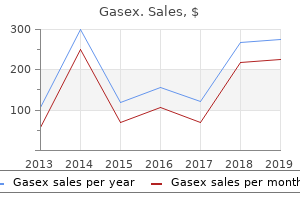
Gasex
Seemant Chatruvedi, M.D. - Assistant Professor of Neurology
- Wayne State University School of medicine
- Detroit, MI
Order 100 caps gasex with amexArthrodesis of the occiput to the atlas for all patients with non-traumatic occipitoatlantal instability is recommended gastritis meals discount gasex 100caps amex. Congenital fusion can occur at any level within the cervical backbone gastritis high fat diet discount 100 caps gasex with amex, but roughly 75% happen in the upper cervical backbone gastritis symptoms baby order gasex 100caps online. Klippel-Feil is usually associated with different skeletal and extraskeletal abnormalities similar to scoliosis (60%) gastritis from alcohol order 100caps gasex free shipping, renal abnormalities (35%, mostly unilateral renal agenesis), Sprengel deformity (30%), deafness (30%) and congenital heart disease (14%, mostly ventricular septal defect). Other associated deformities include hand anomalies such as syndactyly, thumb hypoplasia and further digits. The most constant medical finding is a limited range of movement of the neck, particularly lateral bending. There could also be ache as a result of joint hypermobility or neurological symptoms from instability. Note the presence of the everyday features: brief neck, low posterior hairline and a wry neck. All patients with Klippel�Feil syndrome ought to have an ultrasound analysis of the renal system. Treatment For asymptomatic patients, therapy is unnecessary however dad and mom must be warned of the risks of contact sports activities. Note the presence of several cervical fused vertebral our bodies and also the degenerative changes at adjacent levels. Note the shut relation between the tip of the odontoid and the medulla oblongata. More generally, primary invagination happens in affiliation with occipitoatlantal fusion, hypoplasia of the atlas, a bifid posterior arch of the atlas, odontoid anomalies, Morquio syndrome, Klippel�Feil syndrome and achondroplasia. Basilar impression is frequently related to different congenital neurological anomalies, corresponding to ArnoldChiari malformation and syringomyelia. Neurological signs and signs might not present till the second or third decade of life and may be precipitated by minor trauma. They are usually related to compression of the neural elements and the medulla oblongata on the stage of the foramen magnum or may end up from raised intracranial strain (because the aqueduct of Sylvius turns into blocked). Patients may current with neck ache, headaches in the distribution of the greater occipital nerve, cranial-nerve involvement, ataxia, vertigo, nystagmus, weak point and paraesthesia of the limbs and even sexual dysfunction. Os avis is the term for a rare resegmentation error in which the apical dental phase is attached to the basion on the occiput and to not the dens. The C1�C2 joint has flat lateral articulations, weak posterior ligaments and the ligamentum flavum is replaced with a thin atlantoaxial membrane. This is especially important in patients undergoing operation, as the atlantoaxial joint could subluxate throughout common anaesthetic procedures. Treatment Treatment is dependent upon the diploma of neural compression and reducibility of the deformity and involves surgical decompression and stabilization with a posterior occipitocervical arthrodesis. Its position could be in the regular location of the odontoid course of (orthotopic) or rostrally displaced (dystopic). The os odontoideum accompanies the atlas during the normal flexion-extension motion and leads to biomechanical insufficiency of the apical odontoid and alar ligaments, which in flip can lead to instability beneath physiological loads. Translational instability and dislocation result in posterior spinal twine compression. Vertical instability can be possible with invagination of the dens in the direction of the cranium with brainstem compression and subsequent neurological damage, including respiratory paralysis. Long-standing instability might turn into multidirectional, allowing the C1�C2 unit to become very unstable. Signs and symptoms are the same as these described for different anomalies of the odontoid. Note that the normal vestigial disc house between the dens and the body of the axis could additionally be visible as a radiolucent line until 5 years of age. Open-mouth radiographs show the abnormality and lateral flexion-extension views could show C1� C2 instability with motion between the odontoid and the physique of the axis. The articulation between the atlas and axis comprises one midline atlanto-odontoid joint and two lateral atlantoaxial side joints. The articular capsules of the lateral facets provide stability and are bolstered by necessary ligaments, such as the alar ligaments and the transverse atlantal ligament, which is the thickest and the primary stabilizer of the atlas towards anterior subluxation. The transverse ligament allows rotation, whereas the alar ligaments forestall extreme rotation. Congenital osseous anomalies on this region, such as occipitalization of the atlas, os odontoideum and basilar invagination, can result in an increased danger of segmental instability and neurological compromise. Isolated laxity of the transverse atlantal ligament is a prognosis of exclusion within the setting of persistent atlantoaxial dislocation and not utilizing a predisposing trigger. This abnormality is believed to be secondary to the laxity of the transverse ligament and to the bony anomalies encountered in these sufferers. With age, atlantoaxial articulation becomes more vulnerable and the central nervous system becomes less tolerant of intermittent compression. Some patients could also be misdiagnosed with different conditions that mimic the puzzling scientific image, including multiple sclerosis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Symptomatic sufferers should have surgical stabilization, which consists of C1�C2 posterior fusion with or without decompression. C1�C2 fusions are indicated for patients showing >5 mm of instability on flexion-extension views and people with severe cervical wire compression. Motion preservation will theoretically reduce the incidence of adjoining phase degeneration. The primary symptom related to cervical backbone degenerative disease is neck ache, which has a reported incidence of 30% within the common population. Cervical degenerative disc disease also can current as radiculopathy or myelopathy, because of compression of nerve roots or the spinal twine. The mechanical surroundings within the cervical area is more favourable than within the lumbar region although the pathological features are related. The acute prolapse of the cervical intervertebral disc could also be precipitated by local strain or damage, especially sudden unguarded flexion and rotation, and it normally occurs immediately above or under the sixth cervical vertebra. The extruded disc material migrates posteriorly into the spinal canal and may press on the posterior longitudinal ligament or compress the dura or the nerve roots. Clinical features Unilateral or rarely bilateral arm pain is the primary presentation symptom of cervical disc herniation, and it can be associated with variable levels of neck ache and stiffness. The herniated nucleus pulposus within the spinal canal causes nerve irritation and stress on the nerve roots. Patients may typically complain of ache radiating to the scapular region or to the occiput, normally by compromise of the upper cervical nerve roots. On scientific examination there could additionally be a painful wry neck (torticollis), muscle spasm and tenderness with restricted vary of motion. T2-weighted photographs are extra delicate than T1-weighted pictures for detecting disc degeneration. Miyazaki and colleagues proposed a grading system for the severity of intervertebral disc degeneration consisting of five grades (Table 17. Surgical treatment is reserved for sufferers with persistent or worsening of signs and often includes partial removing of the extruded disc or fusion. Reliability of a magnetic resonance imaging-based grading system for cervical intervertebral disc degeneration.
