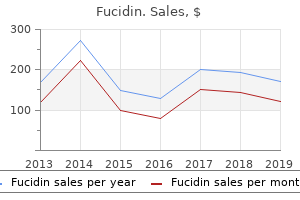
Fucidin
Charles H. Cook, M.D. - Assistant Professor of Surgery and Critical Care
- The Ohio State University Hospitals
- Columbus, OH
Order 10gm fucidin visaGalactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase Glucocerebrosidase Phenylalanine hydroxylase Sphingomyelinase Uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 37 An 11-year-old youngster has had growing episodes of diarrhea for the past 3 years antibiotic pipeline discount fucidin 10 gm without a prescription. Which of the next inborn errors of metabolism is more than likely present in this child Genetic testing indicates that a crucial protein coded by a gene is lacking one phenylalanine amino acid in the protein sequence virus hunter island purchase fucidin 10 gm on line. She was born at time period antibiotic resistance medical journals fucidin 10gm online, but developed belly distention in the first week of life from meconium ileus antibiotics for uti e coli purchase 10gm fucidin with mastercard. She has had frequent bouts of pneumonia with cough productive of thick mucoid sputum for eight years. Each new bout of pneumonia is longer and increasingly nonresponsive to antibiotics. Which of the next is crucial factor inflicting rising frequency and severity of her Pseudomonas infections Some of these sufferers are found to have bilateral agenesis of the vas deferens together with a history of recurrent respiratory tract infections, steatorrhea, and biliary cirrhosis. An abnormality involving which of the following laboratory checks is most likely to be present in these infertile men Scene investigation reveals the infant was inclined with no airway obstruction or proof of trauma. Gross and microscopic examination at autopsy reveals only petechiae of mesothelial surfaces. The distraught mother and father, each manufacturing facility employees, are interviewed by the health worker and point out that the child had not been ill. She finds no gross or microscopic abnormalities at autopsy, and the outcomes of all toxicologic tests are negative. An ultrasound reveals a lesion with the consultant gross appearance proven in the figure. An enucleation of the right eye is performed, adopted by radiation and chemotherapy. Which of the following genetic mechanisms is most likely to produce these findings Aneuploidy Chromosomal translocation Trinucleotide repeat mutation Germline mutation Multifactorial inheritance Uniparental disomy X-linked gene defect 43 A longitudinal research of pediatric neoplasia is carried out. Infants born at term with no abnormalities and no family historical past of malignancies are identified and adopted. Which of the following neoplasms is most probably to be recognized within the first year of life on this cohort His mom has observed that the child has an enlarging stomach over the past three months. The adrenal gland is excised surgically; the histologic look of the mass is shown in the determine. Which of the following features of this lesion is most likely associated with a poor prognosis The mass is excised and on microscopic examination exhibits a triphasic combination of blastemal, stromal, and epithelial cell varieties. Oligohydramnios with diminished amniotic fluid leads to deformations, not disruptions. Rh incompatibility can give rise to erythroblastosis fetalis, which can manifest as hydrops fetalis. In trisomy 18 and other chromosomal abnormalities, an omphalocele centered on the umbilicus is the commonest stomach wall defect. The malformation (anomaly) that initiated the sequence on this case was multicystic renal dysplasia because the kidneys fashioned little fetal urine, which is handed into the amniotic cavity to type the majority of the amniotic fluid. The spectrum of findings on this case is consistent with 3 B the flattened face and deformed feet of this infant recommend oligohydramnios resulting from renal agenesis. The lack of this fluid constricts the developing fetus and restricts pulmonary growth. Infants born to diabetic mothers have an elevated risk of congenital anomalies and not utilizing a specific sample. Trisomy 13 is accompanied by various malformations, together with malformations affecting the kidneys. The external features are quite completely different from these seen on this case, nonetheless, and affected infants virtually at all times have microcephaly and midline defects, such as cleft lip and palate. Multiple genetic susceptibilities, modified by environmental influences, can underlie the looks of 20% to 25% of all start defects. Of the remaining choices, all usually tend to produce multiple defects and to reduce fetal progress. Early amnion disruption might lead to clefts, however more severe defects are current. Albucasis (963-1013 ce) is the "father of surgical procedure" whose notable work, Al-Tasrif, was composed of 30 volumes on medical science, together with 3 volumes on surgery during which he described many surgical procedures. These genes are important in embryonal patterning of limbs, vertebrae, and craniofacial constructions. The findings suggest uteroplacental insufficiency from an intrinsic placental abnormality. One trigger is a cytogenetic abnormality within the creating embryo that occurs just in the trophoblast, and solely placenta is affected. Inborn errors of metabolism corresponding to galactosemia often manifest after birth because maternal metabolism clears any intermediate products of fetal enzyme deficiencies. Trisomy 21 is extra frequent with advancing maternal age, however on this case no fetal anomalies had been famous. Most defects are believed to be attributable to the inheritance of a certain number of genes and by the interplay of these genes with environmental elements. The recurrence rate is believed to be 2% to 7% and is identical for all first-degree relations, regardless of intercourse and relationship to the index case. Dispermy is uncommon and may lead to triploidy, a situation that rarely ends in a stay start. Erythroblastosis fetalis leads to fetal anemia with congestive heart failure and hydrops, but not to malformations. In the previous, thalidomide use was a reason for malformations (almost invariably outstanding limb deformities). Nondisjunctional occasions during meiosis in the maternal ova account for trisomies and monosomies, many of which have related cardiac defects, including ventricular septal defect. This mechanism is unlikely in paternal sperm, however, that are constantly being produced in giant numbers all through life. Children with fetal alcohol syndrome are inclined to be developmentally impaired throughout childhood, but the bodily anomalies are probably to turn out to be much less apparent as the child matures. The liver can have fatty metamorphosis with hepatomegaly and elevated serum transaminases. The main results of congenital rubella happen during organogenesis in the first trimester and lead to more pronounced defects, including congenital coronary heart illness. Maternal diabetes usually ends in a bigger infant, and malformations may be current. Placenta previa, a low-lying placenta at or close to the cervical os, may cause vital hemorrhage on the time of delivery or uteroplacental insufficiency with growth retardation before supply. Placental causes of intrauterine progress retardation lead to uneven development retardation with sparing of the brain. The findings of trisomy 21 are delicate at birth, but typically include brachycephaly, not microcephaly. The absence of different defects suggests 10 A Multiple fetal losses earlier in gestation counsel the probability of a chromosomal abnormality-the mother or father will be the service of a balanced translocation. Because the mom is blood kind A optimistic, fetal loss with erythroblastosis fetalis is unlikely, although other blood group incompatibilities potentially may result in erythroblastosis fetalis. Environmental factors related to delivery defects embody infections, maternal disease such as diabetes mellitus (not gestational diabetes), and teratogens, accounting for up to 10% of start defects.
