Dochicin
Jacob Hogue, M.D. - Department of Pediatrics
- Madigan Army Medical Center
- Tacoma, Washington
Cheap 0.5 mg dochicin free shippingSodium currents from homozygous mutant mice have markedly decreased amplitude and irregular inactivation gating antibiotics xanax interaction purchase dochicin 0.5 mg visa, together with gradual kinetics virus definition biology buy discount dochicin 0.5 mg online, elevated persistent current antibiotic treatment for pink eye generic dochicin 0.5mg mastercard, and depolarized voltage dependence virus 66 dochicin 0.5 mg on-line. Another potential rationalization relates to genetic modifiers or environmental components as suggested by the highly variable nature of the phenotypes related to this mutation in humans. Mutant cardiac sodium channels associated with overlap syndromes exhibit more advanced useful defects. Differences in functional behavior of cardiac sodium present between the 2 strains have been also observed. This finding advised that insufficient sodium channel activation was the mechanism for impaired conduction velocity- an idea corroborated by computational modeling. Differences in cardiac gene expression between strains could contribute to these differences in sodium currents. Specifically, Scn4b encoding the 4 sodium channel auxiliary subunit is expressed at a substantially lower level in proper ventricular tissue from 129P2 mice. Additional research to uncover genetic modifiers may yield new therapeutic targets and enable higher danger stratification strategies. Schroeter A, Walzik S, Blechschmidt S, et al: Structure and function of splice variants of the cardiac voltage-gated sodium channel NaV1. Nademanee K, Veerakul G, Nimmannit S, et al: Arrhythmogenic marker for the sudden unexplained demise syndrome in Thai males. Liu M, Sanyal S, Gao G, et al: Cardiac Na+ current regulation by pyridine nucleotides. Antzelevitch C: Ion channels and ventricular arrhythmias: Cellular and ionic mechanisms underlying the Brugada syndrome. Tukkie R, Sogaard P, Vleugels J, et al: Delay in proper ventricular activation contributes to Brugada syndrome. Nair K, Pekhletski R, Harris L, et al: Escape seize bigeminy: phenotypic marker of cardiac sodium channel voltage sensor mutation R222Q. Morales A, Painter T, Li R, et al: Rare variant mutations in pregnancy-associated or peripartum cardiomyopathy. This chapter focuses on the molecular genetics of inheritable ailments related to cardiac K+ channels, so-called K+ channelopathies. Clinical options and administration of these illnesses are described in detail elsewhere in this guide. The subdivision is based on the chronological order in which the subtypes are reported. Most mutations contain single-nucleotide substitutions in the coding areas (exons) of genes that alter a codon, resulting in the replacement of 1 amino acid by a unique one (missense mutations; roughly two-thirds of all mutations) or the creation of an early (premature) stop codon resulting in the formation of a truncated protein (nonsense mutations). Single-nucleotide substitutions in the noncoding regions (introns) additionally happen and may lead to altered gene transcripts. Mutations additionally contain insertion or deletion of a quantity of nucleotides, which may lead to a shift within the open reading frame, or (when a multiple of three nucleotides are inserted or deleted) to the addition or removing of a quantity of amino acids within the ultimate product, with out affecting the studying frame. Genes Related to Inheritable Potassium Channel Diseases Current Ito,fast Chromosome 1p13. A delicate steadiness between inward and outward ion currents determines the repolarization of ventricular myocytes. Substantial differences in the expression levels of K+ channels between cardiac myocytes in several cardiac regions create a spatial dispersion of repolarization throughout the healthy ventricular myocardium. Most mutations are missense mutations (70%), adopted by frameshift mutations (10%), splice-site mutations (10%), nonsense mutations (5%), and in-frame deletions or insertions (5%). Nonmissense mutations, no matter location, have an estimated predictive worth of more than 99% to be pathogenic, and missense mutations have a excessive predictive value when situated within the transmembrane segments, the pore loop, and the C-terminus of Kv7. In common, interactions between transmembrane segments are believed to be important for regular channel activation, while interactions between the C-termini regulate channel assembly and channel deactivation. Processes instructed to be concerned in defective trafficking and intracellular retention of mutated Kv11. Mutations inside the N-terminus disrupt these interactions and trigger accelerated deactivation. Most of them are missense mutations and are positioned within the single transmembrane section of the protein. This mutation triggered a shift of inactivation towards far more optimistic potentials. In heterologous expression techniques, the mutation caused a shift of voltage-dependent activation toward more negative potentials (indicating earlier channel activation) and accelerated the speed of activation. The mutation abrogated voltage-dependent gating, resulting in instantaneous opening of the Kv7. This signifies the presence of a constitutive repolarizing present, which can explain the affiliation of the V141M mutation with atrial fibrillation. Because Ito is extra expressed in the subepicardial myocytes, that is believed to worsen transmural voltage gradients and supply a substrate for reentrant excitation waves. Shimizu W, Horie M: Phenotypic manifestations of mutations in genes encoding subunits of cardiac potassium channels. Antzelevitch C: Role of spatial dispersion of repolarization in inherited and bought sudden cardiac demise syndromes. Cellular Basis for the J Wave and Associated Arrhythmogenesis Transmural differences within the magnitude of the motion potential notch have long been recognized as the premise for inscription of the electrocardiographic J wave. Genetic Basis of Brugada Syndrome (BrS) Causative Genes Locus BrS1 BrS2 BrS3 BrS4 BrS5 BrS6 BrS7 BrS8 BrS9 BrS10 BrS11 BrS12 Modulatory Genes 15q24-q25 7q35 Xq22. In sufferers with BrS, the looks of outstanding J waves is restricted to the leads dealing with the right ventricular outflow tract, the place Ito is assumed to be most prominent. The more prominent Ito in the best ventricular epicardium offers for a higher outward shift within the stability of present, which promotes the appearance of the J waves in this area of the ventricular myocardium. Repolarization Defects Perturbations of the terminal phase of the motion potential typically referred to as J waves can arise from repolarization or depolarization abnormalities. A easy approach to distinguish between the two mechanisms is to look at the impact of rate or atrial untimely beats. When because of delayed conduction, the notched look ought to turn out to be progressively more accentuated with acceleration of price or prematurity, and when as a end result of repolarization problems, the amplitude of the J wave should progressively diminish. These totally different responses are because of the reality that delayed conduction nearly invariably turns into more accentuated at faster rates or with prematurity, whereas the Ito-mediated action potential notch diminishes as the outcome of insufficient time for Ito to reactivate. Shinohara T, Takahashi N, Saikawa T, et al: Characterization of J wave in a affected person with idiopathic ventricular fibrillation. Rosso R, Kogan E, Belhassen B, et al: J-point elevation in survivors of major ventricular fibrillation and matched management topics: Incidence and medical significance. Early repolarization: Electrocardiographic phenotypes related to favorable long-term consequence. Naruse Y, Tada H, Harimura Y, et al: Early repolarization is an unbiased predictor of occurrences of ventricular fibrillation in the very early section of acute myocardial infarctions. Shimizu W, Matsuo K, Kokubo Y, et al: Sex hormone and gender difference-Role of testosterone on male predominance in Brugada syndrome.
