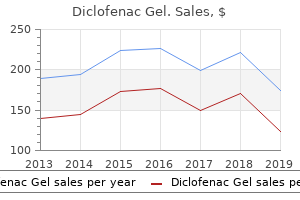
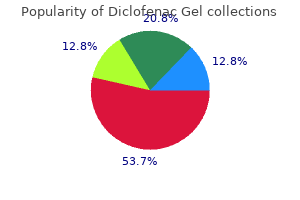
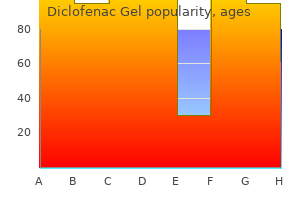
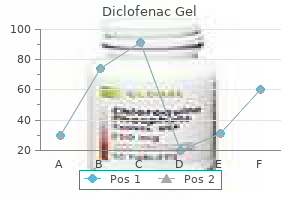
Diclofenac Gel
Thomas W. Sadler, Ph.D. - Senior Genetics Scholar
- Greenwood Genetic Center
- Greenwood, South Carolina
Cheap 20gm diclofenac gel visaOutdoor staff are most often affected and lesions seen on sun-exposed pores and skin are sometimes accompanied by the features of solar elastosis rheumatoid arthritis x ray findings mnemonic purchase diclofenac gel 20 gm with mastercard, giving rise to the synonym of papular elastosis arthritis osteoporosis diet discount diclofenac gel 20gm on line. Juvenile colloid milium: the amorphous materials that characterizes this situation is of epidermal derivation arthritis pain medication names order diclofenac gel 20 gm with amex. Further help for this speculation is given by the identification of serum amyloid p element inside the colloid deposits arthritis knee leg swelling safe diclofenac gel 20gm. Induration of the oral mucosa (including the inner side of the lips, the gingivae, uvula, palate, and flooring of the mouth) begins in childhood and is progressive, so that adults have extensive yellow infiltration. Pathogenesis and histological options the dermis is acanthotic and occasionally papillomatous, with overlying hyperkeratosis. Intracytoplasmic inclusions, probably lysosomal in nature, have also been described. It describes subcorneal and intraepidermal acantholysis with out dyskeratosis in a child with lipoid proteinosis. Despite considerable analysis, the precise pathogenesis of lipoid proteinosis remains an enigma. Subacute or persistent pores and skin involvement consists of pores and skin fragility, blister formation, and progressive scarring. In the hepatic porphyrias the altered synthesis primarily occurs within the liver (porphyria cutanea tarda, hepatoerythropoeitic porphyria, acute intermittent porphyria, aminolevulinic acid (aLa) dehydratase deficiency, variegate porphyria, and hereditary coproporphyria). Of the eight main forms of porphyria, six are related to cutaneous illness (Table 13. Fewer than 20% of affected individuals display symptoms and patients often deny a family historical past. Uroporphyrin I accumulates within the bone marrow, peripheral blood, and other organs. Porphyria affected sufferers develop intense photosensitivity to sunlight in addition to to fluorescent mild, sometimes in infancy. Symptoms include painful and pruritic erythema and swelling which happens inside minutes of solar publicity. In addition, sufferers develop cicatricial alopecia of the scalp, nail modifications, conjunctivitis, ectropion, keratoconjunctivitis, symblepharon, blepharitis, or brown staining of the tooth (erythrodontia). By far the most typical mutation is C73r, which has been present in up to 40% of patients with the illness. It results from increased manufacturing of protoporphyrin due to diminished ferrochelatase (heme synthase) exercise. Porphyria with jaundice, severe persistent hemolytic anemia beginning within the neonatal period, hepatosplenomegaly, and photosensitivity. Up to 80% of sufferers with porphyria cutanea tarda have the sporadic form of the illness. It has been demonstrated that sporadic porphyria cutanea tarda is a multifactorial dysfunction involving a combination of genetic and environmental components. Iron catalyzes the formation of reactive oxygen species and this may enhance uroporphyrin formation by growing the speed at which uroporphyrinogen is oxidized to uroporphyrin, resulting in the manifestations of the illness. Whatever the mechanism, the iron overload has necessary therapeutic implications as venesection can induce a remission. Hereditary coproporphyria Clinical features this very rare autosomal dominant form of porphyria develops because of a deficiency of coproporphyrinogen oxidase. Biochemical evidence of liver involvement is common, but clinical manifestations are uncommon. Hepatoerythropoietic porphyria Clinical features hepatoerythropoietic porphyria is very rare and, in fact, represents the homozygous form of familial porphyria cutanea tarda. Variegate porphyria is associated with diminished exercise of protoporphyrinogen oxidase, the penultimate enzyme within the heme biosynthetic pathway. In mild illness the deposits are delicate and are often limited to the papillary dermal capillaries, but in additional extreme instances the deposits are widespread, happen more deeply within the dermis, and give the vessel walls a attribute. In addition, finely fibrillar materials is usually present both across the vessels and on the epidermal basement membrane area. Neutrophil polymorphs exhibiting leukocytoclasis have been described in acute lesions of erythropoietic protoporphyria and purple cell extravasation is usually evident. Most usually, nevertheless, as proven by antigen mapping experiments, blistering commences in the lamina lucida. Ultrastructural studies suggest that these bodies symbolize a mix of degenerating keratinocytes, colloid bodies, and basement membrane fragments fashioned by repeated blistering and re-epithelialization. Its distinction from the dermal modifications of scleroderma may be very tough, but it has been said that the texture of the collagen bundles is somewhat looser in porphyria. Centrofacial papular lymphangiectasis is characterised by the presence of dilated lymphatics in the superficial dermis. Direct immunofluorescence reveals Ig (usually IgG, IgM, and generally Iga) with C3 around the superficial vasculature in a donut distribution and as a nice granular deposit on the epidermal basement membrane region. On electron microscopic examination, the plane of cleavage is variable: in some it has been proven to be inside the lamina lucida, whereas in others it has been deep to the lamina densa. More recent genome-wide affiliation studies have quickly expanded the knowledge of different genetic defects answerable for the disease. Many patients current initially with acute irritation of the primary metatarsophalangeal joint (podagra). More generally, in primary gout, renal stones are a function, and persistent urate nephropathy (due to deposition of monosodium urate monohydrate salt crystals within the interstitial tissues of the kidney), presenting as gentle proteinuria and hypertension, often develops. In secondarily infected lesions, a neutrophil polymorph infiltrate is typically present. Exogenous ochronosis Clinical options Deposition in the pores and skin of an identical pigment to that seen in alkaptonuria may occur on account of the appliance of phenol (carbolic acid) to leg ulcers, therapy with resorcinol and picric acid, the oral and intramuscular administration of antimalarials such as chloroquine, and the applying to dark pores and skin of bleaching lotions containing hydroquinone, most frequently in black women. In addition to inflicting ochronosis, hydroquinones containing bleaching creams have been shown to be carcinogenic in rodents. Spinal involvement leads to disc herniation, spondylosis, and osteophytosis with resultant limitation of motion and loss of peak. Cardiovascular involvement happens in as a lot as 50% of patients and mainly consists of pigmentation and calcification of the aortic valve, which may lead to stenosis. Ochronotic pigmentation is regularly seen within the hyaline cartilage of the larynx, trachea, and bronchi. The lesions developed as a consequence of the appliance of hydroquinone bleaching cream. Pellagra the pigment shaped has not been characterized but there are some similarities to melanin. With chronicity, massive amorphous eosinophilic granules might develop, resembling colloid milium. Hartnup disease Clinical options hartnup disease is an autosomal recessive disorder characterised by faulty gastrointestinal absorption and renal reabsorption of monoamine and monocarboxylic amino acids because of a defect in the impartial brush border system. In addition to a pellagra eruption (see below), sufferers even have a characteristic aminoaciduria and cerebellar ataxia. Pellagra Clinical options pellagra develops as a consequence of deficiency of nicotinic acid (niacin, vitamin B3) or its precursor tryptophan. Other options generally present include cheilosis, glossitis, angular stomatitis, and oral or perianal sores.
