Florinef
Kristine Wengel, RN, BSN, CCRN - Surgical Critical Care Unit
- Rush-Presbyterian-St. Luke’s Medical Center
- Chicago, IL
Purchase 0.1mg florinef with amexIn the absence of a signal sequence gastritis diet for cats generic florinef 0.1 mg amex, proteins which are synthesized on free ribosomes remain within the cytosol gastritis medicine cvs safe florinef 0.1 mg. Cytoplasmic basophilia is related to cells that produce giant amounts of protein that will stay within the cell gastritis diet öèàí generic 0.1 mg florinef with mastercard. Such cells and their merchandise include creating purple blood cells (hemoglobin) gastritis diet ÿíäåê cheap florinef 0.1 mg without a prescription, developing muscle cells (the contractile proteins actin and myosin), nerve cells (neurofilaments), and keratinocytes of the pores and skin (keratin). In addition, most enzymes of the mitochondrion are synthesized by free polysomes and transferred into that organelle. Collectively, the free ribosomes and membrane-attached ribosomes are answerable for the characteristic cytoplasmic basophilia (Nissl bodies) noticed within the gentle microscope within the perinuclear cytoplasm of neurons. Cells with giant quantities of smooth-surfaced endoplasmic reticulum may exhibit distinct cytoplasmic eosinophilia (acidophilia) when considered in the gentle microscope. It sequesters Ca2, which is crucial for the contractile process and is carefully apposed to the plasma-membrane invaginations that conduct the contractile impulses to the interior of the cell. They modify and detoxify hydrophobic compounds similar to pesticides and carcinogens by chemically converting them into water-soluble conjugated products that can be eradicated from the body. Cell Cytoplasm the Golgi equipment was described more than 100 years ago by histologist Camillo Golgi. In research of osmium-impregnated nerve cells, he discovered an organelle that fashioned networks across the nucleus. It is lively both in cells that secrete protein by exocytosis and in cells that synthesize massive amounts of membrane and membrane-associated proteins similar to nerve cells. This photomicrograph of a plastic-embedded specimen exhibiting the lamina propria of the small gut is stained with toluidine blue. The plasma cells, where appropriately oriented, exhibit a transparent area within the cytoplasm close to the nucleus. These negatively stained regions (arrows) represent extensive accumulation of membranous cisternae that belong to the Golgi apparatus. This electron micrograph shows the in depth Golgi apparatus in an islet cell of the pancreas. Incubation of the trans-Golgi cisternae with the coatomer-depleted cytosol reveals a lower in vesicle formation activity. The Golgi apparatus features in the posttranslational modification, sorting, and packaging of proteins. From there, they journey throughout the transport vesicles from one cisterna to the next. The Golgi equipment accommodates several stacks of flattened cisternae with dilated edges. Glycosylation of proteins and lipids uses several carbohydrate-processing enzymes that add, remove, and modify sugar moieties of oligosaccharide chains. M-6-P is added to these proteins destined to travel to late endosomes and lysosomes (see page 37). The proteolytic cleavage of sure proteins can also be initiated within the cisternae. Four major pathways of protein secretion from the Golgi apparatus disperse proteins to various cell locations. Note two targeting mechanisms of proteins to different surfaces of plasma membrane. This constitutive pathway makes use of vesicles coated with an as but unidentified protein associated with an epithelium-specific adaptor protein. The transported membrane proteins are constantly incorporated into the basolateral cell floor. In liver hepatocytes, nonetheless, the method of protein sorting into the basolateral and apical domains is kind of different. From there, each proteins are endocytosed and sorted into early endosomal compartments. Basolateral proteins are recycled again into the basolateral membrane, whereas apical proteins are transported throughout the cytoplasm to the apical cell membrane through transcytosis. Enzymes destined for lysosomes utilizing M-6-P markers (see web page 37) are delivered into early or late endosomes as they become mature lysosomes. These vesicles undergo a maturation process during which secretory proteins are retained within the vesicle. Mature secretory vesicles finally fuse with the plasma membrane to launch the secretory product by exocytosis. This kind of secretion is characteristic of highly specialized secretory cells found in exocrine glands. The intercellular destination of each protein is determined by the sorting signals which are integrated within the polypeptide chain of the protein. This type of sign is recognized by the sorting equipment, which directs the protein into the appropriately coated transport vesicle. These groups of proteins are first partitioned into separate lipid rafts which are later included into transport vesicles destined for a targeted organelle. Mitochondria Mitochondria are ample in cells that generate and expend large quantities of vitality. Mitochondria have been also known to early cytologists who ob- Cell Cytoplasm served them in cells vitally stained with Janus green B. Videomicroscopy confirms that mitochondria can both change their location and endure transient modifications in form. They could subsequently be compared to cell energy turbines as they migrate from one area of the cell to one other to supply wanted power. Mitochondria additionally localize at sites within the cell where energy is required, as in the middle piece of the sperm, the intermyofibrillar spaces in striated muscle cells, and adjoining to the basolateral plasma-membrane infoldings within the cells of the proximal convoluted tubule of the kidney. Mitochondria advanced from cardio bacteria that were engulfed by eukaryotic cells. Mitochondria display a big selection of shapes, including spheres, rods, elongated filaments, and even coiled constructions. The following structural components of mitochondria possess particular characteristics associated to their functions. This 6- to 7-nm-thick smooth membrane incorporates many voltage-dependent anion channels (also called mitochondrial porins). This hypothesis obtained support with the demonstration that mitochondria possess their very own genome, improve their numbers by division, and synthesize some of their structural (constituent) proteins. Mitochondria possess a complete system for protein synthesis, including the synthesis of their own ribosomes. Translocation of proteins by way of mitochondrial membranes requires power and assistance from several specialized chaperone proteins. Mitochondria are present in all cells besides purple blood cells and terminal keratinocytes. When present in massive numbers, mitochondria contribute to the acidophilia of the cytoplasm due to the massive quantity of membrane they contain. The environment of the intermembrane area is due to this fact much like that of cytoplasm with respect to ions and small molecules. The outer membrane possesses receptors for proteins and polypeptides that translocate into the intermembrane space.
