Colchis
Alfred H. Stammers, MSA, CCP, PBMT - Director of Perfusion Services
- Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Geisinger Health Systems
- Danville, Pennsylvania
Buy generic colchis 0.5mgSkeletal fluorosis-Occurring because of antibiotics for uti uk cheap colchis 0.5 mg on line excess of sodium fluoride content in the soil and water in an area virus mutation order colchis 0.5 mg visa. This reduction in bone mass results in fragile skeleton associated with elevated danger of fractures and consequent pain and deformity infection from dog bite discount 0.5 mg colchis amex. Osteoporosis may be tough to distinguish radiologically from different osteopenias similar to osteomalacia antibiotic resistant bronchitis cheap 0.5mg colchis with visa, osteogenesis imperfecta, osteitis fibrosa of hyperpara thyroidism, renal osteodystrophy and a number of myeloma. Histologically, the next sequential changes seem over a period of time: i) Earliest change is demineralisation and elevated bone resorption starting at the subperiosteal and endosteal floor of the cortex after which spreading to the trabecular bone. Clinical signs of bone disease in advanced renal failure appear in less than 10% of sufferers but radiologic and histologic modifications are observed in fairly massive proportion of circumstances. Hyperphosphataemia, in turn, causes hypocalcaemia which is answerable for secondary hyper parathyroidism. Metabolic acidosis As a result of decreased renal function, acidosis sets by which might cause osteoporosis and bone decalcification. Aluminium interferes with deposition of calcium hydroxyapatite in bone and results in osteomalacia, secondary hyperparathyroidism and osteitis fibrosa cystica. In addition, accumulation of b2microglobulin amyloid in such instances causes dialysisrelated amyloidosis (page 71). Mixed osteomalaciaosteitis fibrosa is the most common manifestation of renal osteodystrophy ensuing from disordered vitamin D metabolism and secondary hyperparathyroidism. Pure osteitis fibrosa results from metabolic compli cations of secondary hyperparathyroidism. Renal rickets resembling the adjustments seen in kids with nutritional rickets with widened osteoid seams may occur (page 244). Osteosclerosis is characterised by enhanced bone density within the higher and lower margins of vertebrae. Metastatic calcification is seen at extraosseous sites corresponding to in mediumsized blood vessels, periarticular tissues, myocardium, eyes, lungs and gastric mucosa (page 36). Such endemic regions exist in some tropical and subtropical areas; in India it exists in some parts of Punjab and Andhra Pradesh. This results in heavily mineralised bones which are thicker and denser but are otherwise weak and deformed (just as in osteopetrosis). In addition, there are also deposits of fluoride in delicate tissues, notably as nodules within the interosseous membrane. There has been some evidence that osteitis deformans is a type of slowvirus an infection by paramyxovirus. Autosomal dominant inheritance and genetic susceptibility have been proposed on the premise of statement of 710 fold higher prevalence of illness in firstdegree relations. Clinically, the monostotic type of the disease may stay asymptomatic and the lesion is discovered incidentally or on radiologic examination. Initial osteolytic stage: this stage is characterised by areas of osteoclastic resorption produced by elevated number of large osteoclasts. The slender space between the trabeculae and cortex is crammed with collagen which progressively becomes less vascular. Quiscent osteosclerotic stage: After many years, exces sive bone formation outcomes and thus the bone becomes more compact and dense producing osteosclerosis. However, newlyformed bone is poorly mineralised, soft and vulnerable to fractures. Radiologically, this stage produces characteristic cottonwool look of the affected bone. Most frequently affected bones are: craniofacial, ribs, vertebrae and long bones of the limbs. Approximately a quarter of cases with polyostotic form have greater than half of the skeleton concerned by illness. Albright syndrome Also called McCuneAlbright syndrome, it is a type of polyostotic fibrous dysplasia asso ciated with endocrine dysfunctions and accounts for lower than 5% of all circumstances. The syndrome is characterised by polyostotic bone lesions, skin pigmentation (caf�aulait macular spots) and sexual precocity, and sometimes different endocrinopathies. Grossly, the lesions appear as sharplydemarcated, localised defects measuring 25 cm in diameter, current within the cancellous bone, having thin and easy overlying cortex. The epiphyseal cartilages are generally spared in the monostotic form however concerned in the polyostotic type of illness. Cut part of the lesion shows substitute of normal cancellous bone of the marrow cavity by gritty, grey pink, rubbery soft tissue which may have areas of haemor rhages, myxoid change and cyst formation. Histologically, the lesions of fibrous dysplasia have characteristic benignlooking fibroblastic tissue organized in a loose, whorled pattern during which there are irregular and curved trabeculae of woven (nonlamellar) bone in the kind fishhook look or Chinese letter shapes. Rarely, malignant change may occur in fibrous dysplasia, most frequently an osteogenic sarcoma. Most generally concerned bones are upper or lower end of tibia or decrease finish of femur. The lesion is generally solitary however not often there could additionally be a number of and bilaterally symmetrical defects. Radiologically, the lesion is eccentrically positioned within the metaphysis and has a sharplydelimited border. Possibly, it arises as a outcome of some developmental defect on the epiphyseal plate, or could be a tumour of histiocytic origin because of close resemblance to fibrohistiocytic tumours (page 855). Renal osteodystrophy is look of skeletal abnor malities appearing in circumstances of persistent kidney disease. In this, fluoride replaces calcium as the mineral within the bone and gets deposited with none regulatory control. It is a benign situation, possibly of develop mental origin, characterised by the presence of localised space of replacement of bone by fibrous connective tissue with a attribute whorled sample and containing trabeculae of woven bone. Three kinds of fibrous dysplasia are distinguished- monostotic, polyostotic, and Albright syndrome. The situation impacts both sex and most sufferers are between 20 and 30 years of age. Histologically, the cyst wall consists of skinny colla genous tissue having scattered osteoclast giant cells and newly shaped reactive bony trabeculae. Clinically, the aneurysmal bone cyst may enlarge over a period of years and produce ache, tenderness and pathologic fracture. Larger lesion (510 cm) occurring usually in response to trauma is referred to as nonossifying fibroma. Microscopically, fibrous cortical defect consists of mobile masses of fibrous tissue showing storiform pattern. There are quite a few multinucleate osteoclastlike big cells, haemosiderinladen macrophages and foamy cells; hence the lesion is also termed histiocytic xanthogranuloma or fibrous xanthoma of bone. Histologic hallmark of lesion is presence of aneurysmal areas crammed with blood, partly lined by endothelium and separated by connective tissue septa containing osteoclastlike giant cells along the wall of vascular spaces. The areas are separated by connective tissue septa containing osteoid tissue, numerous osteoclast like multinucleate giant cells and trabeculae of bone.
