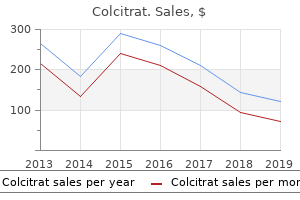
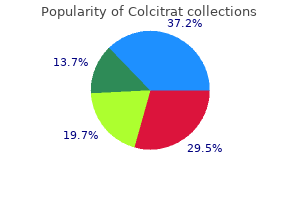
Colcitrat
Jennifer M. Kalish, M.D., Ph.D. - The Childrenĺs Hospital of Philadelphia
- Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Order 0.5mg colcitrat free shippingPepsin secretion is decreased according to the lower in gastric quantity although secretion of pepsin is mediated by acetylcholine antibiotics for dogs bacterial infections buy colcitrat 0.5mg otc. H2 receptors are also present in the uterus virus 64 order 0.5mg colcitrat amex, heart infection def generic colcitrat 0.5 mg without prescription, blood vessels virus 007 discount colcitrat 0.5 mg, ductus arteriosus and the lower oesophageal sphincter. H1 agonism causes contraction of gut clean muscle, whereas H2 agonism Cimetidine Cimetidine is an H2 antagonist with slight anti-androgenic effect that may trigger gynaecomastia and impotence. Peak impact is achieved 80 minutes after oral administration, and the terminal half-life is 2 hours. T lymphocytes have H2 receptors, and blockade of these could inhibit suppressor T-cell function, leading to enhanced immune system activity. This effect could additionally be dangerous in the presence of autoimmune circumstances or after organ transplantation. H2 receptors within the atria are responsible for atrial rhythmicity, and cimetidine might trigger bradyarrhythmias, particularly when given intravenously. The energetic form accumulates inside the parietal canaliculi near the luminal surface and binds to the target enzyme. Famotidine Famotidine is an H2 antagonist that could be intravenously administered twice daily. It reduces acid and pepsin content, reduces gastric volume, and is about 50 occasions stronger than cimetidine. It is excreted within the urine, having a half-life of three hours and a duration of action of 10 hours. Omeprazole the structure of omeprazole constitutes substituted benzimidazole and pyridine rings joined by a sulphoxide link. It is a prodrug, transformed inside the parietal cell to sulphenamide, the energetic type. It has a highly selective impact that will increase over several days to a plateau, most likely as a result of the lowered gastric acid reduces its degradation and increases bioavailability. Plasma distribution half-life is only three minutes, however gradual absorption and accumulation in the parietal cells ends in a protracted therapeutic effect. There is minimal crossing of the blood´┐Ż mind barrier but free crossing of the placenta. Untoward results are limited, although long-term use might end in hypergastrinaemia, thought to be of little consequence. Cytochrome P450 is inhibited, resulting in a chronic half-life of benzodiazepines and phenytoin in addition to other brokers sharing this elimination pathway. Pantoprazole, a second-generation agent, is just like omeprazole though it has greater bioavailability (75%). Gradual absorption and accumulation within the parietal cells results in a chronic therapeutic impact. Nizatidine Nizatidine is at present the H2 antagonist with the shortest half-life (1. Nizatidine also causes non-competitive inhibition of acetylcholinesterase similar to that attributable to neostigmine, and so possesses prokinetic exercise too. Peak impact happens one hundred minutes after oral administration and the terminal half-life is 2. It is metabolised in the liver and binds to cytochrome P450, causing inhibition, but this effect is just about onetenth that of cimetidine and thus rarely achieves medical significance. Prostaglandins Proton pump inhibitors Examples ´┐Ż esomeprazole, omeprazole, pantoprazole the proton pump inhibitors immediately have an result on the acidsecreting pump of the gastric parietal cells, and subsequently bypass the muscarinic, gastrin and H2 receptors. These agents are administered orally in buffered capsules to minimise the effects of gastric acid earlier than arrival at the website of motion. Natural prostaglandins are quickly eradicated, and synthetic analogues have due to this fact been developed. Antacids are given to alleviate signs of dyspepsia and reflux oesophagitis, or to neutralise acid preoperatively when a major danger of acid aspiration exists. In the anaesthetised patient the antacid may be aspirated and trigger damage, an element which influences antacid choice. The simplest antacids are those containing the next bases, both alone or in combination: magnesium carbonate, hydroxide or trisilicate; aluminium hydroxide or glycinate. Solubility and velocity of response are necessary in antacids appropriate for clinical use; sodium and potassium hydroxide are very soluble and are therefore very primary. These readily neutralise the acid, however any extra would render the abdomen contents alkaline, inflicting doubtlessly extra damage than gastric acid. A comparatively giant variety of molecules is required for a chemical impact compared with receptor-based pharmacological methods. Sodium bicarbonate is so readily absorbed that it may trigger iatrogenic non-respiratory alkalosis. Calcium compounds cause constipation, and magnesium compounds have a laxative effect. Such particles if aspirated may result in lung harm much like acid aspiration syndrome. It in all probability enhances mucous secretion from the gastric mucosa and so provides safety from the hydrochloric acid and pepsin in the stomach. Carbenoxolone has mineralocorticoid effects, and sufferers may develop sodium and water retention with hypertension, indicators of fluid overload and potassium depletion. Antispasmodics Antispasmodic agents mostly comprise muscarinic anticholinergic medicine, however embrace direct-acting easy muscle relaxants. Mucoprotective drugs Mucoprotective medication achieve their principal results either via cytoprotective exercise or by enhancing endogenous defence mechanisms. A mechanically protective barrier in opposition to acid harm to the gastric mucosa could also be shaped, and some agents stimulate endogenous secretion of mucus from the gastric mucosa. Anticholinergics Examples ´┐Ż atropine, dicycloverine, hyoscine, propantheline Muscarinic anticholinergic agents scale back acid secretion and cut back gastrointestinal tone, including decrease oesophageal sphincter tone. The dose required usefully to reduce gastric acid secretion causes numerous side effects related to inhibition of other muscarinic receptors. At decrease doses they perform as antispasmodics and are utilized in irritable bowel syndrome and diverticular disease. The muscarinic M1 receptors are present in parasympathetic ganglia supplying parietal gastric cells. The muscarinic receptors affecting the guts, eyes and bladder are primarily M2 receptors. Pirenzipine is a tricyclic antimuscarinic agent which inhibits oesophageal motility and reduces gastric volume and acidity. The discount of lower oesophageal sphincter stress brought on by pirenzipine renders the drug unsuitable in anaesthetic practice (no longer available). Chelates and complexes Examples ´┐Ż bismuth chelate, sucralfate Bismuth chelate the bismuth chelate tripotassium dicitratobismuthate promotes the healing of peptic ulcers. Its mechanism of action is unclear however may be associated to its binding to glycoproteins at the base of the ulcer. Sucralfate Sucralfate is a complex of sulphated sucrose and aluminium hydroxide that, though possessing little antacid activity, has a profound cytoprotective effect.
Enzymatic polychitosamine hydrolisat (Chitosan). Colcitrat. - Patients with kidney failure who are on chronic hemodialysis. When ingested by these patients, chitosan may reduce high cholesterol; improve anemia; and improve physical strength, appetite, and sleep.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Dosing considerations for Chitosan.
- What is Chitosan?
- How does Chitosan work?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- What other names is Chitosan known by?
- Treating periodontitis, a dental condition.