Buy 100caps gasex free shippingTreatment the pure history for tennis elbow is for spontaneous resolution inside 12 months in 90% of circumstances gastritis milk discount gasex 100 caps mastercard. This means identification and avoidance of precipitating elements gastritis diet ������� generic 100caps gasex amex, and an eccentric loading regime for the widespread wrist extensors chronic gastritis gastric cancer order 100 caps gasex mastercard. Steroid injection will provide short-term pain relief but recurrence charges are excessive and the elbow is extra prone to gastritis diet 90x cheap gasex 100 caps free shipping be painful in the lengthy run. It is among the few causes of anterior elbow ache, with pain reproduced on resisted forearm supination. Treatment is as for tennis elbow, besides that, if surgery is required, the tendon is reattached after debridement (a substantial undertaking). In adults, persistent valgus strain causes attenuation of the medial collateral ligament and posteromedial impingement � valgus extension overload. Recurrent olecranon bursitis could be handled by surgical excision however wound therapeutic can be a drawback. Current use is for joint washout for infection, elimination of free bodies, capsular release, elimination of osteophytes, excision of plica, synovectomy, radial head excision, tennis elbow launch and fracture fixation. Technique the chance of this operation is devastating damage to the ulnar nerve, median nerve and posterior interosseous nerve, every of which lies lower than a centimetre from the joint and very near the portals used for entry. Special training, a radical data of the anatomy and specialist strategies are required. Operative repair is best carried out early (within 2 weeks of injury) and quite a few techniques have been reported, however button fixation is the strongest restore method, permitting early rehabilitation. The bursitis could additionally be a results of an infection in one-fifth of cases and differentiation can be difficult. Indications the primary indication is rheumatoid arthritis but enhancements in medical management have resulted in an overall decline within the number of elbow replacements being performed. In trauma, total joint arthroplasty is being outdated by hemiarthroplasty for unreconstructable distal humerus fractures. One ought to think carefully earlier than advocating this operation to sufferers who intend to return to heavy work or leisure activity or to those with single joint involvement. A diversified combination of flexion and extension with pronation and supination is clearly needed. Although the normal elbow is capable of full extension, flexion to about one hundred thirty levels and 90 degrees of each pronation and supination, the functional range of movement is 30�130 degrees of flexion and 50 degrees of both pronation and supination. The forearm is generally in slight valgus relative to the upper arm, the typical carrying angle being about 11 levels. The complex geometry of the joint allows for the truth that, when the elbow is flexed, the forearm comes to lie directly upon the upper arm. The carrying angle may be altered by malunion of a fracture or injury to a physis, leading to cubitus valgus or cubitus varus. Stability is provided by: (1) the relative conformity of the humeral trochlea with the olecranon; (2) the lateral collateral ligament advanced; and (3) the medial collateral ligament (particularly the anterior part). The radial head is a secondary constraint to valgus instability; it can be excised when necessary so lengthy as the medial collateral ligament, humeroulnar articulation and interosseous membrane are intact. Pronation and supination take place on the proximal and distal radioulnar joints, with a small amount of motion within the wrist too. The circular and barely concave upper surface of the radius ensures that in all positions of rotation it retains adequate contact with the capitellum. Unlinked designs are more technically difficult and demand careful attention to soft-tissue stability due to dangers of instability, however 90% good results can be achieved in fastidiously selected sufferers (those with good bone stock and competent ligaments). Semi-constrained implants are the most broadly used and may enable a few of the forces to be absorbed by the gentle tissues whereas sustaining some intrinsic stability. Outcome nearly all of patients with an elbow substitute can expect reduction of ache and a useful range of movement. A good consequence can be achieved in chosen trauma patients (older people with low demand) with hemiarthroplasty or whole elbow substitute. Complications the operation has a comparatively high complication fee, significantly ulnar nerve palsy, aseptic loosening and infection. Distal to the condyle the nerve is closely utilized to the elbow capsule, and there also it might be compromised if the joint is osteoarthitic. It then splits to turn out to be the sensory superficial radial nerve and motor posterior interosseous nerve. In entrance of the elbow lie the brachialis muscle and likewise the median nerve in firm with the great vessels; these relationships make an anterior approach to the elbow difficult. David Warwick & Roderick Dunn the wrist and hand function together, for all sensible purposes, as a single articulated unit. The hand can be unable to perform its vary of complicated movements without the reciprocal motion, positioning and stabilizing motion of the wrist. Loss of motion at the wrist limits the manipulative talent of the fingers and thumb; and ache in the wrist makes it impossible to grip or pinch with full strength. Disorders of the wrist and hand are often interrelated and due to this fact, within the clinical setting, these two items should be examined and analysed together. Swelling, sweating, colour modifications and waxiness recommend complex regional pain syndrome. The posture of the wrist at rest and during movement varies with completely different positions of the hand and fingers. Swelling could signify involvement of either the joint or the tendon sheaths or a ganglion. Loss of function refers primarily to the hand, although the patient may be aware that the issue lies in the wrist. Clicks are widespread and often of no relevance; clunks with ache or weakness could signify instability. The lunotriquetral joint is examined by pinching the lunate with one hand, the triquetral�pisiform with the opposite, after which applying a sheer stress: pain or clicking suggests an incompetent lunotriquetral ligament. The pisotriquetral joint is tested by pushing the pisiform radialwards towards the triquetrum. The central portion of the triangular fibrocartilage is tested by pushing the wrist medially then flexing and increasing it underneath load to elicit ache (the grind test). The distal radioulnar joint is tested for stability by holding the radius and then balloting the ulnar head up and down. Passive movements To compare passive dorsiflexion of the wrists the affected person places his palms together within the position of prayer, then elevates his elbows. Radial and ulnar deviation are measured in either the palms-up or the palms-down position. With the elbows at proper angles and tucked in to the perimeters, pronation and supination are assessed. Active actions Ask the affected person to pull the hand backwards to its limit (extension), then forwards as far as possible (flexion), after which sideways to proper and left (radial and ulnar deviation). These actions are then repeated but carried out in opposition to resistance, to test for muscle energy.
Syndromes - The surgeon uses a bone saw or chisel to make a second cut through the jaw bone. The jaw bone is moved and wired or screwed in place.
- Numbness in part of the body
- Do they bleed easily and without reason?
- Do NOT move the person unless absolutely necessary.
- Diarrhea is severe, or lasts longer than 2 - 3 days
- Tonsillitis
- What other symptoms do you have?
- A-200
Buy gasex 100 caps visaSensibility Sensibility to touch and to pinprick could also be elevated (hyperaesthesia) or unpleasant (dysaesthesia) in certain irritative nerve lesions gastritis diet ������ order 100caps gasex. The area of sensory change may be mapped out on the pores and skin and in contrast with the identified segmental or dermatomal sample of innervation gastritis diet �������� generic 100 caps gasex mastercard. The point of hypersensitivity marks the site of abnormal nerve sprouting: if it progresses distally at successive visits gastritis diet treatment inflammation order gasex 100caps with mastercard, this signifies regeneration; if it stays unchanged gastritis diet ������ cheap gasex 100 caps on line, this suggests an area neuroma. Tests for temperature recognition and two-point discrimination (the capability to acknowledge two touchpoints a few millimetres apart) are additionally used in the evaluation of peripheral nerve accidents. In the vibration take a look at a sounded tuning fork is positioned over a peripheral bony level. Position sense is examined by asking the affected person to discover certain points on the physique with the eyes closed � for example, touching the tip of the nose with the forefinger. The sense of joint posture is tested by grasping the large toe and placing it in numerous positions of flexion and extension. If he or she is transferring a specific joint, take your alternative to examine motion then and there. You will learn rather more by adopting methods of play than by making use of a inflexible system of examination. Infants and young children the infant must be undressed, in a heat room, and positioned on the analyzing couch. Look fastidiously for birthmarks, deformities and irregular actions � or absence of motion. When testing for passive mobility, watch out to avoid horrifying or hurting the child. In the neonate, and all through the primary two years of life, examination of the hips is obligatory, even if the kid appears to be regular. Older children Most youngsters may be examined in the same way as adults, although with completely different emphasis on specific physical options. Seldom need something be accomplished about this; the condition usually improves because the child approaches puberty and only if the gait could be very awkward would one consider performing corrective osteotomies of the femora. However, epidemiological research have proven that they do have a larger than usual tendency to recurrent dislocation. Deformity the boundary between variations of the normal and physical deformity is blurred. Indeed, in the improvement of species, what at one point of time might need been seen as a deformity could over the ages have turned out to be so advantageous as to turn out to be important for survival. An unusual degree of joint mobility can additionally be attained by adults keen to undergo rigorous train and practice, as witness the performances of skilled dancers and athletes, but in most cases, when the workout routines cease, mobility gradually reverts to the normal vary. Kyphosis and lordosis Seen from the facet, the traditional backbone has a series of curves: convex posteriorly within the thoracic region (kyphosis), and convex anteriorly within the cervical and lumbar regions (lordosis). Excessive