Diseases - Al Gazali Donnai Mueller syndrome
- Marburg fever
- Acute myeloblastic leukemia type 7
- Biliary tract cancer
- Mental retardation, unexplained
- Chromosome 21 ring
- Sinus node disease and myopia
- Pierre Robin sequence faciodigital anomaly
- Biliary atresia, extrahepatic
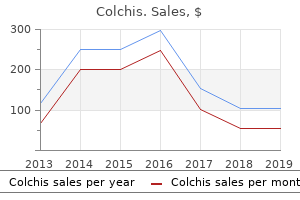
Colchis: 0.5 mg
Buy 0.5mg colchis fast deliveryCardiovascular threat in kidney transplant recipients receiving mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors antibiotic quick guide cheap colchis 0.5mg with mastercard. Beneficial results of early initiation of lipid-lowering remedy following renal transplantation antibiotics for sinus infection clindamycin discount colchis 0.5mg line. Ezetimibe is effective in the treatment of persistent hyperlipidemia of renal allograft recipients bacteria 3 basic shapes order colchis 0.5mg visa. Ezetimibe treatment in hypercholesterolemic kidney transplant sufferers is protected and effective and reduces the decline of renal allograft perform: A pilot study antibiotics for acne short term cheap colchis 0.5mg line. Relationship between inpatient hyperglycemia and insulin treatment after kidney transplantation and future new onset diabetes mellitus. Higher levels of physical activity are associated with a lower threat of abnormal glucose intolerance in renal transplant recipients. Hospitalized atrial fibrillation after renal transplantation within the United States. Obesity and cardiac threat after kidney transplantation: Experience at one center and comprehensive literature evaluation. Cardiac troponin T before and after kidney transplantation: Determinants and implications for posttransplant survival. Serum stem cell factor degree in renal transplant recipients with posttransplant erythrocytosis. Tubular operate in sufferers with hypokalemia induced by sirolimus after renal transplantation. Renal allograft failure in a hyperparathyroid patient following initiation of a calcimimetic. Tertiary hyperparathyroidism in kidney transplant recipients: characteristics of sufferers chosen for various strategies. Benefits associated with antiviral remedy in kidney allograft recipients with persistent hepatitis B infection. Impact of sirolimus, tacrolimus and mycophenolate mofetil on osteoclastogenesis-implications for posttransplantation bone disease. Outcome at 3 years with prednisonefree upkeep routine: A single center expertise with 349 kidney transplant recipients. A 1-year randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled examine of intravenous ibandronate on bone loss following renal transplantation. New-onset gout after kidney transplantation: Incidence, threat elements and implications. Only a decade ago, it was believed that nonimmunologic causes were the main components resulting in continual allograft damage and graft loss. Whereas immunologic causes are actually believed to be mainly responsible for late allograft injury and graft failure, nonimmunologic causes nonetheless symbolize important risk components for (late) graft damage and graft loss. The donor graft itself may current with vital preexisting disease, limiting long-term graft survival. Although some allografts are misplaced because of one specific cause, others accumulate the burden from several different causes with gradual lack of functioning nephrons. Main contributors to late graft injury and late graft loss are summarized in Box 107-2. Female donor gender negatively affects kidney graft survival, with decreased survival when female grafts are transplanted into male recipients (risk ratio 1. Other mechanisms may embody possible differences in the immunogenicity of male and female grafts. Graft survival has steadily improved over the past 25 years because of a reduction in each early and late graft loss. Changes thought not because of rejection-either acute or chronic Box 107-1 Banff classification of renal allograft pathology (2007 update of authentic 1997 classification). It is most likely going that the related arteriolopathy and narrowing of the lumen contribute to improvement of fibrosis and atrophy after watershed infarcts inside areas of ischemia. Local hypoxia leads to formation of free oxygen radicals, which promote mobile demise by apoptosis. Diagnosis and management of recurrent illness are mentioned further in Chapter 108. Calcineurin inhibitor nephrotoxicity impacts all histologic compartments of the transplanted kidney. Confirmation of the prognosis is made by exclusion of other causes, such as donor hyalinosis (which may be detected on the implantation biopsy specimen), diabetes, and hypertensive nephrosclerosis. Striped fibrosis is subjectively defined by a dense stripe of cortical fibrosis and atrophic tubules adjacent to Calcineurin Inhibitor Toxicity the vasculopathy in continual allograft harm resembles systemic vascular illness, elevating the possibility that conventional risk factors for heart problems may be implicated. In a multicenter, retrospective research of 29,751 kidney transplant recipients, elevated systolic blood stress above a hundred and eighty mm Hg (compared with <140 mm Hg) at 1 yr was related to a doubled threat of graft failure at 7 years. Dyslipidemias, together with raised levels of whole ldl cholesterol, lowdensity lipoprotein cholesterol, and triglycerides, and cigarette smoking have additionally been associated with late graft failure. Some research additionally counsel that hyperuricemia, which is widespread in patients with metabolic syndrome, might have a role in chronic allograft injury. The administration of hypertension, dyslipidemia, and other cardiovascular threat components in the transplant recipient is discussed further in Chapter 106. Staining of glomerular capillaries (A) and circumferential staining of peritubular capillaries (B) are typical. Multiple and extreme late acute mobile rejection episodes are predictive of continual graft dysfunction greater than early cellular rejection and acute vascular rejection, which have stronger associations with acute graft loss. Especially in continual antibody-mediated rejection, nevertheless, C4d in peritubular capillaries may be adverse (C4d-negative antibody-mediated rejection). A, Section of a glomerular capillary loop (�24,000) demonstrating mesangial interposition (asterisks), subendothelial expansion and new lamina densa (double arrow), and endothelial hypertrophy (line). Other threat elements are previous nonadherence, psychiatric issues, substance abuse, and inadequate socioeconomic help, and also antagonistic results from immunosuppressive medicine. In a recent study, 14 out of 61 sufferers (23%) who were converted from cyclosporine to everolimus at 3 to four. However, substantial nephron loss could occur before an increase in serum creatinine turns into evident. Persistent or worsening proteinuria can be a late signal of chronic allograft harm. Proteinuria may be assessed by dipstick urine evaluation, by spot urine protein-creatinine ratio, or by measurement of the 24-hour urine protein excretion. The Doppler resistive index offers an estimate of intrarenal (but also systemic) compliance and is most helpful in longitudinal research in the identical affected person to assess progressive graft vascular harm. The role of protocol biopsies in the early detection of continual allograft harm stays controversial. Chronic allograft dysfunction is widespread and can have many causes; nonetheless, whether it is left untreated, it can in the end lead to progressive renal damage, which in turn will heal by scarring and interstitial fibrosis.
