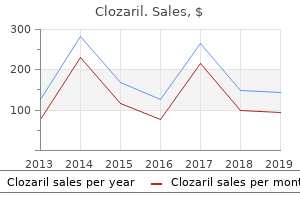
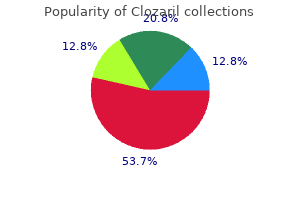
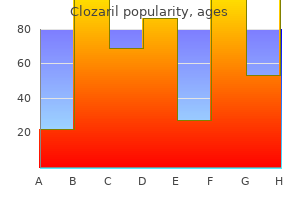
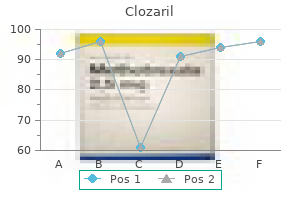
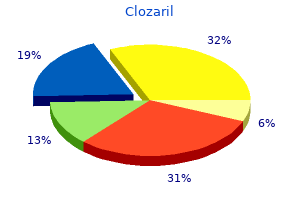
Clozaril
Jean-Pierre Ya red, MD - Director, Critical Care Medicine in the Heart and Vascular Institute
- Cleveland Clinic Foundation
- Cleveland, Ohio
Generic clozaril 25 mg fast deliveryMuscarinic agonists act on the guts to cause bradycardia (decreased heart rate) and on exocrine glands to increase sweating symptoms of anxiety cheap clozaril 25 mg mastercard, salivation treatment of lyme disease clozaril 100mg discount, bronchial secretions treatment of schizophrenia purchase 50 mg clozaril, and secretion of gastric acid medicine for high blood pressure 100mg clozaril mastercard. In vascular easy muscle, these drugs trigger relaxation; the resultant vasodilation can produce hypotension. Activation of muscarinic receptors in the eyes has two results: (1) miosis (pupillary constriction); and (2) contraction of the ciliary muscle, resulting in accommodation for near imaginative and prescient. Therapeutic Uses Although bethanechol can produce a broad spectrum of pharmacologic effects, the drug is approved just for urinary retention. Note that, with the exception of pilocarpine, all of those agents are quaternary ammonium compounds and always carry a optimistic cost. Bethanechol relieves urinary retention by activating muscarinic receptors of the urinary tract. Muscarinic activation relaxes the trigone and sphincter muscles and increases voiding pressure (by contracting the detrusor muscle, which composes the bladder wall). Bethanechol is used to treat urinary retention in postoperative and postpartum sufferers. When sufferers are handled with bethanechol, a bedpan or urinal ought to be available. Bethanechol has been used on an investigational foundation to deal with gastroesophageal reflux. Benefits may result from increased esophageal motility and increased strain within the decrease esophageal sphincter. Specific applications are adynamic ileus, gastric atony, and postoperative stomach distention. In each cases, the ability of bethanechol to improve the tone and motility of intestinal easy muscle could end in rupture of the bowel wall. Because of its capability to contract the bladder detrusor, and thereby improve pressure within the urinary tract, bethanechol can be hazardous to sufferers with urinary tract obstruction or weakness of the bladder wall. In each teams, elevation of pressure throughout the urinary tract could rupture the bladder. By activating muscarinic receptors in the lungs, bethanechol can cause bronchoconstriction. Accordingly, the drug is contraindicated for patients with latent or active bronchial asthma. If given to sufferers with hyperthyroidism, bethanechol may increase heart rate to the purpose of initiating a dysrhythmia. In reaction to hypotension, the baroreceptor reflex makes an attempt to return blood strain to regular. Part of this reflex includes the discharge of norepinephrine from sympathetic nerves that regulate coronary heart rate. However, in hyperthyroid patients, norepinephrine can induce cardiac dysrhythmias. The purpose for this uncommon response is that, in hyperthyroid sufferers, the center is exquisitely delicate to the consequences of norepinephrine, and therefore comparatively small amounts can cause stimulation adequate to elicit a dysrhythmia. Adverse Effects In theory, bethanechol can produce the full range of muscarinic responses as unwanted side effects. Accordingly, the drug is contraindicated for patients with low blood pressure or low cardiac output. At usual therapeutic doses, bethanechol may cause excessive salivation, increased secretion of gastric acid, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea. Bethanechol is contraindicated in patients with gastric ulcers because stimulation of acid secretion might intensify gastric erosion, inflicting bleeding and probably perforation. The drug can be contraindicated for sufferers with intestinal obstruction and for these recovering Preparations, Dosage, and Administration Bethanechol [Urecholine] is out there in tablets (5, 10, 25, and 50 mg) for oral therapy. Administration with food can cause nausea and vomiting, so it should be administered 1 hour earlier than meals or 2 hours after. Cevimeline [Evoxac] is a derivative of acetylcholine with actions very like these of bethanechol. Left untreated, dry mouth can result in multiple problems, together with periodontal illness, dental caries, altered taste, oral ulcers and candidiasis, and difficulty eating and speaking. Cevimeline relieves dry mouth by activating muscarinic receptors on residual healthy tissue in salivary glands, thereby promoting salivation. The drug also will increase tear production, which can help relieve keratoconjunctivitis. Adverse effects outcome from activating muscarinic receptors, and therefore are much like these of bethanechol. To compensate for fluid loss attributable to sweating and diarrhea, patients should enhance fluid consumption. Like bethanechol, cevimeline promotes miosis (constriction of the pupil) and can also cause blurred imaginative and prescient. Activation of cardiac muscarinic receptors can scale back heart fee and sluggish cardiac conduction. Accordingly, cevimeline should be used with warning in patients with a historical past of heart illness. Because miosis can exacerbate symptoms of each narrow-angle glaucoma and iritis (inflammation of the iris), cevimeline is contraindicated for individuals with these issues. Cevimeline can intensify cardiac melancholy caused by beta blockers because both medicine lower heart fee and cardiac conduction. Beneficial effects of cevimeline could be antagonized by medicine that block muscarinic receptors. Among these are atropine, tricyclic antidepressants (eg, imipramine), antihistamines (eg, diphenhydramine), and phenothiazine antipsychotics (eg, chlorpromazine). Mushrooms of the Inocybe and Clitocybe species have a lot of muscarine, therefore their ingestion can produce typical signs of muscarinic toxicity. Interestingly, Amanita muscaria, the mushroom from which muscarine was originally extracted, actually accommodates very little muscarine. Manifestations of muscarinic poisoning outcome from extreme activation of muscarinic receptors. Prominent signs are profuse salivation, lacrimation (tearing), visible disturbances, bronchospasm, diarrhea, bradycardia, and hypotension. Management is direct and particular: administer atropine (a selective muscarinic blocking agent) and provide supportive remedy. By blocking access of muscarinic agonists to their receptors, atropine can reverse most indicators of toxicity. Because the vast majority of muscarinic receptors are situated on constructions innervated by parasympathetic nerves, the muscarinic antagonists are also recognized as parasympatholytic drugs. Additional names for these brokers are antimuscarinic medicine, muscarinic blockers, and anticholinergic medicine.
