Desloratadine
Joshua De Leon, M.D. - Assistant Professor of Medicine
- Mount Sinai School of Medicine
- New York, NY
Generic desloratadine 5mg visaNerve provide to the oesophagus the striated muscle within the upper third of the oesophagus is equipped by the recurrent laryngeal nerve allergy shots and birth control buy desloratadine 5mg visa. The clean muscle is equipped by parasympathetic fibres from the oesophageal branches of the vagus and recurrent laryngeal nerves allergy medicine starts with c generic 5mg desloratadine free shipping. Sympathetic fibres are derived from the sympathetic trunk and are available both immediately from the cardiac plexus or around the blood vessels supplying the oesophagus allergy symptoms without runny nose buy desloratadine 5mg online. Pain is poorly localized and possibly brought on by muscle spasm quite than direct stimuli allergy medicine 25 mg cheap 5 mg desloratadine otc. Vasculature of the oesophagus the cervical oesophagus is supplied by the inferior thyroid artery and left subclavian artery. The thoracic part has a segmental provide instantly from the descending aorta and branches of the bronchial and higher posterior intercostal arteries. The abdominal half is supplied by the left gastric artery, a branch of the coeliac artery, and the left inferior phrenic artery directly from the belly aorta. An extensive venous plexus lies on the skin of the oesophagus and drains in a segmental approach to the inferior thyroid veins (systemic), azygos and hemiazygos veins (systemic) and left gastric vein (portal). The lower finish of the oesophagus is a vital space of portal systemic venous anastomosis. At the higher finish of the oesophagus, longitudinal submucosal veins enter the pharyngeal and laryngeal plexuses. They drain by ascending or descending beneath the mucosa or by piercing the oesophagus. The retropharyngeal and parapharyngeal spaces communicate with one another, which permits unfold of an infection and tumour along fascial planes. This advanced sequence of motor behaviour is an element reflex and partly underneath voluntary control. More lately, videofluoroscopy and endoscopy have been used to examine swallowing, significantly its problems. Swallowing as a motor behaviour is so complex that some particulars have remained troublesome to resolve. The literature is often contradictory, significantly the sooner research based mostly on inferential analysis of radiographic data. This chapter will survey the current state of information concerning the regular anatomy and physiology of swallowing and what could be considered as the boundaries of normality, essential to the understanding of dysphagia. Neural management and the coordination of breathing and swallowing will also be addressed. The fundamental musculature of swallowing controls the jaw, the tongue, the degree of constriction and size of the pharynx and closure of the laryngeal inlet. The elevators and depressors of the jaw play a key role in bolus preparation before the swallow is initiated by grinding and lowering the food between the tooth. Bolus formation is also a function of the tongue, the intrinsic muscle tissue of which are primarily liable for changing the shape of the tongue and the extrinsic muscular tissues altering its place within the mouth. A, Hard palate; B, soft palate; C, nasopharynx; D, pharyngeal isthmus; E, oropharynx; F, laryngopharynx; G, cricoid cartilage; H, thyroid cartilage; I, hyoid bone; J, laryngeal inlet. The actions of the tongue and jaw muscular tissues in bolus formation are aided by that of the lips in maintaining a seal, the buccinator muscle of the cheek in returning food from the vestibule into the oral cavity and the soft palate in stopping nasal regurgitation and untimely movement of fabric into the oropharynx. On leaving the oral cavity, food enters the pharynx, a midline tube roughly 15 cm lengthy steady with the oesophagus beneath and the nasal cavities above and the larynx which opens on its anterior wall. The anterior wall of the pharynx is incomplete and composed of the posterior a part of the tongue superiorly and the larynx inferiorly. This results in a natural division of the pharynx into three areas: nasopharynx, oropharynx and laryngopharynx, similar to those structures that lie anterior to the appropriate part of the pharyngeal tube. The remainder of the pharynx consists, like the entire of the gastrointestinal tract, of 4 layers: the outer areolar, the muscular, the submucous and the internal mucous membrane. The circular muscular tissues are arranged as a triad, the superior, center and inferior constrictors, with the latter being additional subdivided right into a thyropharyngeus and cricopharyngeus part. With the exception of the cricopharyngeus, the constrictor muscle tissue are paired and connect to a posterior midline raphe. The cricopharyngeus types a definite sphincter on the point where the laryngopharynx joins the oesophagus. There are two discrete longitudinal muscle tissue on all sides, the palatopharyngeus and the stylopharyngeus. The larynx is a sequence of cartilages within the wall of the higher a half of the trachea, the principle cartilages being the thyroid, cricoid and arytenoid. The larynx is suspended from the hyoid bone by the thyrohyoid membrane and thyrohyoid muscle. When the suprahyoid and infrahyoid muscular tissues transfer the hyoid bone, in addition they alter the height of the larynx. The epiglottis projects above the hyoid behind the posterior part of the tongue and is attached to the posterior side of the thyroid cartilage. Attached between the epiglottis anteriorly and the arytenoid cartilages posteriorly is the quadrangular membrane, the superior margin of which forms the boundary of the laryngeal inlet. Within this superior border are the aryepiglottic muscles that control the inlet, together with the small thyroepiglotticus muscle which will assist to depress the epiglottis to stop aspiration. Adduction of the vocal cords by the intrinsic muscles of the larynx supplies a second line of defence to the unintentional ingestion of meals or overseas objects. It has a short cervical course before it enters the thorax where it lies posteriorly within the midline and descends, piercing the diaphragm and entering the stomach. The act of swallowing entails a crossing of the stream of liquid and food with that of respiration and this occurs throughout the pharynx. This crossing of the alimentary and ventilatory streams is an evolutionary consequence of the transition in vertebrates from sea to land dwelling. In primitive vertebrates the pharynx is an apparatus for concurrently extracting dissolved oxygen from seawater at the gills and filter feeding on suspended particles. A number of mechanisms have developed to ensure that during regular swallowing no liquid or meals could be aspirated into the lungs through the larynx. Aspiration can lead to severe penalties corresponding to asphyxiation brought on by airway blockage or of occult aspiration with resultant complications. Swallowing has two parts: the passage of the bolus from the oral cavity to the abdomen and airway safety. These similar mechanisms additionally serve to inhibit the ingestion of air into the stomach. The conventional view is that biomechanical events corresponding to motion of the posterior part of the tongue and elevation of the hyoid bone and larynx, related to passing the bolus, are the main occasions of the pharyngeal phase of swallowing. However, videoendoscopic and videofluoroscopic investigations clearly present that the airway protection mechanism is activated first. Ventilation is at all times discussed as part of the traditional strategy of speech manufacturing however swallowing additionally must be fastidiously timed in relation to the respiratory phases and a failure in this may be one cause of swallowing difficulties. The oral section may be split into the (a) (b) preparatory phase where the food is taken into the mouth and broken down, and the oral section correct where the bolus is moved to the again of the tongue. From when the bolus leaves the oral cavity to enter the pharynx until it passes into the oesophagus defines the pharyngeal reflex part. The bolus is then moved previous the protected laryngeal inlet, by way of the pyriform fossae towards the cricopharyngeal sphincter and into the oesophagus.