Generic colchis 0.5mg without prescriptionThe tumour is usually composed of 3 types of cells occurring in various proportions: small cells bacteria quizlet proven 0.5 mg colchis, spindle cells and giant cells xylitol antibiotic discount colchis 0.5mg mastercard. Spindle cell carcinoma these tumours are composed of spindle cells resembling sarcoma antibiotics kidney stones discount colchis 0.5mg fast delivery. Some tumours could comprise obvious sarcomatous part such as areas of osteosarcoma antibiotic 300mg buy colchis 0.5 mg visa, chondrosarcoma or rhabdomyosarcoma. Giant cell carcinoma this type is composed of extremely anaplastic big cells displaying quite a few atypical mitoses, bizarre and lobed nuclei and a few assuming spindle shapes. Cretinism or congenital hypothyroidism is the development of severe hypothyroidism throughout infancy and childhood, and myxoedema is the maturity hypothyroidism. It contains acute (bacterial or fungal infection and radiation injury), subacute (granulomatous thyroiditis) and persistent. Both pairs are normally embedded within the posterior facet of the thyroid substance but separated from it by a connective tissue capsule. There could, however, be variation within the number, location and size of parathyroid glands. The parenchymal cells are of 3 types: chief cells, oxyphil cells and water-clear cells. The chief cells are most numerous and are the most important supply of parathyroid hormone. The function of parathyroid hormone in regulating calcium metabolism within the body is at the following 3 levels. Parathyroid hormone increases renal production of probably the most energetic metabolite of vitamin D, i. The main parathyroid disorders are its practical problems (hyper- and hypoparathyroidism) and neoplasms. These dysfunctions end result from extreme excretion of calcium within the urine due to hypercalcaemia induced by elevated parathyroid hormone stage. Metastatic calcification, especially within the blood vessels, kidneys, lungs, stomach, eyes and other tissues (page 36). Other adjustments similar to pancreatitis, cholelithiasis and peptic ulcers because of hypercalcaemia and high parathyroid hormone degree are less constant options. Hypoparathyroidism is of 3 types-primary, pseudo- and pseudopseudo-hypoparathyroidism. Most common causes of major hypoparathyroidism are: surgical procedures involving thyroid, parathyroid, or radical neck dissection for most cancers. The patients are usually females and are characterised by indicators and symptoms of hypoparathyroidism and other clinical features like quick stature, quick metacarpals and metatarsals, flat nostril, spherical face and a quantity of exostoses. The exocrine part of the gland and its issues have already been mentioned in Chapter 19. The islet cell tissue is tremendously concentrated in the tail than in the head or physique of the pancreas. Ultrastructurally and immunohistochemically, four main and 2 minor types of islet cells are distinguished, each sort having its distinct secretory product and function. Beta or B cells comprise about 70% of islet cells and secrete insulin, the defective response or deficient synthesis of which causes diabetes mellitus. Delta or D cells comprise 5-10% of islet cells and secrete somatostatin which suppresses each insulin and glucagon release. Major disease of endocrine pancreas is diabetes mellitus; others are uncommon islet cell tumours. It may occur at any age and in either sex but is discovered extra incessantly in adult life. Microscopically, majority of adenomas are predominantly composed of chief cells arranged in sheets or cords. Usually, a rim of regular parathyroid parenchyma and fats are present exterior to the capsule which assist to distinguish an adenoma from diffuse hyperplasia. It is anticipated that by the yr 2030 the variety of diabetics globally will double from the current determine of 250 million. However, in the new classification, neither age nor insulindependence are thought-about as absolute standards. Etiologic classification of diabetes mellitus (as per American Diabetes Association, 2007). Systemic Pathology Release Glucose is the key regulator of insulin secretion from -cells by a collection of steps: i) Hyperglycaemia (glucose level more than 70 mg/dl or above 3. Other stimuli influencing insulin launch include nutrients within the meal, ketones, amino acids and so on. Action Half of insulin secreted from -cells into portal vein is degraded within the liver while the remaining half enters the systemic circulation for motion on the target cells: i) Insulin from circulation binds to its receptor on the goal cells. Constitutional components Certain environmental factors such as obesity, hypertension, and degree of bodily activity play contributory role and modulate the phenotyping of the disease. The following biochemical mechanisms have been proposed to explain the development of issues of diabetes mellitus. Failure to take insulin and exposure to stress are the standard precipitating causes. Severe lack of insulin causes lipolysis within the adipose tissues, leading to launch of free fatty acids into the plasma. Thrombotic and bleeding issues are frequent because of high viscosity of blood. The contrasting features of diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar non-ketotic coma are summarised in Table 25. It might result from excessive administration of insulin, missing a meal, or as a outcome of stress. These issues are briefly outlined under and have been discussed intimately in relevant chapters. Besides retinopathy, diabetes additionally predisposes the sufferers to early improvement of cataract and glaucoma. Infections Diabetics have enhanced susceptibility to varied infections corresponding to tuberculosis, pneumonias, pyelonephritis, otitis, carbuncles and diabetic ulcers. This could possibly be because of numerous elements similar to impaired leucocyte functions, decreased mobile immunity, poor blood supply due to vascular involvement and hyperglycaemia per se. The American Diabetes Association (2007) has beneficial definite diagnostic criteria for early diagnosis of diabetes mellitus (Table 25. More sensitive and glucose particular test is dipstick methodology primarily based on enzyme-coated paper strip which turns purple when dipped in urine containing glucose. Besides diabetes mellitus, glucosuria may also happen in certain other circumstances corresponding to: renal glycosuria, alimentary (lag storage) glucosuria, many metabolic disorders, starvation and intracranial lesions. Ketonuria Tests for ketone bodies within the urine are required for assessing the severity of diabetes and never for analysis of diabetes.
Cheap colchis 0.5mg mastercardIn either case antibiotics prior to surgery buy colchis 0.5 mg with amex, the cause for ischaemia is compromised mesenteric circulation bacteria in florida waters buy cheap colchis 0.5mg, whereas ischaemic effect is much less likely to antibiotics zone of inhibition cheap colchis 0.5mg with amex occur within the stomach bacteria have 80s ribosomes order colchis 0.5 mg with visa, duodenum and rectum as a end result of ample collateral blood supply. Depending upon the extent and severity of ischaemia, 3 patterns of pathologic lesions can happen. Miscellaneous causes: i) Strangulated hernia ii) Torsion iii) Fibrous bands and adhesions. The affected areas turn into dark purple and markedly congested and the peritoneal floor is coated with fibrinous exudate. Subsequently, inflammatory cell infiltration and secondary infection happen, leading to gangrene of the bowel. The situation is also referred to as haemorrhagic gastroenteropathy, and within the case of colon as membranous colitis. The affected phase of the bowel is purple or purple however without haemorrhage and exudation on the serosal floor. The modifications could extend into superficial muscularis however deeper layer of muscularis and serosa are spared. Secondary bacterial an infection may supervene resulting in pseudomembranous enterocolitis. Clinically, as in transmural infarction, the features of belly pain, nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea are present, however the modifications are reversible and curable. Inflammatory cell infiltration is marked at the line of demarcation between the infarcted and regular bowel. Ischaemic colitis passes via three phases: infarct, transient ischaemia and ischaemic stricture. However, the surgical submitted specimens usually are of the ischaemic stricture. Thus, the gross appearance could be confused with both of the 2 forms of inflammatory bowel disease. The muscularis can also present inflammatory adjustments and patchy replacement by fibrosis. The blood vessels might show atheromatous emboli, organising thrombi and endarteritis obliterans. A pseudomembrane composed of necrotic epithelium, fibrin and inflammatory cells may develop. In healed cases, stricture formation, malabsorption and brief bowel syndrome are the standard problems. Necrotising enterocolitis is an acute irritation of the terminal ileum and ascending colon, occurring primarily in untimely and low-birth-weight infants. Exogenous elements In addition to function of genetic factors and deranged T-cell mediated immunity, a job for a number of exogenous and environmental elements has been assigned: i) Microbial components: At totally different occasions, role of quite so much of microbes in initiation of inflammatory response by the body has been suspected. Luminal floor of longitudinal reduce section reveals section of thickened wall with slender lumen which is best appreciated in cross-section (arrow) whereas intervening areas of the bowel are uninvolved or skipped. The histological features present are: transmural continual inflammatory cell infiltration, deep fissures into the bowel wall, submucosal widening due to oedema, some distinguished lymphoid follicles and a few non-caseating epithelioid cell granulomas within the bowel wall. In extra continual cases, fibrosis turns into increasingly distinguished in all the layers disrupting muscular layer. The look of colon might vary depending upon the stage and intensity of the disease due to remissions and exacerbations. Mucosa reveals linear and superficial ulcers, normally not penetrating the muscular layer. Crypt distortion, cryptitis and focal accumulations of neutrophils forming crypt abscesses. These may be inner fistulae between the loops of the intestine, or external fistulae corresponding to enterocutaneous, rectal and anal fistulae. Toxic megacolon (Fulminant colitis) is the acute fulminating colitis