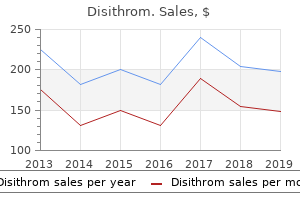
Disithrom
Brian Murphy, RN - Critical Care Department
- Little Company of Mary Hospital
- Evergreen Park, IL
Buy discount disithrom 100mg on-lineThe easiest strategy makes use of cell transplantation oral antibiotics for dogs hot spots cheap disithrom 100 mg with visa, during which single therapeutic cells could be administered to a affected person with kidney failure to restore renal perform antibiotic resistance among bacteria disithrom 500 mg fast delivery. Because this strategy is simpler to administer and fewer invasive than different alternatives treatment for dogs with degenerative myelopathy disithrom 250 mg discount, most studies have been carried out utilizing cell therapy methods [7 virus 58 symptoms 250mg disithrom with visa,8]. Whereas various cells have been studied for potential use in cell therapy [5], engineering of renal constructs has also been tried to facilitate renal regeneration [9,10]. The scaffold supplies help to form three-dimensional (3D) renal constructions that can result in environment friendly integration with the host after implantation. This strategy is ideally applicable to extra serious renal situations that require alternative of diseased kidney tissues. Compared with these two cell-based approaches, a strategy that makes use of endogenous cell sources is rising as a promising alternative for renal regeneration [11]. For environment friendly renal regeneration in situ, there are two objectives: (1) redesign of broken renal tissue after harm towards acceptable microenvironments, and (2) effective infiltration of host cells containing therapeutic potential into the recreated renal niche. In addition, a quantity of approaches to engineering renal constructs and in situ kidney regeneration shall be introduced. For both applications, establishment of a refined cell tradition system is crucial to obtain a sufficient number of therapeutic cells for later transplantation. To this end, varied kinds of cell sources have been identified, characterized, and used to deal with renal ailments (Table 66. Cell Sources: Kidney TissueeDerived Stem and Primary Cells the adult kidney contains over 20 heterogeneous types of cells distributed among the numerous compartments, including vascular, interstitial, glomerular, and tubular constructions with architectural complexity [12]. Disruption of renal homeostasis occurs after harm or within the case of disease, which in flip elicits the release of mobile and molecular signals to interact with cell parts to facilitate regeneration and restore the damaged kidney. Extrinsic regulators within the renal area of interest provoke renal-specific differentiation and self-renewal of assorted renal cells and stem cells. Although the existence and identification of renal stem or progenitor cells in adult kidney tissues have been controversial, quite a few research point out that renal stem and progenitor cells exist in the Bowman capsule, papilla, and tubular sections [7]. Thus, purification and growth of these cells could presumably be sources for cell therapy to deal with renal failure. The Bowman capsule initiates the filtration of blood and era of urine [14]. The Bowman capsule is composed of several layers: the parietal layer, the Bowman area, the visceral layer, and a filtration barrier that contains specific kidney cell sorts. In early studies, a number of cell floor markers were recognized to isolate renal stem cells from the Bowman capsule. However, as a end result of podocytes have restricted capacity for cellular proliferation within the injured kidney, use of stem or progenitor cells that can turn out to be more podocytes is an alternate strategy for the recovery of regular kidney filtration. This is situated in a central region of the kidney that incorporates epithelia of collecting ducts and the loops of Henle that focus urine [7]. In an early study [22], a renal stem-like cell inhabitants with a low cell-cycling fee was recognized. Based on these results, the authors concluded that the renal papilla contained low-cycling cells and is a distinct segment for adult renal stem cells. It has an essential role in reabsorption of electrolytes and proteins and amino acid transportation by way of hydrolase activity. Previously, the S3 phase of proximal tubule was identified as a renal stem area of interest during which a big variety of cells were observed to be mitotically active within the area, as confirmed by the expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen [25]. To identify cellular phenotypes of tubular cells additional, a quantity of research used transgenic animals that specific reporter markers [26e28]. To use kidney tissueederived stem cells for cell-based therapies, efficient isolation and growth of cell populations from renal tubules are needed. The investigators concluded that isolation of a pure inhabitants of human-derived renal tubule cells is possible, and the isolation technique utilizing the markers could be applied to isolate renal stem cells as nicely. Our group has centered on isolating and expanding primary kidney cells that might be simply used in clinical purposes [34]. After in vitro cell tradition, cultivated kidney cells show efficient development capability. Approximately 70e80% of cultured cells are composed of proximal tubular cells; the remaining cells encompass distal tubular cells, accumulating duct cells, podocytes, and other types of cells. Using our established cell culture methods, we further tested the feasibility of cell remedy utilizing autologous cell sources. We evaluated main renal cells from diseased kidneys to determine whether their regular phenotypic and useful traits are retained, and thus might be used for cell therapy [35]. Renal cells from diseased human kidneys retained characteristics much like those of normal kidneys, which suggests that autologous cell sources could additionally be used for cell transplantation to treat sufferers with renal failure [35]. Other Cell Sources: Pluripotent, Fetal, or Adult Stem Cells Various forms of cells isolated from nonrenal tissues have been considered potential cell sources, corresponding to pluripotent cells and stem or progenitor cells from fetal and adult tissues. Both have self-renewable capability and multidifferentiation capacity that theoretically is able to differentiating into any sort of cells. However, moral dilemmas, hazard of cancer from uncontrolled development, and immunogenic points nonetheless have to be resolved before clinical trials may be initiated. However, a sufficiently sophisticated cell culture system for mass cell culture remains to be wanted that can maintain phenotypes and stop teratoma formation and immunogenicity [48] in vivo. Stem cells isolated from grownup tissues have been extensively studied to deal with renal illnesses. Engineering of Cell-Based