curvature constitutes kyphotic or lordotic deformity (also typically referred to as hyperkyphosis and hyperlordosis). The place and course of the curve are specified by phrases similar to thoracic scoliosis, lumbar scoliosis, convex to the right, concave to the left, etc. Postural deformity A postural deformity is one which the patient can, if properly instructed, correct voluntarily. It is necessary to distinguish postural scoliosis from structural (fixed) scoliosis. The former is non-progressive and benign; the latter is normally progressive and may require remedy. Muscle contracture Fibrosis and contracture of muscles that cross a joint will trigger a hard and fast deformity of the joint. Muscle imbalance Unbalanced muscle weak spot or spasticity will lead to joint deformity which, if not corrected, will ultimately become mounted. Joint destruction Trauma, infection or arthritis could destroy the joint and lead to extreme deformity. Site A lump close to a joint is more than likely to be a tumour (benign or malignant); a lump within the shaft could also be fracture callus, inflammatory new bone or a tumour. A benign tumour has a well-defined margin; malignant tumours, inflammatory lumps and callus have a vague edge. Consistency A benign tumour feels bony and hard; malignant tumours typically give the impression that they are often indented. Tenderness Lumps as a result of active inflammation, recent callus or a rapidly rising sarcoma are tender. There are a myriad genetic problems affecting the skeleton, but any considered one of these circumstances is uncommon. Acquired deformities in children may be as a outcome of fractures involving the physis (growth plate); ask about earlier injuries. Other causes embrace rickets, endocrine issues, malunited diaphyseal fractures and tumours. Acquired deformities of bone in adults are often the result of earlier malunited fractures. We contemplate three forms of stiffness specifically: (1) all movements absent; (2) all movements limited; (3) one or two movements restricted. All actions absent Surprisingly, although movement is totally blocked, the patient might retain such good perform that the restriction goes unnoticed till the joint is examined. All actions restricted After extreme damage, motion may be restricted as a result of oedema and bruising. In osteoarthritis the capsule fibroses and actions turn into more and more restricted, but ache happens only on the extremes of motion. Some movements limited When one specific movement suddenly becomes blocked, the cause is normally mechanical. Thus a torn and displaced meniscus could stop extension of the knee but not flexion. The clinical prognosis of cartilage-capped exostosis (osteochondroma) is confirmed by the X-rays. Notwithstanding the extraordinary technical advances of the final few a long time, it remains the most useful methodology of diagnostic imaging. The radiographic image X-rays are produced by firing electrons at excessive pace onto a rotating anode. Similarly, the brilliant picture of a metallic international body superimposed upon that of, say, the femoral condyles may mean that the international physique is in entrance of, inside or behind the bone. The strategy of decoding this image ought to be as methodical as medical examination. It is seductively simple to be led astray by some flagrant anomaly; systematic research is the only safeguard. A handy sequence for examination is: the affected person � the delicate tissues � the bones � the joints. Make certain that the name on the movie is that of your patient; mistaken id is a potent source of error. Localized change Focal abnormalities should be approached in the same method as one would conduct a medical analysis of a delicate tissue abnormality. Bulging outlines around a hip, for instance, might suggest a joint effusion; and soft-tissue swelling around interphalangeal joints could be the first radiographic signal of rheumatoid arthritis.
Buy 100caps gasex fast deliveryBilaterally affected hips are seen in roughly 10% of circumstances and this is extra widespread in women gastritis caused by stress purchase gasex 100caps fast delivery. Initial bony destruction is exacerbated by prolonged gastritis antrum diet gasex 100caps otc, repetitive loading of the hip joint gastritis symptoms livestrong discount gasex 100 caps with visa. Vessels that traverse the cartilage cap are more prone to mechanical compression and are therefore weak over a higher length in these youngsters gastritis bile reflux diet buy 100caps gasex overnight delivery. Abduction and inner rotation stretch the posterior circumflex artery and may completely interrupt flow to the lateral epiphyseal artery because it traverses the capsule. Rather, elevated osteoclast exercise driving bony resorption is followed by persistent fibroblastic proliferation and fibrovascular substitute of trabeculae as an alternative of latest bone formation. Prolonged repetitive loading of the hip joint leads to compression of this weak epiphyseal bone. Range of movement could additionally be lowered, especially in abduction and internal rotation, and hip flexion contracture could additionally be seen in cases of long-standing illness. Prolonged disease results in loss of epiphyseal top and proximal femoral deformity resulting in weakening of musculature around the hip. Imaging Radiographic adjustments could be seen after 3�6 months of illness process, starting with medial joint house widening, cartilage thickening and joint effusion. Lateral subluxation of the femoral head results in additional increases in inferomedial joint area. A fracture line is commonly present within the femoral head, identifying the zone of resorption with an osteoporotic section of the lateral epiphysis. With continued collapse and near-total head involvement the physis becomes increasingly horizontal. Severe disease could progress to adjustments in the acetabulum, early closure of the triradiate cartilage, and bi-compartmentalization of the acetabulum and ischium varum. Necrotic bone is irregularly resorbed and replaced with vascular fibrous tissue as revascularization begins. During this time reossification of the nucleus begins peripherally and progresses centrally as necrotic bone is fully removed. A sequestrum is commonly present along with anterior and lateral metaphyseal reaction and a subchondral fracture line in the anterior half of the epiphysis � Grade three � includes 50�75% with sequestrum and posterior subchondral fracture line. This grading system has demonstrated poor inter-observer reliability; nevertheless, a grade of 3 or four has been proven extremely predictive of poor outcomes. This system may be applied as soon as a fracture line is present, often as much as 8 months before full fragmentation when the Caterall classification can be applied. This classification has demonstrated sturdy prognostic worth and inter-observer reliability. Group A is associated with universally good outcomes; Group B hips generally have poor outcomes in kids older than 6 years and Group C hips have universally poor outcomes. Reduction in weight-bearing has confirmed significantly helpful, however extra human studies are required. Physiotherapy is also beneficial to restore and maintain range of motion in the hip joint. Abduction bracing, using the Newington brace or Petri casting, was used historically to stretch adductors and improve hip vary of movement to a place of higher containment. Patients should be monitored regularly with radiographs over the 24�36-month pure historical past course of the illness. Ultimate shape of the femoral head after reossification will dictate long-term outcomes. Bisphosphonates have increasingly been studied as a approach to cease destruction by delaying resorption of necrotic bone and stopping collapse of the femoral head. Containment alters joint mechanics to distribute forces extra evenly throughout the epiphysis thereby protecting the weak and fragmented femoral head till reossification can occur. Therapies embrace protected weightbearing and activity restriction to cut back mechanical Operative intervention may be indicated in kids with persistent losses in vary of motion or unresolving clinical signs. This normally consists of youngsters over the age of 6 years with Herring B hips and all children with Herring B/C or C hips. Prerequisites for surgical containment include near-normal abduction beneath general anaesthetic and arthrogram demonstrating a containable congruent hip joint. Under the age of 8 years the most typical process is proximal femoral varus osteotomy. This corrects lateral subluxation of the femoral head and reduces level strain of the articular surface by growing head coverage and correcting extreme anteversion brought on by metaphyseal involvement. Correction is performed by way of a medial wedge closing osteotomy and held with a set angle device. Over the age of eight years, or in kids with extra superior illness, pelvic osteotomy is commonly required for sufficient containment. Techniques embrace acetabular shelf osteotomy, Dega- and Salter-innominate osteotomies. Hip joint salvage could also be achieved through a valgus subtrochanteric osteotomy to redirect the head in the direction of the acetabulum and enhance joint congruity, the abductor lever arm and limb-length discrepancy. Pathophysiology Mechanical overloading results in displacement by way of the proximal femoral physis with translation of the metaphysis anteriorly and superiorly in relation of the epiphysis. Slipping of the epiphysis typically happens by way of the hypertrophic zone of the physis. Anatomically the hypertrophic zone typically contains an anastomosis of the metaphyseal epiphyseal blood provides. During adolescence, previous to growth-plate closure the extracapsular arterial ring supplying the metaphysis increases considerably and invests the subphyseal area, terminating at the hypertrophic zone. The epiphyseal facet of the physis is supplied by the artery of the ligamentum teres, a branch of the obturator artery. During adolescence the periosteum begins to thin and the pressure required for displacement to happen is decreased. Increased retroversion of the proximal femur will increase torsional stress and due to this fact rotational instability via the physis. Changes within the shape of the proximal femur throughout development additionally contribute to decreased stability of the physis. During the expansion spurt, significant lengthening of the femoral neck results in increase varus because the neck shaft angle reduces from a hundred and sixty degrees in infants in the path of one hundred twenty five levels in the adult skeleton. This results in a extra vertically oriented physis, with elevated shear forces across the physis. Passive vary of movement demonstrates limitations to abduction, flexion and internal rotation compared to the unaffected aspect. Some sufferers will present with isolated knee ache because of the reflex sensory arc of the leg. Therefore, in adolescents presenting with knee ache of unclear aetiology, plain radiographs of the hip ought to all the time be carried out. Patients typically current following an acute traumatic event, but could report prodromal symptoms for several weeks or months preceding the event.