in which the affected colon is thin-walled and dilated and is prone to perforation and faecal peritonitis. There is deep penetration of the inflammatory cell infiltrate into muscle layer which is disrupted. Pathogenetically talking, these microorganisms may cause enterocolitis by 2 mechanisms-by enteroinvasive bacteria producing ulcerative lesions, and by enterotoxin-producing bacteria leading to non-ulcerative lesions. Subsequently, the mesenteric lymph nodes are affected which show typical tuberculous granulomatous inflammatory reaction with caseation necrosis. In advanced cases, transverse fibrous strictures and intestinal obstruction are seen. Mucosa and submucosa present ulceration and the muscularis could additionally be changed by variable diploma of fibrosis. Grossly, the terminal ileum, caecum and/or ascending colon are thick-walled with mucosal ulceration. But now-a-days as a result of management of tuberculosis in cattle and pasteurisation of milk, just about all circumstances of intestinal tuberculosis are brought on by M. Enteric Fever the term enteric fever is used to describe acute an infection caused by Salmonella typhi (typhoid fever) or Salmonella paratyphi (paratyphoid fever). The margins of the ulcers are barely raised because of inflammatory oedema and mobile proliferation. The primary complications of the intestinal lesions of typhoid are perforation of the ulcers and haemorrhage. The sickness outcomes from both bacterial invasion or bacterial toxigenic impact on the bowel. Staphylococcal meals poisoning Staphylococcus aureus infection acquired from contaminated food produces either gentle food poisoning by enterotoxins, or could cause extra severe form of the illness called pseudomembranous enterocolitis described under. Staphylococcal meals poisoning occurs because of liberation of enterotoxins by the bacteria. Clostridial meals poisoning Infection with anaerobic organisms Clostridium welchii, following consumption of contaminated meat leads to acute food poisoning (page 172). Botulism this could be a severe form of paralysing sickness brought on by ingestion of organism, Clostridium botulinum, which produces neurotoxin. Salmonella food poisoning (Salmonellosis) this is an an infection (and not caused by toxins) occurring as a result of food contaminated by S. Infection happens by faeco-oral route and is seen with poor private hygiene, in densely populated areas, and with contaminated meals and water. It is more prevalent in the tropical countries and primarily impacts the large gut. Here, they invade the epithelium of the mucosa, attain the submucosa and produce the characteristic flask-shaped ulcers (page 178). In advanced cases, typical flask-shaped ulcers having slender neck and broad base are seen. Complications of intestinal amoebic ulcers are: amoebic liver abscess or amoebic hepatitis, perforation, haemorrhage and formation of amoeboma which is a tumour-like mass. Intestinal tuberculosis can occur as major, secondary or hyperplastic ileocaecal kind. In a classic case, there are multiple tranverse ulcers and strictures inflicting intestinal obstruction. There are oval ulcers alongside the lengthy axis of the small intestine and may be difficult by perforation.
Ayegreen (Houseleek). Colchis. - Are there safety concerns?
- What is Houseleek?
- Severe diarrhea; ulcers in the mouth; burns; skin ulcers; warts; itchy, burning skin; and swelling from insect bites.
- How does Houseleek work?
- Dosing considerations for Houseleek.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96518
Order colchis 0.5 mg lineRoutine administration of vitamin K to all newly born infants has led to disappearance of neonatal vitamin K deficiency antimicrobial kerlix cheap 0.5 mg colchis with visa. Complications of remedy: i) Following huge transfusion resulting in antibiotic resistance explained simply cheap 0.5mg colchis fast delivery dilution of platelets and coagulation components antibiotic 825 purchase colchis 0.5mg free shipping. However virus your current security settings order 0.5 mg colchis with visa, unchecked and excessive fibrinolysis could generally be the reason for bleeding. Pathogenesis Although in every case, a definite triggering mechanism has been identified, the sequence of events, in general, could be summarised as beneath. Thrombotic part Endothelial damage from the assorted thrombogenic stimuli causes generalised platelet aggregation and adhesion with resultant deposition of small thrombi and emboli throughout the microvasculature. Consumption part the early thrombotic phase is followed by a phase of consumption of coagulation factors and platelets. Secondary fibrinolysis As a protecting mechanism, fibrinolytic system is secondarily activated at the web site of intravascular coagulation. Plasma fibrinogen ranges are lowered as a end result of consumption in microvascular coagulation. A summary of important laboratory findings in widespread causes of haemostatic abnormalities is summed up in Table 11. The term blood group is utilized to any well-defined system of red blood cell antigens that are inherited traits. Over 20 blood group techniques having roughly 400 blood group antigens are presently recognised. One set of three genes is inherited from each mother or father giving rise to varied complicated combos. The corresponding antigens are similarly named Cc, Ee and solely D since no d antigen exists. Transfusion reactions are usually categorised into 2 sorts: immune and non-immune. Immunologic transfusion reactions could additionally be against red blood cells (haemolytic reactions), leucocytes, platelets or immunoglobulins. Haemolytic transfusion reactions Haemolytic transfusion response may be quick or delayed, intravascular or extravascular. The scientific manifestations are relatively less severe and normally include malaise and fever but shock and renal failure may not often occur. Such delayed reactions are usually the outcomes of previous transfusion or being pregnant (anamnestic reaction). These leucocytes then combination in pulmonary micromutation and launch mediators of increased vascular permeability leading to acute pulmonary oedema and indicators and signs of respiratory failure. Other allergic reactions Besides haemolytic transfusion response, different reactions are as follows: i) Febrile reaction which is normally attributed to immunologic response towards white blood cells, platelets, or IgA class immunoglobulins. Nonimmune Transfusion Reactions this class contains the following opposed results: 1. The danger of circulatory overload is particularly high in sufferers with continual anaemia, and in infants and the aged. Massive transfusion When the quantity of stored blood transfused to bleeding sufferers exceeds their normal blood quantity, it ends in dilutional thrombocytopenia and dilution of coagulation factors. The incidence increases in patients who obtain multiple transfusions corresponding to instances of haemophilia, thalassaemia main, acute leukaemias, acute extreme haemorrhage and so forth. Optimally, platelet transfusions may be given to a patient with platelet depend below 10,000/�l. The serum of an individual contains naturallyoccurring antibodies to A and/or B antigen. There are two primary capabilities of the lymph node-to mount immune response within the physique, and to carry out the operate of active phagocytosis for particulate materials. Peripheral blood B and T lymphocytes on coming into the lymph node are stimulated immunologically which transforms them to undergo cytoplasmic and nuclear maturation which can be within the follicular centre or paracortex as per following sequence and schematically depicted in. Thus, relationship of haematopoietic tissues and lymphoreticular tissues is sort of close. Thus, in current occasions, ailments of leucocytes are studied along with illnesses of lymphoreticular tissues of the physique. Microscopically, the sinusoids are congested, broadly dilated and oedematous and include numerous neutrophils. These are: follicular hyperplasia, paracortical hyperplasia and sinus histiocytosis. After management of infection, majority of circumstances heal completely without leaving any scar. Paracortical lymphoid hyperplasia this is due to hyperplasia of T-cell-dependent space of the lymph node. The condition happens in elderly sufferers with generalised lymph node enlargement and hypergammaglobulinaemia. Dermatopathic lymphadenopathy happens in lymph node draining an space of pores and skin lesion. Sinus histiocytosis or sinus hyperplasia this may be a very common kind found in regional lymph nodes draining inflammatory lesions, or as an immune reaction of the host to a draining malignant tumour or its products. It is associated with characteristic scientific options of painless but large lymphadenopathy with fever and leucocytosis and often runs a benign and self-limiting course. The kinetics of monocytes is less well understood than that of other myeloid cells. The extravascular lifespan of tissue macrophages that are the transformed form of blood monocytes, could vary from a few months to a few years. The granulocytes, in accordance with the looks of nuclei, are subdivided into polymorphonuclear leucocytes and monocytes. Further, relying upon the color and content of granules, polymorphonuclear leucocytes are of 3 sorts: neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils. The myeloblast varies considerably in size (10-18 �m in diameter), having a big spherical to oval nucleus practically filling the cell, has nice nuclear chromatin and accommodates 2-5 well-defined pale nucleoli. It possesses a round to oval nucleus, having nice nuclear chromatin which is barely condensed around the nuclear membrane. The nucleoli are present but are less prominent and fewer than these in the myeloblast. The main distinction of promyelocyte from myeloblast is within the cytoplasm which contains azurophilic (primary or non-specific) granules. Primary granules additionally persist at this stage however formation of new main granules stops. The nucleus of myelocyte is eccentric, round to oval, having somewhat coarse nuclear chromatin and no visible nucleoli. The myeloid cells as a lot as the myelocyte stage proceed to divide and, due to this fact, are included in mitotic or proliferative pool. In people, the bone marrow and the thymus are the first lymphopoietic organs where lymphoid stem cells bear spontaneous division impartial of antigenic stimulation. After antigenic activation, B cells proliferate and mature into plasma cells which secrete particular immunoglobulin antibodies.