Renal Constructs the overall strategy of engineering a renal construct for remedy of renal diseases is to fabricate useful renal buildings in vitro and then implant the constructs for successful integration with host kidney tissues (Table 66. To engineer 3D kidney constructs, cultured renal cells are seeded onto a scaffold; the seeded cells throughout the scaffold are allowed to broaden and mature into renal structures. Kidney tissue possesses a fancy 3D tubular structure and consists of numerous cell types within the renal tissue; due to this fact, selection of the suitable cell sources is a consideration for engineering renal constructs. Although many kinds of renal stem cells have been recognized and characterised, use of stem cells as cell sources for engineering renal constructs is still in its infancy for practical applications [7]. Alternatively, most approaches developed for engineering kidney constructions have used main renal cells which are isolated and expanded with out further purification. Primary cell tradition techniques are now wellestablished to isolate and increase main renal cells that reveal proliferation and differentiation functionality during a number of passages [34]. Another essential factor to think about in the in vitro fabrication of kidney buildings is the effectivity of engineering the appropriate microenvironment, or area of interest, to allow seeded cells to type normal kidney-like structures by way of cellecell/cellematrix interactions [70]. Most of these pure biomaterials require biocompatible characteristics with native tissue and may support and information cellular behaviors such as cell activation, migration, proliferation, and differentiation [72]. Glomerular epithelial and mesangial cells isolated from renal tissues had been expanded on a collagen-based membrane scaffold (collagenevitrigel) with a secure, thin shape. The mixture of collagen with vitrigel provided an optimum setting that mimicked the native glomerular structures, which shaped a reconstructed glomerular tissue when cocultured with renal cells [73]. Subsequently, the cells seeded within the 3D collagen hydrogel scaffold self-assembled into engineered renal tissues that contained each tubules and glomeruli-like structure. Using the collagen gel scaffold system, our group established a 3D renal-like construct for in vivo study. We discovered that major human kidney cells could be expanded in a 3D collagen-based tradition system [34], and these cells retained renal phenotypes that stained positively for proximal and distal tubules and amassing duct markers [34].
Buy generic disithrom 100mgAfter these preliminary events infection prevention week buy 250mg disithrom mastercard, the exercise of proinflammatory mediators abates and an increase in local levels of antiinflammatory mediators similar to resolvins xeloda antibiotics purchase 100 mg disithrom mastercard, protectins antibiotics given for ear infections generic disithrom 100 mg without prescription, and lipoxins (autacoids) is responsible for countering irritation and coincides with the start of the reparative process antibiotic ointment for burns generic disithrom 100mg with mastercard. Both eicosanoids and autacoids are derivatives of arachidonic acid, and the mechanism for a change in synthesis from inflammatory to antiinflammatory mediators has been characterised as "class switching" and occurs by activating enzymes corresponding to 15-lipooxygenase. If irritation in a defect website persists on account of chronic an infection, osseous regeneration is diminished. An wonderful evaluation of the subject of inflammation and bone regeneration could additionally be present in an article by Thomas and Puleo [5]. Once regeneration begins, the kinetics of the different reparative tissues becomes necessary. Unless a physical void is preserved by preventing the ingrowth of epithelium and connective tissue (a technique generally known as osteopromotion by barrier techniques), periodontal regeneration is compromised. Scaffolds in combination with barrier membrane expertise have been shown to be effective in restoring bone quantity, and the addition of exogenous growth elements and gene therapy for the native manufacturing of progress components are further approaches which were studied in preclinical studies [6]. Larger defects of the craniofacial skeleton extending beyond the periodontal defect differ from each other in numerous bodily and biological ways. In this case, the rigidity of the partitions facilitates bone regeneration by protecting biological scaffolds similar to blood clots, therapeutic tissue, and neovasculature. In addition, periosteum lining the bone surfaces and the underlying endosteal surfaces are a wonderful source of cells able to differentiation under the influence of the proper growth elements. Immobilization of the bone ends (with bone plates) is essential to shield early reparative activities such because the secretion of extracellular matrix and neovascularization from mechanical disruption by exterior masses. High-magnification images taken adjacent periosteum and distal to the periosteum can be found on the proper (magnification, 10x). The graft can even function a scaffold and a barrier to the ingrowth of nonosteogenic tissue. Techniques for reconstructing segmental bone defects utilizing tissue engineering principles are described later on this chapter. As described within the strategies for promoting periodontal regeneration, irritation and an infection have important roles in the regenerative capabilities of craniofacial defects. Infection of a graft site is a vital component accounting for a complication rate of 48% in a evaluate of the literature on nonvascularized bone grafting [7]. Strategies for decreasing an infection via implantation of antimicrobial agents shall be described in a later section. The paradoxical relationship between inflammation and bone formation raises theoretical questions about the significance of inflammatory states, however the unfavorable effect of extended inflammation on bone grafting and fracture restore is well-documented [8]. Newer methods to deliver antibiotics locally using gadgets fabricated via tissue engineering shall be described later in this chapter. Other necessary conditions that may cut back the regeneration of bone embody those who compromise the vascularity of the tissue surrounding a bone defect. The function of the vasculature as a supply of inducible cells (pericytes), conduit for inflammatory cells (platelets, macrophages, and monocytes) and important basis for supporting metabolism in all dwelling tissue is well-known [9]. When the blood supply to a defect web site is compromised by therapeutic measures corresponding to radiation therapy, comorbid circumstances. Efforts to reconstruct craniofacial defects troubled by such situations include adjuvant