Gasex: 100 caps
Generic 100caps gasex visaIn 15% of cases diet for gastritis sufferers discount gasex 100caps line, extra aggressive areas of dedifferentiation to high-grade will be seen gastritis triggers purchase gasex 100 caps with mastercard. Surgical excision should purpose to achieve wide excision margins gastritis diet ������������� buy gasex 100caps on-line, as local recurrence is associated with dedifferentiation to high-grade in 80% and consequently worse survival gastritis antibiotics buy generic gasex 100 caps. Five-year survival after extensive resection and chemotherapy has improved from round 50% in 1984 to over 60%. The chance of downgrading tumours earlier than surgery facilitated the evolution of reconstruction methods after tumour resection. Until the start of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in 1978, 80% of sufferers with an extremity osteosarcoma underwent amputation; today, limb-salvage surgical procedure is possible in 90% of cases. Periosteal osteosarcoma Periosteal osteosarcoma is a uncommon tumour and is quite distinct from parosteal osteosarcoma. This predominantly chondroblastic intermediate-grade tumour arises from the periosteum, extra usually in the diaphysis than metaphysis of lengthy bones, particularly the femur and tibia (80% of cases), typically arising earlier within the second decade of life, inflicting a painful mass and 6�12 months of signs at time of diagnosis. The scientific presentation is much like medullary osteosarcoma, though pathological fracture could occur in 25% of telangiectatic osteosarcomas. Plain X-rays (a) show the attribute options of a parosteal osteosarcoma with a bone-forming surface lesion arising from the cortex and merging with the bone. Histologically this can be a true osteosarcoma of intermediate grade with osteoid and chondroid matrix deposition. The management is identical as for conventional medullary osteosarcoma with neoadjuvant chemotherapy and extensive excision; general survival is reported to be 89% at 5 years and 83% at 10 years, with survival rates associated to the event of local recurrence. Although malignant transformation is a rare complication of this disease, most osteosarcomas showing after the age of 40 years fall into this class. X-rays show typical pagetic bone with a lytic harmful mass extending into the soft tissues. The threat of post-radiation sarcoma is dose-dependent and is most typical in the pelvis and scapula (reflecting radiotherapy for cervical/ovarian and breast carcinomas respectively). The time lag between radiotherapy and subsequent improvement of osteosarcoma can range from 6 to 23 years. Clinically and radiologically the options are just like standard osteosarcoma, although post-radiation adjustments (trabecular coarsening and cortical lysis) could also be evident. The therapy principles for secondary osteosarcoma are the identical, nonetheless elderly sufferers poorly tolerate the aggressive chemotherapeutic and surgical therapies provided to young osteosarcoma patients. Chemotherapeutic dose reductions could additionally be potential if there are considerations regarding cardiac and renal toxicity. Consequently, osteosarcoma in aged patients older than sixty five years has a worse prognosis than that of the youthful inhabitants. This group of aggressive malignant cartilage tumours symbolize a spectrum of the identical dysfunction that arises in enchondromas. This is recommended by the remark that enchondromatosis might evolve right into a low-grade chondrosarcoma and that, after excision, radiologically low-grade chondrosarcomas could have areas of upper grade. Chondrosarcomas can current in adults from the third to the eighth a long time, peaking between 40 and 70 years of age, and men are affected more typically than girls. These tumours are slow-growing and are normally current for a lot of months earlier than being found. They produce deep pain and/or a steadily enlarging mass and come up in any bone derived from enchondral ossification. Despite the comparatively frequent occurrence of benign cartilage tumours within the small tubular bones of the hands and toes, malignant lesions are rare at these sites, representing <1% of chondrosarcomas. Chondrosarcomas take numerous varieties, normally designated according to: (a) their location within the bone (central or peripheral); (b) whether they develop with out benign precursor (primary chondrosarcoma) or by malignant change in a pre-existing benign lesion (secondary chondrosarcoma); and (c) the predominant cell sort in the tumour. Approximately 85% are main central chondrosarcomas occupying the medullary cavity. Endosteal scalloping of the cortex and eventual cortical destruction can occur, and there could additionally be a faint periosteal reaction. These avascular tumours reproduce the high sign of hyaline cartilage on T2 weighted sequences. Differentiating features are bone expansion, periostitis, soft-tissue mass and tumour length (mean intramedullary extent eleven. This has significant prognostic significance for the patient, as extra aggressive tumours have greater mortality charges. Resection histology demonstrates a pale, glistening cartilage lesion within the medullary cavity which spreads past the cortex (d). Treatment was by resection of the periacetabulum and pubis and reconstruction with an ice-cream cone prosthesis and hip alternative (h). Dedifferentiated chondrosarcomas symbolize the extremely malignant finish of the chondroid tumour spectrum, developing in 10�15% of central chondrosarcomas, by which a high-grade undifferentiated sarcoma or osteosarcoma coexists with a lower-grade chondroid tumour. The median age is 59 years, with a slight predominance of males, and the commonest websites are the femur and pelvis. They have a very poor prognosis (5-year survival 7�24%), improved solely by broad surgical resection, worsened by pathological fracture (29% of cases), advancing age and metastasis at analysis. Histopathology reveals macroscopically lobular white hyaline cartilage, areas of mineralization and cystic changes, erosion of the cortex and soft-tissue enlargement. Microscopically the high cellularity, atypia, mitoses and permeation into host bone distinguish a chondrosarcoma from an enchondroma. Grade I tumours are normally locally aggressive with low metastatic potential, not like highgrade lesions. Not occasionally, areas of low-grade and high-grade chondrosarcoma could also be seen in the identical tumour. Chondrosarcoma is proof against each chemotherapy and radiation, making surgical excision the only treatment. In high-grade tumours, only broad excision margins are oncologically acceptable to reduce native recurrence. Prognosis is set by the mobile grade, stage, tumour measurement, (axial versus appendicular) web site and the resection margin. A pathological fracture of the femur has a negative prognostic affect in grade I chondrosarcoma and will increase the risk of local recurrence in dedifferentiated femoral chondrosarcomas. In some cases isolated pulmonary metastases could be resected and adjuvant chemotherapy may be contemplated in dedifferentiated or mesenchymal chondrosarcomas. For this reason, others suggest broad resection and reconstruction, balancing the extra severe physical function with reduced danger of native recurrence. Clinical findings embrace uneven limb shortening, swelling of the fingers and toes, and disturbed movements of the interphalangeal joints. After puberty no new enchondromas develop, and tumour development in maturity is taken into account to be malignant degeneration of those tumours.