Order colchis 0.5 mg on lineThis method of drainage allows monitoring for rejection by measurement of urinary amylase and likewise avoids enterotomy-associated risks of infection and leakage infection en la sangre buy 0.5 mg colchis with mastercard. Cystoscopic biopsy via the duodenal cuff is utilized in bladder-drained transplants antimicrobial dressings for wounds cheap colchis 0.5 mg mastercard. With improved surgical strategies infection in stomach 0.5 mg colchis with amex, elevated use of real-time ultrasound antibiotics for dogs petsmart order 0.5 mg colchis overnight delivery, and percutaneous needle biopsy, the outcomes of enteric drainage now match those of bladder drainage. Risk factors for urinary tract infection after pancreas transplantation embody giant bladder capacity, incomplete bladder emptying, excessive bladder urine pH (from pancreatic bicarbonate), bladder and urethral mucosal irritation from activated pancreatic enzymes with the loss of mucosal barrier, extended bladder catheterization, and immunosuppression. Managing Voiding Dysfunction in Bladder-Drained Pancreas Transplants Voiding dysfunction Negative Determine postvoid residual quantity Positive Begin antimicrobial treatment Urine culture If >200 ml Treat with urethral (Foley) catheter or long-term intermittent catheterization If <200 ml Suspect urethritis dysuria syndrome Urodynamics Urinary reflux pancreatitis, which causes pancreas graft dysfunction, could also be related to perigraft stomach pain and fever. It is commonly a result of poor bladder perform and requires drainage with a bladder catheter for 5 to 7 days and assessment of bladder dysfunction. A urethritis dysuria syndrome happens in 2% to 8% of pancreas recipients with bladder drainage and is attributable to uroepithelial exposure to the activated pancreatic proenzymes trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, and procarboxypeptidase. Pancreatic exocrine secretions consist of bicarbonate, amylase, lipase, and proenzymes, which are activated by the enterokinase within the graft duodenal brush border. Increased intravesical enzyme activation occurs with lowgrade urinary infections and urinary stasis, and sufferers will develop voiding ache or penile, glandular, meatal, or vulval ulceration. Enzyme activation may be minimized by therapy of low-count bacteriuria, increase in fluid intake, and frequent voiding. Retrograde urethrography Detrusor dysfunction or bladder outlet obstruction Urethral stricture or disruption Enteric Conversion Treat with urethral (Foley) catheter Treat with -adrenoceptor blockers or transurethral resection of the bladder neck (males) Enteric conversion is an choice for many of the continual urologic issues associated with bladder-drained pancreas transplantation. The indications are urethral disruption, recurrent urine leak, persistent bleeding, chronic urinary tract an infection, dysuria, recurrent hypovolemia, and metabolic acidosis. It is right to wait until 6 to 12 months after transplantation, when attainable, to enable monitoring of urine amylase for early rejection episodes. There could be an acute presentation of graft rejection, not different from that seen in early graft dysfunction. Hyperglycemia secondary to rejection is a late occasion and signifies irreversible graft harm. Patients remain vulnerable to retinal detachment due to scarring secondary to previous retinal injury. Sensory and motor nerve conduction velocities enhance rapidly after pancreas transplantation and then stabilize. Early diabetic nephropathy is characterized by increased glomerular basement membrane thickness and a rise in mesangial quantity. Wellfunctioning pancreas transplants lead to normal fasting blood glucose concentrations, normal glycated hemoglobin ranges, and solely barely irregular oral glucose tolerance testing results. They are associated with high-carbohydrate meals, extreme intake of caffeine or alcohol, extreme train, and, in some sufferers with hypoglycemia, circulating anti-insulin antibodies. A major good factor about pancreas transplantation is restoration of glucagon secretory responses to hypoglycemia. In sort 1 diabetics, the absence of useful beta cells throughout the islet eliminates the normal physiologic response by which intra-islet insulin tonically dampens secretion of glucagon from alpha cells. After pancreas transplantation, hypoglycemic consciousness returns, in addition to partial return of faulty epinephrine secretion throughout insulin-induced hypoglycemia. Nephropathy Hyperglycemia Post-transplantation hyperglycemia may be caused by pancreas graft dysfunction, insufficient insulin launch secondary to excessive tacrolimus or occasionally cyclosporine ranges, resistance to insulin secondary to corticosteroids, weight gain, and insufficient physical exercise. Although the use of tacrolimus has reduced pancreas graft rejection, it also decreases insulin gene transcription. If laboratory and imaging evaluations (see Table 110-1) are regular, hyperglycemia is the outcome of decreased insulin manufacturing or else of peripheral insulin resistance, which can be identified by measurement of glucose usage rates and glucose/arginine-potentiated insulin secretion. In the absence of graft rejection, post-transplantation hyperglycemia ought to first be managed by dietary intervention and train. Insulin may be needed initially however can typically be discontinued as oral hypoglycemic agents Vascular Disease Successful kidney-pancreas transplantation leads to a big enchancment within the management of hypertension in contrast with kidney transplant alone in kind 1 diabetics. The first sequence of islet allotransplantations in sort 1 diabetic patients have been reported in 1977. Pretransplantation debilities (decreased vision, neuropathy, muscle weakness, orthostatic symptoms) could be exacerbated by the surgery and immunosuppressive drugs. The new child outcomes had been prematurity (39 of 50), low start weight (32 of 50), other neonatal issues (28 of 50), and neonatal dying (1 of 50). Ten patients had rejections that resulted in grafts loss, and 58% of the patients required cesarean section. Hypertension, prematurity, preeclampsia, and growth retardation incessantly difficult the pregnancies, even with good renal operate. Consensus opinion is that pregnancy is secure by 1 yr after transplantation under the next conditions: no rejection has occurred in the past 12 months, graft function is stable, no lively infections that might have a adverse influence on the fetus. The common gestational period is 35 � 2 weeks; the average birth weight is 2150 � 680 g. However, there could probably be destabilization of the transplanted kidney and likewise islet dysfunction as a end result of most kidney transplant immunosuppression protocols included corticosteroids. Nevertheless, there were useful results from improved glycemic management on both survival and function of transplanted kidneys. The causes for this failure fee may embrace subtherapeutic islet implant mass, high rate of engraftment failure, islet damage in the liver (the site of implantation) by direct native poisonous results of the immunosuppressants, ineffective immunosuppression that fails to forestall rejection, recurrent autoimmune diabetes, and islet practical exhaustion. Early immunosuppressive regimens were relatively ineffective in preventing allograft rejection compared with their impact on vascularized pancreas grafts. Most if not all immunosuppressive brokers have been related to impaired beta cell operate and lowered graft revascularization. Overall achievement of insulin independence was 65% within the first yr after islet infusion (with or without reinfusion), and by yr 2 this fee increased to 75%. More success with insulin independence was reported in nonuremic kind 1 diabetics transplanted with an average of 800,000 islets by use of the Edmonton protocol, a corticosteroid-free immunosuppression regimen of daclizumab, sirolimus, and low-dose tacrolimus. The disrupted exocrine and endocrine components are purified by centrifugation (4), and the islet preparation free from exocrine components is transplanted by intrahepatic portal vein infusion (5). Effective mechanical and physical strategies to seal the catheter monitor cut back the risk of postprocedural bleeding. Although earlier stories point out that the two-layer technique for pancreas preservation improves islet isolation outcome, our latest information present no useful effect of the two-layer method on islet isolation and transplantation outcomes. Mouth ulcers happen in 90% of sufferers and usually reply to simple antiseptic measures or topical triamcinolone ointment along with a reduction in the dose of sirolimus. Forty-three % of recipients complained of edema, extreme enough in 12% to necessitate a change in the immunosuppressive regimen. In a current analysis, 82% of 118 islet recipients in three North American centers had been insulin free at 1 yr.