Generic clozaril 25 mg on lineTo administer a drug on an empty abdomen means to administer it no much less than 1 hour earlier than a meal or 2 hours after medicine 600 mg trusted clozaril 50 mg. Medication orders frequently fail to point out when a drug must be administered with respect to meals treatment of uti order 50 mg clozaril amex. Of best concern are interactions that scale back beneficial responses to conventional medicine and interactions that increase toxicity ombrello glass treatment clozaril 100 mg low cost. Through the same pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic mechanisms by which conventional medicine interact with one another symptoms you may be pregnant clozaril 100 mg without a prescription. Unfortunately, reliable details about dietary dietary supplements is largely lacking, including information on interactions with conventional brokers. Interactions which were nicely documented are discussed as applicable all through this text. Dietary dietary supplements and their interactions are mentioned at size in Chapter 108. Drug-drug interactions might lead to intensified results, diminished results, or an entirely new impact. Potentiative interactions are beneficial when they improve therapeutic results and detrimental once they enhance adverse results. Inhibitory interactions are useful once they lower opposed effects and detrimental once they lower useful results. Competition for protein binding hardly ever leads to a sustained or important improve in plasma levels of free drug. Drugs that induce hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes can accelerate the metabolism of different medicine. When an inducing agent is added to the regimen, it might be essential to enhance the dosages of other medication. Conversely, when an inducing agent is discontinued, dosages of other drugs may must be decreased. Drugs that act as antagonists at a particular receptor will diminish the consequences of medication that act as agonists at that receptor. The end result may be helpful (if the antagonist prevents poisonous results of the agonist) or detrimental (if the antagonist prevents therapeutic results of the agonist). We may help scale back the risk of opposed interactions by minimizing the number of medicine the affected person is given and by taking a thorough drug historical past. Reducing the extent of absorption reduces peak therapeutic responses; decreasing the rate of absorption merely delays the onset of results. Grapefruit juice can inhibit the intestinal metabolism of certain medication, thereby increasing their absorption, which in turn will increase their blood ranges. When the medicine order says to administer a drug on an empty abdomen, this means administer it both 1 hour before a meal or 2 hours after. The largest considerations are increased toxicity and decreased therapeutic effects of the traditional agent. Likewise, adverse occasions are extra common in sufferers receiving multiple drugs than in patients taking only one drug. Among hospitalized inpatients, 1,735,500 skilled adverse outcomes because of drug reactions and drugs errors and, of these, over fifty three,800 sufferers died. Common examples embody drowsiness brought on by traditional antihistamines and gastric irritation attributable to aspirin. Some unwanted aspect effects develop soon after drug use starts, whereas others might not seem till a drug has been taken for weeks or months. Toxicity the formal definition of toxicity is the diploma of detrimental physiologic results caused by extreme drug dosing. Examples include coma from an overdose of morphine and severe hypoglycemia from an overdose of insulin. For example, when administered in therapeutic doses, many anticancer medicine trigger neutropenia (profound lack of neutrophilic white blood cells), thereby putting the affected person at excessive threat of infection. This neutropenia could also be known as a toxicity even though it was produced when dosage was therapeutic. For an allergic response to happen, there must be prior sensitization of the immune system. Once the immune system has been sensitized to a drug, reexposure to that drug can trigger an allergic response. The intensity of allergic reactions can range from gentle itching to extreme rash to anaphylaxis. Adverse reactions can range in intensity from mildly annoying to life threatening. Scope of the Problem Drugs can adversely have an result on all physique systems in varying levels of intensity. Severe reactions embody potential fatal situations similar to neutropenia, hepatocellular damage, cardiac dysrhythmias, anaphylaxis, and hemorrhage. The depth of an allergic reaction is set primarily by the degree of sensitization of the immune system, not by drug dosage. Put another means, the intensity of allergic reactions is largely unbiased of dosage. As a result, a dose that elicits a really sturdy response in a single allergic patient may elicit a really gentle reaction in one other. In truth, most critical reactions are attributable to only one drug family-the penicillins. Other drugs famous for inflicting allergic reactions include the nonsteroidal antiinflammatory medicine (eg, aspirin) and the sulfonamide group of compounds, which includes certain diuretics, antibiotics, and oral hypoglycemic brokers. Because a selection of medication could cause physical dependence of one kind or one other, and because withdrawal reactions have the potential for hurt, patients must be warned in opposition to abrupt discontinuation of any medication with out first consulting a well being professional. Idiosyncratic Effect An idiosyncratic effect is defined as an uncommon drug response resulting from a genetic predisposition. Paradoxical Effect A paradoxical impact is the alternative of the intended drug response. A common instance is the insomnia and excitement that may happen when some youngsters and older adults are given benzodiazepines for sedation. Iatrogenic Disease An iatrogenic disease is a disease that happens as the results of medical care or treatment. Iatrogenic diseases are almost identical to idiopathic (naturally occurring) ailments. Physical Dependence Physical dependence is a state in which the physique has adapted to drug exposure in such a method that an abstinence syndrome will result if drug use is discontinued. Physical dependence develops during long-term use of sure drugs, similar to opioids, alcohol, barbiturates, and amphetamines. A number of other centrally performing medicine (eg, ethanol, barbiturates, amphetamines) can promote dependence. Furthermore, some medication Carcinogenic Effect the term carcinogenic impact refers to the power of sure drugs and environmental chemical substances to cause cancers. Ironically, several of the medicine used to deal with cancer are among those with the greatest carcinogenic potential.