Dochicin 0.5 mg lineA meticulous historical past taking may reveal presence of any of the following predisposing factors: � Injury to the eye by vegetative matter infection z trailer 0.5 mg dochicin overnight delivery, nail virus war proven 0.5 mg dochicin, foreign body virus wear discount 0.5mg dochicin with amex, and so forth generic antibiotics for acne buy generic dochicin 0.5mg on-line. Lids present oedema, blepharospasm, lashes may be matted and trichiasis may be present generally. Cornea on meticulous examination might reveal: �Loss of regular corneal transparency. It could be decreased by any of the following measures: � Preoperative use of mitomycin-C � Postoperative use of antimitotic drops similar to mitomycin-C or thiotepa � Surgical excision with naked sclera � Surgical excision with mucous membrane grafts � Best methodology is surgical excision followed by autolimbal conjunctival graft. Pinguecula is a degenerative condition of the conjunctiva characterised by formation of a yellowish white triangular patch near the limbus. Depending upon the etiology, conjunctival xerosis may be divided into two teams: I. Parenchymatous xerosis: It happens due to cicatricial disorganisation of the conjunctiva as seen in following circumstances: � Trachoma � Membranous conjunctivitis � Stevens-Johnson syndrome � Pemphigus � Pemphigoid � Conjunctival burns (thermal, chemical or radiational) � Prolonged exposure of conjunctiva as in lagophthalmos. In progressive pannus, the infiltration is seen forward of the parallel blood vessels, while in regressive pannus it stops short and the blood vessels extend beyond the corneal haze. Efforts should be made to describe the kind of corneal ulcer whether or not bacterial, fungal, viral, degenerative or dietary. Related Questions Define keratitis Keratitis refers to inflammation of the cornea. It is characterised by corneal oedema, cellular infiltration and conjunctival reaction. Define corneal ulcer Corneal ulcer may be outlined as discontinuation in the regular epithelial surface of the cornea associated with necrosis of the encircling corneal tissue. Classify keratitis Keratitis could be categorised in two ways: topographically and etiologically. Ulcerative keratitis (corneal ulcer): It can be further classified variously as follows: 1. Purulent corneal ulcer or suppurative corneal ulcer (mostly bacterial and fungal corneal ulcers are purulent). Nonpurulent corneal ulcer (most of the viral, chlamydial, allergic and different noninfective corneal ulcers are nonsuppurative). Traumatic keratitis, which may be as a end result of mechanical trauma, chemical burns, radiational burns or thermal burns. Common bacteria related to corneal ulceration are: Pseudomonas pyocyanea, streptococcus pneumoniae, E. What is the prerequisite for many of the infecting brokers to produce corneal ulceration Nonsuppurative �Interstitial keratitis �Disciform keratitis Damage to the corneal epithelium is a prerequisite for most of the infecting organisms to produce corneal ulceration. Damage to corneal epithelium might occur in following types: � Corneal abrasion due to small overseas physique, misdirected cilia, trivial trauma, etc. After therapeutic of corneal ulcer following problems could additionally be left as sequelae: � Keractasia � Corneal opacity which may be nebular, macular, leucomatous or adherent leucoma � Anterior staphyloma which often follows a sloughing corneal ulceration. Name the micro organism which might invade the intact corneal epithelium and produce ulceration. Stage of progressive infiltration Stage of active ulceration Stage of regression Stage of cicatrization. Descemetocele formation associated with extreme corneal oedema are the indicators of an impending corneal perforation. A clinical analysis of bacterial corneal ulcer is made in patients with a greyish white central or marginal ulcer related to marked ache, photophobia, blepharospasm, lacrimation, circumcorneal congestion, purulent/mucopurulent discharge, presence or absence of hypopyon with or without vascularization. Following perforation of a corneal ulcer, immediately pain decreases and affected person feels some scorching fluid (aqueous) coming out of the eyes. Meticulous history should be taken and a radical A purulent corneal ulcer associated with assortment of pus within the anterior chamber brought on by Pneumococcus is called hypopyon corneal ulcer: Name the widespread organisms liable for hypopyon corneal ulceration. Common micro organism producing hypopyon ulcer are: Pneumococcus, Pseudomonas, Gonococcus and Staphylococcus. General physical and systemic examination ought to be carried out to elucidate the related malnutrition, diabetes mellitus and some other chronic debilitating disease. Laboratory investigations the attribute hypopyon ulcer brought on by Pneumococcus is identified as ulcus serpens. Toxic iridocyclitis Secondary glaucoma Descemetocele Corneal perforation, which may be complicated by: � Iris prolapse � Subluxation or dislocation of the lens � Anterior capsular cataract � Purulent iridoc yclitis usually leading to endophthalmitis and even panophthalmitis � Intraocular haemorrhage within the form of a vitreous haemorrhage or expulsive choroidal haemorrhage. Treatment of uncomplicated corneal ulcer How will you deal with a case of non-healing corneal ulcer Specific treatment for the trigger: Bacterial corneal ulcer is treated by topical and systemic antibiotics. It is preferable to begin concentrated amikacin (40�100 mg/ml) eyedrops along with fortified cephazolin (33 mg/ml) eyedrops each one hourly for first 5 days and then reduced to 2 hourly, three hourly, 4 hourly and 6 hourly. Subconjunctival injection of gentamicin 40 mg and cephazolin 125 mg as soon as a day for 5 days ought to be given in sloughing corneal ulcer. Removal of any recognized cause of nonhealing: A thorough search ought to be made to find out any already missed explanation for nonhealing and when discovered it should be eliminated. Chemical cauterization with pure carbolic acid or 10 to 20% trichloroacetic acid could also be considered in indolent instances. Lowering of intraocular stress by simultaneous use of acetazolamide 250 mg qid orally, 0. Therapeutic keratoplasty, when available, is taken into account the most effective mode of therapy. However, in need of it, depending upon the dimensions and placement of the perforation measures like, use of a tissue glue (cyanoacrylate), bandage gentle contact lens or conjunctival flap could additionally be used over and above the conservative management with strain bandage. Marginal catarrhal ulcer is a superficial ulcer located near the limbus, normally seen in affiliation with continual staphylococcal blepharoconjunctivitis. Excessive use of topical antibiotics and steroids predispose the cornea far fungal infections. A typical fungal corneal ulcer is dry wanting, greyish white with elevated rolled out margins and delicate feathery finger-like extensions into the surrounding stroma beneath the intact epithelium. A history of trauma (especially by vegetative material) and scientific indicators out of proportion to the signs, i. Dendritic ulcer is a typical epithelial lesion of the recurrent herpetic keratitis. Sometimes, the branches of the dendritic ulcer enlarge and coalesce to type a big epithelial usually generally identified as geographical or amoeboid ulcer. Name the predisposing/precipitating stress stimuli which set off an assault of herpetic keratitis. It is characterized by a focal disc-shaped patch of stromal oedema without necrosis. Associated diminished corneal sensations and fine keratic precipitates differentiate it from other causes of stromal oedema. Punctate epithelial keratitis � Viral keratitis, neuroparalytic keratitis, diabetic neuropathy and leprosy. In it, frontal nerve is extra frequently affected than the lacrimal and Chapter 24 Clinical Ophthalmic Cases 535 nasociliary nerve.
Diseases - Valinemia
- Glycogen storage disease type VI
- Chromosome 20, trisomy
- Lysine alpha-ketoglutarate reductase deficiency
- Galactosamine-6-sulfatase deficiency
- Teratocarcinosarcoma
- Leukodystrophy, globoid cell
- Hypercalcinuria idiopathic
- Chromosome 1, uniparental disomy 1q12 q21
- Jones syndrome
Generic dochicin 0.5 mg with visaName the assorted modalities for correction of aphakia and enumerate benefits and drawbacks of every virus kansas city cheap dochicin 0.5 mg online. Advantages: (i) Less magnification (5%) of the picture antimicrobial versus antibiotic dochicin 0.5mg online, (ii) Elimination of aberrations and prismatic impact of thick glasses antibiotics for acne marks generic dochicin 0.5 mg line, (iii) Wider and better visual field virus going around september 2014 purchase 0.5 mg dochicin with visa, (iv) Cosmetically better accepted by young individuals. Disadvantages: (i) More price, (ii) Cumbersome to put on, especially in old age and in childhood, (iii) Corneal problems might occur. Advantage: It presents all the advantages which the contact lenses offer over the spectacles. Optic disc seems giant, pale and at its temporal edge characteristic myopic crescent is present. Astigmatism is a sort of refractive error, whereby the refraction varies within the completely different meridia. Complicated cataract Choroidal haemorrhage Tears and haemorrhage in the retina Vitreous haemorrhage Retinal detachment. Contact lens prescription, which replaces the anterior floor of the cornea for refraction. In radial keratotomy operation, a number of radial incisions are given in the periphery of cornea (leaving central 4 mm optical zone) to be able to flatten the curvature of cornea. Herein the rays of light entering the eye are centered on the retina in one meridian and both in entrance (simple myopic astigmatism, or behind (simple hypermetropic astigmatism) the retina in different meridian. In this condition, gentle rays are targeted in front of the retina in a single meridian and behind the retina in the other meridian. Range of accommodation is the gap between the near level and much point of the eye. Aniseikonia is outlined as a condition, whereby the pictures projected to the visible cortex from the 2 retina are abnormally unequal in measurement and form. Amplitude of lodging is the difference between the dioptric energy wanted to focus at close to and much level. Common causes of insufficiency of accommodation are: � Premature sclerosis of the lens. Its value varies with age; being about 7 cm at 10 years of age and about 25 cm at about 40 years of age. The end point of neutralization is both no movement or just reversal of the motion of the pupillary shadow. With movement of the pink reflex indicates either emmetropia or hypermetropia or myopia of less than 1D. What inferences are drawn from the movement of the red reflex when concave mirror retinoscope is used A darkroom ideally 6-m long or which could be converted into 6 meters by the use of a aircraft mirror. A trial field containing spherical and cylindrical lenses of variable plus and minus powers, a pinhole, an occluder and prisms. The inferences drawn while using a concave mirror are reverse to that of airplane mirror. What is the point of neutralization whereas utilizing a