Buy cheap colchis 0.5mg lineValues are lowered in acute and continual diffuse liver diseases and in malnutrition antibiotics xanax discount colchis 0.5mg. Both these exams are done after analysis of signs of obstruction since these exams are contraindicated in cholestasis antibiotic resistance jobs order colchis 0.5mg. Blood tests for manufacture of proteins antibiotic resistance future purchase 0.5 mg colchis with visa, lipids and carbohydrates are routinely done antibiotic resistance executive order buy colchis 0.5 mg visa. Bilirubin pigment has high affinity for elastic tissue and hence jaundice is especially noticeable in tissues rich in elastin content material. Jaundice turns into clinically evident when the whole serum bilirubin exceeds 2 mg/dl. A rise of serum bilirubin between the traditional and a couple of mg/dl is generally not accompanied by seen jaundice and is known as latent jaundice. Conjugated bilirubin is certain to albumin in two types: reversible and irreversible. Besides, it additionally happens in poisoning with chloroform, carbon tetrachloride and certain medication. However, hyperbilirubinaemia due to first three mechanisms is especially unconjugated whereas the final selection yields primarily conjugated hyperbilirubinaemia. Hence, presently pathophysiologic classification of jaundice is based on predominance of the kind of hyperbilirubinaemia. The presence of bilirubin in the urine is evidence of conjugated hyperbilirubinaemia. Extrahepatic cholestasis (Extrahepatic biliary obstruction) Mechanical obstruction. Predominantly Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinaemia this type of jaundice may result from the next three sets of circumstances: 1. In premature infants, the liver is poor in enzyme necessary for conjugation while the rate of red cell destruction is excessive. This results in icterus neonatorum which is especially extreme in haemolytic illness of the newborn due to maternal isoantibodies (page 319). The defect in excretion may be inside the biliary canaliculi of the hepatocyte and within the microscopic bile ducts (intrahepatic cholestasis or medical jaundice), or there may be mechanical obstruction to the extrahepatic biliary excretory equipment (extrahepatic cholestasis or obstructive jaundice). The features of intrahepatic cholestasis include: predominant conjugated hyperbilirubinaemia due to regurgitation of conjugated bilirubin into blood, bilirubinuria, elevated ranges of serum bile acids and consequent pruritus, elevated serum alkaline phosphatase, hyperlipidaemia and hypoprothrombinaemia. Liver biopsy in circumstances with intrahepatic cholestasis reveals milder diploma of cholestasis than the extrahepatic problems. Canalicular bile stasis ultimately causes proliferation of intralobular ductules adopted by periportal fibrosis and produces a picture resembling biliary cirrhosis (page 609). The widespread causes are gallstones, inflammatory strictures, carcinoma head of pancreas, tumours of bile duct, sclerosing cholangitis and congenital atresia of extrahepatic ducts. Prolonged prothrombin time in such circumstances exhibits improvement following parenteral administration of vitamin K, whereas hypoprothrombinaemia as a outcome of hepatocellular disease exhibits no such enchancment in prothrombin time with vitamin K administration. Liver biopsy in cases with extrahepatic cholestasis exhibits more marked modifications of cholestasis. This ends in dilatation of bile ducts and rupture of canaliculi with extravasation of bile producing bile lakes. Stasis of bile predisposes to ascending bacterial infections with accumulation of polymorphs across the dilated ducts (ascending cholangitis). It is as a outcome of of rise in bilirubin degree within the blood (hyperbilirubinaemia) above regular (0. All types of liver cell harm lead to necrosis of liver cells within the hepatic lobule which can be diffuse (submassive to massive), zonal and focal. The features widespread to all these circumstances are presence of icterus but virtually regular liver function exams and no well-defined morphologic modifications except in Dubin-Johnson syndrome. Some of these situations are thought-about under, while others are mentioned elsewhere within the relevant sections. Crigler-Najjar Syndrome Crigler-Najjar syndrome is a rare type of familial non-haemolytic jaundice with very excessive unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia. Type I Crigler-Najjar syndrome this is inherited as an autosomal recessive disorder. Dubin-Johnson Syndrome Dubin-Johnson syndrome is autosomal recessive dysfunction characterised by predominant conjugated hyperbilirubinaemia (usually less than 5 mg/dl) with genetic defect in canalicular excretion of conjugated bilirubin. Cholestasis in small proliferated ductules in the portal tract and between necrotic liver cells. The situation could, subsequently, have varied grades of destruction starting from complete absence of bile ducts termed atresia, to discount in their number called paucity of bile ducts. Extrahepatic Biliary Atresia the extrahepatic bile ducts fail to develop usually so that in some cases the bile ducts are absent at delivery, while in others the ducts may have been fashioned but begin present process sclerosis within the perinatal period. The baby has extreme pruritus, pale stools, darkish urine and elevated serum transaminases. Death is usually as a outcome of intercurrent infection, liver failure, and bleeding as a end result of vitamin K deficiency or oesophageal varices. Histologically, the condition should be distinguished from idiopathic neonatal hepatitis as surgical remedy is possible in extrahepatic biliary atresia however not within the latter. Besides, -1-antitrypsin deficiency also produces related look in liver biopsy. Transformation of hepatic parenchyma to neonatal (giant cell) hepatitis in 15% of circumstances. The situation most likely has its origin in viral infection acquired during intrauterine period or in the neonatal period. In some cases, intrahepatic biliary atresia is related to -1-antitrypsin deficiency. Viral an infection could act singly, but extra typically its impact is modified by sure exogenous components corresponding to by administration of salicylates, aflatoxins and insecticides. These results trigger mitochondrial damage and decreased exercise of mitochondrial enzymes in the liver. Within a week after a viral sickness, the kid develops intractable vomiting and progressive neurological deterioration as a outcome of encephalopathy, eventually leading to stupor, coma and dying. Characteristic laboratory findings are elevated blood ammonia, serum transaminases, bilirubin and prolonged prothrombin time. Neonatal hepatitis or big cell hepatitis is morphologic change seen in conjugated hyperbilirubinaemia as a outcome of identified infectious and metabolic causes. The major manifestations are briefly mentioned below and diagrammatically illustrated in. Hepatic encephalopathy (Hepatic coma) Neuropsychiatric syndrome might complicate liver illness of both acute and persistent sorts. Hyperkinetic circulation All forms of hepatic failure are related to a hyperkinetic circulation characterised by peripheral vasodilatation, increased splanchnic blood move and increased cardiac output. These adjustments end in tachycardia, low blood stress and decreased renal operate. The acute renal failure is often associated with oliguria and uraemia however with good tubular operate.