- Helping to remake tissue after plastic surgery.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96617
Colcitrat: 0.5 mg
Purchase colcitrat 0.5 mg otcThe nerve has three sensory nuclei antibiotic wound infection purchase colcitrat 0.5 mg on-line, spinal antibiotic 10 cheap 0.5mg colcitrat visa, mesencephalic and superior (in the pons) antibiotics for uti cause diarrhea buy discount colcitrat 0.5mg line, and one motor (also within the pons) infection 4 weeks after wisdom teeth removal purchase 0.5mg colcitrat with amex. It passes forward to the trigeminal ganglion, which is located on the petrous temporal bone. The three divisions, ophthalmic, maxillary and mandibular, emerge from the anterior border of the ganglion. Ophthalmic division: passes forward on the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus (below oculomotor and trochlear nerves) and divides into three branches: lacrimal, frontal and nasociliary. The branches of the nasociliary nerve are the anterior ethmoidal, posterior ethmoidal, infratrochlear and lengthy ciliary nerves. Maxillary division: runs along the inferior border of the cavernous sinus beneath the ophthalmic nerve and leaves the skull via the foramen rotundum. After traversing the pterygopalatine fossa the nerve is termed the infra orbital nerve and it emerges through the infra-orbital foramen to provide adjoining areas of the face. Fibres pass to the pterygopalatine ganglion and the maxillary nerve has the next branches: zygomatic, posterior superior alveolar and infra orbital which themselves branch into smaller nerves. It supplies motor fibres to the muscle tissue of facial expression, parasympathetic secretomotor fibres to the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands and style sensation from the anterior twothirds of the tongue. The fibres associated with taste pass to the geniculate ganglion and thence to the nucleus of the tractus solitarius, from which they then cross to the opposite lateral nucleus of the thalamus, ending within the sensory cortex. The secretomotor fibres come up in the superior salivary nucleus within the pons, near the motor nucleus. The nerve leaves the pons to run laterally at the aspect of the vestibulocochlear nerve though the internal auditory meatus to the facial ganglion, the place it takes a pointy posterior turn to pass downwards through the stylomastoid foramen. Just earlier than this level it gives off the chorda tympani, which later joins the lingual nerve to provide taste sensation to the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. After rising from the stylomastoid foramen the facial nerve is entirely motor and has the next branches: posterior auricular, digastric and stylohyoid. The nerve is shaped in the internal meatus and then passes medially to be part of the mind stem on the cerebromedullary angle. Efferent fibres cross to the opposite facet to kind the auditory striae in the flooring of the fourth ventricle, these from the ventral nucleus notably forming the trapezoid body in the pons. Fibres ascend from the trapezoid physique in the lateral lemniscus to attain the medial geniculate body, and thence to the auditory cortex. Vestibular fibres arising from the semicircular ducts, saccule and utricle pass to the vestibular ganglion in the inside meatus and in the end terminate in the vestibular nuclei within the floor of the fourth ventricle. The carotid department of the glossopharyngeal supplies the carotid physique and carotid sinus. The rostral a half of the nucleus ambiguus (strictly vagus) is the nucleus of the motor path to stylopharyngeus. The nerve passes through the jugular foramen and pierces the pharyngeal wall between superior and center constrictor muscular tissues. There are two main branches, the tympanic department and the carotid branch, which is of importance as it provides the carotid sinus and carotid physique. The third nucleus is the nucleus of the tractus solitarius, which is anxious with taste sensation. The vagus emerges from the medulla lateral to the olive as a gaggle of rootlets, then leaves the skull by way of the jugular foramen as a single trunk. At the level of the bottom of skull the vagus has two ganglia, the superior and inferior sensory ganglia. Below the inferior ganglion the vagus receives a communication from the accent nerve representing its cranial root. The nerve has two roots, a small cranial root travelling by means of the vagus and a larger spinal root from nuclei within the upper 5 cervical segments of the spinal cord. The nerve arises in the vertebral canal and ascends through the foramen magnum into the posterior cranial fossa. It leaves the cranium by means of the jugular foramen and passes anterior to the internal jugular vein into the body of sternomastoid. Subsequently the nerve crosses the posterior triangle of the neck to pierce trapezius. The nerve has its nucleus within the floor of the fourth ventricle and arises as a collection of rootlets which go away the medulla between pyramid and olive. The nerve passes downwards between the inner carotid artery and jugular vein to the level of the angle of the jaw, where it loops over the lingual artery earlier than reaching hyoglossus and genioglossus and terminating in direct motor innervation of the muscle tissue of the tongue. The hypoglossal nerve receives some fibres from the ventral ramus of C1 at the stage of the bottom of cranium. The majority of those fibres move into the descendens hypoglossi, which descends as a discrete branch, being joined by the descendens cervicalis (made up of fibres from C2 and C3) to type the ansa hypoglossi, which supplies omohyoid, sternothyroid and geniohyoid. Vagus (X) the vagus nerve is the longest and most widely distributed of the cranial nerves. It supplies motor innervation to the larynx, bronchial muscles, gastrointestinal tract and the center (through cardio-inhibitory fibres). Sensory supply is distributed to the dura mater, respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract and heart. The vagus also offers secretomotor innervation to the bronchial mucus glands and gastrointestinal tract. The dorsal nucleus of the vagus is a combined motor and sensory centre situated below the floor of the fourth ventricle. Five fused sacral segments kind the sacrum, and the coccyx has four fused segments. Special zones Thoracic inlet the thoracic inlet slopes downwards and forwards, making an angle of 60 to the horizontal. The form of the inlet is claimed to be kidney-shaped, due to the protrusion of the physique of T1 into what would in any other case be an oval. The thoracic inlet transmits the trachea, oesophagus, massive vascular trunks (brachiocephalic, left carotid and left subclavian arteries and brachiocephalic vein), vagi, thoracic duct, phrenic nerves and cervical sympathetic chain. The first rib has a rounded head with a side that articulates with the physique of T1, an extended neck and a tubercle that articulates with the transverse means of T1. The scalene tubercle on the medial border of the rib signifies the attachment of the scalenus anterior muscle. The intercostal muscular tissues are arranged as follows: the external intercostal muscle descends in an indirect manner forwards from the lower border of the rib above to the higher border of the rib below. The inside intercostal muscle is an incomplete sheet between the ribs and the pleura which attaches to the sternum, costal cartilages and ribs. The contents of the intercostal area are the elements of the neurovascular bundle. These (from high to bottom) are the posterior intercostal vein, the posterior intercostal artery and the intercostal nerve. Between the pleura and the neck of the rib lie the sympathetic trunk, the big department of the anterior primary ramus of T1 passing to the brachial plexus and the superior intercostal vessels. Abdominal wall Structure crucial muscle of the stomach wall is the rectus abdominus.