Buy desloratadine 5mg without a prescriptionThe commonest indication has been for post-traumatic visual loss owing to direct or indirect damage allergy shots itchy cheap desloratadine 5mg otc, similar to skull base fracture allergy medicine yellow desloratadine 5 mg on line, a overseas physique or haematoma allergy knoxville tn discount desloratadine 5 mg otc. These patients have often suffered a number of accidents allergy forecast round rock quality desloratadine 5 mg, and as a outcome of the situation of the affected person, the visible loss may not be immediately obvious. Attempts have been made to compare surgery and megadose parental steroids, and whereas the latter treatment has been recommended,38 another research by Levin et al. Meningiomas of the skull base produce a hyperostotic reaction in adjoining bone together with a mass impact from the soft tissue component that may immediately impact on the orbital apex. These adjustments often predominantly affect the lateral compartment of the apex enabling area to be created medially, thereby buying time for patients in whom the course of illness is often indolent. Surgical strategies the orbital apex may be approached externally from above, laterally, medially or mixtures thereof. An extracranial transnasal endoscopic strategy may be employed for medial decompression however, when a more intensive unilateral or bilateral decompression of the nerve is required, a craniofacial approach should be considered. The bone thickens at this level and infrequently must be thinned utilizing an irrigated sheathed endoscopic drill previous to elimination. The dissection can be continued along the lateral wall of the sphenoid to a variable degree dependent upon the person pathology and anatomy. The orbital periosteum is then incised from posterior to anterior using a disposable sickle-bladed knife. The depth and extent of this again varies from case to case however contains release of the tendinous ring of Zinn generally. In theory, full opening of the optic nerve sheath ought to lead to an indication of cerebrospinal fluid however, in follow, this is rarely seen. It ought to be remembered that the ophthalmic artery could lie in the inferior medial quadrant of the optic nerve sheath in roughly 15 percent of cases40 and subsequently incisions must be restricted to the superomedial quadrant. However, in circumstances of extrinsic compression of the nerve, there ought to be no must open the sheath. There is, nonetheless, no definite proof of benefit for this procedure after traumatic optic neuropathy. It would, nevertheless, appear that maintenance of maxillary aeration � quite than direct support of orbital tissues � is extra significant in avoiding this drawback as evidenced by the event of idiopathic cases. Where more extensive bone removal is required, a craniofacial method permits decompression of the optic nerve as much as the optic chiasm on one or each side. Although in 4 circumstances illness finally rendered the patients blind, the decompression preserved or improved failing vision in two people until near their deaths and provided useful palliation. In view of the probable benefits of high-dose steroids after major damage, a placebo-controlled randomized trial comparing medical and surgical therapies for optic canal decompression is tough to justify. Die drickentlastlung der augenjokle durch entfurnung der aussern orbitalwant bei hochgradigen expohthalmos und koneskutwer hornhauterkrongkung. A range of situations including orbital complications of bacterial rhinosinusitis, mucocoeles, vasculitic situations and tumours of the nose and sinuses might present with eye signs. Endoscopic orbital decompression with preservation of an inferomedial bony strut: minimization of post-operative diplopia. Long-term follow-up and up to date observations on 305 instances of orbital decompression for dysthyroid orbitopathy. The medial orbital strut within the prevention of publish decompression dystopia in dysthyroid ophthalmopathy. Treatment of thyroid ocular myopathy with adjustable and nonadjustable suture strabismus surgery. Craniofacial resection for tumors of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses � a seventeen 12 months experience. For some this can be a minor inconvenience however for others it could be extraordinarily troublesome, and a source of social embarrassment as it can alter refraction and imply that the patient has to wipe their eye(s) perpetually. Epiphora may additionally be secondary to the excessive manufacturing of tears or arise from proximal obstruction in the drainage system on the punctum or frequent cannaliculus. Such idiopathic obstruction turns into more frequent with rising age and exhibits a female preponderance. The incidence of nasolacrimal obstruction is estimated to involve roughly 10 p.c at forty years growing to 35�40 % at ninety years of age. The nasolacrimal duct exits from the inferior level of the lacrimal sac and continues in an inferior direction with a slight lateral or medial angulation for 12 mm before coming into the nostril 10�15 mm behind the anterior finish of the inferior turbinate and 16 mm above the ground of the nasal cavity excessive within the inferior meatus. The lacrimal bone that articulates inferiorly with the bottom of the inferior turbinate forms the posterior wall of the bony canal while the frontal process of the maxilla varieties its anterior boundary. The lacrimal sac itself lies protected in the concavity of the lacrimal fossa within the medial orbital wall. The lacrimal fossa is formed by the lacrimal bone and by the frontal strategy of the maxillary bone. The latter varieties the anterior lacrimal crest and the rest of the anterior part of the lacrimal fossa and includes very dense bone. The posterior aspect of the inferior portion of the lacrimal sac lies on the very skinny lacrimal bone and this space, which is immediately anterior to the attachment of the uncinate course of, is well entered using an endonasal approach. The lacrimal fossa is 15 mm in length, 4�8 mm in breadth and a pair of mm in depth with the sac having two-thirds of its peak above the insertion of the middle turbinate and onethird beneath. The sac is encapsulated in a dense layer of fascia with contributions from the medial canthal tendon, the orbicularis oculi muscle and the periosteum of the medial orbital wall. This has the impact that an infection within the sac tends to stay confined to the sac inflicting growing strain and pain but with out unfold into the orbit or face. In approximately 8 % of cases, an anterior ethmoidal air cell, the lacrimal cell, lies medial to the lacrimal bone and has to be opened so as to achieve entry to the lacrimal fossa. The exterior approach was subsequently modified by many surgeons including DupuyDutemps and Bourget,four who emphasised the significance of sutured mucosal flaps. With the development of contemporary nasal endoscopes almost a hundred years later a resurgence of interest within the endonasal approach has taken place. Commencing with a punctum in each eyelid (approximately 6 mm from the medial canthus) the canaliculi initially run at 901 to the lid margin for 1�2 mm earlier than turning to run parallel with the lid margin. An inability to flush via the inferior canaliculus signifies obstruction at the web site of the punctum or inferior canaliculus while reflux of saline via the other canaliculus indicates the obstruction is extra distal. Massaging of the sac could produce a discharge from the puncti consistent with chronic dacrocystitis. Nasal endoscopic examination is especially geared toward excluding anatomical abnormalities that will intrude with profitable endonasal surgery but may even detect any uncommon pathology that may affect success rates. A history of trauma involving the lateral nasal wall is prone to end in lower success charges as thick bone will make an endonasal approach more difficult. The lacrimal sac with its connected periosteum is dissected free from the lacrimal fossa and is retracted laterally. A vertical slit is made in the exposed nasal mucosa and, similarly, a corresponding vertical slit is made in the lacrimal sac and the flaps created are sutured collectively to create an epithelially lined rhinostomy.
Syndromes - Before intercourse, and during it if needed, put a couple of drops of water-based lubricant on the penis.
- How often do you have sexual activity?
- Angiography to help block the blood vessel that is bleeding or to deliver medicine to help cause the blood vessels to tighten to stop the bleeding
- Thoroughly work the shampoo into dry pubic hair and surrounding area for at least 5 minutes.
