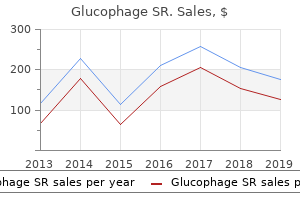
Glucophage SR
Michael L. Cunningham, M.D., Ph.D. - Seattle Children’s Hospital Craniofacial Center
- Seattle, Washington
Discount 500 mg glucophage sr otcSholl the pathologic definition of respiratory bronchiolitis-interstitial lung illness is an area of controversy among pulmonary pathologists treatment hepatitis b buy glucophage sr 500 mg with visa. Reports of respiratory bronchiolitis-interstitial lung illness describe the presence of respiratory bronchiolitis with the extension of fibrosis and irritation into the alveolar buildings symptoms 3dpo purchase 500mg glucophage sr visa. Patients are heavy people who smoke with restrictive pulmonary function tests or interstitial markings on standard chest X-ray schedule 8 medications list order glucophage sr 500mg without prescription. In distinction to respiratory bronchiolitis symptoms cheap glucophage sr 500 mg free shipping, these patients are symptomatic, with complaints of cough and shortness of breath; the signs, nevertheless, are most likely to be nonprogressive, in distinction to different outlined forms of interstitial lung disease. Although many studies have used the presence of alveolar wall fibrosis to distinguish between respiratory bronchiolitis and respiratory bronchiolitis-interstitial lung illness, this distinction has been challenged by studies that reveal peribronchiolar alveolar wall fibrosis in a big minority of (asymptomatic) smokers. Similarly, the findings on high-resolution computed tomography-including centrilobular nodularity and floor glass opacities-overlap within the two teams; nonetheless, the presence of reticular modifications has solely been described in the context of respiratory bronchiolitis-interstitial lung illness. Desquamative interstitial pneumonia is taken into account to be on a spectrum with respiratory bronchiolitis-interstitial lung illness. Although desquamative interstitial pneumonia sample could be seen in quite so much of contexts-including connective tissue diseases, drug reactions, and as an idiopathic process (see also Chapters 97 and 135)-it is most extremely associated with smoking. On computed tomography scanning, desquamative interstitial pneumonia seems as lower lobe�predominant ground glass opacities admixed with normal-appearing lung. Microscopically, desquamative interstitial pneumonia in smokers is characterised by large clusters and sheets of pigmented macrophages and large cells throughout the airspaces. Interstitial fibrosis and inflammation ought to be current in a pattern that resembles nonspecific interstitial pneumonia; certainly some radiology research have instructed that desquamative interstitial pneumonia can progress to nonspecific interstitial pneumonia. Progressive disease is reported in a minority of sufferers, but most sufferers stabilize or enhance with smoking cessation and corticosteroid therapy. Histologic Features Airspace macrophages containing fine yellow to tan pigment are visible. Alveolar septa show patchy chronic irritation and fibrosis radiating from the respiratory bronchioles. In desquamative interstitial pneumonia, the pigmented macrophages kind clusters and sheets with filling of the alveolar spaces, with related inflammation and fibrosis of the alveolar septa. Sholl Cigarette smoking leads to a proinflammatory chemokine milieu that triggers the differentiation and activation of Langerhans cells; consequently, people who smoke demonstrate an elevated variety of Langerhans cells in the lung. Patients may current with cough and dyspnea, or spontaneous pneumothorax, or they might have lung nodules detected incidentally on imaging studies. Computed tomography studies present small nodules and cysts; the latter become more pronounced with illness progression. Smoking cessation is the first line of remedy and will result in disease remission in many patients. Immunosuppression is indicated in sufferers with progressive disease (see also Chapter 47). Histologic Features Granulomatous irritation centered on the bronchioles; the bronchiolar epithelium is often denuded and the bronchiolar wall might appear dilated. In people who smoke, pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis might be seen on a background of respiratory bronchiolitis. Severe emphysematous change is clear within the distal, subpleural lung tissue (right facet of image). Histologically, related interstitial fibrosis was described as alveolar septal thickening by dense acellular collagen invariably accompanied by respiratory bronchiolitis and emphysematous modifications. The severity of the fibrosis varies throughout the concerned lung, with accentuation within the subpleural and peribronchiolar compartments. These adjustments are noticed in each present and former people who smoke, including those who stop a number of decades prior. In the unique description, all sufferers had undergone lobectomy for an area neoplastic process, mostly commonly non�small cell lung carcinoma, and the cohort was biased toward upper lobe resections. The radiographic correlates in the authentic description of smoking-related interstitial fibrosis were nonspecific, described as areas of fibrosis or scarring; the minority showed emphysema. Clinically, smokers with combined fibrosis and emphysema on high-resolution computed tomography scans can have unexpectedly normal spirometry findings regardless of lowered total 906 lung capability, and some authors have speculated that smokingrelated interstitial fibrosis could be the pathologic correlate of this mixed physiologic disturbance. The differential prognosis of smoking-related interstitial fibrosis consists of ordinary interstitial pneumonia (which can be distinguished primarily based on its temporal variability and the presence of numerous fibroblast foci), asbestosis, and pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Histologic Features Uniform, acellular collagen deposition results in thickening of the alveolar septae. The interstitial thickening could present accentuation in the subpleural and peribronchiolar compartments of the lung. Respiratory bronchiolitis is invariably present; a desquamative interstitial pneumonia pattern of ample airspace macrophages could additionally be seen. Inflammatory cells are sparse and are enriched within the respiratory bronchioles according to the association with respiratory bronchiolitis. Kim Hypersensitivity pneumonitis is a diffuse lung disease attributable to inhalational exposure to natural antigens. The former term, extrinsic allergic alveolitis, underscores the significance of the diffuse cellular interstitial infiltrate on this illness. Interestingly, smoking appears to provide a protecting benefit, as smokers are much less likely to endure from hypersensitivity pneumonitis. In the acute and subacute types, sufferers usually present with shortness of breath, cough, and occasionally systemic symptoms, similar to malaise and fever. The persistent kind develops over a longer interval, with progressive dyspnea, cough, weight loss, and end-stage fibrotic lung disease. The basic imaging findings are described as upper lobe predominant, ill-defined floor glass nodules, with a centrilobular distribution and immediate subpleural sparing. In chronic types, there may still be some vague centrilobular nodules, however elevated reticulation, fibrosis, and even radiographic cysts of honeycombing could additionally be identified. Histologic Features Acute Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis 912 Acute and organizing lung injury with fibrin, diffuse alveolar damage, granulomatous pneumonitis, and organizing pneumonia. Subacute Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Diffuse cellular interstitial infiltrates, which can show a centrilobular distribution. Centrilobular poorly shaped interstitial granulomas, consisting of loose aggregates of histiocytes with or with out multinucleated big cells in a background of lymphoplasmacytic inflammation. Granulomas ought to be troublesome to establish; if granulomas are numerous, present necrosis, or are apparent from scanning magnification, an alternate diagnosis should be thought-about. Chronic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Fibrotic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia sample of fibrosis or airway-centered pattern of fibrosis. Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis could additionally be superior with microscopic honeycomb remodeling and fibroblast foci, mimicking the identical old interstitial pneumonia sample of pulmonary fibrosis. Extensive chronic small airways reworking within the type of peribronchiolar metaplasia, mucostasis, and continual bronchiolitis. Scattered interstitial poorly shaped granulomas with or with out multinucleated big cells.