Safe 10gm fucidinThere are geographic variations in the distribution of various haemoglobinopathies world over as proven in Homozygous State:Sickle Cell Anaemia antibiotics for uti flucloxacillin purchase 10 gm fucidin amex. Following abnormalities are observed an important and extensively prevalent sort of haemoglobinopathy is as a result of of good antibiotics for sinus infection trusted fucidin 10gm the presence of sickle haemoglobin (HbS) within the purple blood cells virus chikungunya cheap fucidin 10 gm line. B antibiotic resistance factors discount fucidin 10 gm visa, Mechanism of polymerisation and consequent sickling of purple cells containing HbS. Mechanism of sickling: During deoxygenation, the purple cells containing HbS change from biconcave disc form to an elongated crescent-shaped or sickle-shaped cell. Reversible-irreversible sickling: the oxygen-dependent sickling course of is often reversible. There is normally extreme persistent haemolytic anaemia (primarily extravascular) with onset of aplastic crisis in between. The blood film shows sickle cells and target cells and features of splenic atrophy similar to presence of HowellJolly our bodies. A constructive sickling check with a reducing substance corresponding to sodium metabisulfite (described above). Haemoglobin electrophoresis exhibits no regular HbA however reveals predominance of HbS and 2-20% HbF. All these recurrent vaso-occlusive episodes throughout their lives due disorders behave like delicate type of sickle cell illness. Their to obstruction to capillary blood circulate by sickled purple cells analysis is made by haemoglobin electrophoresis and upon deoxygenation or dehydration. Some of them are related to ii) Macroinfarcts involving mostly the spleen scientific manifestations, while others are of no consequence. The molecular lesion in HbC is substitution of lysine for glutamic acid at -6 globin chain place. About 3% of Sikhs dwelling in Punjab are affected with HbD haemoglobinopathy (called HbD Punjab, also recognized as HbLos Angeles). HbD Punjab arises from the substitution of glutamine for glutamic acid at -121 globin chain place. Thalassaemias had been first described in individuals of Mediterranean nations (North Africa, Southern Europe) from where it derives its name `Mediterranean anaemia. Normally, a person inherits two -globin genes situated one each on two chromosomes eleven, and two -globin genes one each on two chromosomes sixteen, from every father or mother i. Depending upon whether or not the genetic defect or deletion lies in transmission of - or -globin chain genes, thalassaemias are categorized into - and - thalassaemias. Thus, sufferers with -thalassaemia have structurally regular -globin chains however their production is impaired. Similarly, in -thalassaemia, -globin chains are structurally normal however their production is decreased. Each of the 2 main kinds of thalassaemias might occur as heterozygous (called - and -thalassaemia minor or trait), or as homogygous state (termed - and -thalassaemia major). A classification of varied kinds of thalassaemias alongwith the medical syndromes produced and salient laboratory findings are given in Table 12. A deficiency of -globin chains in -thalassaemia leads to large excess of -chains throughout the creating pink cells. Part of those extreme -chains are removed by pairing with -globin chains as HbF, whereas the remainder unaccompanied -chains precipitate rapidly throughout the red cell as Heinz bodies. Thus, such pink cells *In a traditional grownup, distribution of haemoglobin is as under: HbA (22) = 95-98%, HbA2 (22) (a minor variant of HbA) = 1. HbE arises from the substitution of lysine for glutamic acid at -26 globin chain place. Like other irregular haemoglobins, HbE haemoglobinopathy may occur as asymptomatic heterozygous HbE trait, compensated haemolytic homozygous HbE illness, or as double heterozygous states together with other haemoglobinopathies similar to HbE- thalassaemia and HbE thalassaemia. Haemoglobin O-Arab Disease Hb O-Arab illness was first identified in an Arab household however has now been detected in American blacks too. Unstable-Hb Haemoglobinopathy the unstable haemoglobins are these haemoglobin variants which endure denaturation and precipitation within the pink cells as Heinz our bodies. These give rise to what is called congenital non-spherocytic haemolytic anaemia or congenital Heinz physique haemolytic anaemia. These disorders have both autosomal dominant inheritance or develop from spontaneous mutations. The unstable haemoglobins arise from either a single amino acid substitution within the globin chain or as a end result of deletion of one or more amino acids throughout the globin chain in order that the firm bonding of the haem group within the molecule is disturbed leading to formation of methaemoglobin and precipitation of globin chains as Heinz bodies. Patients with -thalassaemia minor, then again, have very delicate ineffective erythropoiesis, haemolysis and shortening of red cell lifespan. The thalassaemias are mostly because of deletion of one or more of the -chain genes situated on short arm of chromosome sixteen. If born alive, the options much like extreme Rh haemolytic illness are current (page 340). HbH Disease Deletion of three -chain genes produces HbH which is a globin chain tetramer (4) and markedly impaired -chain synthesis. The severity of anaemia fluctuates and will fall to very low ranges during being pregnant or infections. Introduction to Haematopoietic System and Disorders of Erythroid Series -Thalassaemia Trait -thalassaemia trait might happen by the next molecular pathogenesis: By deletion of two of the four -chain genes in homozygous type referred to as homozygous -thalassaemia, or in double heterozygous type termed heterozygous -thalassaemia. It is suspected in a affected person of refractory microcytic hypochromic anaemia in whom iron deficiency and -thalassaemia minor have been excluded and the affected person belongs to the high-risk ethnic group. The sufferers of -thalassaemia trait could have the following haematological findings: 1. The molecular pathogenesis of the -thalassaemias is extra complex than that of -thalassaemias. Instead, most of -thalassaemias come up from various kinds of mutations of -globin gene ensuing from single base adjustments. The image � is used to point out the entire absence of -globin chain synthesis while + denotes partial synthesis of the -globin chains. Some of the necessary ones having effects on -globin chain synthesis are as underneath. Depending upon whether or not a half of splice website stays intact or is completely degraded, it may end in + thalassaemia or � thalassaemia. Depending upon the extent of discount in -chain synthesis, there are three forms of -thalassaemia: 1. These end in extreme formation of alternate haemoglobins, HbF (2 2) and HbA2 (2 2). Anaemia begins appearing within the first 4-6 months of life when the switch over from -chain to -chain production occurs.
Diseases - Neuropathy, hereditary sensory, type I
- Epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica, dominant type
- Microphthalmia camptodactyly mental retardation
- Glucocorticoid deficiency, familial
- Adolescent benign focal crisis
- Proximal myotonic myopathy
- Goitre
- Exstrophy of the bladder-epispadias
- Deafness, autosomal dominant nonsyndromic sensorineural
- Lung agenesis heart defect thumb anomalies
Discount 10 gm fucidin with visaCritical coronary narrowing (more than 75% compromised lumen) is of nice significance within the causation of such infarcts duration of antibiotics for sinus infection fucidin 10gm on-line. Atherosclerotic plaques with superimposed thrombosis and intramural haemorrhage are significant in about 90% circumstances antibiotic prophylaxis 10gm fucidin overnight delivery, and non-atherosclerotic causes within the remaining 10% instances infection xbox 360 fucidin 10 gm amex. This is because subendocardial myocardium is generally least nicely perfused by coronaries and thus is extra weak to any reduction within the coronary move antimicrobial hand soap fucidin 10gm overnight delivery. Infarcts have been categorized in a selection of ways by the physicians and the pathologists: 1. Right ventricle is much less susceptible to infarction because of its thin wall, having less metabolic requirements and is thus adequately nourished by the thebesian vessels. Stenosis of the left anterior descending coronary artery is the commonest (40-50%). Stenosis of the left circumflex coronary artery is seen least regularly (15-20%). The gross and microscopic modifications in the myocardial infarction vary according to the age of the infarct and are therefore described sequentially (Table 16. The transmural infarcts, which by definition contain the whole thickness of the ventricular wall, often have a thin rim of preserved subendocardial myocardium which is perfused immediately by the blood within the ventricular chamber. The subendocardial infarcts which affect the inside subendocardial half of the myocardium produce less welldefined gross modifications than the transmural infarcts. During the next forty eight to 72 hours, the infarct develops a yellow border because of neutrophilic infiltration and thus turns into more well-defined. However, the time taken by an infarct to heal by fibrous scar might vary depending upon the size of the infarct and adequacy of collateral circulation. As elsewhere within the physique, myocardial ischaemia induces ischaemic coagulative necrosis of the myocardium which finally heals by fibrosis. However, sequential light microscopic adjustments are noticed as described below and diagrammatically proven in. First week: the development of changes takes place in the following way: i) In the primary 6 hours after infarction, often no detectable histologic change is observed in routine light microscopy. The muscle fibres on the margin of the infarct present vacuolar degeneration known as myocytolysis. The neutrophilic infiltrate is properly developed and extends centrally into the interstitium. Second week: the changes are as under: i) By 10th day, a lot of the necrosed muscle at the periphery of infarct