strategies to mitigate against the compromised vascularity such because the transfer of well-vascularized tissue beds or chemical modulators of angiogenesis. An example of the crucial position of the vasculature is supplied on this histological section. New bone formation associated with neovascularization from the periosteum is seen as osteogenesis progresses from the vascularized margin upward. Nonvascular autogenous bone grafts had been thought-about the reference normal for the repair of bone defects. Common donor sites for bone harvest included the ilium, tibia, and calvarium [11,12]. Free tissue transfer strategies added the use of vascularized flaps anastomosed to local vessels when defect websites have been contaminated or associated with compromised vascularity [13]. These flaps are harvested from areas with an axial blood provide which are isolated and anastomosed to vessels close to the defect website to produce an immediately "living" transplant. The mostly used websites are chosen for their ease in harvest, modest donor website morbidity, and talent to embrace a large volume and number of tissue varieties nourished from a single vascular pedicle [15]. When delicate tissue is missing or when a vascularized delicate tissue bed is required, the anterior lateral thigh flap or radial forearm flap can be used. For defects requiring composite delicate tissue and bony reconstruction, options include the fibula, scapula, and deep circumflex iliac arteryenourished ilium flaps. Technical considerations with these strategies embrace the morbidity related to graft harvest, the patency and size of vessels, the period of surgical procedure, and the recovery time [16]. Implantable Scaffolds To allow damaged bone to get replaced with functional tissue, engineers have developed a wide range of supplies that serve to stimulate the adherence and proliferation of osteogenic cells. Some of these applied sciences mimic the biomechanical and/or biochemical properties of native bone, whereas others try to recapitulate the anatomy [18e20]. In 1881, Sir William MacEwen of Rothesay used tibial bone wedges from three donors to reconstruct a humeral defect in a 3-year-old child, which represented the primary printed account of interhuman bone grafting [21]. The process was unsuccessful; nonetheless, later studies recognized the elements affecting graft acceptance and rejection and established the parameters of allogeneic grafting. Nevertheless, regardless of advancements in growing allogeneic, xenogeneic, and artificial substitutes, autogenous bone grafts remain the reference standard for reconstructing segmental bone defects [22]. By definition, bone grafts may be classified as an autograft, allograft, or xenograft, depending on the source [23]. In contrast, alloplastic implants are synthetically manufactured, inorganic, and biocompatible [24]. Whereas autologous bone grafts produce the most predictable results, alloplastic supplies provide a number of advantages over biologically derived materials. They could be fabricated to fit a patient-specific defect and the resorption rate could be controlled by adjusting material properties and compared with autologous grafts, to present extra material than can be typically harvested from a patient while avoiding a second surgical donor website. Ceramics Numerous ceramics can be found; calcium phosphate (CaP)-based ceramics symbolize the most widely used bioactive ceramic. CaPs supply wonderful biocompatibility, possess exceptional osteoactivity, and have a chemical and crystalline structure close to those of native bone mineral [25]. Since changing into obtainable for scientific use in 1992, CaP ceramics have been used with success within craniofacial surgical procedure [26,27]. Both of those formulations can be produced as a paste, which allows the surgeon to inject and mould the cement before ultimate setting occurs, and which makes CaPs a beautiful choice for dental and orthopedic functions. Depending on the formulation of the CaP, the pore and particle measurement, and the metabolic exercise of the 892 50. To speed up the degradation of CaP-based scaffolds, a number of studies have investigated the introduction of macropores to increase the surface space of the implant and speed up tissue integration [29e31]. The use of macroporosity has gained a lot of curiosity owing to improved degradation kinetics and improved tissue infiltration. This permits the engineer to improve degradation kinetics additional, reproduce tissue structure more exactly, and enhance tissue infiltration [32e34]. In that study, the authors fabricated custom implants through the use of three-dimensional powder printing to restore defects in human cadaver skulls.
Safe disithrom 250 mgDegradation of electrospun nanofiber scaffold by short wave length ultraviolet radiation therapy and its potential functions in tissue engineering antibiotic 48 hours contagious disithrom 100mg sale. Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) porous scaffolds for tissue engineering and regenerative medication antibiotics ototoxic discount disithrom 500mg free shipping. Degradation and cytotoxicity of lotus-type porous pure magnesium as potential tissue engineering scaffold material bacteria generally grow well in foods that purchase 500 mg disithrom otc. A new method for the preparation of hydrophilic poly(L-lactide) porous scaffold for tissue engineering by utilizing lamellar single crystals antibiotics for uti toddler discount disithrom 250mg on-line. Application of macromolecular components to cut back the hydrolytic degradation of polyurethanes by lysosomal enzymes. Corrosion degradation and prevention by surface modification of biometallic supplies. Electrochemical and floor modifications on N�-ion-implanted 316 L stainless-steel. Nucleation and growth of apatite on chemically treated titanium alloy: an electrochemical impedance spectroscopy research. The recruitment of two consecutive and totally different waves of host stem/progenitor cells in the course of the improvement of tissue-engineered bone in a murine model. Hydrogels in managed launch formulations: community design and mathematical modeling. Mathematical mannequin accurately predicts protein launch from an affinity-based delivery system. Mimicking biological supply via feedback-controlled drug release methods primarily based on molecular imprinting. Biomaterial-based drug supply techniques for the controlled release of neurotrophic elements. Growth issue delivery-based tissue engineering: common approaches and a review of latest developments. Sulfonamide-based pH- and temperature-sensitive biodegradable block copolymer hydrogels. Genetically engineered protein in hydrogels tailors stimuli-responsive traits. Sequential delivery of angiogenic progress elements improves revascularization and coronary heart operate after myocardial