easy airplane mirror retinoscope Mirror retinoscopes, which may consist of a simple plane mirror or a combination of a plane mirror (on one end) and a concave mirror (on the opposite end). What are some great advantages of a streak retinoscope over a easy airplane mirror retinoscope The streak retinoscope is more sensitive than the spot retinoscope in detecting astigmatism. While performing retinoscopy, if the shadow seems to swirl round, what does it indicate While performing retinoscopy with dilated pupil, one central and one other peripheral shadow may be seen. When a cycloplegic retinoscopy has been performed, how many dioptres should be deducted to compensate for the ciliary tone Cycloplegics are used earlier than retinoscopy in patients where the examiner suspects that accommodation is abnormally energetic and can hinder the exact retinoscopy. It is a computerized refractometer which rapidly estimates the refractive error of the patient objectively when it comes to sphere, cylinder with its axis and interpupillary distance. When retinoscopy is carried out with a aircraft mirror at a distance of 1 m; what inferences are drawn Depending upon the movement of the red reflex vis-a-vis movement of the airplane mirror, following inferences are drawn: Duochrome test is based on the precept of chromatic aberrations. In it, the patient is requested to tell the clarity of the letters with purple background visa-vis green background. To an emmetropic affected person, letters of each the colors look equally sharp; while to a barely myopic affected person the pink letters appear sharper and to a slightly hypermetropic affected person the green letters look sharper. Used in ophthalmic equipments corresponding to gonioscope, keratometer, applanation tonometer, etc. The cross cylinder effect is obtained by combining a spherical lens with a cylindrical lens (double the power of spherical lens) with opposite signal �0. A cross cylinder is used to verify the strength and axis of the cylinder subjectively. While testing, the pink glass is stored in front of the right eye and the green glass is kept in front of the left eye. Slit-lamp biomicroscopic examination of the fundus by: � Indirect slit-lamp biomiscroscopy � Hruby lens biomicroscopy � Contact lens biomicroscopy. It is primarily carried out to assess the state of fundus and detect the opacities of ocular media. The ophthalmoscope was invented by Babbage in 1848, nevertheless, its significance was not recognized, and it was reinvented by von Helmholtz in 1850. A small gap and a mole on the iris appear as a black spot on indirect illumination. On distant direct ophthalmoscopy, the mole appears black (as earlier) but a red reflex is seen via the outlet within the iris. A greyish reflex seen on distant direct ophthalmoscopy signifies either a detached retina or a tumour arising from the fundus. Direct Ophthalmoscopy It is essentially the most generally practised method for routine fundus examination. Distant Direct Ophthalmoscopy It should be carried out routinely before the direct ophthalmoscopy, because it provides plenty of helpful data (vide infra). In direct ophthalmoscopy, the picture is erect, virtual and about 15 instances magnified in emmetropes (more in myopes and fewer in hypermetropes). Patients right eye should be examined by the observer with his or her proper eye and left with the left eye. Once the retina is concentrated the small print must be examined systematically starting from disc, blood vessels, the 4 quadrants of the general background and the macula (see page 507�509 for systematic observations to be made on ophthalmoscopy). Indirect Ophthalmoscopy Indirect ophthalmoscopy launched by Nagel in 1864, is now a very fashionable method for examination of the posterior section. Magnification of image relies upon upon the dioptric energy of the convex lens, position of the lens in relation to the eyeball and refractive state of the eyeball. With a stronger lens, picture shall be smaller, however brighter and visual field might be more. Formation of reflexes by the two surfaces of convex lens may be eliminated by barely tilting the lens and use of aspheric lens. Patient is made to lie within the supine place, with one pillow on a bed or couch and instructed to hold both eyes open. In apply, binocular ophthalmoscope with head band or that mounted on the spectacle body is employed most regularly. The examiner moves around the head of the patient to examine totally different quadrants of the fundus. By asking the patient to look in extreme gaze, and utilizing scleral indenter, the entire peripheral retina up to ora serrata can be examined.
Generic dochicin 0.5 mg on-lineThe tumour commonly involves the superonasal quadrant; but may invade any a half of the orbit holistic antibiotics for sinus infection buy dochicin 0.5 mg line. Treatment includes: � Surgical excision biopsy is feasible only for a nicely circumscribed localised tumour ucarcide 42 antimicrobial purchase dochicin 0.5mg on line. Chemotherapy usually leads to a good prognosis in embryonal sarcomas however not in alveolar sarcomas (most malignant) antimicrobial qualities discount 0.5 mg dochicin. Optic nerve alone is affected in 28% of circumstances antibiotic resistance in hospitals dochicin 0.5 mg, 72% involve the optic chiasma, typically with mid-brain and hypothalamic involvement. It is characterised by gradual visual loss associated with a gradual, painless, unilateral axial proptosis occurring in a baby usually between 4 and 8 years of age. Fundus examination might show optic atrophy (more common) or papilloedema and venous engorgement. Clinical prognosis is properly supported by X-rays displaying uniform common rounded enlargement of optic foramen in 90% of circumstances. Treatment includes: � Observation, with none remedy, is really helpful for patients having stationary tumour, with good imaginative and prescient, and non-disfiguring proptosis. This tumour usually presents with early visible loss related to limitation of ocular actions, optic disc oedema or atrophy, and a slowly progressive unilateral proptosis. However, the presence of opticociliary shunt is pathognomic of an optic nerve sheath meningioma. It may present both as a solitary tumour or as a part � Observation is beneficial if visible acuity is good. Orbital invasion could occur via: floor of anterior cranial fossa, superior orbital fissure and optic canal. These are characterised by greater proptosis and lesser visible impairment than the primary intraorbital meningiomas. In such instances, proptosis is because of hyperostosis on the lateral wall and roof of the orbit. Management of secondary orbital (sphenoid wing) meningiomas is as beneath: Chapter 17 Diseases of Orbit V. Clinical options embrace: Proptosis, which is painless, progressive with medial displacement of the globe. Treatment includes radiotherapy or chemotherapy relying upon the grade and spread of tumour. These diseases primarily have an effect on kids with an orbital involvement in 20% of instances. It is a chronic disseminated form of histiocytosis involving both gentle tissues and bones in older kids of both sex. It is characterised by a triad of proptosis, diabetes insipidus and bony defects within the skull. Unifocal or multifocal eosinophilic granuloma is characterised by a solitary or a number of granulomas involving the bones. Carcinoma-from lungs (most widespread in males), breast (most widespread in females), prostate, thyroid and rectum. Etiology Blow-out orbital fractures generally end result from trauma to the orbit by a relatively massive, often rounded object, similar to tennis ball, cricket ball, human fist. The drive of the blow causes a backward displacement of the eyeball and a rise within the intraorbital stress; with a resultant fracture on the weakest point of the orbital wall. Impure blow-out fractures: these are associated with other fractures about the center third of the facial skeleton. Periorbital oedema and blood extravasation in and across the orbit (such as subconjunctival Chapter 17 Diseases of Orbit 423. Emphysema of the eyelids occurs extra regularly with medial wall than flooring fractures. Paraesthesia and anaesthesia in the distribution of infraorbital nerve (lower lid, cheek, side of nose, higher lip and upper teeth) are quite common. Ipsilateral epistaxis because of bleeding from maxillary sinus into the nose is incessantly famous in early levels. Three components liable for producing enophthalmos are: � escape of orbital fats into the maxillary sinus; � backward traction on the globe by entrapped inferior rectus muscle; and � enlargement of the orbital cavity from displacement of fragments. Nevertheless, the attention should be rigorously examined to exclude the risk of intraocular damage. Superior method is used for the lesions positioned within the superoanterior part of the orbit. Inferior approach is appropriate for the lesions positioned in the inferoanterior part of the orbit. In this strategy, lateral half of the supraorbital margin with the quadrilateral piece of bone forming the lateral orbital wall is temporarily removed. In this method, orbit is opened via its roof and thus, primarily is the area of neurosurgeons. Transfrontal orbitotomy is used to decompress the roof of the optic canal and to discover and take away when potential tumours of the sphenoidal ridge involving the superior orbital fissure. Systemic antibiotics must be given to stop secondary infection from the maxillary sinus. Cold compresses, immediately following trauma might lower swelling by inflicting vasoconstriction. Surgical administration Surgical repair to restore continuity of the orbital flooring could additionally be made with or without implants. Incarceration of tissues in the fracture ensuing, in globe retraction and elevated applanation tension on attempted upward gaze. It is indicated only when the lesion is readily palpable via the eyelids and is judged to be mainly in entrance of the equator of eyeball. Depending upon the situation of the lesion the anterior orbitotomy can be performed by any of the next approaches. This strategy offers an access to the orbit (through its roof) and anterior and center cranial fossa concurrently. Exenteration is indicated for malignant tumours arising from the orbital constructions or spreading from the eyeball. The term eyewall has been restricted for the outer fibrous coat (cornea and sclera) of the eyeball. Open-globe damage is associated with a full-thickness wound of the sclera or cornea or both. The two wounds will must have been caused by the same agent (earlier known as double perforation). In view of the above, mechanical ocular accidents may be discussed underneath following headings: � Extraocular foreign bodies, � Blunt trauma, � Open globe accidents, and � Sympathetic ophthalmitis. A foreign body could additionally be impacted within the Ocular Injuries 427 � Corneal ulceration might happen as a complication of corneal overseas body. The ordinary foreign bodies: � In industrial staff are particles of iron (especially in lathe and hammer-chisel workers), emery and coal. A overseas physique produces instant: � Discomfort, profuse watering and redness in the eye.