is eliminated. Many pigmented macrophages containing yellow-brown lipofuscin (derived from breakdown of myocardial cells) and golden brown haemosiderin (derived from lysed erythrocytes in haemorrhagic areas) are seen. The pigmented macrophages might persist for an extended length in the scar, typically for years. A abstract of the sequence of gross and microscopic adjustments in myocardial infarction of various duration is introduced in Table sixteen. The ischaemic damage to myocardium is reversible if perfusion is restored throughout the first 30 minutes of onset of infarction failing which irreversible ischaemic necrosis of myocardium units in. Institution of thrombolytic therapy with thrombolytic agents such as streptokinase and tissue plasminogen activator (door-to-needle time <30 minutes). However, attempt at reperfusion is fraught with the risk of ischaemic reperfusion injury (Chapter 3). Further myonecrosis during reperfusion happens because of rapid inflow of calcium ions and technology of poisonous oxygen free radicals. Third week: Necrosed muscle fibres from larger infarcts continue to be eliminated and replaced by ingrowth of newly formed collagen fibres. By particular strategies like electron microscopy, chemical and histochemical studies, changes can be demonstrated in early infarcts before detectable mild microscopic alterations seem. Analysis of tissues from early infarcts by chemical and histochemical techniques has proven numerous findings. These are as follows: i) Glycogen depletion in myocardial fibres within 30 to 60 minutes of infarction. Based on the above observations and on leakage of enzymes from the ischaemic myocardium, alterations within the concentrations of varied enzymes are detected within the blood of those patients. There are two kinds of cTn: cardiac troponin T (cTnT); and cardiac troponin I (cTnI). These happen because of ischaemic injury or irritation to the conduction system, leading to irregular rhythm. Other causes of arrhythmias include leakage of K+ from ischaemic muscle cells and increased focus of lactate and free fatty acids in the tissue fluid. Shock may be accompanied by peripheral circulatory failure, oliguria and psychological confusion. Thromboemboli from either supply may cause occlusion of the pulmonary, renal, mesenteric, splenic, pancreatic or cerebral arteries and cause infarcts in these organs. Other sites of rupture are via interventricular septum and rupture of a papillary muscle in infarct of the left ventricle. Rupture at any of these websites occurs often in the first week and is often deadly. Cardiac aneurysms impair the perform of the heart and are the widespread websites for mural thrombi. Sterile pericarditis showing on concerning the second day is widespread over transmural infarcts. It could also be because of autoimmune response as evidenced by circulating anti-heart antibodies in the serum of those sufferers. In majority of instances, coronary atherosclerosis causes progressive ischaemic myocardial harm and substitute by myocardial fibrosis. The mechanism of improvement of myocardial fibrosis can be explained by one of the following ideas: i) Myocardial fibrosis represents healing of minute infarcts involving small scattered teams of myocardial fibres. Sudden ischaemic demise myocardial ischaemia is nearly all the time by deadly arrhythmias, mainly ventricular asystole or fibrillation. At autopsy, such instances reveal mostly critical atherosclerotic coronary narrowing (more than 75% compromised lumen) in a quantity of of the three major coronary arterial trunks with superimposed thrombosis or plaque-haemorrhage. Grossly, the most important finding is marked hypertrophy of the center, mainly of the left ventricle. In superior instances, there could also be myocardial oedema and foci of necrosis within the myocardium. Thus, cor pulmonale is the right-sided counterpart of the hypertensive coronary heart illness described above. Chronic cor pulmonale is extra common and is commonly preceded by chronic pulmonary hypertension (Chapter 17). Chronic lung illnesses as well as diseases of the pulmonary vessels cause elevated pulmonary vascular resistance.
Cheap 10 gm fucidin with visaHeterotopias Arrest of normal neuronal migration alongside the radial glial cells may end up in grossly seen lots of "heterotopic" gray matter infection behind ear quality fucidin 10gm. These collections come in many shapes and sizes and can be found just about anywhere between the ventricles and the pia bacteria eating flesh cheap 10gm fucidin with amex. They can be solitary or multifocal and exist either as an isolated phenomenon or in affiliation with different malformations antimicrobial xylitol 10gm fucidin fast delivery. The most typical is ventriculomegaly adopted by agenesis of the corpus callosum and cortical dysplasia virus upload order 10gm fucidin with amex. Collections of spherical or ovoid nodules indent the lateral walls of the ventricles, giving them a distinctive "lumpy-bumpy" appearance. The overlying cortex usually seems thinned, however sulcation and gyration are usually regular. The involved portion of the affected hemisphere is abnormally small, and the overlying cortex seems skinny and sometimes dysplastic (37-35). The overlying cortex is thin, and the underlying ventricle usually seems distorted (37-36). Although these have been described with megalencephaly and polymicrogyria, most are probably part of the "double cortex" type of lissencephaly (see below). The major differential diagnosis of subcortical heterotopia is neoplasm, most particularly gangliocytoma. The giant, focal, mass-like collection of gray matter, skinny overlying cortex are typical. Malformations as a end result of widespread irregular transmantle migration embody agyria, pachygyria, and band heterotopia. Agyria is outlined as a thick cortex with absence of surface gyri ("complete" lissencephaly). The white matter is severely lowered in volume and infrequently contains foci of heterotopic neurons. In the most severe varieties, the cerebral hemispheres are smooth with poor operculization and underdeveloped sylvian fissures. Coronal sections reveal a markedly thickened cerebral cortex with broad gyri and decreased volume of the underlying white matter (37-38). From the outermost to the innermost, these layers are (1) a skinny subpial molecular layer, (2) a skinny outer cortex composed of disorganized large Clinical Issues Epidemiology and Demographics. Patients with band heterotopia sometimes present with developmental delay and a milder seizure dysfunction. The right hemisphere demonstrates milder lissencephaly with band heterotopia ("double cortex" syndrome) and skinny outer cortex. A thick band of relatively well-delineated dense cortex surrounds a thinner, clean band of white matter (37-39A). A deeper, thick layer of arrested migrating neurons is frequent and should mimic band heterotopia (37-39B) (37-39C). The corpus callosum has a thin flat body with a extra vertically oriented splenium. Differential Diagnosis Extremely untimely brain is smooth at 24-26 gestational weeks and normally has a "lissencephalic" appearance (see Chapter 35). In microcephaly with simplified gyral pattern, the head circumference is a minimum of three normal deviations beneath normal. Too few gyri, abnormally shallow sulci, and a standard or skinny (not thick) cortex are current. Cobblestone Lissencephaly Cobblestone lissencephaly is also recognized as type 2 lissencephaly and is genetically, embryologically, pathologically, and radiologically distinct from sort 1 ("traditional") lissencephaly. The cerebellum is usually small, and its folia are regularly fused and disorganized. Etiology Cobblestone cortex results from abnormalities caused by defects within the limiting pial basement membrane. Overmigration of neuroblasts via these breaches results in an extracortical layer of aberrant grey matter nodules-the "cobblestones"-on the mind surfaces. The histopathology of kind 2 lissencephaly shares many options with polymicrogyria. Unlike sort 1 ("classic") lissencephaly, no recognizable laminations are identified. There are numerous areas by which a breach in the pial-glial limitans has occurred, presumably providing a migratory route for aberrant neurons. Most sufferers current through the first 12 months of life, however the relative diploma of weak point varies. The eye findings are often present at birth, and motor retardation usually presents earlier than symptoms brought on by mind involvement. Note enlarged, fused collicular plate, small pons with "kinked" look to the midbrain, and the skinny upwardly arched corpus callosum. The brainstem is normally hypoplastic and appears "kinked", the tectum is enlarged, and the cerebellum appears small and dysmorphic with abnormal foliation. In polymicrogyria, the absence of eye anomalies and muscle weak spot are helpful distinguishing features. Note irregular sulcation and the irregular corticalwhite matter interface within the affected regions. Note several foci of tiny nodules ("gyri piled on prime of gyri"), giving mind floor irregular "pebbly" appearance. The appearance of a number of tiny nodules of grey matter piled on top of gyri is attribute. Commissural and Cortical Maldevelopment Malformations Secondary to Abnormal Postmigrational Development According to Barkovich et al. The look is that of tiny miniature gyri piled on high of other disorganized gyri (37-43). Generalized (13%), frontal (5%), and parasagittal parietooccipital (3%) sites are much less common. Part or all of the brain surface is covered by innumerable heaped up and fused tiny gyri, giving it a "lumpy-bumpy" look that has been likened to the feel and appear of Morocco leather-based (37-44). Bilateral disease-especially in the perisylvian regions-is current within the majority of instances. In the unlayered type, a continuous molecular layer is present without any discernible laminar organization. A laminar structure composed of a molecular layer, outer neuronal layer, nerve fiber layer, and inside neuronal layer is present. Differential Diagnosis the major differential prognosis of polymicrogyria is type 2 lissencephaly (cobblestone malformation).