Generic 100 caps gasex visaThe vertebral body is cancellous gastritis diet fruit buy gasex 100 caps on line, but the higher and lower surfaces are condensed to type sclerotic endplates gastritis root word discount gasex 100 caps otc. In childhood these are coated by cartilage gastritis muscle pain cheap gasex 100 caps mastercard, which contributes to vertebral development gastritis gurgling order 100caps gasex mastercard. Later the peripheral rim ossifies and fuses with the physique, but the central space stays as a skinny layer of cartilage adherent to the intervertebral disc. The resultant force, which passes by way of the nucleus pulposus of the lowest lumbar disc, is due to this fact much higher than if the column were loaded instantly over its centre. Even at rest, tonic contraction of the posterior muscle tissue balances the trunk, so the lumbar backbone is always loaded. When the intradiscal stress in volunteers during numerous activities was measured, it was found to be as excessive as 10�15 kg/cm 2 while sitting, about 30% much less on standing upright, and 50% much less on lying down. Leaning forward or carrying a weight produces much greater pressures, though when a heavy weight is lifted breathing stops and the belly muscle tissue contract, turning the trunk right into a tightly inflated bag that cushions the force anteriorly against the pelvis. Lying supine with Intervertebral disc the disc consists of a central avascular nucleus pulposus � a hydrophilic gel manufactured from protein-polysaccharide, collagen fibres, sparse chondroid cells and water (88%), surrounded by concentric layers of fibrous tissue � the annulus fibrosus. If the physicochemical state of the nucleus pulposus is regular, the disc can withstand virtually any load that the muscles can help; whether it is irregular, even small will increase in pressure can produce adequate stress to rupture the annulus. Movements the axis of movements within the thoracolumbar backbone is the nucleus pulposus; the disposition of the side joints determines which movements happen. In the thoracic spine the aspect joints face backwards and laterally, so rotation is relatively free; flexion, extension and tilting are potential but are grossly restricted by the ribs. The costovertebral joints are concerned in respiration and their limitation is an early characteristic of ankylosing spondylitis. Spinal canal the shape of the canal adjustments from ovoid within the upper part of the lumbar spine to triangular within the decrease. Variations are frequent and embrace the trefoil canal, whose form is mainly due to thickening of the laminae. Blood provide In addition to the spinal arteries, which run the length of the twine, segmental arteries from the aorta ship branches by way of the intervertebral foramina at each stage. The column features like a crane, the load in front of the backbone being counterbalanced by contraction of the posterior muscle tissue. Antibiotic remedy in sufferers with chronic low again pain and vertebral bone edema (Modic type 1 changes): a double-blind randomized clinical controlled trial of efficacy. Systematic literature evaluation of imaging options of spinal degeneration in asymptomatic populations. Surgical versus non-surgical therapy for vertebral compression fracture with osteopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Prevalence of vertebral endplate signal (Modic) modifications and their affiliation with non-specific low back pain - A systematic literature review. Comparative effectiveness evidence from the Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial. Spinal twine the spinal cord ends at about L1 in the conus medullaris, but lumbosacral nerve roots proceed in the spinal canal as the cauda equina and go away at acceptable ranges decrease down. The dural sac continues as far as S2, and each time a nerve root leaves the backbone it takes with it a dural sleeve as far as the exit from the intervertebral foramen. These dural sleeves can be outlined by contrast-medium radiography (radiculography). Intervertebral foramina and nerve roots Each intervertebral foramen is bounded anteriorly by the disc and adjoining vertebral bodies, posteriorly by the aspect joint, and superiorly and inferiorly by the pedicles of adjoining vertebrae. The segmental nerve roots depart the spinal canal via the intervertebral foramina, each pair beneath the vertebra of the identical number (thus, the fourth lumbar root runs between L4 and L5). The segmental blood vessels to and from the twine additionally pass through the intervertebral foramen. Occlusion of this little passage may occasionally compress the nerve root immediately or may trigger nerve root ischaemia (especially when the spine is held in extension). Ultrasound imaging will confirm that the femoral head is located outside the acetabulum. Pathophysiology Embryonically the femoral head and acetabulum develop from a single cleft of primitive mesenchymal cells. The femoral head stays enlocated normally but relative progress ends in least protection at round time period. Dislocation (or dysplasia) of the hip can happen at specific points of time during growth. The first time at which dislocation might occur is 10 weeks when the lower extremity limb bud rotates medially. Dislocation at these early levels results in irregular growth of all components of the hip joint and is thus termed a teratological dislocation. During the ultimate four weeks of gestation, mechanical forces play a large half in the positioning of the hip joint. In the left occiput anterior position, the most common prenatal fetal position, the left hip is adducted towards the maternal sacrum, growing the chance of dislocation. Postnatally, swaddling of the lower extremities holds the hips in extension and adduction and can be a further contributing factor to subluxation or dislocation in some international locations. In the subluxed place, the labrum is flattened beneath the stress of the femoral head and becomes flattened or everted. Dislocation of the femoral head results in stretching of the inferior capsule and adductors which, if untreated, might lead to contractures and restricted vary of abduction. The Barlow and Ortolani tests are the mainstays in examination of the newborn hip. The Barlow manoeuvre is a provocation take a look at carried out by adducting the flexed hip and making use of light anterior to posterior strain so as to push the femoral head superior and posterior over the sting of a shallow acetabulum. The Ortolani test is a relocation manoeuvre carried out by gently manipulating the flexed hip from adduction to abduction to deliver the femoral head anteriorly again into the acetabulum from a dislocated place. At a later stage, medical examination findings might embrace asymmetrical skin folds, though most consultants feel that these are generally not vital. Imaging the introduction of ultrasound imaging, within the Nineteen Eighties, allowed visualization of the soft-tissue elements of the infant hip together with the cartilage of the femoral head and acetabulum, the capsule and the labrum. The use of multiplanar and dynamic ultrasound allows visualization of the femoral head inside the acetabulum and evaluation of the form and depth of the acetabular cup. Ultrasound is greatest used for children earlier than 6 months of age, after which ossification of constructions makes plain radiographs more and more extra helpful. Consensus was reached at a meeting involving both Graf and Harcke that described the Dynamic Standard Minimum Examination combining a static coronal image and a transverse stress image for optimal assessment of the toddler hip. Clinical screening is clearly wise, but debate persists on the specific benefits, in comparability with price and risk of overtreatment, of selective or common ultrasound screening. The remedy of Ortolani-positive hips, dislocated at relaxation but reducible, should start as soon as sensible. At 2 weeks, failure to enhance both clinically or on the idea of an ultrasound is an indication to start treatment.
Castoreum. Gasex. - Are there safety concerns?
- How does Castoreum work?
- Dosing considerations for Castoreum.
- Menstrual abnormalities, anxiety, sleeping disorders, and other conditions.
- What is Castoreum?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96336
Order gasex 100 caps overnight deliveryEntry into the joint is confirmed when saline flows simply into the joint or gastritis detox diet order gasex 100 caps without prescription, if the joint was distended beforehand gastritis diet ����� 100caps gasex amex, by the outflow when the trocar is withdrawn gastritis diet ���� purchase 100 caps gasex free shipping. All compartments of the joint are now systematically inspected; with special devices and gastritis daily diet plan buy 100caps gasex otc, if needed, by way of a quantity of portals, biopsy, partial meniscectomy, patellar shaving, removal of free bodies, synovectomy, ligament substitute and many other procedures are possible. A firm bandage is applied; the arthroscopic portals are often sufficiently small not to require sutures. Postoperative restoration is remarkably speedy with most circumstances carried out as day-case surgical procedure. Reflex sympathetic dystrophy (which might resemble a low-grade an infection in the course of the weeks following arthroscopy) is sometimes troublesome. It often settles down with physiotherapy and therapy with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; sometimes it requires more radical treatment. Emerging evidence suggests that the indications for arthroscopic intervention are narrowing and that intervention charges might well cut back with time. Technique the patient is anaesthetized (though local anaesthesia may suffice for short procedures) and a thigh tourniquet usually utilized. Published results recommend that the operation supplies substantial improvements in ache and performance over a 7�10-year period. Intra-articular reconstructions the introduction of meniscal and articular cartilage reconstruction methods has led to considerable curiosity in applying the beneficial biomechanical effects of osteotomy to the youthful affected person who has a full-thickness chondral lesion or an absent meniscus. With the event of joint substitute strategies, the operation progressively fell into disuse, or at best was seen as a temporizing measure to buy time for sufferers who would in the end undergo some form of arthroplasty. However, improvements in technique and the introduction of operations for meniscal and articular cartilage repair have led to renewed interest in this process. The rationale for osteotomy is predicated on both biomechanical and physiological ideas. Malalignment of the limb leads to extreme loading and stress in a half of the joint and consequently increased damage to the articular cartilage in that area � the medial compartment if the knee is in varus and the lateral compartment in a valgus knee. Osteotomy and correction of deformity will enhance the load-bearing mechanics of the joint. Technique For sound biomechanical reasons, a varus deformity is finest corrected by a valgus osteotomy at the proximal end of the tibia, whereas a valgus deformity must be corrected by a varus osteotomy at the femoral supracondylar level. Angles should be accurately measured and the place of correction carefully mapped out on X-rays earlier than starting the operation. A excessive tibial valgus osteotomy may be performed both by removing a pre-determined wedge of bone primarily based laterally and then closing the gap (closing wedge technique) or by opening a wedge-shaped hole on the medial aspect (opening wedge technique). In the lateral closing wedge method the fibula must first be launched both by dividing it decrease down or by disrupting the proximal tibiofibular joint. Two transverse cuts are made, one parallel to the joint surface and one other just below that, angled to create the desired laterally based wedge. The wedge of bone is eliminated and the fragments are then approximated and stuck within the corrected place either with staples or with compression pins. An opening wedge valgus osteotomy on the medial facet provides some advantages: the ability to adjust the diploma of