Cheap 20 gm diclofenac gel with amexAfter needle puncture rheumatoid arthritis onset buy discount diclofenac gel 20gm line, the free circulate of fluid from the syringe will expel tissue that may have clogged the needle and can confirm that the tip of the needle is in the proper place and never lodged within the uterine wall or the intestinal wall crippling arthritis definition generic diclofenac gel 20gm free shipping. Use saline rather than air as a outcome of if air is used arthritis compression gloves diclofenac gel 20gm with visa, it could be difficult to interpret the presence of free peritoneal air on subsequent radiographs can you have arthritis in your neck buy diclofenac gel 20 gm amex. To avoid the necessity to change the syringe through the procedure, use 1% lidocaine for both anesthesia and affirmation of correct needle place- ment; nonetheless, the bacteriostatic property of this agent precludes its use if the procedure is performed to get hold of fluid for culture. Avoid aspirating any blood that has accumulated within the vagina from previous needle punctures or from cervical bleeding because this will give the misunderstanding of a optimistic tap. Bleeding from the puncture website in the vaginal wall can be minimized by adding epinephrine to the local anesthetic. Blood or fluid could additionally be obtained immediately but can also be obtained when the needle is withdrawn from the peritoneal cavity. Therefore it may be very important aspirate repeatedly whereas steadily withdrawing the needle. If no fluid is aspirated, reintroduce the needle and direct it solely slightly to the left or proper of the midline. Directing the needle too far laterally might end in puncture of the mesenteric or pelvic vessels. Some physicians favor the usage of a 19-gauge butterfly needle held with ring forceps. An assistant must aspirate the tubing while the physician controls positioning and withdrawal of the needle. Interpretation of Results Interpretation of the results of culdocentesis depends totally on whether or not any fluid was obtained. It ought to be noted that in the absence of a pathologic condition, 2 to three ml of clear yellowish peritoneal fluid could be aspirated. In addition, when lower than 2 ml of clotting blood is obtained, that is additionally considered to be a nondiagnostic faucet as a end result of the source of this small amount of blood will be the puncture web site on the vaginal wall. Brenner and colleagues14 reported no blood from culdocentesis in 5% of patients with confirmed ectopic pregnancies even when rupture had occurred. In the sequence of sixty one sufferers with surgically confirmed ectopic being pregnant reported by Cartwright and associates,15 culdocentesis carried out inside 4 hours of surgery was optimistic in 70%, adverse in 10%, and insufficient in 20%. Insert a bivalve pelvic speculum and open it broadly by using each the height (A) and angle (B) thumbscrews. Swab the vaginal wall within the space of the rectouterine pouch with antiseptic adopted by a small quantity of sterile water. Administer a local anesthetic with a separate 25- or 27-gauge needle or with the needle that might be used for culdocentesis. The website of needle entry is 1 cm posterior to the point at which the vaginal wall joins the cervix (x). Free move of fluid will affirm correct needle placement in the rectouterine pouch. This method presents a built-in guide to needle depth and allows good control of the needle during puncture. Use the assistance of an assistant to aspirate whilst you management needle place and withdrawal. They outlined a positive tap as nonclotting blood with a hematocrit of larger than 15%. When culdocentesis is used to diagnose a ruptured ectopic being pregnant, a "negative faucet" is one which yields pus or clear, straw-colored peritoneal or cystic fluid. A great amount of clear fluid (>10 ml) indicates a probable ruptured ovarian cyst, aspiration of an intact corpus luteal cyst, ascites, or possibly carcinoma. The significance of this fluid and interpretation of the results are outlined in Table fifty seven. Intraperitoneal blood from any source (ectopic being pregnant, ovarian cyst, ruptured spleen) might stay unclotted after aspiration for days within the syringe because of the defibrination exercise of the peritoneum. In one series, the hematocrit of blood from a ruptured ectopic pregnancy was 15% or greater in 97% of circumstances. Complications Culdocentesis is probably certainly one of the most secure procedures carried out in the emergency setting, and there are in all probability fewer issues with this method than with peripheral venous cannulation. Because the most typical problems end result from puncture of a pelvic mass, careful bimanual examination of the patient should assist forestall this drawback. Occasionally, one will aspirate air or fecal matter, thereby confirming inadvertent puncture of the rectum. Isoardi K: review article: the use of pelvic examination throughout the emergency department within the evaluation of early being pregnant bleeding. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: suggestions for the laboratory-Based Detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae � 2014. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines 2015: Bacterial Vaginosis. Hjelm D, Hallen A, Domeika M: Cervical, urine and vaginal specimens for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis by lignase chain reaction in ladies: a comparability. Ellis H, editor: Clinical Anatomy: A Revision and Applied Anatomy for Clinical Students, ed 5, Oxford, 1972, Blackwell Scientific, p 129. In Kistner rW, editor: Gynecology: Principles and Practice, ed 2, Chicago, 1971, 12 months Book Medical, p 304. Durham B, lane B, Burbridge l, et al: Pelvic ultrasound performed by emergency physicians for the detection of ectopic pregnancy in sophisticated first trimester pregnancies. Elliot M, riccio J, Abbott J: Serous culdocentesis in ectopic pregnancy: a report of two instances brought on by co-existent corpus luteum cysts. Clinicians must be acquainted with local documents before performing a sexual assault examination. Careful step-by-step planning and using written protocols guarantee one of the best care for victims and aids within the prosecution of assailants and the exoneration of wrongly accused subjects. If medically and logistically potential, interviews should be carried out in a private room separate from the examination room. A guidelines of local requirements for sexual assault examination should be included within the kits and serves as a reminder for all the required medicolegal procedures to be accomplished. Although this chapter is devoted primarily to the evaluation of grownup feminine sexual assault sufferers, guidelines for the evaluation of grownup male sexual assault patients, feminine child sufferers, male child sufferers, and accused assailants are supplied in separate sections of this chapter. The same examiners designated to carry out adult feminine examinations could simply carry out male victim and assailant examinations; however, examination of a child sexual assault patient often requires appreciable experience and coaching. When potential, medical workers with specialized coaching in the examination of child sexual assault patients ought to carry out these examinations. Federal laws ensures all victims the best to a forensic examination and remedy of sexual assault regardless of their cooperation with authorized investigation or their desire to initially pursue prosecution. Coercion into sexual contact by intimidation, threats, or fear also defines sexual assault. State laws differ slightly on the definition of exact acts that constitute sexual contact and on which populations are unable to give authorized consent.