- Lung biopsy (rarely performed)
- Lack of interactive play
Trusted 5 mg desloratadinePlacebo-controlled multicenter randomised trial of interferon beta-1b in remedy of secondary progressive multiple sclerosis allergy treatment toddlers purchase 5mg desloratadine with amex. A randomized trial of acyclovir for 7 days or 21 days with and without prednisolone for therapy of acute herpes zoster allergy forecast fairfield ct purchase desloratadine 5 mg. Economical multiple-site intradermal immunisation with human diploid-cell-strain vaccine is efficient for post exposure rabies prophylaxis allergy medicine nightmares order 5 mg desloratadine free shipping. Cerebello-pontine tumor diagnosed for six years as a tic doloureux: the signs of the irritation of the ninth and twelfth cranial nerves anti allergy medicine in japan purchase desloratadine 5 mg without a prescription. Incidence and medical options of glossopharyngeal neuralgia, Rochester, Minnesota, 1945�1984. Combined hyperactive dysfunction syndrome of the cranial nerves: Trigeminal neuralgia, hemifacial spasm and glossopharyngeal neuralgia: 11-year expertise and evaluate. Observations on the etiology of trigeminal neuralgia, hemifacial spasm, acoustic nerve dysfunction and glossopharyngeal neuralgia: Definitive microsurgical remedy and leads to 117 patients. Refereed articles have been retrieved using the key words dysphagia, swallowing, swallowing issues, and the search focussed on analysis and management. This report is useful to think about in some element as it illustrates how an evaluation of the evidence can importantly inform the necessity for medical development and change. In order to study the evidence for dysphagia intervention, four questions were tackled. How does the prognosis of dysphagia or aspiration affect therapy courses and patient outcomes When is noninvasive remedy applicable, and when should feeding tubes be utilized in certain affected person populations. Four thousand, 600 and forty-six gadgets had been retrieved within the type of journal articles, book chapters, manuscripts, monographs, net pages and private communications. In this systematic evaluation, the general conclusion when it comes to design was that the subject sizes within the research had been almost universally too low, with resulting low statistical energy and therefore unreliable results. The proof regarding the first question above instructed that a significant reduction within the incidence of pneumonia was observed when a scientific programme of diagnosis and treatment of dysphagia in an acute stroke management plan was carried out. Thus, it was impossible to determine the purely diagnostic talents of every check employed. Aspiration (the entry of food or liquid into the airway below the extent of the true vocal folds) and penetration (entry of food or liquid into the larynx to the level of, but not below, the true vocal folds) might, or may not, be signs of dysphagia. The association between demonstration of occasional or continual aspiration and development of aspiration pneumonia is, as but, unknown. Often, we make the assumption that detection of aspiration will have a direct hyperlink to the development of pneumonia however this will not be the case as, though the amount and frequency of aspiration could also be essential, there may be different elements that play an much more necessary position. One study has discovered that dependency on others for feeding was a dominant threat issue for creating aspiration pneumonia, somewhat than dysphagia alone. For individuals undergoing treatment for head and neck (H&N) cancer, for example, a decision may need to be made early in planning treatment for momentary or everlasting dietary support where the treatment is prone to be protracted, as affected person consolation and motivation � in addition to hydration and nutrition � are necessary considerations. If radiotherapy is pursued, then assessment and remedy begins if/when swallowing problems are reported. Usually, if sufferers are in hospital, then speech therapy is daily for inpatients, with ongoing outpatient (usually weekly) appointments after discharge. However, the swallowing therapist will often have seen the patient all through the course of the planned interventions so as to monitor adjustments in swallowing function and to provide a source of care, help and information for patient and family. Psychological distress, notably anxiousness, is a typical sequela of dysphagia; worry of their disease and of swallowing could also be widespread displays in patients with H&N most cancers. Patients undergoing chemotherapy and radiotherapy sometimes experience loss of urge for food and could additionally be anorexic in consequence. Such adjustments could additionally be efficient in reducing or eliminating aspiration in 75�80 percent of patients5, 9 including infants, children and some sufferers with cognitive impairment. Postural changes which were proven to be efficient in medical research studies embrace the following. Chin down (widens valleculae to prevent the bolus from coming into the airway; reduces risk of aspiration). This is used with patients where a unilateral vocal fold palsy or a hemi laryngectomy leads to aspiration in the course of the swallow. This is used in cases of unilateral oral and pharyngeal palsy on the same side (illustrated by residue on the identical facet of the mouth and pharynx). This posture is used where cricopharyngeal dysfunction is demonstrated (by seen residue in the pyriform sinuses). These manoeuvres have good evidence-based analysis to assist their use, albeit generally in a single population studied, or with a small number of topics. There is evidence that these strategies may also end in lowering the delay to triggering the pharyngeal stage of the swallow in some patients. A explicit quantity of meals could elicit a quicker pharyngeal swallow and this must be regulated. If eating too shortly, food can rapidly construct up within the pharynx and aspiration might ensue. The software of thermal/tactile stimulation to enhance sensory input and thereby set off a more efficient/ speedier triggering of the pharyngeal swallow, has been nicely developed and described. The mirror is then firmly rubbed along the anterior faucial arches, four or 5 occasions, before presenting the bolus to be swallowed. They could include: rising downward stress of the spoon against the tongue when meals is presented; presenting a bitter bolus (lemon flavoured barium); presenting a cold bolus; presenting a bolus needing chewing; presenting a larger Generally, elimination of certain food consistencies may be essential, however maybe must be thought of because the last compensatory strategy. This typically results in noncompliance with advice and/or issue in adhering to remedy. Food preferences, non secular and cultural sensitivities have to be acknowledged, as that is likely to enhance compliance with remedy suggestions. Direct therapy involves the patient being taught to achieve control over the bolus, using small quantities of meals or liquid, utilizing specified swallowing sequences. This is only used when patients can successfully swallow small quantities with no aspiration. Typically, prostheses are used when patients are left with part, or all, of the taste bud ablated and a defect left in the reconstructed area. An acrylic or plastic palatal obturator can then be manufactured by the maxillofacial prosthodontist to tackle the defect. This raise might enhance hypernasality in speech in addition to reducing nasal reflux during swallowing. A palate-lowering, reshaping or augmentation device for these sufferers could mean that the remaining tongue can achieve tongue�palate contact throughout swallowing for better oral bolus transit, and a normal food regimen may be resumed. Usually, the affected person will use a mirror for visible suggestions and will be inspired to extend the target structure. This gadget consists of a bulb placed in the mouth behind the entrance tooth (rather like a big lollipop on a stick) and this bulb, containing strain transducers, is then related to a computerized feedback show. The flange on the bulb is held by the patient on the tongue, behind the front enamel and the affected person pushes onerous in opposition to the bulb till the tongue pressure is sufficient to result in a green mild being illuminated on the computerized show. This mild then has to be held green, by tongue endurance, for a specified time (say five seconds). The settings could also be modified because the resistance improves and muscular power is regained.
Discount desloratadine 5 mg overnight deliveryHerpetic allergy medicine mixed with alcohol buy cheap desloratadine 5mg online, fungal or cytomegalovirus mucosal infections could cause dysphagia and is normally seen in severely immunocompromised sufferers allergy forecast georgia buy 5 mg desloratadine with visa. In addition allergy forecast dallas buy generic desloratadine 5mg line, candidal infections are extra frequent in patients on broad spectrum antibiotics or steroids allergy forecast killeen discount desloratadine 5mg. However, candida affecting the hypopharynx and oesophagus is probably not apparent to the clinician. Oesophagoscopy is the investigation of choice for diagnosis when a swab could be taken. Tuberculosis is a continual an infection that may trigger dysphagia by both a mucosal lesion or compression of the oesophagus by enlarged lymph nodes. Clinical examination might show erythema and oedema of the posterior larynx and lower pharynx, but normally a versatile oesophagoscopy is required for diagnosis. The inflammatory changes seen within the oesophagus range from mild erythema, which is equivocal proof of reflux, to erosions, confluent ulceration or stricture formation in more severe cases. Twenty-fourhour ambulatory oesophageal pH monitoring is essentially the most correct way of confirming the prognosis and is useful when commonplace investigations are regular. In Patterson Brown�Kelly or Plummer�Vincent syndrome, dysphagia principally affects middle-aged or elderly ladies and is associated with atrophic gastritis and irondeficiency anaemia with its related clean tongue, angular stomatitis and koilonychia. The dysphagia is due to hyperkeratinization with internet formation in the postcricoid area and could be seen on barium swallow, however might not at all times be discovered at rigid endoscopy. The dysphagia and the hyperkeratinization are treated with iron substitute, but the net might have dilatation. The condition is associated with the event of postcricoid carcinoma in a small share of patients. Systemic autoimmune disorders8 are related to dysphagia in a large proportion of instances, although the mechanism differs between illness groups. Diagnosis of this group of circumstances relies on the clinical image and auto-antibody profile. Dermatomyositis is a diffuse inflammatory situation affecting skin and skeletal muscle related to malignancy in a excessive proportion of patients. Benign pemphigoid and epidermolysis bullosa are characterized by subepidermal and submucosal blisters respectively, resulting in scarring and obstruction of the pharynx and oesophagus. Rheumatoid arthritis may involve the cricoarytenoid joint with resultant hoarseness and dysphagia. Sarcoid is a granulomatous disease that will trigger dysphagia by compression of the oesophagus by involved lymph nodes. Nutcracker oesophagus also causes noncardiac chest pain associated with dysphagia. Manometry reveals regular peristaltic waves of high amplitude within the distal oesophagus. Neoplastic Both benign and malignant tumours might cause dysphagia by mechanical obstruction and likewise by neuromuscular invasion. In the oral