Buy 100mg clozaril otcPatients at present utilizing immediate-release quetiapine could also be switched to extended-release quetiapine on the equal whole daily dosage treatment vertigo discount 50 mg clozaril with mastercard. The beneficial dosage is 150 to 300 mg once daily symptoms 9 weeks pregnant generic clozaril 25 mg with mastercard, using the extended-release formulation symptoms quitting tobacco generic 100 mg clozaril fast delivery. Approved indications are schizophrenia medicine cabinets recessed order clozaril 50 mg online, acute bipolar mania, main depressive dysfunction, agitation related to schizophrenia or bipolar mania, and irritability related to autism spectrum dysfunction. However, like all different antipsychotics, the drug could increase mortality in older-adult sufferers with dementia-related psychosis. Specifically, at synapses the place transmitter concentrations are low, aripiprazole will bind to receptors and thereby trigger average activation. Conversely, at synapses where transmitter concentrations are excessive, aripiprazole will compete with the transmitter for receptor binding, and hence will cut back receptor activation. Researchers recommend that dopamine system stabilization explains why aripiprazole can improve constructive and negative signs of schizophrenia whereas having little or no effect on the extrapyramidal system or prolactin release. In patients with schizophrenia, the drug can improve positive symptoms, unfavorable symptoms, and cognitive operate. Quetiapine was launched in 1997, and has since become one of the topselling medication on the planet, with gross sales of $4. Quetiapine carries a moderate threat of serious metabolic results (ie, weight achieve, diabetes, and dyslipidemia). Common unwanted effects embody sedation (from H1 blockade) and orthostatic hypotension (from alpha blockade). Like different antipsychotics, quetiapine increases the chance of demise in older-adult sufferers with dementia-related psychosis. Cataracts developed in dogs fed four instances the utmost human dose for six or 12 months. The risk of anticholinergic results, prolactin elevation, and metabolic results (weight gain, diabetes, dyslipidemia) is low. Blockade of H1 receptors can promote drowsiness, and blockade of alpha-adrenergic receptors can promote hypotension. Asenapine has native anesthetic properties, and hence can numb the mouth when the sublingual tablets dissolve. Like other antipsychotic medicine, asenapine could enhance mortality in older-adult patients with dementia-related psychosis. Rarely, patients have skilled extreme allergic reactions, including angioedema and life-threatening anaphylaxis. Warn sufferers not to swallow the tablets, and instruct them to avoid eating and drinking for 10 minutes after dosing. Also, inform them to not be alarmed if their mouth gets numb when the tablet dissolves (asenapine can act like a local anesthetic). The traditional dosage is 5 mg twice every day for patients with schizophrenia, and 10 mg twice day by day for sufferers with bipolar dysfunction. Increasing the dosage above 10 mg twice day by day provides no clinical profit, however will improve the chance of sure unwanted effects. No dosage adjustment is needed in sufferers with renal impairment, or in sufferers with mild or average hepatic impairment. Aripiprazole is well absorbed following oral administration, both within the presence and absence of meals. Aripiprazole and its lively metabolite-dehydro-aripiprazole-have extended half-lives: 75 hours and 94 hours, respectively. Because elimination is gradual, (1) dosing may be done as quickly as a day and (2) about 14 days (four halflives) are required to achieve steady-state (plateau) plasma drug levels. The most common side effects are headache, agitation, nervousness, anxiety, insomnia, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and somnolence. Although aripiprazole can block alpha1-adrenergic receptors, the incidence of orthostatic hypotension is low (1. Like other antipsychotic medication, aripiprazole could improve mortality in older-adult patients with dementia-related psychosis. Aripiprazole for oral therapy is on the market in normal tablets (2, 5, 10, 15, 20, and 30 mg) and answer (1 mg/mL), each sold as Abilify, and in orally disintegrating tablets (10 and 15 mg) sold as Abilify Discmelt. The recommended oral dosage-both initial and maintenance-is 10 or 15 mg as soon as a day, administered with or without food. The extended-release depot preparation [Abilify Maintena] is out there in 300-mg and 400-mg doses to be given as soon as month-to-month. Dosage may be elevated by as much as 5 mg/day, however at intervals of no much less than 1 week. The preliminary dosage is 2 mg/day, and the similar old upkeep dosage is 5 to 15 mg/day. Iloperidone is administered by mouth, and plasma levels peak 2 to 4 hours after dosing. The most common adverse results are dry mouth, somnolence, fatigue, nasal congestion, and orthostatic hypotension, which can be extreme throughout preliminary remedy. Iloperidone carries a low risk of diabetes and dyslipidemia, but may cause significant weight acquire. Like different antipsychotic medication, iloperidone could improve mortality in older-adult sufferers with dementia-related psychosis. Accordingly, in patients taking such inhibitors, dosage of iloperidone must be reduced. Iloperidone [Fanapt] is supplied in tablets (1, 2, four, 6, eight, 10, and 12 mg) for oral dosing. A 4-day titration pack (2 tablets every of 1, 2, four, and 6 mg) is out there to begin treatment. To minimize hypotension during preliminary therapy, dosage should be titrated as follows: on days 1, 2, three, 4, 5, 6, and seven, give twice-daily doses of 1, 2, four, 6, 8, 10, and 12 mg, respectively. Asenapine is formulated as a sublingual pill to enable absorption directly across the oral mucosa. The drug carries a low risk of weight gain, diabetes, or dyslipidemia, and has few interactions with different agents. When asenapine is swallowed and absorbed from the gut, it undergoes in depth first-pass metabolism, making bioavailability very low (<2%). In distinction, when the drug is administered sublingually, it will get absorbed directly across the oral mucosa, and thereby avoids first-pass metabolism. As a end result, bioavailability is relatively excessive (about Lurasidone Actions and Therapeutic Use. In medical trials, dosages of 20, forty, 80, and one hundred twenty mg/day have been clearly superior to placebo. In medical trials, the most common opposed occasions have been somnolence, akathisia, parkinsonism, nausea, agitation, and anxiousness. Like different antipsychotic medication, lurasidone might enhance mortality in older-adult patients with dementia-related psychosis. Lurasidone [Latuda] is supplied in tablets (20, 40, 60, 80, and a hundred and twenty mg) for dosing with meals (at least 350 calories).