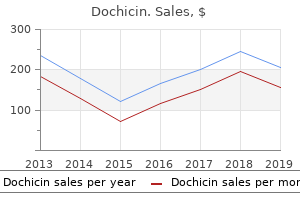
Dochicin: 0.5 mg
Purchase dochicin 0.5 mg onlineIt is a number one reason for blindness in developed countries antibiotics and diabetes cheap dochicin 0.5 mg without a prescription, in inhabitants above the age of 65 years antimicrobial body wash discount 0.5 mg dochicin with amex. Certain danger elements which may have an effect on the age of onset and/or progression embrace heredity antibiotic quizzes order 0.5 mg dochicin visa, nutrition antimicrobial use in food animals cheap 0.5mg dochicin fast delivery, smoking, hypertension, exposure to solar light, hyperopia, blue eyes and cataract significantly nuclear opacity. Patients may complain of distorted imaginative and prescient and problem in studying because of central shadowing. However, the impact is brief lasting and repeated injections are required at an interval of 1�3 months. Senile or idiopathic (83%), extra frequent in females aged 60�80 years than males (F:M, three:1). Other causes of macular gap embrace: cystoid macular oedema, vitreomacular traction, postsurgical, myopia, post-laser therapy, epiretinal membrane traction and post-inflammatory. Clinical options Symptoms embrace: Differential diagnosis of fundus appearance embody: � Macular pucker (epiretinal membrane) with pseudohole, � Solar retinopathy, � Intraretinal cyst. Investigations � Decreased vision, sometimes round 6/60 level for a full thickness gap and better for a partial gap. Based on the fundus appearance (best examined with 78/90D slit-lamp examination), the macular hole can be classified into 4 levels. Fundus fluorescein angiography reveals early foveal hyperfluorescence without leak within the late part in sufferers with stage 2 to 4 macular holes. Normally, these two layers are loosely hooked up to one another with a possible space in between. Hence, really speaking the time period retinal detachment is a misnomer and it should be retinal separation. Retinal degenerations predisposed to retinal detachment are as follows: � Lattice degeneration, � Snail observe degeneration, � White-with-pressure and white-without-or occult strain, � Acquired or retinoschisis, and � Focal pigment clumps. Clinical features Prodromal signs include: � Dark spots (floaters) in entrance of the eye (due to speedy vitreous degeneration), and � Photopsia, i. Once the retinal break is fashioned, the liquified vitreous might seep by way of it separating the sensory retina from the pigment epithelium. Localised relative loss in the field of regard (of detached retina) is seen by the affected person in early stage which progresses to a total loss when peripheral detachment proceeds progressively in the path of the macular area. Sudden look of a darkish cloud or veil in entrance of the attention is complained by the sufferers when the detachment extends posterior to equator. Plane mirror examination or Distant Direct ophthalmoscopy reveals an altered purple reflex in the pupillary space. It is of particular value in patients with hazy media especially in the presence of dense cataracts and vitreous haemorrhage. Retinal detachment, is best examined by indirect ophthalmoscopy utilizing scleral indentation (to improve visualization of the peripheral retina anterior to equator). These could also be small or might assume the form of balloons in large bullous retinal detachment. These could additionally be spherical, horse-shoe formed, slit-like or within the form of a large anterior dialysis. Retinal breaks are most incessantly found within the periphery (commonest within the upper temporal quadrant). All the retinal breaks ought to be detected, precisely localised and sealed by producing aseptic chorioretinitis, with cryocoagulation, or photocoagulation or diathermy. Maintenance of chorioretinal apposition is required for at least a couple of weeks. Scleral buckling is achieved by inserting an explant (silicone sponge or strong silicone band) with the assistance of mattress type sutures applied in the sclera. Main steps of this process are: � Pars plana, 3-port vitrectomy (see web page 261) is finished to remove all membranes and vitreous and to clean the perimeters of retinal breaks. Prophylactic measures are notably indicated in patients having associated high-risk elements like myopia, aphakia, retinal detachment in the fellow eye or historical past of retinal detachment in the family. Etiology Radially-oriented explant is most effective in sealing an isolated gap, and circumferential explant (encirclage) is indicated in breaks involving three or more quadrants. Then correct positioning of the affected person is finished in order that the break is uppermost and the fuel bubble stays involved with the tear for 5�7 days. This process is indicated in: Common causes of exudative retinal detachment could be grouped as underneath: 1. These embrace: toxaemia of being pregnant, renal hypertension, blood dyscrasias and polyarteritis nodosa. Treatment sympathetic ophthalmia, posterior scleritis, and orbital cellulitis; iii. Vascular ailments similar to central serous retinopathy and exudative retinopathy of Coats; iv. Uveal effusion syndrome is characterised by bilateral detachment of the peripheral choroid, ciliary body and retina. Clinical options Treatment of the cause is required in many of the instances, as the exudative retinal detachment as a outcome of transudate, exudate and haemorrhage might undergo spontaneous regression following absorption of the fluid. Etiology Exudative retinal detachment may be differentiated from a simple major detachment by: � Absence of photopsia, holes/tears, folds and undulations. Retinoblsatoma is confined to infancy and really younger kids normally seen between 1 and a pair of years of age. Classification of retinal tumours is given below and only a few, that are generally seen are described. It is the commonest intraocular tumour of childhood occurring 1 in 15,000 to 20,000 stay births. Some details about incidence of retinoblastoma are as below: Of all cases, only 10% are familial (inherited by autosomal dominant mode) and the rest about 90% occur sporadically. Thus, the retinoblastoma both occurs as heritable (germline) instances (40%) or non-heritable somatic instances (60%). In such cases first hit (mutation) happens in one of the two alleles of retinoblastoma gene on the germ cells (gametes), earlier than fertilization. This happens in 40% of all circumstances both due to inheritence from the affected father or mother (10% cases) or sporadically in one of the gametes (30% cases). This means mutation will happen in all of the somatic cells (predisposing to develop even nonocular tumours such as osteosarcoma). Second hit (mutation) occurs late within the postzygote section and affects second allele of one or more retinal cells, leading to multifocal and usually bilateral tumour formation. Heritable case can transmit the disease by autosomal dominant approach to 50% of offsprings. About 60% of retinoblastoma cases happen sporadically by each hits (mutations) occurring in the identical retinal cell within the embryo after fertilization. Retinoblastoma arises as malignant proliferation of the immature retinal neural cells which are small round cells with large nuclei, i. The tumour mainly consists of small spherical cells with large nuclei, resembling the cells of the nuclear layer of retina. These cells may current as a highly undifferentiated or well-differentiated tumour.