Cheap florinef 0.1 mg otcThe epithelium adjustments from pseudostratified columnar to simple ciliated columnar gastritis test order 0.1mg florinef overnight delivery, and a few columnar cells even lack cilia gastritis que es discount 0.1 mg florinef fast delivery. Smooth muscle occupies a comparatively bigger portion of the bronchiolar wall than of the bronchial wall gastritis symptoms loose stools cheap 0.1 mg florinef overnight delivery. The smallest diameter conducting bronchioles gastritis symptoms in hindi buy cheap florinef 0.1mg on-line, the terminal bronchioles, are lined with easy ciliated cuboidal epithelium during which Clara cells, cells that secrete a surface-active agent that forestalls luminal adhesion of bronchiolar walls throughout expiration, are discovered among the many ciliated cells. Respiratory bronchioles are the primary a half of the bronchial tree that enables gas change to happen. Respiratory bronchioles represent a transition zone during which each air conduction and gas trade occur. Scattered, thin-walled evaginations of the lumen of the respiratory bronchiole are referred to as alveoli; these are the buildings by which gasoline change between the air passages and the blood capillaries occurs. Surrounding the bronchiole, comprising a lot of the lung substance, are the air spaces or alveoli of the lung. The final portion of a bronchiole that leads into respiratory bronchioles is recognized as a terminal bronchiole. The respiratory bronchiole has a wall composed of two parts: One consists of recesses that have a wall much like that of the alveoli and are thus capable of fuel trade; the other has a wall shaped by small cuboidal cells that seem to rest on a small bundle of eosinophilic material. The outer surface of lung tissue is the serosa (S); it consists of a lining of mesothelial cells resting on a small quantity of connective tissue. The alveolar ducts terminate in alveolar sacs, enlarged areas surrounded by clusters of alveoli that open into the spaces. This consists of the alveolar epithelial cells and their basal lamina, the basal lamina of the underlying capillary endothelium and the endothelial cells, themselves, and some other connective tissue parts which will lie between the 2 basal laminae. Some basal cells are nonetheless present, thus the designation pseudostratified columnar. Elsewhere, the epithelium might be ciliated simple columnar, and simply before it becomes a respiratory bronchiole, the epithelium may include cuboidal or low columnar nonciliated cells. Characteristically, the wall of the respiratory bronchiole consists of alternating thick and thin areas. The thick regions are similar to the wall of the bronchiole besides that cuboidal Clara cells instead of columnar epithelium type the surface. The thin regions have a wall just like the alveolar wall; this is thought of below. The respiratory bronchiole proven in lower left determine is slightly more distal than the world seen in top right determine. Structurally, it exhibits essentially the identical options as those seen in upper proper figure besides that there are fewer Clara cells and the smooth muscle is somewhat thinner. The central component of the alveolar wall is the capillary (C) and, in certain places, related connective tissue. On each side, the place it faces the alveolus (A), a flat squamous cell is interposed between the capillary and the air areas. In some locations, the kind I cell is separated from the capillary endothelial cell by a single basal lamina shared by the two cells. This is the thin portion of the alveolar�capillary complex, readily seen within the upper a part of the figure (arrows). Elsewhere, connective tissue is interposed between the pneumocyte sort I cell and the endothelial cell of the capillary; each of those epithelial cells retains its own basal lamina. This cell usually shows a rounded (rather than flattened) form, and the nucleus is surrounded by a noticeable quantity of cytoplasm, a few of which can seem clear. The septal cell produces a surface-active agent different from that of the Clara cell, which additionally acts in allowing the lung to expand. The kidneys play an necessary role in physique homeostasis by conserving fluids and electrolytes and by disposing metabolic waste. Like the lungs and liver, the kidneys retrieve important supplies and eliminate wastes. To keep homeostasis, kidneys preserve water, electrolytes, and sure metabolites. The kidneys are important in maintaining fixed plasma pH by regulating acid�base balance, which is achieved by excreting hydrogen ions when bodily fluids become too acidic or excreting bicarbonates when bodily fluids turn out to be too basic. The kidneys play an important position in regulating and maintaining the composition and quantity of extracellular fluid. The kidneys are highly vascular organs; they receive approximately 25% of the cardiac output. In the human physique, vitamin D is derived from two sources: � Skin, in which vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is rapidly produced by the action of ultraviolet light on the precursor 7-dehydrocholesterol. Typically, 30 minutes to 2 hours of daylight publicity per day can provide sufficient vitamin D to fulfill every day physique requirements for this vitamin. In the blood, vitamin D3 is certain to vitamin D�binding protein and transported to the liver. The related compound vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) undergoes the same conversion steps as vitamin D3 and produces the same biologic effects. Patients with end-stage chronic kidney ailments have insufficient conversion of vitamin D into lively metabolites resulting in vitamin D3 deficiency. In adults, vitamin D3 deficiency is manifested by impaired bone mineralization and reduced bone density. Therefore, patients with persistent kidney diseases, particularly those on extended renal hemodialysis are sometimes supplemented with vitamin D3 and calcium to avoid extreme disturbance of calcium homeostasis because of secondary hyperparathyroidism, a condition prevalent in these sufferers. Vitamin D3 deficiency in childhood results in rickets, a illness that causes irregular bone ossification. Initially, plasma is separated from the cells and enormous proteins to produce a glomerular ultrafiltrate of the blood or major