Order 25mg clozaril with visaDosage and Administration Earlier we famous the Rights of Drug Administration and agreed on their significance medicine school generic 50 mg clozaril amex. The following examples illustrate this level: � Certain medicine have multiple indication medications you can take while breastfeeding generic clozaril 50mg overnight delivery, and dosage might differ relying on which indication the drug is used for symptoms acid reflux 25mg clozaril sale. Aspirin symptoms gout purchase clozaril 25 mg otc, for example, is given in low doses to relieve pain and in excessive doses to suppress irritation. Morphine, for instance, may be administered by mouth or by injection (eg, subcutaneous, intramuscular, intravenous). Accordingly, if a large dose intended for oral use have been to be mistakenly administered by injection, the result could show deadly. The nurse who understands the pharmacology of morphine is unlikely to make this error. The infusion have to be monitored closely, and, if extravasation happens, corrective steps should be Preadministration Assessment All drug therapy begins with assessment of the affected person. Preadministration assessment is mentioned here and once more beneath Application of the Nursing Process in Drug Therapy. The following guidelines may help guarantee correct administration: Read the medicine order rigorously. Verify the identification of the patient by comparing the name on the wristband with the name on the drug order or medication administration record. Verify the identity of the drug, the amount of drug (per pill, quantity of liquid, etc. As a nurse, you might provide these supportive measures immediately, by way of affected person training, or by coordinating the activities of other healthcare providers. Minimizing Adverse Effects All drugs have the potential to produce undesired results. Common examples include gastric erosion caused by aspirin, sedation caused by older antihistamines, hypoglycemia brought on by insulin, and excessive fluid loss caused by diuretics. When medicine are employed correctly, the incidence and severity of such occasions can be lowered. Measures to reduce adverse occasions include figuring out high-risk sufferers by way of the affected person history, making certain correct administration via affected person training, and educating patients about activities that might precipitate an adverse occasion. For instance, timely administration of glucose will forestall mind harm from insulin-induced hypoglycemia. After all, that is the method that tells us whether a drug is helpful or is inflicting hurt. To make an analysis, you must know the rationale for therapy and the nature and time course of the meant response. When evaluating responses to a drug that has multiple utility, you are capable of do so provided that you realize the specific indication for which the drug is getting used. When the drug is used for hypertension, you need to monitor for a reduction in blood pressure. In distinction, when this drug is used for angina, you must monitor for a discount in chest ache. Obviously, profitable therapy requires lively and knowledgeable participation by the affected person. Examples embody (1) enhancing drug therapy of bronchial asthma via breathing workouts, biofeedback, and emotional support; (2) enhancing drug therapy of arthritis via train, bodily remedy, and relaxation; and (3) enhancing drug therapy of hypertension Minimizing Adverse Interactions When a affected person is taking two or more medicine, these drugs may work together with each other to diminish therapeutic effects or intensify antagonistic effects. For example, the flexibility of oral contraceptives to shield in opposition to pregnancy may be reduced by concurrent remedy with carbamazepine (an antiseizure drug), and the risk of thromboembolism from oral contraceptives may be increased by smoking cigarettes. These include taking an intensive drug historical past, advising the patient to avoid overthe-counter drugs that may work together with the prescribed treatment, monitoring for opposed interactions recognized to occur between the medication the patient is taking, and being alert for as-yet unknown interactions. To minimize harm, you should know the early indicators of toxicity and the procedure for toxicity administration. In your function as educator, you must give the patient the following data: � Drug name and therapeutic category (eg, penicillin: antibiotic) � Dosage � Dosing schedule � Route and technique of administration � Expected therapeutic response and when it should develop � Nondrug measures to improve therapeutic responses � Duration of therapy � Method of drug storage � Symptoms of main antagonistic results, and measures to decrease discomfort and hurt � Major adverse drug-drug and drug-food interactions � Whom to contact within the occasion of therapeutic failure, severe antagonistic reactions, or severe adverse interactions To talk this data effectively and accurately, you have to first understand it. In the following dialogue, we think about the connection between patient training and the next aspects of drug therapy: dosage and administration, selling therapeutic effects, minimizing opposed effects, and minimizing antagonistic interactions. This is very essential for routes which could be unfamiliar (eg, sublingual for nitroglycerin) and for techniques that can be troublesome (eg, subcutaneous injection of insulin). Careful consideration have to be paid to the affected person who, due to incapacity (eg, visual or intellectual impairment, restricted guide dexterity), might discover self-medication tough. Just as patients must know when to take their drugs, they need to know when to stop. In some cases (eg, treatment of acute pain), patients ought to discontinue drug use as soon as signs subside. In other cases (eg, therapy of hypertension), patients should know that remedy will probably continue lifelong. For some circumstances (eg, gastric ulcers), medication may be prescribed for a specific time interval, after which the affected person ought to return for reevaluation. Certain drugs are chemically unstable and deteriorate rapidly if stored improperly. If the drug has been prescribed by trade name, the affected person must be given its generic name, too. This data will cut back the chance of overdose that can result when a patient fails to realize that two prescriptions that bear totally different names truly include the same drugs. For insulin remedy to be most beneficial, the patient should modify doses to accommodate changes in food regimen and subsequent glucose ranges. With certain oral contraceptives, for example, if one dose is missed, the omitted dose should be taken together with the next scheduled dose. However, if three or extra doses are missed, a brand new cycle of administration should be initiated. The affected person should know the name of the Promoting Therapeutic Effects To participate absolutely in attaining the therapeutic goal, sufferers must know the nature and time course of expected beneficial results. With this knowledge, sufferers might help consider the success or failure of remedy. By recognizing therapy failure, the informed patient will be succesful of search well timed implementation of alternative remedy. With some medicine, corresponding to these used to treat despair and schizophrenia, beneficial effects are delayed, taking several weeks to turn into maximal. Awareness that remedy may not produce quick results allows the patient to have realistic expectations and helps reduce anxiousness about therapeutic failure. For example, although medication are useful in managing high ldl cholesterol, train and food plan are additionally essential. Teaching the patient about nondrug measures can greatly increase the chances of success. Minimizing Adverse Effects Knowledge of opposed drug results will enable the affected person to keep away from some opposed effects and reduce others via early detection. The affected person who has been taught to recognize these early signs can respond by ingesting glucose or other fast-acting carbohydraterich foods, thereby restoring blood sugar to a safe stage. In addition, the informed patient is ready to notify the prescriber on the first signal that an infection is growing, thereby allowing early therapy. In distinction, the affected person who has not acquired sufficient education is at increased threat of sickness or death from an infectious illness.