Fucidin: 10 gm

Purchase 10 gm fucidin with visaDisease onset is usually insidious bacteria zapper for acne buy fucidin 10gm otc, as at least 30% of anterior horn cells are misplaced earlier than weakness turns into clinically apparent antibiotics side effects fucidin 10gm discount. Although median survival from analysis to death is between three and 4 years antimicrobial coating cheap fucidin 10 gm online, 10% of patients survive beyond 10 years infection game fucidin 10 gm low price. Evidence of widespread muscle atrophy affecting limb and intercostal muscle tissue and the diaphragm is typical at autopsy. Macroscopically, the mind is usually unremarkable, but mild focal atrophy of the precentral gyrus may be seen in some cases. Voxel-based morphometry could demonstrate refined gray matter atrophy within the precentral gyri. Changes are usually most outstanding within the posterior limbs of the internal capsules and cerebral peduncles (33-55). Wallerian Degeneration Axonal degeneration can happen through several mechanisms, the commonest being anterograde (or wallerian) and retrograde ("dying back") degeneration. In illnesses such as a quantity of Dementias and Brain Degenerations 1109 (33-59) A affected person with acute WaD was imaged three weeks following left hemisphere tumor resection. Other affected locations embody the corpus callosum, optic radiations, fornices, and cerebellar peduncles. In continual WaD, midbrain and pons volume loss ipsilateral to a harmful lesion. Microscopic findings embrace early adjustments of myelin disintegration and axon breakdown. Terminology WaD is an intrinsic anterograde degeneration of distal axons and their myelin sheaths caused by detachment from-or damage to-their proximal axons or cell bodies. Etiology In the mind, WaD most often occurs after trauma, infarction, demyelinating illness, or surgical resection. The distal part of the axon then undergoes progressive fragmentation that proceeds directionally along the axon stump. After the initial insult, the myelin sheath first retracts from its axon on the nodes of Ranvier, followed by axonal degeneration. The myelin sheath itself then degenerates with breakdown of its protein components and degradation of the lipids. Clinical Issues Imaging abnormalities in WaD (see below) appear to correlate with motor deficits and poor end result. Atrophy of the ipsilateral cerebral peduncle is the commonest finding in continual WaD (33-58). The development of visible WaD following stroke, trauma, or surgical procedure is unpredictable. Chronic adjustments of WaD embrace foci of frank encephalomalacia with volume loss of the ipsilateral peduncle, rostral pons, and medullary pyramid. Dementias and Brain Degenerations improve on T1 C+, however acute degeneration could show transient gentle enhancement (33-61). These embody the corticopontocerebellar tract, dentate-rubro-olivary pathway (Guillain-Mollaret triangle), posterior column of the spinal cord, limbic circuit, and optic pathway. Etiology Unlike other degenerations, in hypertrophic olivary degeneration, the degenerating structure (the olive) turns into hypertrophic somewhat than atrophic. Cerebellar signs and olivary hypertrophy usually develop many months after the inciting occasion. Interruption of the dentato-thalamo-cortical pathway is acknowledged as its anatomic substrate. Differential Diagnosis the most important differential diagnosis of WaD is main neurodegenerative illness. Anatomy of the Medulla and GuillainMollaret Triangle Two outstanding ventral bulges are present on the anterior floor of the medulla: the pyramids and olives. The pyramids are paired buildings, separated within the midline by the ventral median fissure of the medulla. The pyramids contain the ipsilateral corticospinal tracts above their decussation. The olives are a crenulated complex of grey nuclei that are lateral to the pyramids and separated from them by the ventrolateral (preolivary) sulcus (33-62). Three distinct patterns develop, all related to the placement of the inciting lesion. Olivary hypertrophy is seen grossly as uneven enlargement of the anterior medulla. The triangle is composed of the ipsilateral inferior olivary nucleus (green), the dentate nucleus (blue) of the contralateral cerebellum, and the ipsilateral red nucleus (red). Interruption of the Guillain-Mollaret triangle functionally deafferents the olive. Although adjustments can typically be detected within 3 or four weeks after the initial insult, maximum hypertrophy happens between 5 and 15 months. Although the hypertrophy typically resolves and atrophy finally ensues, the hyperintensity could persist indefinitely. Brainstem quantity loss is usually extra outstanding than cerebellar atrophy, which frequently impacts the vermis without involving the hemispheres. Imaging typically shows a traditional cerebellum with spinal cord and/or brainstem volume loss. The affected hemisphere demonstrates diffuse quantity loss with encephalomalacia and gliosis. The superior sagittal sinus and interhemispheric fissure are often displaced throughout the midline (33-70). Atrophy of the contralateral cerebellum is widespread, secondary to crossed cerebellar diaschisis. As the developing brain bends and expands, it forms forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain vesicles. The forebrain cavity divides into two lateral ventricles, which develop as outpouchings from the rostral third ventricle and are related to it by the interventricular foramen (foramen of Monro) (34-1). The fourth ventricle develops from the hindbrain cavity and merges proximally with the aqueduct and caudally with the central canal of the spinal cord. In the coronal plane, the developing lateral and third ventricles kind a central Hshaped monoventricle that continues inferiorly into the aqueduct after which connects to the fourth ventricle. At the eleventh or twelfth gestational week, the inferomedial side of the fourth ventricular roof thins and opens, creating the foramen of Magendie. The foramina of Luschka open shortly thereafter, establishing communication between the developing ventricular system and subarachnoid house. Choroid Plexus the embryonic choroid plexus types the place infolded meningeal mesenchyme-the tela choroidea-contacts the ependymal lining of the ventricles. The invagination occurs along the entire choroidal fissure, a slender cleft that lies in the medial lateral ventricle between the fornix and the thalamus. Initially, the fetal choroid plexus is giant relative to the dimensions of the lateral ventricles, occupying practically threequarters of the ventricular lumen. As the mind and ventricular system develop, the choroid plexus progressively diminishes in relative volume. The third ventricle communicates with the fourth ventricle through the cerebral aqueduct (of Sylvius).