infarction. A review of developments and limitations in hydrogel-rapid prototyping for tissue engineering. Bioactive Ti metallic analogous to human cancellous bone: fabrication by selective laser melting and chemical therapies. Biomaterials with persistent progress factor gradients in vivo speed up vascularized tissue formation. Theoretical and experimental quantification of the position of diffusive chemogradients on neuritogenesis within three-dimensional collagen scaffolds. Anisotropic porous biodegradable scaffolds for musculoskeletal tissue engineering. The engineering of organized human corneal tissue via the spatial steerage of corneal stromal stem cells. Instrumented cardiac microphysiological gadgets by way of multimaterial three-dimensional printing. Effect of floor roughness of hydroxyapatite on human bone marrow cell adhesion, proliferation, differentiation and detachment power. The effects of mixed micron-/submicron-scale floor roughness and nanoscale options on cell proliferation and differentiation. Correlation of cell adhesive behaviors on superhydrophobic, superhydrophilic, and micropatterned superhydrophobic/superhydrophilic surfaces to their floor chemistry. Directional migration of vascular smooth muscle cells guided by a molecule weight gradient of poly(2hydroxyethyl methacrylate) brushes. Polymeric biomaterials for tissue regeneration: from surface/interface design to 3D constructs. Injectable poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid scaffolds with in situ pore formation for tissue engineering. Accelerated wound healing by injectable microporous gel scaffolds assembled from annealed constructing blocks. Injectable, pore-forming hydrogels for in vivo enrichment of immature dendritic cells. Non-invasive and non-destructive characterization of tissue engineered constructs utilizing ultrasound imaging technologies: a evaluation. Magnetic resonance imaging of ferumoxide-labeled mesenchymal stem cells seeded on collagen scaffolds-relevance to tissue engineering. Novel biocatalytic polymer-based antimicrobial coatings as potential ureteral biomaterial: preparation and in vitro performance evaluation. Antibacterial performance of polydopamine-modified polymer surfaces containing passive and energetic components. Biomaterial-associated infection: finding the finish line in the race for the surface. Effect of Tris-acetate buffer on endotoxin removing from human-like collagen used biomaterials. Removing endotoxin from metallic biomaterials with compressed carbon dioxide-based mixtures. Effect of pattern preparation on the in vitro genotoxicity of a lightweight curable glass ionomer cement. Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of resin monomers in human salivary gland tissue and lymphocytes as assessed by the single cell microgel electrophoresis (Comet) assay. Biocompatibility of biomaterials: hemocompatibility, immunocompatiblity and biocompatibility of strong polymeric materials and soluble targetable polymeric carriers. Innate immunity activation on biomaterial surfaces: a mechanistic model and coping strategies. Direct synthesis of heparin-like poly(ether sulfone) polymer and its blood compatibility. Hollow fiber membrane modification with practical zwitterionic macromolecules for improved thromboresistance in artificial lungs. Biocompatible slippery fluid-infused films composed of chitosan and alginate via layer-by-layer selfassembly and their antithrombogenicity. Visualization and evaluation of biomaterial-centered thrombus formation inside an outlined crevice beneath move. Facile fabrication of lubricant-infused wrinkling surface for stopping thrombus formation and an infection.
500mg disithrom visaAll forty sufferers achieved successful mandibular continuity that was functionally useful infection sepsis cheap 250 mg disithrom with mastercard. Alveolar ridge demonstrating wonderful height and width for placement of 4 5 � 13-mm implants antibiotics running out order 500mg disithrom with visa. In addition antibiotic for acne purchase disithrom 250 mg, there was no donor website morbidity antibiotics for dogs diarrhea buy 100 mg disithrom otc, intraoperative time was reduced, hospital stay was shorter, and total costs had been lower in contrast with more traditional methods of mandibular reconstruction. Bioreactors If the will is to use residing biological tissue and keep away from donor site morbidity, one other technique employs bioreactors to grow tissues in geometries matching the defect in either in vitro or in vivo environments [85]. A rotating wall bioreactor has been successfully used to cultivate elastic cartilage [87]. Tissue obtained from sufferers had been differentiated into cartilage progenitor cells and injected into a porous scaffold of collagen, hydroxyapatite, and chondroitin sulfate. After tradition for six weeks, differentiated chondrocytes and elastic fibers have been observed in histology. Although the formation of tissue engineered grafts is feasible in vitro, it is important to contemplate how these tissues will acquire vitamins in vivo. For small tissues, the transport of nutrients and byproducts may be enough; nonetheless, for large tissues, the diffusion rates will not be enough for the tissue to survive [88]. By introducing vasculature into the assemble, cells deep inside the tissue can obtain acceptable vitamin and gasoline exchange. In vivo bioreactors have been used to generate vascularized flaps that match the geometry of the defect [85,89e91]. Using strategies beforehand discussed, in vivo bioreactors could be designed to encourage bone growth in a chamber of desired dimensions. As with osteopromotion strategies, development issue incorporation or cell seeding can be used directly within the defect to encourage bone progress. These techniques can be utilized to grow bone in bioreactors in animal models [89e91]. Because of the shut proximity to the intercostal arteries and veins working below the ribs, tissue from the bioreactor chambers might be eliminated with the nearby vasculature and transferred to a mandibular defect as a vascularized flap. Whereas some chambers had been crammed with autograft (requiring harvest from elsewhere within the body), these full of artificial graft allowed for the formation of mineralized tissue and reconstruction of huge mandibular defects. Incorporation of growth factors to in vivo bioreactors can also be used to promote advantageous ectopic bone growth [90]. Analysis showed the formation of recent bone with vascular provide that might be used for mandibular reconstruction. As an various alternative to loading scaffolds with growth components, cells may be seeded onto scaffolds to promote tissue development in in vivo bioreactors [91]. After 4 weeks of in vitro tradition, the cell-seeded scaffolds have been implanted within the omenta of rats. However, the formation of