Purchase 50mg clozaril mastercardRather symptoms for pregnancy generic clozaril 100mg without a prescription, we limit the dialogue to those aspects of peripheral nervous system physiology that have a direct bearing on your ability to perceive medicine medicine the 1975 discount clozaril 100 mg on line. Just how the parasympathetic nervous system elicits these responses is discussed later beneath Functions of Cholinergic Receptor Subtypes medicine uses clozaril 50mg free shipping. From the previous dialogue we can see that the parasympathetic nervous system is worried primarily with what may be called the "housekeeping" chores of the physique (digestion of food and excretion of wastes) medicine for diarrhea cheap clozaril 25mg on-line. A variety of poisons act by mimicking or blocking results of parasympathetic stimulation. Among these are pesticides, nerve gases, and poisonous compounds found in certain mushrooms and vegetation. The basic mechanisms by which the autonomic nervous system regulates physiologic processes are mentioned beneath. Functions of the Sympathetic Nervous System the sympathetic nervous system has three main capabilities: � Regulating the cardiovascular system � Regulating body temperature � Implementing the acute stress response (commonly referred to as a "fight-or-flight" reaction) the sympathetic nervous system exerts multiple influences on the center and blood vessels. Stimulation of sympathetic nerves to arterioles and veins causes vasoconstriction. Release of epinephrine from the adrenal medulla results in vasoconstriction in most vascular beds and vasodilation in certain others. By influencing the guts and blood vessels, the sympathetic nervous system can obtain three homeostatic goals: � Maintenance of blood move to the mind � Redistribution of blood circulate during train � Compensation for lack of blood, primarily by inflicting vasoconstriction the sympathetic nervous system helps regulate body temperature in 3 ways: (1) By regulating blood move to the pores and skin, sympathetic nerves can increase or lower warmth loss. By dilating floor vessels, sympathetic nerves enhance blood flow to the skin and thereby accelerate warmth loss. Many therapeutic agents produce their effects by altering functions beneath sympathetic control. These medication are used primarily for results on the center, blood vessels, and lungs. Agents that alter cardiovascular function are used to treat Patterns of Innervation and Control Most structures under autonomic management are innervated by sympathetic nerves and parasympathetic nerves. The relative influence of sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves is determined by the organ into account. In many organs that receive twin innervation, the influence of sympathetic nerves opposes that of parasympathetic nerves. In some organs that obtain nerves from each divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the results of sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves are complementary, rather than reverse. For example, within the male reproductive system, erection is regulated by parasympathetic nerves whereas ejaculation is controlled by sympathetic nerves. If makes an attempt at reproduction are to succeed, cooperative interaction of each methods is required. A few constructions under autonomic management receive innervation from only one division. The principal instance is blood vessels, that are innervated completely by sympathetic nerves. In summary, there are three primary patterns of autonomic innervation and regulation: � Innervation by each divisions of the autonomic nervous system by which the results of the 2 divisions are opposed � Innervation by each divisions of the autonomic nervous system during which the consequences of the two divisions are complementary � Innervation and regulation by only one division of the autonomic nervous system Feedback Regulation Feedback regulation is a course of that permits a system to adjust itself by responding to incoming info. Feedback loop of the autonomic nervous system, these nerves incessantly exert opposing influences. If both divisions had been to send impulses simultaneously, the resultant conflicting instructions could be counterproductive (like working heating and air conditioning simultaneously). By having only one division of the autonomic nervous system provide the basal management to an organ, conflicting alerts are avoided. The branch of the autonomic nervous system that controls organ function more usually than not is alleged to provide the predominant tone to that organ. The vascular system, which is regulated nearly solely by the sympathetic nervous system, is the principal exception. The main components of this loop are (1) a sensor, (2) an effector, and (3) neurons connecting the sensor to the effector. In response to these instructions, the effector makes applicable changes in the course of. From a pharmacologic perspective, an important feedback loop of the autonomic nervous system is one which helps regulate blood pressure. Feedback (reflex) control of blood stress is achieved as follows: (1) Baroreceptors located within the carotid sinus and aortic arch monitor modifications in blood strain and ship this data to the brain. Accordingly, when blood strain falls, the baroreceptor reflex causes vasoconstriction and will increase cardiac output. Conversely, when blood pressure rises too high, the baroreceptor reflex causes vasodilation and reduces cardiac output, thereby inflicting blood pressure to drop. Note that there are two neurons within the pathway leading from the spinal wire to organs innervated by parasympathetic nerves. The junction (synapse) between these two neurons occurs within a construction known as a ganglion. The anatomy of the parasympathetic nervous system offers two basic websites at which drugs can act: (1) the synapses between preganglionic neurons and postganglionic neurons and (2) the junctions between postganglionic neurons and their effector organs. Like the parasympathetic nervous system, the sympathetic nervous system employs two neurons in the pathways main from the spinal twine to organs beneath its control. As with the parasympathetic nervous system, the junctions between these neurons are situated in ganglia. Neurons main from the spinal cord to the sympathetic ganglia are termed preganglionic neurons, and neurons leading from ganglia to effector organs are termed postganglionic neurons. The medulla of the adrenal gland is a feature of the sympathetic nervous system that requires comment. Although not a neuron per se, the adrenal medulla may be seemed on because the useful equivalent of a postganglionic neuron of the sympathetic nervous system. Autonomic tone offers a basal degree of management over which reflex regulation is superimposed. When an organ is innervated by each divisions of the autonomic nervous system, one division-either sympathetic or parasympathetic-provides many of the basal management, thereby obviating conflicting instruction. As with the parasympathetic nervous system, drugs that affect the sympathetic nervous system have two common websites of motion: (1) the synapses between preganglionic and postganglionic neurons (including the adrenal medulla), and (2) the junctions between postganglionic neurons and their effector organs. Because this pathway accommodates just one neuron, peripherally performing drugs that have an effect on somatic motor system operate have just one web site of action: the neuromuscular junction (ie, the junction between the somatic motor nerve and the muscle). Norepinephrine is the transmitter launched by virtually all postganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system. The only exceptions are the postganglionic sympathetic neurons that go to sweat glands, which employ acetylcholine as their transmitter. Understanding these receptors is central to understanding peripheral nervous system pharmacology. All effort that you spend money on studying about these receptors now will be rewarded as we focus on peripheral nervous system medication in later chapters.