Purchase fucidin 10 gm free shippingA Gram stain of necrotic exudate from the wound web site has the looks shown in the figure virus scan software purchase 10gm fucidin mastercard. Through which of the following mechanisms is that this organism most likely inflicting intensive tissue necrosis Elaboration of lipopolysaccharide Inhibition of phagocytic cell operate Resistance to multiple antibiotics Superinfection with Candida albicans Toxin-mediated lecithin degradation forty two A 25-year-old soldier incurs multiple pores and skin wounds that get contaminated and produce intensive tissue harm within a day virus yardville nj purchase fucidin 10gm amex. Culture of necrotic tissue from deep inside one of the wounds reveals anaerobic spore-forming gram-positive rods virus 43215 buy generic fucidin 10 gm on-line. Which of the following microscopic pathologic reactions are the toxins produced by these organisms most probably to cause Candida albicans Chlamydia trachomatis Herpes simplex virus Mycobacterium tuberculosis Treponema pallidum Infectious Diseases a hundred and one 46 A 50-year-old girl residing in Port-au-Prince has observed a small vesicle on her right labium majus for the past 4 days what causes antibiotic resistance yahoo 10 gm fucidin amex. A biopsy of one of the lymph nodes is carried out and microscopically exhibits a number of abscesses in which central necrosis is surrounded by palisading histiocytes. These scientific and pathologic findings are most probably brought on by which of the next situations Candida albicans vaginitis Chlamydia trachomatis cervicitis Gardnerella vaginalis vaginosis Herpes simplex virus an infection of the perineum Treponema pallidum infection of the external genitalia forty seven A 15-year-old boy has developed a small eschar on his left forearm across the website of a tick chunk he acquired 6 days ago. A hemorrhagic rash involving the trunk, extremities, palms, and soles then develops over the next three days. Borrelia burgdorferi Leishmania braziliensis Mycobacterium leprae Rickettsia rickettsii Yersinia pestis 48 A 10-year-old girl with leukemia undergoes hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. A bronchoalveolar lavage is carried out; the fluid was stained with Gomori methenamine silver stain and analyzed microscopically, as shown within the determine. Babesia microti Borrelia burgdorferi Giardia lamblia Rickettsia rickettsii Wuchereria bancrofti 52 A 45-year-old man experiences malaise and fatigue, which slowly turn out to be extra noticeable over a 2-month period. He has pronounced splenomegaly, an increased liver span, and generalized lymphadenopathy. Borreliosis Echinococcosis Leishmaniasis Lyme illness Schistosomiasis Typhus 50 An 11-year-old boy from Liberia has had episodic fevers for two weeks. He developed a severe headache per week in the past and has turn out to be progressively extra somnolent. Which of the next organs is most likely to serve as the reservoir for proliferation of the infectious agent producing this illness It turns into a 1-cm nodule with a central despair, and then ulcerates over the next month. On bodily examination, the 2-cm ulcerated lesion has an indurated border, and there are three smaller satellite lesions. Microscopic examination of a stool specimen exhibits ova and small rhabditoid larvae. Which of the next infectious ailments is most probably to produce these findings Cysticercosis Onchocerciasis Schistosomiasis Strongyloidiasis Trichinosis fifty seven A 17-year-old boy has had generalized muscle pain with fever for 1 week. All of his muscle tissue are tender to palpation, however he has a standard vary of motion, and no significant decrease in muscle power. Two months later, he exhibits progressive losing with cachexia and decreased mentation. Central America Polynesia Southeast Asia Southern Europe West Africa Hemorrhagic fever Influenza Poliomyelitis Scrub typhus Trichinosis fifty eight A 29-year-old man has had hematuria for the past month. Cystoscopy is performed, and the whole bladder mucosa is erythematous and granular. Which of the next histologic findings is more than likely to be seen in these samples Acid-fast bacilli of Mycobacterium avium advanced Eggs of Schistosoma haematobium Larvae of Trichinella spiralis Migrating Ascaris lumbricoides Taenia solium cysts fifty five A 9-year-old youngster who resides in a mud hut in Paraguay has a sore persisting on her face for four days. Physical examination shows an indurated space of erythema and swelling just lateral to the left eye, accompanied by posterior cervical lymphadenopathy. Two days later, she has malaise, fever, anorexia, and edema of the face and lower extremities. Which of the following pathologic findings is most likely to develop in this affected person These persons are discovered to have a persistent dermatitis that preceded their blindness. Ocular lesions embody punctate keratitis and focal corneal opacities, sclerosing keratitis, iridocyclitis with glaucoma, and retinitis. Investigators decide that the an infection is acquired through cercariae that penetrate the pores and skin. Which of the following pathologic findings is more than likely to be present in these contaminated people as a consequence of the infection Dilated cardiomyopathy Scrotal elephantiasis Hepatic fibrosis Mucocutaneous ulcers Urinary bladder carcinoma 62 Within the identical day, an emergency division is visited by 20 people, all of whom work in the same building. Over the previous day, all of them experienced the sudden onset of high fever, headache, backache, and malaise. Over the subsequent 2 days, they develop a maculopapular rash on the face, forearms, and mucous membranes of the oropharynx. Chlamydia psittaci Francisella tularensis Hantavirus Mycobacterium kansasii Rickettsia typhi Variola major 60 A 40-year-old man has had progressive enlargement of the best leg for the past 6 years, resulting in the appearance shown within the determine. Infection with which of the next organisms is most probably to be current on this man Amebiasis tends to produce dysentery, with a bloody diarrhea, because the organisms can invade the mucosa. Aspergillosis is seen in immunocompromised patients, significantly patients with neutropenia, and is a uncommon reason for a diarrheal illness. Hydatid illness brought on by Echinococcus produces space-occupying cystic lesions in viscera. Typhoid fever produces diarrhea, and the organisms can invade mucosa and disseminate to produce many systemic symptoms. There is typically a mononuclear infiltrate extending to the lamina propria, with a neutrophilic exudate overlying the ulcerated areas. Granulomatous inflammation could additionally be seen with granulomatous colitis (Crohn disease) and intestinal tuberculosis (rare). An increase in mononuclear inflammatory cells could additionally be seen with milder forms of enterocolitis caused by viruses, Giardia, and Salmonella spp. The determine exhibits two single-cell protozoa invading tissue with inflammatory cells. Entamoeba histolytica organisms are proof against gastric acid and may invade the colonic submucosa by way of contact-dependent cytolysis. The amebae not only produce native necrosis with ulceration and hemorrhage, but also acquire access to the venules of the portal system, which drains to the liver. The colonic lesions sometimes have disappeared by the point the liver lesions seem. In some instances, there can be intensive mucosal involvement with attribute flaskshaped (similar to an Erlenmeyer flask) ulcerations just like these seen in different extreme inflammatory bowel diseases. Bacillus cereus is a explanation for meals poisoning (most often as a contaminant in reheated fried rice) and has a brief incubation time. Giardiasis tends to involve the small gut and produces variable irritation, but no ulceration. Salmonellosis more typically involves the small intestine and typically produces self-limited enteritis, although more extreme disease with dissemination to other organs can happen with Salmonella typhi an infection. Cholera is characterized by huge, secretory diarrhea without intestinal mucosal invasion or necrosis. The small intestinal villous destruction with atrophy leads to decreased absorption of sodium and water. The growth of IgA antibodies from secretory immunity in the bowel to rotavirus floor antigens supplies older children and adults a relative resistance to rotavirus an infection. Such antibodies are current in maternal milk and confer some extent of resistance to infants who breast-feed. By the age of 3 years, just about every individual has been infected by rotaviruses no much less than as quickly as. The first an infection is the most probably to be symptomatic; subsequent infections are sometimes mild or asymptomatic.
Filaginella uliginosa (Cudweed). Fucidin. - What is Cudweed?
- Dosing considerations for Cudweed.
- How does Cudweed work?
- A gargle or rinse for diseases of the mouth or throat.
