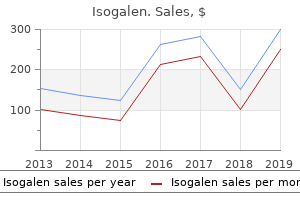
Isogalen
Shomoukh AlShamekh, M.D. - Cole Eye Institute
- Cleveland Clinic
- Cleveland, Ohio
Buy cheap isogalen 30mgLow doses of aspirin block platelet thromboxane A2 synthesis acne quitting smoking quality 10 mg isogalen, which outcomes in skin care guide isogalen 20 mg sale lowered platelet aggregation and blood viscosity skin care juarez isogalen 10 mg otc. It occurs when the heart receives poor oxygen because of blood vessel narrowing skin care tips for winter isogalen 20mg line, which ends up primarily from growing older and also from cigarette smoking, excessive cholesterol levels, weight problems, and diabetes. The 3 types are secure angina (exertional or typical angina), caused by atherosclerosis, with treatment to cut back cardiac load and improve myocardial blood circulate; vasospastic angina (variant or Prinzmetal angina), attributable to extreme coronary vessel contraction, with chest pain at relaxation and medicines aimed to cease vasospasm; and unstable angina (crescendo angina), during which pain occurs without stress. Nitrates and blockers are used, as are calcium channel antagonists if the mechanism is vasospasm. Reducing platelet perform and thrombotic episodes helps decrease mortality in unstable angina. Another group of brokers, organic nitrites (eg, amyl nitrite, isobutyl nitrite), contain the nitrite practical group. Sublingual dosing relieves acute attacks, whereas long-acting medicine (oral, transdermal) with a slow onset of motion are used for extended prophylaxis. Loss of nitrate efficacy brought on by tolerance could be reversed by use of sulfhydrylyielding agents similar to N-acetylcysteine. Rupture usually happens in lipid-rich and foam cell-rich peripheral margins and should result in thrombosis and arterial occlusion. Drugs are given long-term to scale back the number of attacks, just before certain activities to forestall acute attacks, and through assaults to relieve pain and strain. Nitroglycerin is more effective than nitroprusside, a similar natural nitrate, in decreasing venous return but is less efficient in expanding arteries. Ca2+ binds to calmodulin in easy muscle and troponin in the coronary heart and affects muscle contraction. Results are unfavorable inotropic (force of contraction), chronotropic (rate), and dromotropic (conduction) effects. Systolic failure is the lack of the ventricle to empty normally; diastolic dysfunction is the shortcoming of the ventricle to fill correctly. Aging, smoking, weight problems, fat, ldl cholesterol, inactivity, viruses, and genetic defects promote heart failure; danger is also elevated by hypertension and diabetes. Accumulation of fatty deposits in coronary heart arteries leads to coronary artery disease. The most common types of heart failure-caused by broken heart muscle-are handled with medicine to enhance quality of life and survival. Glycosides enhance coronary heart contractility and contraction pressure by activating Na+-K+ pumps on coronary heart cells. Blockers corresponding to propranolol are particularly useful for exertional angina however are ineffective in opposition to vasospastic angina. They are utilized in mixture with calcium channel antagonists (eg, dihydropyridines, verapamil, diltiazem), natural nitrates, or each to deal with cardiac symptoms which would possibly be proof against a single drug. Dihydropyridines, however not diltiazem and verapamil, can be utilized in such a combination. Digoxin is the commonest digitalis preparation; digitoxin is used when an extended halflife is required (7 days versus 1-2 days for digoxin). After digitalis restores heart function, its use is sustained to stop recurrence of heart failure. Digitalis could reduce the development price of coronary heart harm in some sufferers, particularly these in whom a rise in end-diastolic pressure and volume will happen. Digitalis reduces sympathetic tone by instantly blunting the baroreceptor response. Medical circumstances (eg, anemia, fever, heart failure, electrolyte imbalance) might cause arrhythmias. Synchronized electrical shock (defibrillation), electronic pacemakers, and radiofrequency ablation are nondrug treatments. If symptomatic and severe (rates 40/min) with nonreversible cause, think about everlasting pacing. No intervention except symptomatic Sinus bradycardia (60 bpm) If asymptomatic, no intervention. If symptomatic and extreme (rates 40/min) with nonreversible trigger, consider short-term pacing. Premature atrial complexes Premature ventricular complexes If asymptomatic, no intervention. Warfarin, an anticoagulant, is used for atrial fibrillation to stop strokeinducing blood clots. The most typical adverse effect of warfarin is bleeding, from mild nosebleed to life-threatening hemorrhage. Antiarrhythmic drugs, such as amiodarone and sotalol, maintain the normal rhythm of the guts. The selective blockers have fewer central adverse effects than nonselective blockers, such as propanolol. Level of blood stress is associated with cardiovascular occasions in a continuous, graded, and apparently impartial trend. This pressure, or blood pressure, is a measure of how much work is required by the guts to push blood by way of the arteries. The 2 numbers used to indicate blood pressure correspond to systole and diastole (eg, 120/80 mm Hg). The systolic (top) number reflects strain of blood towards arterial walls that outcomes from contraction of the heart. The diastolic quantity (bottom) displays arterial blood stress whereas the center is filling and resting between beats. High blood pressure in adults is outlined as a constantly increased blood strain of 140/90 mm Hg or greater. Hypertension is called the "silent killer" because it causes critical complications without apparent signs. Liver Adrenal Medulla Cortex Hypertension Cortical tumor might enhance aldosterone output. Renin substrate (angiotensinogen) Compression of extrarenal or intrarenal vessels promotes output of renin by juxtaglomerular cells. Diuretics have been the main antihypertensive medication for many years and are still thought to be the most effective remedy for AfricanAmerican and elderly patients and the most effective agents for preventing stroke. Thiazides (eg, chlorothiazide, chlorthalidone) are taken alone for reasonable hypertension or utilized in combination with other drug types. Potassium-sparing agents (eg, amiloride, spironolactone) enhance potassium retention by kidneys and increase K+ levels in the body. Na+ H2O Na+ K+ Compression of extrarenal or intrarenal vessels promotes output of renin by juxtaglomerular cells. Aldosterone promotes Na+ and H2O retention, K+ excretion, and arteriolar constriction.
Red Yeast. Isogalen. - Indigestion, diarrhea, improving blood circulation, spleen and stomach problems, and other conditions.