Cheap clozaril 100 mg overnight deliveryCuneonavicular joint: It is a plane synovial joint between the convex articular surface of the anterior side of the top of navicular and the concavity produced by the posterior features of the three cuneiform bones medicine cabinet discount clozaril 25 mg amex. A fibrous capsule surrounds the joint however the cavity may be speaking with the cuneocuboid joint via a deficiency in the capsule medicine ball workouts order 50mg clozaril overnight delivery. Dorsal and plantar cuneonavicular ligaments which move from the navicular bone to every of the cuneiforms on the respective features reinforce the capsule symptoms nausea buy clozaril 100 mg with amex. Intercuneiform joints: Weak dorsal and stronger plantar and interosseous ligaments bind the three cuneiforms collectively 8h9 treatment order 100 mg clozaril mastercard. Cuneocuboid joint: It is a airplane synovial joint between the round aspect on the lateral surface of the lateral cuneiform bone and the spherical aspect on the medial surface of the cuboid bone. An interosseous cuneocuboid ligament connects the anterior elements of the contiguous sides of the 2 bones. The ligament subsequently stretches underneath the entire length of the lateral longitudinal arch. As this arch is of lesser peak than the medial one, an extended band stretching from pillar to pillar may help maintain the arch than shorter ties between smaller segments. Short plantar ligament (or plantar calcaneocuboid ligament): It is also a ligament between the calcaneus and the cuboid. It passes from the anterior tubercle of the calcaneus to the cuboid bone proximal to the groove for the peroneus longus. It lies deep between the talus and the calcaneus and passes from the sulcus tali to the sulcus calcanei becoming a member of the talus and calcaneus within the interval between the subtalar and talocalcaneonavicular joints. Talonavicular ligament: It is a ligament on the dorsal aspect of the foot extending between neck of talus posteriorly and the dorsal side of navicular bone anteriorly. Cuboideonavicular ligaments: There are three of these ligaments, namely-(1) the dorsal, (2) the plantar and (3) the interosseous cuboideonavicular ligaments. The dorsal and the plantar ligaments extend between the adjoining elements of the corresponding surfaces the interosseous ligament extends between the contiguous sides of the two bones. These ligaments facilitate the midfoot-hindfoot rotation on the transverse tarsal aircraft Cuneonavicular ligaments: There are two units of them-(1) the dorsal and (2) the plantar cuneonavicular ligaments. Each set has three ligaments running from the navicular to the three cuneiforms on the respective surfaces. Intercuneiform ligaments: Dorsal intercuneiform ligaments run between the cuneiforms on the dorsal surface, the plantar ligaments on the plantar surface and the interosseous ligaments on their contiguous surfaces. Cuneocuboid ligaments: Dorsal cuneocuboid ligament connects the two bones on the dorsal floor, plantar ligaments on the plantar surface and the interosseous ligament on their contiguous surfaces. These are the end to finish joints and participate within the longitudinal arches of the foot. The aspect to aspect joints are those which take part in the transverse arch of the foot. The sides of adjacent bones articulate with each other but are connected by strong plantar and interosseous ligaments. It is in contact above with the pinnacle of the talus and its higher surface types part of the articular surface of the talocalcaneonavicular joint the tibialis posterior tendon turns into the sole underneath this ligament and varieties a sling for it and the pinnacle of talus. Weight of the body tends to drive the top of talus down between the calcaneus and navicular. The plantar calcaneonavicular ligament along with the assist it receives from the sling motion of tibialis posterior, resists this tendency By this motion, the ligament also helps in the maintenance of medial longitudinal arch thus justifying its specific appellation-the spring ligament. The stem of the Y is connected posteriorly to the anterior part of the higher surface of the calcaneus. Anteriorly, it splits into two bands-one passing to the dorsal facet of the cuboid bone and one other to the dorsal aspect of the navicular bone. It is connected posteriorly to the plantar floor of the calcaneus (to a rounded ridge in front of the medial and lateral tubercles); and anteriorly to a ridge on the plantar floor of the cuboid bone, distal to the groove for the peroneus longus. Some fibres of the ligament are extended over the peroneus longus m All the tarsal joints are supplied by branches of deep peroneal nerve on the dorsal facet and by branches of medial and lateral plantar nerves on the plantar side. All these joints are synovial of the aircraft variety Dorsal and plantar tarsometatarsal ligaments connect the corresponding bones. Two interosseous ligaments are current; one connects the lateral aspect of the medial cuneiform to the medial side of the second metatarsal; the opposite connects the lateral side of the lateral cuneiform to the medial facet of the fourth metatarsal. The medial cavity is between the primary metatarsal and the medial cuneiform; the intermediate cavity is between the second and third metatarsals and the intermediate and lateral cuneiforms; the lateral cavity is between the fourth and fifth metatarsals and the cuboid. The arch rests posteriorly on the tubercles of the calcaneus, and anteriorly on the heads of the metatarsals. The summit of the arch is formed by the talus (medial a half of the superior surface). The posterior shaped by the calcaneus is s steep slope and the anterior pillar fashioned by navicular, cuneiforms, the bases of the medial three matatarsals and ending in the heads of the identical metatarsals is a gradual slope. The arch rests posteriorly on the calcaneus and anteriorly on the heads of the lateral two metatarsals. The posterior pillar formed by the lateral part of the calcaneus is short and has a sharper decline than that of the medial arch. The anterior pillar formed by the cuboid, bases of the lateral two metatarsals ends within the heads of the identical metatarsals and has a far shorter gradient. It can properly be famous that calcaneus is frequent to both arches and varieties the common posterior pillar. The lateral longitudinal arch is far flatter than the medial arch and rests on the bottom whereas standing the transverse arch is greatest marked in the midst of the foot It is fashioned by the cuneiforms, cuboid and the bases of the metatarsal bones. At the extent of the metatarsal shafts and the metatarsal heads, the arch is flatter; however the formation of the arch is shown by the truth that the heads of second to fourth metatarsals bear much less weight than the heads of the first and the fifth metatarsals. The medial and lateral longitudinal arches form the pillars of the transverse arch. Individually, each foot has only half an arch and the complete transverse arch is fashioned when the ft are positioned together. As a results of the transverse arch, the medial border of the foot remains off the ground in its center half. The bases of the lateral 4 metatarsals articulate to type four small synovial cavities. A small fibrous capsule is current and is strengthened by robust plantar and collateral ligaments. The dorsal facet of the capsule is replaced by dorsal digital expansion the plantar ligaments of all of the 5 joints are interconnected by the deep transverse metatarsal ligament. In flexion, the toes are drawn collectively and in extension they spread apart and likewise transfer somewhat laterally. Both the tarsometatarsal and intermetatarsal joints are equipped by deep peroneal and medial and lateral plantar nerves. The positioning of the talus at a degree greater than the remainder of the tarsal bones is essential.