Cheap 0.5 mg colcitrat otcShould the direction of movement of the target be at right angles to the ultrasound beam antibiotic milk order colcitrat 0.5mg mastercard, relative movement in the path of or away from the probe is minimised and a poor Doppler signal outcomes antibiotics for uti not working generic colcitrat 0.5 mg free shipping. A traditional example typically quoted of the Doppler impact is the rise in tone of a practice whistle because it approaches a listener antibiotics for dogs for sale cheap 0.5 mg colcitrat visa, and its fall in tone because the train passes by and speeds away antibiotics nausea cure buy colcitrat 0.5 mg low price. Different forms of probe can be utilized, various in size, form of field and frequency range. A frequent probe utilized in nerve blocks or vascular entry is 28 mm extensive, producing a parallel-sided subject 1 mm thick. The depth of penetration can be adjusted relying on the machine and probe, but sometimes could vary from 2 to 6 cm. This could be visualised as a area with the approximate dimensions of a bank card. The usefulness of a B-mode scan will depend on its resolution of detail, the width of the sphere coated and the depth of penetration. The pulses of ultrasound produced will have a mark´┐Żspace ratio which, together with the ultrasound frequency (and wavelength), the design of the probe and the facility of the scanner, will determine the efficiency. The mark´┐Żspace ratio is the ratio of the time spent on the excessive amplitude (mark) to the time spent on the low amplitude (space) of the sign. There is usually a trade-off between increasing frequency to get hold of extra element within the Interpretation of B-mode scans When decoding a B-mode scan a information of the underlying anatomy is essential, and an consciousness of limitations and artefacts is helpful. Limitations and artefacts r B-scan display ´┐Ż only represents a thin twodimensional slice of tissue. Hence an injection needle will solely be visualised if it lies throughout the 1 mm thickness of the ultrasound area and crosses the direction of the beam. Application of a high-intensity exterior magnetic field causes all these microscopic magnetic dipoles to align with this external area. This characteristic frequency is dependent upon the construction of the nucleus and the magnitude of the magnetic area surrounding it. Oedematous tissues appear brighter towards regular tissues, and hence the appearance of pathological areas is often enhanced due to oedema. Abnormal collections of fluid can additionally be visualised more readily through the use of T2-weighted pictures. Relaxation is taken into account as consisting of two elements: r Relaxation of the transverse component, which is the decay of the precessional motion to zero. This course of is an exponential course of additionally contributed to by the lack of coherence or dephasing of the precessional spin of every nucleus. It is characterised by a time constant T2 (spin´┐Żspin time fixed: the time taken to lose 37% of its most displacement value). This is an inverse exponential process and characterised by a time constant T1 (spin´┐Żlattice time constant: the time taken to get well 63% of its unique equilibrium value). This magnetic subject is generated throughout the magnet (in a tunnel) but an outer or fringe subject exists which might cause interference with exterior apparatus or tools. It is essential that this magnetic area is free from inhomogeneities, which can impair the quality of the ultimate image. T1-weighted photographs often show good contrast between tissues with clear boundaries. T1 weighting can improve the distinction between grey and white matter in comparison with T2 weighting, because of the higher distinction in T1 values as in contrast with Magnetic area power Magnetic area energy is measured because the density of magnetic lines of pressure or magnetic flux density. Wavelengths of radio signals are hundreds of metres (>102 m), while those of radiation are within the order of 10-12 m or much less. Light is a kind of electromagnetic wave forming a narrow band of frequencies which may be outlined as these frequencies detectable by the human retina. These phenomena embrace the action of sunshine on photocells and photomultipliers, as applied in oximetry and spectrophotometry. In some machines the same set of coils may be used for receiving and transmitting. Transverse waves, gentle waves and lightweight rays A mild wave can be visualised as being analogous to a surface wave on water occurring when a stone is dropped into a pond. The surface wave is formed by water particles shifting up and down, and the form of a wave as it moves throughout the surface is called a wavefront. The wave strikes across the surface in a airplane at right angles to the particle movement. The course that waves journey in is often represented by a single straight line at proper angles to the aircraft of particle motion giving rise to the wave. The o lowest frequencies of visible gentle are darkish red, with wavelengths of round seven-hundred nm, whereas the highest frequencies visible are violet, with wavelengths of around four hundred nm. This worth is now used to give the definition for the standard unit of size, the metre. When mild passes from a dense medium to a much less dense medium, its path is deviated away from the normal. The refraction of the light could be quantified using two angles, the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r). The deviation produced is dependent on the ratio of the speeds of sunshine in air and glass (c1 and c2 respectively), which shall be a continuing. Refraction is also answerable for the actions of lenses, including that in the eye. In this case the angle of incidence (i) is always equal to the angle of reflection (r). Reflection is utilized in mirrors, and within the design of dish aerials or mirrors to focus mild or other waves. Total internal reflection When light passes from a dense medium to a less dense medium. This is used within the development of prisms to information gentle in optical tools, and also in the usage of optical fibres to conduct gentle in fibreoptic tools. This means that the particle movement giving rise to the wave is in a plane at right angles to the direction by which the wave is travelling. Frequently the particle motion happens in many alternative instructions inside the plane described. This type of light is claimed to be unpolarised, and it could be thought of to be a mixture of vertical and horizontal parts. Unpolarised gentle could also be filtered so that only mild with particle oscillation in a single course (vertical or horizontal) is allowed to cross. Luminous depth and the candela It is required generally to quantify the luminous depth or brightness of a supply. This could be defined by the quantity of light energy emitted per second (power) through unit strong angle (steradian) by the supply, and is measured in candelas. The candela is the luminous intensity of a source emitting light at 540 ´┐Ż 1012 Hz with an depth of 1/630 watt per steradian. Combining the above two legal guidelines provides: r the Lambert´┐ŻBeer legislation, which relates the transmitted light to each molar concentration and thickness of the solution layer by expressing the absorbance as: Absorbance = c d where is molar extinction coefficient c is molar concentration d is thickness Light transmission and absorbance (optical density) When gentle passes via a substance a number of the energy is absorbed. The absorption of light power is dependent on the size of the trail travelled and the absorptive properties of the substance.
0.5mg colcitrat amexIn persistent failure virus file scanner order colcitrat 0.5mg visa, blood pressure is often maintained best treatment for dogs fleas purchase colcitrat 0.5 mg fast delivery, but signs and signs due to can i get antibiotics for acne buy colcitrat 0.5mg without a prescription congestion develop antibiotics for acne doxycycline effective colcitrat 0.5 mg. Many of the physiological parameters and indices reflecting aspects of cardiac efficiency change in cardiac failure. The systemic circulation receives oxygenated blood from the left facet of the guts via the aorta and returns desaturated blood to the right facet of the guts in the venae cavae. The desaturated blood is delivered to the pulmonary circulation from the best ventricle by way of the pulmonary artery to be oxygenated and to exchange carbon dioxide. The composition of blood vessel partitions is mainly a mixture of elastic tissue, fibrous tissue and easy muscle. The aorta walls are predominantly elastic and fibrous tissue with little clean muscle, whereas the vena cava walls consist largely of clean muscle and fibrous parts. Structure and performance Blood vessel partitions are mainly structured in three layers. The adventitia is the outer layer and is made up of connective tissue with nerve fibres. The center layer or media is of varying thickness and accommodates primarily easy muscle. The innermost layer is the intima and consists of the endothelium, basement membrane and supporting connective Blood vessel diameter and wall thickness A main factor determining thickness is mean arterial stress. Blood vessel perform the arteries transport blood under excessive stress to the tissues, the place they divide into smaller arterioles, which Fundamentals of Anaesthesia, third version, ed. The management of regional perfusion depends on reflexes and autoregulation, which depend on arteriolar control. Pressure and move in the vascular system Flow and circulate velocity Function of the organ systems is dependent upon the amount of blood flowing per unit time via them, or the quantity circulate price. The total circulate by way of the systemic circulation or the lungs is equal to the cardiac output. Flow velocity defines how briskly fluid is shifting at any given point and has units of centimetres per second. In a blood vessel the circulate velocity of blood varies between the centre of the vessel and the vessel wall. There the exchange of fluid, vitamins, electrolytes and other substances between the interstitial fluid and the blood take place. The venules collect blood from the capillaries, and join together into veins to transport the blood back to the center. The flow (Q) is then associated to the mean flow velocity (v) by Q = vA this relationship may be utilized to the vascular system as a whole, since the quantity and diameter of any kind of blood vessel determines the total cross-sectional area offered to move at that stage in the vascular system. The larger the entire cross-sectional area of any given generation of vessels, the slower the speed of blood flow by way of those vessels. These flow velocities replicate the features of supply and distribution in the aorta and arteries, as opposed to perfusion and trade in the capillaries. In an individual vessel, if the cross-sectional space is reduced by a constriction such as a valve or an atheromatous plaque, the circulate velocity will increase by way of the constriction. Such will increase in circulate velocity can have an result on the characteristics of the blood circulate, making it turbulent and leading to an elevated tendency in direction of thrombus formation. This shear stress is elevated with increased move velocity, producing a drive that tends to pull endothelium and plaques away from the wall, leading to dissection or emboli. There are additional contributions of energy to circulate from skeletal muscle contraction and negative intrathoracic stress during inspiration. These mechanisms create a strain distinction across the vascular system that produces the total move (cardiac output) via the vascular system. The viscosity of the blood is a significant determinant of this part of resistance. The second element of opposing forces arises from the conversion of pump work into saved power. This happens when potential vitality is saved by the elasticity of distended vessel walls or by gravity as blood is pumped to a greater height within the body. If the pressure difference utilized throughout a vascular bed had been fixed the reactive component can be minimal. It may be applied to the systemic vascular circulation, the pulmonary circulation or a given visceral circulation. The forces opposing blood flow through a vascular system are composed of two major parts. This According to the Hagen´┐ŻPoiseuille legislation, which describes laminar flow in tubes, the circulate resistance, R, depends on the size of the tube and the viscosity of the fluid, however inversely related to the fourth energy of the radius. This is because of elevated pink cell aggregation and leucocyte adherence to vessel walls at low move velocities. Blood viscosity the rheological properties of blood describe its flowresistive properties. In a Newtonian fluid these resistive properties are depending on a relentless, the coefficient of viscosity. Blood, nevertheless, is a suspension of cells, and although the viscosity may be determined to give an apparent worth, this worth varies considerably with blood composition and flow conditions. The elements causing this variation in obvious viscosity embrace: r Haematocrit ´┐Ż an increase in haematocrit to zero. At normal haematocrit the in vivo blood Arterial system the main perform of the arterial system is to distribute and deliver blood to the capillary beds all through the peripheral vascular system. A secondary arterial operate is to convert the high-pressure pulsatile blood flow of the aorta into the low-pressure steady circulate of the capillary beds. Arterial elements Flow velocity In systole, the guts ejects a stroke quantity of 70´┐Ż90 ml blood into the aorta. The coronary heart generates a mean move velocity of 70 cm s-1, with a peak velocity of a hundred and twenty cm s-1, which makes flow within the aorta turbulent. It can be obtained from the product of cardiac output and systemic vascular resistance. An estimate of imply arterial stress could additionally be made by taking the diastolic plus one-third of the pulse strain. The most strain is the systolic arterial strain (about a hundred and twenty mmHg) and the minimum is the diastolic arterial strain (about 70 mmHg). The distinction between diastolic and systolic is the heartbeat strain, normally about 50 mmHg. The aortic strain wave changes in magnitude and shape occur because it travels by way of the arterial system. The form of the pressure wave narrows and high-frequency features such because the incisura (end-systolic notch) turn into dampened because it strikes distally.