Diclofenac Gel: 20 gm
Generic 20gm diclofenac gelPathogenesis and histological options the disorder has been mapped to chromosome 8p22�23 with some genetic heterogeneity arthritis diet primal blueprint discount diclofenac gel 20gm online, but a causative gene has not yet been recognized arthritis bra 20gm diclofenac gel overnight delivery. Further features are inflammatory borders rheumatoid arthritis onset purchase diclofenac gel 20 gm with amex, extreme hyperhidrosis arthritis medication etodolac buy diclofenac gel 20 gm overnight delivery, maceration, and ugly smell. In addition, constricting bands (pseudoainhum), brachydactyly, nail dystrophy, lesions on knees and elbows, the perioral area and even oral leukokeratosis can be noticed. Pathogenesis and histological options Striate palmoplantar keratoderma is a heterogeneous condition. Dark-staining granular and filamentous materials inside the prickle cell layer accompanied by slight separation of the keratinocytes has also been described. Palmoplantar keratoderma eighty one Pathogenesis and histological features the gene defect has not been identified as yet. Lesions are usually asymptomatic, however sometimes pain, tenderness or burning are options. Keratosis punctata of the palmar creases Clinical features Keratosis punctata of the palmar creases (keratotic pits of the palmar creases) is a variant of punctate keratoderma by which the lesions are confined to the palmar and digital creases. Marginal papular acrokeratoderma Clinical options Marginal papular acrokeratoderma refers to a fancy, complicated, and overlapping group of issues which incorporates acrokeratoelastoidosis of Costa, focal acral hyperkeratosis, mosaic acral keratosis, degenerate collagenous plaques of the palms, digital papular calcific elastosis, and keratoelastoidosis marginalis of the palms. Focal acral hyperkeratosis is clinically identical to acrokeratoelastoidosis, patients presenting with keratotic papules along the perimeters of the arms, fingers, and toes. Keratoelastoidosis marginalis of the hands is an identical condition described in australians by which keratotic papules develop at sites of trauma alongside the index finger and thumb. Calcified variants of degenerative collagenous plaques are often identified as digital papular calcific elastosis. In huriez syndrome (keratosis palmoplantaris diffuse with sclerodactyly, sclerothylosis) patients current with a diffuse delicate palmoplantar keratoderma, scleroatrophic skin of the limbs, hypohidrosis, hypoplasia, and dystrophy of the nails. It has an early onset with a high risk of metastasis in the third to fourth many years. Most apparently, immunohistochemical and ultrastructural research revealed an absence of Langerhans cells in concerned skin. Other characteristics are starfish-like keratoses affecting the dorsal surfaces of the arms, ft, wrists, forearms, elbows. Pathogenesis and histologic features Mutations on chromosome 1q21 that result in aberrant, elongated C-terminal domains of 1 loricrin allele could lead to an irregular loricrin expression, and impairment of cross-linking to itself and different cornified envelope proteins. Nail dystrophy is commonly predominant, however hair defects and palmoplantar keratoderma are additionally found. Scalp alopecia (from hair thinning to full baldness) is the rule, and facial, axillary, and pubic hair is often sparse or totally absent. Scattered cells (on the proper aspect of the field) show perinuclear vacuolization and the parakeratotic keratinocytes in the decrease horny layer characterize transitional cells. Pathogenesis and histological features the gene responsible for this situation has been mapped to 13q11� 12. Lesions are often fissured and extremely painful, making strolling exceedingly tough or inconceivable. Superinfection with bacteria and fungi, particularly Candida albicans, contributes to the issues and as a result lesions are frequently very malodorous. It is characterized by symmetrical and marked palmoplantar keratoderma generally affecting the dorsal aspects of the arms and toes. Growth retardation, laxity of the big joints, and corneal involvement are occasional manifestations. Histological options the plaques are characterized by large hyperkeratosis, often with foci of vertically orientated parakeratosis. This patient is a 12-year-old child, however the severity of the periodontal destruction is what could be expected in an individual aged 60 years. Desmosomes, notably in the lower suprabasal layers, are small and lowered in quantity. It is characterised by restricted and normally gentle focal Pachyonychia congenita kind I Clinical features Focal (nonepidermolytic) palmoplantar keratoderma with oral hyperkeratosis (Jadassohn-Lewandowsky syndrome, focal palmoplantar keratoderma with oral hyperkeratosis, palmoplantar ectodermal dysplasia type I) is usually associated with an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance although an autosomal recessive variant has been described. Pathogenesis and histological features this variant of focal palmoplantar keratoderma is heterogeneous. Although the nail plate seems to be thickened, a lot of the modifications are, in fact, due to massive hyperkeratosis of the nail mattress, resulting in elevation and bending of the nail plate; (B) on this view, the subungual hyperkeratosis is more obvious. Later painful punctuate, sometimes striated and circumscribed hyperkeratoses of digits, palms, and soles evolve, typically accompanied by hyperhidrosis. Clinical and biochemical improvement could additionally be achieved by a low phenylalanine-low tyrosine diet. Carvajal-Huerta syndrome Clinical options the Carvajal-huerta syndrome is an autosomal recessively inherited illness with palmoplantar keratoderma, woolly hair, and dilated cardiomyopathy. In these patients, dilatation of the left ventricle, along with alterations in muscle contractility, could lead to congestive coronary heart failure and demise. Pathogenesis and histological features Mutations within the gene on chromosome 6p24 encoding desmoplakin have been found. Pathogenesis and histological options the situation has been mapped to 17q23-qter region (teC locus) distal to the keratin gene cluster, thereby excluding a keratin gene mutation. Clavus Clavi (corns) are extremely common painful keratotic lesions that develop on the dorsal or lateral side of the toes, usually as a consequence of ill-fitting sneakers. Multiple eccrine syringofibroadenomas and squamous cell carcinomas may come up on the acral surfaces in older patients. Acquired palmoplantar keratoderma and inside malignancy acquired diffuse palmoplantar keratoderma might symbolize a paraneoplastic phenomenon related to a number of internal malignancies including carcinoma of the bronchus, esophagus, abdomen, urinary bladder, and myeloma. Differential diagnosis acrokeratosis verruciformis-like features might sometimes be seen in linear epidermal nevi. It consists of a pigmented or reddish atrophic center bordered by a peripheral grooved keratotic ridge, from the center of which a keratotic core (cornoid lamella) initiatives at an obtuse angle. It often � � presents in maturity as persistent lesions that are extremely resistant to remedy. Disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis: on this variant, the lesions are small and discrete. While they might contain the follicle, their most common origin is from nonadnexal epithelium. The dermis in the course of the center on the lesion appears atrophic and the papillary dermis incorporates ectatic blood vessels. Liquefactive degeneration of the basal cell layer of the epithelium is sometimes present and infrequently there are conspicuous cytoid bodies. In the dermis, a non-specific chronic inflammatory cell infiltrate and telangiectatic vessels are generally seen. Cornoid lamella formation, nevertheless, does happen as a non-specific finding in a variety of situations together with psoriasis vulgaris, seborrheic, photo voltaic keratosis, verruca vulgaris, and squamous cell and basal cell carcinomas. It is characterized by a very protracted course, many patients having lesions for many years. Characteristically, removal of the dimensions is associated with pinpoint bleeding, a characteristic that distinguishes this dysfunction from stucco keratoses. Note the cytoid bodies markers such as cytokeratin 1 and 10, filaggrin, and loricrin are absent.