urine, which is then modified by selective resorption and particular secretion by the cells of the kidney. The ultimate urine incorporates water and electrolytes in addition to waste merchandise, corresponding to urea, uric acid, and creatinine, and breakdown merchandise of assorted substances. They prolong from the 12th thoracic to the third lumbar vertebrae, with the right kidney positioned slightly decrease. On the higher pole of each kidney, embedded throughout the renal fascia and a thick protective layer of perirenal adipose tissue, lies an adrenal gland. The medial border of the kidney is concave and accommodates a deep vertical fissure, referred to as the hilum, by way of which the renal vessels and nerves cross and the expanded, funnel-shaped origin of the ureter, known as the renal pelvis, exits. Although not shown in the illustration, the area between and round these constructions is stuffed largely with free connective tissue and adipose tissue. Synthesis and secretion of the acid protease renin, an enzyme concerned in management of blood stress and blood quantity. Renin is produced by juxtaglomerular cells and cleaves circulating angiotensinogen to launch angiotensin I (see pages 713�714). Cortex and Medulla Examination with the naked eye of the minimize face of a contemporary, hemisected kidney reveals that its substance may be divided into two distinct regions: hilum renal vein medullary rays � � Cortex, the outer reddish-brown part Medulla, the a lot lighter colored inner half minor calyx renal artery renal pelvis medulla the color seen in the minimize floor of the unfixed kidney displays the distribution of blood in the organ. Approximately 90% to 95% of the blood passing through the kidney is in the cortex; 5% to 10% is in the medulla. The nephron is the basic practical unit of the kidney and is described in a following section.
Buy 0.1mg florinefT lymphocytes differentiate within the thymus and account for nearly all of circulating lymphocytes gastritis chronic fatigue discount 0.1 mg florinef visa. They work together with B lymphocytes and are important for initiating antibody-mediated immune responses that management extracellular pathogens gastritis diet ëóííûé order florinef 0.1 mg. They kill other target cells such as virus-infected cells gastritis medication list order florinef 0.1 mg fast delivery, cancer-transformed cells gastritis diet zantrex purchase florinef 0.1mg fast delivery, cells contaminated with intracellular microorganisms, parasites, and transplanted cells. Regulatory (suppressor) T lymphocytes characterize a phenotypically various inhabitants of T lymphocytes that can functionally suppress an immune response to international and self-antigen by influencing the activity of different cells in the immune system. Other suppressor T cells may also function in suppressing B-cell differentiation and in regulating erythroid cell maturation within the bone marrow. Gamma/delta (/) T cells are strategically positioned on the interfaces of the external and inside environments and function as the primary line of protection towards invading organisms. They encounter antigen on the floor of the epithelial cells even before it enters the physique. Lymphatic System B lymphocytes differentiate in the bursa-equivalent organs and take part in humoral immunity. These cells are additional subdivided by their capacity to secrete cytokines (see pages 452�453). Lymphocyte Development and Differentiation Lymphocytes bear antigen-independent differentiation within the major lymphatic organs. They encompass two heavy (H) and two light (L) polypeptide chains linked by disulfide bonds (S�S). Both H and L chains are composed of domains of amino acids that are fixed (at the carboxy-terminus) or variable (at the aminoterminus) in their sequence. The five totally different immunoglobulin (Ig) isotypes are determined by the sort of heavy chain current. An antibody molecule binds an antigen (Ag) at the two websites of the amino-terminus, where the heavy and light-weight chains are associated with each other. Digestion of an antibody molecule by the proteolytic enzyme papain cleaves the antibody into two Fab fragments and one crystallizable Fc fragment. Many cells categorical Fc receptors on their surfaces, which anchor antibodies at the Fc fragment. Initially, lymphocytes are genetically programmed to recognize a single antigen out of nearly an infinite variety of attainable antigens, a course of referred to as antigen-independent proliferation and differentiation. Lymphocytes bear antigen-dependent activation within the secondary lymphatic organs. Immunocompetent lymphocytes (together with plasma cells derived from B lymphocytes and with macrophages) manage round reticular cells and their reticular fibers to form the adult effector lymphatic tissues and organs. Within these secondary (peripheral) lymphatic organs, T and B lymphocytes endure antigen-dependent activation into effector lymphocytes and reminiscence cells. The preliminary reaction of the physique to invasion by an antigen, either a overseas molecule or a pathogenic organism, is the nonspecific protection often known as the inflammatory response. The inflammatory response could either sequester the antigen, physically digest it with enzymes secreted by neutrophils, or phagocytose and degrade the antigen within the cytoplasm of macrophages. Degradation of antigens by macrophages could result in subsequent presentation of a portion of the antigen to immunocompetent lymphocytes to elicit a selected immune response. This response is characterised by a lag period of a quantity of days before antibodies (mostly IgM) or particular lymphocytes directed in opposition to the invading antigen can be detected in the blood. The initial response to an antigen is initiated by only one or a number of B lymphocytes that have been genetically programmed to reply to that specific antigen. After this preliminary immune response, a few antigen-specific B lymphocytes remain in circulation as reminiscence cells. The secondary immune response is usually extra speedy and extra intense (characterized by greater levels of secreted antibodies, normally of the IgG class) than the first response due to the presence of particular memory B lymphocytes already programmed to respond to that particular antigen. The