correction intra-operatively and the option to appropriate deformities in the sagittal aircraft as properly as the coronal airplane; it also makes it pointless to disrupt the tibiofibular joint. If a varus osteotomy is required � normally for energetic patients with isolated lateral compartment illness and valgus deformity of the knee � this is carried out on the supracondylar level of the femur. The technique mostly employed is a medial closing wedge osteotomy, designed to place the mechanical axis at zero. The fragments ought to be firmly fastened with a bladeplate; in lots of instances postoperative cast immobilization Indications Deformity of the knee Severe varus or valgus deformity. Localized articular floor destruction Patients with unicompartmental osteoarthritis or advanced localized osteonecrosis, notably when this is related to deformity within the coronal aircraft, might profit from an osteotomy which offloads the affected space. Provided the joint is secure and has retained a reasonable range of motion, this provides an acceptable various to a unicompartmental arthroplasty. By realigning the joint, load is transferred from the medial compartment to the centre or a little in the path of the lateral aspect. Slight over-correction might further offload the medial compartment however marked valgus ought to be averted as this will rapidly result in cartilage loss in the lateral compartment. An different however less regularly used method to perform osteotomy is to deploy an Ilizarov circular exterior fixator and gradually dynamically right the deformity over a period of time. Results High tibial valgus osteotomy, when performed for osteoarthritis, provides good results offered (1) the illness is confined to the medial compartment; and (2) the knee has a great range of movement and is stable. Relief of pain is sweet in 85% of instances within the first year however drops to roughly 60% after 5 years. More trendy medial opening wedge osteotomy techniques can achieve satisfactory postoperative alignment in 93% of sufferers and survivorship charges of 94% at 5-year, 85% at 10-year, and 68% at 15-year follow-up, with conversion to total knee arthroplasty as the tip point. The clinical outcomes of distal femoral varus osteotomy have been good in selected patients. Substantial enhancements in pain and performance may be expected in roughly 90% of patients. A stiff knee is a considerable incapacity; it makes climbing troublesome and sitting in crowded areas distinctly awkward. In international locations with superior medical amenities the most typical indication is failed total knee replacement (either septic or aseptic). Contraindications Contraindications embody extreme common incapacity due to age or multiple joint illness, especially if related to issues within the ipsilateral hip or ankle; amputation or knee fusion of the other limb; and chronic non-union of a periarticular fracture or huge periarticular bone loss. Finally, affected person reluctance may be an important issue, though a brief interval in a plaster cylinder earlier than operation might convince the patient that a rigidly stiff leg is best than a painful and unstable knee. Complications Compartment syndrome within the leg that is an important early complication of tibial osteotomy. Early options of compartment compression in the leg are generally mistaken for these of a deep vein thrombosis; this error must be averted at all costs as a end result of the resultant delay in beginning remedy may make the distinction between full recovery and everlasting loss of function. Peroneal nerve palsy Correction of a long-standing valgus deformity can stretch and damage the peroneal nerve. Failure to appropriate the deformity Under- or overcorrection of the deformity are actually failures in technique. Delayed union and non-union these complications may be avoided by guaranteeing that fixation of the bone fragments is stable and safe. The posterior vessels and nerves are protected and the ends of the tibia and femur eliminated by means of straight saw cuts, aiming to finish with 15 levels of flexion and seven degrees of valgus as the place of fusion. In every case at operation all the articular surfaces are replaced � with metal on the femoral facet, polyethylene on a steel tray on the tibial side (mono-block polyethylene tibial parts may be used) and usually polyethylene alone on the patella. It is essential to ensure appropriate placement of the implants so as to reproduce the normal mechanics of the knee as carefully as attainable. The tibial and patellar parts are fixed usually with cement, whereas the femoral component could additionally be press-fitted but is more generally cemented. It is necessary: (1) to overcome deformity (the knee should lastly be about 7 levels valgus); (2) to promote stability (by tailoring the bone cuts so that the collateral ligaments are equally tense in both flexion and extension); and (3) to allow rotation (otherwise cemented prostheses are liable to loosen). The growth of appropriate prostheses and instrumentation in latest times has led to huge enhancements in technique, so the results at the moment are just like these of hip substitute.
Order gasex 100caps with mastercardTreatment is therefore based on the level of symptoms and includes excision gastritis symptoms diarrhoea 100 caps gasex free shipping, avoiding damaging the uninvolved articular cartilage gastritis diet ideas buy discount gasex 100 caps online. In patients with giant lesions gastritis lettuce generic gasex 100 caps on-line, with secondary deformities chronic gastritis flare up generic gasex 100 caps with amex, corrective osteotomies may be undertaken without excision. Involvement of load-bearing bones leads to ache and progressive deformity and should require therapy in the type of corrective osteotomy. Patients may present with pathological fractures in beforehand asymptomatic areas and require conventional fixation and biological augmentation with autologous bone graft or bone substitutes. Patients with intensive involvement may require limb equalization surgical procedure involving a mix of lengthening and progress modulation with guided development or formal epiphysiodesis. Debulking and grafting of lesions within the hand are often required to improve function and any suspicious lesion requires acceptable staging followed by broad native excision. A single bone (monostotic) is often involved, but involvement could additionally be more intensive (polyostotic) in 20% of circumstances. It is a sporadic situation, which is normally unilateral with a reported prevalence of 1:a hundred 000, however there are occasional stories of a familial tendency. There is failure of bone formation in the cartilaginous columns arising from the physis. This causes enlargement of unossified cartilage throughout the bone and leads to physeal damage, with shortening and angular deformity of affected bones and a risk of pathological fracture. Involvement of the palms and toes is frequent and, in severe circumstances, results in severe disability. Malignant transformation to chondrosarcoma occurs, particularly with a quantity of digital lesions, but the prevalence of this important complication is unknown. The skeletal manifestations are generally extra severe and the chance of malignant transformation is considerably greater. The estimated danger of malignant change in both tissue is of the order of 50%, and these patients must be under lifelong surveillance. Radiographs of lengthy bones have attribute radiolucent streaking, extending from the physis into the metaphysis. Patients often current within the second decade with progressive limb deformity or following a fracture through a previously asymptomatic lesion. Nonspecific bone ache, swelling and tenderness are also common presenting symptoms. Proximal femur, tibia, pelvis and foot are regularly concerned, however ribs, skull and bones of the higher limbs are also affected. Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia, in affiliation with precocious puberty and caf�-au-lait spots with irregular borders is called Albright McCune syndrome. Malignant transformation to osteosarcoma, fibrosarcoma or chondrosarcoma happens in 0. Note the development in ossification following normalization of the proximal femoral anatomy. Bisphosphonates have been used to alleviate bone ache and have useful however unpredictable effect. Bone grafting is frequently used as an adjunct however the impact on union is unpredictable. Disorders of collagen synthesis result in a various group of clinical conditions and this part discusses frequent disorders encountered in orthopaedic practice. Patients with a suspected diagnosis ought to endure an echocardiogram to evaluate the aortic root and all patients being thought of for surgery should have an in depth cardiovascular evaluation. Specific orthopaedic management is directed at addressing painful or unstable joints, and physiotherapy is a central element of treatment. Persistent instability and extreme and deteriorating joint ache, refractory to non-operative treatment, could require a surgical solution. The complications of surgical procedure, particularly those associated with wound healing, are increased in this situation due to fragile pores and skin, excessive bleeding and vascular fragility. Instrumented spinal fusion is required in patients with progressive scoliosis and the extent is decided to forestall junctional degeneration secondary to hypermobility. The scientific features embody joint hypermobility, multiple joint dislocations and distinct facial features together with nasal bridge flattened, prominent brow and hypertelorism. The majority of circumstances are inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern but a extra extreme autosomal recessive subtype can be acknowledged and is related to cleft palate, quick stature and cardiovascular anomalies. Cervical kyphosis and talipes are sometimes present in infancy and affected individuals develop dislocations of hips, knees, shoulders and radial heads in childhood. Cervical spine radiology is essential within the first 12 months of life to determine cervical kyphosis. Neonatal ultrasound of the hips is critical to determine acetabular dysplasia or hip dislocation. Tactical radiology is often necessary to consider the structure of joints which are susceptible to dislocation. Management of sufferers with important cervical kyphosis includes surgical stabilization in the first 18 months of life. In the absence of neurological indicators, in situ posterior fusion offers enough stability. Patients with unilateral involvement are normally managed with open reduction and realignment osteotomy. Affected people have fragile pores and skin, joint hypermobility, vascular fragility and severe myalgia. The inheritance sample is variable and most instances have an autosomal dominant pattern. Diagnosis is usually based on the constellation of scientific indicators, significantly the diploma of ligamentous laxity. Affected individuals might develop cardiac anomalies including aortic root dilatation and mitral valve prolapse. Structural penalties, including congenital talipes equinovarus, progressive kyphoscoliosis and developmental dysplasia of the hips are additionally current. Shoulder, ankle and patella�femoral instability are frequent, and approximately 50% of people develop persistent musculoskeletal ache and are prone to early-onset osteoarthritis. Knee dislocation presenting at start can be treated with closed discount and serial casting. It has an approximate incidence of 1:10 000 and impacts the musculoskeletal, ocular and cardiovascular techniques. Scoliosis is present in 50% of patients and is usually related to pectus excavatum. Severe ligamentous laxity produces a planovalgus foot deformity and recurrent joint dislocations. Extraskeletal manifestations include superior lens dislocation, spontaneous pneumothorax and aortic root dilatation resulting in dissection. The diagnosis is usually made on the idea of the scientific findings and, when suspected, ought to prompt an echocardiogram to assess aortic root involvement. All patients in whom surgery is deliberate ought to bear preoperative cardiovascular examination and echocardiogram.