vasculature permitting for flap transfer was not investigated. With sturdy assist for the efficacy of in vivo bioreactors in animal models, a number of bioreactor methods have been used clinically [53e56,92]. The earliest reported case concerned angle-to-angle mandibular resection owing to a recurring ameloblastoma [53]. After 4 months, the flap was harvested and transferred with vasculature to the mandible. After 7 weeks inside the latissimus dorsi muscle, the mineralized tissue, titanium mesh, and adjoining vasculature have been transferred to the mandible. The flap confirmed reworking after transfer and the affected person had an improved level of mastication after reconstruction completed. Unfortunately, after 13 months, the mesh fractured and the gingiva grew to become disrupted, resulting in an infection and necrosis of the mandible replacement [92]. Many of the human in vivo bioreactor studies require the necessity for morcellized autograft or bone marrow. The patient may speak and eat meals; nevertheless, 5 months after transfer, the flap became infected. After three months throughout the gastric omentum, the free tissue flap was harvested and used to reconstruct the mandible. Adjuvant Therapies Antibiotics When repairing craniomaxillofacial tissue defects, proximity to bacterial flora is an important consideration. The oral cavity hosts over 500 bacterial species, including many species of Streptococcus [93], and the nasal cavity has been proven to be colonized by Staphylococcus aureus in 21% of sufferers at admission [94]. In facial fracture restore, an infection charges could be as excessive as 42% if no antibiotics are received earlier than surgery [95]. The use of cefazolin sodium has been shown to cut back the speed of an infection to 9% in the course of the surgical restore of facial fractures [95]. The authors famous that the amount of obtainable knowledge might have restricted the statistical energy of their evaluation, nevertheless. For clean-contaminated wounds similar to those commonly seen in sufferers with head and neck cancers, antibiotic prophylaxis turns into mandatory [97]. In instances in which the upper aerodigestive track is entered, the an infection fee is far greater. In addition, these infections are often polymicrobial, and the chosen antibiotic ought to cowl cardio, anaerobic, and gram-negative flora [97]. From a tissue engineering perspective, local antibiotic launch is an thrilling avenue for exploration. A scaffold designed to promote bone development, by material properties or the incorporation of bioactive molecules, may probably deliver antibiotics to a neighborhood space, thereby assuaging a variety of the systemic results of the antibiotic. Using an contaminated composite defect in a rabbit mandible, clindamycin-loaded poly(methyl methacrylate) house maintainers have been proven to clear an infection [98]. These clinically out there merchandise include gels, chips, fibers, and polymers consisting of a range of antimicrobials such as tetracycline, metronidazole, and doxycycline. After a quantity of days of controlled drug release to the site of the periodontal disease, degradation occurs for so much of of these products whereas others should be surgically eliminated [99]. Although the species distribution of craniofacial infection has not changed much over the years, the antibiotic resistance of these organisms is growing [100]. The production of b-lactamases has limited the efficacy of penicillin in opposition to some gram-negative species, and others are increasingly proof against clindamycin. This rising resistance has led researchers to explore different potential methods of combatting an infection [101,102]. Human saliva contains antimicrobial peptides that can trigger bacterial cell dying [102]. Antimicrobial peptides can be designed with different practical teams and may be modified to bind hydroxyapatite selectively [101].
Order disithrom 500 mg without prescriptionElectrospinning is among the most helpful techniques for producing a tubular scaffold of artificial polymers [73 virus 20 orca cheap 500 mg disithrom with amex,74] virus or bacteria buy 500 mg disithrom free shipping. However antimicrobial countertops buy generic disithrom 100 mg line, due to the tubular-shaped geometry of the vascular scaffolds antibiotics for acne nausea generic disithrom 500 mg on-line, cell seeding onto the outside surface of the scaffold fails to achieve environment friendly cell penetration into the vascular scaffolds. In addition, the secondary harvested cell sheet could be subsequently layered onto the first cell sheet and the graft can continue to be wrapped with multiple cell sheets. On the other hand, cell necrosis throughout the multilayer cell sheets must be addressed. In the earlier study, a pulsatile perfusion bioreactor system was used to improve the diet provide and fuel exchange. In addition, the pulsatile flow and stress to the cell sheetevascular scaffold led to tissue maturity that might face up to the extent of blood flow from the native artery. It has been confirmed that many several sorts of cells may be utilized to fabricate cell sheets utilizing a thermoresponsive surface. On the other hand, residing tissues are composed of multiple cell sorts in which cell-to-cell interactions affect and keep the event of characteristic physiological features and actions. Micropatterning on a thermoresponsive surface supports the fabrication of copatterned cell sheets [84,85]. Adapted with permission from Tsuda Y, Kikuchi A, Yamato M, Nakao A, Sakurai Y, Umezu M, et al. The use of patterned twin thermoresponsive surfaces for the collective restoration as co-cultured cell sheets. Regulating Cell Orientation in Cell Sheet Engineering Intelligent Surfaces for Regulating Cell Orientation Native tissues typically kind specific buildings which may be well-known necessary elements for producing an appropriate performance [86e89]. Ideally, engineered tissues should be produced in an environment that closely mimics the microstructure of native tissue. For example, in native skeletal muscle, the bundle structure of highly oriented myofibers is essential for generating mechanical functions. Micropatterning approaches can be used to regulate the cell orientation on tradition substrates [90]. Although a variety of microfabricated substrates have been reported, typical substrates have limitations to releasing the well-organized cell monolayer from the tradition surface. Because the clever surface permits the harvest of aligned cells as a single-cell sheet, cell sheet engineering overcomes these limitations to facilitate the design of 3D cell orientation within a densely packed cell setting. To obtain this, a quantity of kinds of micropatterned thermoresponsive substrates have been developed [91,92]. Using these substrates, cell orientation is first regulated 2D and