secondary response is the idea of most immunizations for widespread bacterial and viral diseases. Some antigens, corresponding to penicillin and insect venoms, may set off intense secondary immune responses that produce hypersensitivity reactions similar to kind I, also referred to as anaphylactic hypersensitivity (see Folder 14. The two forms of particular immune responses are the humoral and cell-mediated responses. In general, an encounter with a given antigen triggers a response characterised as both a humoral immune response (antibody production) or a cell-mediated immune response. When this tissue was destroyed in the hen embryos (by both surgical removing or administration of excessive doses of testosterone), the grownup chickens were unable to produce antibodies, resulting in impaired humoral immunity. The chickens additionally demonstrated a marked discount in the number of lymphocytes present in particular bursa-dependent areas of the spleen and lymph nodes. Thus, the "B" refers to the bursa of Fabricius in birds or the bursa-equivalent organs in mammals. Investigators finding out new child mice found that removing of the thymus leads to profound deficiencies in cell-mediated immune responses. The rejection of transplanted pores and skin from a heterologous donor is an instance of cell-mediated immune response. Thymectomized mice demonstrate a marked discount within the variety of lymphocytes present in particular regions of the spleen and the lymph nodes (thymus-dependent areas). The areas of depletion differ from those recognized after removal of the bursa of Fabricius in the chicken. These affected lymphocytes have been subsequently named T lymphocytes or T cells; thus, the "T" refers to thymus. These antibodies are produced by B lymphocytes and by plasma cells derived from B lymphocytes. Cell-mediated immunity is mediated by specific T lymphocytes that attack and destroy virus-infected host cells or foreign cells. Cell-mediated immunity is important within the defense towards viral, fungal, and mycobacterial infections, as well as tumor cells. The expression of this gene complicated produces molecules that are specific not only to the person cell that produces them but in addition to the tissue sort and diploma of cellular differentiation. To understand how the particular immune responses (humoral and cell-mediated responses) are initiated, one should grasp the central role performed by the helper and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes can only react to "foreign" antigen exposed on cells, such as those reworked by most cancers or infected with a virus. This signal stimulates the T cell to secrete interleukins, which in turn stimulate T cells to divide and differentiate. Such reactions are noticed in sensitized humans after insect bites or injections of penicillin. There are several kinds of hypersensitivity reactions; however, the commonest kind is the allergic response (type I, quick, or anaphylactic hypersensitivity). The response normally develops about 15 to half-hour from the time of exposure to the antigen (allergen) and will trigger a wide range of signs involving skin (urticaria and eczema), eyes (conjunctivitis), nasal cavities (rhinorrhea, rhinitis), lungs (asthma), and alimentary tract (gastritis). Allergic reactions are mediated by IgE antibodies which may be answerable for the antibody-induced discharge of 449 mast cell or basophil granules. Eosinophils are attracted by eosinophil chemotactic factor to the positioning of mast cell degranulation, where they neutralize the results of mediators released by mast cells and basophils.
Buy florinef 0.1mg without prescriptionFor a detailed description of three pathways utilized in autophagy gastritis colitis purchase florinef 0.1 mg online, see pages forty one to 43 gastritis diet espanol 0.1 mg florinef fast delivery. Both external and inside stimuli can set off apoptosis by activating the enzymatic caspase cascade gastritis diet ÷òî order florinef 0.1mg line. Failure to arrest the cell cycle before mitosis happens causes issues with chromosome separation gastritis diet queen trusted 0.1mg florinef, which triggers the apoptotic pathway and cell death. Paraptosis is an alternate, nonapoptotic cell death that could be induced by progress factor receptors. On a mobile stage, paraptosis is characterised by the formation of a quantity of large vacuoles within the cell cytoplasm together with mitochondrial swellings. Pyroptosis is a type of cell dying induced by infection with certain microorganisms that generate intense inflammatory reactions. Necroptosis is a regulated caspase-independent cell death mechanism that might be induced in several cell sorts. Although it occurs under regulated situations, necroptotic cell demise is characterised by the identical morphologic options as unregulated necrotic death. Necrostatin-1 is a selected inhibitor of necroptosis that significantly reduces ischemic injury in affected tissues. Entosis is a specific receptor-regulated course of that entails cadherins and the formation of anchoring cell-to-cell junctions between two related kinds of cells. This course of ought to be distinguished from cell cannibalism, which is a nonspecific course of noticed in metastatic tumors that involves cancer cells "eating" and killing the immune cells that are directed in opposition to them. Two forms of chromatin are discovered in the nucleus: a dispersed form referred to as euchromatin and a condensed kind referred to as heterochromatin. In dividing cells, chromatin is condensed and organized into discrete our bodies referred to as chromosomes. The nuclear envelope, formed by two membranes with a perinuclear cisternal house between them, separates the nucleoplasm from the cytoplasm. The nuclear lamina is composed of nuclear lamins, a specialized sort of intermediate filaments, and lamin-associated proteins. The G1 section is normally the longest and probably the most variable phase of the cell cycle; it begins at the finish of mitosis (M phase). This phase additionally contains crucial checkpoint within the cell cycle, the restriction level, at which the cell evaluates its own replicative potential. Mitosis occurs in the M part and is managed by the spindle-assembly and chromosome-segregation checkpoints. Passage via the cell cycle