Buy gasex 100 caps otcHowever gastritis aguda trusted gasex 100 caps, neuroimaging studies have discovered the frontal 501 Chapter 21: Disruptive Behavior Disorders lobe to be associated with violence and aggression gastritis symptoms temperature 100 caps gasex for sale. These embody mood disorders and anxiety problems gastritis diet ������������� gasex 100 caps generic,8 in addition to studying and cognitive issues gastritis diet v8 order 100 caps gasex fast delivery. Treatments ought to involve the parents; in most cases, core objectives of therapy include improving parenting abilities and parent-child interactions. Evidence-based psychosocial remedies embrace parent administration training, multimodal interventions (eg, multisystemic therapy), and particular person interventions (eg, cognitive behavioral therapy), every of which will be described in this chapter. Thus, a parent is taught a new set of abilities to use with the kid, together with ways to reward prosocial behaviors and methods to tackle noncompliant behaviors. Through educating, youngsters are taught to discover adaptive solutions to their problems in areas corresponding to dealing with anger and social skills. Techniques such as role playing, structured actions, modeling the conduct, tales, and using games facilitate educating. In some instances, modified cognitive-behavioral remedy and day treatment could additionally be part of the intervention. While disruptive conduct disorders are often chronic, early identification and intervention of downside behaviors can usually enhance the functioning of affected youngsters and families. Review of the proof base for remedy of childhood psychopathology: externalizing problems. Intermittent explosive dysfunction within the National Comorbidity Survey Replication Adolescent Supplement. Age and gender variations in oppositional conduct and conduct issues: a cross-sectional household examine of middle childhood and adolescence. Toward establishing an empirical basis for the prognosis of oppositional defiant dysfunction. Factor structure of the Eyberg Child Behavior Inventory: a mother or father rating scale of oppositional defiant conduct toward adults, inattentive conduct, and conduct downside habits. The measurement of aggressive behavior: reflections on the usage of the Overt Aggression Scale and the Modified Overt Aggression Scale. Nature � nurture: genetic vulnerabilities interact with physical maltreatment to promote conduct issues. Prospective results of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, conduct dysfunction, and intercourse on adolescent substance use and abuse. Family and parenting interventions for conduct dysfunction and delinquency: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Outcomes of conduct problems in adolescence: 40 year follow-up of national cohort. Mood problems are diagnoses of which a disturbance in mood, both melancholy or mania, is the underlying disorder that causes useful impairment as nicely as cognitive and somatic changes. Among all children assembly criteria for a behavioral or emotional disorder, nervousness and temper issues are a variety of the most prevalent psychiatric circumstances seen in youngsters and adolescents. Withdrawing motivation and reducing exercise might enable an individual to conserve his or her efforts in situations by which that energy would be wasted or worsen the state of affairs. Primary pediatric health care professionals play an necessary position in selling the social-emotional well being of children (see Chapter 12, Social and Emotional Development), and so they usually serve as an entry level to behavioral well being providers and therapy. The reasons are multifactorial and include time limitations, reimbursement constraints, and lack of behavioral health professionals to whom sufferers could be referred to as quickly as identified. History and key questions are sometimes probably the most useful method to start to assess the severity of a behavioral downside. Parents and kids may be reluctant to deliver their anxiousness and depressive signs to the attention of a medical professional due to issues of being "labeled" with a mental health disorder or worry of being handled with treatment; nonetheless, adolescents report an elevated willingness to disclose psychological health data if their confidentiality is assured. Therefore, primary pediatric health care professionals should convey an fascinated and nonjudgmental angle toward their households so as to encourage the child or adolescent and mother or father to share their issues. Young youngsters develop attachment to their caregivers early in life and expertise normative fears at separation, such as at bedtime or when being dropped off at baby care or preschool. As kids start to discover the setting around them, worry of animals or objects of their surroundings develops as a protective response. While kids with age-typical fears will attempt to avoid or escape triggers that provoke their anxiousness, children with nervousness disorders typically go to extreme lengths. The presentation of tension issues can range, and children could present in much less anticipated ways. Anxiety problems could additionally be differentiated from one another by conditions that set off the nervousness or worry. Generalized anxiety dysfunction is the most typical type of tension disorder, and panic disorder and agoraphobia are the least common. Preventing this "cascade of psychopathology" is one key cause for early recognition and remedy. In a latest population-based research of preschoolers, approximately 23% of children met criteria for two anxiety problems, and 8% met criteria for three. Preschoolers with generalized anxiousness dysfunction have been more than likely to have a co-occurring anxiousness or nonanxiety disorder. In a examine that examined the comorbidity of 1,035 adolescents between 12 and 17 years old, the comorbidity fee within nervousness issues was 14. Temperamental factors, corresponding to shyness or behavioral inhibition, which even have a genetic part, also play a role. Although there are clear genetic underpinnings, developmental and psychosocial vulnerabilities, as well as acute and persistent stressors, contribute to their genesis and presentation. Functional imaging studies have shown decreased exercise in the right orbitofrontal cortex and anterior cingulate cortex and increased exercise within the amygdala, which is linked to concern responses. Although drugs that prevent the reuptake of serotonin, thereby rising serotonin levels, have been correlated with a discount in anxiousness symptoms, the precise mechanism of that is unclear. There have also been adjustments to the diagnostic standards for agoraphobia, specific phobia, and social anxiety disorder, along with modifications in symptom period necessities. The child could turn into socially withdrawn, exhibit unhappiness, or have issue concentrating on work or play. The youngster can also expertise excessive worry about getting lost or being kidnapped, if separated from his or her attachment determine. Additional issues triggered by separation or worry of separation could embody sleep disturbances (eg, refusal to sleep alone), repeated nightmares, and somatic symptoms (which may include headaches, stomachaches, nausea, and/or vomiting). The symptoms last more than 1 month, and their onset is generally earlier than 5 years of age. The child could communicate at house or with immediate relations but might not verbally respond to others when spoken to . Selective mutism results in impairment of social communication, occupational, and educational achievement. Exposure to the phobic object or state of affairs constantly ends in quick worry or nervousness, which can be manifested in crying, tantrums, freezing, or clinging behaviors.