then the aligned cells are stacked as cell sheets layer by layer. Microgrooved polydimethylsiloxane substrates are extensively used to control cell alignment, and the same technique may be utilized to produce aligned cells on the thermoresponsive surface [93]. As a end result, the floor features to regulate cell orientation and release the cell sheet. The width of the patterns is a key issue within the regulation of cell orientation, and the previous study demonstrated that a 50 � 50-mm striped pattern was appropriate for producing a cell sheet composed of aligned cells. Because of the distinction in the cell-to-surface affinity on the surfaces, cells are aligned parallel to the stripe patterns simply by cell seeding. This suggests that the cell orientation influences the bodily properties of cell sheets. In addition, the cell alignment induces a change within the biological properties of cell sheets. Adapted with permission from Takahashi H, Nakayama M, Shimizu T, Yamato M, Okano T. Anisotropic cell sheets for developing three-dimensional tissue with well-organized cell orientation. Therefore, this could doubtlessly enhance vascularization in multilayered cell sheets. Arrangement of Three-Dimensional Orientation Using Cell Sheet Layering Techniques Because cell sheets could be manipulated using a gelatin gel-coated plunger [53], cell sheets composed of aligned cells can be layered while sustaining the designed orientation. In some native tissues, tissue anisotropy is organized 3D and the orientation of their buildings is important for particular mechanical and biological features. For example, native myocardial tissue consists of multiple layers of aligned cardiomyocytes which are oriented in numerous directions throughout the entire tissue [88,89,96]. This well-organized 3D oriented structure is important for generating the anisotropic electrical propagation found within the native myocardium. However, it remains troublesome to prepare different cell orientations vertically using standard biomaterial scaffolds. This technique is easy and versatile for creating a wide range of tissue architectures. As described earlier, the cell-dense tissue construction is important for multiple cell sheets to communicate with each other throughout the layered cell sheet construct. Therefore, this system of arranging cell orientation within engineered tissues is expected to be helpful for producing biomimetic myocardial tissues. Skeletal Muscle Tissue Engineering Because native skeletal muscle tissue is manufactured from extremely oriented myofibers, the orientation of muscle cells needs to be regulated to produce biomimetic muscle tissue constructs [97e99]. Adapted with permission from Takahashi H, Shimizu T, Nakayama M, Yamato M, Okano T. The use of anisotropic cell sheets to control orientation through the self-organization of 3D muscle tissue. After reaching confluence, the aligned myoblasts can be harvested as a single continuous cell sheet by reducing the culture temperature to 20 C. In addition, regulating the aligned orientation stimulates the formation of longer myotubes, compared with randomly oriented myoblasts. This aligned structure shall be necessary for producing biomimetic muscle tissue [100]. Moreover, as a result of the aligned myotubes can be layered with cell sheet expertise, this mix supports the manufacturing of 3D aligned muscle tissues, which is required for scaling up skeletal muscle tissues. Consequently, all myoblasts grew to become aligned within the layered cell sheet assemble. Furthermore, this self-organizing conduct permits us merely to produce 3D myotube constructs with a single orientation. Myoblasts in the tissue assemble are capable of self-adjust their 3D orientation exactly. This cell sheetebased expertise provides a new potential for constructing advanced tissues composed of natively oriented cell assemblies, notably for skeletal muscle tissue [58]. Scaffold-based tissue engineering continues to develop, however cell sheet engineering has additionally expanded its distinctive features and benefits to create a model new field in regenerative medicine. Intelligent surfaces permitting us to use cell sheets have been applied to human clinical research that deliver therapeutic cells to 482 28. Moreover, the cell sheet transplantation method will probably be applied to different tissue regeneration purposes within the near future.
Disithrom: 500 mg, 250 mg, 100 mg
Buy generic disithrom 500mg on-lineAcceleration of thrombin-antithrombin advanced formation in rat hindquarters by way of heparinlike molecules bound to the endothelium bacteria reproduce using purchase disithrom 100mg fast delivery. Vascular cell-derived fibrinolytic regulators and atherothrombotic vascular disorders (Review) antibiotics for uti prophylaxis discount disithrom 250 mg with visa. Production of prostacyclin and fibrinolysis modulators by endothelial cells cultured in the presence of polyethylene terephthalate antibiotic resistance today trusted disithrom 250 mg. Cytokine expression in vitro by cultured human endothelial cells in contact with polyethylene terephthalate coated with pyrolytic carbon and collagen infection treatment buy disithrom 250mg with amex. Precoating expanded polytetrafluoroethylene grafts alters production of endothelial cell-derived thrombomodulators. Perturbations in paracrine control of the circulation: position of the endothelial-derived vasomediators, endothelin-1 and nitric oxide. Basic fibroblast progress factor improves myocardial perform in chronically ischemic porcine hearts. Bioabsorbable polymer scaffolds for tissue engineering able to sustained development issue delivery. Tissue engineering as a platform for managed launch of therapeutic agents: implantation of microencapsulated dopamine producing cells within the brains of rats. Silicon micromachining to tissue engineer branched vascular channels for liver fabrication. Chimeric vessel tissue engineering driven by endothelialized modules in immunosuppressed Sprague-Dawley rats. Biodegradable scaffold with built-in vasculature for organ-on-a-chip engineering and direct surgical anastomosis. Renal senescence, mobile senescence, and their relevance to nephrology and transplantation. Haematopoietic stem cells undertake mature haematopoietic fates in ischaemic myocardium. Novel injectable bioartificial tissue facilitates targeted, much less invasive, large-scale tissue restoration on the beating coronary heart after myocardial harm. Fibrin glue alone and skeletal myoblasts in a fibrin scaffold preserve cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Injectable fibrin scaffold improves cell transplant survival, reduces infarct expansion, and induces neovasculature formation in ischemic myocardium. Implantation of bone marrow mononuclear cells utilizing injectable fibrin matrix enhances neovascularization in