Generic colcitrat 0.5mg free shippingThis small distinction is then multiplied into a big longitudinal gradient by the countercurrent arrangement treatment for sinus infection in horses purchase colcitrat 0.5mg without prescription. This limb produces a rise in the osmolality of the encircling interstitium by the extrusion of sodium and accompanying ions antibiotics for dogs at petsmart order colcitrat 0.5mg on-line. Both thin and thick segments of the ascending limb are impermeable to water antibiotics simplified purchase 0.5 mg colcitrat mastercard, in order that water is unable osmotically to comply with the extruded ions antimicrobial iphone 5 case purchase 0.5 mg colcitrat visa. The entry of solutes into the cells across the apical membrane includes co-transport of sodium, chloride and potassium, with the stoichiometry of one Na+, two Cl- and one K+, so the method is electrically impartial. This transport may be inhibited by loop diuretics, corresponding to furosemide and bumetanide. The descending limb is permeable to water and, to a lesser extent, can be permeable to NaCl. The fluid inside the descending limb will due to this fact come to osmotic equilibrium with the interstitium. In impact, then, one can consider the transport of NaCl out of the ascending limb as being directed into the descending limb. The fluid in the ascending tubule leaving the medulla and coming into the cortex is hypotonic to plasma, with an osmolality of about one hundred mOsm kg-1 H2 O. However, some nephrons possess short loops of Henle, and these are unlikely to decrease the osmolality of the ascending limb fluid to 100 mOsm kg-1 H2 O. Long and short loops of Henle Only 15% of the nephrons (the juxtamedullary nephrons) have lengthy loops of Henle that cross deeply into the medulla. However, the accumulating tubules of all the nephrons (both cortical and juxtamedullary) cross via the medulla. Thus, solely the long-looped nephrons (15% of the total) produce the medullary gradient that concentrates the urine produced by all of the nephrons. There are also variations in sodium reabsorption between the long- and short-looped nephrons. Vasopressin additionally will increase the urea permeability of the medullary amassing tubules, but has no effect on the urea permeability of the cortical amassing tubules. This impermeability of the cortical part of the collecting tubule to urea is doubtless considered one of the components that make urea so essential in the urine concentration mechanism. Importance of urea in countercurrent multiplication Previously, the countercurrent multiplication course of has solely been thought of when it comes to NaCl transport into the interstitium. However, a considerable fraction of the medullary interstitial osmolality, particularly in the papillary region, is attributable to urea (up to 50%). This excessive interstitial urea focus is obtained by diffusion of urea from the medullary accumulating tubules, which have an vasopressin-dependent permeability to urea. Urea is freely filterable at the glomerulus, and about 50% of the filtered load is reabsorbed within the proximal tubule. As the tubular fluid passes down the descending limb into the medulla, it passes into the high interstitial urea focus established by diffusion from the collecting tubules, as described above. The tubular urea focus thus increases by diffusion from the interstitium in both the descending and ascending limbs, which are permeable to urea. In the distal and cortical amassing tubules, the urea concentration rises further, because of water reabsorption, since these segments are almost impermeable to urea. Initially, when the medullary accumulating tubule is reached, the high urea focus in the tubule causes the diffusion of urea out of the tubule into the interstitium (under the affect of vasopressin), which maintains the excessive medullary urea concentration. Urea thus recycles between medullary collecting tubule and medullary interstitium via the tubular fluid. This produces a high interstitial urea focus that helps to improve the final urea focus within the urine. The most attainable urinary osmolality is greater when urea excretion is excessive because a proportion of this extra urea enters the medullary interstitium. The potential distinction throughout the distal tubular wall varies with distance alongside the tubule. In the early half, the lumen is constructive with respect to the interstitium (as in the ascending limb of Henle), but in the later elements the luminal potential becomes adverse and will reach -45 mV. The accumulating tubules the collecting tubules have cortical and medullary sections, the 2 sections having considerably completely different properties. Both are comparatively impermeable to water, urea and NaCl, but the water permeability is elevated by vasopressin. If medullary capillaries served this objective, the osmotic gradient constructed up by the loop of Henle would be dissipated. This permits the vasa recta to exchange nutrients for waste products within the renal medulla, without washing away the solutes liable for medullary hypertonicity. As the descending vasa recta pass into the medulla, water is osmotically abstracted from the capillary blood, into the interstitium, in change for solutes (NaCl and urea). More and extra water is extracted, as the blood passes further into the medulla, till, at the tip of the loop, the plasma has almost the same osmolality as the encircling interstitium. Since the plasma concentrations of diffusible solutes and plasma osmolality within the vasa recta just about assume interstitial values, the differences between descending and ascending limbs turn out to be very small. However, the accumulating tubules turn out to be impermeable to water, and the massive volumes coming into the medullary accumulating tubules cross through and are excreted. In addition, the collecting tubules additionally turn into impermeable to urea, preventing the attainment of maximal medullary interstitial osmolality. This in turn additionally reduces water reabsorption from the descending limb of the loop of Henle. Thus, when no vasopressin is current (diabetes insipidus), urine volume is about 23 litres per day, with an osmolality as low as 60 mOsm kg-1 H2 O. Note that adrenal steroids (cortisol) must be current for vasopressin to have its maximum impact on water permeability. Osmoreceptors and the control of plasma osmolality Osmoreceptors within the vicinity of the supraoptic and paraventricular areas of the anterior hypothalamus, supplied with blood by the interior carotid artery, regulate the discharge of the hormone vasopressin. These receptors, and others within the lateral preoptic space of the hypothalamus, additionally affect thirst. Normal plasma osmolality is associated with a plasma vasopressin concentration of about four pg ml-1. Lowering the plasma osmolality reduces vasopressin focus and raising the plasma osmolality increases the plasma vasopressin focus. This coupling of the vasopressin-sensitive concentrating mechanism to the exact control of vasopressin launch via the osmoreceptors provides an excellent regulatory mechanism for plasma osmolality. Renal results of vasopressin the principle determinant of whether the urine might be copious and dilute, or low in volume and concentrated, is the level of circulating vasopressin. It is these 23 litres which are mainly both excreted or reabsorbed, depending on the extent of circulating vasopressin. In the presence of vasopressin, the amassing tubule wall is permeable to water, so the hypertonic medullary interstitium leads to the osmotic abstraction of water from the tubule. Vasopressin also makes the accumulating tubules permeable to urea, which leaves the tubule in this area and contributes to the osmolality of the renal medulla. Vasopressin levels may be elevated Synthesis and storage of vasopressin Vasopressin is synthesised within the hypothalamus (supraoptic nucleus) as part of a giant precursor molecule.