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Red Yeast work?
- What other names is Red Yeast known by?
- High cholesterol.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96889
Isogalen: 40 mg, 30 mg, 20 mg, 10 mg, 5 mg
20mg isogalen visaMicrognathia causes posterior and superior displacement of the tongue or glossoptosis with effacement of the oropharynx skin care with hyaluronic acid buy isogalen 40 mg amex. Radioulnar synostosis on this case (not shown) led to a analysis of Nager syndrome acne breakout buy discount isogalen 30mg online. The toddler has the everyday facial findings of distinguished glabella acne y estres generic isogalen 30mg visa, broad nasal root skin care 45 years old cheap 40mg isogalen amex, hypertelorism, and upward slant of the palpebral fissures. Achiron R et al: Development of the fetal tongue between 14 and 26 weeks of gestation: in utero ultrasonographic measurements. Idiopathic (Left) Sagittal transabdominal ultrasound within the 3rd trimester to assess "size lower than dates" shows a quite spectacular view of the fetal tongue flicking the umbilical cord. Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome (Left) 3D surface-rendered view of the face in a fetus with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome reveals the tongue protruding between the lips. The same techniques apply to creating 3D surface-rendered pictures of the ears as to the face. The respiratory diverticulum arises from the laryngotracheal groove close to the primordial esophagus caudal to the 4th pharyngeal pouches. The sequential evolution of the respiratory diverticulum to the tracheal bud and the primitive lung is proven. Note the shut relationship of the creating tracheobronchial tree and lungs to the primitive esophagus. The axial aircraft of part (right) shows communication between the tracheal bud and the foregut. The tracheoesophageal folds fuse within the midline to separate the trachea from the esophagus. Note that the proper bronchial bud is vertically oriented and the left follows a more horizontal course. Further progress and branching of the distal primitive airway forms rudimentary segmental bronchi. The rudimentary bronchus intermedius gives rise to primitive proper center and right lower lobe bronchi. Note the airway differentiation into the rudimentary lobar bronchial branches (shown in different colors) and segmental bronchial branches. Note that the green and red bronchial branches symbolize different portions of the primitive left higher lobe. The interplay between the primitive tracheobronchial tree and the encircling primitive mesenchyme induces the event of lung parenchyma. There is an elevated variety of vessels inside the primitive mesenchyme, some of which abut the airway wall. Respiration is feasible at the end of this stage of lung improvement, but these infants require intensive take care of survival. Respiration is possible, and lots of infants born at this stage of pulmonary improvement survive with proper medical administration and help. The airway epithelium is thin, and lots of capillaries bulge into the airway lumen establishing mature alveolar-capillary interfaces. In the first trimester, the lungs and liver are similar in echogenicity, however the lungs become more hyperechoic as alveolar growth progresses, creating extra acoustic interfaces. The diaphragm is finest evaluated in this projection to ensure it has been seen in its entirety. Fluidfilled structures, including the trachea, bronchi, stomach, and small bowel, are all very excessive signal and simply distinguished on T2weighted sequences. It is hypoechoic when compared to the lungs and has a slightly reticular look. The inner mammary arteries, branches of the subclavian arteries, flank the thymus, creating a field look. An elevated ratio normally indicates that the guts is dilated (cardiomegaly), however it could also occur when the chest is small. If the transducer is angled, it might give the faulty impression of a diaphragmatic hernia. When evaluating the four-chamber view, picture an imaginary line drawn from the midvertebral physique through the sternum, dividing the chest in half. Only the proper atrium and a portion of the best ventricle ought to project to the best of this line. A second imaginary line can be drawn alongside the interventricular septum; the angle between these lines signifies the cardiac axis. Early in gestation, the lungs could be similar in echogenicity to the liver however turn into more echogenic with advancing gestational age. Fetal respiratory movements may be observed during real-time scanning and are essential for normal lung improvement. In addition to development elements, fetal lung fluid capabilities as a stent, maintaining growing airways distended. Decreased fetal lung fluid, which is often the results of oligohydramnios, leads to hypoplasia, while increased fetal lung fluid. Breathing can be an indicator of total fetal nicely being and is a element of the biophysical profile. The liver is greater in sign intensity than lung, fluid-filled small bowel is low in sign intensity, but meconium-filled massive bowel will be high in sign depth. On T2-weighted imaging, the lungs are larger in signal depth than the encircling musculature. The sign intensity of the lungs will increase all through gestation reflecting the fluid throughout the enlarging alveoli. It has an intermediate sign depth on T2weighted pictures and is located within the superior portion of the mediastinum, often displaying angular borders. Approach to Fetal Chest Mass It is essential to have a systematic strategy when viewing the fetal chest and growing an applicable differential for a chest mass. Each of the diagnostic entities shall be discussed in detail in the subsequent chapters. Any shift in the cardiac axis is extremely suspicious for a thoracic mass or, alternatively, a cardiac defect. While a traditional axis guidelines out most important chest lots, small masses could not essentially deviate the axis and may be missed. It is important to notice, nonetheless, that a left-sided hernia could comprise only bowel &/or liver, with the abdomen remaining beneath the diaphragm. This is the primary and most essential query as quickly as it has been determined that a chest mass is present. The lung will float inside an effusion and have a wing-like appearance, whereas a cystic mass will displace and compress the lung.