infarcted myocardium. Effect of injectable alginate implant on cardiac remodeling and performance after recent and old infarcts in rat. Injectable self-assembling peptide nanofibers create intramyocardial microenvironments for endothelial cells. Cardiomyocytes derived from human embryonic stem cells in pro-survival components improve operate of infarcted rat hearts. Artificial matrix helps neonatal cardiomyocytes restore injured myocardium in rats. Engineered coronary heart tissue grafts enhance systolic and diastolic function in infarcted rat hearts. Synthesis, characterization and therapeutic efficacy of a biodegradable, thermoresponsive hydrogel designed for application in continual infarcted myocardium. A synthetic non-degradable polyethylene glycol hydrogel retards antagonistic postinfarct left ventricular remodeling. Intracoronary injection of in situ forming alginate hydrogel reverses left ventricular transforming after myocardial infarction in Swine. Thickening of the infarcted wall by collagen injection improves left ventricular function in rats: a novel strategy to preserve cardiac operate after myocardial infarction. Safety and efficacy of an injectable extracellular matrix hydrogel for treating myocardial infarction. Theoretical impression of the injection of material into the myocardium: a finite element model simulation. Apoptosis in related medical situations: contribution of apoptosis in myocardial infarction. Acute myocardial infarction in humans is related to activation of programmed myocyte cell demise in the surviving portion of the heart. Optimizing engineered heart tissue for therapeutic purposes as surrogate heart muscle. Autospecies and post-myocardial infarction sera enhance the viability, proliferation, and maturation of 3D cardiac cell tradition. Pulsatile cardiac tissue grafts utilizing a novel three-dimensional cell sheet manipulation technique functionally integrates with the host coronary heart, in vivo. Cardiac repair in Guinea pigs with human engineered coronary heart tissue from induced pluripotent stem cells. Cardiac restore in a porcine mannequin of acute myocardial infarction with human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiovascular cell populations. Human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiac progenitors for severe coronary heart failure remedy: first medical case report. Development of a organic ventricular help system: preliminary information from a small animal model. The use of extracellular matrix as an inductive scaffold for the partial alternative of functional myocardium. Increased myocyte content and mechanical perform within a tissue-engineered myocardial patch following implantation. Improved left ventricular aneurysm restore with bioengineered vascular clean muscle grafts. Scaffold-based three-dimensional human fibroblast culture provides a structural matrix that supports angiogenesis in infarcted coronary heart tissue. Prevascularization of cardiac patch on the omentum improves its therapeutic outcome. Physiological function and transplantation of scaffold-free and vascularized human cardiac muscle tissue. Taking the death toll after cardiomyocyte grafting: a reminder of the significance of quantitative biology. Survival and development of neonatal rat cardiomyocytes transplanted into grownup myocardium. In addition to this, the liver possesses a unique regenerative capacity; it is able to regenerate most of its operate after shedding as much as three-quarters of its mass as a outcome of partial hepatectomy or poisonous damage. However, it was not till 1967 when short-term success was achieved with 1-year survival after transplantation [2]. However, right now, the variety of sufferers waiting for a liver transplant far exceeds the variety of transplants performed. Although 6729 transplants were carried out, 1821 patients died while waiting for a donor and 1290 patients have been faraway from the record as a outcome of they have been too sick for transplantation during that year [4].
Buy generic disithrom 500 mgStimulatory silica microparticles (green) contained within the scaffold promote T-cell activation and enlargement antibiotics for sinus infection how long cheap disithrom 100mg, followed by migration of the activated immune cells into the surrounding setting antibiotics on birth control 500 mg disithrom with amex. T cells delivered to the resection cavity through the biomaterial scaffold had been found to proliferate at the resection site (167-fold versus injected antibiotics effective against strep throat buy 100 mg disithrom with amex, prestimulated cells delivered without the scaffold) and preserve a nonexhausted phenotype antimicrobial wood generic 250 mg disithrom visa, whereas intravenously injected T cells amassed in the spleen and liver instead. The efficacy of this method in preclinical fashions of improperly resected or metastatic cancer illustrates the potential for a biomaterials method to present localized supply of antitumor immune cells while enabling their proliferation and activation within the face of an adverse tumor microenvironment. Although rational mixtures of immunotherapies that affect multiple factors in the cancer-immunity cycle have been proven to be more efficacious, our understanding of most cancers immunobiology continues to be removed from complete. Nonetheless, speedy progress witnessed in the field of most cancers immunotherapy justifies confidence that increasingly efficient immunotherapies could be designed as the parts required for a strong antitumor response become more and more clear. The capability of engineered biomaterial methods to control the spatiotemporal distribution of cells and bioactive factors will permit them to have an essential key position in studying how biomaterialeimmune system interactions work, but then additionally to exploit these characteristics to form an evolving anticancer immune response. It remains to be seen whether essentially the most profitable biomaterials-based most cancers immunotherapies might be used to improve present therapies such as focusing on immune-modulating antibodies and/or adoptively transferred immune cells extra effectively to the tumor, enhancing the technology of antigen-specific immune effector cells by way of higher priming, or curtailing the antagonistic tumor microenvironment. Regardless, the continued improvement of safer and more practical immunotherapies will rely upon the efficient integration of ideas across a broad spectrum of disciplines and collaboration between scientists and clinicians to enable for the effective translation of these applied sciences to the clinic. Adaptive immune system the response of antigen-specific lymphocytes to antigen, including the development of immunological reminiscence. Adoptive T-cell remedy A specific immunotherapy technique which includes the isolation and