is driven by a two-protein advanced consisting of cyclin and cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk). These proteins are synthesized and degraded at regular intervals during each cycle. Mitosis follows the S phase of the cell cycle and contains 4 phases: prophase, throughout which chromosomes condense and turn out to be visible, the nuclear envelope disassembles, and the mitotic spindle develops from microtubules; metaphase, which involves the alignment of chromosomes within the equatorial plate; anaphase, during which the sister chromatids start to separate and are pulled to reverse poles of the cell; and telophase, which involves the reconstruction of the nuclear envelope and the division of cytoplasm. During the prophase of meiosis I (reductional division) homologous chromosomes are paired and the recombination of genetic material happens between maternal and paternal pairs. Apoptosis occurs under normal physiologic circumstances to remove faulty or senescent cells without inflammatory response of the tissue. At the sunshine microscope level, the cells and extracellular components of the varied organs of the body exhibit a recognizable and often distinctive pattern of group. This organized arrangement reflects the cooperative effort of cells performing a specific perform. Therefore, an organized aggregation of cells that function in a collective method is identified as a tissue [Fr. Cells within tissues are linked to each other by specialised anchoring junctions (cell-to-cell attachments, page 98). Cells additionally sense their surrounding extracellular surroundings and communicate with each other by specialized intercellular junctions (gap junctions, page 98); facilitating this collaborative effort permits the cells to function as a practical unit. Other mechanisms that permit the cells of a given tissue to operate in a unified method embrace particular membrane receptors that generate responses to various stimuli. Despite their disparate structure and physiologic properties, all organs are made up of solely four fundamental tissue types. Connective tissue underlies or helps the other three primary tissues, both structurally and functionally. Nerve tissue receives, transmits, and integrates data from outside and inside the body to control the actions of the physique. The tissue idea provides a foundation for understanding and recognizing the numerous cell sorts inside the physique and the way they interrelate. Despite the variations normally look, structural organization, and physiologic properties of the Each fundamental tissue is outlined by a set of general morphologic characteristics or functional properties. Each kind may be additional subdivided according to particular characteristics of its various cell populations and any special extracellular substances that may be current. Another type of contractile tissue, myoepithelium, functions as muscle tissue however is usually designated epithelium due to its location. Rather, college students are suggested to study the options or traits of the totally different cell aggregations that define the four basic tissues and their subclasses. Epithelial cells, whether or not arranged in a single layer or in Tissues: Concept and Classification a number of layers, are always contiguous with one another. The intercellular house between epithelial cells is minimal and devoid of any construction except where junctional attachments are current. Free surfaces are characteristic of the exterior of the physique, the outer floor of many inner organs, and the lining of the body cavities, tubes, and ducts, both those who finally talk with the exterior of the body and people which are enclosed. The enclosed body cavities and tubes embody the pleural, pericardial, and peritoneal cavities in addition to the cardiovascular system. Classifications of epithelium are often based on the form of the cells and the number of cell layers quite than on perform. Only the highest layer of squamous cells is in touch with the lumen; the other cells are connected with each other by specialised cell-to-cell anchoring junctions or to the underlying connective tissue (lower dark-stained backside layer) by specialised cell-to-extracellular matrix anchoring junctions. The nature of the cells and matrix varies in accordance with the perform of the tissue. Thus, classification of connective tissue takes under consideration not only the cells but in addition the composition and organization of the extracellular matrix. Embryonic connective tissue derives from the mesoderm, the center embryonic germ layer, and is current within the embryo and within the umbilical fold. An H&E�stained section exhibiting a pancreatic duct lined by a single layer of contiguous cuboidal epithelial cells. The free floor of the cells faces the lumen; the basal surface is in apposition to the connective tissue.
Buy discount florinef 0.1mg lineInterleukins promote progress and differentiation of T cells gastritis chronic nausea generic florinef 0.1mg on line, B cells gastritis nerviosa purchase florinef 0.1 mg without prescription, and hematopoietic cells gastritis emergency room order 0.1mg florinef fast delivery. Mutations in the genes encoding several cytokine receptors have been identified in several immunodeficiency disorders gastritis diet ìóçûêà order florinef 0.1 mg, bacterial sepsis, sure lymphoid cancers, and diseases of autoimmunity. Cytokines have been used with promising outcomes to forestall transplant rejection, reverse mobile deficiencies after chemotherapy and radiation remedy, and deal with sure cancers. Lymphatic System the interaction between most antigens and antibodies is inadequate to stimulate immune responses. They secrete a quantity of cytokines, together with lymphokines, complement parts, and interleukins, in addition to acid hydrolases, proteases, and lipases. The overseas (exogenous) antigen (orange) is endocytosed and partially digested by proteolytic degradation in endosomes (grey pathway). After contact with an antigen, macrophages endure considered one of two activation processes characterized by multiple practical and morphologic changes. M1 macrophages turn out to be avidly phagocytotic with a higher ability to lyse ingested pathogenic microorganisms and overseas antigens. They promote inflammation, the