Purchase glucophage sr 500 mg free shippingThe vary of values among the many replicates is represented for each point by the bar medicine 911 buy glucophage sr 500 mg overnight delivery. The human adenovirus kind 5 E4 Orf3 protein induces disruption of those constructions medicine gustav klimt glucophage sr 500 mg lowest price, with relocalization of some elements medicine holder trusted glucophage sr 500 mg, corresponding to particular Pml isoforms symptoms for hiv glucophage sr 500mg amex, to viral replication centers and of others to the cytoplasm for degradation. This viral protein is an E3 ubiquitin ligase, which catalyzes addition of polyubiquitin chains to proteins, thereby targeting them for destruction by the proteasome (Box 9. This viral protein (red) and Pml protein (green) have been examined by oblique immunofluorescence. In the presence of the E4 Orf3 protein, Pml foci are rearranged to track like structures that contain this viral protein. This arrangement will increase the native concentrations of proteins that must interact with one another, or with viral origin sequences or replication forks, favoring such intermolecular interactions by the regulation of mass action. In addition, the high native concentrations of replication templates and proteins are more doubtless to enable environment friendly recruitment of the products of 1 replication cycle as templates for the subsequent. Viral replication facilities additionally serve as foci for viral gene expression, presumably partially by concentrating templates for transcription with the proteins that perform or regulate this process. When they enter the nucleus, infecting adenoviral or herpes simplex virus sort 1 genomes, and people of papillomaviruses and polyomaviruses, localize to preexisting nuclear bodies that contain the cellular promyelocytic leukemia proteins (Pmls). In contrast, ubiquitinylation is determined by the sequential activation of three enzymes, a ubiquitin-activating enzyme (E1), a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (E2), and an E3 ubiquitin ligase that catalyzes switch of ubiquitin from the E2 enzyme to a Lys residue of the substrate. The human E1-activating enzyme Ubal cooperates with a number of E2s and a really giant number of E3s, which decide substrate specificity. Ubiquitin itself incorporates a number of Lys residues to which an additional molecule of the small protein modifier can be linked. Indeed, the substrates of E3 ubiquitin ligases could additionally be polyubiquitinylated via several types of linkages among ubiquitin moieties, or monoubiquitinylated. As illustrated, the character and site of the modification determines whether or not the substrate protein is targeted for degradation by the proteasome (polyubiquitinylation at K48 of ubiquitin molecules) or its activity regulated. The reversible addition of other small proteins discovered subsequently, corresponding to Sumo (small ubiquitin-like modifier) proteins and ubiquitin-like protein-Nedd8, can also regulate the location or exercise of proteins. The genomes of members of various families encode proteins which would possibly be themselves E3 ubiquitin ligases or that kind these enzymes with distinct specificities upon affiliation with elements of mobile E3 ubiquitin ligases. Viral proteins that redirect the actions of cellular E3 ubiquitin ligases are extra numerous. The sequential motion of the enzymes required to covalently link ubiquitin to a Lys residue in a substrate protein and the two major courses of E3 ubiquitin ligases are shown. As indicated, the character of the modification determines its impression on the goal protein. For instance, publicity of cells to antiviral cytokines (interferons) will increase each the number and measurement of Pml bodies. However, different advantages conferred by the degradation or dispersal of Pml body proteins are more doubtless to be virus particular. Nevertheless, several can establish long-term relationships with their hosts and host cells, in which the number of genomes produced is limited. Various mechanisms that achieve copy number control are described in this part. Although the latter viruses are widespread in hosts infected by adenovirus-associated viruses, the possibilities that a selected host cell shall be infected simultaneously by two viruses are very low. The technique of exploiting other viruses to present important features would therefore seem to impose an obstacle to reproduction of particular person adenovirus-associated virus particles. The two bigger proteins encoded by this area, Rep 78/68, are multifunctional and management all phases of the viral life cycle (Table 9. One of essentially the most unusual features of the integration response is that it happens preferentially close to one finish of human chromosome 19. In the absence of Rep protein, as in cells infected by typical adenovirus-associated virus vectors (Chapter 3), viral genomes generally persist as episomal concatemers. It is assumed that double-stranded, circular genomes form initially, for instance, upon annealing of complementary single-stranded genomes, and then endure recombination to give rise to concatemers. A attribute property of herpesviruses is the establishment of latent infections in specific cell types, for instance, neurons and B cells within the case of alphaherpesviruses and Epstein-Barr virus, respectively. Studies of the betaherpesvirus human herpesvirus 6 have prompted consideration of another mode of herpesviral latency. Primary an infection with human herpesvirus 6, which is widespread in the human inhabitants, happens early in life, and in 25 to 35% of instances is related to growth of fever and a characteristic rash in infants (roseola infantum). The virus establishes latency following main an infection, and reactivation from this state can cause severe illness, particularly in immunocompromised individuals. The human herpesvirus 6 genome accommodates a unique sequence bounded by direct repeats. It is thought that integration is the results of homologous recombination between the telomere repeat sequences in the viral genome and present on the ends of human chromosomes. The latent human herpesvirus-6A genome specifically integrates in telomeres of human chromosomes in vivo and in vitro. This pattern is attribute of human B cells latently contaminated by Epstein-Barr virus. Characteristic features of latent EpsteinBarr virus an infection embrace expression of only a small variety of viral genes, the presence of a finite variety of viral genomes, and replication from a specialized origin. The Epstein-Barr virus genome is maintained in nuclei of latently contaminated cells as a secure round episome, present at 10 to 50 copies per cell. The concentrations and activities of both are tightly controlled during the cell cycle. A cyclin-dependent kinase that accumulates during the G2 and M phases phosphorylates both Mcm proteins and Cdc6. This modification induces nuclear export of the previous and degradation of the latter. As a consequence of such regulatory mechanisms, the prereplication complicated can kind only within the G1 section, ensuring firing of the origin once per cell cycle. The availability of mobile replication proteins solely in late G1 and S can account for the timing of Epstein-Barr virus replication in latently contaminated cells. The mechanisms that management once-per-cycle firing of eukaryotic origins, a course of termed replication licensing, have been initially elucidated in budding yeasts, which include compact origins of replication. These proteins accumulate within the nucleus throughout S phase, but are subsequently degraded (Cdc6) or sequestered (Cdt1). One parameter necessary for such temporal regulation is phosphorylation of telomere repeat-binding protein 2 (Trf2) early during S phase by Chk2, a kinase implicated in management of replication timing in yeast. Trf2 binds to three copies of a telomere repeat-related sequence in OriP and interacts with each Orc and histone deacetylases. Phosphorylation of Trf2 by Chk2 inhibits these capabilities and is believed to contribute to stopping too-early initiation of OriP-dependent replication.
Diseases - Dysencephalia splachnocystica or Meckel Gruber
- Malignant germ cell tumor
- Yusho disease
- Influenza
- Schizoaffective disorder
- Craniometaphyseal dysplasia recessive type
- Meadows syndrome[disambiguation needed]
- Ambral syndrome
- Atrophic vaginitis
- Pinealoma
Cheap glucophage sr 500 mg otcThis protein is phosphorylated at specific positions by the cellular tyrosine kinase Src symptoms 5 days before missed period buy glucophage sr 500mg low price, which performs an essential role in the regulation of actin dynamics in uninfected cells symptoms in early pregnancy buy glucophage sr 500mg lowest price. The coincidence of the information of the projecting actin and viral particles gives yellow-orange alerts medicine 2410 buy 500mg glucophage sr mastercard, indicating that the particles are projected from the cell surfaces on the tips of actin tails medicine news order glucophage sr 500 mg visa. When infected cells are plated with uninfected cells, such actin-containing structures to which virus particles are connected could be seen extending from the former into the latter. Cellular projections containing actin tails with virus particles at their suggestions can extend from infected cells towards neighboring uninfected cells, suggesting that they might facilitate direct cell-to-cell unfold of infectious particles. More importantly for speedy spread of vaccinia virus, they mediate a remarkable mechanism of repulsion of virus particles from infected cells (Box 13. Intranuclear Assembly the issue of egress is especially acute for the enveloped herpesviruses, because the nucleocapsids assemble within the nucleus. The pathway by which the virus leaves the cell has been a topic of fierce controversy, centered on where and when the viral envelope is acquired. The second envelopment, by which particles purchase their envelopes, takes place on the cytoplasmic surfaces of compartments of the trans-Golgi community. Some tegument proteins accumulate at the websites of secondary envelopment and are required for this step. Once the nucleocapsid reaches the trans-Golgi community, interactions between these two lessons of tegument protein must take place previous to envelopment. Some latest observations hint that such viral proteins may function via some elements of the cellular Escrt machinery that mediates the discharge of less complicated enveloped viruses. The A36R protein (red) present in the outer membranes of wrapped virus particles binds to the light chain of the kinesin motor, which then transports the particles to the cell periphery. Remodeling of cortical actin by viral proteins allows shut strategy of the particles to the plasma membrane. Fusion of the outer membrane of wrapped virus particles with the plasma membrane releases cell-associated virus particles, which carry the B5R glycoprotein (blue) of their new outer membrane. This viral protein activates the mobile Src tyrosine kinase, presumably through interplay with one or more mobile membrane proteins (X). Src then phosphorylates the membrane-associated A36R protein, a modification proven by genetic experiments to be essential for formation of actin tails. Furthermore, A36 