Order colcitrat 0.5mg onlineThe trophoblast differentiates into two layers virus removal free download buy 0.5mg colcitrat with mastercard, the thick outer syncytiotrophoblast and the skinny inside cytotrophoblast infection 6 weeks after hysterectomy purchase 0.5 mg colcitrat. The cytotrophoblast cell columns and their masking syncytiotrophoblast extend as villous stems into the lacunae of maternal blood inside the decidua zombie infection pc purchase colcitrat 0.5 mg without prescription. These villous stems type the framework from which the villous tree will later develop virus 86 purchase 0.5mg colcitrat with visa. Cellular differentiation of the villous mesoderm leads to the formation of blood cells and blood vessels and types the villous vascular community. Cytotrophoblastic cells develop into the lumens of the maternal spiral vessels inside the decidua, where they exchange the endothelial cells, invading and destroying the musculoelastic medial tissue. As a results of the destruction of the sleek muscle, the walls of the spiral vessels in the decidua turn into thin and their vasoconstrictor exercise is lowered. This wave of trophoblastic invasion starts at 10 weeks and is complete by sixteen weeks. A second wave of vascular trophoblastic invasion happens from 16 to 22 weeks and extends more deeply into the myometrial parts of the spiral arteries. Failure of this physiological change is present in pre-eclampsia and intrauterine growth retardation. Further maturation of the villi results in a marked discount in the cytotrophoblast element and reduces the diffusional distance between the fetal villi and maternal intervillous blood. At term in humans, only a single layer of fetal chorionic tissue (syncytiotrophoblast) separates maternal blood and fetal capillary endothelium. Musculoskeletal system Placental production of the hormone relaxin stimulates generalised ligamentous leisure. This results in widening of the pubic symphysis, elevated mobility of the sacroiliac, sacrococcygeal and pubic joints. Weight achieve Weight increases by 10´┐Ż12 kg because of increases in maternal physique water and fats, the fetus, placenta, amniotic fluid and the uterus. At term, 40% of the weight gained is commonly in the fetus, amniotic fluid, placenta and uterus. Breast enlargement is typical in normal being pregnant, because of human placental lactogen secretion. Enlarged breasts may be a cause of inauspicious intubation and the use of a short-handle laryngoscope or polio blade might help to overcome this drawback. The placenta Although the placenta seems as a physical barrier between maternal and fetal tissues, it brings the maternal and fetal circulation into shut apposition for physiological change across a large area. Fetal wellbeing is dependent upon good placental perform for the supply of nutrients and the removing of waste merchandise. The placenta is connected to the developing embryo by a connecting stalk that subsequently becomes the umbilical cord containing the umbilical vessels. The intervillous house is a large cavernous expanse into which the villous trees attain. Blood enters the intervillous spaces and flows into loosely packed areas, then into densely packed intermediate and terminal villi. However, the relative path of the blood circulate is haphazard and behaves like a concurrent system, though with maternal blood circulate exceeding fetal blood circulate. Maternal placental blood circulate is a lowpressure system; the strain in the intervillous area is on average 10 mmHg. The increasing calls for of the growing fetus require 100´┐Ż150 spiral arteries to feed directly to the placenta. The maternal circulation by way of the intervillous area is fully developed by 20 weeks. Blood circulate will enhance from 50 ml min-1 at 10 weeks to between 500 and 800 ml min-1 at time period. Two umbilical arteries arising from the fetal inside iliac arteries carry deoxygenated fetal blood via the umbilical twine to the placenta, and a single umbilical vein returns oxygenated blood to the fetus. Fetal sinusoids formed within the terminal villi present a big endothelial floor space and make it the ideal area for maternal´┐Żfetal exchange. Each villous tree drains into a large vein that perforates the chorionic plate to turn into chorionic veins. Each of the venous tributaries courses in path of the umbilical wire attachment web site, where they empty into one umbilical vein. By term, the mature placenta is oval and flat with a mean weight of 500 g, common diameter of 20 cm and thickness of three cm. Uterine blood flow Uterine blood move is influenced by intrinsic and extrinsic factors. Uterine vascular resistance is affected by endogenous and exogenous vasoconstrictors. Endogenous vasoconstrictors such as catecholamines are increased by stress and ache throughout labour. Placental transport Mechanisms of placental transport Cellular membrane transport mechanisms are discussed intimately in Section 2, Chapter 1 (pages 208´┐Ż11). Other factors affecting oxygen transfer embrace the form of the fetal oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve and the Bohr effect. At the gas trade interface, fetal blood provides up carbon dioxide, turns into more alkaline (left shift) and develops a higher affinity for oxygen. The maternal blood on the other hand takes up carbon dioxide, turns into more acidic (right shift) and promotes launch of oxygen. This is referred to as the double Bohr impact, and it accounts for 2´┐Ż8% of the transplacental transfer of oxygen. The placenta is a metabolically energetic organ, using 30% of the whole oxygen delivered to it. The Glucose Glucose crosses the placenta by facilitated transport, which is stereospecific for the d-isomer. Amino acids Amino acids cross the placenta by the use of secondary energetic transport. Much of the transplacental transfer of amino acids occurs by the use of linked carriers for both amino acids and sodium. The transport of sodium down its concentration gradient drags amino acids into the cells. Electrolytes and water Sodium and water cross the placenta by simple diffusion and bulk transport. However, some immunoglobulins, significantly IgG, cross the placenta by pinocytosis. Until the top of the eighth week, the corpus luteum continues to secrete progesterone. The placenta progressively takes over this function and turns into answerable for the secretion of progesterone which reaches a peak simply earlier than labour. It is probably going that the interplay between these placental peptides is important in the control of development and growth of the fetus.
Syndromes - Nervousness or inappropriate laughter
- Are there side-to-side eye movements?
- Stool test for bleeding
- Removable dental work should be taken out just before the scan.
- Behavior changes
- Vaginal and labial itching, burning
- Examples of OTC brands of acetaminophen are Tylenol, Paracetamol, and Panadol.