cavity, most tumours are malignant and of these ninety five % are squamous cell carcinomas. The affected person may current with a lump within the mouth or with an ulcer that will end in odynophagia. In the oropharynx, most malignant tumours are squamous cell in origin and normally ulcerative and a small proportion are lymphomas which present as easy enlargements. The affected person normally presents with a sore throat, referred otalgia or dysphagia and the tumour ought to be visible clinically. In the hypopharynx, rare benign tumours can be found corresponding to leiomyomas, lipomas and fibrolipomas which cause dysphagia. The majority of tumours are squamous cell carcinomas, 60 percent occurring within the pyriform fossa. Large tumours are apparent from the symptomatology and should be seen on medical examination. Small tumours and tumours of the postcricoid area or the cervical oesophagus may be more difficult to diagnose. In the oesophagus, benign leimyomas could be discovered often however the majority of tumours are squamous carcinomas. Dysphagia of brief duration in an elderly male who smokes and drinks and which progresses from solids to liquids is classical. Examination might present weight reduction and anaemia, cervical lymphadenopathy and hoarseness with a bovine cough in advanced illness, but there could also be little to find in early illness. In all circumstances of pharyngeal and oesophageal malignancy, the diagnosis is confirmed by biopsy performed underneath general anaesthesia in order to assess and stage the tumour. Oesophageal motility issues these disorders can produce extreme dysphagia in the absence of visible abnormalities, the diagnosis being made by manometry. Achalasia (cardiospasm) is as a result of of failure of relaxation of the decrease oesophageal sphincter with progressive dilation and hypertrophy of the oesophageal wall above. The condition is indistinguishable from Chagas disease, seen in patients from South America and which is due to an infection by Trypanosoma cruzi and which destroys the ganglion cells. Patients complain of progressive dysphagia to fluids after which solids and eventually regurgitation of undigested food. Manometry is used to establish the prognosis in early illness when the classic barium appearance has not but developed and reveals failure of relaxation of the lower oesophageal sphincter, absence of oesophageal peristalsis and a raised resting strain in the oesophagus. Diffuse oesophageal spasm causes angina-like chest ache in the presence of normal coronary arteries and dysphagia. Manometry shows repetitive nonperistaltic, multipeaked contractions of excessive amplitude of the body of the oesophagus with intermittent regular peristalsis and incomplete decrease oesophageal sphincter rest. Chapter 153 Causes of dysphagia] 2033 Nasopharyngeal carcinomas are recognized for their diversified presentations and may present with cranial nerve palsies from skull base invasion leading to speech and swallowing issues and hoarseness. Skull base tumours, such as craniopharyngomas and chordomas, could cause dysphagia by compression of the parapharyngeal house or invasion of the cranial nerves. Enlarged mediastinal lymph nodes because of lymphoma, or lymph node metastases, bronchial carcinoma or thyroid malignancy especially if retrosternal, can all trigger dysphagia by external compression of the oesophagus. Neurological Neurological causes of dysphagia10 mostly affect the oropharyngeal part of swallowing. In general, patients who current with an acute dysfunction inflicting dysphagia, such as a stroke, are likely to improve with time, whereas sufferers with continual neurological issues will expertise progressive swallowing difficulties. Diagnosis of the specific swallowing problem in these situations is made by a careful head and neck examination, assessment by a speech and swallowing therapist and particular studies together with barium videofluoroscopy. Cerebrovascular accident or stroke is probably the most typical neurological dysfunction inflicting dysphagia by affecting the cortex or the corticobulbar tracts (pseudobulbar palsy) or by affecting the bulbar nerve nuclei (bulbar palsy). Factors contributing to the dysphagia embody delayed triggering of the swallowing reflex, cricopharyngeal dysfunction and lowered tongue management and pharyngeal contraction and cough.
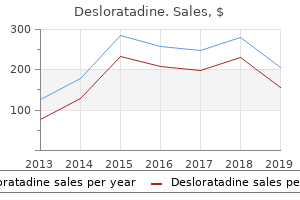
Desloratadine: 5 mg
Generic desloratadine 5mg on lineMarginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve this has a variable course allergy symptoms low grade fever cheap 5mg desloratadine visa, however it can be accurately located at the point where it crosses the mandible allergy shots springfield mo discount desloratadine 5mg visa. It crosses with the facial artery allergy shots problems desloratadine 5mg on line, which can be palpated anterior to the masseter muscle allergy treatment pipeline generic desloratadine 5mg. The lower restrict of the nerve is the larger cornu of the hyoid, so that incisions below this could not harm the nerve. The submandibular triangle contains the submandibular salivary gland, deep fascia, lymph nodes, anterior facial vein, facial artery and the marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve. It incorporates the lower carotid sheath, the infrahyoid strap muscular tissues, higher aerodigestive tract, the thyroid and parathyroid glands. Posterior triangle the boundaries are the anterior border sternocleidomastoid, posterior stomach digastric and the superior belly of omohyoid. Muscles Digastric Vessels Nerves Viscera Other Jugular chain of lymph nodes the posterior triangle may be divided into two by the omohyoid, which varieties the lateral neck triangle and the subclavian triangle. Stylohyoid and mylohyoid Superior stomach of the omohyoid Strap muscle tissue External carotid artery and Internal and exterior laryngeal Thyroid and larynx branches (except posterior nerves auricular) Internal and anterior jugular Nerve to mylohyoid Submental and vein and tributaries submandibular glands Hypoglossal nerve Chapter 137 Surgical anatomy of the neck Table 137. It splits to enclose the trapezius, the omohyoid, sternocleidomastoid, the strap muscles and the parotid gland. The superior attachment is to the external occipital protuberance, the superior nuchal lines, the mastoid tip and the zygomatic arch. The splitting of this fascial layer around the parotid forms a deep layer, which fuses with the fascia around the internal carotid artery. The boundaries are the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid, the anterior border of the trapezius and the superior border of the inferior stomach of the omohyoid muscle. It incorporates the cervical plexus, fibrofatty tissue, lymph nodes and the accessory nerve. It incorporates 80 % of the lymph nodes of the neck, the carotid arteries, the inner jugular vein, in addition to the vagus nerve. The boundaries are the lower border of the inferior belly of omohyoid, the clavicle and the posterior border sternocleidomastoid. The contents are fibrofatty tissue, the scalene muscle tissue, the brachial plexus and the subclavian vessels, together with the thyrocervical trunk. The trapezius muscle covers the cervico-occipital region and represents the posterior neck. Movement of the hyoid and strap muscles during swallowing elevates the fascia in order that thyroid lumps characteristically move on deglutition. The deep fascia has three layers, a superficial layer, middle or visceral layer and a deep layer. This arises from the ligamentum nuchae and the spinous processes of the cervical vertebrae. It splits to enclose the postvertebral muscle tissue, passes laterally across the scalene muscular tissues after which forms a layer over the vertebrae. It forms the ground of the posterior triangles and allows the pharynx to glide throughout deglutition. Superficial cervical fascia it is a thin layer that invests the platysma muscle. Submental area it is a midline space that lies between the anterior bellies of the digastric muscle tissue. Submandibular house the superficial boundary is the submandibular gland and digastric muscle, the deep boundary is the mylohyoid muscle. It communicates with the ground of mouth around the posterior border of the mylohyoid. It communicates through the fibres of the superior constrictor with retropharyngeal and parapharyngeal spaces. It is bounded medially by the superior constrictor and laterally by the pterygoid muscles, the mandible and deep lobe of the parotid gland. The parapharyngeal area is split by the styloid process and its attachments into the prestyloid and poststyloid areas. The prestyloid area accommodates ectopic salivary tissue, whereas the poststyloid accommodates carotid arteries, inside jugular vein, cranial nerves 9�12, cervical sympathetic chain and lymph nodes. The radiological displacement sample of this fats pad is helpful for diagnosing lesions on this area. Prestyloid and lateral lesions will displace the fat posteromedially, whereas poststyloid lesions will displace this fats anteriorly. Parapharyngeal house this space is probably the most complicated and clinically most necessary area. It is shaped like an inverted pyramid, the highest of which is the base of cranium and the inferior part is Retropharyngeal space this sits between the two parapharyngeal areas and is steady with each. The posterior restrict is the prevertebral fascia and the contents are solely lymph nodes. It continues inferiorly behind the oesophagus and finally communicates with the posterior mediastinum. Pretracheal area this lies anterior and lateral to the thyroid cartilage and deep to the strap muscular tissues. Prevertebral this is the potential house that lies between the cervical vertebrae and anterior longitudinal ligament posteriorly and the prevertebral fascia anteriorly. It extends right down to the third thoracic vertebra where the fasica is sure to the vertebra. The prevetebral fascia is thin and infections in this area can rupture instantly by way of into the posterior mediastinum. The sternal head is a thick tendon, which inserts into the anterior and lateral floor of the manubrium. The clavicular head is muscular and inserts into the medial third of the clavicle. The superior attachment is attached to the lateral side of the mastoid tip, in addition to the lateral half of the superior nuchal line. The muscle is functionally two with the clavicular fibres being mainly attached to the mastoid and the sternal head to the superior nuchal line. This offers a posh motion, which tilts the top to the shoulder on the same facet, rotates the pinnacle to the opposite aspect and assists longus coli in neck flexion. The motor nerve provide is the spinal accessory motor and the anterior rami of C234 segments offers sensory and proprioceptive function. Its blood provide comes from the superior and inferior ends of the muscle with anastamoses in the middle of the muscle. The superior pedicle is from the branches of the occipital artery and the inferior pedicle is derived from the superior thyroid vessels. It has a wide origin from the medial third of the superior nuchal line, the ligamentum nuchae all the means down to the seventh cervical vertebra, and all the spinous processes and interspinal ligaments all the way down to the twelfth thoracic vertebra. The superior fibres insert into the clavicle and acromium and the inferior fibres from the thoracic vertebrae insert into the backbone of the scapular. The motion of this muscle is to rotate the scapular in order that the glenoid fossa points up. Sternocleidomastoid this is essentially the most prominent and important muscle in the neck in relation to surgical procedure so is price learning in some element.
