a category D drug by means of being pregnant danger. Mechanism of action-The azoles intervene with fungal cell membrane permeability by inhibiting the synthesis of ergosterol. These drugs act on the step of 14-demethylation of lanosterol, which is catalyzed by a fungal cytochrome P450 isozyme. With increasing use of azole antifungals, particularly for long-term prophylaxis in immunocompromised and neutropenic sufferers, resistance is occurring, presumably via adjustments within the sensitivity of the target enzymes. Ketoconazole-Because it has a slim antifungal spectrum and causes more opposed effects than different azoles, ketoconazole is now hardly ever used for systemic mycoses. However, ketoconazole continues to be used for continual mucocutaneous candidiasis and can additionally be efficient against dermatophytes. Fluconazole-Fluconazole is a drug of alternative in esophageal and oropharyngeal candidiasis and for many infections caused by Coccidioides. Fluconazole is the drug of selection for treatment and secondary prophylaxis towards cryptococcal meningitis and is an alternative drug of selection (with amphotericin B) in treatment of lively disease because of Cryptococcus neoformans. Itraconazole-This azole is at present the drug of choice for systemic infections caused by Blastomyces and Sporothrix and for subcutaneous chromoblastomycosis. Itraconazole is an alternate agent within the treatment of infections attributable to Aspergillus, Coccidioides, Cryptococcus, and Histoplasma. In esophageal candidiasis, the drug is active towards some strains resistant to fluconazole. Itraconazole is also used extensively in the remedy of dermatophytoses, especially onychomycosis. Voriconazole-Voriconazole has an even wider spectrum of fungal activity than itraconazole. It is a codrug of alternative for treatment of invasive aspergillosis; some research report greater efficacy than amphotericin B. Posaconazole-The broadest-spectrum triazole, posaconazole has exercise against most species of Candida and Aspergillus. Classification and pharmacokinetics-Caspofungin is an echinocandin, the primary of a novel class of antifungal agents. Used intravenously, the medicine distribute widely to the tissues and are eliminated largely by way of hepatic metabolism.
Diseases - Spastic angina with healthy coronary artery
- Right ventricle hypoplasia
- Rumination syndrome
- Adrenal hyperplasia
- Notalgia paresthetica
- Myelofibrosis
- Chromosome 8 deletion
- Kennerknecht Sorgo Oberhoffer syndrome
- Legionellosis
- Palant cleft palate syndrome
Clonidine: 0.1 mg
Cheap clonidine 0.1mg mastercardFrom 2009 to 1016 hypertension guideline update jnc 8 0.1mg clonidine mastercard, the average number of outbreaks elevated to 7 per year with a peak of 11 outbreaks in 2014 zartan blood pressure medication buy 0.1 mg clonidine. Most of those outbreaks are associated with dairy merchandise or prepackaged uncooked produce hypertension statistics 0.1mg clonidine sale. These outbreaks emphasize the ever present nature of this organism and its capacity to simply contaminate foods throughout any stage of the meals handling course of arrhythmia joint pain purchase clonidine 0.1mg on-line. Antigenic Classification Serologic classification is finished solely in reference laboratories and is primarily used for epidemiologic research. Less labor intensive, genomic-based strategies have been developed but serotyping stays the gold standard. It is catalase optimistic and has a tumbling end-over-end motility at 22�28�C but not at 37�C; the motility check quickly differentiates Listeria from diphtheroids which might be members of the normal microbiota of the pores and skin. The organism has several adhesin proteins (Ami, Fbp A, and flagellin proteins) that facilitate bacterial binding to the host cells and that contribute to virulence. It has cell wall floor proteins known as internalins A and B that work together with E-cadherin, a receptor on epithelial cells, selling phagocytosis into the epithelial cells. After phagocytosis, the bacterium is enclosed in a phagolysosome, where the low pH activates the bacterium to produce listeriolysin O. This enzyme, along with two phospholipases, lyses the membrane of the phagolysosome and allows the listeriae to escape into the cytoplasm of the epithelial cell. The organisms proliferate, and ActA, one other listerial floor protein, induces host cell actin polymerization, which propels them to the cell membrane. Pushing against the host cell membrane, they trigger formation of elongated protrusions referred to as filopods. These