ex vivo expansion of tumor-specific T cells, and then reinfusion to the patient. Antigen presenting cells Highly specialized cells that can course of antigens and show their peptide fragments on the cell floor together with molecules required for T-cell activation. The main antigen-presenting cells for T cells are dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells. The antigen receptor on B lymphocytes, often referred to as the B-cell receptor, is a cell-surface immunoglobulin. After activation by antigen, B cells differentiate into cells producing antibody molecules of the same antigen specificity as this receptor. Cancer vaccine A specific immunotherapy strategy that goals to train the immune function to recognize and destroy cancer cells. This is often accomplished by offering each an antigen expressed by the most cancers cells and an adjuvant to stimulate era of T cells particular to that cancer antigen. Chemokines Chemokines are small chemoattractant proteins that stimulate the migration and activation of cells, especially phagocytic cells and lymphocytes. Clonal T cell growth Clonal enlargement is the proliferation of antigen-specific lymphocytes in response to antigenic stimulation; it precedes their differentiation into effector cells. Corona A serum protein shell that types around a nanoparticle, particularly charged nanoparticles, after introduction into a protein-rich surroundings such as blood. Costimulatory molecules the proliferation of lymphocytes requires each antigen binding and the receipt of a costimulatory signal. Cytokines Cytokines are proteins made by cells that have an result on the habits of different cells. Cytokines made by lymphocytes are sometimes referred to as lymphokines or interleukins, but the generic time period "cytokine" is used on this book and most of the literature. Cytotoxic T cells or lymphocyte Tcells that may kill other cells are called cytotoxic Tcells. Dendritic cells Dendritic cells, also called interdigitating reticular cells, are present in T-cell areas of lymphoid tissues. They have a branched or dendritic morphology and are probably the most potent stimulators of T-cell responses. It is distinct from the follicular dendritic cell that presents antigen to B cells. Enhanced permeation and retention effect A phenomenon by which molecules of a certain measurement, typically nanoparticles and/or medication, are most likely to accumulate in tumor tissue more so than they do in normal tissue. Many consider that this is a results of leaky tumor vasculature and inadequate lymphatic drainage of solid tumors. The most efficient helper T cells are also called Th2 cells, which make the cytokines interleukins-4 and 5. Hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity the physical property of a fabric to either repel or promote water from binding to its floor. Immunoediting A dynamic course of by which tumors survive assault by the immune system. Typically described as three phases: elimination of immunologically vulnerable cells, equilibrium, and finally, immunologic escape. Immunogenic Any molecule that may elicit an adaptive immune response on injection into a person or animal known as an immunogen, and thus is assessed as being immunogenic. In apply, solely proteins are fully immunogenic as a result of only proteins may be recognized by T lymphocytes. Immunologic escape the purpose at which a tumor is no longer vulnerable to immune surveillance and begins to progress by method of progress and malignancy. Immunologic reminiscence When an antigen is encountered more than once, the adaptive immune response to every subsequent encounter is speedier and more practical, a vital feature of protective immunity known as immunological memory. Immunosuppressive A attribute of one thing that promotes the inhibition or downregulation of immune responses. Immunotherapy the prevention or treatment of disease through the use of or stimulating elements of the immune system. Innate immune system Cells which are liable for the early phases of the host response to an damage or immunologic insult during which a big selection of innate resistance mechanisms recognize and respond to the presence of a pathogen. The more basic time period "cytokine" is often used, however the time period "interleukin" is used to name specific cytokines corresponding to interleukin-2. Macrophages Macrophages are large mononuclear phagocytic cells necessary in innate immunity, in early nonadaptive phases of host defense, as antigen-presenting cells, and as effector cells in humoral and cell-mediated immunity. They are migratory cells deriving from bone marrow precursors and are present in most tissues of the body. Mononuclear phagocytic system A community of phagocytic cells positioned within the reticular connective tissue which may be extremely answerable for the clearance of nanosized and microsized materials from the blood. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells A heterogeneous group of immature myeloid immune cells which have been proven to induce vital immunosuppressive effects, especially in pathogenic situations corresponding to in continual infections or cancer. Nanotechnology the manipulation and engineering of supplies which are within the nanometer-size vary, sometimes lower than one hundred nm. Natural killer cells Large granular, non-T, non-B lymphocytes that kill certain tumor cells. Natural killer cells are necessary in innate immunity to viruses and other intracellular pathogens, as properly as in antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Pattern recognition receptors Receptors that bind to pathogen-associated molecular patterns, which are typical of micro organism or many commercially used adjuvants.
References - Daudon M, Estepa L, Viard JP, et al: Urinary stones in HIV-1-positive patients treated with indinavir, Lancet 349(9061):1294n1295, 1997.
- Sawaya H, Sebag IA, Plana JC, et al. Assessment of echocardiography and biomarkers for the extended prediction of cardiotoxicity in patients treated with anthracyclines, taxanes, and trastuzumab. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 2012;5(5):596- 603.
- Dakik HA, Kleiman NS, Farmer JA, et al: Intensive medical therapy versus coronary angioplasty for suppression of myocardial ischemia in survivors of acute myocardial infarction: A prospective randomized pilot study. Circulation 1998;98:2017-2023.
- Paduch DA, Niedzielski J: Semen analysis in young men with varicocele: preliminary study, J Urol 156:788n790, 1996.
- Black JD, Dolly JO. Selective location of acceptors for botulinum neurotoxin A in the central and peripheral nervous systems. Neuroscience 1987; 23: 767-79.
- W. T. Humphries, D. L. Millier, and R. H. Wildnauer, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. 23, 359, 1972; W. T. Humphries and R. H. Wildnauer, J. Invest. Dermatol. 59, 9, 1972.
|