Buy isogalen 40mg on lineIn hyponatremic sufferers acne treatment for sensitive skin buy isogalen 40mg on-line, tubular reabsorption of lithium is elevated acne 17 year old male discount isogalen 20 mg overnight delivery, resulting in skin care 20s purchase isogalen 40 mg online elevated plasma concentrations and toxicity acne jeans mens purchase 20mg isogalen. Protein binding modifications can improve the free fraction of valproic acid, predisposing to elevated responsiveness. Antiparkinsonian Drugs Tricyclic Antidepressants In addition to their use for Parkinson illness and hyperprolactinemia problems, dopaminergic drugs are used to treat stressed legs and other limb motion disorders in patients with renal impairment. Most are hepatically cleared and safe, though dopaminergic agents might exacerbate postural hypotension. Amantadine110 is extremely dependent on renal excretion, and dose modification is crucial. Simple analgesics (acetaminophen) are used as normal, though aspirin must be prevented at therapeutic doses and opioids used cautiously (see discussion of analgesics). Naratriptan relies the most on renal excretion (50%), and a lower maximum dose is recommended. Antimigraine Drugs Other Antidepressants Antipsychotics Psychotropic Drugs Most psychotropics are fat soluble and nondialyzable, endure important hepatic metabolism, and are excreted as inactive compounds. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Monoamine oxidase inhibitors are extensively metabolized by the liver. Drug-drug interactions with immunosuppressive brokers: Review of the in vitro practical assays and role of cytochrome P450 enzymes. Drug remedy in sufferers undergoing haemodialysis (clinical pharmacokinetic considerations). Drug therapy in sufferers undergoing peritoneal dialysis: Clinical pharmacokinetic issues. Pharmacokinetic principles during continuous renal alternative therapy: Drugs and dosage. The use of opioid analgesia in end-stage renal illness sufferers managed without dialysis. Plasma levels of morphine and morphine glucuronides within the remedy of cancer pain: Relationship to renal perform and route of administration. Selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors: A sample of nephrotoxicity similar to conventional nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Nitrofurantoin, sulfamethizole and cephalexin urinary concentrations in unequally functioning pyelonephritic kidneys. Clinical pharmacokinetics of antibiotics in sufferers with impaired renal function. Pharmacokinetics of meropenem in topics with numerous degrees of renal impairment. Clinical pharmacokinetics of cefotaxime in patients with normal and decreased renal function. Single- and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of ceftazidime in infected patients with various levels of renal function. Pharmacokinetics of cefazolin in patients with renal failure; special reference to hemodialysis. Benzodiazepines are extensively metabolized by the liver to a range of lively and inactive metabolites. Short-acting benzodiazepines are most well-liked, and the dose must be titrated cautiously according to response. The dose of midazolam must be reduced due to changes in plasma protein binding. Benzodiazepines Vaccines Live vaccines (bacillus Calmette-Gu�rin, oral poliovirus, rubella, typhoid, yellow fever, and varicella) in immunosuppressed patients are contraindicated because of the potential for inflicting illness. Attenuated vaccines (diphtheria-tetanus, hepatitis B, influenza, meningococcal, and pneumococcal) may be used; however impaired response in immunocompromised people may lead to insufficient protection (see Chapter 84). Immunization ought to ideally happen a minimum of 1 month before initiation of immunosuppression. After transplantation, the immune response may be inadequate for at least 6 to eight months, that means that vaccination ought to be withheld until then. Administration of vitamin dietary supplements (B, C, and folic acid) is beneficial after dialysis. Factors related to medicine related issues in ambulatory hemodialysis patients. The intestine as a barrier to drug absorption: Combined role of cytochrome P450 3A and P-glycoprotein. Effects of aluminum hydroxide and calcium carbonate antacids on the bioavailability of ciprofloxacin. The effect of persistent renal failure on hepatic drug metabolism and drug disposition. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous ciprofloxacin in normal and renally impaired topics. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in kids and adults with normal and impaired renal function. Pharmacokinetics of metronidazole in sufferers with varying levels of renal failure. Pharmacokinetic concerns in the treatment of tuberculosis in patients with renal failure. Renal impairment and amphotericin B formulations in sufferers with invasive fungal infections. Pharmacokinetics of famciclovir in subjects with varying degrees of renal impairment. Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of peginterferon alfa-2b in sufferers with renal insufficiency. Efficacy and safety of adefovir dipivoxil in kidney recipients, hemodialysis patients, and patients with renal insufficiency. Pharmacokinetics of lamivudine in human immunodeficiency virus�infected patients with renal dysfunction. Pharmacokinetics of telbivudine in topics with various degrees of renal impairment. Pharmacokinetics and dosage adjustment of oseltamivir and zanamivir in sufferers with renal failure. Pharmacokinetic research of ordinary heparin and low molecular weight heparin in sufferers with continual renal failure. Bivalirudin pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: Effect of renal operate, dose, and gender. Dosing lepirudin in patients with heparininduced thrombocytopenia and regular or impaired renal function: A single-center expertise with sixty eight patients. Influence of severe renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of oral ximelagatran and subcutaneous melagatran. The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of argatroban: Effects of age, gender, and hepatic or renal dysfunction. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of eptifibatide in topics with normal or impaired renal perform.