filopods are ingested by adjoining epithelial cells, macrophages, and hepatocytes, the listeriae are launched, and the cycle begins once more. Culture and Growth Characteristics Listeria grows well on media such as 5% sheep blood agar on which it displays the attribute small zone of hemolysis round and under colonies. The organism is a facultative anaerobe and is catalase optimistic, esculin hydrolysis optimistic, and motile. Listeria produces acid however not gas from utilization of a variety of carbohydrates. Listeria organisms isolated from scientific specimens incessantly present variation in length and sometimes in shape as well. Immunocompromised individuals can develop Listeria meningoencephalitis, bacteremia, and (rarely) focal infections. Listeria is one of the extra frequent causes of meningitis in this group of patients. Clinical presentation of Listeria meningitis varies from insidious to fulminate and is nonspecific. The diagnosis of systemic listeriosis rests on isolation of the organism in cultures of blood and spinal fluid. In ruminants (eg, sheep), Listeria could trigger meningoencephalitis with or with out bacteremia. Clinical cures have been obtained with ampicillin, erythromycin, or intravenous trimethoprim�sulfamethoxazole. Aerobic Non�Spore-Forming Gram-Positive Bacilli 201 They are catalase unfavorable and vancomycin resistant (80% of lactobacilli). In humans, erysipelas is brought on by group A -hemolytic streptococci and is far different from erysipelas of swine. It often happens on the fingers by direct inoculation on the website of a cut or abrasion (and has been known as seal finger and whale finger). Pus is often not present at the an infection site, which helps differentiate it from staphylococcal and streptococcal pores and skin infections. Erysipeloid can resolve without remedy after 3�4 weeks or extra quickly with antibiotic therapy. Additional clinical types of an infection (both rare) are a diffuse cutaneous kind and bacteremia with or without endocarditis. Erysipelothrix is very susceptible to penicillin G, the drug of alternative for severe infections. The micro organism may appear singly, briefly chains, randomly, or in long nonbranching filaments. The colony morphology and Gram-stain look range relying on the expansion medium, incubation temperature, and pH. Pulmonary nocardiosis is the primary clinical presentation since inhalation is the primary route of bacterial publicity. A variety of signs could occur, including fever, night time sweats, weight reduction, chest pain, cough with or with out sputum production, and shortness of breath. Likewise, chest radiographs might present focal infiltrates, multifocal nodules, and even cavity formation. Pulmonary consolidations may develop, but granuloma formation and caseation are rare. Hematogenous unfold from the lung usually includes the central nervous system, where abscesses develop in the brain, resulting in a wide range of clinical displays. Nocardia brasiliensis is associated with most main cutaneous infections that usually end result from trauma. The organisms are generally weakly acid-fast optimistic when stained by the modified Kinyoun method. The organism is a explanation for disease in cattle, sheep, and swine and may trigger extreme pulmonary and extrapulmonary infections in foals. Other species of the varied genus Rhodococcus are current in the environment but rarely trigger illness in humans. New species proceed to be acknowledged, and at least 30 species have been implicated as causes of human infections. The most common species related to the vast majority of instances of human infections are listed in Table 12-1. Each of those is answerable for a broad range of ailments, and every species or complicated has unique drug susceptibility patterns. The pathogenic nocardiae, much like many nonpathogenic species of Nocardia, are found worldwide in soil and in water. The ordinary presentation is as a subacute to persistent pulmonary an infection which will disseminate to other organs, usually the mind or the pores and skin. Diagnostic Laboratory Tests Specimens encompass sputum, pus, spinal fluid, and biopsy material. Gram-stained smears reveal Gram-positive bacilli, coccobacillary cells, and branching filaments. Molecular methods are required for species-level identification, which is necessary for both epidemiologic and remedy functions. Morphology and Identification Nocardia species are aerobic and grow on a variety of media. Microscopically in clinical specimens, nocardiae appear as filamentous organisms with hyphae-like branching.