Discount desloratadine 5 mg with mastercardThe tracheostomy tapes ought to be fastened using a safe knot on either side of the neck allergy vacuum cleaner 5 mg desloratadine free shipping, and the neck should be in a impartial position gluten allergy symptoms uk buy desloratadine 5 mg line. If the tapes are secured with the neck in extension then the tapes might be too loose and the tube may turn out to be dislodged allergy forecast jonesboro ar discount desloratadine 5mg online. After an uncomplicated procedure allergy testing tulsa desloratadine 5mg cheap, the cuff not often needs to be inflated for greater than the first 12 hours. Humidification and elimination of secretions the nostril and pharynx, under regular circumstances, are responsible for warming and humidifying the air before it Chapter one hundred seventy five Tracheostomy] 2301 Intermediate: � displacement of the tube; � surgical emphysema; � pneumothorax/pneumomediastinum; � an infection: perichondritis; � tube obstruction by secretions or crusts; � tracheal necrosis; � tracheoarterial fistula; � tracheo-oesophageal fistula; � dysphagia. Long term: � stenosis; � decannulation issues; � tracheocutaneous fistula; � disfiguring scar. Complication charges quoted within the literature vary between 4 and 31 % for percutaneous tracheostomy and between 6 and 66 p.c for surgical tracheostomy. Meticulous attention to the details of the method reduces the complication fee to nearly zero in elective noncomplicated instances carried out by an experienced team. The complication is best prevented by good surgical method and meticulous haemostasis on the time of surgery. Inexperienced operators who stray from the midline might inadvertently cause harm to the carotid artery, the oesophagus or recurrent laryngeal nerves. In sufferers with emphysema the domes of the lungs could extend into the lower neck and lateral dissection may lead to a pneumothorax. If inadequate exposure has been obtained then damage to the anterior or posterior wall of the trachea turns into more likely. If the operative area is additional obscured by poor haemostasis then injury to the cricoid or first tracheal ring are additionally extra frequent. The integrity of the cricoid ring is very important and if harm is identified on the time of surgery then the tracheostomy must be relocated decrease in the trachea and the edges of the cricoid laceration repaired. However, in an emergency tracheostomy, when the prime consideration is the establishment of an airway, scant regard is paid to haemostasis till the tube is secured in place, and under these circumstances there may be considerable bleeding. The usual sources of bleeding are the anterior thyroid vessels and the isthmus of the thyroid. Packing of the wound is widely practised in the presence of haemorrhage but must be thought to be little more than a brief lived procedure prior to re-exploration. Displacement of the tube into the pretracheal house usually goes unnnoticed because the patient continues to breath while the gentle tissues steadily prolapse around the tracheal opening which slowly seals. The affected person turns into more and more dyspnoeic, and by the time the severity of the obstruction becomes apparent the tube may be extraordinarily difficult to exchange. It is crucial that the patient is cared for by nurses who fully comprehend the potential issues and are experienced enough to establish early warning indicators. The patency of the lumen could be checked by the passage of a flexible endoscope by way of the tube to observe the distal finish throughout respiration. If the angle of the tube means that the tip is impinging on the posterior wall then the tube can be modified for certainly one of a different kind, or an extended tube may be required to bypass an space of tracheomalacia. The subcutaneous air can track up so far as the decrease eyelids and down into the higher chest. In essentially the most extreme instances the tube could become dislodged by the huge swelling, necessitating quick opening of the wound and repositioning of the tracheostomy tube. In percutaneous tracheostomy, surgical emphysema has been reported in association with posterior tracheal wall laceration. However, the incidence may be lowered if a totally hermetic seal is used following decannulation. If a fistula is the outcomes of granulation tissue then silver nitrate cautery to the granulations can effect closure of the fistula. In persistent circumstances the tract must be excised and the wound closed properly in layers. Adequate suction of secretions utilizing an aseptic method, together with enough humidification and normal wound management, ought to stop secondary an infection. A poor method with cartilage damage on the time of tracheostomy will predispose to infection and this in flip may result in perichondritis and tracheal necrosis. The primary causes of stenosis following tracheostomy are harm to the cricoid cartilage or first tracheal ring on the time of tracheostomy or injury to the tracheal wall from a poorly positioned tube which rubs against the mucosa inflicting irritation. In most cases, significantly if the initial cuffed tube has been modified for an uncuffed, fenestrated tube, there should be enough airflow across the tube to permit the patient to breath simply with the tube lumen occluded. In this case the tube can be blocked off with some form of obturator, during the daytime initially, and then for a full 24 hours, adopted by decannulation. If the patient is unable to breath around the tube then the tube can be downsized, to enable extra room for airflow around the tube, prior to the decannulation sequence. Once the tube has been eliminated the stoma have to be occluded with an airtight dressing. In most instances several gauze swabs lined with an occlusive dressing will be sufficient. It is important to change the dressing whenever an air leak turns into apparent to avoid a persistent tracheocutaneous fistula. In these cases a much slower sequence of tube occlusion ought to be followed with decannulation happening over the course of several days or an entire week. The fistula could make itself recognized if the affected person starts to aspirate meals and saliva despite the presence of a cuffed tracheostomy tube. Tracheoarterial fistulae usually current as a sudden huge haemorrhage with none premonitory signs. They occur most commonly in beforehand irradiated sufferers in whom a low tracheostomy has been carried out. The commonest vessel to be affected is the brachiocephalic artery, though there are reports of tracheocarotid fistulae. It is assumed that the fistula develops on account of mucosal necrosis secondary to stress from the elbow, cuff or tip of the tracheostomy tube. Pressure ought to be utilized to the artery via the tracheostomy, the affected person should be appropriately resuscitated and the wound should be explored to ligate the bleeding vessel. Problems from comorbidities should be considered, notably in cases of multiple trauma. The technique of tracheostomy chosen should be one in which the operator is skilled. Best medical practice [Technique should cause minimal trauma and in particular protect cartilage. � Deficiencies in present data and areas for future research $ $ $ $ What is the optimum time to carry out an elective tracheostomy in a patient requiring long-term ventilation What, if any, are the benefits of early tracheostomy in a basic intensive care unit inhabitants What are the present short- and long-term complication rates for surgical tracheostomy What are the professionals and cons of surgical and percutaneous tracheostomies as determined by a randomized, blinded, controlled and doubtless multicentre prospective trial, in really comparable teams of patients The influence of percutaneous tracheostomy on intensive care unit follow and coaching. Emergency and elective airway procedures: tracheostomy, cricothyroidotomy and their variants. Partial resection of the one remaining lung with the aid of respiratory therapy.
Lactobacillus Helveticus (Lactobacillus). Desloratadine. - Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
- How does Lactobacillus work?
- What is Lactobacillus?
- Preventing diarrhea in children caused by antibiotics or hospitalization.
- Ulcerative colitis. Some research suggests that taking a specific combination product containing lactobacillus, bifidobacteria, and streptococcus might help induce remission and prevent relapse.
- Treating diarrhea caused by the bacterium Clostridium difficile. Bacterial vaginal infections.