Order gasex 100capsIf the situation is suspected gastritis symptoms child gasex 100caps line, the patient should be questioned about attainable contacts through the previous days or even weeks and they need to be examined for different signs of genitourinary infection gastritis colitis purchase 100caps gasex otc. Joint aspiration could reveal a excessive white blood cell depend and typical Gram-negative organisms gastritis radiology buy gasex 100caps mastercard, but bacteriological investigations are often disappointing acute gastritis symptoms treatment order 100caps gasex overnight delivery. Samples should also be taken from the varied mucosal surfaces and checks ought to be carried out for other sexually transmitted infections. Patients will often reply quite quickly to a third-generation cephalosporin given intravenously or intramuscularly. However, keep in mind that many sufferers with gonococcal an infection also have chlamydial an infection, which is resistant to cephalosporins; each are delicate to quinolone antibiotics corresponding to ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin. Complications Infants underneath 6 months of age have the best incidence of complications, most of which affect the hip. The most evident risk elements are a delay in prognosis and remedy (more than four days) and concomitant osteomyelitis of the proximal femur. Subluxation and dislocation of the hip, or instability of the knee should be prevented by appropriate posturing or splintage. Damage to the cartilaginous physis or the epiphysis within the rising youngster is the most critical complication. Sequelae include retarded progress, partial or full destruction of the epiphysis, deformity of the joint, epiphyseal osteonecrosis, acetabular dysplasia and pseudarthrosis of the hip. Articular cartilage erosion (chondrolysis) is seen in older sufferers and this may lead to restricted motion or full ankylosis of the joint. The patient may present with an acutely painful, infected joint and marked systemic features of bacteraemia or septicaemia. In some circumstances the an infection is confined to a single, unusual site such as the sacroiliac joint; in others several joints could also be affected concurrently. Opportunistic an infection by uncommon organisms could produce a extra indolent medical image. Patients with staphylococcal and streptococcal infections usually respond nicely to antibiotic therapy and joint drainage; opportunistic infections may be harder to control. Even in affluent communities the incidence of sexually transmitted diseases has increased (probably related to the increased use of non-barrier contraception) and with it the risk of gonococcal and syphilitic bone and joint ailments and their sequelae. The an infection is acquired only by direct mucosal contact with an infected individual � carrying a danger of greater than 50% after a single contact! Lyme disease, which also originates with a spirochaetal an infection, is healthier thought to be because of a systemic autoimmune response and is mentioned in Chapter 3. The ones who survive manifest pathological modifications similar to those described above, though with modified scientific appearances and a contracted timescale. The organism also can cross the placental barrier and enter the fetal blood stream directly during the latter half of being pregnant, giving rise to congenital syphilis. In acquired syphilis a primary ulcerous lesion, or chancre, seems at the web site of inoculation a few month after preliminary infection. This normally heals with out remedy but, a month or more after that, the disease enters a secondary section characterised by the appearance of a maculopapular rash and bone and joint adjustments due to periostitis, osteitis and osteochondritis. After a variable length of time, this part is adopted by a latent period which may continue for a few years. The time period is somewhat deceptive as a outcome of in about half the circumstances pathological lesions proceed to seem in numerous organs and 10�30 years later the patient may present again with tertiary syphilis, which takes numerous varieties including the looks of huge granulomatous gummata in bones and joints and neuropathic problems in which the loss of sensibility provides rise to joint breakdown (Charcot joints). In congenital syphilis, the first an infection may be so severe that the fetus is either stillborn or the toddler Clinical features of acquired syphilis Early options the affected person usually presents with ache, swelling and tenderness of the bones, particularly those with little soft-tissue covering, such because the frontal bones of the cranium, the anterior surface of the tibia, the sternum and the ribs. Late features the typical late feature, which can seem only after many years, is the syphilitic gumma, a dense granulomatous lesion associated with local bone resorption and adjacent areas of sclerosis. X-rays might show thick periosteal new bone formation at other sites, particularly the tibia. The other well-recognized feature of tertiary syphilis is a neuropathic arthropathy because of loss of sensibility in the joint � most characteristically the knee. The baby is sick and irritable and examination could show pores and skin lesions, hepatosplenomegaly and anaemia. Several websites may be involved, usually symmetrically, with slight swelling and tenderness on the ends or alongside the shafts of the tubular bones. Late congenital syphilis Bone lesions in older youngsters and adolescents resemble those of acquired syphilis and some features occurring 10 or 15 years after delivery may be manifestations of tertiary disease, the end result of gumma formation and endarteritis. Gummata seem both as discrete, punched-out radiolucent areas in the medulla or as extra in depth destructive lesions in the cortex. Secondary skin lesions appear 1�4 months later and successive lesions could go on to pustular ulceration; as each heals it leaves a pale tell-tale scar. This secondary stage is followed by an extended latent interval, merging right into a tertiary stage during which skeletal modifications similar to these of syphilis develop � periosteal new bone formation, cortical destruction and osteochondritis. In areas the place the illness is endemic, the standard skin lesions and an related lymphadenopathy are shortly recognized. Elsewhere, additional investigations may be referred to as for � serological tests and darkfield examination of scrapings from one of many skin lesions. Treatment Treatment with benzylpenicillin, preferably given by intramuscular injection, is effective. For those who are hypersensitive to penicillin, erythromycin is a satisfactory different. The initial lesion is a small break up in the skin (a minimize, thorn-scratch, insect bite or other minor abrasion), which is then contaminated with all types of filth or stagnant water. The most probably infecting organisms are Fusiformis fusiformis and Borrelia vincentii (both frequent in faeces). This leads to an indolent ulcer which defies most types of topical treatment (and certainly conventional remedies native to these components of the world) Treatment Early lesions will normally respond to intramuscular injections of benzylpenicillin given weekly for three or 4 doses. Yaws fifty two Yaws is a non-venereal spirochaetal an infection caused by Treponema pertenue. Early circumstances of tropical ulcer may respond to benzylpenicillin or erythromycin given day by day for per week. Ulcers should be cleansed every single day and kept covered with moist or non-adherent dressings. Late instances of ulceration would require painstaking cleaning and de-sloughing together with broadspectrum antibiotics efficient against the causative anaerobic Gram-negative organisms as well as secondary infecting microbes cultured from swab samples. Soft-tissue and bone destruction could also be severe enough to require in depth debridement and skin-grafting. The skeletal manifestations of the disease are seen mainly within the backbone and the large joints, however the an infection could appear in any bone or any synovial or bursal sheath. The ulcer could ultimately bore its means into the soft tissues and the underlying bone; sometimes, after a few years, it offers rise to a regionally invasive squamous-cell carcinoma. Clinical features What begins as a small inflamed scratch or cut develops over a couple of days into a large pustule.
References - deGroat WC, Vizzard MA, Araki I, et al: Spinal interneurons and preganglionic neurons in sacral autonomic reflex pathways, Prog Brain Res 107:97n111, 1996.
- Wapner RJ, Sorokin Y, Mele L et al. Long-term outcomes after repeat doses of antenatal corticosteroids. N Engl J Med 2007; 357: 1190-8.
- Gill AJ, Hes O, Papathomas T, et al: Succinate dehydrogenase (SDH)-deficient renal carcinoma: a morphologically distinct entity: a clinicopathologic series of 36 tumors from 27 patients, Am J Surg Pathol 38(12):1588n1602, 2014.
- Buell JF, Gross TG, Hanaway MJ, et al. Chemotherapy for posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder: the Israel Penn International Transplant Tumor Registry experience. Transplant Proc. 2005; 37:956-957.
- Wang XY, Degos F, Dubois S, et al. Glypican- 3 expression in hepatocellular tumors: diagnostic value for preneoplastic lesions and hepatocellular carcinomas. Hum Pathol. 2006;37:1435-1441.
- Rowlatt JF, Rimoldi MJA, Lev M. The quantitative anatomy of the normal child's heart. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1963;10:499-88.
- Zhu Y, Ye X, Zhu B, et al: Comparisons between the 2012 new CKD-EPI (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration) equations and other four approved equations, PLoS ONE 9:2014.
- Abbott J, Hawe J, Hunter D et al. Laparoscopic excision of endometriosis: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Fertil Steril 2004; 82: 878-84.
|