Buy clonidine 0.1 mg cheapHuman parvovirus B19 replicates in immature erythroid cells and causes a quantity of adverse penalties blood pressure higher at night buy clonidine 0.1 mg free shipping, together with aplastic disaster blood pressure zetia buy discount clonidine 0.1mg on-line, fifth illness heart attack and vine cover order clonidine 0.1mg overnight delivery, and fetal demise (see Chapter 31) blood pressure chart by weight purchase clonidine 0.1mg otc. At least sixty seven types infect people, especially in mucous membranes, and a few types can persist in lymphoid tissue. Adenoviruses could cause acute respiratory diseases, conjunctivitis, and gastroenteritis. The virus consists of a 27-nm icosahedral nucleocapsid core inside a intently adherent envelope that contains lipid and the viral surface antigen. The floor protein is characteristically overproduced throughout replication of the virus, which takes place within the liver, and is shed into the bloodstream. Hepadnaviruses such as Hepatitis B virus could cause acute and chronic hepatitis; persistent infections are related to a excessive danger of creating liver most cancers. Anelloviridae Anelloviruses (from Latin anello that means ring) are small (~30 nm in diameter), icosahedral virions that lack an envelope. Anelloviruses include the torque teno viruses, and are globally distributed in the human inhabitants and lots of animal species. Polyomaviridae Polyomaviruses are small (45 nm), nonenveloped, heat-stable, solubilization-resistant viruses exhibiting cubic symmetry, with 72 capsomeres. The name derives from Greek poly(many) and �oma (tumor) and refers to the power of a few of these viruses to produce tumors in infected hosts. Most animal species harbor continual infections with one or more polyomaviruses (see Chapter 43). The name refers to Latin herpes (creep), describing the spreading nature of skin lesions attributable to these viruses. The nucleocapsid is one hundred nm in diameter, with cubic symmetry and 162 capsomeres, surrounded by a lipidcontaining envelope. Latent infections may final for the life span of the host, often in ganglial or lymphoblastoid cells. Human herpesviruses include herpes simplex varieties 1 and 2 (oral and genital lesions), varicella-zoster virus (chickenpox and shingles), cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus (infectious mononucleosis and association with human neoplasms), human herpesviruses 6 and seven (T cell lymphotropic), and human herpesvirus eight (associated with Kaposi sarcoma). Papillomaviridae Papillomaviruses are much like polyomaviruses in some respects however with a larger genome (8 kb) and particle dimension (55�60 nm). The name refers to Latin papilla (nipple) and Greek �oma (tumor) and describes wart-like lesions produced by these viral infections. There are many forms of human papillomaviruses, and sure high-risk varieties are causative brokers of genital cancers in humans (see Chapter 43). Poxviridae Poxviruses are large brick-shaped or ovoid viruses 220�450 nm long � 140�260 nm broad � 140�260 nm thick. The name derives from Anglo-Saxon pokkes which means pouch, referring to their attribute vesicular pores and skin lesions. Reoviruses of people include rotaviruses, which have a distinctive wheel-shaped appearance and cause gastroenteritis. Some are pathogenic for humans (smallpox, vaccinia, molluscum contagiosum); others that are pathogenic for animals can infect humans (cowpox, monkeypox) (see Chapter 34). Picornaviridae