Discount 20gm diclofenac gel free shippingA B external chemical zeel rheumatoid arthritis purchase 20 gm diclofenac gel overnight delivery, bodily arthritis foundation 20 gm diclofenac gel overnight delivery, and biological agents may play a role in the improvement of conjunctival tumors arthritis herbs buy diclofenac gel 20gm online. Neoplasms originating within the eyeball arthritis in feet young age purchase diclofenac gel 20 gm fast delivery, eyelid or orbit, as well as metastases from distant tumors, may invade the conjunctiva. Examination Because the conjunctiva is readily seen, tumors on the ocular surface are usually recognized and recognized at an early stage. Because many of these lesions have attribute clinical options, an experienced ophthalmologist can usually make an correct prognosis by clinical examination alone. Since evaluating conjunctival lesions underneath the diffuse lighting of an operating microscope may be tough, the extent of conjunctival and corneal involvement must be accurately documented by slit-lamp examination previous to therapy. Fluorescein or rose Bengal stains can be utilized to delineate irregular epithelium and tumor margins, especially when lesions are diffuse. Conjunctival lesions ought to be photographed externally or through a slit lamp to precisely document the tumors and their margins. Conjunctival lesions that adhere to the sclera might point out scarring or malignancy. If malignancy is suspected, the preauricular and submandibular areas have to be palpated for enlarged lymph nodes to check for regional metastases. For giant conjunctival lesions, fully removing the tumor can severely compromise the ocular surface, or it could be unimaginable to totally excise the lesion; in such cases, an incisional biopsy is warranted. Incisional biopsy can be acceptable if the tumor is to be handled with radiotherapy, chemotherapy or local means such as cryotherapy or topical chemotherapy. Some tumors have subtypes that, regardless of having identical histogeneses, present or behave differently due to special histological buildings, options or locations. Other conjunctival tumors arise primarily from the vascular, fibrous, neural, histiocytic, myogenic, myxoid, lipomatous or lymphoid tissues in the conjunctival stroma. In this chapter, the classification of conjunctival and corneal tumors is based on the second edition of the World well being Organization International histological Classification of tumors. Differential analysis In the scientific differential analysis of conjunctival tumors, the gross characteristics of the lesion have to be considered along with clinicopathological correlation. Conjunctival tumors are normally categorised as being melanocytic or nonmelanocytic on the premise of the scientific presence or absence of brown� black pigmentation and histological evidence of melanocytes; however, nonmelanocytic tumors can additionally be pigmented. While melanoses are superficial�epithelial, nevi and melanoma also can contain the stroma. In bulbar conjunctival melanosis, the lesions are movable with the conjunctiva; in melanoma, the lesions are often mounted. Most nonmelanocytic tumors are epithelial and are located on the floor of the conjunctiva. Stromal tumors, including metastases in the stroma, usually have easy surfaces. Benign epithelial tumors Congenital epibulbar tumors identified in infancy and childhood are often hamartomas or choristomas. Caruncular lesions current a special challenge within the differential prognosis of conjunctival and cutaneous tumors. When tumors unfold from surrounding constructions into the conjunctiva, the first tumor is often recognized besides in lots of circumstances of pagetoid unfold of sebaceous gland carcinoma of the eyelid, which may originate within the conjunctiva itself. Conjunctival squamous papilloma often occurs in the inferior fornix or bulbar conjunctiva but could present in any part of the conjunctiva, including the palpebral conjunctiva, lid margin, caruncle, and plica semilunaris. In adults, conjunctival squamous papilloma is usually single and unilateral, generally arising near the limbus or bulbar conjunctiva. Conjunctival squamous papilloma is generally broad-based and flat and may become massive, masking a lot of the conjunctiva; occasionally, a lesion covers the cornea and interferes with imaginative and prescient. Differentiating such lesions clinically from squamous cell carcinoma may be difficult. Conjunctival squamous papillomas are normally nonkeratinized; however, average keratinization typically occurs. Benign epithelial tumors irregular mobile proliferation and differentiation confined to the conjunctival epithelium could cause thickening, papillary or nodular focal elevation of the conjunctiva, or plaquelike opacification (leukoplakia). Inverted papilloma Clinical features Inverted papillomas are exceedingly uncommon, solid or cystic solitary nodules that occur within the limbus, plica semilunaris, and tarsal conjunctiva. Pathogenesis and histological options histologically, lobules of proliferating nonkeratinized, noninflamed epithelial cells invaginate underlying connective tissue. It is characterized by bilateral elevated fleshy plaques surrounded by dilated conjunctival vessels on the nasal or temporal perilimbic bulbar conjunctiva and causes the eye to seem pink. Clinically and histologically, reactive epithelial hyperplasia could also be troublesome to differentiate from conjunctival squamous cell carcinoma. Dacryoadenoma Clinical features Dacryoadenoma, an exceedingly rare conjunctival tumor that happens in children and younger adults, is a translucent pink lesion that occurs within the bulbar, forniceal or palpebral conjunctiva. Histological options histologically, the lesion shows marked invasive acanthotic epithelium with keratin-filled pseudocysts, hyperkeratosis, and parakeratosis. Histological options histologically, dacryoadenoma is a proliferation of benign epithelioid cells that kind glandular lobules similar to the lacrimal gland. In one reported case, scattered myoepithelial cells had been related to acinar-type epithelium, and goblet cells were intermixed. Reproduced with permission from Munro S, Brownstein S, Liddy B (1993) Conjunctival keratoacanthoma. Oncocytoma Clinical features Oncocytoma, also identified as oxyphilic cell adenoma, is a quite frequent lesion of the lacrimal gland that always arises as a slow-growing, benign yellow�tan or reddish lesion within the caruncle or adjacent plica semilunaris and canthal conjunctiva. Histological features histologically, large cells with eosinophilic granular cytoplasm are arranged in nests, cords or sheets that will type glandular or ductal constructions. Epithelial cysts Clinical features Conjunctival epithelial cysts are common and could additionally be congenital or acquired. Clinically, these cysts are easy, translucent lesions which contain clear fluid; nonetheless, the fluid may be turbid or contain epithelial debris layered like pseudohypopyon in the lumen. Histological features histologically, epithelial inclusion cysts are lined with conjunctival epithelium. Ductal cysts are lined with two layers of epithelium and should comprise periodic acid-Schiff-positive materials. Keratotic plaque Clinical options Keratotic plaque is a white leukoplakic lesion that normally develops in the interpalpebral region of the limbic or bulbar conjunctiva. Actinic keratosis Clinical options actinic keratosis, a precancerous lesion also referred to as conjunctival dysplasia, actinic keratosis selection, is a rarely recognized focal leukoplakic lesion occurring on the intrapalpebral limbus, usually over a chronically inflamed pinguecula or pterygium. It is uncommon in the Northern hemisphere and is rather more typically seen in countries closer to the equator and in areas the place persons are exposed to sunlight more incessantly. Premalignant and malignant epithelial tumors concurrent leukoplakia or squamous papilloma. New therapy methods together with photodynamic remedy, mitomycin C, and interferon alpha-2b have decreased the recurrence fee considerably.