destruction of extracellular matrix, and apoptosis. In distinction, macrophages which are activated by interleukins are called alternatively activated macrophages (M2 macrophages). They downregulate irritation, promote rebuilding of extracellular matrix and cell proliferation, and stimulate angiogenesis. A detailed description of both types of macrophages, their activation pathways, and their functions is offered in Chapter 6, Connective Tissue. These vessels take away substances and fluid from the extracellular areas of the connective tissues, thus producing lymph. Because the walls of the lymphatic capillaries are extra permeable than the partitions of blood capillaries, giant molecules, including antigens and cells, acquire entry more readily into the lymphatic capillaries than into blood capillaries. Within the lymph nodes, overseas substances (antigens) conveyed in the lymph are trapped by the follicular dendritic cells. This cytokine stimulates the macrophage to remodel into classically activated (M1) macrophage to destroy the micro organism inside its phagosomes. The T cell then makes copies of the virus, which are extruded from the T cell via exocytosis. They usually die of secondary infections attributable to opportunistic microorganisms or most cancers. Several new teams of drugs are being developed that embrace fusion and integrase inhibitors. Some lymphocytes transfer to the T and B domains of the lymph node; others pass through the parenchyma of the node and depart via an efferent lymphatic vessel. Ultimately, the lymphocytes enter a significant lymphatic vessel-in this case, the proper lymphatic trunk-that opens into the junction of the best inside jugular and right subclavian vein. The lymphocytes proceed to the arterial aspect of the circulation and, through the arteries, to the lymphatic tissues of the physique or to tissues the place they take part in immune reactions. Some lymphocytes move via the substance of the node and leave by way of the efferent lymphatic vessels, which lead to the right lymphatic trunk or to the thoracic duct. In turn, both of these channels empty into the blood circulation at the junctions of the internal jugular and subclavian veins on the base of the neck. The lymphocytes are conveyed to and from the assorted lymphatic tissues through the blood vessels. Lymphocytes and other free cells of this tissue are discovered in the lamina propria (subepithelial tissue) of those tracts. These cells are strategically positioned to intercept antigens and provoke an immune response. After contact with antigen, they travel to regional lymph nodes, the place they undergo proliferation and differentiation. Progeny of these cells then return to the lamina propria as effector B and T lymphocytes. The extremely cellular, diffuse lymphatic tissue contains fibroblasts, plasma cells, and eosinophils. However, essentially the most plentiful cell element, whose presence characterizes diffuse lymphatic tissue, is the lymphocyte, which may be identified by its small, round, dark-staining nucleus. The germinal middle develops when a lymphocyte that has acknowledged an antigen returns to a primary nodule and undergoes proliferation. The lighter staining is attributable to the massive immature lymphocytes (lymphoblasts and plasmablasts) that it incorporates. This photomicrograph exhibits a bit of the wall of the small intestine (duodenum). Short villi and intestinal glands are present within the upper part of the micrograph. The lymphocytes in the germinal middle are larger than these in the denser region of the nodule. They have more cytoplasm, so their nuclei are extra dispersed, giving the appearance of a much less compact mobile mass. The presence of enormous numbers of eosinophils, additionally regularly noticed within the lamina propria of the intestinal and respiratory tracts, a sign of persistent irritation and hypersensitivity reactions. Lymphatic nodules are discrete concentrations of lymphocytes contained in a meshwork of reticular cells. In addition to diffuse lymphatic tissue, localized concentrations of lymphocytes are generally found within the partitions of the alimentary canal, respiratory passages, and genitourinary tract. A lymphatic nodule consisting chiefly of small lymphocytes is recognized as a main nodule. The capsule (Cap) consists of dense connective tissue from which trabeculae (T) penetrate into the organ. The subcapsular sinus is steady with the trabecular sinuses that course along the trabeculae. It consists of densely packed lymphocytes and accommodates the distinctive high endothelial venules (not seen at this magnification). The medullary sinuses receive lymph from the trabecular sinuses as nicely as lymph that has filtered by way of the cortical tissue. The stratified squamous epithelium that varieties the floor of the tonsil dips into the underlying connective tissue in quite a few locations, forming tonsillar crypts. In effect, the lymphatic nodule has actually grown into the epithelium, distorting it and ensuing in the disappearance of the more typical, well-defined epithelial�connective tissue boundary. The germinal heart is a morphologic indication of lymphatic tissue response to antigen.
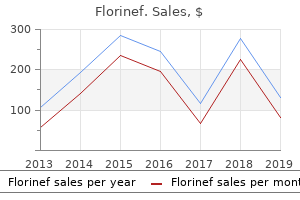
Florinef: 0.1 mg
Purchase florinef 0.1mg amexSuccess of the enzyme-replacement therapy is often limited by insufficient biodistribution of recombinant enzymes and high costs gastritis diet salad cheap florinef 0.1 mg visa. In some instances gastritis yogurt buy discount florinef 0.1 mg on line, synthetic chaperones can assist within the folding of mutated enzymes to enhance their stability and advance their lysosomal delivery gastritis treatment and diet cheap florinef 0.1 mg amex. Generally gastritis symptoms for dogs cheap 0.1mg florinef otc, autophagy could be divided into three well-characterized pathways: Proteasome-Mediated Degradation In addition to the lysosomal pathway of protein degradation, cells have a capability to destroy proteins without involvement of lysosomes. Such a course of happens inside giant cytoplasmic or nuclear protein complexes referred to as proteasomes. Proteasomemediated degradation is used by cells to destroy irregular proteins that are misfolded, denaturated, or include abnormal amino acids. This pathway additionally degrades