0.5 mg colchis for saleTumour grossly limited to the true pelvis with adverse nodes however with microscopic seeding of abdominal peritoneal surfaces antimicrobial proteins buy colchis 0.5 mg with mastercard. Diseases associated to being pregnant and placenta are quite a few and type the topic matter of discussion in obstetrics antibiotic blue pill discount colchis 0.5mg overnight delivery. Certain conditions corresponding to inflammation of the placenta and chorionic membranes (placentitis and chorioamnionitis) antibiotics hallucinations buy cheap colchis 0.5 mg, placental gross abnormalities antibiotic drugs list purchase colchis 0.5mg with mastercard. For unknown causes, frequency of hydatidiform mole varies in several regions of the world; the incidence in Asia and Central America is about 10 times larger than in the United States. The foetal portion of the placenta is composed of quite a few functional items referred to as chorionic villi and comprise the main a half of placenta at term. The villous core is covered by an inside layer of cytotrophoblast and outer layer of syncytiotrophoblast. Approximately 50% of cases occur following hydatidiform mole, 25% following spontaneous abortion, 20% after an in any other case regular pregnancy, and 5% develop in an ectopic being pregnant. It may be non-invasive or invasive, the former being full (classic) or partial mole. Gestational choriocarcinoma is a highly malignant and extensively metastasising tumour of trophoblast however responds higher to chemotherapy compared from gonadal choriocarcinoma. On per vaginum and speculum examination, the cervix is ulcerated and bleeds on touch. The whole ductallobular epithelial system has bilayered lining: the internal epithelium with secretory and absorptive function, and an outer supporting myoepithelial lining, each having characteristic ultrastructure and immunoreactivity. In a fullydeveloped nonlactating female breast, the epithelial part comprises lower than 10% of the total quantity however is extra important pathologically since majority of lesions pertain to this portion of the breast. Each lobe consists of breast lobules which drain their secretions via its accumulating duct system and opens into the nipple via its personal primary excretory duct, lactiferous duct. However, there are a couple of inflammatory lesions, benign tumours and tumourlike lesions which can be confused clinically with breast most cancers. These are associated with periductal and interstitial chronic inflammatory modifications. The etiology of the situation stays unknown however it seems to start with peri ductal irritation followed by destruction of the elastic tissue to cause ectasia and periductal fibrosis. Silicone breast implants implanted on breast most cancers patients after mastectomy or as breast augmentation cosmetic surgical procedure may rupture or silicone might slowly leak into encompass ing breast tissue. Eventually, a surrounding fibrous capsule varieties and after an extended interval it could even be calcified. Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis is an unusual type of reaction round lobules and ducts within the absence of any known etiology. The usual massive cyst is rounded, translucent with bluish color prior to opening (bluedome cyst). B, Non-proliferative fibrocystic changes-fibrosis, cyst formation, adenosis and apocrine metaplasia. Of all of the ductal hyperplasias, atypical ductal hyper plasia is extra ominous and has to be distinguished from intraductal carcinoma (page 752). The proliferated epithelial cells in the atypical ductal hyperplasia partially fill the duct lumen and produce irregular microglandular areas or cribriform pattern. Atypical lobular hyperplasia is carefully related to lobular carcinoma in situ (page 752) but differs from the latter in having cytologically atypical cells only in half of the ductules or acini. Grossly, the lesion may be coexistent with other parts of fibrocystic illness, or might type an isolated mass which has onerous cartilagelike consistency, resembling an infiltrating carcinoma. Such excessive oestrogenic activity in males is seen in young boys between 13 and 17 years of age (pubertal gynaecomastia), in men over 50 years (senescent gynaecomastia), in endocrine ailments associated with increased oestrogenic or decreased androgenic activity. Proliferative fibrocystic changes (atypical hyperplasia) carries four to 5 times elevated risk to develop invasive breast cancer later. Among the necessary benign breast tumours are fibroadenoma, phyllodes tumour (cystosarcoma phyllodes) and intraductal papilloma. Carcinoma of the breast is an important malignant tumour which occurs as noninvasive (carcinoma in situ) and invasive most cancers with its numerous morphologic varieties. The reduce floor is firm, greywhite, barely myxoid and should present slitlike spaces fashioned by compressed ducts. Pericanalicular sample is characterised by encircling plenty of fibrous stroma around the patent or dilated ducts. Occasionally, the fibrous tissue factor within the tumour is scanty, and the tumour is as an alternative predominantly composed of closelypacked ductular or acinar proliferation and is termed tubular adenoma. The minimize floor is greywhite with cystic cavities, areas of haemorrhages, necrosis and degenerative changes. Thus, phyllodes tumour resembles fibroadenoma aside from marked stromal overgrowth. The histologic criteria thought of to distinguish benign, borderline and malignant categories of phyllodes tumour are based mostly on following cellular features of stroma: i) frequency of mitoses; ii) cellular atypia; iii) cellularity; and iv) infiltrative margins. Menstrual and obstetric history Total length of mens trual life is instantly associated to increased risk. Histologically, an intraductal papilloma is characterised by a quantity of papillae having welldeveloped fibrovascular stalks attached to the ductal wall and coated by benign cuboidal epithelial cells supported by myoepithelial cells. However, there was some decline in mortality from the breast most cancers in recent times in developed countries due to both early diagnosis and trendy remedy. The incidence of breast most cancers is highest within the perimenopausal age group and is rare earlier than the age of 25 years. Clinically, the breast cancer usually presents as a solitary, painless, palpable lump which is detected quite often by self examination. Thus, all breast lumps, no matter the age of the affected person must be eliminated surgically. Additional strategies such as stereotactic biopsy and frozen section are immensely priceless to the surgeon for immediate pathological analysis in doubtful cases. Carcinoma of the breast arises from the ductal epithelium in 90% cases whereas the remaining 10% originate from the lobular epithelium. On reduce part, the involved space exhibits cystically dilated ducts containing cheesy necrotic material (in comedo pattern), or the intraductal tumour may be polypoid and friable resembling intraductal papilloma (in papillary pattern). Histologically, the proliferating tumour cells within the ductal lumina may have four types of patterns in numerous combinations: strong, comedo, papillary and cribriform. They are discovered extra frequently in the left breast, often within the upper outer quadrant. Retraction of the nipple and attachment of the tumour to underlying chest wall could also be present. The sectioned surface of the tumour is greywhite to yellowish with chalky streaks and often extends irregularly into the surrounding fat. Infiltrating (Invasive) Lobular Carcinoma Invasive lobular carcinoma includes about 10% of all breast cancers. Infiltrating cells could also be organized concentrically around ducts in a targetlike pattern. Medullary Carcinoma Medullary carcinoma is a variant of ductal carcinoma and comprises about 2% of all breast cancers. Histologically, colloid carcinoma incorporates large amount of extracellular epithelial mucin and acini filled with mucin.