- Lactose intolerance.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96769
Desloratadine 5 mg with amexChapter 156 Oesophagal diseases] 2063 Presentation and management the most common symptom allergy jokes order 5 mg desloratadine visa, by far kaiser oakland allergy shots generic desloratadine 5 mg otc, is heartburn allergy forecast gilbert az cheap 5 mg desloratadine with mastercard, normally exacerbated by stooping or consuming a heavy meal allergy shots before surgery purchase desloratadine 5 mg amex. Less frequent symptoms include atypical chest pain, dysphagia and globus due to reflex oesophageal or cricopharyngeal spasm, nocturnal bronchial asthma and hoarseness of the voice because of acid overflow into the larynx, and tooth decay. Patients with a suspected prognosis of myocardial infarction might be found to have an oesophageal cause for their ache in 25 p.c of circumstances. Patients with extra persistent symptoms will current to their basic practitioner. Having excluded serious disease, the affected person should be treated medically with high-dose proton pump inhibitors as a lot as 30 mg bd lansoprazole or lansoprazole 30 mg mane and ranitidine 300 mg nocte. Severe oesophagitis may be confused with malignancy, even on biopsy, and it is suggested that rebiopsy on remedy is undertaken to make sure of the analysis. Further investigation is reserved for many who fail medical treatment, require full-dose therapy to control signs or are being thought-about for surgery. It is essential that these checks be carried out with sufferers off therapy for five days to keep away from a false negative end result. The presence of low amplitude peristalsis in the presence of reflux is of no significance for remedy. This measures the intraluminal pH over 24 hours, and with using diary cards and marking the recording, signs can be accurately associated with the pH. There is a small group of sufferers with 24-hour pH measurements in the regular vary, i. These sufferers have the so-called irritable oesophagus and current a therapeutic challenge. This will produce a adverse 24-hour pH measurement however is constructive for bile using the Bilitec probe which detects bile pigment. What is crucial to the end result is that the operation is carried out for the right reasons and by an skilled surgeon. It is accepted that repair of the crura is important as is fixation of the wrap to the gastro-oesophageal junction and or crura to forestall slippage. Dysphagia is lowered by performing the wrap and crural repair with a 48F or larger bougie within the oesophagus. Complications of this surgery embrace oesophageal perforation, dysphagia, gas bloat and chest ache. Dysphagia could also be the outcome of a slipped wrap, which is an early complication of the laparoscopic strategy and a late complication of open surgery. Late failure should be investigated by barium swallow, endoscopy and repeat 24-hour pH and manometry. The function of surgical procedure Debate exists as to the role of surgical procedure in the uncomplicated affected person. Some clinicians advocate surgery for any affected person who requires regular remedy for symptom management. They argue that this avoids long-term drug ingestion and over time is cheaper to the health economy. In one of the best hands, however, a profitable result will solely be achieved with surgical procedure � Visic 1 � in 85�90 p.c of cases. Good indications for surgery are quantity reflux, failure to respond to medical therapy with optimistic pH and manometry and confirmed oesophagitis. Reasonable indications are breakthrough signs on decreasing treatment, and strange shows of reflux with positive research. Dubious indications include the irritable oesophagus and symptoms with unfavorable research. Surgery has no function in patients with aerophagia, useful gut problems or these with main anxiousness disorders. Complications of gastro-oesophageal reflux Severe long-standing reflux may find yourself in oesophageal ulceration and stricture formation. Such ulcers could bleed and perforate and be troublesome to differentiate from cancer. Multiple biopsies and aggressive medical therapy adopted by rebiopsy are obligatory. Although many procedures are described, the operation that has stood the take a look at of time is a floppy 360 1 Nissen fundoplication. Chapter 156 Oesophagal diseases] 2065 Stricture and ulceration are good indications for elective antireflux surgical procedure when malignancy has been excluded. Young patients can be safely treated expectantly with H2R antagonists or proton pump inhibitors. The operation of choice is probably a laparoscopic 360 1 floppy Nissen fundoplication. The risk of malignant change is minimal if the epithelium is absolutely differentiated cardiac-type epithelium. Such adjustments are patchy and multiple biopsies � 4 quadrant, every centimetre are really helpful. With high-grade dysplasia, nonetheless, the prospect of an early carcinoma being discovered in the specimen is up to 50 percent. Patients with a fully differentiated epithelium want follow-up each three years, those with delicate dysplasia each six months and people with severe dysplasia, confirmed by two impartial pathologists, ought to be thought-about for extra radical therapy. Mild dysplasia should be treated by full-dose medical remedy with proton pump inhibitors and follow-up, as described, with multiple biopsies. If this reverts to fully differentiated epithelium the periods between repeat endoscopy may be extended. Some motility problems, achalasia, could be treated with a excessive diploma of success however others will reply much less nicely to therapy. It is also important to acknowledge these circumstances corresponding to visceral myopathy, which may characterize a generalized intestine failure, from others, and pseudoachalasia, which can be masking malignancy. As beforehand talked about, up to 30 % of sufferers with a diagnosis of myocardial infarction, admitted as an emergency, might be found to have an oesophageal cause for his or her ache, and motility problems account for over 50 p.c of those patients. The diagnosis is made with oesophageal manometry after exclusion of more critical conditions by endoscopy and barium research. Diffuse oesophageal spasm and nutcracker oesophagus these situations are characterised by extreme chest pain and dysphagia. They primarily involve the decrease twothirds of the oesophagus, can be related to muscle hypertrophy and with contraction pressures within the area of 400-mm mercury stress. As the signs are intermittent, ambulatory manometry could also be required to confirm the prognosis. The results of treament are typically disappointing though calcium channel blockers might present some reduction. Scleroderma There is an affiliation between scleroderma and different connective tissue problems and dysphagia and reflux. The mural fibrosis of the lower two-thirds of the oesophagus produces low-amplitude contractions and little in the best way of lower oesophageal sphincter exercise.

Buy desloratadine 5 mg amexThe involved space is best excised and repaired with both a rotation flap or free flap allergy symptoms of kidney problems cheap 5 mg desloratadine free shipping. Most now advocate radical surgical procedure for even early illness with the objective of obtaining an en-bloc clearance of the tumour allergy symptoms webmd buy cheap desloratadine 5mg on-line. Careful imaging may have demonstrated the tumour extent and facilitates transnasal debulking earlier than major radiotherapy with healing doses of 60�65 Gy delivered over six weeks allergy medicine with adderall generic 5 mg desloratadine with amex. Approximately six weeks after the completion of radiotherapy allergy treatment skin proven desloratadine 5mg, the affected person should have a deliberate craniofacial resection to embody fully any residual tumour. High high quality prosthetic rehabilitation is essential and requires the assistance of a maxillofacial laboratory. With a palatal resection, the defect have to be sealed with either an obturator fitted with tooth to restore both speech and regular deglutition or by a free composite flap utilizing microvascular strategies. Orbital resections go away an apparent cosmetic deformity and the Branemark system of titanium implants has revolutionized the becoming of facial prostheses. The choice is decided by the extent of the tumour and quantity of bone that wants to be removed. Medial maxillectomy involves the clearance of the lateral wall of the nose together with the ethmoid sinuses. Palatal resection together with the adjacent alveolus is used for tumours of the oral cavity that involve the exhausting palate. This is technically incorrect as palatal fenestration was initially described for placing radium implants into the cavity of the antrum containing tumour. It offers wonderful publicity to the nasal cavities, postnasal house, antra and pterygopalatine fossae. In selected instances, good publicity of the ethmoids is obtained, but for ethmoid malignancy the lateral rhinotomy incision gives higher publicity. The number of the operation depends on the preoperative evaluation, but usually if the palate or zygoma is involved a complete maxillectomy is indicated. In most different tumours a lateral rhinotomy or midfacial degloving approach will this entails the entire removal of the higher jaw, preferably as a bony field containing the tumour. Some feel that an oral endotracheal tube will get in the way when fabricating the prosthesis and so favor a nasal tube placed in the contralateral nostril. If the anterior fossa is opened, the affected person must be loaded with phenytoin at the time of induction and maintained on this prophylactically for three months. The maxilla is free of the cranium by osteotomies by way of the frontal process of the maxilla. The physique of the zygoma, the midline of the palate and the pterygoid plates must be freed posteriorly. The palatal osteotomy is positioned in the floor of the nasal cavity and may be made both with an oscillating or gigli saw. The pterygoid plates are finest separated from the maxilla with a curved osteotome and subsequently dissected free from the muscular tissues. The remaining bony attachments are the posterior ethmoid cells and posterior antral roof, and these break readily on mobilizing the maxilla. The remaining soft tissue attachments are freed with Mayo scissors and the maxilla removed. Bleeding from the inner maxillary artery is controlled initially by packing after which by utility of a Ligaclip. The transverse limb ought to be placed close to the lid margin to stop postoperative oedema of the decrease lid. An incision alongside the crest of the philtrum and stepped on the lip is more acceptable than a midline incision. The mucosal incision along the midline of the onerous palate turns laterally on the junction with the soft palate passing behind the maxillary tuberosity after which round the alveolus anteriorly. Following removal of the maxilla, additional tissue must be resected to ensure complete tumour clearance and promote drainage from the remaining sinuses. The ethmoid cells must be