regular short-lived regulatory proteins that must be quickly inactivated and degraded, such as mitotic cyclins that regulate cell-cycle progression, transcriptional elements, tumor suppressors, or tumor promoters. At first, the advanced containing Atg12�Atg5�Atg16L proteins attaches to part of endoplasmic reticulum and localizes the isolation membrane. Together they change the form of the isolation membrane, which bends to enclose and seal an organelle destined for digestion within the lumen of the autophagosome. Once the autophagosome is completed, the Atg12�Atg5�Atg16L advanced and Atg8 dissociate from this structure. After focused delivery of lysosomal enzymes, the autophagosome matures right into a lysosome. The isolation membrane disintegrates within the hydrolytic compartment of a lysosome. Microautophagy can be a nonspecific process during which cytoplasmic proteins are degraded in a slow, continuous process under normal physiologic circumstances. In microautophagy, small cytoplasmic soluble proteins are internalized into the lysosomes by invagination of the lysosomal membrane. Chaperone-mediated autophagy is the one selective strategy of protein degradation and requires assistance from specific cytosolic chaperones similar to heat-shock chaperone protein called hsc73. This process is activated throughout nutrient deprivation and requires the presence of concentrating on indicators on the degraded proteins and a particular receptor on the lysosomal membrane. Chaperone-mediated autophagy is answerable for the degradation of approximately 30% of cytoplasmic proteins in organs such because the liver and kidney. This electron micrograph reveals a quantity of autophagosomes containing degenerating mitochondria. The tagging response is catalyzed by three ubiquitin ligases known as ubiquitin-activating enzymes E1, E2, and E3. In a cascade of enzymatic reactions, the targeted protein is first marked by a single ubiquitin molecule. This creates a sign for consecutive attachment of a number of other ubiquitin molecules, resulting in a linear chain of ubiquitin conjugates. A protein goal for destruction within the proteasome should be labeled with no much less than four ubiquitin molecules in the form of a polyubiquitin chain that serves as a degradation signal for proteasome complicated. The first group of illnesses outcomes from a lack of proteasome perform because of mutations in the system of ubiquitin-activating enzymes. This leads to a decrease in protein degradation and their subsequent accumulation in the cell cytoplasm. The second group of ailments results from an accelerated degradation of proteins by overexpressed proteins involved on this system. The recent discovery of specific proteasome inhibitors holds promise for therapy of cancers and certain viral infections. This degradation pathway entails tagging proteins destined for destruction by a polyubiquitin chain and its subsequent degradation in proteasome complex with the release of free reusable ubiquitin molecules. The regulatory particle on the other side of the chamber releases brief peptides and amino acids after degradation of the protein is accomplished. Rough-Surfaced Endoplasmic Reticulum the protein synthetic system of the cell consists of the tough endoplasmic reticulum and ribosomes. The cytoplasm of a wide range of cells engaged mainly in protein synthesis stains intensely with basic dyes. That portion of the cytoplasm that stains with the basic dye known as ergastoplasm. Ribosomes measure 15 to 20 nm in diameter and include a small and enormous subunit. After posttranscriptional and chloramphenicol inhibit protein synthesis by binding to completely different portions of bacterial ribosomes. These sign sequences (signal peptides) are often found within the sequence of the first group of 15 to 60 amino acids on the amino-terminus of a newly synthesized protein. For occasion, nearly all proteins that are transported to the endoplasmic reticulum have a signal sequence consisting of 5 to 10 hydrophobic amino acids on their amino-termini. Polyribosomes are current on the cytoplasmic surface of the membrane surrounding the cisternae. The image of a ribosome-studded membrane is the origin of the term rough endoplasmic reticulum. The differences between the structure of prokaryotic (bacterial) and eukaryotic ribosomes were exploited by researchers, who discovered chemical compounds (antibiotics) that bind to bacterial ribosomes, thereby destroying a bacterial an infection with out harming the cells of the contaminated particular person. Thus, within the upper proper and left, the membranes of the reticulum have been minimize at a right angle to their floor. In the middle, the reticulum has twisted and is proven as in an aerial view (from above the membrane). The first group of 15 to 60 amino acids on the amino-terminus of a newly synthesized polypeptide types a signal sequence (signal peptide) that directs protein to its vacation spot. The sign sequence is cleaved from the polypeptide by sign peptidase and is subsequently digested by signal peptide peptidases. On completion of protein synthesis, the ribosome detaches from the translocator protein. For integral membrane proteins, sequences along the polypeptide could instruct the forming protein to cross back and forth by way of the membrane, creating the functional domains that the protein will exhibit at its last membrane. On completion of protein synthesis, the ribosome detaches from the translocator protein and is again free in the cytoplasm. These modifications embody core glycosylation, disulfidebond and internal hydrogen-bond formation, folding of the newly synthesized protein with the assistance of molecular chaperones, and partial subunit assembly. Defective proteins are right here deglycosylated, polyubiquitylated, and degraded inside proteasomes (see page 43). Secretory cells embrace glandular cells, activated fibroblasts, plasma cells, odontoblasts, ameloblasts, and osteoblasts. After a vesicle is shaped, the coat elements dissociate from the vesicle and are recycled to their website of origin. Note that the surface coat of those vesicles is completely different from that of clathrin-coated vesicles. It also contains several enzymes, including phospholipase A2, monoamine oxidase, and acetyl coenzyme A (CoA) synthase.