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96626
Buy fucidin 10gm without a prescriptionThrombi might lower or stop the blood supply to part of an organ or tissue and trigger ischaemia which may subsequently end in infarction vyrus 985 c3 generic fucidin 10 gm online. The thrombus or its part may get dislodged and be carried alongside in the bloodstream as embolus to lodge in a distant vessel antimicrobial material generic 10 gm fucidin mastercard. Human beings possess inbuilt system by which the blood remains in fluid state usually and guards towards the hazards of thrombosis and haemorrhage antibiotic resistance powerpoint buy discount fucidin 10gm line. However infection red line cheap fucidin 10gm mastercard, harm to the blood vessel initiates haemostatic restore mechanism or thrombogenesis. To this are added the processes that comply with these primary events: activation of platelets and of clotting system. The integrity of blood vessel wall is necessary for sustaining normal blood circulate. An intact endothelium has the next functions: i) It protects the flowing blood from the thrombogenic affect of subendothelium. B, Endothelial injury exposes subendothelium, initiating adherence of platelets and activation of coagulation system. D, Activated coagulation system forms fibrin strands during which are entangled some leucocytes and purple cells and a tight meshwork is fashioned called thrombus. A, Normal non-activated platelet, having open canalicular system and the cytoplasmic organelles dispersed within the cell. B, Early adhesion phase, exhibiting dilatation of the canalicular system with formation of pseudopods and the organelles present in the centre of the cell. Endothelial damage is of major significance in the formation of arterial thrombi and thrombi of the guts, especially of the left ventricle. A number of components and conditions might trigger vascular harm and predispose to the formation of thrombi. These are as under: i) Endocardial injury in myocardial infarction, myocarditis, cardiac surgery, prosthetic valves. Following endothelial cell injury, platelets come to play a central role in regular haemostasis in addition to in thrombosis. Normal non-activated platelets have open canalicular system with cytoplasmic organelles (granules, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum) dispersed all through the cytoplasm. The activated platelets then endure launch reaction by which the platelet granules are launched to the exterior. Two major forms of platelet granules are released: a) Alpha granules containing fibrinogen, fibronectin, plateletderived growth factor, platelet factor 4 (an antiheparin) and cationic proteins. As a sequel to platelet activation and launch response, the phospholipid complex-platelet issue 3 will get activated which performs essential role in the intrinsic pathway of coagulation. However, stable haemostatic plug is shaped by the motion of fibrin, thrombin and thromboxane A2. Coagulation mechanism is the conversion of the plasma fibrinogen into solid mass of fibrin. The coagulation system is concerned in both haemostatic course of and thrombus formation. The blood is kept in fluid state usually and coagulation system saved in check by controlling mechanisms. Plasmin, a potent fibrinolytic enzyme, is fashioned by the action of plasminogen activator on plasminogen present within the regular plasma. The platelets are current within the slow-moving laminar stream adjoining to the central stream whereas the peripheral stream consists of most slow-moving cell-free plasma near endothelial layer. When blood slows down, the blood cells together with platelets marginate to the periphery and type a kind of pavement near endothelium (margination and pavementing). While stasis allows a higher release of oxygen from the blood, turbulence may very well injure the endothelium leading to deposition of platelets and fibrin. The occurrence of thrombosis in some circumstances similar to in nephrotic syndrome, superior cancers, in depth trauma, burns and through puerperium is defined on the premise of hypercoagulability of blood. The effect of hypercoagulability on thrombosis is favoured by advancing age, smoking, use of oral contraceptives and obesity. Hypercoagulability may happen by the following modifications in the composition of blood: i) Increase in coagulation components. Predisposing Factors A number of primary (genetic) and secondary (acquired) elements favour thrombosis. Primary (Genetic) factors: i) Deficiency of antithrombin ii) Deficiency of protein C or S iii) Defects in fibrinolysis iv) Mutation in issue V Secondary (acquired) elements: a) Risk components: i) Advanced age ii) Prolonged bed-rest iii) Immobilisation iv) Cigarette smoking b) Clinical circumstances predisposing to thrombosis: i) Heart illnesses. Beside the variations in mechanisms of thrombus formation at these websites, the medical effects of those are much more totally different. Arterial thrombi produce ischaemia and infarction, whereas cardiac and venous thrombi trigger embolism. The common morphologic features of thrombi are as under: Grossly, thrombi may be of various shapes, sizes and composition relying upon the site of origin. Microscopically, the composition of thrombus is decided by the rate of circulate of blood i. The lines of Zahn are shaped by alternate layers of light-staining aggregated platelets admixed with fibrin meshwork and dark-staining layer of pink cells. It shows traces of Zahn composed of granular-looking platelets and fibrin meshwork with entangled purple cells and leucocytes. Microscopy Origin of Thrombi Thrombi could come up from the heart, arteries, veins or in microcirculation. They are extra frequent in the atrial appendages, particularly of the right atrium, and on mitral and aortic valves referred to as vegetations which can be seen in infective endocarditis and non-bacterial thrombotic endocarditis (Chapter 16). Cardiac thrombi are mural (non-occlusive) as are the mural thrombi encountered in the aorta in atherosclerosis and in aneurysmal dilatations. Agonal thrombi are formed shortly earlier than death and may happen in either or each the ventricles. The examples of main types of vascular thrombi are as beneath: Arterial thrombi: i) Aorta: aneurysms, arteritis. Distinguishing features between thrombi fashioned in rapidly-flowing arterial circulation and slow-moving venous blood are given in Table 5. Thrombus prompts the fibrinolytic system with consequent launch of plasmin which can dissolve the thrombus utterly leading to decision. Usually, lysis is full in small venous thrombi whereas massive thrombi is in all probability not dissolved. Phagocytic cells (neutrophils and macrophages) appear and begin to phagocytose fibrin and cell particles. Arterial Thrombi Formed in rapidly-flowing blood of arteries and heart Common in aorta, coronary, cerebral, iliac, femoral, renal and mesenteric arteries Formed following endothelial cell harm.
Buy discount fucidin 10gm onlineApoptosis includes individual cells antibiotic resistance vietnam order fucidin 10gm online, without grossly obvious in depth or localized areas of tissue necrosis antibiotic for strep throat cheap fucidin 10 gm without prescription. Glutathione in the cytosol helps to reduce mobile injury from many poisonous metabolites and free radicals antibiotics for uti not sulfa discount 10gm fucidin overnight delivery. Nitric oxide synthase in macrophages produces nitric oxide infection xrepresentx lyrics buy 10gm fucidin otc, which aids in destroying organisms undergoing phagocytosis. Failure of the sodium pump leads to increased cytosolic sodium and cell swelling with injury. Glutathione peroxidase reduces such injury by catalyzing the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide. Lactate dehydrogenase is present in quite so much of cells, and its elevation in the serum is an indicator of cell damage and dying. As hormone levels drop, the endometrium breaks down, sloughs off, after which regenerates. Caseous necrosis is typical of granulomatous inflammation, ensuing mostly from mycobacterial infection. Heterophagocytosis is typified by the clearing of an area of necrosis through macrophage ingestion of the necrotic cells. Liquefactive necrosis can occur in any tissue after acute bacterial an infection or within the brain after ischemia. The free iron contributes to technology of mobile free radicals by way of the Fenton reaction. Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and vitamin E each act as antioxidants to protect in opposition to free radical injury, albeit over a long time body. Superoxide dismutase helps break down superoxide anion to hydrogen peroxide, thus scavenging free radicals. An ischemic damage to most inner organs produces a pattern of cell demise known as coagulative necrosis. Note the faint outlines of renal tubules and glomerulus in the figure, but no cellular nuclei. Caseous necrosis may be seen in numerous types of granulomatous irritation, typified by tuberculosis. Gangrenous necrosis is a type of coagulative necrosis that normally results from ischemia and affects limbs. Liquefactive necrosis occurs after ischemic harm to the brain and is the sample seen with abscess formation. Caspase activation is a universal function of apoptosis, regardless of the initiating cause. Apoptosis induced in recipient cells from donor lymphocytes happens with graft-versus-host illness. However, the reperfusion of broken 26 C this histologic picture is typical of apoptosis produced by chemotherapeutic agents. The launch of cytochrome c from the mitochondria is a key step in lots of forms of apoptosis, and it leads to the activation of caspases. Alcohol is a hepatotoxin appearing through increased acetaldehyde accumulation that promotes hepatic steatosis. Decreased serum albumin ranges and increased prothrombin time recommend alcohol-induced hepatocyte harm. Endonucleases are generated following caspase activation and result in nuclear fragmentation. Mutations in p53 could permit accumulation of genetic injury, a course of that promotes unregulated cell development (neoplasia). Hemosiderin is a storage type of iron that appears in tissues of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Lipofuscin is a golden brown pigment that increases with aging in cell cytoplasm, mainly in cardiac myocytes and in hepatocytes. Cell death may eventually be triggered by autophagy, however by a unique mechanism than apoptosis, a type of single cell necrosis in which cell fragmentation happens. There is slow autophagy with growing older, however autophagy is accelerated with stressors such as malnutrition and continual disease. Hyaline is a generic time period for intracellular or extracellular protein accumulations appearing pink and homogeneous with H&E staining. Weight discount is achieved primarily by way of atrophy of adipocytes, not inhibition of cell proliferation. This granular golden brown pigment seen adjoining to the myocyte nucleus within the determine has minimal impact on cellular operate typically. Bilirubin, another breakdown product of hemoglobin, imparts a yellow appearance (icterus) to tissues. Glycogen is elevated in some inherited enzyme issues, and when the center is involved, heart measurement will increase. Melanin pigment is answerable for pores and skin tone: the more melanin, the darker the pores and skin. Resolution of hemorrhage can produce hemosiderin pigmentation, which imparts a brown color to tissues. Hepatic failure may result in jaundice, characterised by a yellow colour in tissues. About 10 to 20 mg of iron per day is misplaced with normal desquamation of epithelia; menstruating women lose barely more. Over time, hemosiderosis entails increasingly more tissues of the physique, notably the liver, but in addition skin. Initially, hemosiderin deposits are present in Kupffer cells and different mononuclear phagocytes in the bone marrow, spleen, and lymph nodes. Amyloid is an abnormal protein derived from quite lots of precursors, corresponding to immunoglobulin light chains. Chronic renal illness reduces phosphate excretion by the kidney, leading to an increase in serum phosphate. Because the solubility product of calcium and phosphorus should be maintained, the serum calcium is depressed, triggering increased parathyroid hormone output to enhance the calcium degree, which promotes calcium deposition. The granulomas of tuberculosis have caseous necrosis with dystrophic calcification. Another type of dystrophic calcification happens when atherosclerotic lesions calcify. This allows testicular germ cells to retain the flexibility to divide all through life. Amyloid deposition within the coronary heart sometimes happens throughout the myocardium and the vessels.