exenterated utterly and each the sphenoid and frontal sinuses opened widely. The support of the globe is complex and virtually all the medial and inferior orbital partitions could be eliminated without the eye sinking. Orbital exenteration is achieved by an extraperiosteal dissection and transection of the muscle cone at the apex with Mayo scissors. Bleeding from the ophthalmic artery could be stopped by applying local stress or bipolar coagulation. Following orbital exenteration, the eyelids are preserved but the lid margins and tarsal plates are excised to give a clean skin-lined cavity to which an onlay prosthesis can be fitted. To counter this, a gap is drilled in the zygomatic arch by way of which a wire could be handed and secured to cleats on the prosthesis. For more in depth tumours, an enbloc resection can be achieved by combining this operation with an anterior craniofacial approach. The incision is cosmetically very acceptable as it passes alongside the lateral border of the nostril to the higher edge of the alar margin. For more intensive resections, the incision may be continued into the nasal cavity with out compromising the ultimate cosmetic outcome. The upper lateral cartilage is free of the nasal bones on the pyriform opening and the soft tissue flap is elevated from the frontal wall of the maxilla and nasal bones. The orbital periosteum is elevated as for an external ethmoidectomy and the decrease a half of the lacrimal sac is exposed by nibbling away the anterior lacrimal crest. The orbital contents can then be utterly freed medially by dividing the sac low down and also by freeing the insertion of the inferior oblique tendon and trochlea by sharp dissection from the orbital rim. Access to the anterior nasal cavities could be increased by eradicating the nasal bones with little beauty defect. The first is thru the anterior wall of the maxilla simply medial to the inferior orbital foramen curving medially into the nasal cavity. Further osteotomies are made alongside the lower border of the lateral nasal wall in the inferior meatus, and throughout the ground of the orbit in the direction of the foramen of the anterior ethmoidal artery. Finally, an higher osteotomy is sustained forward via the frontal process of the maxilla and nasal bone then right down to the pyriform aperture. This frees the whole block of the lateral nasal wall and ethmoid complex, apart from their posterior attachments just in entrance of the optic and sphenopalatine foramina. In this region the bone could be very skinny and easily fractured by elevating the block medially. Virtually all of the mucosa of the nostril may be included as a cuff with the main specimen, the posterior and antral mucosal attachments being freed by scissors. The view obtained following the removal of this primary block of tissue is superb and the resection is prolonged into the sphenoid and frontal sinuses or alternatively into the pterygopalatine fossa. In explicit, they tend to give poor clearance of tumours in the region of the frontonasal duct and lacrimal sac. Similarly, more in depth involvement of the anterior fossa is healthier managed by extra conventional mixed procedures with the neurosurgeons. The applicable selection of method has been best summarized by Cheesman and Reddy33 who subclassified the craniofacial procedures into three varieties. This process is basically an prolonged medial maxillectomy using a lateral rhinotomy incision.
Discount desloratadine 5 mg with amexFirstly allergy treatment wiki desloratadine 5mg generic, diaphragmatic contraction is inhibited making simultaneous respiratory and swallowing unimaginable underneath regular circumstances allergy medicine safe while breastfeeding generic desloratadine 5mg on line. The bolus is propelled over the epiglottis by the action of the constrictors contracting in sequence allergy zucchini order desloratadine 5mg amex. It is commonly mentioned that once the bolus of meals has handed the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches then swallowing turns into reflexive allergy medicine for diabetics cheap 5mg desloratadine fast delivery. As the bolus is moved into the oropharynx, a reflex closure of the glottis is initiated during which there are preparatory actions of the vocal folds and the laryngeal inlet prior to a full closure of the larynx. Supraglottically, there needs to be approximation of the ventricular folds, tensing of the sides of the laryngeal opening and lowering of the epiglottis. Reflex closure of the glottis is initiated and apnoea onset occurs approximately zero. Laryngeal elevation also happens as the suprahyoid muscular tissues move the hyoid bone anteriorly, contributing to pharyngeal dilation. Raising the larynx narrows the laryngeal inlet and strikes it in the course of the pharyngeal floor of the epiglottis as the laryngeal cartilages move anteriorly. The interarytenoid, aryepiglottic and thyroepiglottic muscle tissue all assist to shut the margin of the laryngeal aditus within the manner of a drawstring purse. This movement is often described as occurring in two distinct levels, with the primary bringing the epiglottis from a vertical to a nearly horizontal place and the second moving the upper third of the epiglottis to below the horizontal to cover the narrowed laryngeal aditus. The precise contribution of active and passive mechanisms to this two part closure is unclear. Some authors state that both actions happen passively as a outcome of actions of adjacent buildings and forces generated by compression of the pre-epiglottic adipose fat pad, and inside the ligamentous attachments of the epiglottis, or by a combination of the 2. Early studies instructed that airway safety was further maintained by the bolus splitting after passing the base of tongue, shifting laterally by way of the pyriform sinuses and rejoining to move into the oesophagus. Recent evidence has shown that solids are inclined to go straight over the epiglottis, while liquids are diverted laterally. This is probably a characteristic of bolus properties rather than swallow biomechanics. The pharynx constricts behind the bolus as the superior constrictor muscle contracts. The bolus is carried down the pharynx by a coordinated peristaltic wave by which the three constrictor muscle tissue contract in the acceptable sequence. The bolus leaves the oropharynx and enters the laryngopharynx passing over the closed laryngeal aditus and arytenoid cartilages and getting into the pyriform fossae within the decrease part of the laryngopharynx. In common with all complex motor behaviours, swallowing is organized and coordinated by a hierarchical sequence of constructions within the brain. This extends from the motor neurones throughout the motor nuclei of the brainstem up to the cortex. The act of swallowing is regulated by sensory suggestions, though the significance of this has only been totally acknowledged just lately. The initiation of swallowing can either be as a voluntary act or a reflex as the outcome of stimulation of the appropriate mucosa in the oral cavity. This emphasizes the truth that as swallowing is partly a reflex activity and partly voluntary, its neural management is split between two main regions of the mind: the cerebral cortex and the brainstem. Studies have shown that several areas of the cortex contribute to the voluntary management of swallowing. The voluntary initiation of swallowing involves bilateral areas of the prefrontal, frontal and parietal cortices. Stimulation right here produces swallowing exercise in the acceptable muscle tissue of the oral cavity, pharynx, palate and larynx. Cortical projections to the muscles of the larynx, pharynx, palate and upper face are bilateral while projections to different muscle tissue may be unilateral or bilateral. This is substantiated by research using transcranial magnetic stimulation of the frontal swallowing centre. The pharyngeal and oesophageal phases of swallowing are controlled from more rostromedial areas of the cortex within the anterior inferior and center frontal gyri. In most individuals, swallowing management is asymmetrical with the projection from one hemisphere being bigger than the other, unbiased of handedness. It has been hypothesized that this explains both the prevalence of swallowing Oesophageal part the cricopharyngeus relaxes and the anterior superior motion of the laryngohyoid complex acts to open the upper oesophageal sphincter. The bolus passes by way of the sphincter and strikes alongside the oesophagus by peristalsis. Recovery then occurs because the intact projection from the undamaged hemisphere is reorganized. There are essential areas within the brainstem essential for the management of swallowing and these are located significantly throughout the medulla. Descending pathways project to these medullary swallowing centres from the frontal swallowing areas inside the cortex. These most likely include pathways in each the dorsolateral and ventromedial descending systems through the ventral and lateral corticobulbar tracts. Within the medulla there are a variety of neurone groups involved within the control of swallowing. Swallowing is initiated by contact sensation or strain from the liquid or food throughout the posterior part of the oral cavity, epiglottis or oropharynx. Thus the nuclei receiving afferent enter from these regions, which embody the nucleus tractus solitarius and the spinal trigeminal nucleus, are very important. Afferent input from the jaw, muscular tissues of mastication, lips and tongue can be important to the control of swallowing. These shield delicate tissues from the high forces generated during mastication, to trigger the reflex and to sense the scale and consistency of the bolus, additionally as part of the set off mechanism. The efferent pathways from the medulla and pons to the muscles involved in swallowing involve a quantity of cranial motor nuclei. The most essential are the nucleus ambiguus for the muscles of the palate, pharynx and larynx, the hypoglossal nucleus for the muscles of the tongue and the motor nuclei of the trigeminal and facial nerves for the muscle tissue of the jaws and lips. In addition, motor neurones inside the cervical spinal wire management the muscle tissue of the neck including the infrahyoid. Between these input and output pathways are interposed two main groups of neurones that appear to be important for the coordination and regulation of swallowing by the medulla. The first lies within the dorsal region of the medulla above the nucleus of the solitary tract. These two neuronal groups are typically referred to as the lateral and medial medullary swallowing centres. A variety of proof, much of it emanating from the laboratory of Jean,21 supports the view that these two neuronal teams are vital within the management of swallowing. The dorsal group would appear to be the site of convergence of sensory enter from the various nuclei and is probably essential in the sequencing of swallowing. In any reflex system, excitation of agonist muscular tissues and their synergists might be accompanied by inhibitory outputs to the corresponding antagonist muscle tissue.