Discount diclofenac gel 20 gm free shippingSurrounding and embedding this epithelial component is a considerably myxoid and fibrillary stroma containing elongate and wavy spindle cells arranged in loosely formed fascicles beginning arthritis in fingers cheap 20 gm diclofenac gel fast delivery. Histological features these lesions are all characterized by the presence of well-formed lobules or small clusters of sebocytes situated excessive in the lamina propria and opening immediately onto the epithelial floor arthritis + pins and needles in feet generic diclofenac gel 20gm. Sebaceous hyperplasia Clinical options Sebaceous hyperplasia is a common situation which is frequently clinically misdiagnosed as basal cell carcinoma arthritis pain relief medication for dogs buy 20 gm diclofenac gel visa. Nonetheless curing arthritis diet book order 20gm diclofenac gel with visa, the name sebaceous hyperplasia is definitely indicative of a well-defined clinicopathologic entity. Nevus sebaceus is single, round or oval, well circumscribed and usually measures 1�6 cm in biggest dimension. It commonly affects the pinnacle and neck, particularly the scalp the place it presents as a yellowish, flat or mamillated patch of alopecia. Other sites of predilection embrace the forehead, temples, around the central face, and behind the ears. Nevus sebaceus Nomenclature and classification schemes for the epidermal nevus syndrome are advanced, with overlapping entities and variable related defects. Nevus sebaceus can coexist with other epidermal nevi, including verrucous epidermal nevus, possibly representing a continuum of manifestations. Sebaceous glands are variably hyperplastic and excessive, diminished in quantity and even absent. In early infancy the sebaceous glands often present a transient enlargement beneath the lingering affect of maternal hormones, however they then diminish in size till adolescence after they bear marked proliferation. Virtually all lesions present irregularities of morphology and distribution of sebaceous glands. Apocrine glands are current within the center of the field; (B) high-power view showing apocrine glands. B Steatocystoma and sebocystomatosis Clinical features Steatocystoma multiplex (sebocystomatosis), characterised by autosomal dominant inheritance, usually presents in adolescence. More localized variants presenting on the face, scalp, nostril, and vulva have been described. Steatocystoma probably represents a real sebaceous cyst since its lining mirrors the point where the sebaceous duct enters the hair follicle. Sebaceous adenoma is rare and incessantly misdiagnosed clinically as a basal cell carcinoma. It presents most frequently in older people (mean age 60 years) as a tan, pink-to-red or yellow papulonodule measuring roughly 0. By convention, greater than half of the lobule in sebaceous adenoma is composed of mature sebaceous cells. Lesions predominantly have an result on the face and scalp though a single report has described a case growing on the chest. It consists of a number of variably sized, discrete nodules, symmetrically distributed and separated by dense eosinophilic connective tissue. Focal glandular differentiation with apocrine features has been famous on uncommon occasion. Occasional tumors might show superficial elements reminiscent of seborrheic keratosis or verruca vulgaris. Sebaceous adenoma typically presents as a solitary nodular lesion in the superficial dermis, frequently changing. It ought to be noted, nevertheless, that focal sebaceous adenoma-like features might typically be seen in a background of more typical sebaceoma. Of more importance is distinction from well-differentiated sebaceous carcinoma and recognition that the lesion may represent a cutaneous marker of Muir-torre syndrome. Immunohistochemistry utilizing eMa and D2�40, which are expressed by sebaceoma, and Ber-ep4, which labels basal cell carcinoma, may be helpful in limited biopsies, however the distinction can normally be made morphologically in intact specimens. Sebaceoma should also be differentiated from trichoblastoma with sebaceous differentiation. When sebaceoma was originally defined, the authors supposed it to substitute the confusing term sebaceous epithelioma and to clearly define a novel entity distinct from each sebaceous adenoma and basal cell carcinoma with sebaceous differentiation. We agree that the time period of sebaceous epithelioma is complicated and may now not be used. Of utmost importance is recognition that a big selection of benign sebaceous lesions with variable architecture and proportion of basaloid cells form the benign end of the Muir-torre spectrum. Superficial epithelioma with sebaceous differentiation Clinical options Superficial epithelioma with sebaceous differentiation is a uncommon tumor, with lower than 20 cases having been documented. Sebomatricoma the time period sebaceous epithelioma has been the supply of considerable confusion, largely as a outcome of different authors have taken it to mean different things whereas others have used it indiscriminately with out exact definition. In addition, the bizarre benign sebaceous neoplasms associated with Muir-torre syndrome have been additionally included in this definition. Basal cell carcinoma with sebaceous differentiation Clinical options Basal cell carcinoma with sebaceous differentiation is exceedingly rare, few cases having been revealed with even fewer photomicrographs. Some authors have reported an association with inner malignancy, but diagnostic criteria within this household of neoplasms have advanced considerably since that report. Basal cell carcinoma with sebaceous differentiation reveals features of basal cell carcinoma with proliferation of palisading basaloid cells, often in a nodular form, retraction artifact, and unfastened stroma wealthy in mucin. Within these nodules are foci of variable numbers of mature sebocytes, generally with formation of cysts because of holocrine secretion. Differential analysis Superficial epithelioma with sebaceous differentiation ought to be distinguished from follicular infundibulum tumor. Sebaceous carcinoma 1501 Sebaceous carcinoma Clinical options Sebaceous carcinoma is rare and has traditionally been divided into two teams: an aggressive periocular variant comprising about 75% of instances and an extraocular type considered by some to be much less aggressive. Many lesions are mistaken for basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and whilst a chalazion or continual blepharoconjunctivitis. A B Extraocular sebaceous carcinoma extraocular sebaceous carcinoma accounts for about one-quarter of all circumstances. Metastasis and mortality are believed by many authors to approximate to that of periocular tumors and the sample of metastasis is similar. Documented circumstances have been described within the oral and buccal mucosa, hypopharynx, pulmonary bronchus, parotid and submandibular glands, uterine cervix, and in dermoid cysts or benign cystic teratomas of the ovary. Necrosis is incessantly present, generally giving rise to a comedo-like look (. Keratinization leading to diagnostic confusion with squamous cell carcinoma is sometimes a feature and there may be an associated foreign body large cell response. Infiltration of the perineural area and lymphatic or vascular invasion are variable options. If the prognosis is doubtful, ultrastructural examination typically reveals nonmembrane-bound intracytoplasmic lipid inclusions. Common associations embrace gastrointestinal (53%), bladder and renal pelvis (11%), endometrium (10%), breast (5%), and hematological malignancies (5%). Sebaceous tumors that are readily classifiable additionally symbolize markers for this syndrome. Occasionally, nonetheless, well-differentiated variants merge into a histological continuum with other sebaceous tumors. It could additionally be differentiated from clear cell squamous carcinoma and clear cell hidradenocarcinoma by optimistic staining for lipid and adverse periodic acid-Schiff, alcian blue or mucicarmine staining for glycogen and mucin.