Buy cheap fucidin 10 gmThere are 2 major anatomical lobes-right and left virus under a microscope discount fucidin 10 gm online, the proper being about six instances the size of the left lobe antimicrobial x ray jackets buy fucidin 10gm online. The liver has a double blood supply-the portal vein brings the venous blood from the intestines and spleen infection limited mobile al purchase 10gm fucidin mastercard, and the hepatic artery coming from the coeliac axis supplies arterial blood to the liver antibiotic ointment for babies generic fucidin 10gm free shipping. The hexagonal or pyramidal construction with central vein and peripheral 4 to 5 portal triads is termed the classical lobule. The venous drainage from the liver is into the right and left hepatic veins which enter the inferior vena cava. Lymphatics and the nerve fibres accompany the hepatic artery into their branchings and terminate around the porta hepatis. The hepatic parenchyma is composed of numerous hexagonal or pyramidal classical lobules, each with a diameter of 0. Each classical lobule has a central tributary from the hepatic vein and on the periphery are 4 to 5 portal tracts or triads containing branches of bile duct, portal vein and hepatic artery. Cords of hepatocytes and blood-containing sinusoids radiate from the central vein to the peripheral portal triads. The functioning lobule or liver acinus as described by Rappaport has a portal triad within the centre and is surrounded at the periphery by portions of several classical lobules. A hepatocyte has three surfaces: one dealing with the sinusoid and the space of Disse, the second dealing with the canaliculus, and the third dealing with neighbouring hepatocytes. These canaliculi be part of at the periphery of the lobule to drain finally into terminal bile ducts or ductules (canal of Hering) which are lined by cuboidal epithelium. Thus a battery of liver perform checks are employed for accurate analysis, to assess the severity of harm, to choose prognosis and to consider remedy. Water-soluble conjugated bilirubin provides direct van den Bergh response with diazo reagent within one minute, whereas alcohol-soluble unconjugated bilirubin is decided by oblique van den Bergh reaction. The serum of regular adults contains less than 1 mg/ dl of whole bilirubin, out of which lower than 0. Bilirubinuria seems in patients of hepatitis before the affected person turns into jaundiced. An improve in urobilinogen within the urine is found in hepatocellular dysfunctions corresponding to in alcoholic liver illness, cirrhosis and malignancy of the liver. The main bile acids (cholic acid and cheno-deoxycholic acid) are fashioned from ldl cholesterol within the hepatocytes. To perceive the mechanisms underlying biliary pathology, it is very important perceive normal bilirubin metabolism (page 596). Amino acid and protein metabolism: i) Serum proteins (total, A/G ratio, protein electrophoresis) ii) Immunoglobulins iii) Clotting factors iv) v) 2. Serum ammonia Aminoaciduria Hypoalbuminaemia in hepatocellular ailments; hyperglobulinaemia in cirrhosis and chronic lively hepatitis Nonspecific alterations in IgA, IgG and IgM Prothrombin time and partial thromboplastin time extended in patients with hepatocellular disease Increased in acute fulminant hepatitis, cirrhosis, hepatic encephalopathy In fulminant hepatitis Increased in cholestasis, decreased in acute and persistent diffuse liver illness and in malnutrition Decreased in hepatic necrosis Lipid and lipoprotein metabolism: Blood lipids (total serum cholesterol, triglycerides and lipoprotein fractions) 3. Most of these bile acids are reabsorbed through enterohepatic circulation and attain the liver. A mixture of serum transaminases and alkaline phosphatase estimation is sufficient to diagnose liver harm. Serum alkaline phosphatase is produced by many tissues, particularly bone, liver, intestine and placenta and is excreted in the bile. Elevation in activity of the enzyme can thus be found in illnesses of bone, liver and in being pregnant. The best elevation (3 to 10 instances normal) occurs in biliary tract obstruction. The dedication of some other serum enzymes is done generally but without any further diagnostic advantage over the above mentioned enzyme assays. Amino acids derived from the diet and from tissue breakdown are metabolised within the liver to ammonia and urea. Based on these metabolic features of the liver, serum estimation of proteins, immunoglobulins and ammonia and aminoaciduria are employed to assess the liver cell harm. Liver cells synthesise albumin, fibrinogen, prothrombin, alpha-1-antitrypsin, haptoglobin, ceruloplasmin, transferrin, alpha fetoproteins and acute part reactant proteins. The blood ranges of these plasma proteins are decreased in extensive liver damage. Hypoalbuminaemia may happen in liver illnesses having significant destruction of hepatocytes. The ranges of serum immunoglobulins produced by lymphocytes and plasma cells (IgG, IgM and IgA) present nonspecific abnormalities in liver ailments and symbolize inflammatory or immune response somewhat than liver cell dysfunction. IgA is the predominant immunoglobulin in bile and its level is raised in cirrhosis, IgG is markedly raised in chronic active hepatitis and IgM is markedly elevated in main biliary cirrhosis. Hepatic artificial perform of several clotting elements can be assessed by a couple of simple coagulation exams. Prothrombin time and partial thromboplastin time, both of which replicate the activities of assorted clotting factors, are extended in sufferers with hepatocellular disease. High blood levels of ammonia are present in acute fulminant hepatitis, cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy. Lipids synthesised within the liver embrace cholesterol and ldl cholesterol esters, phospholipids and triglycerides. These lipids are insoluble in water and are carried in circulation with three major types of lipoproteins which contain apoproteins. Estimations of total serum ldl cholesterol, triglycerides and lipoprotein fractions are frequently carried out in patients with liver illness. These include the next: i) Smooth muscle antibody to actin component of muscle is fashioned in certain hepatic disorders with hepatic necrosis. It appears that hepatocytes have a protein which is immunologically much like actin. About 80-85% of the bilirubin is derived from the catabolism of haemoglobin current in senescent pink blood cells. The remaining 15-20% of the bilirubin comes partly from non-haemoglobin haemcontaining pigments corresponding to myoglobin, catalase and cytochromes, and partly from ineffective erythropoiesis. Bilirubin on release from macrophages circulates as unconjugated bilirubin in plasma tightly sure to albumin. On coming in touch with the hepatocyte surface, unconjugated bilirubin is preferentially metabolised which includes three steps: hepatic uptake, conjugation and secretion in bile. Appearance of conjugated bilirubin within the intestinal lumen is adopted by both direct excretion in the stool as stercobilinogen which imparts the normal yellow color to stool, or could also be metabolised to urobilinogen by the action of intestinal bacteria. Conjugated bilirubin is generally not reabsorbable whereas its metabolic product, urobilinogen, is reabsorbed from the small gut and reaches enterohepatic circulation. Schematic representation of hepatic phase of bilirubin the major variations between unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin are summarised in Table 21.