stays sure to kinesin in vaccinia virus-infected cells that lack Src or which might be treated with inhibitors of this kinase. Phosphorylated A36R binds through adapter (Grb and Nck) and scaffolding (N-Wasp) proteins to proteins that induce actin polymerization. Such polymerization drives the formation of actin tail-containing protrusions that project cell-associated virus particles away from the host cell. The viral F11 protein-induced inhibition of signaling via the small G protein RhoA results in increased microtubule dynamics and facilitates transport of progeny virus particles to the plasma membrane. Such inhibition additionally stimulates the migration of vaccinia virus-infected cells, a property that promotes unfold of progeny virus particles. In natural infections, the host defenses are an essential reason for infected-cell destruction. Such exercise assuredly contributes to the escape of newly assembled virus particles from the nucleus and would possibly contribute to lysis of the host cell. A small viral protein can be needed for efficient nuclear disruption and lysis of cells contaminated by human adenovirus. The extreme inhibition of cellular protein synthesis towards the tip of the infectious cycle and disruption of cytoplasmic intermediate filaments upon cleavage of their parts by the viral L3 protease are likely to facilitate launch of adenovirus particles by compromising the structural integrity of the infected cell. When poliovirus replicates in polarized epithelial cells resembling those lining the gastrointestinal tract (a natural web site of infection), progeny virus particles are released solely from the apical floor by a nondestructive mechanism. Maturation of Progeny Virus Particles Proteolytic Processing of Structural Proteins the products of meeting of a quantity of viruses are noninfectious particles. In all circumstances, proteolytic processing of particular proteins with which the particles are initially constructed converts them to infectious virions. Measurement of the rate of enhance in the dimension of vaccinia virus plaques in various cell strains indicated that the virus crossed one cell every 1. This rate of unfold is considerably higher than could be defined by both the assembly of progeny virus particles or the induction of infected-cell motility, both of which require 5 to 6 h after the initial infection. Mutant viruses defective for formation of actin tails infected new cells only every 5 to 6 h, in maintaining with the kinetics of the infectious cycle. This finding implicated actin tail formation in the speedy unfold of vaccinia virus. Green virus particles were detected on red actin tails in cells that contained no viral factories or progeny virus particles. These structures appeared earlier than viral factories, and particles on a red actin tail induced the formation of a new actin tail upon recontact with the identical cells (see the determine and Movie 13. The viral A33 and A36 proteins, that are required for formation of actin tails, are made early in the infectious cycle and accumulate within the plasma membrane at the edges of plaques. Mutant viruses that direct the synthesis of those proteins late quite than early in an infection produce only small plaques. Furthermore, the synthesis of just these two proteins in uninfected cells allowed the formation of 5 20 actin tails within 15 to 30 min after exposure to extracellular enveloped virus particles. These observations identified a previously unrecognized mechanism of spread of vaccinia virus particles, repulsion from contaminated cells on actin tails towards neighboring cells. This process prevents superinfection and therefore accelerates the rate of unfold of the virus. Shown are actin tails fashioned 50 fifty five on the times indicated (min) after infection, and before the appearance of large green viral factories at fifty five min. The time-lapse movie shows such a cell and induction of a brand new actin tail when a virus particle at the tip of a red actin tail recontacts the cell floor. Proteolytic cleavage of structural proteins introduces an irreversible response into the meeting pathway, driving it in a forward course. This modification can also make an important contribution to resolving the contradictory necessities of assembly and virus entry. One consequence of proteolytic processing is the change of covalent linkages between particular protein sequences for a lot weaker noncovalent interactions, which could be disrupted in a subsequent infection. A second is the liberation of latest N and C termini at every cleavage website and, therefore, alternatives for added protein-protein contacts. Such modifications in chemical bonding among structural proteins clearly facilitate virus entry, for the proteolytic cleavages that introduce them are necessary for infectivity. Accordingly, viral proteases and the structural penalties of their actions are of appreciable interest. Moreover, these enzymes are wonderful targets for antiviral medicine, as exemplified by the success of therapeutic brokers that inhibit the human immunodeficiency virus kind 1 protease. These proteins, usually known as the nuclear export advanced, associate with each other at the inside surface of the internal nuclear membrane and bind the proteins that type the lamina (lamins A/C and B) and mobile protein kinase C. These modifications are thought to disrupt the interactions that type the nuclear lamina. Upon fusion with the outer nuclear membrane, this membrane is lost as unenveloped nucleocapsids are released into the cytoplasm.
Glucophage sr 500mg otcThe field of immunology is bewildering to many medications of the same type are known as discount glucophage sr 500 mg amex, even to those who work in closely associated disciplines medicine nausea cheap glucophage sr 500mg line. Contemplating the sheer quantity and diversity of cell varieties medicine clip art 500 mg glucophage sr mastercard, soluble proteins symptoms 16 weeks pregnant buy discount glucophage sr 500 mg line, signal transduction pathways, and anatomical locations could be overwhelming. In efforts to convey this complexity, textbooks and evaluations usually revert to comparisons either with warfare, and the notion that different features of the military possess completely different expertise, or with the medical profession, by which quick immune responders are equated with emergency medical technicians and the later adaptive response in comparison with specialized surgeons. As metaphors may be helpful, we propose that the immune response is very similar to an orchestra taking half in a symphony: many devices contribute at discrete instances and with unique sounds to create the ultimate piece. The bassoon could seem in both the primary motion and the third, the violins may be active all through however carrying totally different tunes and performed at completely different volumes, and the cymbals may be silent until the final climactic measures. The innate immune response is crucial in antiviral protection as a outcome of it could be activated quickly, functioning within minutes to hours of infection. The instant response to an infection is based on two coupled processes: detection and alarm. Microbes include unique components, together with sure carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and proteins, which are acknowledged by mobile sample recognition receptors current either on the cell floor or within the cytoplasm. Binding of a specific ligand to a sample recognition receptor initiates a signal transduction cascade that ends in activation of cytoplasmic transcription regulatory proteins such as Nf-kb and interferon regulatory factors. Apoptosis is a normal biological process that can be induced by the biochemical alterations initiated by virus infection. Most cells synthesize interferon when contaminated, and the released interferon inhibits reproduction of a wide spectrum of viruses. The problem of clearly explaining how the dynamic defensive response is coordinated is additional compounded by the reality that we still have no idea all the parameters that govern the timing of the host response. That is, if we revert to our symphony metaphor, we all know of no particular conductor who leads the complete process. Consequently, we should continuously reevaluate what we thought we understood as new ideas and gamers are recognized. Progress is fast: since the final edition of this textbook, many crucial questions have been answered or clarified. This text describes the immune response from a temporal viewpoint; on this chapter, we discuss the events that occur immediately after an infection (the intrinsic response) by way of 2 to four days postchallenge (the innate response). We use terms similar to "intrinsic" and "innate" as a end result of they aid in telling the story, however, of course, the immune response is aware of no such distinctions. The coevolution of viruses with their hosts has resulted within the selection of viruses that can survive, despite host defenses. The genomes of successful pathogens, which may evolve far faster than the hosts they infect, encode proteins that modify, redirect, or block each step of host protection. Indeed, for each host protection, there will be a viral counter-offense, even for these viruses with genomes that encode a small variety of proteins. Consequently, the exploration of how viruses reproduce of their hosts led to the discovery of crucial immunological principles, as we will see throughout this chapter and the next. The First Critical Moments of Infection: How Do Individual Cells Detect a Virus Infection A viral an infection in a host can start solely once bodily and chemical limitations are breached and virions encounter dwelling cells which are both susceptible and permissive (Chapter 2). All cells have the capability to react defensively to varied stresses, similar to starvation, temperature extremes, irradiation, and an infection. Some of these safeguards preserve mobile homeostasis, while others have developed to detect cellular invaders rapidly. These cell-autonomous (that is, can be completed by a single cell in isolation), protecting programs, that are inherent in all cells of the body, are termed intrinsic cellular defenses to distinguish them from the specialized defenses possessed by "skilled" cells of the innate and adaptive arms of the immune system. Intrinsic defenses are among the many most conserved processes in all of life, shared by humans, fruit flies, vegetation, and micro organism. In contrast, specialised immune cells and effector proteins appeared a lot later in evolution, through the emergence of multicellular organisms. How the intrinsic defenses are induced within the first cell to be contaminated within a host, or in an adjacent phagocytic cell, similar to a macrophage or dendritic cell, is kind of much like our personal expertise when something in our surroundings adjustments: we understand a distinction only within the context of what we recall as regular. As we are in a position to distinguish "familiar" and "completely different," the immune response distinguishes "self " from "nonself. Specific protein detectors recognize structures which might be distinctive to microbes or their genomes. Once a microbe has been detected, the contaminated cell must then sound the alarm to provoke the