Wisconsin Ginseng (Ginseng, American). Diclofenac Gel. - Is Ginseng, American effective?
- Stress, anemia, insomnia, gastritis, impotence, fever, attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), HIV/AIDS, fibromyalgia, breast cancer, and other conditions.
- Are there safety concerns?
- What other names is Ginseng, American known by?
- Dosing considerations for Ginseng, American.
- Preventing respiratory tract infections such as the common cold or influenza in adults.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96929
Discount diclofenac gel 20 gm with mastercardWhen the middle cerebral artery bifurcates or trifurcates early rheumatoid arthritis xeljanz buy diclofenac gel 20gm amex, the orbitofrontal artery originates from the extra anterior trunk of the center cerebral artery arthritis in neck facet joints generic 20 gm diclofenac gel fast delivery. Supplies the orbital side of the middle and inferior frontal gyri and sometimes the inferior a half of the pars orbitalis of the inferior frontal gyrus arthritis bent fingers treatment discount diclofenac gel 20gm otc. Prefrontal Artery Constitutes the anterior part of the operculofrontal or candelabra group painkillers for dogs with arthritis 20 gm diclofenac gel with visa. Supplies the lateral aspect of the frontal lobe anterior to the sylvian triangle, including the pars marginalis of the inferior frontal gyrus, and the pars orbitalis and pars opercularis of the inferior frontal gyrus. It could have a typical origin with the orbitofrontal artery or the precentral artery. It emerges from the sylvian fissure at the level of the pars orbitalis of the inferior frontal gyrus. In lateral angiograms it has an inclined path anterior and superior beyond the anterior portion of the sylvian fissure. It divides into two trunks, which further divide into 4 to six branches supplying the center and inferior frontal gyri. Precentral Artery When the middle cerebral artery bifurcates, the precentral artery arises from the anterior trunk. When the middle cerebral artery trifurcates it arises from the anterior or center trunk. The precentral artery emerges from the sylvian fissure at or behind the pars opercularis of the inferior frontal gyrus and has an almost vertical course. It is the most vertical branch of the middle Sylvian Segment of the Middle Cerebral Artery. The term ascending frontal artery advanced includes the operculofrontal or candelabra group and the arteries of the central sulcus. The inferior level of the triangle is shaped by the horizontal segment of the center cerebral artery, the anterior superior point is shaped by essentially the most anterior artery within the insula as it begins to loop inferiorly to leave the sylvian fissure, and the posterior superior point is formed by probably the most posterior artery because it begins to loop inferiorly to leave the insula. The superior border of the triangle is drawn by connecting the arteries within the superior limiting sulcus before they loop inferiorly to depart the sylvian fissure. In frontal projection the insular branches of the middle cerebral artery curve gently outward until they attain the superior limiting sulcus. The anterior portion of the insula is more medially positioned than the posterior portion. The candelabra group could bifurcate or trifurcate symmetrically in the proximal part of its course, suggesting the form of a candelabrum. The posterior branches always supply the premotor area and may provide accent to the motor strip. The arteries of the central sulcus are one or two in quantity, with an adjunct artery to the motor strip in about 50% of cases from the operculofrontal branch. The arteries within the central sulcus may come up as a separate part of the ascending frontal complex or from one other trunk within the sixteen Atlas of Vascular Anatomy cerebral artery. It supplies the pars opercularis of the inferior frontal gyrus, the posterior a half of the center frontal gyrus, and the inferior two thirds of the precentral gyrus. Central Arteries the central arteries have variable origin, dependent on the division pattern of the middle cerebral artery. When the center cerebral artery is a single vessel it could originate from a standard trunk with the anterior parietal artery. The central artery runs near the fissure of Rolando as two branches encircling the operculum. It provides the precentral and postcentral gyri, and runs with a slight posterior superior inclined course after emerging from the fissure. This artery emerges from the posterior third of the sylvian fissure at the base of the ascending parietal gyrus to pass upward and posterior within the postcentral sulcus. It provides the ascending parietal gyrus, the higher portion of the central sulcus, and the anterior a half of the primary two parietal gyri. The posterior parietal artery is essentially the most posterior of the ascending branches of the middle cerebral artery. It varies in measurement and website of origin and will originate from the anterior or posterior trunk of a bifurcated center cerebral artery. It emerges from the sylvian fissure at the degree of the parietal operculum and passes backward and upward in the posterior part of the parietal lobe. Supplies the posterior a part of the first and second parietal gyri and the supramarginal gyrus. Angular Artery It is the terminal and largest department of the middle cerebral artery. Its origin is from the posterior trunk of the center cerebral artery when it bifurcates, and when it trifurcates the angular artery arises from the middle or posterior trunk. The artery emerges on the finish of the sylvian fissure, operating over the superior temporal gyrus. This is the most horizontal branch of the center cerebral artery in lateral angiograms and the most posterior branch of the sylvian fissure in a Towne view of angiography. It provides the posterior part of the superior temporal gyrus, the supramarginal gyrus, the angular gyrus, and the first two occipital gyri. Temporo-occipital Artery the temporo-occipital artery may have a standard origin with the angular artery and could also be typically considered a department of the angular artery. The measurement of this artery is inversely proportional to the size of the posterior temporal artery. Supplies the world posterior to and above the realm often provided by the posterior temporal artery. Posterior Temporal Artery the posterior temporal artery arises from the posterior trunk of the middle cerebral artery if a bifurcation or trifurcation is present. It is a single branch generally and exits the sylvian fissure through the posterior part, crossing the external surface of the superior temporal gyrus. Runs by way of the superior temporal sulcus, crossing the middle temporal gyrus, and terminating reverse the preoccipital fissure. Supplies the middle and posterior part of the superior temporal gyrus, the posterior third of the middle temporal gyrus, and the posterior extremity of the inferior temporal gyrus. Leaves the sylvian fissure opposite or slightly behind the pars opercularis of the inferior frontal gyrus. Supplies the temporal gyri anterior to the territory of supply of the posterior temporal artery. Anterior Temporal Artery Supplies the remainder of the anterior portion of the temporal lobe. Descends posteriorly over the temporal gyri, immediately behind the temporal polar artery to terminate on the level of the center temporal sulcus. Temporal Polar Artery this is a relatively constant vessel that passes forward to the anterior and inferior aspects of the tip of the temporal lobe to supply the anterior portions of the superior, middle, and inferior temporal gyri. The artery is situated above the tentorium, and initially (embryologically) derives the blood supply from the interior carotid artery. The posterior cerebral artery shifts its origin from the carotid to the basilar system in the ultimate levels of embryonic development, and the ultimate origin is from the basilar artery bifurcation at the interpeduncular fossa. In the fetal type the posterior cerebral artery originates from the internal carotid artery.