Buy 0.5mg dochicin with amexThese embrace: � Infantile nystagmus syndrome infection url mal dochicin 0.5mg without prescription, � Fusion maldevelopment nystagmus syndrome bacteria streptococcus purchase dochicin 0.5 mg overnight delivery, and � Spasmus nutans syndrome antimicrobial vinyl flooring purchase dochicin 0.5 mg. It is characterized by erratic waveform with or without roving eye actions related to lowered visual acuity due to virus yardville purchase 0.5 mg dochicin visa above talked about circumstances. Conjugate horizontal jerk nystagmus with � May lower with induced convergence, elevated fusion, extraocular muscle surgery, contact lenses, and sedation. Low�amplitude pendular nystagmus (dual-jerk waveform), jerk in path of fixing eye. While testing visual acuity in such sufferers, one eye must be fogged (by including plus lenses in front) rather than occluding to decrease induction of latent nystagmus. It is related to harmful lesions of vestibular system such as labyrinthitis and vestibular neuritis. Central vestibular nystagmus � Infantile onset � Abnormal head posture and head oscillation which improve (disappears) during childhood. Usually spontaneously remits clinically in 2 to 8 years, remains present with eye motion recordings. It is usually related to posterior fossa illnesses and is typical of compression on the stage of foramen magnum. Conjugate, horizontal jerk nystagmus current within the main gaze characterized by spontaneous course changes each 60�90 seconds, with 10-15 second hole or null interval, i. It occurs usually because of vestibulo-cerebellar illnesses corresponding to demyelination and Arnold Chiari malformation. Nystagmus as a end result of problems of gaze holding Late onset or acquired nystagmus is usually characterised by oscillopsia, and is often related to other neurological abnormalities. Slow, conjugate horizontal jerk nystagmus in the path of gaze (no nystagmus in primary gaze). It is special sort of pathologic gaze evoked nystagmus which is unilateral or uneven nystagmus normally of the abducting and sometimes of the adducting eye. Classically associated with pinealoma, but can also happen with different neoplasms, stroke, trauma or multiple sclerosis. Tumours within the cerebello-pontine angle, produce a low-frequency, massive amplitude nystagmus, when the affected person appears towards the facet of the lesion, and a high-frequency, small-amplitude nystagmus, when the affected person seems towards the side reverse to the lesion. The nystagmus that occurs on gaze in the direction of the aspect of the lesion is gaze-evoked nystagmus attributable to faulty gaze holding, whereas the nystagmus that happens during gaze in path of the side reverse the lesion is caused by vestibular imbalance. If a patient with gaze-evoked nystagmus makes an attempt to look eccentrically for a sustained interval, the nystagmus begins to decrease in amplitude and will even reverse the course, this is known as centripetal nystagmus. If the eyes are then returned to the central position, a short-lived nystagmus with gradual drifts in the direction of the prior eccentric gaze occurs. Both centripetal and rebound nystagmus mirror an try by brainstem or cerebellar mechanisms to appropriate for the drift of gaze-evoked nystagmus. Causes of rebound nystagmus include: � Cerebellar diseases, � Lateral medullary infarction, and � Tumours confined to the flocculus. Acquired pendular nystagmus � Usually disconjugate with horizontal, vertical and torsional elements. Superior oblique myokymia is characterized by monocular, speedy, intermittent, torsional and vertical actions (which are best seen on slit-lamp examination). Each eyelid is divided by a horizontal furrow (sulcus) into an orbital and tarsal part. The two lids meet one another at medial and lateral angles (or outer and inside canthi). In Caucasians with the lids open, the lateral canthus is about 2 mm larger than the medial canthus. When the eyes are open it measures about 10�11 mm vertically within the centre and about 28�30 mm horizontally. The lateral, ciliary portion consists of a rounded anterior border, a sharp posterior border (placed against the globe) and an intermarginal strip (between the 2 borders). The gray line (which marks junction of pores and skin and conjunctiva) divides the intermarginal strip into an anterior strip bearing Chapter 15 Disorders of Eyelids 363 2�3 rows of lashes and a posterior strip on which openings of meibomian glands are arranged in a row. The splitting of the eyelids when required in operations is completed at the stage of gray line. It comprises three parts: the orbital, palpebral (pretarsal and preseptal parts) and lacrimal. There are two plates of dense connective tissue, one for each lid, which give form. The upper and lower tarsal plates join with each other at medial and lateral canthi; and are hooked up to the orbital margins by way of medial and lateral palpebral ligaments. Those from lateral half of the lids drain into preauricular lymph nodes and people from the medial half of the eyelids drain into submandibular lymph nodes. It is a really uncommon anomaly during which lids fail to develop and the pores and skin passes continuously from the eyebrow to the cheek hiding the eyeball. Occasionally, the lids could also be very small or virtually absent and the situation is known as ablepharon. Epiblepharon refers to a congenital anomaly in which a horizontal fold of tissue rides above the lower eyelid margin. Euryblepharon refers to unilateral or bilateral horizontal widening of palpebral fissure. Sensory nerve supply is derived from branches of the trigeminal nerve corresponding to lacrimal, supraorbital and supratrochlear nerves for upper lid; and the infraorbital nerve with infratrochlear branch for lower lid. Bacterial Blepharitis Bacterial blepharitis, also called persistent anterior blepharitis, or staphylococcal blepharitis or ulcerative blepharitis, is a continual an infection of the anterior part of the lid margin. Inflammations of the lid itself, which embrace dermatitis, stye, hordeolum internum, insect bites, cellulitis and lid abscess. Inflammations of the conjunctiva, corresponding to acute purulent, membranous and pseudomembranous conjunctivitis. Inflammations of the orbit, which embody orbital cellulitis, orbital abscess and pseudotumour. Local causes are: cavernous sinus thrombosis, head harm and angioneurotic oedema. General causes are congestive heart failure, renal failure, hypoproteinaemia and severe anaemia. Predisposing elements, often none, could not often include chronic conjunctivitis and dacryocystitis. Clinical features Symptoms embrace continual irritation, itching, mild lacrimation, gluing of cilia, and gentle photophobia. Complications and sequelae of lengthy standing bacterial blepharitis include: � Lash abnormalities similar to madarosis (sparseness or absence of cilia), trichiasis (misdirected cilia), and poliosis (graying of lashes). It is a particularly common disease which can be divided into following medical varieties.
Asian Water Plantain (Water Plantain). Dochicin. - Are there safety concerns?
- How does Water Plantain work?
- What is Water Plantain?
- Bladder and urinary tract diseases.
- Dosing considerations for Water Plantain.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96365
Generic 0.5mg dochicin amexThe "X" marks the location of the top of the commissure infection around the heart order dochicin 0.5mg with mastercard, and is marked on the surface of the neoaorta with a marking suture antibiotic for dog uti generic dochicin 0.5mg on line. Torsion of the Coronary Artery Some surgeons choose to excise the coronary ostia as buttons antibiotics hearing loss 0.5 mg dochicin free shipping, instead of tongues of tissue from the aortic root antibiotics for sinus infection nhs cheap 0.5mg dochicin amex. When this technique is used, extreme care should be taken to stop rotation and distortion of the coronary artery button throughout reimplantation. Circumflex Coronary Artery Arising from the Right Coronary Artery If the circumflex coronary artery arises from the proper coronary artery, a trapdoor could additionally be created in the neoaorta to prevent kinking of the takeoff of the circumflex department. Alternatively, the proper coronary artery ostium could also be implanted greater on the neoaorta. When the circumflex arises from the right coronary artery, the pulmonary artery ought to be transected as far distally as possible to enable a excessive reimplantation of the best coronary button. Occasionally, the anastomosis must be carried out on the ascending aorta distal to the suture line becoming a member of the neoaortic root to the distal aorta. Intramural Coronary Artery A shallow, U-shaped incision is made within the proximal neoaorta adjoining to the situation of the beforehand prepared aortic tongue of tissue containing the concerned coronary ostium P. The upper edge of the aortic tongue is sutured to the lower portion of this U-shaped opening in the neoaortic root with a 7-0 Prolene suture. The neoaortic root is anastomosed to the ascending aorta posteriorly, securing the suture line on both sides where it meets the coronary artery anastomosis. A piece of autologous pericardium is cut within the acceptable form, and sewn into place to create a convex roof over the remaining opening. This technique allows the coronary artery to maintain its unique orientation, and P. Injury to the Neoaortic Leaflets Care have to be taken when making the opening within the neoaortic root first with the knife blade after which with the punch to defend the valve leaflets from damage. Reconstructing the Aorta the distal ascending aorta is anastomosed to the neoaortic root with operating 6-0 or 7-0 Prolene suture. Size Difference between the Neoaortic Root and Ascending Aorta If a discrepancy between the diameter of the distal ascending aorta and neoaortic root exists, the excess tissue can often be gathered within the posterior suture line. Hemostasis of the Posterior Suture Line Care have to be taken to ensure hemostasis of the aortic suture line, especially posteriorly, because this is relatively inaccessible after the repair is accomplished. Side-by-Side Great Vessels When the aorta and pulmonary artery are side by facet, the Lecompte maneuver will not be carried out. The distal ascending aorta is mobilized laterally and anastomosed to the neoaortic base. Intracardiac Repair the atrial septal defect or balloon atrial septostomy and a ventricular septal defect, if current, are closed via a proper atriotomy incision (see Chapters 19 and 21). Alternatively, a ventricular septal defect could be closed via one of the semilunar valves. If that is carried out through the posterior (pulmonary) valve, great care must be taken to keep away from the conduction system. After closing the right atrium, the aortic cross-clamp may be removed or left in place until the pulmonary artery reconstruction is finished. Reconstructing the Pulmonary Artery If the aorta is to stay clamped, the clamp must now be moved to the ascending aorta above the pulmonary artery confluence. The defect created within the neopulmonary base is stuffed both with two separate patches, or with a rectangular patch of glutaraldehyde-treated pericardium ("pantaloon"). The patch must be roughly twice so lengthy as the remaining neopulmonary sinus. A slit-like or V-shaped incision is made midway alongside the lengthy fringe of this rectangular patch. The resultant neopulmonary root is then anastomosed to the pulmonary artery confluence with a 6-0 Prolene suture. Supravalvular Pulmonary Stenosis A well-recognized late complication of arterial swap procedures is supravalvular pulmonary stenosis. This can be minimized by leaving a beneficiant cuff of pericardium when reconstructing the neopulmonary root. The reconstructed neopulmonary artery base is anastomosed to this opening in the proper pulmonary artery with a 6-0 Prolene suture. Completing the Operation the aortic cross-clamp is eliminated, and deairing carried out by way of the cardioplegic needle gap, which is subsequently closed with a 7-0 Prolene horizontal mattress suture. When rewarming is completed, the affected person is weaned off cardiopulmonary bypass, taking care