Isogalen 40mg cheapRegional citrate anticoagulation involves calcium chelation within the extracorporeal blood circuit with calcium reversal skin care 2013 purchase 10mg isogalen. A less complicated strategy has been described by which the citrate infusion is combined with regular calcium dialysate and no calcium infusion acne 6 months after giving birth cheap 10mg isogalen visa. The constructive calcium flux through the hemodialyzer maintains calcium stability without the need for a separate infusion and offers partial chelation of the undialyzed citrate tretinoin 05 acne 20mg isogalen amex. Frequent monitoring and titration of citrate dose have normally been advocated to hold the ionized calcium within a therapeutic range acne rosacea pictures purchase 5 mg isogalen visa. Many facilities now use a simplified fixed-dose anticoagulant citrate dextrose A protocol that minimizes the want to measure postfilter calcium or regulate the citrate infusions. Major complications of regional citrate anticoagulation include systemic hypocalcemia and metabolic alkalosis from citrate toxicity, particularly in patients with liver dysfunction. Regional heparin anticoagulation entails neutralization of heparin by infusion of protamine into the venous blood-line. It may be complicated by rebound bleeding, occurring when neutralization with protamine wears off faster than the anticoagulation from heparin. Furthermore, protamine could trigger sudden hypotension, bradycardia, or anaphylactoid reactions. Such studies could but yield definitive knowledge, but within the interim, modality selection is dependent upon probably the most clinically applicable fee of solute and fluid removing for the given clinical state of affairs. Certain patients are finest treated with a lower-efficiency modality, such as those who are hemodynamically unstable, including those with cardiogenic shock. Its use was largely limited to pediatrics, however current advances have resulted in renewed curiosity in adults. Ventricular help devices are blood pumps that assist the left and/or proper ventricles in patients with refractory coronary heart failure or cardiogenic shock. They are used as a bridge to recovery, as a bridge to transplantation, or for long-term therapy in sufferers ineligible for transplant. Acute kidney damage is widespread in patients with circulatory and/ or respiratory failure. However, special consideration must be given to volume management in these sufferers, not solely as a outcome of quantity overload is related to worse outcomes, but also because volume management facilitates weaning of mechanical circulatory help and permits for better delivery of vitamin. Monitoring volume standing in sufferers on steady move mechanical circulatory assist gadgets could be particularly difficult. Patients have minimal pulses, so specialised blood stress cuffs with low pulsatility modes are wanted, or blood circulate is monitored with flowmeters or Doppler. Because continuous flow pumps are dependent on preload, hypovolemia results in left ventricular collapse with subsequent fall in mechanical circulatory support move, pump overdrive, hypotension, and ventricular arrhythmias. This must be corrected by light volume administration whereas other causes of preload discount. Decreasing the pump speed and treating arrhythmias ought to normally be carried out only after detailed session. An different methodology of accessing the circulation is directly via the mechanical circulatory help circuit. Blood move by way of the filter is decided by the strain gradient between the arterial port (located postpump, where the pressure is positive) and the venous port (located prepump, where the strain is negative). The ultrafiltrate, dialysate, and/or replacement fluid volumes are regulated via infusion pumps. However, the infusion pumps are a supply of errors; thus the accuracy of the infused and removed volumes ought to be confirmed (especially in infants). The method used must be determined by the provision of appropriate equipment and the skill and expertise of the staff. Technical Aspects of Acute Renal Replacement Therapy During Mechanical Circulatory Support 1. Parenteral anticoagulants: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). European Best Practice Guidelines Expert Group on Hemodialysis, European Renal Association. Chronic intermittent haemodialysis and prevention of clotting within the extracorporal system. Effects of early high-volume steady venovenous hemofiltration on survival and restoration of renal function in intensive care sufferers with acute renal failure: A prospective, randomized trial. Timing of renal replacement remedy and clinical outcomes in critically unwell sufferers with extreme acute kidney injury. The impact of sodium and ultrafiltration modeling on plasma volume and haemodynamic stability in intensive care patients receiving haemodialysis for acute renal failure: A potential, stratified, randomized, cross-over study. Use of on-line blood quantity and blood temperature monitoring during haemodialysis in critically unwell sufferers with acute kidney harm: A single-centre randomized managed trial. Efficacy and cardiovascular tolerability of extended dialysis in critically unwell patients: A randomized managed research. Changes in renal perform after implantation of continuous-flow left ventricular help gadgets. Regional citrate anticoagulation in continuous venovenous hemofiltration in critically unwell sufferers with a high danger of bleeding. Improving the delivery of steady renal substitute remedy using regional citrate anticoagulation. Regional citrate anticoagulation for steady venovenous hemodiafiltration utilizing calcium-containing dialysate. Continuous renal substitute therapies for the therapy for acute renal failure in intensive care patients. Back to the longer term: Extended dialysis for therapy of acute kidney damage within the intensive care unit. Establishing a dialysis therapy/ affected person outcome hyperlink in intensive care unit: Acute dialysis for sufferers with acute renal failure. The Hannover Dialysis Outcome study: Comparison of ordinary versus intensified prolonged dialysis for treatment of sufferers with acute kidney damage in the intensive care unit. Slow steady hemodialysis-new remedy for acute renal failure in critically unwell patients. Meta-analysis: Lowmolecular-weight heparin and bleeding in sufferers with severe renal insufficiency. Ross and Kevin Damman Nephrologists are being more and more consulted relating to fluid management in sufferers with refractory coronary heart failure. These circumstances subsequently could exacerbate heart failure, which leads to a vicious cycle of reduced cardiac output and kidney dysfunction. However, other pathophysiologic mechanisms that might have necessary therapeutic implications have now been elucidated and are discussed within the following paragraphs. In the cardiorenal syndrome low cardiac output is crucial side of heart failure. Secondary (hyper)aldosteronism (resulting in increased sodium retention), increased systemic vascular resistance (thereby placing more strain on the heart), and better cardiac filling pressures may reduce cardiac output as described by There has been a growing appreciation that by way of a quantity of pathways right-sided congestion and renal venous hypertension trigger kidney dysfunction.