Discount 10gm fucidin amexPeripheral pulmonary thromboemboli are most probably to produce persistent pulmonary hypertension and develop over weeks to months infection 2 game cheats discount fucidin 10gm on-line. Infarcts of most solid parenchymal organs such because the kidney antibiotics newborns best 10 gm fucidin, coronary heart antibiotics lyme disease order fucidin 10 gm online, and spleen exhibit coagulative necrosis antibiotic resistance cases discount 10gm fucidin with visa, and emboli from the left heart usually go to these organs. At high pressures, corresponding to happen throughout a deep scuba dive, nitrogen is dissolved in blood and tissues in large quantities. Fat globules in pulmonary arteries are a feature of fats embolism, which normally follows trauma. Platelet thrombi could kind with microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, such as thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Complement C3b generated by micro organism by way of the choice pathway acts as an opsonin. Plateletactivating issue mediates many options of acute inflammation and in massive portions can cause vasoconstriction and bronchoconstriction. Toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 is a superantigen released by staphylococcal organisms that is a potent activator of T lymphocytes, inducing cytokine launch with septic shock. Vasodilation is a characteristic of septic shock, typically as a end result of gram-negative endotoxemia. Elevated creatine kinase suggests an acute myocardial infarction, which produces cardiogenic shock. Increased blood urea nitrogen focus is a characteristic of renal failure, not the purpose for renal failure. Basal ganglia hemorrhages are more typical of hypertension, not hypotension with shock. There are 12 gentle brown macules averaging 2 to 5 cm in diameter on the pores and skin of the trunk. Which of the next inheritance patterns is most probably to be current on this household Autosomal dominant Autosomal recessive Mitochondrial Multifactorial X-linked recessive four An 8-year-old girl experiences sudden extreme dyspnea. On examination, she has upper airway obstruction from delicate tissue swelling in her neck. Both dad and mom and two female siblings are unaffected by this downside, but a male sibling has skilled an identical episode. Which of the following genetic abnormalities is more than likely to account for the findings on this girl Autosomal dominant mutation Genomic imprinting Germline mosaicism Random X inactivation Spontaneous new mutation 3 A feminine toddler born at term shows failure to thrive and failure to obtain developmental milestones. A pedigree reveals only this baby is affected out of 4 generations on both sides of the family. Cultured fibroblasts show accumulation of an intermediate product in a metabolic pathway in which multiple enzymes are involved. What is the more than likely recurrence danger for this condition in siblings of this toddler He states that his father, aunt, and brother took this drug and had antagonistic unwanted effects, together with excessive bleeding, when prescribed the recommended dose. Which of the next genetic tests will help determine probably the most acceptable dose of clopidogrel for this man A genetic defect involving which of the next substances is most likely to be present in this patient This genetic disorder most likely resulted from a mutation involving a gene encoding for which of the following Mitochondrial enzyme Lysosomal enzyme Cell floor receptor protein Structural protein. On examination she has hyperextensible joints and fragile, extremely stretchable pores and skin. Frameshift Nonsense Point Three�base pair deletion Trinucleotide repeat eight A 4-year-old girl has sudden onset of proper hip ache. Congenital syphilis Deficient collagen synthesis Diet missing in vitamin D Multiple congenital anomalies Trauma from battering 12 A 22-year-old woman delivers an apparently healthy feminine toddler after an uncomplicated being pregnant. Analysis of which of the following factors is most probably to help in the diagnosis of this condition Some of the children in these families are noticed to have early atheroma formation. Affected individuals in these families are more than likely to have a mutation in a gene encoding a cell surface receptor for which of the next A bone marrow biopsy is obtained and microscopically exhibits numerous pale phagocytic cells crammed with nice vacuoles (secondary lysosomes). A liver biopsy specimen exhibits cells crammed with clear vacuoles that stain positive for glycogen. Hurler syndrome McArdle illness Pompe disease Tay-Sachs disease Von Gierke illness 17 A 25-year-old woman stops going to her aerobic exercise class due to extreme muscle cramps that have occurred throughout every session for the previous 2 months. An inherited defect by which of the next substances is most likely to explain her findings Dystrophin Fibrillin Glucose-6-phosphatase Lysosomal glucosidase Muscle phosphorylase Spectrin 14 A 10-year-old baby has had recurrent otitis media for the past 8 years. A bone marrow biopsy is carried out, and excessive magnification of the pattern reveals the findings depicted within the figure. These children have had coarse facial options, corneal clouding, joint stiffness, hepatosplenomegaly, and psychological retardation, and a lot of died in childhood. At autopsy, a variety of the children had subendothelial coronary arterial deposits that brought on myocardial infarction. Laboratory testing of the toddler now reveals increased urinary excretion of mucopolysaccharides. Bone marrow biopsy is carried out, and the accumulated mucopolysaccharides are found in macrophages ("balloon cells" full of minute vacuoles). Which of the next enzyme deficiencies is most likely to be seen on this infant Adenosine deaminase -l-Iduronidase Glucocerebrosidase Glucose-6-phosphatase Hexosaminidase A Lysosomal glucosidase Sphingomyelinase 18 A 6-month-old male infant has failure to thrive and stomach enlargement. On bodily examination, the infant has marked muscle weakness and hepatosplenomegaly. The microscopic appearance of myocardial fibers at autopsy is shown in the determine. A deficiency of which of the following enzymes is most probably to be present in this toddler Which of the following karyotypic abnormalities is most probably to be present on this girl Deletion of q arm - del(22q) Isochromosome - 46,X,i Paracentric inversion - inv(18) Ring chromosome - r(13) Robertsonian translocation - t(14;21) 23 A 39-year-old woman offers start to a time period toddler with an umbilical hernia, Brushfield spots on the iris, macroglossia, low-set ears, oblique palpebral fissures, and a coronary heart murmur. Which of the next chromosomal abnormalities, affecting autosomes, is most probably to be present in the somatic cells of this youngster Haploidy Monosomy Mosaicism Tetraploidy Triploidy 21 An 11-year-old mentally retarded boy is prepared to perform activities of day by day residing, together with feeding and dressing himself. On bodily examination, he has brachycephaly and indirect palpebral fissures with prominent epicanthal folds. Physical examination of the infant soon after supply shows rocker-bottom toes, a small face and mouth, and low-set ears. He has a historical past of recurrent infections, including otitis media, diarrhea, and pneumonia. Physical examination exhibits an erythematous right tympanic membrane, a cleft palate, and murmur suggestive of congenital coronary heart illness. Anomalies include microcephaly, a cleft lip and palate, scalp defects, and the discovering proven in the figure. A metaphase unfold is proven within the figure, with probes to two totally different areas on chromosome 22. Multiple congenital anomalies are current, including ventricular and atrial septal defects, horseshoe kidney, and omphalocele. Based on the findings shown in the determine, which of the next karyotypic abnormalities is more than likely to be present on this fetus Physical examination shows he has bilateral gynecomastia, decreased testicular size, lowered body hair, and increased length between the soles of his toes and the pubic bone. Laboratory studies show elevated follicle-stimulating hormone degree and barely decreased testosterone stage. Strong pulses are palpable in the higher extremities, but there are solely weak pulses in the decrease extremities. Which of the next forms of genetic issues is more than likely to be current in this affected person Trinucleotide repeat expansion Genetic imprinting X-linked inheritance sample Mitochondrial mutation Uniparental disomy 31 A 22-year-old primigravida notes absent fetal movement for two days.
References - Stenzl A, Colleselli K, Poisel S, et al: Rationale and technique of nerve sparing radical cystectomy before an orthotopic neobladder procedure in women, J Urol 154(6):2044n2049, 1995. Stenzl A, Draxl H, Posch B, et al: The risk of urethral tumors in female bladder cancer: can the urethra be used for orthotopic reconstruction of the lower urinary tract?, J Urol 153(3 Pt 2):950n955, 1995. Stenzl A, Colleselli K, Bartsch G: Update of urethra-sparing approaches in cystectomy in women, World J Urol 15(2):134n138, 1997.
- Katz J, Tielsch JM. Lifetime prevalence of ocular injuries from the Baltimore Eye Survey. Arch Ophthalmol. 1993;111:1564-1568.
- Peattie AB, Plevnik S, Stanton SL: Vaginal cones: a conservative method of treating genuine stress incontinence, Br J Obstet Gynaecol 95(10):1049n1053, 1988.
- Quaynor, H., Raeder, J.C. Incidence and severity of postoperative nausea and vomiting are similar after metoclopramide 20 mg and ondansetron 8 mg given by the end of laparoscopic cholecystectomies. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2002;46:109-113.
|