Buy 0.5mg colchis free shippingHomozygous loss of p53 gene permits genetically damaged and unrepaired cells to survive and proliferate resulting in malignant transformation virus 912 for sale 0.5mg colchis with amex. Inherited breast cancer constitutes about 5-10% cases antimicrobial gauze pads order 0.5mg colchis with visa, it tends to happen at a comparatively youthful age and more usually tends to be bilateral antibiotics used for sinus infection colchis 0.5 mg for sale. The contrasting features of growth-promoting oncogenes and growth-suppressing anti-oncogenes are summarised in Table 7 5 infection control procedures buy colchis 0.5 mg online. In cancer cells, the operate of apoptosis is interfered due to mutations in the above genes which regulate apoptosis within the regular cell. However, it has been seen that after repetitive mitosis for a maximum of 60 to 70 times, telomeres are lost in regular cells and the cells cease to bear mitosis. Neovascularisation in the cancers not only supplies the tumour with oxygen and vitamins, but the newly shaped endothelial cells also elaborate a few growth components for progression of main as well as metastatic most cancers. In terms of molecular biology, this attribute of cancer is due to the truth that with passage of time most cancers cells acquire increasingly heterogeneity. Cancer-A Sequential Multistep Molecular Phenomenon: Multistep Theory It needs to be appreciated that most cancers occurs following a number of sequential steps of abnormalities within the goal cell. The phenomena of mobile transformation by chemical carcinogens (as additionally different carcinogens) is a progressive course of involving three sequential phases. In some circumstances, the procarcinogen may be detoxified and rendered inactive metabolically. Besides these two, additional factors corresponding to age, intercourse and nutritional standing of the host also play some function in determining response of the individual to chemical carcinogen. A few examples are the occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma in circumstances of viral hepatitis, association of endometrial hyperplasia with endometrial carcinoma, effect of oestrogen in breast cancer. Promoters of carcinogenesis are substances such as phorbol esters, phenols, hormones, synthetic sweeteners and drugs like phenobarbital. Progression of Carcinogenesis Progression of cancer is the stage when mutated proliferated cell shows phenotypic options of malignancy. Initiator Carcinogens Chemical carcinogens which can provoke the method of neoplastic transformation are further categorised into 2 subgroups-direct-acting and indirect-acting carcinogens or procarcinogens. They are weakly carcinogenic and are implicated within the etiology of the lymphomas and leukaemias in human beings. It consists of the next four categories: i) Polycyclic fragrant hydrocarbons They comprise the largest group of frequent procarcinogens which, after metabolic activation, can induce neoplasia in lots of tissues in experimental animals and are also implicated in a quantity of human neoplasms. The following examples have evidence to support the etiologic role of those substances: a) Smoking and lung most cancers: There is 20 instances larger incidence of lung most cancers in people who smoke of 2 packs (40 cigarettes) per day for 20 years. Radiation, each ultraviolet light and ionising radiation, is an important physical agent. The role of radiation as carcinogenic agent is mentioned below while its non-neoplastic issues are described in Chapter three (page 16). Non-radiation physical agents are the varied forms of injury and are less necessary. Ultraviolet gentle and ionising radiation differ in their mode of motion as described beneath: 1. These sufferers have been found to have about twice larger incidence of malignant tumours and thus its use was discontinued. The effect relies upon upon numerous factors corresponding to kind of radiation, dose, dose-rate, frequency and varied host elements corresponding to age, particular person susceptibility, immune competence, hormonal influences and sort of cells irradiated. Bacteria Helicobacter pylori, a gram-positive spiralshaped micro-organism, colonises the gastric mucosa and has been present in cases of continual gastritis and peptic ulcer; its prolonged an infection could lead to gastric lymphoma and gastric carcinoma; this subject is discussed in detail in Chapter 18. Therefore, biologic carcinogenesis is basically viral carcinogenesis, described beneath. Viral Oncogenesis: General Aspects Support to the etiologic role of oncogenic viruses in causation of human cancers is based on the next: 1. In vitro assay of specific viral gene merchandise which produce effects on cell proliferation and survival. Thus, such virus-infected host cells after having undergone genetic adjustments enter cell cycle and produce next progeny of remodeled cells which have traits of autonomous development and survival finishing their position as oncogenic viruses. The provirus is built-in into the host cell genome producing `transformed host cell. Integration of viral genome into the host cell genome happens which requires essential presence of functional T-antigen. These are: Papovaviruses, Herpesviruses, Adenoviruses, Poxviruses and Hepadna viruses. These viruses appear to replicate in the layers of stratified squamous epithelium. The condition is characterised by a quantity of skin warts and a genetic defect within the cell-mediated immunity. About one-third of cases develop squamous cell carcinoma in the sun-exposed warts. Thus the brakes in cell proliferation are eliminated, permitting the uncontrolled proliferation. It can be shown to be causative for infectious mononucleosis, a self-limiting disease in humans. The tumour is prevalent in South-East Asia, especially in the Chinese, and in Eskimos. All the members of acute remodeling viruses found so far are faulty viruses by which the actual v-onc has substituted other important genetic material such as gag, pol and env. Slow reworking viruses trigger neoplastic transformation by insertional mutagenesis i. Another clinically significant aspect mentioned right here is the final prognosis of tumours. Certain cancers evoke vital lymphocytic infiltrate composed of immunocompetent cells and such tumours have considerably higher prognosis. For instance, rare spontaneous disappearance of malignant melanoma quickly from the primary site which may then reappear as metastasis. Existence of immune surveillance is substantiated by increased frequency of cancers in immunodeficient host Important groups of carcinogenic agents having position in carcinogenesis are chemical, physical and biologic agents. Chemical carcinogenesis happens by induction of mutation in the proto-oncogenes and anti-oncogenes and goes by way of sequential levels of initiation, promotion and development. Currently, varied teams of tumour antigens are as follows: i) Oncoproteins from mutated oncogenes Protein products derived from mutated oncogenes end in expression of cell floor antigens on tumour cells. However, regardless of the existence of immune mechanisms, many of the cancers outsmart these host defenses and achieve an upper hand in their battle against the host as a outcome of failed immune regulatory mechanisms. Activated macrophages mediate cytotoxicity by manufacturing of oxygen free radicals or by tumour necrosis factor. Some of the local effects of tumours are as under: i) Compression Many benign tumours pose only a cosmetic drawback.
References - Baxter RA. Histologic effects of ultrasound-assisted lipoplasty. Aesthet Surg J. 1999;19:109-14.
- Kunin CM: Detection, prevention and management of urinary tract infections, 4th ed, Philadelphia, 1987, Lea & Febiger. Kunin CM: The quantitative significance of bacteria visualized in the unstained urinary sediment, N Engl J Med 265:589n590, 1961.
- Cazorla O, Vassort G, Garnier D, et al: Length modulation of active force in rat cardiac myocytes: Is titin the sensor? J Mol Cell Cardiol 31:1215-1227, 1999.
- Picard JY, Cate RL, Racine C, et al: The persistent Mullerian duct syndrome: an update based upon a personal experience of 157 cases, Sex Dev 11(3):109n125, 2017.
- Aujard F, Herzog ED, Block GD. Circadian rhythms in firing rate of individual suprachiasmatic nucleus neurons from adult and middle aged mice. Neuroscience 2001;106:255-61.
- Green RC, Cupples LA, Kurz A, et al. Depression as a risk factor for Alzheimer disease: The MIRAGE study. Arch Neurol. 2003;60: 753-759.
- Hsi ED, Singleton TP, Swinnen L, Dunphy CH, Alkan S. Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue-type lymphomas occurring in post-transplantation patients. Am J Surg Pathol 2000; 24:100.
|