Clozaril 100mg for saleEscitalopram [Lexapro symptoms parkinsons disease generic 25 mg clozaril with mastercard, Cipralex] is available in tablets (5 symptoms jaw bone cancer 50mg clozaril, 10 medications varicose veins clozaril 50 mg visa, and 20 mg) and an oral resolution (5 mg/5 mL) treatment diabetes type 2 cheap 100 mg clozaril fast delivery. The really helpful initial dosage is 10 mg/day, taken within the morning or evening, with or without meals. However, in sufferers with severe renal impairment, a dosage reduction could additionally be required. Antidepressants could enhance the chance of suicide, particularly during the early phase of remedy. Children/ adolescents Pregnant women Breast-feeding ladies Older adults Desvenlafaxine Desvenlafaxine [Pristiq], approved in 2008, is the most important active metabolite of venlafaxine. At this time, desvenlafaxine is permitted only for major depression, in contrast to venlafaxine, which is approved for main despair, generalized anxiety dysfunction, panic disorder, and social phobia. Desvenlafaxine is well absorbed following oral administration, each within the presence and absence of food. The drug undergoes some hepatic metabolism, and is excreted in the urine as metabolites and father or mother drug. The most typical are nausea, headache, dizziness, insomnia, diarrhea, dry mouth, sweating, and constipation. Like all different antidepressants, desvenlafaxine could enhance the risk of suicide in youngsters and young adults. Some neonates exposed to the drug in utero have required extended hospitalization, respiratory support, and tube feeding. Additional issues include hyponatremia, sustained hypertension, serotonin syndrome, bleeding, seizures, and withdrawal signs if the drug is discontinued abruptly. As with venlafaxine, combining desvenlafaxine with one other serotonergic drug increases the chance of serotonin syndrome. The recommended dosage is 50 mg as quickly as daily, taken with or with out meals, about the same time each day. Increasing the dose above 50 mg/day presents no therapeutic benefit, however does increase the risk of unwanted side effects. In sufferers with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance lower than 30 mL/min), the dosage ought to be reduced to 50 mg each different day. To decrease withdrawal reactions, the drug ought to be discontinued slowly (by gradually increasing the dosing interval). Venlafaxine is well absorbed following oral administration, both within the presence and absence of food. In the liver, much of every dose is converted to desvenlafaxine, an energetic metabolite. The half-life is 5 hours for the parent drug and eleven hours for the lively metabolite. The most typical is nausea (37% to 58%), followed by headache, anorexia, nervousness, sweating, somnolence, and insomnia. Venlafaxine can even trigger dose-related sustained diastolic hypertension; blood stress ought to be monitored. Some sufferers expertise sustained mydriasis (dilation of the pupil), which may increase the risk of eye injury in these with elevated intraocular pressure or glaucoma. Like all other antidepressants, venlafaxine could improve the risk of suicide, especially in children and young adults. Clinical trials have proven that duloxetine is clearly superior to placebo: Treatment reduces depressive symptoms and may reduce bodily pain related to melancholy (eg, backache). Furthermore, benefits may develop shortly, in some circumstances inside 2 weeks of beginning treatment. In addition, duloxetine seems much less nicely tolerated than the other medications generally used to treat melancholy. In addition to its use in melancholy, duloxetine is permitted for fibromyalgia, generalized anxiousness dysfunction, ache of diabetic peripheral neuropathy, and chronic musculoskeletal ache, together with low back pain and pain from osteoarthritis. The drug is used off-label for stress urinary incontinence (in contrast to urge urinary incontinence). In sufferers with extreme renal impairment, levels of duloxetine and its metabolites are significantly elevated, and in those with severe hepatic impairment, the half-life is significantly prolonged. In clinical trials, the most typical antagonistic effects had been nausea, dry mouth, insomnia, somnolence, constipation, decreased urge for food, fatigue, increased sweating, and blurred imaginative and prescient. Duloxetine may cause a small enhance in blood strain, and therefore blood strain should be measured at baseline and periodically thereafter. Elevation of serum transaminases, indicating liver harm, occurs in about 1% of sufferers. There have been reviews of hepatitis, hepatomegaly, cholestatic jaundice, and elevation of transaminases to greater than 20 occasions the higher limit of normal. As with venlafaxine, abrupt cessation of remedy may cause a withdrawal syndrome. Symptoms embrace nausea, vomiting, dizziness, headache, nightmares, and paresthesias. Like all other antidepressants, duloxetine might increase the danger of suicide, especially in children and younger adults. Animal research indicate that duloxetine interferes with fetal and postnatal improvement, inflicting decreased fetal weight, decreased postnatal survival, and neurologic disturbances. Use of duloxetine late in pregnancy can also result in withdrawal syndrome in the toddler. Two studies are presently recruiting pregnant and/or lactating ladies to examine these results further. One accomplished study discovered duloxetine in the breast milk of 6 lactating girls who received 40 mg twice daily for 3. The combination of duloxetine with heavy alcohol consumption greatly increases the chance of liver injury. Interaction with thioridazine is of particular concern owing to a threat of significant ventricular dysrhythmias. Duloxetine [Cymbalta] is on the market in delayed-release capsules (20, 30, and 60 mg) that ought to be swallowed whole, with or without food. The usual dosage for melancholy is 40 to 60 mg/day initially, followed by 60 to 120 mg/day for upkeep. For all other indications-depression, generalized anxiety dysfunction, ache of diabetic neuropathy, and persistent musculoskeletal pain-the dosage is 30 mg once daily for 1 week, adopted by 60 mg as soon as day by day for upkeep. In medical studies, patients taking levomilnacipran showed important clinical enchancment in depressive signs. Levomilnacipran is on the market in 20-, 40-, 80-, and 120-mg capsules and is taken once daily. The most common antagonistic results are sedation, orthostatic hypotension, and anticholinergic effects. Specifically, each teams produce various degrees of sedation, orthostatic hypotension, and anticholinergic results. This delay means that antidepressant effects are as a outcome of adaptive adjustments brought on by extended reuptake blockade, and not to reuptake blockade instantly.