Cheap diclofenac gel 20 gm otcIf blood cultures subsequently grow enterococci prone to penicillin and aminoglycosides rheumatoid arthritis z deformity order diclofenac gel 20gm amex, which antibiotic(s) would you utilize to deal with this patient His past medical history is outstanding for placement of a prosthetic mitral valve 5 months previous to dog arthritis medication metacam order 20 gm diclofenac gel mastercard admission king bio arthritis pain & joint relief generic diclofenac gel 20gm amex. He stories reasonable alcohol consumption and smokes one pack of cigarettes per day how to stop arthritis in fingers naturally buy diclofenac gel 20gm line. Examination is otherwise exceptional for venous jugular distension, crackles at the bases of both lungs, and a low-pitched early diastolic murmur. Laboratory analysis is remarkable for a peripheral blood leukocyte rely of 12,four hundred cells/mm3 with 70% neutrophils and a hemoglobin content material of 13. Blood cultures are drawn and a decision is made to empirically treat the patient whereas awaiting their results. She is receiving minimal respiratory assist, and the nurse reports scant respiratory secretions on suctioning. The surgical wound is just minimally erythematous with out purulence or drainage, and stool is current in the colostomy bag. Laboratory evaluation is outstanding for a peripheral blood leukocyte rely of 13,four hundred cells/mm3 with 85% neutrophils. You ask that blood cultures be obtained, the catheter be eliminated, and the catheter tip sent for culture. His physical examination is outstanding for diffuse stomach tenderness with rigidity, rebound, and guarding. Laboratory evaluation reveals a peripheral blood leukocyte depend of 23,one hundred cells/mm3 with 95% neutrophils. If this affected person had cystic fibrosis and had just lately been hospitalized and had up to now obtained a quantity of programs of antibiotics for respiratory infections, which antibiotic(s) would you employ to empirically deal with him This patient has pneumonia, as evidenced by the latest onset of fevers, chills, a productive cough, an elevated peripheral blood leukocyte count, and an infiltrate on his chest radiograph. The pneumonia is classed as group acquired as a end result of the affected person has not recently been hospitalized or in any other case uncovered to the health care setting or taken antibiotics. The most common bacterial causes of community-acquired pneumonia in adults are Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Legionella spp. The age of the patient, the productive cough, and the lobar consolidation would make one suspicious of a "typical" organism, as opposed to an "atypical" organism. Appropriate antibiotic decisions embrace an oral macrolide (azithromycin, clarithromycin, erythromycin) or doxycycline. An intravenous quinolone with antistreptococcal exercise (moxifloxacin, levofloxacin) would even be applicable. If this is the case, the remedy routine can be narrowed and targeted on this pathogen. Note that there have been a number of reviews suggesting that sufferers with bacteremic pneumococcal pneumonia have better outcomes with mixture therapy consisting of a -lactam plus a macrolide (azithromycin) in comparison with -lactams alone, so combination therapy could be considered. Appropriate antibiotics could be azithromycin or a quinolone (either levofloxacin or moxifloxacin). This affected person has pneumonia, as evidenced by the brand new onset of fever, elevated production of purulent respiratory secretions, an elevated peripheral blood leukocyte count, and an infiltrate on her chest radiograph. The pneumonia is classed as hospital acquired as a outcome of it developed after the affected person was in the hospital. In such a affected person, one should be especially involved about Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter spp. The presence of many gram-negative bacilli in the endotracheal aspirate suggests P. Appropriate remedy would include one agent from every of the 2 groups of antibiotics. Group 1 includes antipseudomonal cephalosporins (ceftazidime, cefepime), carbapenems (imipenem, meropenem), and extended-spectrum penicillin/ -lactamase inhibitor combinations (piperacillin/tazobactam). Group 2 consists of quinolones (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin) and aminoglycosides (gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin). The presence of gram-positive cocci in the tracheal aspirate suggests Staphylococcus aureus. Thus, an applicable regimen can be the mix of antibiotics described in "c" with the addition of linezolid or vancomycin. Appropriate therapy would come with two agents with antipseudomonal activity, such as an antipseudomonal cephalosporin (ceftazidime, cefepime) or piperacillin in combination with either ciprofloxacin or an aminoglycoside (gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin). Actual choices ought to be guided by local resistance patterns and the previous antibiotic publicity of this affected person. Also, recall that ciprofloxacin has the best antipseudomonal exercise of the quinolones. This affected person has acute cystitis, as evidenced by the symptoms of dysuria, frequency, and a positive urine dipstick. The absence of fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, or flank ache make pyelonephritis unlikely. This urinary tract an infection could be categorized as "uncomplicated" acute cystitis because the patient is younger, wholesome, not pregnant, not hospitalized, and with out proof of structural abnormalities of her urinary tract. Appropriate remedy for this affected person could be a 5-day course of nitrofurantoin or probably a 3-day course of oral trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole if she lives in a region by which the prevalence of uropathogens resistant to this agent is less than 20%. If this patient resided in a region in which resistance to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole was frequent, nitrofurantoin would be applicable therapy. A previous analysis of diabetes would predispose this affected person to an infection by a broader vary of bacteria and would cause her urinary tract an infection to be categorised as a "complicated" acute cystitis. This affected person has acute pyelonephritis, as evidenced by symptoms of fever, chills, dysuria, frequency, and flank ache. This case of acute pyelonephritis would be classified as uncomplicated as a result of the affected person is younger, wholesome, not pregnant, not hospitalized, and without proof of structural abnormalities of her urinary tract. Because this affected person is dehydrated and unable to tolerate oral intake, she ought to be hospitalized and receive intravenous antibiotics in addition to hydration. Appropriate empiric antibiotic therapy can be a quinolone (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin); an aminoglycoside (gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin) with or without ampicillin; an extended-spectrum penicillin (piperacillin) with or with out an aminoglycoside; a third-generation cephalosporin (ceftriaxone, cefotaxime) with or without an aminoglycoside; or a carbapenem (imipenem, meropenem, doripenem, ertapenem). An appropriate antibiotic routine would be a single intramuscular dose of a cephalosporin (ceftriaxone, cefotaxime, cefoxitin probenecid) plus oral doxycycline. This patient could have acute bacterial meningitis, as evidenced by the acute onset of fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, headache, confusion, and a stiff neck. Examination of the cerebrospinal fluid is important to definitively make the analysis. In an adult affected person, acute bacterial meningitis is most regularly caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae or Neisseria meningitidis. In an older particular person corresponding to this patient, Listeria monocytogenes and aerobic gram-negative bacilli are additionally a priority. Even a delay of several hours can have a detrimental effect on the outcomes of sufferers with acute bacterial meningitis. Empiric remedy in this patient would include a third-generation cephalosporin (ceftriaxone or cefotaxime) to cowl N. Because this patient is older than 50 years, ampicillin also wants to be added to cowl L. The gram-positive cocci in pairs seen on Gram stain of the cerebrospinal fluid point out that S.