Buy isogalen 30mg without a prescriptionThe lung volumes (not shown) had been mildly low on this fetus; for poorly understood reasons acne pustules discount isogalen 20mg free shipping, patients with large omphalocele might develop pulmonary hypoplasia acne xlr discount isogalen 10 mg amex. No bowel gas is seen within the mass scin care buy isogalen 30 mg otc, typical of an enormous omphalocele containing solely liver acne excoriee isogalen 40 mg sale. No pneumothorax or bell-shaped chest is noted to recommend vital pulmonary hypoplasia. Frolov P et al: Clinical threat factors for gastroschisis and omphalocele in humans: a review of the literature. Mac Bird T et al: Demographic and environmental danger elements for gastroschisis and omphalocele in the National Birth Defects Prevention Study. Natural History & Prognosis � Premature delivery in up to 42% � Survival 75-95% if normal chromosomes & no other anomalies � Overall survival past neonatal period Small/minor: Up to 92%; giant: Up to 67% � Poor prognosis with Associated structural or chromosomal abnormalities: Mortality 80-100% Omphalocele rupture Pulmonary hypoplasia Treatment � Fetus: Amniocentesis for karyotype; no intervention � Birth: Delivery at tertiary facility C-section for giant omphalocele to forestall dystocia, rupture Respiratory help in big omphalocele patients with pulmonary hypoplasia pneumothorax, respiratory misery 406 radiologyebook. There is sustained protrusion of the liver into the belly wall defect (which is covered by skin). This protuberant mass is larger than the rounded opacity seen with an umbilical hernia. Note the characteristic appearances of the intraabdominal metallic coiled spring at the base of the silo as well as the overlying bar from which the silo bag is suspended. Small-caliber meconiumcontaining bowel protrudes with a cystic lesion into the amniotic fluid. A cystic mass of necrotic bowel protruded from the defect, according to a closed gastroschisis. Bergholz R et al: Complex gastroschisis is a different entity to simple gastroschisis affecting morbidity and mortality-a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gamba P et al: Abdominal wall defects: prenatal prognosis, newborn administration, and long-term outcomes. Page R et al: Gastroschisis: antenatal sonographic predictors of antagonistic neonatal end result. Ruano R et al: the affiliation of gastroschisis with other congenital anomalies: how necessary is it Beaudoin S et al: Gastroesophageal reflux in neonates with congenital abdominal wall defect. No urinary bladder is seen, although the amniotic fluid quantity is regular, typical of cloacal exstrophy. Attachment of the fetal body to the placenta ends in trunk distortion & scoliosis. The bowel is mildly dilated diffusely & accommodates quite a few air-fluid levels, suggesting ileus. Adjacent bowelwall thickening & a localized fluid collection (not shown) confirmed perforated appendicitis. There is a crescent signal (with a rim of colonic gas outlining the intussusceptum). A small bowel loop is seen in the far proper abdomen (from the lateralization of the ileum). Microscopic Features � Composed of same layers as adjacent small bowel however with addition of heterotopic gastric or pancreatic rests � Risk of cancer: Malignant carcinoid, adenocarcinoma in older sufferers 9. The loop has a beak configuration at its inferior side, extremely suggestive of a colonic volvulus. This appearance may be seen in almost 1/3 of sigmoid volvulus cases (as in this patient). These findings counsel ischemic bowel, & a transmesenteric inner hernia was found at surgical procedure. The mass is of intermediate sign depth general however is mildly hyperintense compared to the background liver. A hypointense septation & adjoining foci of increased T2 sign are famous anteriorly. Tumor thrombus expands vessels, is echogenic, & can have inner Doppler move (with arterial move inside a venous thrombus being notably suggestive). Note the enlarged hepatic artery with colour aliasing (as in comparison with the traditional shade Doppler appearance of the portal vein) as a end result of undersampling of high-velocity flow supplying the lesions. Interrogation of an enlarged artery shows elevated velocities wrapping around the scale. Fernandez-Pineda I et al: Differential prognosis and management of liver tumors in infants. Congenital Hemangioma � Large heterogeneous hypervascular mass in new child liver � Early progressive peripheral enhancement; patchy, usually large, central foci of nonenhancement on delayed pictures � � high-output coronary heart failure 7. Umbilical Venous Catheter Extravasation � Irregular fluid assortment in neonatal hepatic parenchyma adjacent to malpositioned umbilical venous catheter radiologyebook. Dhingra S et al: Update on the new classification of hepatic adenomas: scientific, molecular, and pathologic characteristics. Ultrasonographic Findings � Heterogeneous well-defined mass, may be hyperechoic because of lipid content or hemorrhage radiologyebook. The mass has a concerning nodule-in-nodule look with a small hypointense space. The hepatic radiotracer is slowly excreted by the kidneys into the urinary bladder. Microscopic Features � Periportal fibrosis, proliferation of small intrahepatic ducts, absent extrahepatic bile ducts, absence of multinucleated giant cells in liver 10. Demographics � Affects 1 in 10,000-13,000 newborn infants � Jaundice evident in immediate perinatal period � No gender or racial predilection Natural History & Prognosis � Prompt diagnosis essential to surgical success Initially, hepatocyte perform preserved; hepatocyte operate steadily deteriorates � Kasai portoenterostomy temporarily efficient in 90% if carried out < 2 months of age; to < 50% if > 3 months of age 450 radiologyebook. Note the anomalous pancreaticobiliary junction with the pancreatic duct inserting into the common bile duct proximal to the sphincter of Oddi. Natural History & Prognosis � Low-grade biliary obstruction may develop cirrhosis & portal hypertension � Complications: Bile duct perforation, biliary stone formation, bacterial cholangitis with subsequent hepatic abscess & sepsis, biliary strictures, low-grade biliary obstruction cirrhosis & portal hypertension, growth of bile duct carcinomas Prevalence of most cancers (adenocarcinoma) in choledochal cysts: 2-18% (5-35x risk) Both Caroli disease & Caroli syndrome associated with threat of cholangiocarcinoma (100x that of general population) 7. Treatment � Type I: Complete surgical excision + biliary drainage procedure, sometimes Roux-en-Y choledochojejunostomy 454 radiologyebook. Several of the ducts have a visible central dot of low sign depth due to encased portal radicles. The dilated ducts have a central dot of low signal intensity according to entrapped portal radicles. The kidneys are markedly enlarged & hyperintense because of innumerable small cysts, additionally typical of Caroli illness. The central dot represents the portal radicle surrounded by a dilated intrahepatic bile duct. The central dot sign of Caroli illness is seen at quite a few websites on this image. Infection � Viral pathogens, significantly cytomegalovirus � No particular imaging findings 9. At biopsy, these lesions had been shown to characterize adenomas & hepatocellular carcinoma.