not to overfill the center. Examining Coronary Perfusion After the aortic cross-clamp is removed, the heart is examined for perfusion in all coronary distributions. Further mobilization of the coronary artery in query could also be required, or a coronary anastomosis might must be repositioned. Most often, this consists of mobilizing the left or right inner thoracic artery from the chest wall as an in situ conduit. Occasionally, the left subclavian artery could additionally be ligated distally, transected, and the distal end anastomosed to the proximal left anterior descending or circumflex coronary artery. Dysrhythmias Rhythm disturbances throughout rewarming or quickly after cardiopulmonary bypass is discontinued are most frequently secondary to coronary perfusion problems within the absence of preoperative tachyarrhythmias. Stretching of the Coronary Arteries Overdistention of the guts in the instant postbypass period could stretch the transposed coronary arteries. Therefore, quantity should be administered rigorously to these sufferers for the primary 24 to 48 hours postoperatively to keep away from this doubtlessly fatal complication. Suture Line Bleeding Bleeding can be a downside because of the intensive suture traces. Bleeding websites ought to be carefully sutured with adventitial horizontal mattress 7-0 Prolene sutures. If bleeding from the aorta is noted after discontinuation of cardiopulmonary bypass, reinstitution of bypass may be required. Takedown of the pulmonary artery anastomosis to enable access to the aortic suture line could also be needed. Coronary Artery Spasm the transposed coronary arteries are susceptible to spasm within the postbypass and early postoperative intervals. Intravenous calcium solution ought to be given very cautiously to forestall coronary artery spasm. Most of these patients also have ventricular septal defects, pulmonary valve abnormalities, and/or Ebsteinoid modifications of the tricuspid valve. The traditional surgical approach ("functional repair") has been to repair the associated lesions only. This leaves the patient with a morphologic proper ventricle and tricuspid valve because the systemic ventricle and atrioventricular valve. More lately, some centers have advocated an anatomic repair, the "double switch" procedure, in certain subgroups of these sufferers. Patients with two sufficient ventricles and a normal pulmonic valve bear an arterial switch procedure combined with a Senning or Mustard atrial swap. Theoretically, a double change process ought to improve the long-term outcome of these patients, who typically develop progressive tricuspid regurgitation and proper ventricular failure, by making the morphologic left ventricle the systemic ventricle and putting the abnormal tricuspid valve in the decrease stress pulmonary circulation. However, correct patient choice is crucial, and heaps of patients require a multistaged pulmonary banding procedure to train the left ventricle.
Dochicin 0.5 mg genericBar M antibiotics for acne doxycycline buy dochicin 0.5mg mastercard, Eiswirth M: Turbulence as a result of infection elbow generic dochicin 0.5mg without prescription spiral breakup in a steady excitable medium bacteria on the tongue buy dochicin 0.5 mg fast delivery. Chudin E antibiotic resistance evolution generic dochicin 0.5mg, et al: Intracellular Ca(2+) dynamics and the steadiness of ventricular tachycardia. Matiukas A, et al: Near-infrared voltage-sensitive fluorescent dyes optimized for optical mapping in blood-perfused myocardium. It is believed that atrial arrhythmias can be attributable to focal ectopic activity, localized reentry, or a number of propagating wavelets. Several experimental and medical studies have shown that different mechanisms lead to differences in the traits of spatiotemporal group of atrial arrhythmias. In current years, computational modeling has offered a framework of multiscale integrated fashions for the research of cardiac arrhythmias. Computer simulations of atrial tissue have supplied hypotheses which have been tested experimentally and, moreover, have been used to examine and to clarify experimental and clinical observations. This chapter evaluations the insights offered by these atrial models, with emphasis on the contributions of three-dimensional (3D) atrial models, and shows numerous examples of atrial arrhythmias simulated using a practical 3D model of human atria developed by our group. Brief Summary of Atrial Computer Models Several pc atrial fashions have been developed and used to examine atrial arrhythmias and to consider the efficacy of various therapeutic approaches. They included anisotropic properties of the tissue and heterogeneous electrophysiological properties to study the contributions of various anatomical constructions in normal atrial conduction. In 2009, our group developed a 3D atrial model that built-in practical geometry and construction, as properly as heterogeneous electrical properties, with detailed fiber orientation in the whole atria. Several experimental observations have been made concerning the role of anatomical construction and electrophysiological heterogeneity in atrial electrical activity in each physiological and pathologic conditions. Canavan et al55 confirmed that underneath physiological situations, the last activation of atrial tissue occurred just before 120 ms. Recently, laptop models have additionally been used to systematically evaluate the efficacy of different mixtures of the ablation lines. The ablation traces have been of two to three elements of thickness and 0 conductivity, simulating perfect transmural obstacles to the wave entrance propagation. This chapter described some examples of how a practical human atrial model can facilitate understanding of the relationship between different characteristics of signals recorded within the atrial floor and the propagation patterns that induced them. Wolf P, Benjamin E, Belanger A, et al: Secular tendencies in the prevalence of atrial fibrillation: the Framingham research. The "main circle" idea: A new model of circus motion in cardiac tissue without the involvement of an anatomical impediment. Berenfeld O, Mandapati R, Dixit S, et al: Spatially distributed dominant excitation frequencies reveal hidden group in atrial fibrillation in the Langendorff-perfused sheep coronary heart. Mansour M, Mandapati R, Berenfeld O, et al: Leftto-right gradient of atrial frequencies during acute atrial fibrillation within the isolated sheep coronary heart. Jacquemet V: A Biophysical Model of Atrial Fibrillation and Electrograms: Formulation, Validation and Applications [PhD thesis], Lausanne, �cole Polytechnique F�d�rale de Lausanne, 2004. Ruchat P, Dang L, Virag N, et al: A biophysical mannequin of atrial fibrillation to define the suitable ablation sample in modified maze. Dang L, Virag N, Ihara Z, et al: Evaluation of ablation patterns using a biophysical mannequin of atrial fibrillation. In Programs and Abstracts of the 36th Annual International Conference of Computers in Cardiology, 2009, Park City, Utah, pp 449�452. Tob�n C: Modelizaci�n y evaluaci�n de factores que favorecen las arritmias auriculares y su tratamiento mediante t�cnicas quir�rgicas [PhD thesis], Valencia, 2010, Universitat Polit�cnica de Val�ncia. In Programs and Abstracts of the sixth International Conference on Functional Imaging and Modeling of the Heart, 2011, New York, pp 223�232. Nathan H, Eliakim M: the junction between the left atrium and the pulmonary veins: An anatomic examine of human hearts. Feng J, Yue L, Wang Z, et al: Ionic mechanisms of regional action potential heterogeneity in the canine proper atrium. Presented on the thirtieth Annual International Conference of Computers in Cardiology, 2003, Thessaloniki Chalkidiki, pp 777�780. Hansson A, Holm M, Blomstrom P, et al: Right atrial free wall conduction velocity and degree of anisotropy in sufferers with stable sinus rhythm 359 sixteen. Takahashi Y, Sanders P, Jais P, et al: Organization of frequency spectra of atrial fibrillation: Relevance to radiofrequency catheter ablation. Saoudi N, Cos�o F, Waldo A, et al: A classification of atrial flutter and regular atrial tachycardia according to electrophysiological mechanisms and anatomical bases; a Statement from a Joint Expert Group from the Working Group of Arrhythmias of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Sueda T, Nagata H, Orihashi K, et al: Efficacy of a simple left atrial procedure for continual atrial fibrillation in mitral valve operations. Kobza R, Kottkamp H, Dorszewski A, et al: Stable secondary arrhythmias late after intraoperative radiofrequency ablation of atrial fibrillation: Incidence, mechanism, and therapy. The common strategy consists of two coupled issues, simulating the electrical and mechanical capabilities of the center. Cardiac tissue has orthotopic passive electrical conductivities that arise from the cellular group of the guts into fibers and laminar sheets. Global conductivity values are obtained by combining fiber and sheet organization with myocyte-specific local conductivity values. Current flow in the tissue is driven by the active processes of ionic exchanges throughout myocyte membranes. Compared with the evolution of mobile ionic fashions, the event of myofilament models has been slower and harder, as no clear consensus has been reached relating to the mathematical method to mannequin myofilament dynamics. An 361 the cyclic pumping of the center arises from the synergy of its electrical and mechanical features. Understanding the individual features has been the topic of intense analysis in primary science and scientific cardiology. Over the years, experimental and clinical research have supplied significant insight into the electrical and mechanical activity of the beating heart from the molecular to the organ stage. With present experimental strategies restricted in their incapability to explore the three-dimensional coupled electrical and mechanical activity within the heart concurrently and with sufficient spatiotemporal resolution, computer modeling of whole-heart electromechanical perform is rapidly turning into an important investigative device in its personal proper. Today, owing to developments in computational techniques and tools as well as in picture processing, electromechanical modeling of the guts has turn out to be a comprehensive methodology that mixes detailed information concerning the electrophysiological and mechanical processes across the spatial scales in the coronary heart, and serves to provide a higher stage of understanding of the advanced electromechanical interactions within the heart. In this chapter, we current an summary of the current stateof-the-art in whole-heart electromechanical modeling, specializing in realistic-geometry biophysically detailed mannequin developments. We first present the final framework in modeling the electromechanical conduct of the guts. We then showcase the highly effective utility of such practical electromechanical fashions in revealing mechanisms at play in the normal and diseased coronary heart by reviewing the most recent insights obtained with such fashions. We conclude this chapter with a dialogue of the developments in patient-specific electromechanical modeling, emphasizing translational efforts towards bringing computer modeling of coronary heart electromechanics from the realm of the fundamental science into the clinic. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med 2:489�506, 2010; Gurev V, Lee T, Constantino J, et al: Models of cardiac electromechanics primarily based on individual hearts imaging data: Image-based electromechanical models of the guts. In the mechanics part of the model, deformation of the organ is described by the equations of continuum mechanics,four with the passive properties of the myocardium described by a constitutive legislation. The most comprehensive formulation of cardiac tissue constitutive relation could be found in a recent article by Holzapfel and Ogden. To simulate this feedback mechanism, the stretch and stretch fee calculated from the mechanics element serve as an enter into the electrical element: They decide the conductance of stretch-activated channels, the latter represented throughout the mobile ionic model.