Picornaviruses are small (28�30 nm), ether-resistant viruses exhibiting cubic symmetry. The teams infecting people are enteroviruses (polioviruses, coxsackieviruses, echoviruses, parechoviruses, and rhinoviruses [more than a hundred serotypes inflicting common colds]) and hepatovirus (hepatitis A). Rhinoviruses are acid labile and have a excessive density; different enteroviruses are typically acid secure and have a decrease density. Picornaviruses infecting animals embrace foot-and-mouth illness of cattle and encephalomyocarditis of rodents (see Chapter 36). Arboviruses and Rodent-Borne Viruses Arboviruses and rodent-borne viruses are ecologic groupings (not a virus family) of viruses with diverse physical and chemical properties. The arboviruses (there are greater than 350 of them) have a fancy cycle involving arthropods as vectors that transmit the viruses to vertebrate hosts by their bite. Arboviruses infect people, mammals, birds, and reptiles and use mosquitoes and ticks as vectors. Human pathogens embrace dengue, yellow fever, West Nile fever, and encephalitis viruses. Rodent-borne viruses establish persistent infections in rodents and are transmitted without an arthropod vector. The viruses in these ecologic groupings belong to several virus families, together with arenaviridae, bunyaviridae, flaviviridae, reoviridae, rhabdoviridae, and togaviridae (see Chapter 38). Astroviridae Astroviruses are comparable in dimension to picornaviruses (28�30 nm), but particles show a particular star-shaped define on their surfaces. These agents are related to gastroenteritis in humans and neurological illness in some animals (see Chapter 37). Caliciviridae Caliciviruses are much like picornaviruses however slightly bigger (27�40 nm). Important human pathogens are the noroviruses (eg, Norwalk virus), the trigger of epidemic acute gastroenteritis. Togaviridae Many arboviruses which may be main human pathogens, referred to as alphaviruses-as nicely as rubella virus-belong to this group. Picobirnaviridae Picobirnaviruses are small (35�40 nm) nonenveloped viruses with icosahedral structure. Reoviridae Reoviruses are medium-sized (60�80 nm), ether-resistant, nonenveloped viruses having icosahedral symmetry. Arenaviridae Arenaviruses are pleomorphic, enveloped viruses ranging in measurement from 60 to 300 nm (mean, 110�130 nm). Replication happens within the cytoplasm with assembly through budding on the plasma membrane. The virions incorporate host cell ribosomes throughout maturation, which provides the particles a "sandy" look. Most members of this household are unique to tropical America (ie, the Tacaribe complex). These viruses require maximum containment circumstances within the laboratory (see Chapter 38). Coronaviruses resemble orthomyxoviruses however have petal-shaped floor projections arranged in a fringe, much like a solar corona. Coronavirus nucleocapsids develop in the cytoplasm and mature by budding into cytoplasmic vesicles. Coronaviruses of animals readily set up persistent infections and include mouse hepatitis virus and avian infectious bronchitis virus (see Chapter 41). The segmented nature of the viral genome permits ready genetic reassortment when two influenza viruses infect the identical cell, presumably fostering the excessive rate of natural variation amongst influenza viruses. Viral reassortment and transmission from different species is thought to clarify the emergence of recent human pandemic strains of influenza A viruses (see Chapter 39).