Purchase 20 mg isogalen mastercardUpper Mesorectum: Posterior Mesorectal Anatomy Dissection commences behind the rectum skin care cream purchase isogalen 30 mg otc, staying between the plane of the parietal peritoneum and the fascial layer investing the mesorectum acne girl generic isogalen 5 mg amex. The initial dissection is in the midline posteriorly and continues right down to skin care jobs generic isogalen 40 mg amex the extent of the levator muscle tissue acne 8 days before period order 10 mg isogalen with mastercard, demonstrating the bilobed appearance of the intact mesorectum. Adequate distraction of tissues assists in demonstration of the right anatomic planes. Dissection continues laterally on both sides until the rectum becomes tethered by the anterior peritoneal attachments at the pouch of Douglas. By dissecting on this unfastened areolar tissue, the presacral fascia and the fascia of the mesorectum are separated, allowing a cold, oncologically acceptable dissection. The rectosigmoid junction is drawn anteriorly and cephalad, putting the unfastened areolar tissue beneath tension to permit dissection. The dissection then continues distally until the levators are seen to curve distally into the anal canal, defending the anterolateral neurovascular bundles. Laparoscopic Lateral pelvic attachment of retractor mesorectum Mesorectum the upper rectum is drawn posteriorly, inserting the anterior attachments beneath rigidity to allow dissection. This method leaves a transverse staple line that may be easily seen from above, sitting just into the upper anal canal throughout the sling of the levators, prepared for a stapled coloanal anastomosis. In these circumstances the intraabdominal dissection proceeds as beforehand described till the anal canal is reached. An operating anoscope is used to visualize the dentate line, which is incised circumferentially with cautery. The dissection is sustained to the interior sphincter, which is transected circumferentially. An intersphincteric dissection is then carried out becoming a member of the prior aircraft of dissection from above. The anastomosis between the neorectum and the anal canal may then be sutured or stapled. A defunctioning proximal ostomy is usually created to mitigate problems of anastomotic leak. Intersphincteric aircraft (dotted line) Dentate line Internal sphincter External sphincter Intersphincteric plane Dentate line With the use of an working anoscope, the dentate line could be incised and intersphincteric resection carried out. Tumors above the levator muscle tissue can sometimes be treated with sphincter-sparing methods. Digital rectal examination and proctoscopy are performed to confirm tumor location and to assess feasibility of a sphincter-sparing method. Digital vaginal examination and vaginoscopy are carried out with the proctoscope to assess for native invasion. Endorectal ultrasound is used for staging to assess the necessity for preoperative chemoradiation. Long-course remedy is routinely used, and surgery is often carried out eight weeks after radiation remedy. The affected person is reassessed with proctoscopy and the response to chemoradiation is famous. Some patients not thought to be candidates for a low anterior resection could additionally be determined to be suitable for sphincter-sparing procedures when assessed after neoadjuvant remedy. For patients with sphincter involvement or adjacent organ involvement earlier than neoadjuvant remedy, the surgeon should excise the clinically involved tissue en bloc. Location from anal verge should be noted in addition to location and tumor traits previous to neoadjuvant or surgical therapy. A digital exam can decide tumor characteristics, native invasion, and fixation of tumor. Anatomic location of the tumor may help to predict possible invasion into prostate or vagina anteriorly, aspect wall or coccyx posteriorly. It is essential to decide invasion of the levator muscle tissue distally prior to therapy. Endorectal ultrasound can stage the tumor infiltration (T stage) in addition to presence or absence of pathologic nodes. These findings will decide whether the affected person is a candidate for surgical remedy or neoadjuvant chemoradiation. Water-filled balloon Ultrasound transducer Endorectal ultrasonography assesses depth of tumor penetration and diploma of perirectal involvement Ultrasonogram. Rectal tumor invades perirectal fats Perirectal fats Muscularis/ fats interface Muscularis Muscularis/ submucosa interface Submucosa/ mucosa Mucosa/H2O balloon interface H2O Ultrasound transducer Ultrasonogram. This method allows a bloodless mobilization of the descending colon to the midline. If difficult to discover, dissection both proximally towards the kidney or distally into the pelvis can assist in identifying the ureter. The mobilization is extended to the foundation of the mesentery, and the inferior mesenteric artery is identified at its takeoff from the aorta. The mesentery is divided perpendicularly to the extent of the marginal artery, just proximal to the first sigmoidal department. The colon is split proximal to the first sigmoid department, and pulsatile arterial move is confirmed in the marginal artery. For rectal tumors, a high ligation of the inferior mesenteric artery at its takeoff from the aorta is performed. The dissection is carried out to the marginal artery proximal to the first sigmoidal department. Superior mesenteric artery Middle colic artery Jejunal and ileal Marginal artery Transverse mesocolon (intestinal) arteries Straight arteries (arteriae rectae) Marginal artery (Common Inferior Inferior pancreatico- portion) mesenteric duodenal Posterior artery arteries Anterior Left colic artery Marginal artery Ascending branch Right colic artery Descending department Ileocolic artery Colic branch Ileal department Marginal artery Anterior cecal artery Posterior cecal artery Appendicular artery Marginal artery Sigmoid arteries Sigmoid mesocolon B. Note the close proximity of the sympathetic plexus to the inferior mesenteric artery. Internal iliac artery Median sacral artery (from abdominal aorta) Middle rectal artery Branch of superior rectal artery Straight arteries (arteriae rectae) Superior rectal artery Inferior rectal artery Hypogastric nerves Inferior mesenteric ganglion, artery, and plexus fifth lumbar splanchnic nerve Gray rami communicantes Pelvic splanchnic nerves (parasympathetic) Piriformis muscle Gluteus maximus muscle and sacrotuberous ligament Coccygeus (ischiococcygeus) muscle and sacrospinous ligament Pudendal nerve Levator ani muscle Inferior anal (rectal) nerve Perineal nerve Dorsal nerve of penis Inferior mesenteric artery at takeoff from aorta Inferior mesenteric vein Sacral splanchnic nerves (sympathetic) Inferior hypogastric (pelvic) plexus Obturator nerve and artery Ductus deferens and plexus Vesical plexus Rectal plexus Prostatic plexus Cavernous nerves of penis C. It is helpful to place a figure-of-eight absorbable suture within the uterine fundus, retracting it anteriorly, and securing the suture to the self-retaining retractor. In open surgical cases, the dissection is greatly facilitated by means of lighted, deep pelvic retractors. Mobilization of the rectum and its investing mesorectum and fascia begins behind the inferior mesenteric vessels, in the unfastened areolar tissue between the mesorectal fascia and the presacral fascia. Unless an extended resection is being performed, the ureters are generally easily protected as a outcome of they lie deep to the fascia of the retroperitoneum. The right and left hypogastric nerves are recognized and swept posteriorly and are carefully avoided. The dissection continues posteriorly to the pelvic flooring with the use of electrocautery. Dissection of the pelvis proceeds posteriorly, then laterally, and at last anteriorly. By lifting the rectosigmoid junction anterior and cephalad and indenting the mesentery, this avascular plane could be recognized and entered, anterior to the nerves.