Discount dochicin 0.5mgFactors that exacerbate swelling antimicrobial therapy publisher order dochicin 0.5 mg with amex, corresponding to hypoxia bacterial spores cheap dochicin 0.5mg online, hypercapnia and hyperthermia antibiotics for dogs with salivary gland infection dochicin 0.5mg on-line, ought to probably be corrected virus 1980 imdb buy dochicin 0.5mg without a prescription. Small asymptomatic petechiae are much much less important than haematomas, which may be associated with neurological decline. The use of anticoagulants and thrombolytics will increase the chance of great haemorrhagic transformation, but should be weighed in opposition to the benefits of those agents. Management of sufferers with haemorrhagic transformation of infarct is determined by the amount of bleeding and symptoms, and clot evacuation could also be applicable in deteriorating patients. Haemorrhagic transformation in sufferers with cerebellar infarction significantly will increase the chance of deterioration. Seizures Poststroke seizures inside the first 24 hours after stroke onset occur in 2% to 33% of sufferers, and the late seizure fee ranges from 3% to 67%. Status epilepticus is rare, however continuing partial seizure exercise should be considered in patients after stroke who deteriorate or fail to recover at an anticipated price. Recommendations on the use of particular person anticonvulsants are based on the established administration of seizures complicating any neurological sickness. Neurological issues after stroke About 25% of sufferers with acute stroke have neurological deterioration inside the first forty eight hours and, of those, an important neurological causes are: � � � � Progressive or recurrent stroke (one third of patients) Ischaemic brain swelling (one third) Haemorrhagic transformation of an infarct (10%) Seizure (10%) Recurrent stroke Using the definition of recurrent stroke as neurological deterioration after 24 hours or more after the incident event, involving Medical Complications of Stroke 25 Continence and constipation after stroke Urinary incontinence Between 32% and 79% of stroke sufferers are incontinent instantly after stroke. Incontinence is related to increased morbidity and mortality, carer pressure and institutionalisation, and is linked with stroke severity. All patients with a stroke ought to receive an preliminary assessment on admission, primarily to exclude retention and an infection (Table 5. If at two weeks the incontinence persists, additional assessments and a administration plan must be initiated. For urge incontinence, instructed by signs of frequency and urgency, bladder training and reducing caffeine intake are appropriate. The first-line remedy for stress incontinence or combined signs is pelvic flooring exercices. Retention or incomplete emptying is suggested by symptoms of a residual quantity >100 ml, recurrent infections and fixed dribbling. In acute urinary retention, patients may require catheterisation whereas additional assessments of the purpose for retention are undertaken. This contains bettering mobility, loose clothing for fast entry and ensuring a call bell and film cards (if appropriate) are available. Faecal incontinence and constipation Bowel dysfunction is frequent after stroke, with up to 40% affected by faecal incontinence and up to 60% with constipation. Most bowel dysfunction can be improved by resolving faecal loading (assessed by rectal examination or stomach x-ray) and treating infective diarrhoea. Swallowing difficulties put the patient susceptible to aspiration, malnutrition and dehydration. Plans for hydration, diet (within 48 hours) and regular mouth care should be made while ready for specialist assessments. Nutrition All patients need their nutritional standing and danger of malnutrition assessed on admission along with their capacity to swallow. Documentation of their dietary consumption together with common dietary assessments will inform the team if the patient is taking adequate amounts. Normal bowel behavior and present pattern Drug historical past Awareness of have to defaecate/level of consciousness Cognition and communication Stool chart. It can theoretically worsen cerebral ischaemia through a drop in blood pressure and raised haematocrit, and will increase the chance of venous thromboembolism. Daily haematocrit, urea and electrolytes must be monitored in the acute section, as these are extra delicate indicators than medical signs of dehydration. Nutritional Support in Adults: Oral nutrition support, enteral tube feeding and parenteral vitamin. The core multi-disciplinary stroke group consists of: � � � � � � � � nurse physician occupational therapist physiotherapist speech and language therapist � Other important members of a complete stroke group may embody: � � Rehabilitation is a vital part of stroke restoration for nearly all of patients and ought to be supplied to everybody requiring rehabilitation, no matter their stroke severity. It is a dynamic course of that goals to promote recovery from the direct and often devastating consequences of stroke. In these circumstances the place recovery is no longer possible, rehabilitation goals to facilitate adjustment and be certain that individuals lead as full and significant a life as possible. Interventions supplied by the multi-disciplinary group purpose to cut back impairments caused by stroke, promote recovery in daily life activities and guarantee participation in the wider community context, for instance returning to work and interesting in leisure pursuits and hobbies. Psychosocial recovery is as necessary, if no more so, than the bodily penalties of stroke. Each team member has a valuable half to play in this course of and the synergistic involvement of all rehabilitation employees is essential in figuring out the potential recovery of each affected person. Consequently, common coaching of workers and collaborating in instructional sessions are basic parts of all stroke care provision. Rehabilitation process the rehabilitation staff consists of a broad variety of specialists, each of whom has their own space of expertise but additionally the power to overlap their abilities to ensure that the affected person receives probably the most complete and consistent care potential. The first step in the rehabilitation process is a comprehensive assessment, which is carried out by every group member. Continuous assessment is important because the affected person makes their own pure restoration from stroke, thereby making certain that interventions are as well timed and appropriate as possible. To be clinically significant, assessments ought to be standardised and have proven psychometric properties. The length of time taken to administer a chosen assessment also wants to be thought-about, as lengthy assessments will prove difficult to implement in busy medical settings. Occupational therapist the occupational therapist is primarily involved with selling activities of day by day residing. Basic self-care duties are at all times focused first and embody objects such as these illustrated in Box 6. The house go to will indicate the environmental diversifications or aids to independence required earlier than hospital discharge. Second stair rails, seize handles for property entry and bathing tools are generally prescribed. The house visit also acts as a confidence-building train for both the affected person and carer, and may reassure all events, including health-care staff, that a return residence shall be profitable. Problems similar to these have been shown to adversely affect rehabilitation progress. Stroke Rehabilitation 29 will the physiotherapist gradually incorporate dynamic standing stability earlier than encouraging any first steps. Frequently this activity is carried out in the physiotherapy health club and will require the assistance of multiple member of workers and various other pieces of apparatus, such as a standing frame or hoist. Only when this has been achieved do they flip their consideration to communication and language reacquisition. Observational studies report that the majority of stroke patients in hospital spend their time predominantly engaged in non-therapeutic exercise. The proof would recommend that this can be due to the increased documentation and paperwork required by scientific governance procedures, together with insufficient numbers of therapy employees. Increased repetition of focused therapeutic actions (such as dressing follow or sitting to stand) has been shown to have a helpful impression on rehabilitation end result.