Generic florinef 0.1mg otcNote the small vessels and capillary community within the perivascular connective tissue surrounding every hepatic triad inside the portal canal gastritis symptoms patient florinef 0.1 mg cheap. Also note the periportal area of Mall gastritis diet ïîðîíî trusted florinef 0.1mg, located between the portal canal and the outermost hepatocytes gastritis food to eat buy florinef 0.1mg. This house can be full of a small quantity of connective tissue during which lymph drainage begins gastritis diet 13 buy florinef 0.1mg with amex. From right here, blind-ended lymphatic capillaries type larger lymphatic vessels that accompany branches of the hepatic artery. The sinusoids result in a terminal hepatic venule (central vein) that in flip empties into the sublobular veins. Blood leaves the liver by way of the hepatic veins, which empty into the inferior vena cava. Structural Organization of the Liver As launched previously, the structural elements of the liver include: and the liver acinus. It is based on the distribution of the branches of the portal vein and hepatic artery within the organ and the pathway that blood from them follows because it ultimately perfuses the liver cells. In young people as much as 6 years of age, the liver cells are organized in plates two cells thick. Blood vessels, nerves, lymphatic vessels, and bile ducts travel inside the connective tissue stroma. With this data as background, one can now consider several ways to describe the group of these structural components to understand the main functions of the liver. At the middle of the lobule is a relatively large venule, the terminal hepatic venule (central vein), into which the sinusoids drain. The plates of cells radiate from the central vein to the periphery of the lobule, as do the sinusoids. At the angles of the hexagon are the portal areas (portal canals), unfastened stromal connective tissue characterized by the presence of the portal triads. This connective tissue is finally steady with the fibrous capsule of the liver. At the sides of the portal canal, between the connective tissue stroma and the hepatocytes, is a small space referred to as the periportal area (space of Mall). Thus, the morphologic axis of the portal lobule is the interlobular bile duct of the portal triad of the basic lobule. These lines outline a roughly triangular block of tissue that features those parts of three traditional lobules that secrete the bile that drains into its axial bile duct. This idea permits a description of hepatic parenchymal construction corresponding to that of other exocrine glands. The liver acinus is the structural unit that provides one of the best correlation between blood perfusion, metabolic exercise, and liver pathology. A traditional liver lobule can be schematically diagramed as a six-sided polyhedral prism with portal triads (hepatic artery, portal vein, and bile duct) at every of the corners. The blood vessels of the portal triads ship distributing branches along the edges of the lobule, and these branches open into the hepatic sinusoids. The long axis of the lobule is traversed by the terminal hepatic venule (central vein), which receives blood from the hepatic sinusoids. Note that a wedge of the tissue has been faraway from the lobule for higher visualization of the terminal hepatic venule. Interconnecting sheets or plates of hepatocytes are disposed in a radial sample from the terminal hepatic venule to the periphery of the lobule. The liver acinus is lozenge-shaped and represents the smallest useful unit of the hepatic parenchyma. The brief axis of the acinus is outlined by the terminal branches of the portal triad that lie along the border between two traditional lobules. The lengthy axis of the acinus is a line drawn between the two central veins closest to the quick axis. This photomicrograph reveals a cross-section of a pig liver lobule stained by the Mallory-Azan technique to visualize connective tissue parts. Note the comparatively thick interlobular connective tissue (stained blue) surrounding the lobules. The terminal hepatic venule (central vein) is seen within the center of the lobule. Note that in contrast to the pig liver, the lobules of the human liver lack connective tissue septa. The boundaries of a lobule can be approximated, nevertheless, by drawing a line (dashed line) from one portal canal to the next, thus circumscribing the lobule. The outlines of a basic hepatic lobule, portal lobule, and liver acinus are seen on this section of the liver tissue. Note that the hexagonal-shaped traditional lobule (red) has the terminal hepatic venule (central vein) on the center of the lobule and the portal canals containing portal triads at the peripheral angles of the lobule. The triangular portal lobule (green) has a portal canal on the center of the lobule and terminal hepatic venules (central veins) on the peripheral angles of the lobule. A diamondshaped liver acinus (multicolor) has distributing vessels on the equator and terminal hepatic venules (central veins) at each pole. It consists of adjoining sectors of neighboring hexagonal fields of basic lobules partially separated by distributing blood vessels. The terminal hepatic venules (central veins) in this interpretation are at the pointed edges of the acinus as a substitute of in the center, as in the basic lobule. The portal triads (terminal branches of the portal vein and hepatic artery) and the smallest bile ducts are shown at the corners of the hexagon that outlines the cross-sectioned profile of the traditional lobule. This idea permits an outline of the exocrine secretory operate of the liver corresponding to that of the portal lobule. Zone 3 is farthest from the brief axis and closest to the terminal hepatic vein (central vein). This zone corresponds to probably the most central part of the basic lobule that surrounds the terminal hepatic vein. On the other hand, cells in zone 3 are the first to present ischemic necrosis (centrilobular necrosis) in situations of lowered perfusion and the primary to present fat accumulation. Normal variations in enzyme activity, the quantity and dimension of cytoplasmic organelles, and the scale of cytoplasmic glycogen deposits are additionally seen between zones 1 and 3. Cells in zone 2 have functional and morphologic traits and responses intermediate to these of zones 1 and three. Blood Vessels of the Parenchyma the blood vessels that occupy the portal canals are known as interlobular vessels. Only the interlobular vessels that type the smallest portal triads send blood into the sinusoids. The bigger interlobular vessels department into distributing vessels that are positioned on the periphery of the lobule. The central vein programs by way of the central axis of the basic liver lobule, becoming larger as it progresses through the lobule and empties into a sublobular vein.
References - Fields, H. L., Rowbotham, M., & Baron, R. (1998). Postherpetic neuralgia: Irritable nocioceptors and deafferentation. Neurobiology of Diseases, 5, 209n227.
- Gonzaga CC, Calhoun DA: Resistant hypertension and hyperaldosteronism, Curr Hypertens Rep 10(6):496n503, 2008.
- Smith, C.P., Nishiguchi, J., O'Leary, M., Yoshimura, N., Chancellor M.B. Single-institution experience in 110 patients with botulinum toxin A injection into bladder or urethra. Urology 2005;65:37-41.
- Mandelzweig L, Battler A, Boyko V, et al: The second Euro Heart Survey on acute coronary syndromes: Characteristics, treatment, and outcome of patients with ACS in Europe and the Mediterranean Basin in 2004.
- Panis Y, Poupard B, Nemeth J, Lavergne A, Hautefeuille P, Valleur P. Ileal pouch/anal anastomosis for Crohn's disease. Lancet 1996;347:854.
|