Syndromes - Percutaneous urinary procedures
- Male pattern baldness
- Difficulty swallowing
- Adrenal hormones
- Cancer or tumor
- An acute ear infection that does not clear completely
- May feel sharp, crampy, or dull
- Liver infection (chronic hepatitis)
Purchase isogalen 10mg with amexThree major bulges seem by approximately day 28 of gestation: the forebrain (prosencephalon) acne home remedies purchase 30 mg isogalen visa, midbrain (mesencephalon) acne 7 dpo isogalen 20mg generic, and hindbrain (rhombencephalon) acne 5 year old effective 30mg isogalen. At roughly day 36 acne scars quality 5mg isogalen, the pos terior (caudal) portion of the forebrain develops into the dien cephalon; the anterior part develops into the telencephalon (eventually cerebral hemispheres). The cerebral cortex has a selected outline by 6 months however develops sulci and gyri solely within the three months earlier than delivery. The growing mind is affected, espe cially in the first trimester, to injuries brought on by various chemi cals similar to medication. Efforts aimed to establish these substances and design medicine that can facilitate or enhance their actions are ongoing. The medial mind surface reveals complex, extremely organized, struc tures of the hemispheres. For example, the somatosensory (motorsensory and sensorimotor) regions of the frontal and parietal lobes and the premotor cortex of the frontal lobe are concerned with initiation, activation, and perfor mance of motor exercise and reception of main sensations. Interconnections among parietal (integration and interpretation of sensory information), temporal (reception and interpretation of auditory information), and occipital (vision) lobes provide an organized, integrated system. Association pathways provide added organized communication by way of intrahemispheric and inter hemispheric connections. At firing stage Na conductance is tremendously elevated, giving rise to strong inward Na present. Na conductance returns to regular; K conductance increases, causing hyperpolarization. In common, myelin ated neurons conduct impulses more rapidly than do nonmyelin ated neurons. The magnitude of the electrical potential distinction across the neuronal membrane within the resting state, termed the resting membrane potential, is dependent upon the relative intracellular and extracellular concentrations of Na+ and Cl- (higher on the outside) and K+ (higher on the inside). The cytoplasmic electrical potential is extra adverse than the extracellular fluid by approxi mately -70 mV. The potential distinction is partly maintained by an Na+/K+ lively transport change mechanism (ion pump). If the membrane is depolarized from its resting potential to approximately -40 mV (threshold potential), an action potential develops: the membrane potential continues to improve to approximately +20 to +30 mV and then returns to its resting degree, in approximately one thousandth of a second. Resting state: Motor nerve cell proven with synaptic boutons of excitatory and inhibitory nerve fibers ending close to it. Temporal excitatory summation: A sequence of impulses in 1 excitatory fiber together produce a suprathreshold depolarization that triggers an action potential. Spatial excitatory summation with inhibition: Impulses from 2 excitatory fibers reach motor neuron however impulses from inhibitory fiber stop depolarization from reaching threshold. Partial depolarization: Impulse from 1 excitatory fiber has brought on partial (below firing threshold) depolarization of motor neuron. Spatial excitatory summation: Impulses in 2 excitatory fibers cause 2 synaptic depolarizations that together reach firing threshold triggering an action potential. E (Excitatory fiber) I (Inhibitory fiber) E (Excitatory fiber) Motor neuron Motor neuron Axon mV 20 70 60 70 60 70 70 I (Inhibitory fiber) ninety mV A�. Only I fires Long-lasting partial depolarization in E terminal No response in motor neuron 60 70 70 80 C. During chemical synaptic transmission, neurotransmitters change postsynaptic membrane permeability to ions. For examination ple, increased permeability to Na+ produces excitation, and increased permeability to K+ and Cl- produces inhibition. Drugs have an effect on various sites alongside neuronal pathways, together with neurotransmitter synthesis, storage, and launch; receptor activation and inhibition; modulation of intra synaptic neurotransmitter metabolism or reuptake; and direct secondmessenger pathway results. The source of hysteria may not be appar ent and certainly may not be external; an underlying biochemical defect and genetic predisposition are hypothesized. Clinical anxiousness, whether continual or in the form of a panic assault, often produces somatic signs, impedes normal functioning, and adversely impacts the quality of life. The issues are roughly twice as widespread (possibly extra often reported) in girls than in males. Both endogenous and exterior components likely con tribute to susceptibility and expression of the clinical drawback. Drugs for treating anxiousness issues, or anxiolyt ics, include benzodiazepines and buspirone. Subclassification of benzodiazepines relies on pace of onset or period of action, metabolism, and opposed effects. Benzodiazepines are safer than barbitu rates (largely obsolete); antagonistic effects include dependence, ataxia, and drowsiness. Diazepam, chlordiazepoxide, prazepam, and the prodrug clorazepate bear hepatic metabolism to the intermediate oxazepam. Alprazolam, flurazepam, lorazepam, and triazolam directly bear conjugation earlier than excretion. Zolpidem and zaleplon resemble benzodiazepines in pharmacol ogy but differ chemically. Internal causes embrace congenital defects, inborn errors in metabolism, infection, trauma, fever, intracranial hemorrhage, and malignancy. External causes embrace metabolic, electrolyte, and other biochemical disorders; anoxia; and hypoglycemia as well as extra doses of medicine or abrupt cessation of medicine. Epilepsy, a kind of seizure disorder, is a heterogeneous symptom advanced char acterized by recurrent, unprovoked seizures and impacts approxi mately 1% of the inhabitants. The principal mechanism of motion of most present antiepileptic medication entails action on voltagegated ion channels or on inhibitory or excit atory neurotransmitter perform. Clonic part Cyanosis Incontinence Unresponsive Epileptic cry Antiepileptic Agents C. The seizure begins with tonic stiffening of the limbs in an prolonged place, with arching of the again, adopted by synchronous clonic jerks of muscle tissue of the limbs, body, and head. A period of postictal lethargy, confusion, and disorientation follows the seizure. Generalized tonicclonic status epilep ticus is a lifethreatening emergency and almost at all times requires intravenous treatment for seizure control. Drugs for tonic clonic (and partial) seizures include carbamazepine, phenytoin, valproic acid, and primidone; those for standing epilepticus embrace diazepam and lorazepam. Adverse results corresponding to sedation, con fusion, and hepatic toxicity and drug interactions occur. Drugs for these seizures include carbam azepine, phenytoin, valproic acid, and primidone. Tingling of contralateral limb, face, or aspect of physique Central Postcentral sulcus Precentral gyrus gyrus Leg Trunk Arm Face Grimacing Focal motor. Fp1-F3 F3-C3 C3-P3 P3-O1 Fp2-F4 F4-C4 C4-P4 P4 - O2 Contraversive: head and eyes turned to reverse side Autonomic. Hears ringing or hissing noises Impairment of consciousness: cognitive, affective signs Repetitive sharp waves over right central region Complex Partial Seizures Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Formed auditory hallucinations. These seizures normally happen in children, are often outgrown in adolescence, can disrupt aca demic efficiency, and are handled with ethosuximide and val proic acid and with clonazepam.