Purchase 0.5 mg dochicin fast deliveryA number of experiments have decided the precise molecular interactions involved in the G-induced Kir3 antimicrobial cleaner quality dochicin 0.5 mg. Channelopathies Over four decades ago how quickly do antibiotics work for sinus infection generic 0.5mg dochicin otc, a mouse with a striking locomotor deficiency (weaving) was described antibiotics no dairy purchase 0.5 mg dochicin free shipping, and the defect has subsequently been traced to a naturally occurring gain-in-function mutation in the Kir3 antibiotic diarrhea treatment discount dochicin 0.5 mg. A mixture of biochemistry and cell electrophysiology in heterologous expression systems was used to reveal that a heterozygous G387R mutation on the Kir3. It remains unresolved whether or not this subunit composition exists in atrial tissue of different animals and humans. Recently, the novel gain-of-function mutation (S422L substitution) in the pore-forming Kir6. The general architecture of Kir channels has been properly established, and fine particulars of their construction and performance have been revealed with the help of several obtainable crystal buildings of cloned channels. How are Kir channels sorted into microdomains in the sarcolemma, corresponding to T-tubules or intercalated discs, and the way do they work together with other proteins inside these microdomains These questions undoubtedly will be the focus of a lot investigation in the close to future. Enkvetchakul D, Jeliazkova I, Bhattacharyya J, et al: Control of inward rectifier K channel activity by lipid tethering of cytoplasmic domains. Wischmeyer E, Doring F, Karschin A: Acute suppression of inwardly rectifying Kir2. Zaza A, Rocchetti M, Brioschi A, et al: Dynamic Ca2+-induced inward rectification of K+ present in the course of the ventricular motion potential. Wettschureck N, Offermanns S: Mammalian G proteins and their cell kind specific functions. Kitamura H, Yokoyama M, Akita H, et al: Tertiapin potently and selectively blocks muscarinic K(+) channels in rabbit cardiac myocytes. Voigt N, Trausch A, Knaut M, et al: Left-to-right atrial inward rectifier potassium current gradients in sufferers with paroxysmal versus chronic atrial fibrillation. For example, Ca2+ pumps within the E1 state interact Ca2+ with excessive affinity at one facet of the membrane, and in the state their E2 lowered affinity for Ca2+ releases it to the alternative membrane side. Several Ca2+ pump isoforms have been described in animal cells, differing primarily in tissue distribution, regulatory properties, and some mechanistic peculiarities. The isoform range displays the existence of separate primary gene products, but also the incidence of complicated patterns of alternative splicing that increase very significantly the variety of variants of each of the three pumps. The analysis of the differential properties of the Ca2+ pump isoforms is a vigorously investigated topic that has essential linkages to the final strategy of mobile Ca2+ homeostasis, which in animal cells is regulated by a number of nonmembrane Ca2+-binding proteins and of membrane-intrinsic Ca2+ channels and transporters. The transporters interact with Ca2+ with high or low affinity, and thus operate both as fantastic tuners of cytosolic Ca2+ or come into play each time the concentration of Ca2+ increases to ranges sufficient for their low affinity. The Na/ Ca-exchanger of the plasma membrane and the mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake and launch systems are the low-affinity regulators of cytosolic Ca2+. The three pumps, against this, control Ca2+ effectively even within the low concentrations of the cytosol at rest. A simplified reaction cycle of the P-type adenosine triphosphatases (pumps)adaptedtotheCa2+pumps. The rearrangements of transmembrane helices M1-M6 induced by the rotation of the A area enable protons and water molecules to enter and stabilize the empty Ca2+ binding websites. Differences in their spatial mobile distribution may justify their copresence. However, structural observations indicate that pentamers can also interact with the pump. Luminal Ca2+ buffering by calnexin is much less vital, and the acidic C-terminus of the protein protrudes into the cytosol. These findings would be compatible with distinct Ca2+ subcompartments in the Golgi equipment endowed with differentCa2+ regulating molecular elements. Most of the preliminary work on the pump dealt with erythrocytes, but it steadily became clear that the pump is present and lively in all animal cells, together with these of excitable tissues. According to solid and abundant evidence, and thus to common consensus, the beat-to-beat export of bulk Ca2+ from coronary heart cells is indeed carried out by the Na/ Ca-exchanger. J Biol Chem 282:25640�25648, 2007; Brini M, Coletto L, Pierobon N, et al: A comparative functional analysis of plasma membrane Ca2+ pump isoforms in intact cells. Acidic phospholipids bind to two sites: one is the fundamental C-terminal calmodulin binding domain, and the other is a stretch of roughly 40 predominantly fundamental amino acids in the cytosolic loop connecting transmembrane domains 2 and three. It has been calculated that the focus of phosphatidyl-serine within the environment of the pump would in precept be sufficient for about 50% stimulation of its exercise. Kinases have also been discovered to activate the pump by phosphorylating residues in its C-terminal tail. Meanwhile, protein kinase C acts on all pump variants, and protein kinase A acts on only one of the isoforms. An intriguing mechanism of pump activation is that generated by a dimerization (oligomerization) course of that occurs by way of the C-terminal calmodulin binding area; its physiologic significance is obscure. All mechanisms of activation act by increasing the Ca2+ affinity of the pump; in their absence, the Km (Ca2+) of the pump is as excessive as 20 �M, but drops to zero. The pump can be also activated irreversibly, and that occurs when its C-terminal tail, which includes the calmodulin binding domain, is shaved off by the Ca2+-dependent protease calpain. In this case, the activation is linked to the elimination of the autoinhibitory C-terminal tail of the pump. The irreversible activation by calpain might turn into important in conditions of pathologic Ca2+ overload that would demand the uninterrupted maximal capacity of the pump to extrude Ca2+ from the cytosol. As talked about earlier, alternative splicing processes affect all 4 fundamental primary transcripts of the pump, tremendously rising the number of isoforms. Most of the splice variants described within the literature have additionally been documented at the protein degree. Site A corresponds to the cytosolic loop of the pump molecule that connects transmembrane domains 2 and 3, website C to the C-terminal calmodulin binding area. The full details of the splicing operations and its complexities are mentioned elsewhere. The pump variants without the inserts are termed z; these with the extra exon are termed x. For instance, in people solely variant w (all exons included), variant x (only the forty two bp exon included), and variant z (no additional exon included) have been detected. Only scarce information is on the market on the functional penalties of the splicing operation at site A. Information on the consequences of the slicing operation at web site C on the exercise of the pump is more abundant, and recent findings can lead to essential practical developments. The insertion of the novel sequence roughly in the midst of the calmodulin binding domain leads, as anticipated, to the lowering of the calmodulin affinity for the pump. However, predictions on the results to be expected from the insertion of the novel sequence in the calmodulin binding area are difficult by the surprising observation that the insert tends to reconstitute the original whole calmodulin binding area; 8 of the primary 10 residues of the insert are indeed both similar or conservative, with respect to those or the original C-terminal half of the calmodulin binding area they substitute.
References - Cillo U, Vitale A, Grigoletto F, et al. Intention-totreat analysis of liver transplantation in selected, aggressively treated HCC patients exceeding the Milan criteria. Am J Transplant. 2007;7:972-981.
- Matolo NM, Colten SE, Fontanetta AP, et al. Traumatic duodenal injuries: an analysis of 32 cases. Am Surg. 1975;6:331-336.
- Philips JA, Ernst JD. Tuberculosis pathogenesis and immunity. Annu Rev Pathol 2012; 7: 353-384.
- Liu N, Olson EN: MicroRNA regulatory networks in cardiovascular development, Dev Cell 18(4):510-525, 2010.
- Fowler JE Jr, Bigler SA, Kilambi NK, et al: Relationships between prostatespecific antigen and prostate volume in black and white men with benign prostate biopsies, Urology 53(6):1175n1178, 1999.
- Spoulou V, Giannaki M, Vounatsou M, et al. Long-term immunity to measles, mumps and rubella after MMR vaccination among children with bone marrow transplants. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2004;33:1187-1190.
- Anderson JR, Nawarskas JJ: Pharmacotherapeutic management of pulmonary arterial hypertension, Cardiol Rev 18(3):148-162, 2010.
|