- Allergic reaction
- Bluish color to the lips and face
Buy 0.5 mg colcitrat free shippingSpasticity produced by decerebration is most marked within the extensor group of muscles as these are the antigravity muscle tissue helping the animal to preserve its posture can antibiotics for uti delay your period purchase 0.5 mg colcitrat fast delivery. In the prone place the rigidity is minimal antibiotics that cover pseudomonas trusted colcitrat 0.5mg, while if the animal is on its back the rigidity is maximal antibiotic resistance in livestock discount colcitrat 0.5mg without prescription. When the head of the decerebrate animal is turned to one side antimicrobial kitchen towels discount colcitrat 0.5 mg mastercard, the limbs on that facet turn into extra rigidly extended and the limbs on the opposite aspect turn out to be much less rigid. Midbrain elements Midbrain components may be studied by interrupting the neural pathways on the superior border of the midbrain. In the midbrain animal, the phasic postural reflexes are intact in order that the animal can stand, walk and correct its position. Rigidity is seen solely when the animal is at rest, as it is because of static postural reflexes. The righting reflexes, such as the labyrinthine righting reflex, body on head righting reflex, neck righting reflex, and body on body righting reflex, are important for maintaining the normal position of the animal. Spinal twine elements the stretch reflex has already been described intimately earlier. Additionally, proprioceptors in opposing flexor and extensor muscle tissue contribute to the upkeep of an upright stance. The elevated efferent discharge causes facilitation of the stretch reflex, resulting in rigidity. Postural reactions like hopping and putting response are significantly affected by decortication. Brain-stem parts these components can be studied by transection of the mind stem at the superior border of the pons. From the third ventricle it travels to the fourth ventricle by way of the aqueduct of Sylvius. It enters the cerebral subarachnoid house via the median foramen of Magendie and lateral foramina of Luschka. Arachnoid villi are projections of arachnoid into the venous sinuses which are lined by a singlelayered endothelium of the venous sinuses. This blood´┐Żbrain barrier is very permeable to water, carbon dioxide, oxygen and most lipid-soluble substances such as risky anaesthetic brokers. The barrier is impermeable to plasma proteins and enormous molecular weight substances. Normal intracranial pressure ranges between 5 and 15 mmHg, though this varies with arterial pulsation, respiratory, coughing and straining. These compartments are all contained inside the inflexible cranial vault, and a change in volume of 1 compartment is accompanied by a reciprocal change in another compartment (The Monro´┐ŻKellie doctrine). Venous distension is a typical explanation for increased cerebral venous quantity and might occur from jugular venous obstruction, elevated intrathoracic strain, raised central venous pressure, head-down tilt and so forth. The globe is protected by the sclera, which becomes transparent within the anterior part of the eye often known as the cornea. Aqueous humour is produced by the ciliary processes and catalysed by the action of carbonic anhydrase; it passes from the posterior chamber by way of the pupil into the anterior chamber of the attention. It is then drained right into a vein by way of the canal of Schlemm (located at the angle of the anterior chamber). The interior floor of the globe is lined by the retina, except where the optic nerve leaves the eye and where the ciliary muscle begins. The ciliary muscle modifications the strain of the suspensory ligaments, which alters the convexity of the lens and thereby achieves accommodation. The visible pathway Electrical potential is generated when gentle reaches the photoreceptors on the retina. This potential is then transmitted to the ganglion cells via the bipolar and/or the horizontal and amacrine cells. Axons from the ganglion cells converge at the blind spot of the optic disc to kind the optic nerve. From here, synaptic connections are made via the optic radiation to the first visual cortex, giving rise to a topographical projection of the visible subject around the calcarine fissure. Some fibres of the optic tracts relay to the superior colliculi, which are concerned within the control of eye actions or posture. Lesions within the visual pathway will give visual area defects based on their place. These are located alongside the outer floor of the retina adjacent to the pigment epithelium. The blood supply of the photoreceptors is derived from the choroid and never from blood vessels on the inner retinal floor. Rods are uniformly distributed throughout the retina and are responsible for evening and monochromatic imaginative and prescient. Cones, however, are concentrated in the fovea and are answerable for brilliant and color imaginative and prescient. The latter traverses the subarachnoid house and enters the brain stem on the pontomedullary junction. Hearing Structure of the ear the ear is split into exterior, middle and inside compartments. The exterior compartment consists of the pinna, which directs sound waves by way of the exterior auditory meatus to the tympanic membrane. Vibrations of the tympanic membrane transmit sound power to the middle ear, which consists of the ossicles: malleus, incus and stapes. The center ear is air-filled and is linked to the pharynx through the Eustachian tube, which permits equilibration of pressure to occur between the middle ear and the environment. The inner ear is fluid-filled: the scala media is full of endolymph, while the scala vestibuli and tympani, being joined at the helicotrema, are crammed with perilymph. The organ of Corti is made up of an epithelium of hair cells and supporting cells. Each hair cell is anchored on the basilar membrane and has a bundle of hairs projecting from its tip into the scala media. The Mechanism of hearing Sound waves produce vibrations of the tympanic membrane that lead to movements of the ossicles. Movements of the footplate of the stapes within the oval window are transformed to stress waves in the scala vestibuli. These pressure waves are then transmitted within the endolymphatic canal to reach the basilar membrane. Such oscillations trigger displacements of the tectorial membrane with respect to the basilar membrane. The resulting receptor potential is then transmitted via the underlying ganglion cells to the cochlear nerve.
Generic 0.5mg colcitrat overnight deliveryIt is useful in higher gastrointestinal haemorrhage and in surgical procedure in haemophiliacs antimicrobial light discount 0.5 mg colcitrat with visa, and it can be administered orally or intravenously antibiotic question bank generic 0.5 mg colcitrat mastercard. More importantly natural antibiotics for sinus infection buy discount colcitrat 0.5 mg online, endothelial cells generate new cyclo-oxygenase virus black muslim in the white house cheap 0.5 mg colcitrat, whereas platelets are unable to . Aspirin should be stopped 7´┐Ż 10 days before surgical procedure to permit regeneration of normally functioning platelets. Prostacyclin Synthetic prostacyclin (epoprostenol) inhibits platelet aggregation and dissipates platelet aggregates. It can be utilized in haemodialysis, however have to be given as an infusion due to a short half-life (about 3 minutes). Prostacyclin can also be a potent vasodilator, so patients ought to be observed for hypotension, flushing and complications. Fibrinolytic inhibitors Examples ´┐Ż aprotinin, tranexamic acid the fibrinolytic inhibitors act by inhibiting the enzymatic activity of plasmin on fibrin. They are used to prevent the Other haemostatic modifiers Viscosity Dextrans reduce the viscosity of blood and may scale back the incidence of venous thrombus formation by enhancing the flow characteristics of the comparatively slow-flowing venous circulation. These are reduced by broad-spectrum antibiotics and are poor in the new child (haemorrhagic disease of the newborn). This may be useful to lower surgical oozing in mild haemophilia, and in instances of large transfusion, when clotting components are decreased. At present, anticoagulants either depend on a reduction in levels of clotting factors (oral anticoagulants) or on the enhancement of antithrombin. Future developments could contain the direct inhibition of particular clotting components. Platelet action Ethamsylate reduces capillary bleeding, probably by correcting abnormal platelet adhesion. After therapy has commenced, the length of remedy must be determined and frequently reassessed, together with the need to modify the antibiotic(s) in terms of both type and dose, depending on the scientific situation of the affected person and laboratory results. Antimicrobial therapy in renal failure Most antibiotics or their metabolites are renally excreted. Accumulation of potentially toxic compounds could subsequently come up unless cautious monitoring and dose adjustments are carried out. Cell membrane permeability Drugs that selectively interfere with cell membrane permeability are active against bacterial and fungal cells. Negatively charged lipids are plentiful in the cell membranes of Gram-negative micro organism and are the target of polymyxins such as colistin and polymyxin B. Imidazoles and triazoles interfere with sterol synthesis, and toxicity occurs with larger doses. Polyenes such as amphotericin and nystatin bind to the fungal sterols and open pores within the membrane, resulting in destruction of the molecular composition of the cytoplasm. Protein synthesis Where bacterial and human ribosomes differ, they can be targeted by antibiotics. They target structures and features specific to the target microbe or those that have an alternative metabolic pathway in human cells. These mechanisms goal 4 groups of microbial sites: r Cell wall r Cell membrane r Protein synthesis r Nucleic acid synthesis Beta-lactams that is the only largest group of antimicrobial agents presently obtainable, and consists of penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems and monobactams. Mechanism of motion Cell wall synthesis Bacteria have a cell wall to forestall swelling and lysis in hypotonic environments. The cell wall includes Nacetyl glucosamine, acetyl muramic acid and a polypeptide, which form multiple cross-links. The cell wall can range from a quantity of molecular layers thick in Gramnegative micro organism to one hundred layers within the Gram-positive organisms. Penicillins and cephalosporins present synergy with antibiotics acting on targets inside the bacterial cell because the cell-wall changes increase the permeability of the cell to different compounds. It remains efficient as prophylaxis for sufferers susceptible to developing endocarditis. Flucloxacillin Flucloxacillin and related compounds (methicillin, cloxacillin) are unaffected by staphylococcal -lactamase however have a narrower spectrum of activity than benzylpenicillin. Flucloxacillin is well absorbed orally however high protein binding (95%) limits its diffusion into some compartments, notably cerebrospinal fluid. Flucloxacillin may rarely cause cholestatic jaundice and hepatitis, and it have to be used with warning in patients with hepatic impairment. Penicillins Examples ´┐Ż amoxicillin, azlocillin, benzylpenicillin, flucloxacillin, mezlocillin, piperacillin Adverse effects these are few. Benzylpenicillin Spectrum of activity Benzylpenicillin is lively towards Gram-positive micro organism, most anaerobes and certain Gram-negative cocci (Neisseria spp. Piperacillin, azlocillin and mezlocillin these drugs are distinguished from amoxicillin primarily by their activity towards Pseudomonas aeruginosa and associated species. These medicine are sodium salts, and the excessive doses required to treat severe sepsis might cause sodium overload. They are primarily used for known or suspected Pseudomonas infections and, in combination with aminoglycosides, for the remedy of febrile neutropenic patients. Pharmacokinetics Benzylpenicillin is unstable in acid and have to be given parenterally. It is distributed broadly, penetrating pleural, pericardial, peritoneal and synovial spaces, however not cerebrospinal fluid within the absence of meningeal inflammation. It is excreted primarily by tubular secretion within the kidney with an elimination half-life of half-hour. It is active towards bacteria lined by benzylpenicillin and various other Gram-negative species, Haemophilus influenzae and most fecal streptococci. Amoxicillin is secure in gastric acid, and achieves good bioavailability after oral administration. Co-amoxiclav (clavulanic acid and amoxicillin combination) has been significantly successful. May not often trigger cholestatic jaundice and hepatitis and have to be used with caution in patients with hepatic impairment. Adverse results Cephalexin occasionally causes hypersensitivity, diarrhoea and belly discomfort, and barely Stevens´┐ŻJohnson syndrome. Cefuroxime Cefuroxime is more lively than cephalexin against a lot of the Enterobacteriaceae, and has useful activity against Haemophilus influenzae. It is excreted unchanged in the urine, one-half being the end result of tubular secretion, with a half-life of eighty minutes. Cefuroxime is used within the therapy of urinary, softtissue, bone, intra-abdominal and pulmonary infections and septicaemia. Cephalosporins Examples ´┐Ż cefotaxime, ceftazidime, cephalexin, cefuroxime these compounds are primarily based on cephalosporin C, a fermentation product of Cephalosporium acremonium cultivated from a Sardinian sewage outfall in 1948. It is also moderately lively against some enterobacteria (including Escherischia coli).