collection of events that lead to an applicable defense. The sequential nature of host defenses is depicted because the breaching of successive obstacles by viral an infection. When these obstacles are penetrated, additional host defenses, together with intrinsic and innate defenses, come into play to comprise the an infection. Activation of acquired immune defenses (also known as adaptive immunity) is usually enough to include and clear any infections that escape intrinsic and innate protection. In rare situations, host defenses may be absent or inefficient, and severe or deadly tissue damage and host sickness or demise may finish up. Tailoring the immune response to the pathogen continues as the an infection proceeds, and at every important juncture of immune defense. Cell Signaling Induced by Receptor Engagement As quickly as virus particles interact their receptors, mobile sign transduction pathways are activated. Remember that no cell surface protein is simply a viral receptor: viruses have been selected to co-opt cellular proteins for viral entry (Volume I, Chapter 5). Many cell surface proteins are linked to intracellular molecules, such that binding of the traditional ligand to the receptor triggers pathways that enable the cell to reply to adjustments in its setting. Thus, even earlier than the virus enters the cell, the dynamics of ion circulate, membrane permeability, protein modification and localization, and host gene transcription may change. Receptor-Mediated Recognition of Microbe-Associated Molecular Patterns A second way that cells respond to infection is by interaction of intracellular elements with microbial proteins or nucleic acids. Microbes include distinctive parts, including bacterial and fungal carbohydrates. Pattern recognition receptors have been first identified in vegetation, which exhibit the only detection-to-alarm process: certain plant proteins are both the detector and the signal transducer that drives cell behavior. In distinction, most mammalian sample recognition receptors transmit indicators by partaking with a number of cytoplasmic adapter molecules that finally provoke a mobile response, often by influencing gene expression. Perhaps using multiple adapter proteins in animals allowed for diversification of the alarm to a common detection sign, or conversely, for the integration of numerous signals to a standard node, corresponding to nuclear factor-kb (Nf-kb). Our first insights into the immunological nature of these pathogen receptors came from Drosophila developmental genetics (Box 3. We now understand that all intrinsic and innate protection systems arose early in the evolution of multicellular organisms, and stay completely essential for survival of mature organisms in a microbe-filled world. Members of different families of receptors detect particular motifs that are attribute of invading microbes in single cells (Table three. The Toll-like receptor (Tlr) household consists of 10 members in humans (12 in mice) which may be present both on the cell surface or within lysosomes, the place getting into viruses first appear (Box three. When Wieschaus confirmed the unusual mutant Drosophila embryos to N�sslein-Volhard, she exclaimed, "Toll!
Glucophage SR: 500 mg

Cheap glucophage sr 500mg on-lineTo infect the respiratory tract efficiently treatment 8th march generic glucophage sr 500 mg, virus particles should not be captured or swept away by mucus symptoms thyroid purchase 500 mg glucophage sr with amex, neutralized by antibody treatment brown recluse spider bite 500 mg glucophage sr mastercard, or destroyed by alveolar macrophages treatment concussion order glucophage sr 500 mg without prescription. Cells within the cell membrane under the mucus have tiny hair-like projections referred to as cilia. A group of applied mathematicians evaluated the distance and "hang time" of various sized droplets produced after a sneeze, utilizing the identical strategies as ballistics experts learning gunfire. As many as forty,000 droplets may be launched in a single sneeze, some traveling at over 200 miles an hour. Heavier droplets (seen within the photo) succumb to gravity and fall rapidly, whereas smaller droplets (less than 50 m in diameter) can stay within the air until the droplet dehydrates. Alimentary Tract the alimentary tract is one other major web site of viral invasion and dissemination (Table 2. Virus particles that infect by the intestinal route should, at a minimal, be immune to extremes of pH, proteases, and bile detergents. Like the pores and skin, the intestine has numerous bodily, chemical, and protein-based barriers that collectively restrict viral survival and infection: the stomach is acidic, the intestine is alkaline, and proteases and bile detergents are present at excessive concentrations. In addition, mucus traces the complete tract, and the luminal surfaces of the intestines comprise antibodies and phagocytic cells. Moreover, the small and enormous intestines are coated in a thick (50- m) paste of symbiotic micro organism that not solely aids in digestion and homeostasis but in addition imposes a formidable physical barrier for virus particles to entry the cells beneath (Box 2. Consequently, each our eukaryotic defenses and the commensal bacteria that occupy the small gut could be obstacles to viral infection. In many cases, nevertheless, commensal micro organism actually facilitate viral infection of the host. For example, when the intestinal microbiota of mice was depleted with antibiotics before inoculation with poliovirus, an enteric virus, the animals were discovered to be less prone to disease. Further investigation showed that poliovirus binds lipopolysaccharide, the most important outer element of Gram-negative micro organism, and publicity of poliovirus to micro organism enhanced host cell association and infection. Furthermore, three different unrelated enteric viruses, reovirus, mouse mammary tumor virus, and murine norovirus, also have enhanced an infection in the presence of intestinal bacteria. These outcomes indicate that interactions with intestinal microbes promote enteric virus infection. Commensal microbes and interferon-lambda determine persistence of enteric murine norovirus an infection. Intestinal microbiota promote enteric virus replication and systemic pathogenesis. Untreated mice Antibiotic-treated mice Bacteria Virus particle Gut lumen Poliovirus replica Poliovirus pathogenesis Poliovirus replica Poliovirus pathogenesis Gut lumen 34 Chapter 2 Saliva in the mouth presents an initial obstacle to virus entry. While saliva is generally water, it does comprise lysozymes and other enzymes which assist in the breakdown of meals but additionally can destabilize viral particles. One kind of antibody found in saliva, secretory IgA (Chapter 4), may directly bind and inactivate incoming viral particles. While passage from the mouth to the abdomen is generally thought-about a fast journey following a swallow, cells in the oropharynx (for instance, the tonsils and the back of the throat) appear to be permissive for human papillomaviruses, which can cause oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Papillomaviruses, historically thought to be restricted to the genitourinary or urogenital tract, are probably delivered to the throat during oral intercourse and may affect each men and women, as both semen and vaginal secretions can carry infectious papillomavirus particles. Once in the abdomen, a virus particle should endure stomach acid, which typically has a pH of 1. Mucus can also be abundant in the stomach, where it coats the liner and helps to prevent the highly corrosive gastric acid from attacking the stomach itself. Mucus also serves as a trap for virus particles, much as within the respiratory tract. This brush border, along with a surface coat of glycoproteins and glycolipids and the overlying mucus layer, is permeable to electrolytes and vitamins however presents a barrier to microorganisms. Once in the small intestine, pathogens can be attacked by small antimicrobial peptides known as defensins, that are secreted by Paneth cells. These cells, which lie at the base of the microvillus crypt, secrete large granules filled with enteric alpha-defensins, also referred to as cryptdins. These small (30-amino-acid) peptides serve primarily to inactivate bacteria by destabilizing the bacterial cell wall or by interfering with bacterial metabolism. Recently, a job of those small peptides in antiviral defense has also been demonstrated. While a broadly held view is that defensins exert their antimicrobial capabilities by disrupting lipid membranes, research with viruses, together with nonenveloped viruses with no lipid coat, reveal more-diverse features of these peptides, together with adverse results on viral entry and motion to the nucleus. Defensins really promote the infection of some viruses, corresponding to human immunodeficiency virus sort 1 and human adenovirus, likely by rising attachment of the virus particles to their cellular receptors. Each is shaped by totally different cell types that are organized by cell-cell adhesion within an extracellular matrix. A part of the epithelium has been enlarged, and a typical M cell is shown surrounded by two enterocytes. Lymphocytes and macrophages move out and in of invaginations on the basolateral facet of the M cell. Despite the formidable obstacles, some viruses reproduce extensively in intestinal epithelial cells. Scattered all through the intestinal mucosa are lymphoid follicles which are lined on the luminal side with a specialised follicle-associated epithelium consisting primarily of columnar absorptive cells and M (membranous epithelial) cells. The M cell cytoplasm could be very skinny, leading to a membrane-like bridge that separates the intestinal lumen from the subepithelial space. It is thought that M cell transcytosis is the mechanism by which some enteric viruses acquire entry to deeper tissues of the host. After crossing the mucosal epithelium, a virus particle could enter lymphatic vessels and capillaries of the circulatory system, facilitating unfold within the host. After attaching to the M cell floor, reovirus subviral particles are transported to cells underlying the lymphoid follicle, where the virus is reproduced and then spreads to other tissues. In some instances, the hostile environment of the alimentary tract actually facilitates infection. For instance, reovirus particles are transformed by host proteases within the intestinal lumen into infectious subviral particles, the form that subsequently infects intestinal cells. Human immunodeficiency virus may be introduced efficiently on account of anal intercourse. Anal intercourse may cause abrasions inside the rectum, stripping away the protecting mucus and damaging the epithelial lining, resulting in damaged capillaries. Human immunodeficiency virus particles can pass by way of such broken epithelia to acquire entry to the blood for environment friendly transport to lymph nodes, where an infection and reproduction can ensue. Once in the follicle, the virus can infect migratory lymphoid cells and spread throughout the physique. Approximately one in six folks between 15 and 50 years of age has genital herpes, and as this can be a lifelong an infection, the danger of transmission to future intercourse companions is excessive.