Buy generic clonidine 0.1 mg on-lineDapsone is nicely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is widely distributed in tissues arrhythmia bradycardia order clonidine 0.1 mg line. Side effects are widespread arterial duplex purchase clonidine 0.1 mg with visa, together with hemolytic anemia hypertension treatment guidelines buy 0.1mg clonidine with visa, gastrointestinal intolerance heart attack trey songz mp3 cheap clonidine 0.1mg mastercard, fever, itching, and rashes. Isoniazid is rapidly and completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is partly acetylated and in part excreted within the urine. It is active in vitro against some Gram-positive and Gram-negative cocci, some enteric micro organism, mycobacteria, chlamydiae, and poxviruses. Although many meningococci and mycobacteria are inhibited by lower than 1 g/mL, extremely resistant mutants occur in all microbial populations in a frequency of 10-6�10-5. The extended administration of rifampin as a single drug permits the emergence of those highly resistant mutants. Rifampin is properly absorbed after oral administration, broadly distributed in tissues, and excreted primarily by way of the liver and to a lesser extent into the urine. However, no much less than two doses weekly should be given to avoid a "flu syndrome" and anemia. Unfortunately, some extremely resistant meningococcal strains are selected out by this procedure. Occasional adverse effects include rashes, thrombocytopenia, light-chain proteinuria, and impairment of liver operate. Rifaximin is a by-product of rifampin that possesses a further pyridoimidazole ring. Ethambutol Ethambutol is an artificial water-soluble, heat-stable D isomer of the structure shown under. Resistance to ethambutol emerges pretty rapidly among mycobacteria when the drug is used alone. Therefore, ethambutol is at all times given in combination with other antituberculous drugs. The most typical unwanted side effects are visible disturbances, however these are rare at commonplace dosages: Reduction in visual acuity, optic neuritis, and perhaps retinal damage occur in some sufferers given excessive doses for a number of months. Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 411 Pyrazinamide Pyrazinamide is expounded to nicotinamide. It is readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and extensively distributed in tissues. The major antagonistic effects of pyrazinamide are hepatotoxicity (1�5%), nausea, vomiting, hypersensitivity, and hyperuricemia. The antimicrobial agent whose structure is shown beneath is taken into account the drug of option to treat infections brought on by which one of many following microorganisms Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to the drug shown in Question 1 is attributable to (A) the action of acetyltransferase (B) the motion of -lactamase (C) Substitution of the d-Ala-d-Ala dipeptide with the d-Alad-Lac dipeptide in the cell wall peptidoglycan (D) Decreased permeability of the bacterial cell wall to the drug (E) S. All of the following statements about antimicrobial resistance of enterococci are right except (A) Enterococci are proof against sulfamethoxazole� trimethoprim in vivo. A 20-year-old Asian girl, a latest immigrant to the United States, develops fever and a cough productive of blood-streaked sputum. Given the history and chest radiography findings, which of the next drug regimens could be the most effective appropriate preliminary therapy while awaiting culture results Which one of many following groups of antimicrobial agents acts on microorganisms by inhibiting protein synthesis Tigecycline, a new glycylcycline antibiotic with good exercise towards a selection of pathogens, is greatest used for treatment of which of the next infections The drug of first selection for the remedy of significant anaerobic infections attributable to B. The nucleic acid is encased in a protein shell, which can be surrounded by a lipid-containing membrane. Viruses are parasites on the genetic degree, replicating only in residing cells and are inert in the extracellular surroundings. The viral nucleic acid contains info necessary to cause the infected host cell to synthesize virus-specific macromolecules required for the manufacturing of viral progeny. During the replicative cycle, quite a few copies of viral nucleic acid and coat proteins are produced. The coat proteins assemble together to type the capsid, which encases and stabilizes the viral nucleic acid in opposition to the extracellular setting and facilitates the attachment and penetration by the virus upon contact with new vulnerable cells. The virus infection might have little or no impact on the host cell or might end in cell injury or dying. Viruses range tremendously in structure, genome group and expression, and techniques of replication and transmission. Viruses are recognized to infect unicellular organisms, similar to mycoplasmas, bacteria, and algae, and all greater crops and animals. Much data on virus�host relationships has been obtained from research on bacteriophages, the viruses that attack micro