Purchase 5 mg desloratadine visaThe Repose tongue base suspension suture supplies another attention-grabbing alternative for rising the size of the retrolingual house with relatively low morbidity however allergy forecast houston texas generic desloratadine 5mg with visa, again allergy medicine linked to alzheimer's buy discount desloratadine 5 mg, no comparative research can be found within the literature allergy medicine for 18 month old discount desloratadine 5 mg fast delivery. Planned tracheostomies are indicated for tongue base procedures corresponding to genioglossus development or laser midline glossectomy allergy testing raleigh buy desloratadine 5 mg mastercard. A large multicentre research comparing problems of the three most regularly performed procedure can be useful. Radiofrequency ablation appears to be related to significantly much less postoperative pain, making it rather more appropriate as an outpatient or day-case procedure. Similar to other therapies, results deteriorate with time and in one collection success deteriorated from seventy two to 52 p.c in a mean of 14 months. It was postulated that adjustments in overbite could probably be lessened by preserving chunk opening to a minimum. Ideally, the location of obstruction must be assessed throughout normal physiological sleep and then additional analysis to develop an appropriate approach is required. From a surgical viewpoint the three primary palatal procedures produce pretty comparable results that every one deteriorate with time. Radiofrequency tissue quantity reduction appears at present to be the choice with least morbidity though the outcomes could additionally be slightly less good and the benefits might decline extra rapidly than the opposite two procedures. Reduced nasal cross-sectional space promotes increased nasal resistance to airflow and promotes inspiratory collapse of both the oro- and hypopharynx. Concerns have been raised about each the usage of opioids, because of the chance of sedation and respiratory depression, particularly in sufferers with obstructive sleep apnoea and using nonsteroidal antiinflammatory medication, on account of the chance of bleeding. However, certainly one of them or a mixture of each is required in more than forty percent of patients; the whole dosage may be minimized by giving it as a steady infusion. The outcomes of palatal surgical procedure for loud night time breathing are all pretty related and all deteriorate over time. With acceptable becoming to reduce chunk opening, ache and modifications in dental occlusion could be avoided. Recently, improved definitions and higher monitoring techniques have allowed for clearer definitions of the syndromes inside this spectrum. The operator then examines the upper aerodigestive tract, within the supine place with a nasendoscope, to determine the level(s) of obstruction. It is related to a big profile of complications, which are being increasingly regarded as unacceptable. The specific problems embrace extreme postoperative ache, haemorrhage (2�14 percent), respiratory events corresponding to airways obstruction as a result of laryngospasm, postoperative pulmonary oedema and hypoxia (2�11 percent), nasal Chapter 178 the surgical administration of snoring] 2335 Best clinical practice [Detailed clinical evaluation of loud night breathing sufferers by historical past, physical examination, physique mass index and Epworth sleepiness score can be utilized to display screen out nonapnoeic snorers with a sensitivity of ninety three % and specificity of 60 % and thus prioritize additional investigations. A comparability of sleep nasendoscopy with continous pharyngeal and oesophageal pressure manometry during sleep. Alcohol ingestion influences nocturnal cardiorespiratory exercise in loud night breathing and non loud night breathing males. Risk components associated with habitual snoring and sleep disordered inhaling a multi-ethnic Asian population: a population based mostly study. Interaction of sleep disturbances, gastrooesophageal reflux and persistent laryngitis. The position of history, Epworth sleepiness score and body mass index in figuring out non apneic snorers. A medical decision rule to prioritise polysomnography in sufferers with obstructive sleep apnoea. Omission of polysomnography in widespread snoring: widespread causes and medico-legal implications. Sleep nasendoscopy: a way of evaluation in snoringand obstructive sleep apnoea. Sedation with a target controlled propafol infusion system throughout evaluation of the upper airway in snorers. A grading system for sufferers with obstructive sleep apnoea � primarily based on sleep nasendoscopy. The worth of sedation nasendoscopy: A comparison between snoring and non-snoring sufferers. Validity of sleep nasendoscopy in the investigation of sleep related respiration problems. Quantitative pc assisted digital imaging higher airway analysis for obstructive sleep apnoea. Use of three-dimensional computed tomography scan to consider airway patency for patients present process sleep disordered breathing surgery. Simple predictors of uvulopalatopharyngoplasty end result in the treatment of obstructive sleep apnoea. Patients notion of facial look after maxillomandibular advancement for obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. � � � Chapter 178 the surgical administration of loud night breathing Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. Postoperative pain and side effects after laser-assisted uvulopharyngoplasty, laser assisted uvulopalatoplasty, and radiofrequency tissue quantity reduction in primary snoring. Resolution of severe sleepdisordered respiration with a nasopharyngeal obturator in two cases of nasopharyngeal stenosis complicating uvulopalatopharyngoplasty. Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty changes elementary frequency of the voice � a potential study. Retrospective survey of long term outcomes and affected person satisfaction with uvulopalatopharyngoplasty for snoring. A randomized trial of laser assisted uvulopalatoplasty in the treatment of mild obstructive sleep apnoea. Multilevel temperature managed radiofrequency therapy of palate base of tongue and tonsils in adults with obstructive sleep apnoea. Complications of temperature-controlled radiofrequency volumetric tissue reduction for sleep-disordered respiration. Voice high quality after radiofrequency volumetric tissue discount the taste bud in habitual snorers. The effect of unilateral and bilateral nasal obstruction on snoring and sleep apnea. Polysomnographic effects of nasal surgical procedure for snoring and obstructive sleep apnea. Therapeutic electrical stimulation of the hypoglossal nerve in obstructive sleep apnea. The long run evaluation of tracheostomy within the administration of obstructive sleep apnea. Temporary tracheostomy in the surgical remedy of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: personal expertise.
References - Houghton J, Stoicov C, Nomura S, et al. Gastric cancer originating from bone marrow-derived cells. Science 2004;306:1568.
- Castaneda - Zuniga WR, Formanek A, et al. The mechanism of balloon angioplasty. Radiology 1980; 135:565.
- Salim A, Brown C, Inaba K, et al. Improving consent rates for organ donation: the effect of an inhouse coordinator program. J Trauma. 2007;62:1411-1414; discussion 1414-1415.
- Wizemann TM, Pardue M-L, editors: Exploring the biological contributions to human health: does sex matter? Washington, DC, April 25, 2001, Institute of Medicine Board of Health Sciences Policy. 18.
- Hebert AA, Friedlander SF, Allen DB. Topical fluticasone propionate lotion does not cause HPA axis suppression. J Pediatr 2006;149:378-82.
- Duthie HL, Moore TH, Bardsley D, et al: Surgical treatment of gastric ulcers. Controlled comparison of Billroth-I gastrectomy and vagotomy and pyloroplasty. Br J Surg 57:784, 1970.
- Bapat VN, Varma GG, Hordikar AA, Sivaraman A, Agrawal NB, Tendolkar AG. Right-ventricular fibroma presenting as tricuspid stenosis-a case report. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1996;44:152-154.
|