Trusted 0.5 mg colcitratThe blood´┐Żbrain barrier has the next capabilities: r To provide tight management over ionic (H+ bacteria dies at what temperature buy generic colcitrat 0.5 mg, Na+ antibiotics for uti biaxin order colcitrat 0.5 mg fast delivery, K+ infection synonym buy colcitrat 0.5mg lowest price, Ca2+ antimicrobial use colcitrat 0.5 mg with mastercard, Mg2+) concentrations within the interstitial fluid, as a result of brain cells are extremely delicate to ion adjustments r To protect the mind from transient adjustments in plasma glucose, the primary substrate for the mind r To shield the mind from endogenous and exogenous toxins within the plasma r To prevent release of central neurotransmitters into the systemic circulation Fetal circulation the fetus and placenta form a unit during which the placenta allows the fetus to change carbon dioxide and metabolic waste merchandise for oxygen and nutrients from the maternal circulation. In the fetus the left and right sides of the center work in parallel, not like the grownup circulation, where the ventricles work in series. The fetal ventricles, appearing in parallel, pump blood through the systemic vessels and the placenta, that are additionally arranged in parallel. The right side of the center provides two-thirds of the fetal cardiac output, which matches to provide the decrease half of the fetus. The above pattern of fetal circulation is as a end result of of the following vascular features in the fetus, which convert to the grownup configuration instantly or quickly after birth: r Umbilical arteries ´┐Ż two arteries that arise from the internal iliac arteries and carry 60% of the cardiac output to the placenta. This reduces pulmonary arterial pressures and increases blood circulate to the left atrium. Umbilical vessels constrict strongly when uncovered to trauma, rigidity, catecholamines, angiotensin and PaO2. These stimuli occur at birth and placental circulation ceases, resulting in a rise in systemic vascular resistance and arterial stress. These modifications make left atrial pressure larger than right atrial strain and have a tendency to shut the foramen ovale. The mechanism for this closure has not been fully identified, though a excessive PaO2 seems to initiate the closure and publicity to a low PaO2 can reverse the closure within the neonate. Prostaglandins preserve the patency of the ductus arteriosus, and indomethacin may be successful in closing a patent ductus arteriosus in a neonate. Oxygen saturation in the fetus the fetal blood is oxygenated from venous pools within the placenta. Thus, oxygen saturations at various factors in the fetal circulation are decrease than their equivalents within the adult. The glomeruli, proximal tubules and distal tubules are within the outer part of the kidney, the cortex, whereas the loops of Henle and the accumulating ducts extend down into the deeper part, the medulla. Cortical nephrons possess glomeruli positioned in the outer two-thirds of the cortex and have very short loops of Henle, which only prolong a brief distance into the medulla or might not reach the medulla in any respect. In contrast, nephrons whose glomeruli are in the inside third of the cortex (juxtamedullary nephrons) have long loops of Henle that cross deeply into the medulla. In people about 15% of nephrons are long-looped, however there are additionally intermediate forms of nephron. These are interlobular arteries, and the afferent arterioles that offer the glomerular capillaries department off from the interlobular arteries. Efferent arterioles are portal vessels, since they carry blood from a capillary community on to a second capillary community. The efferent arterioles from nephrons in the outer two-thirds of the cortex branch to type a dense community of peritubular capillaries, which encompass all of the cortical tubular parts. Vasa recta and peritubular capillaries ultimately drain into the renal vein which leaves the kidney at the hilum. The kidneys have a really high oxygen consumption, however due to the excessive blood flow, the arteriovenous oxygen difference across the kidney is small. The renal cortex receives far more oxygen than it requires, in order that the arteriovenous O2 distinction is only 1´┐Ż2%. However, the medullary blood supply is just simply adequate for the oxygen necessities of medullary cells, as a outcome of the vasa recta association causes oxygen to shortcircuit the loops of Henle. In the cortex, the main perform of the blood provide is to provide flow for glomerular filtration and oxygen for sodium reabsorption. Of the blood to the kidney, >90% enters via the renal artery and provides the renal cortex, which is perfused at about 500 ml a hundred g-1 tissue min-1 (100 occasions higher than resting muscle blood flow). The the rest of the renal blood provide goes to the capsule and the renal adipose tissue. Some of the cortical blood passes to the medulla; the outer medulla having a blood move of a hundred ml a hundred g-1 min-1, while the inner medulla receives 20 ml a hundred g-1 min-1. Almost the entire blood that enters the kidneys does so at the renal hilum, through the renal artery. The renal artery branches to kind a quantity of interlobar arteries, which themselves branch to give rise to arcuate (or arciform) arteries, which pass along the boundary between cortex and medulla. From these arcuate arteries, branches journey out at proper angles, via the cortex towards the capsule. Glomerular filtration the glomerulus A glomerulus is a knot of capillaries fed by an afferent arteriole and drained by an efferent arteriole. In the central part of the glomerular tuft are irregularly formed cells, termed mesangial cells. These are phagocytic and may stop the accumulation, within the basement membrane, of macromolecules which have escaped from the capillaries. The cells may have a structural role in holding the delicate glomerular construction in place and, as properly as, are capable of contraction. The significance of the renal lymphatic drainage is incessantly missed, however in reality the amount of lymph draining into the renal hilum per minute is about zero. This layer is assumed to keep the basement membrane by the phagocytosis of macromolecules. Since the filtrate is derived from plasma, and the common person has only three litres of plasma, it follows that this same plasma is filtered (and reabsorbed in the tubules) many instances in the middle of a day. Molecular size is the main determinant of whether or not a substance is filtered or retained within the capillaries. Plasma albumin, with a molecular weight of sixty nine 000 daltons, passes through the filter in minute quantities (retarded also by its cost, as mentioned above). Molecular shape and charge additionally influence filtration, but mainly of large molecules. For example, the speed of filtration of albumin, which has a unfavorable charge, is simply about 1/20 that of uncharged dextran molecules of the identical molecular weight. This is as a end result of of the adverse expenses of the heparan sulphate proteoglycan in the glomerular basement membrane, and the sialoglycoproteins on the foot processes, which repel anionic macromolecules. The glomerular filter the glomerular ultrafiltrate varieties the idea of the urine finally produced by the kidney. The capillary endothelium acts as a screen to prevent blood cells and platelets from coming into contact with the principle filter, which is the basement membrane. It forms a continuous layer and is the primary filtration barrier allowing the passage of molecules based on their measurement, shape and cost. It consists of collagen and other glycoproteins, together with giant amounts of heparan sulphate proteoglycan, with a large number of negative costs. The cell physique has projections (trabeculae) that encircle the basement membrane around the capillary. There is an approximate steadiness between the formation and reabsorption of tissue fluid, any extra being drained by lymphatics.