Generic glucophage sr 500mg onlineThe particles formed by fusion of wrapped virus particles with the plasma membrane stay cell related due to a exceptional exercise: they induce an extra dramatic reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton just under the positioning of fusion symptoms 6 days after iui order 500 mg glucophage sr amex. This conundrum led to the early proposal that the crescent membrane is synthesized de novo from cellular lipids 300 medications for nclex buy glucophage sr 500mg on-line. Furthermore symptoms vitamin d deficiency glucophage sr 500 mg on line, when a heterologous signal sequence was added to the N terminus of A9 treatment bacterial vaginosis generic glucophage sr 500 mg, the signal sequence was cleaved Cryo-electron tomography of vaccine virus-infected HeLa cells showing a 0. Repression of L2 synthesis resulted in full inhibition of vaccinia virus replica and meeting of mature virus particles. Some immature virus-like particles did assemble but contained significantly reduced quantities of several viral membrane proteins. Existence of an operative pathway from the endoplasmic reticulum to the immature poxvirus membrane. Analysis of viral membranes shaped in cells contaminated by a vaccinia virus L2 deletion mutant suggests their origin from the endoplasmic reticulum. J Virol 87:1861�1871 A B the black arrows indicate the ends of the crescent membrane that sometimes curl away from the coated scaffold area, and the white arrows the small membrane curls which are seen near patches of the scaffold protein. In the right panel, the crescent membrane and scaffold have been rendered in green and red, respectively. Viral particles hooked up to the tips of actin tails are propelled by the polymerization of actin on the front finish of the tail and its depolymerization at the back end. Formation of actin tails in vaccinia virus-infected cells requires the same viral protein (A36) that enables transport of wrapped virions along microtubules. The viral envelope is acquired upon budding of tegument-containing structures into compartments of the trans-Golgi network. Virus particles fashioned on this means are thought to be transported to the plasma membrane in secretory transport vesicles and released upon membrane fusion, as illustrated. The reactions are illustrated in the electron micrographs of cells contaminated by the alphaherpesvirus pseudorabies virus. Mettenleiter, Federal Research Center for Virus Diseases of Animals, Insel Riems, Germany. Many viral genomes reach the nucleus by the use of nuclear pore complexes (Chapter 5). Toward the tip of infectious cycles, progeny genomes of a quantity of viruses, including influenza viruses and retroviruses, are exported to the cytoplasm by way of these buildings, whereas particles that full assembly in the nucleus (for example, adenoviruses and polyomaviruses) escape that organelle upon destruction and lysis of the host cell. When initially discovered, nuclear budding of newly assembled nucleocapsids of alphaherpesviruses was a virus-specific mechanism with no counterpart in uninfected cells. Binding of Wnt to its receptor, Drosophila frizzled-2 (Dfz2), on a postsynaptic cell induces endocytosis of the receptor, its cleavage, and import of the C-terminal segment (Dfz2C) into the nucleus. Like budding of herpesviral nucleocapsids, formation of Dfz2C-containing granules and invaginations of the inside nuclear membrane require protein kinase C and phosphorylation of lamins. A budding mechanism could be necessary for export of very massive constructions, be they ribonucleoprotein granules or viral assemblies. Nuclear envelope budding allows giant ribonucleoprotein particle export during synaptic Wnt signaling. Such granules have been noticed shifting away from the nucleus during time-lapse imaging. Human cells mock infected or contaminated with herpes simplex virus 1 for sixteen h were examined by oblique immunofluorescence. The surfaces of these vesicles are sites of genome replication and meeting (top). It has been proposed that as autophagosome-like vesicles are formed from these membranes later in infection, they enclose virus particles. Maturation of such particle-containing vesicles in a manner analogous to the maturation of autophagosomes would lead to full or partial degradation of the inside membrane. Subsequent fusion of the mature vesicle with the plasma membrane would launch virus particles. Virus particles released from hepatocytes contaminated in tradition have been found to be enclosed within membrane vesicles that carried 1 to four particles. Such membrane-enclosed particles were also noticed within the blood of people affected by hepatitis A virus an infection. These particles are infectious and proof against inhibition by neutralizing antibodies. It has therefore been proposed that hepatitis A virus particles bud into multivesicular our bodies upon interaction of the capsid with such proteins. Such processing performs an essential part in the mechanisms by which most infectious retroviruses are assembled and launched. Efficient and orderly meeting additionally depends on "spacer" peptides which are removed during proteolysis. It is therefore impossible that retrovirus particles could be constructed appropriately from mature Gag proteins. Indeed, alterations that improve the catalytic exercise of the viral protease inhibit budding and production of infectious particles, indicating that premature processing of the polyproteins is detrimental to meeting. Such covalent linkage additionally precludes environment friendly exercise of virion enzymes, which are incorporated as Gag-Pol polyproteins. These two cryo-electron micrographs present the maturation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 virus particles. Alteration of amino acids on this interface inhibits core meeting and formation of infectious viral particles in infected cells, according to this mannequin. The retroviral proteases belong to a large household of enzymes with two aspartic acid residues on the energetic site (aspartic proteases). The viral and cellular members of this household are related in sequence, particularly across the active web site, and are additionally comparable in three-dimensional construction. All aspartic proteases include an active site shaped between two lobes of the protein, each of which contributes a catalytic aspartic acid. The retroviral proteases are homodimers in which every monomer corresponds to a single lobe of their mobile cousins. Consequently, the lively web site is fashioned solely upon dimerization of two equivalent subunits. This property undoubtedly helps keep away from untimely activity of the protease within contaminated cells, by which the low focus of the polyprotein precursors mitigates in opposition to dimerization. Indeed, dimerization of the protease appears to be price limiting for maturation of virus particles. Consequently, synthesis of the protease as a part of a polyprotein precursor not only allows incorporation of the enzyme into assembling particles but in addition contributes to regulation of its exercise. These properties raise the question of how the protease is activated, a step that requires its cleavage from the polyprotein. It is subsequently thought that such activity of the polyproteins initially releases protease molecules inside the particle. Furthermore, it has been proven, utilizing Gag-Pol proteins yielding distinguishable cleavage merchandise, that the preliminary proteolytic cleavages are intramolecular.
Aster helenium (Elecampane). Glucophage SR. - Coughs, asthma, bronchitis, nausea, diarrhea, worms which infest the gut (hookworm, roundworm, threadworm, and whipworm), and other conditions.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- What is Elecampane?