Cheap diclofenac gel 20 gm onlineAngiogram of the aortic arch exhibiting the frequent origin of the left frequent carotid artery and the brachiocephalic trunk arthritis gel medication order 20 gm diclofenac gel with amex. A and B account for about 73% of all arch department variations and 22% of the anomalies found in the basic population arthritis in dogs medication purchase diclofenac gel 20 gm mastercard. B arthritis yoga poses generic 20gm diclofenac gel mastercard, Origin of the left widespread carotid from the mid to upper brachiocephalic artery arthritis in neck bone spurs safe 20gm diclofenac gel. Aortic arch angiogram showing unbiased origin of four main branches of the arch directly from the arch. Aortic arch angiogram showing the origin of the proper frequent carotid artery immediately from the arch, in addition to the left carotid artery and the left subclavian artery. The proper subclavian artery arises directly from the distal facet of the aortic arch. A�B, Aortic arch angiogram showing anatomic variation with the frequent origin of each widespread carotid arteries, direct origin of the left vertebral artery from the aorta, regular origin of the left subclavian artery, and unbiased posterolateral origin of the proper subclavian artery from the arch. Aortic arch angiogram displaying anatomic variation, with the brachiocephalic trunk giving origin to the left common carotid artery, and the proper common carotid artery with impartial origin directly from the aorta, as the first department of the aortic arch. Selective angiogram of the intercostobronchial trunk displaying filling of the two first intercostal arteries and simultaneous filling of the best superior and inferior bronchial arteries. A, Anterior view of the angiogram of the intercostobronchial trunk displaying filling of the second intercostal artery and right bronchial arteries. B, Lateral view of the angiogram of the identical artery as in (A) showing that the intercostal artery is posterior and the bronchial arteries comply with a more central or anterior course, along with the bronchus. Angiogram of a bronchial artery common trunk giving origin to a proper bronchial artery and a left bronchial artery. A, Selective angiogram of a common bronchial trunk exhibiting the branches to proper and left. B, Lateral view showing the proper and left bronchial arteries following a central or anterior direction. Selective angiogram of a common trunk displaying the vascular parts both in the bronchial wall and in peribronchial tissues. Ventral side of the kinds of bronchial arterial provide, based on the angiographic data of seventy two patients. The proper intercostobronchial trunk arises laterally or dorsally; the remaining single bronchial arteries and customary bronchial trunk come up from the ventral side of the aorta. A, Angiogram exhibiting aberrant origin of the proper bronchial artery from the best thyrocervical trunk. B, Angiogram exhibiting aberrant origin of the Left Bronchial Artery from the Right Thyrocervical Trunk. Angiogram showing the importance of the thoracoabdominal arterial anastomoses by way of the inner mammary arteries, allowing reconstitution of the frequent femoral arteries through the anastomoses with the inferior epigastric arteries. Note the occluded abdominal aorta, which triggered the event of the collateral circulation. B and C, Lateral proper and left views of the thoracoabdominal arterial anastomoses through the superior epigastric arteries and the inferior epigastric arteries. Descending thoracic aortogram displaying the posterior intercostal arteries and an enlarged left bronchial artery. A, Thoracic aortogram showing the enlarged posterior intercostal arteries due to the occlusion of the left subclavian artery, in an attempt to reconstitute the left brachial artery. A, Selective angiogram of the best internal mammary artery, showing filling of the anterior intercostal arteries. The anterior intercostal arteries are much smaller than the posterior intercostal arteries. Continued B rachiocephalic veins, also known as innominate veins, are massive veins on the higher thorax and characterize united trunks of the interior jugular veins and subclavian veins. The tributaries 8 Veins of the Thorax are the proper vertebral, inner thoracic, inferior thyroid, and sometimes the first proper intercostal veins. The left brachiocephalic vein is 6 cm lengthy, following an indirect path to the proper path to join the right brachiocephalic vein to form the superior vena cava. Tributaries are the left vertebral, inner thoracic, inferior thyroid, superior intercostal, thymic vein, and pericardiophrenic veins. Variations of the brachiocephalic veins include coming into the proper atrium separately and the configuration of a left vena cava. There is a pretracheal venous plexus, from which the left inferior vein descends to enter the left brachiocephalic vein, and the right inferior thyroid vein crosses the neck to open in the right brachiocephalic vein. Azygos Vein the azygos vein is fashioned by the confluence of the ascending lumbar veins, subcostal veins, and lumbar azygos. It ascends within the posterior mediastinum as much as the level of the fourth vertebra, the place it arches anteriorly above the best pulmonary hilum, ending in the superior vena cava. Tributaries are the posterior intercostal veins, the hemiazygos, the accessory hemiazygos veins, and the esophageal, mediastinal, and pericardial veins. When current, the trunk formed by the subcostal and ascending lumbar veins is a significant tributary of the azygos vein. The azygos vein begins laterally to the vertebral bodies however turns anterior to the thoracic backbone because it approaches the vena cava. It is around 7 cm in size and is shaped by the confluence of the brachiocephalic veins. The 196 Atlas of Vascular Anatomy Hemiazygos Vein the hemiazygos vein begins on the left side, ascending anteriorly to the spine, crossing the column, and reaching the azygos vein. Tributaries are the lower three posterior intercostal veins, a typical trunk shaped by the left ascending lumbar vein, and the subcostal vein. The proper bronchial vein joins the azygos, and the left joins the left superior intercostal or hemiazygos vein. Esophageal Veins the esophageal veins run alongside the esophagus and drain to the azygos vein, and the more distal veins drain into the portal venous system through the left gastric vein. Accessory Hemiazygos Vein the accessory hemiazygos vein outcomes from the confluence of a quantity of posterior intercostal veins, descending laterally to the thoracic backbone, reaching the azygos vein. Veins of the Vertebral Spine (See Chapter 6) There is a big and sophisticated venous plexus around the vertebral column. They are companions of the posterior intercostal arteries, working along the subcostal groove. On the right, the second, third, and fourth posterior intercostal veins kind the best superior intercostal vein. There are anterior intercostal veins, which are small tributaries of the interior thoracic and musculophrenic veins. Bronchial veins are additionally discovered on both sides, draining blood from bigger hilar structures and the bronchial tree. The right inner thoracic vein terminates extra proximally on its brachiocephalic vein than does the left. The left pericardiophrenic vein terminates on the left brachiocephalic vein; it may additionally terminate on the interior thoracic vein or superior intercostal vein. Note the vertical course of the right brachiocephalic vein and the horizontal course of the left brachiocephalic vein.
References - Deters LA, Dagrosa LM, Herrick BW, et al: Ultrasound guided ureteroscopy for the definitive management of ureteral stones: a randomized, controlled trial, J Urol 192(6):1710n1713, 2014.
- James CF, Modell JH, Gibbs CP, et al: Pulmonary aspiration: effects of volume and pH in the rat, Anesth Analg 63:665-668, 1984.
- Decousus H, Prandoni P, Mismetti P, et al: Fondaparinux for the treatment of superficialvein thrombosis of the legs, N Engl J Med 363(13):1222-1232, 2010.
- Hughes KM, Lang JC, Lazare R, et al: Measurement of oxybutynin and its N-desethyl metabolite in plasma, and its application to pharmacokinetic studies in young, elderly and frail elderly volunteers, Xenobiotica 22:859, 1992.
- Theorell-Haglow J, Lindberg E, Janson C. What are the important risk factors for daytime sleepiness and fatigue in women? Sleep 2006;29(6):751-7.
|