Discount 0.5mg colcitratThermocouples A thermocouple is an electrical circuit composed of two different metals bacteria legionella buy 0.5mg colcitrat otc, joined to type two separate identical junctions antibiotic resistance news article buy 0.5 mg colcitrat free shipping. The metals commonly used embrace copper´┐Żconstantin (copper/nickel alloy) bacteria from bees possible alternative to antibiotics cheap 0.5 mg colcitrat visa, and platinum´┐Żrhodium antibiotic resistance diagnostics generic colcitrat 0.5 mg amex. Humidity measurement Historically the measurement of humidity was an important contribution to the protected follow of anaesthesia. The mixture of static electrical sparks, and the use of flammable anaesthetic gases. One of the measures used to reduce static electricity, and therefore the incidence of fires and explosions, was to preserve the relative humidity within the working theatre above 50%. When the temperature of the tube decreases to the dew point, small droplets of water condense on the outside. The temperature of the ether on the dew level corresponds to the absolute humidity of the surrounding air, and can be determined from tables. The enhance in hair size is proportional to the humidity of the surrounding air. If one end of the hair is fastened to a lightweight lever, the change in length can be amplified and measured. The accuracy is poor, and the measured range is proscribed to between 15% and 85% relative humidity (though that is still adequate to measure humidity within the working theatre). The temperature of the wet thermometer is decided by the speed of evaporation of water from the wick, and therefore the humidity of the surrounding air. The distinction between the 2 recorded temperatures decreases as the humidity will increase. Using specific tables, the relative humidity could be obtained from the measured temperature distinction. The electrical conductivity of certain substances varies relying on the quantity of absorbed water. Most of the methods of assessing pain dimensions are widespread to each affected person and observer. A additional dimension defining the character of a pain situation is the classification into acute and persistent ache (see Section 2, Chapter 10, page 429). In acute ache, these indicators are reflected by autonomic modifications, which can be recorded and scored. This method supplies a fast, sensitive measure of humidity and is usually used in management systems for air-conditioning techniques. Measurement of pain Pain is amongst the most tough physiological phenomena to quantify, but its impression on the individual affected person, and on well being care in general, make assessment an important a part of scientific practice. Single-dimension pain measurement Single-dimension measurements could be applied to both acute and continual ache situations, and include: r Use of physique chart for pain location ´┐Ż a simple diagram on which the affected person or observer marks the areas corresponding to the pain. It can be utilized for various parameters corresponding to pain, temper, pain relief and disability. Current opinion is that visual analogue scales are reliable when used with the appropriate group of sufferers and under controlled circumstances. These scales are marked by numbers, or photos of faces, to symbolize growing or reducing ache. The gradation is thus not steady, however is restricted to a finite variety of decisions. This could make the results more reproducible in some cases and the tactic may be easier to use for patients, but a lack of sensitivity may finish up. Multiple word descriptor lists can be utilized to produce multidimensional ache assessment. It consists of a physique map and word descriptor sections for evaluating the intensity and other characteristics of pain. It is a relatively involved questionnaire taking round 20 minutes or more to full, relying on patient expertise. Alternatively pain charts may be designed for observers or carers to document goal evaluation information on a diary/timetable basis, to optimise postoperative analgesia. Assessment of pain in children Pain evaluation in kids is dependent on the age and expertise of the kid, and is affected significantly by their interplay with their dad and mom. Age (years) Infant 1´┐Ż3 Method Observation ´┐Ż crying, motor withdrawal Observation ´┐Ż crying, withdrawal, facial features, lip smacking, aggressive behaviour Pictorial-ranking scales Colour-matching scales Visual analogue scales Number-ranking scales Multidimensional scales 3´┐Ż5 5´┐Ż12 Multidimensional pain measurement these strategies may be applied to produce a more complete assessment of a pain situation by combining assessment of a quantity of ache dimensions. Equipment can then be linked to these outlets by non-interchangeable flexible hosing. The pipeline terminal retailers encompass Schrader sockets which might be clearly labelled and colour-coded for the service or fuel. They are matched for a selected connecting versatile pipeline by a collar indexing system. The terminal finish consists of an listed Schrader probe that fits into its specific terminal socket. Nitrous oxide supply Nitrous oxide is equipped from a central financial institution of gasoline cylinders, which comprise a combination of liquid and fuel (critical temperature of nitrous oxide is 36. These are connected to the distribution pipeline community by a control panel, which regulates the fuel strain. The management may also present native heating so as to avoid condensation and freezing because of the cooling attributable to the evaporation of the liquid nitrous oxide. In a hospital two types of supply are required, a low-pressure provide (420 kPa) for anaesthetic machines and ventilators, and a higher-pressure provide (700 kPa) to provide energy for surgical equipment. The pipeline community may be provided both by a financial institution of air cylinders or by a local compressor system. If an area compressor is used care have to be taken to make sure the purity of the compressed air produced. The excessive circulate charges used to remove waste anaesthetic gases might scale back suction ranges during surgical procedure. Suction vacuum methods incorporate bacterial filtration and drainage to get rid of aspirated body fluids. Random cylinders from a batch could also be destructively tested by the manufacturers utilizing water underneath strain. Cylinders may be inspected endoscopically for cracks and defects on their inside surfaces, they usually can be examined ultrasonically. Cylinder valve outlet Pin index holes Bodok seal Index pins Estimation of cylinder contents the contents of a cylinder, for both gases and vapours, are estimated by weighing the cylinder and subtracting the burden of the empty cylinder or tare weight. Cylinder contents can thus be estimated by weighing a cylinder and subtracting the tare weight of the cylinder. This system prevents the mistaken cylinder from being connected to an anaesthetic machine. The cylinder valve block face matches up to the inlet port of the anaesthetic machine. This face contains the gas outlet from the cylinder, which is made gas-tight by a steel and rubber ring seal, the Bodok seal. In the case of vapours (such as nitrous oxide or carbon dioxide) the contents of the cylinders are a mixture of fuel and liquid. The filling ratio is outlined as the weight of the substance contained divided by the load of a volume of water equal to the interior quantity of the cylinder.
References - Waller A. Experiments on the section of the glossopharyngeal and hypoglossal nerves of the frog and observations of the alterations produced thereby in the structure of their primitive ibers. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 1850;140:423-429.
- Mannucci PM, Bettega D, Chantarangkul V, Tripodi A, Sacchini V, Veronesi U. Effect of tamoxifen on measurements of hemostasis in healthy women. Arch Intern Med 1996;156:1806-1810.
- Branton PA, Lininger R, Tavassoli FA. Papillary endothelial hyperplasia of the breast: the great impostor for angiosarcoma: a clinicopathologic review of 17 cases. Int J Surg Pathol. 2003;11(2):83-87.
- van Gils MPMQ, Hessels D, Hulsbergen van de Kaa CA, et al: Detailed analysis of histopathological parameters in radical prostatectomy specimens and PCA3 urine test results, Prostate 68:1215n1222, 2008.
- Wibbenmeyer LA, Wade TP, Chen RC, et al. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy can disseminate in situ carcinoma of the gallbladder. J Am Coll Surg. 1995;181(6):504-510.
- Ellis IO, Galea M, Broughton N, Locker A, Blamey RW, Elston CW. Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. II. Histological type. Relationship with survival in a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology. 1992;20(6):479-489.
- Abate N, Chandalia M, Snell PG, et al: Adipose tissue metabolites and insulin resistance in nondiabetic Asian Indian men, J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:2750n2755, 2004.
- Hood, D. D., Curry, R., & Eisenach, J. C. (2003). Intravenous remifentanil produces withdrawal hyperalgesia in volunteers with capsaicin-induced hyperalgesia. Anesthesia & Analgesia, 97(3), 810n815.
|