- How does Elecampane work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Dosing considerations for Elecampane.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96052
Purchase glucophage sr 500mg without prescriptionHistologic Features Silicatosis is characterised by the perivascular and peribronchiolar deposition of birefringent silicate particles treatment 3 phases malnourished children purchase 500mg glucophage sr otc, mendacity within variably sized collagen deposits permatex rust treatment discount 500mg glucophage sr mastercard. There are six completely different lesions which might be present: macules medications 2355 cheap glucophage sr 500 mg visa, nodules treatment non hodgkins lymphoma buy glucophage sr 500 mg without a prescription, fibrosis, and mud deposits inside bronchiolar walls, overseas physique granulomas, interstitial fibrosis, and massive fibrosis. Silicate nodules are hard, fibrotic nodular lesions measuring 2 to 10 mm, generally discovered within the higher and middle lung zones. Fibrosis and dirt deposits might happen within the partitions of membranous (terminal) bronchioles, respiratory bronchioles, and alveolar ducts; they symbolize a type of mineral dust�induced small airway illness. Interstitial fibrosis may be discovered in additional advanced illness and exhibits interstitial pneumonia with fibrosis with plentiful dust particles, with or with out big cells. Massive fibrosis is seen in advanced silicatosis and is characterised by marked fibrosis, likely as a end result of nodule coalescence, with innumerable mud particles; there could additionally be related pleural thickening. Smith Mixed pneumoconiosis and mixed-dust pneumoconiosis are characterised by macules or fibrotic lesions, which can or could not have accompanying silicotic nodules, with a clinical history of mixed-dust exposure. Mixed pneumoconiosis has distinctive histologic options of two separate pneumoconioses, similar to asbestosis, with its characteristic pattern of fibrosis and asbestos our bodies, and silicosis, with its characteristic silicotic nodules. Exposure to silicates contaminated with silica, for instance, may produce pulmonary lesions that are neither silicotic nodules nor pure silicate nodules, but as a substitute a hybrid lesion. Patients present generally with dyspnea and cough and show variable pulmonary operate check outcomes. Prognosis can be variable, with some sufferers relatively unaffected and others progressing to end-stage lung illness and finally death. Varying combos of macules, mixed-dust fibrotic nodules, and silicotic nodules. Mixed-dust fibrotic nodules are often stellate, "medusa head" lesions with central whorled hyalinized collagen and surrounding collections of dust-laden macrophages that extend into lung parenchyma. Silicotic nodules are agency discrete round lesions of paucicellular whorled hyalinized collagen. Polarized mild shows birefringent needles of crystalline silica, in addition to birefringent plates of silicates. Smith Coal dust is predominantly made up of noncrystalline carbon, in addition to varying quantities of quartz (crystalline silica), mica, and kaolin. Patients could also be asymptomatic; nonetheless, sufferers with progressive massive fibrosis may have extreme dyspnea and hypoxemia, may progress to cor pulmonale, and may die of disease. The amount of quartz making up the coal dust varies among coal types and significantly results the diploma of lung change. Coal mud nodules are primarily a mix of coal mud and quartz silica and, therefore, a lesion of mixed-dust pneumoconiosis. The amount of quartz silica current determines the quantity of hyalinized collagen current in the coal dust nodule. Coal mud nodules could additionally be additional divided into micronodules (up to 7 mm) and macronodules (7 to 2 cm). With superior disease, progressive massive fibrosis happens, with confluent areas of fibrosis 2 cm and larger, and is seen predominantly within the upper lung lobes. If the confluent areas present cavitation, concomitant tuberculosis should be thought of. Differential diagnosis consists of cigarette-related 1317 and environment-related anthracotic pigment deposition. Histologic Features Aggregates of dust-laden macrophages with little attendant fibrosis, termed coal dust macules, are seen predominantly in the higher lung lobes, with associated focal emphysema. Coal mud macules lie inside the partitions of respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, and adjacent alveoli. Fibrotic nodules containing dust-laden macrophages, termed coal dust nodules, evolve from coal mud macules and may be found in respiratory bronchioles. Coal dust nodules could show a central area made up of whorls of dense hyalinized collagen, with surrounding dust-laden macrophages, imparting a "medusa head" appearance to the nodule. Coal dust nodules can also be found within the interlobular septa and in peribronchial and subpleural connective tissue. Coal dust nodules are often seen in affiliation with coal mud macules; each are predominantly discovered within the higher lung lobes. Smith Giant-cell interstitial pneumonia is the histologic correlate of the scientific analysis of hard-metal pneumoconiosis. Patients inhale exhausting metals, usually cobalt, occupationally, in industries such because the alloy and ceramics industries, and tool, drilling gear, and armament manufacturing industries. Patients present with rising dyspnea and are found to have restrictive changes and small lung volume by pulmonary function testing. Occupational historical past and testing by way of analytic electron microscopy, energy-dispersive x-ray elemental evaluation, or different methods help within the correct analysis of giant-cell interstitial pneumonia. Multinucleated large cells in alveoli, containing as a lot as 20 to 30 nuclei, are a attribute finding. Smith Pulmonary siderosis, typically a disease of iron foundry workers, welders, steel mill staff, and miners, is characterised by the buildup in lung parenchyma of exogenous iron particles. Iron is minimally fibrinogenic and has been termed an inert mineral; siderosis sufferers typically could additionally be asymptomatic even while displaying radiologic modifications of pulmonary fibrosis. Even so, extremely heavy exposures to iron could trigger small airway fibrosis and fibrous nodules. In comparability, silicosiderosis, attributable to office exposure to each iron and silica, is a mixed-dust pneumoconiosis. In other mixed-dust pneumoconioses, iron may be current but contribute little to the illness clinically. Differential analysis, aside from silicosiderosis and different mixed-dust pneumoconioses, is continual passive congestion. Chronic passive congestion exhibits giant numbers of hemosiderin-laden macrophages in airspaces. Although each iron deposits and hemosiderin stain positively with iron stain similar to Prussian blue, solely iron deposits show the black to darkish brown facilities within the pigment deposits and the golden halo surrounding them. Histologic Features Peribronchiolar and perivascular iron pigment deposition is attribute of siderosis. Iron, which is generally iron oxide, reveals an oval to spherical, reddish brown to reddish black dust in lung parenchyma. Macules, made up of perivascular and peribronchiolar deposits of iron, iron-laden macrophages, and ferruginous our bodies, with little fibrotic response, might happen. Nodules, made up of parenchymal deposits of iron, iron-laden macrophage, and ferruginous our bodies, with little fibrotic response, may be seen. In patients with silicosiderosis, elevated fibrosis with regularly dense hyalinized collagen is seen.
Purchase glucophage sr 500 mg otcHistologic Features Historic options of chronic lung illness of prematurity (bronchopulmonary dysplasia) medications like prozac buy glucophage sr 500 mg lowest price, including alternating areas of lung collapse and overexpansion treatment xerophthalmia cheap glucophage sr 500mg overnight delivery, are hardly ever seen within the era of surfactant administration treatment yeast glucophage sr 500 mg amex. Chronic lung disease of prematurity now usually presents with uniform alveolar simplification and enlargement medicine jobs effective glucophage sr 500mg. Although fibrosis is often scant, small clean muscle bundles usually extend into the alveolar walls. Secondary pulmonary hypertensive adjustments are common, with muscularization of arterioles and muscular hypertrophy of pulmonary arteries. Interstitial Emphysema Interstitial emphysema is most commonly seen in ventilated preterm infants, though it could rarely happen in full-term infants. Histologic Features Air rupture into the interstitial connective tissue of the bronchovascular bundles create areas unlined by endothelium or epithelium. In cases of persistent interstitial emphysema, foreign body�type large cells might partially line the airspaces. Although most of the alveolar septa are thin, patchy pulmonary interstitial glycogenosis was present. Husain Only a small subset of infants born with meconium-stained amniotic fluid develop meconium aspiration syndrome characterised by respiratory distress and, in extreme instances, by pulmonary hypertension. The pathogenetic mechanisms may embody airway obstruction, inflammation, inactivation of surfactant, and pulmonary hypertension. The analysis is usually made clinically, but biopsy could additionally be performed to rule out different causes of pulmonary hypertension within the newborn. Chronic intrauterine meconium aspiration has been reported to cause infarcts and granulomatous inflammation. This could hardly ever be a major disorder, which can be generalized or confined to the lungs, however is more generally seen secondary to congenital heart disease. Lymphangiectasia could additionally be a element of other issues of the lung, similar to sequestrations or congenital pulmonary airway malformations. In distinction, lymphangiomatosis refers to elevated, abnormally anastomosing lymphatic spaces within the bronchovascular bundles and pleura. Histologic Features Distended lymphatics are present in bronchovascular bundles and within the pleura. Artifactual dilation of lymphatics can be produced by perfusion of the lung even through the airways, and care ought to be taken in making this prognosis. Lymphangiomatosis has elevated, abnormally anastomosing channels in the pleura and septa. Lymphangioma is a localized vascular malformation with a regional increase in number. The dilated areas are surrounded by an endothelial lining without muscle within the wall (B). Husain Jennifer Pogoriler Juvenile respiratory papillomatosis often presents in young kids with hoarseness. Papillomas mostly involve the larynx and often recur requiring multiple surgical procedures. Rarely, the papillomas might extend to the decrease respiratory tract, including the alveoli the place they develop alongside the alveolar floor. Histologic Features Squamous papillomas are usually confined to the upper airways, and lung involvement is uncommon. This was the 25th excision on the age of 10 years (B), larger power of which shows solely mild dysplasia (C). His disease progressed to involve the lungs grossly seen right here at autopsy at the age of thirteen years (E). These patients are essential to determine because of the risk of different tumor growth in themselves or affected family members. There is an abrupt transition from adjacent regular lung to cystic 1461 spaces composed of variably skinny septa. The collapsed cyst has a variably thick fibrous wall (B) lined by flattened to cuboidal epithelium (C). Mesenchymal cells are condensed under the epithelium with clear skeletal muscle differentiation (B and C). Husain Primary lung tumors in kids are uncommon and mostly embody inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor, carcinoid tumor, and salivary gland�type carcinomas. Other tumors which will occur in kids as primary lung tumors embrace leiomyoma, myofibroma, and synovial sarcoma and have the same histologic options as elsewhere within the physique. Infantile hemangioendothelioma may present in infants as a bronchial mass with options just like these seen in the skin and subcutaneous tissue of the top and neck. Fetal lung interstitial tumor and congenital peribronchial myofibroblastic tumor are tumors which are particular to the pediatric lung. Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor Histologic Features Most widespread primary lung tumor in kids. Nodular assortment of spindled cells with variable quantities of admixed inflammatory cells. Congenital Peribronchial Myofibroblastic Tumor As the name suggests, this rare entity has been diagnosed in perinatal or neonatal patients. Previously this was known as congenital leiomyosarcoma or congenital fibrosarcoma; mortality may be excessive owing to the size of the tumor and development of cardiac failure and hydrops in the fetus. However, in patients who survive to resection, malignant conduct has not been reported. Histologic Features Mass fashioned by sheets of spindled cells in fascicles, usually with intensive cartilaginous plates. Degree of proliferation and differentiation might range with the stage of growth. Fetal Lung Interstitial Tumor this rare tumor presents prenatally or within the first few months of life. Variably sized airspaces with thickened septa stuffed by bland ovoid cells with clear cytoplasm. Cytoplasm is periodic acid�Schiff positive/diastase delicate, consistent with glycogen. Infantile Hemangioendothelioma Histologic Features Rare benign tumor often associated with the large airways. Similar histology to tumors more commonly seen in the skin and liver: small vessels with plump endothelium. Synovial Sarcoma Histologic Features Synovial sarcoma can rarely current as a pleural mass in kids or young adults and, in a cystic kind, may cause spontaneous pneumothorax. At low power, a mixture of mobile however well-differentiated cartilage and spindled cells are seen (B and C), though in comparatively completely different quantities in several areas of the tumor. The spindled cells and cartilaginous areas are cellular, however the nuclei are low grade.

Order 500 mg glucophage sr amexEarly modifications embrace edema medicine 035 cheap 500mg glucophage sr with amex, reactive pneumocytes medicine 8 soundcloud buy glucophage sr 500 mg visa, and treatment tinea versicolor order 500 mg glucophage sr amex, if severe symptoms ulcer 500 mg glucophage sr visa, hyaline membranes. It could also be seen in patients recovering from acute rejection, infection, or another harm to the transplanted lung. The primary differential prognosis is from bronchiolitis obliterans, which is dense scar tissue (mature collagen) in the submucosa of small airways. Histologic Features Organizing pneumonia within the transplanted lung is similar to that seen in the nontransplant setting. There are intra-alveolar plugs of free myxoid fibrous tissue (Masson bodies), which can have few inflammatory cells, similar to macrophages, lymphocytes, and plasma cells. Husain Most posttransplant lung biopsies are performed either as rejection surveillance or to consider symptoms suggestive of an infection or rejection. Several different pathologies may be current, which need to be thought of in the differential analysis. It is a localized assortment of mature small lymphocytes, typically with a number of capillaries, and may have anthracotic pigment or hemosiderin in it. Small poorly shaped granulomas with multinucleated large cells or intra-alveolar foreign body�type big cells are highly suggestive. Neutrophils may be current in alveoli or inside bronchial and bronchiolar epithelium, with or with out other inflammatory cells. Kaposi sarcoma is characterised by a spindle-cell proliferation with extravasated red blood cells. The incidence varies from 1% (in renal transplant patients) to 5% (in intestinal and lung transplant patients). Husain In any immunocompromised host, including other organ and stem cell transplant recipients, the lungs are susceptible to an infection with each opportunistic and nonopportunistic organisms as described in the sections on an infection. Histologic Features Morphology of infection is dependent upon the type of an infection and host response. Note the in depth bacterial progress, especially around blood vessels, with no inflammatory response in the lung. There is whole occlusion of the bronchiolar lumen by granulation tissue and fibrosis. Correlations have been noticed between the pattern of interstitial lung disease and the underlying analysis. The type and severity of signs attributable to lung involvement reflect the sample of disease; widespread options embody persistent cough and dyspnea. In follicular bronchiolitis, hyperplastic lymphoid tissue impinges on bronchioles and terminal airways, typically resulting in small airways obstruction by pulmonary perform testing and air trapping visible on chest computed tomography (see also Chapter 51). Rheumatoid nodules are generally asymptomatic, but their multifocal, well-circumscribed character can mimic metastatic illness radiographically, triggering lung biopsy to rule out malignancy (see additionally Chapter 57). The pleura seems fibrotic with granulation tissue formation, most evident on the top of the image. The sampled lung is diffusely and homogenously infiltrated by persistent inflammatory cells, and the pulmonary arteriolar partitions are significantly thickened because of medial hyperplasia. Airspace calcifications are seen, doubtless representing aggregated endogenous mobile breakdown merchandise. Numerous lymphoid follicles are evident on the interface of the fibrosis and preserved lung. Chest computed tomography showed an idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis sample of lung involvement. Larsen Amiodarone is a standard antiarrhythmic agent and can be regularly used in congestive coronary heart failure and ischemic heart disease to forestall sudden cardiac dying. While the chance of toxicity is immediately associated to the dose and duration of therapy, pulmonary toxicity might occur even with small doses and quick remedy duration. Likewise, no particular laboratory findings are diagnostic of amiodarone lung disease, and the diagnostic workup often contains analysis of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and/or lung biopsies. Even when characteristic options are seen microscopically, not considered one of the histologic options are particular for amiodarone toxicity, and clinicopathologic correlation is important, as with all therapeutic drug reactions. Cytologic Features Abundant finely vacuolated foamy macrophages, a feature simply representing exposure to the drug and not indicating toxicity in and of itself, usually accompanied by other mixed inflammatory cells. Histologic Features Organizing pneumonia with plentiful intra-alveolar foamy macrophages. Chronic interstitial pneumonitis with foamy macrophages and variable levels of interstitial fibrosis. Transmission Electron Microscopic Features Alveolar macrophages with lamellar inclusions. Differential Diagnosis the histologic features of amiodarone lung toxicity are nonspecific and a big selection of other processes enter the differential prognosis. If diffuse alveolar injury or organizing pneumonia is seen, an infectious etiology must be considered, including careful evaluation for viral inclusions and special stains for viruses and fungal organisms as acceptable, in addition to microbiologic cultures. Other concerns may embody systemic connective tissue diseases, which can present identical patterns of harm. If significant chronic small airway pathology, mucostasis, or peribronchiolar metaplasia is current, the potential of secondary lipid accumulation from small airways obstruction should be thought-about because the cause for foamy macrophage accumulation. Congestive coronary heart failure can even result in macrophage accumulation in airspaces, though these macrophages are often 1221 frivolously pigmented. Although not shown right here, these nodular lesions may even undergo central necrosis in some cases. Larsen Methotrexate is a folic acid antagonist that results in impaired synthesis of nucleic acids, thereby lowering cellular proliferation. These antiproliferative results are helpful for treating not solely quite a lot of malignancies but in addition a multitude of autoimmune and inflammatory disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis. Serious unwanted effects of methotrexate include hepatic, pulmonary, and bone marrow toxicity. Although pulmonary toxicity most commonly happens after continual low-dose therapy, it might possibly also happen acutely, particularly when higher doses are utilized. Clinical manifestations are varied, and methotrexate pneumonitis can current with a wide selection of nonspecific pulmonary and systemic signs. Although most cases current in a subacute style, some sufferers could present with rapidly progressive acute respiratory failure that can be life-threatening. No specific medical features or laboratory tests can be found to diagnose methotrexate pneumonitis, and the prognosis could be notoriously difficult to establish and requires a high index of medical suspicion. Histologic Features Granulomatous interstitial pneumonia, with scattered giant cells and small poorly fashioned, nonnecrotizing granulomas. Differential Diagnosis Depending on the medical situation, the differential analysis of methotrexate pneumonitis sometimes includes an infection associated to immunosuppression, exacerbation of an underlying connective tissue illness, and reactions to other drugs. Evaluation should always embrace a cautious seek for proof of infection, similar to viral inclusions or distinguished neutrophilic irritation, and particular stains for microorganisms also wants to be carried out when patterns of acute injury.