organism. Capsomeres: Morphologic units seen within the electron microscope on the surface of icosahedral virus particles. Nucleocapsid: the protein�nucleic acid complicated representing the packaged type of the viral genome. The term is usually used in cases by which the nucleocapsid is a substructure of a extra complicated virus particle. Genome sequencing is now usually performed early in virus identification, and comparisons with databases present detailed info on the viral classification, predicted protein composition, and taxonomic relatedness to different viruses. Virion morphology, including measurement, form, type of symmetry, presence or absence of peplomers, and presence or absence of membranes. Genome group and replication, together with gene order, quantity and position of open studying frames, strategy of replication (patterns of transcription, translation), and cellular sites (accumulation of proteins, virion assembly, virion release). Virus protein properties, including quantity, dimension, amino acid sequence, modifications (glycosylation, phosphorylation, myristoylation), and functional actions of structural and nonstructural proteins (transcriptase, reverse transcriptase, neuraminidase, fusion activities). Physicochemical properties of the virion, including molecular mass, buoyant density, pH stability, thermal stability, and susceptibility to physical and chemical brokers, particularly solubilizing agents and detergents. Biologic properties, including pure host vary, mode of transmission, vector relationships, pathogenicity, tissue tropisms, and pathology. In extra complicated virions (herpesviruses, orthomyxoviruses), this consists of the nucleocapsid plus a surrounding envelope. This structure, the virion, serves to switch the viral nucleic acid from one cell to another. They resemble genes that have acquired the capability to exist independently of the cell. Some viral sequences are associated to portions of cellular genes encoding protein functional domains. However, poxviruses are so giant and sophisticated that they could symbolize evolutionary merchandise of some cellular ancestor. Universal System of Virus Taxonomy A system has been established in which viruses are separated into main groupings-called families-on the basis of virion morphology, genome structure, and techniques of replication. Within every household, subdivisions called genera are normally based mostly on organic, genomic, physicochemical, or serologic variations.
Order clonidine 0.1mg with mastercardSyphilitic infection may remain subclinical arrhythmia definition medical buy clonidine 0.1mg cheap, and the patient might move via the first or secondary stage (or both) with out symptoms or indicators but develop tertiary lesions heart attack 22 years old generic clonidine 0.1 mg mastercard. In about 30% of circumstances hypertension 150 100 best clonidine 0.1 mg, early syphilitic infection progresses spontaneously to full cure with out therapy prehypertension young adults generic clonidine 0.1mg overnight delivery. In one other 30%, the untreated an infection stays latent (principally evident by positive serologic check results). In the remainder, the illness progresses to the "tertiary stage" characterized by the event of granulomatous lesions (gummas) within the pores and skin, bones, and liver; degenerative modifications within the central nervous system (meningovascular syphilis, paresis, tabes); or cardiovascular lesions (aortitis, aortic aneurysm, aortic valve insufficiency). In all tertiary lesions, treponemes are very uncommon, and the exaggerated tissue response must be attributed to hypersensitivity to the organisms. However, treponemes can often be discovered within the eye or central nervous system in late syphilis. Both reagin and antitreponemal antibody can be used for the serologic diagnosis of syphilis. Some of the infected fetuses die, and miscarriages end result; others are stillborn at term. The reagin titer in the blood of the kid rises with lively infection but falls with time if antibody was passively transmitted from the mother. Human infection is usually transmitted by sexual contact, and the infectious lesion is on the pores and skin or mucous membranes of genitalia. In 10�20% of circumstances, however, the first lesion is intrarectal, perianal, or oral. Based on experiments in rabbits, as few as 4 to eight spirochetes may trigger an infection. Dark-Field Examination A drop of tissue fluid or exudate is placed on a slide, and a coverslip is pressed over it to make a thin layer. The preparation is then examined under oil immersion inside 20 minutes of collection with dark-field illumination for typical motile spirochetes. Treponemes disappear from lesions within a few hours after the beginning of antibiotic remedy. Immunofluorescence Tissue fluid or exudate is spread on a glass slide, air-dried, and despatched to the laboratory. It is mounted, stained with a fluoresceinlabeled antitreponeme antibody and examined by means of immunofluorescence microscopy for typical fluorescent spirochetes. The nontreponemal checks can give quantitative