Clozaril: 100 mg, 50 mg, 25 mg
Order 25mg clozarilIt continues further downwards and at the level of the ankle medicines 604 billion memory miracle buy 50mg clozaril fast delivery, takes a medial flip to go under cowl of the flexor retinaculum medicine ethics cheap clozaril 100mg overnight delivery, where it divides into its two terminal branches symptoms 8 days after iui order clozaril 25 mg online, specifically (1) the medial and (2) the lateral plantar nerves medications jock itch clozaril 25 mg generic. It passes additional downwards over the popliteal vessels, crossing them from lateral to medial side. Then it comes to lie on the popliteus muscle, underneath cover of gastrocnemius and plantaris. As the nerve enters the again of leg, it passes deep to the soleus muscle and rests on the tibialis posterior muscle and the posterior side of tibia. Accompanied by the posterior tibial vessels, it runs on the intermuscular septum separating the superficial muscular tissues from the deep muscles of the posterior compartment of leg In its course to the ankle, the nerve is first medial after which lateral to the posterior tibial vessels. As it crosses the ankle, it takes a medial deviation and lies midway between the medial malleolus and calcaneus. At this stage, it comes underneath cover of the flexor retinaculum and lies between the tendons of flexor digitorum longus and flexor hallucis. Branches when the tibial nerve is incorporated within the sciatic trunk: the 2 branches at this degree are the nerve to hamstrings and the articular branch to knee. Branches within the popliteal fossa: these may be grouped into three units: Articular branches to the knee: Two slender branches, one of which pierces the oblique popliteal ligament and the opposite accompanies the inferomedial genicular artery; both supply the buildings of the knee joint. Muscular branches: Five branches; the branches to the two heads of gastrocnemius and the plantaris enter the concerned muscles at those aspects the place they form the inferior borders of the popliteal fossa; the nerve to soleus enters the muscle on its superficial floor; the remaining nerve of this set, namely, the nerve to popliteus deserves special description. This nerve, because it turns around the distal border of the muscle, gives out muscular branches to the tibialis posterior, a branch to the interosseous membrane, an articular branch to the tibiofibular syndesmosis and a medullary department to the tibia. Cutaneous department: this is the sural nerve; from the popliteal fossa, the nerve runs between the two heads of gastrocnemius and then lies on the tendocalcaneus It pierces the deep fascia within the middle third of the leg and turns into cutaneous. It is immediately joined by the peroneal communicating branch of the widespread peroneal nerve. It then runs downwards and reaches the foot by winding across the again of the lateral malleolus, together with the small saphenous vein. The sural nerve provides cutaneous branches to the lateral facet and back of the lower third of the leg, the ankle, the heel (the lateral calcaneal branches) and the lateral border of the foot and the little toe, articular branches to ankle and tarsal joints. On the dorsum of the foot, the sural nerve communicates with the branches of the superficial peroneal nerve. Through this communication, it may reinforce or exchange these branches of the superficial peroneal nerve to the adjacent sides of the 4th and fifth or the third and 4th toes. Muscular branches: these are usually four in number, particularly (1) the nerve to soleus, (2) nerve to tibialis posterior, (3) nerve to flexor digitorum longus and (4) the nerve to flexor hallucis longus. The nerve to flexor hallucis longus usually accompanies the peroneal artery and in addition supplies it. Cutaneous branches: these are the medial calcaneal branches, which pierce the flexor retinaculum to ok sf ks f ks. Starting from under cowl of the flexor retinaculum, it programs ahead in the sole deep to abductor hallucis and reaches the interval between the abductor hallucis and the flexor digitorum brevis. The nerve is accompanied by the medial plantar vessels and ends by dividing into its 4 terminal branches. Muscular branches: these provide the abductor hallucis and the flexor digitorum brevis. A medullary branch to the fibula and an articular branch to the ankle joint are also given by the tibial nerve. Terminal branches of the medial plantar nerve: these are the four common plantar digital nerves and are numbered from the medial to the lateral. The first branch separates off from the primary nerve before the opposite terminal branches, runs forward in the interval between the abductor hallucis and the flexor digitorum brevis, provides a department to the latter muscle after which pierces the deep fascia just posterior to the ball of the big toe. It gives cutaneous branches to the medial facet of the foot and ends as the plantar digital nerve for the medial facet of the large toe. It supplies a branch to the primary lumbrical and then turns into superficial by piercing the deep fascia within the interval between the first and the second toes. It ends by dividing into two plantar digital nerves for the adjacent sides of the first and the second toes. The third and the fourth branches coursing slightly laterally, supply small twigs to the joints of the foot and then turn into superficial in the intervals between the second and third and the third and fourth toes respectively. Once superficial, they divide into the plantar digital nerves for the adjoining sides of these toes. Muscular branches: these provide the flexor digitorum accessorius and the abductor digiti minimi. Terminal branches of the lateral plantar nerve: There are two terminal branches, particularly (1) the superficial and (2) the deep branches. The superficial branch passes ahead in the interval between the flexor digitorum brevis and the abductor digiti minimi and divides into the medial and lateral common plantar digital branches. The medial widespread plantar digital branch runs ahead further to the house between the fourth and the fifth toes, turns into cutaneous and then divides into two plantar digital branches to the adjacent sides of those toes. The digital nerves additionally supply the metatarsophalangeal and interphalangeal joints. As it reaches the base of the fifth metatarsal bone, it divides into the superficial and deep terminal branches. It provides the tarsal and tarsometatarsal joints, the interossei muscles, the adductor hallucis muscle and the lateral three lumbrical muscles. From the bifurcation of the sciatic nerve on the superior angle of the popliteal fossa, the common peroneal nerve reaches its termination about an inch distal to the pinnacle of fibula. The nerve (still as part of the sciatic trunk) enters the thigh at the lower border of quadratus femoris Initially, it lies in the angle between the gluteus maximus superolaterally and the hamstrings medially. Following the tendon of this muscle, the nerve runs obliquely to the lateral part of the popliteal fossa and passes over the lateral head of gastrocnemius to reach the again of the top of fibula. Branches when the common peroneal is included in the sciatic trunk: the two branches at this level are the nerve to quick head of biceps and the articular branch to knee. Cutaneous branches: the two cutaneous branches in this class are the lateral cutaneous nerve of the calf and the peroneal communicating nerve. It arises in widespread with the peroneal communicating nerve within the popliteal fossa, pierces the deep fascia over the lateral head of gastrocnemius and provides the skin and fascia of the lateral a part of the again of leg within the upper two-thirds. Peroneal communicating department: It arises in the popliteal fossa, passes over the lateral head of gastrocnemius but deep to the deep fascia and reaches the middle third of the leg. Recurrent branch: It arises instantly proximal to the terminal division of the widespread peroneal and passes ahead underneath cover of the peroneus longus. Terminal branches of the common peroneal nerve: these are the superficial and deep peroneal nerves. Muscular branches: these are given off to the muscular tissues of the anterior compartment of the leg, particularly the tibialis anterior, the extensor hallucis longus, the extensor digitorum longus and the peroneus tertius.
References - Kushner BH, LaQuaglia MP, Bonilla MA, et al: Highly effective induction therapy for stage 4 neuroblastoma in children over 1 year of age, J Clin Oncol 12:2607n2613, 1994.
- Hoyos CM, Yee BJ, Phillips CL, et al: Body compositional and cardiometabolic effects of testosterone therapy in obese men with severe obstructive sleep apnoea: a randomised placebo-controlled trial, Eur J Endocrinol 167:531n541, 2012.
- Van Thiel D, el-Ashmawy L, Love K, et al. Response to hepatitis B vaccination by liver transplant candidates. Dig Dis Sci. 1992;37: 1245-1249.
- Santini D, Abbate A, Scarpa S, et al: Surviving acute myocardial infarction: Survivin expression in viable cardiomyocytes after infarction. J Clin Pathol 2004;57: 1321-1334.
- Tsai CF, Shiau MY, Chang YH, et al. Trends of mycobacterial clinical isolates in Taiwan. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2011; 105: 148-152.
|