Order glucophage sr 500mg fast deliveryMature particles are produced upon cleavage of the precursor proteins listed to the best of the younger particle treatment 4th metatarsal stress fracture generic glucophage sr 500mg with amex. The area of the genome containing the enhancer symptoms 4 dpo bfp generic 500mg glucophage sr fast delivery, origin of replication (Ori) medicine 95a pill purchase 500 mg glucophage sr amex, and packaging signal is shown treatment 4 addiction discount glucophage sr 500mg otc, with positions (base pairs) within the round genome indicated beneath. The Sp1-binding sites inside the packaging sequence are required for genome packaging. Although the mobile genome incorporates many such binding sites, the particular arrangement of sequences acknowledged by Sp1 in the viral packaging sign is exclusive. The observation that this mobile protein stimulates the in vitro meeting of infectious virus particles by an order of magnitude is in maintaining with a task in mediating indirect recognition of the packaging sign by capsid proteins. Subsequently, extremely cooperative interactions among the structural items seem to drive the concerted meeting of the capsid, concomitantly with displacement of Sp1 and nonspecific binding of capsid proteins to viral minichromosomes. The products of a minimum of seven herpes simplex virus 1 genes are dedicated to encapsidation of the viral genome. This unusual property is thought to assist retroviruses survive intensive damage to their genomes (Chapter 7). It has therefore been suggested that one operate of this protein is to stabilize the protein shell so that it can withstand the stress exerted by the encapsidated genome. Sequences essential for packaging of retroviral genomes, termed psi, vary significantly in complexity and site. These models had been confirmed by various observations, together with the outcomes of site-directed mutagenesis. The mounted dimensions of the closed icosahedral capsids or nucleocapsids of many viruses impose an upper restrict on the scale of viral nucleic acid that can be accommodated. The specificity with which the viral genome is included into assembling structures may also be the outcome of the coupling of encapsidation with its synthesis. It was deduced from these properties that the T4 genome is circularly permuted and terminally redundant. Furthermore, when sequences are deleted from, or inserted into, the genome, the size of the terminal repeats will increase or decreases to the corresponding diploma. It has been appreciated for a number of years that formation of an infectious virus particle requires incorporation of no less than one copy of every of the eight genomic segments. Packaging of the bacteriophage 6 genome offers clear precedent for a selective mechanism. Nevertheless, it has become clear within the last decade that the packaging of influenza virus genome segments is selective. These sequences comprise the brief 5 and 3 noncoding areas of each section but prolong brief distances into adjoining coding regions. Purified influenza A virus particles had been examined by scanning transmission electron tomography. In most circumstances, the precursors to these enzymes are synthesized as C-terminal extensions of the Gag polyprotein. The low effectivity with which Gag-Pol polyproteins are translated determines their concentrations relative to Gag within the cell and in virus particles (1:9). Hybridization with a mix of Cy3- and Cy5-labeled probes towards a single phase established that the efficiency of colocalization was high (see the figure). The copy number of each phase in viral particles was examined by using photobleaching. These experiments provided compelling evidence for selective and efficient packaging of all the parts of this segmented genome in every virus particle. As illustrated in the merged picture, the nice majority (90%) of particles are labeled with both probes (right). Enveloped viruses assemble by certainly one of two mechanisms, distinguished by whether or not acquisition of the envelope follows assembly of internal buildings or whether or not these processes happen simultaneously. Acquisition of an Envelope the formation of many types of virus particle requires envelopment of capsids or nucleocapsids by a lipid membrane carrying viral proteins. Most such enveloped viruses assemble by advantage of particular interactions amongst their elements at a cellular membrane before budding and pinching off of a brand new virus particle. Whether particles assemble at the plasma or an inside membrane is set by the destination of viral proteins that enter the Sequential Assembly of Internal Components and Budding from a Cellular Membrane the assembly of the internal buildings of most enveloped virus particles and their interplay with a cellular membrane modified by insertion of viral proteins are spatially and temporally separated. In sort I budding, exemplified by alphaviruses, corresponding to Sindbis virus, each the envelope glycoproteins and the interior capsid are important. These observations point out that lateral interactions among the many envelope heterodimers, in addition to these of the heterodimers with the capsid, cooperate to drive budding. For instance, in the case of rhabdoviruses and orthomyxoviruses, internal matrix proteins alone can drive budding. However, this process is inefficient or ends in deformed or incomplete particles in the absence of envelope glycoproteins or the internal ribonucleoprotein. The M1 protein interacts with each viral nucleocapsids and the inner surface of the plasma membrane to direct the assembly of progeny particles at that membrane. The cellular membranes destined to type the envelopes of virus particles comprise viral integral membrane proteins that play essential roles within the attachment of virus particles to , and their entry into, host cells. The crucial function and specificity of these interactions within the last steps in assembly are illustrated by the failure of a chimeric Sindbis virus containing the coding sequence for the E1 glycoprotein of a special togavirus to bud efficiently. The heterodimeric glycoproteins (E1 plus E2) are shaped and transported to the plasma membrane. However, these chimeras exhibit an altered conformation and fail to bind to nucleocapsids at the plasma membrane. Binding of viral glycoproteins to inside components also appears to be essential for the manufacturing of structurally extra complicated enveloped viruses. Coordination of the Assembly of Internal Structures with Acquisition of the Envelope the choice pathway of acquiring an envelope, in which assembly of internal buildings and budding from a mobile membrane are largely coincident in house and time, is exemplified by many retroviruses. Assembling cores of the majority first seem as crescent-shaped patches on the internal floor of the plasma membrane. Specific segments of Gag mediate the orderly association of polyprotein molecules with one another and are required for correct meeting. Certain sequences present only in the Gag polyprotein also govern morphology, for their removing leads to the meeting of misshapen particles. Such GagEnv interactions guarantee specific incorporation of viral glycoproteins into virus particles. Nor can a mannequin based mostly solely on Gag-Env interactions account for the convenience with which "international" viral and mobile glycoproteins are included within the envelopes of all retroviruses. However, replica of such viruses more generally ends in destruction (lysis) of the host cell. Large portions of assembled virus particles may accumulate within infected cells for hours, and even days, prior to their launch. Assembly and Budding on the Plasma Membrane the discharge of enveloped virus particles from the plasma membrane is an intricate course of that includes induction of membrane curvature by viral parts (bud formation), bud development, and fusion of the membrane (scission) to liberate virus particles. As mentioned in the previous part, interactions among inside viral proteins and the membrane (and/ or viral glycoproteins within it) induce membrane curvature and bud formation. It was therefore concluded that these Gag sequences are required for the fusion reaction that separates the viral envelope from the plasma membrane. Subsequently, functionally analogous sequences, termed late-assembly (L) domains, have been identified in Gag proteins of several other retroviruses.
References - Lichtenstein IH, MacGregor RR. Mycobacterial infections in renal transplant recipients: report of five cases and review of the literature. Rev Infect Dis. 1983;5(2):216-226.
- Knox R, Steinthorsson G, Sumpio B: Celiac artery aneurysms: A case report and review of the literature. Int J Angiol 9:99, 2000.
- Richardson SK, Lin JH, Vittorio CC, et al. High clinical response rate with multimodality immunomodulatory therapy for Sezary syndrome. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma 2006;7:226-32.
- Boulet LP, FitzGerald JM, Levy ML, et al. A guide to the translation of the Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) strategy into improved care. Eur Respir J 2012; 39: 1220-1229.
- Deng, D., Rutman, M., Raz, S., Rodriguez, L.V. Presentation and management of major complications of midurethral slings: Are complications under-reported? Neurourol Urodynam 2007;26:46-52.
- Bhoyrul, S., Vierra, M.A., Nezhat, C.R., Krummel, T.M., Way, L.W. Trocar injuries in laparoscopic surgery. J Am Coll Surg 2001;192:677-683.
|