outcomes utilizing serial twofold dilutions. An estimate of the amount of reagin present in serum can be expressed as the titer or as the highest dilution giving a positive outcome. Quantitative outcomes are valuable in establishing a diagnosis and in evaluating the impact of remedy. Positive nontreponemal take a look at outcomes develop after 2�3 weeks of untreated syphilis and are positive in excessive titer in secondary syphilis. Positive nontreponemal take a look at outcomes typically revert to unfavorable, usually in 6�18 months and customarily by three years after effective therapy of syphilis. A optimistic nontreponemal check end result late after therapy for syphilis suggests ineffective therapy or reinfection. Serologic Tests for Syphilis these tests use both nontreponemal or treponemal antigens. Nontreponemal tests-The nontreponemal tests are universally used as screening exams for syphilis. The tests are widely obtainable, lend themselves to automation with ease of efficiency in massive numbers, and have a low value. In addition to their perform as screening exams, they can be utilized to follow the efficacy of therapy. The antigens in these tests comprise measured amounts of cardiolipin, cholesterol, and purified lecithin in quantities sufficient to yield a standardized amount of reactivity. Historically, the cardiolipin was extracted from beef heart or liver with added lecithin and cholesterol to improve response with syphilitic "reagin" antibodies. Reagin is a mix of IgM and IgG antibodies reactive with the cardiolipin�cholesterol�lecithin advanced. All of the checks are based mostly on the reality that the particles of the lipid antigen stay dispersed in normal serum however flocculate when combining with reagin. The checks are used to decide if a constructive outcome from a nontreponemal test is really constructive or falsely positive. A positive result of a treponemal test on a serum specimen that can be optimistic on a nontreponemal check is a powerful indication of T. The traditional treponemal exams are less helpful as screening tests as a result of once positive after initial syphilitic an infection the checks stay constructive for life independent of therapy for syphilis. The treponemal antibody tests are most likely to be extra costly than the nontreponemal take a look at, which is necessary when large groups of individuals (eg, blood donors) are being screened. The test uses oblique immunofluorescence to detect reactive antibodies, together with killed T. A typical Jarisch-Herxheimer response could happen inside hours after therapy is begun. An aliquot of serum at a regular dilution is added to a sensitized nicely of a microdilution plate. After washing, addition of an enzyme-labeled conjugate, and further washing, a precursor substrate is added. Because some of these assays can be found as high-throughput automated exams, many laboratories have now reversed the traditional algorithm for screening. Instead of screening with the nontreponemal take a look at and verifying with a treponemal assay, the high throughput permits screening with a extra delicate treponemal take a look at. The benefit to this approach is that sufferers with early illness or untreated latent illness are extra likely to be detected (see earlier discussion). There are some considerations about variability in assay efficiency among these tests that end in extra false positives when testing low-prevalence populations. Epidemiology, Prevention, and Control With the exceptions of congenital syphilis and the rare occupational exposure of medical personnel, syphilis is acquired via sexual exposure. Consequently, control measures depend on (1) immediate and sufficient treatment of all found instances, (2) follow-up on sources of an infection and contacts so that they are often handled, and (3) protected sex with condoms. Therefore, it is very important consider the potential of syphilis when any one sexually transmitted illness has been discovered. The tertiary stage includes severe disease with central nervous system or cardiac manifestations. Immunity A individual with lively or latent syphilis appears to be resistant to superinfection with T. However, if early syphilis is treated adequately and the an infection is eradicated, the individual once more turns into fully susceptible.
References - Gaston M, Rosse WF; The Cooperative Group. The Cooperative Study of Sickle Cell Disease: Review of study designs and objectives. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 4:197-201, 1982.
- Hofman MA, Swaab DF. Living by the clock: the circadian pacemaker in older people. Ageing Res Rev 2006;5:33-51.
- Posnick JC, Wells M, Pron GE. Pediatric facial fractures: evolving patterns of treatment. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1993; 51(8):836-844.
- Bauchet L, Segnarbieux F, Martinazzo G, et al: Neurosurgical treatment of hyperactive bladder in spinal cord injury patients, Neurochirurgie 47:13n24, 2001.
- Neuman M: Perioperative complications and early follow-up with 100 TVTSECUR procedures, J Minim Invasive Gynecol 15:480n484, 2008.
|