Cheap isogalen 20mg with visaThe family historical past was negative for split hand/foot acne bp5 discount 40 mg isogalen with amex, syndactyly acne extraction dermatologist cheap 5mg isogalen, orofacial clefts b5 discount isogalen 5mg line, or different birth defects acne dark spot remover buy generic isogalen 20mg line. Syndactyly is particularly troublesome to see on prenatal ultrasound, especially involving the ft. Note the syndactyly involving digits 2-3 of the hand and the large cleft of the foot with missing toes 2-3. This is the postsurgical appearance of the digits; surgery was carried out to provide greater function. Lower extremity findings differ however a persistent "pike" position with hyperextended knees is a standard finding. Some flexion creases had been present, but others were deficient as a result of lack of movement in utero. Arthrogryposis, Akinesia Sequence Musculoskeletal (Left) Clinical photograph of a stillborn infant illustrates a peculiar hand position with ulnar deviation of the wrist, adducted thumb, and abducted 2nd finger. The easy palmar surfaces of the hand and fingers infer lack of movement in utero. No spontaneous motion of the hip, knee, or ankle joints was seen from the early 2nd trimester on. Flexion creases on the palmar surfaces of the hands are sometimes underdeveloped or absent. These joint abnormalities are sometimes seen at the time of midtrimester screening ultrasounds. Note the thin, atrophic-appearing arm with the extended elbow and internally rotated flexed hand. Arthrogryposis can be attributable to many alternative entities and genetic counseling should be offered in all instances. The mineralization appears normal, unlike other causes of bent bones, such as osteogenesis imperfecta or hypophosphatasia. Demographics � Epidemiology Incidence of 1:50,000-200,000 � Unilateral in 90% of instances 766 Proximal Focal Femoral Dysplasia Musculoskeletal (Left) At 21 weeks, this right femur appeared bowed however was the downside femur when imaged. If the contralateral regular left femur was not compared, this could be mistaken for beam artifact. Closer look at the left hip also shows a shallow acetabulum and superolateral dislocation of the femoral head. In this case, the left lower extremity is short compared to the right, with solely the tibia present. Measure femur and humerus on either side to compare Consider measuring all extremity bones if femur/humerus is dramatically brief � More probably skeletal dysplasia If isolated to 1 long bone, could be focal defect of that limb � Check morphology of affected extremity � Assess morphology of osseous buildings Are long bones straight vs. Note the distinction is extra pronounced within the third trimester, which is often the case. This is most frequently constitutional and you must verify the stature of the mother and father. The combination of rhizomelic limb shortening and huge cystic hygroma is extremely suggestive of Turner syndrome. Osteogenesis Imperfecta Osteogenesis Imperfecta (Left) In this fetus, the cranium is poorly mineralized and deformed by transducer stress. The close to field buildings of the brain are unusually properly seen because of the dearth of reverberation. Careful imaging of the ribs also identified a beaded appearance suggestive of fractures. Thanatophoric Dysplasia Thanatophoric Dysplasia (Left) Image reveals term stillborn toddler with sort I thanatophoric dysplasia. The tiny chest and disproportionately giant head and lengthy trunk are readily apparent. Note also the spicules on the inferior iliac wings and platyspondyly involving the lumbar backbone. The calvarium is abnormally formed with a cloverleaf look (kleeblattsch�del), often with excessive frontal prominence. Micromelia is famous in addition to the extremely small thorax, especially compared with the a lot larger abdomen. The limbs are quite quick and the pseudoarthroses are due to a quantity of fractures in utero. Osteogenesis Imperfecta 776 Angulated Bones Musculoskeletal Diabetic Embryopathy Diabetic Embryopathy (Left) this new child has diabetic embryopathy-related caudal regression as a end result of uncontrolled maternal diabetes. Note the fastened posture of the brief decrease extremities and the popliteal pterygia as a outcome of lack of joint movement in utero. Diabetic Embryopathy Diabetic Embryopathy (Left) Clinical photograph reveals severe decrease extremity anomalies on this preterm infant of a poorly controlled diabetic. Femoral hypoplasia with absent tibia and fibula, irregular angulation of the "ankle", and preaxial polydactyly are present. Campomelic Dysplasia Campomelic Dysplasia (Left) the scapulae are invariably absent or hypoplastic in campomelic dysplasia. The radiograph (different case) exhibits the scapular spines are present, however the blades are fully missing. When evaluated, absent creases had been additionally famous, because of decreased fetal motion of the hand in utero. The ankle appeared fixed in position, and the deviation is characteristically toward the side of the hypoplastic or lacking bone. Ossification is regular, and no fractures were seen in the mildly shortened long bones. The femur is ragged showing with irregular angulation and a heterogeneous echotexture to the bone. Hypophosphatasia Fetal Trauma (Left) Photograph of a new child with perinatal deadly hypophosphatasia exhibits gentle bowing of the extremities due to the angulated bones. Presence or absence of fractures most essential clue for differential � Are fractures generalized or restricted to portion of skeleton. Underossified bones in fetal akinesia sequence are the consequence of lack in motion in utero. Undermineralization of the entire skeleton is noted with fractures as a prominent function. The calvarium is underossified and the lengthy bones are "crumpled" as a result of multiple fractures. Note the dearth of ossification of the spine, a distinguishing feature of this dysfunction. Hypoplasia and undermineralization of bones of the pelvis and lower limbs are additionally widespread findings.
Buy discount isogalen 20mg onlineThe venous tributaries may be ligated and divided as needed skincare for 40 year old woman buy generic isogalen 20 mg, permitting the saphenous vein to be mirrored either anteriorly or posteriorly to facilitate enough fascial lysis acne pictures cheap 10mg isogalen. Posteromedial incision Transverse intermuscular septum Superficial posterior compartment Superficial flexor muscular tissues Soleus Gastrocnemius Plantaris tendon Anterior compartment Extensor muscular tissues Tibialis anterior Extensor digitorum longus Extensor hallucis longus Anterior tibial a acne 4 year old discount isogalen 10mg visa. Anterolateral incision Anterior intermuscular septum Lateral compartment Peroneal muscles Peroneus longus Peroneus brevis Superficial peroneal n acne home treatments proven isogalen 10mg. Posterior intermuscular septum Fibula Crural (encircling) fascia Fascial incision into superficial posterior compartment Fascial incision into lateral compartment Fascial incision into deep posterior compartment Tibia Fascial incision into deep anterior compartment Anterior intermuscular septum Junction of transverse intermuscular septum with crural fascia Superficial peroneal n. In addition to coming into the posterior deep compartment within the middle and distal leg, the soleus should be detached from the tibia for enough lysis of the proximal portion of the posterior deep compartment. The lateral incision is positioned approximately 1 cm anterior to the border of the fibula. Care must be taken to avoid harm to the superficial fibular nerve because it emanates from beneath the fibularis (peroneus) longus muscle. Proximally, the frequent fibular (peroneal) nerve can be inadvertently injured. The anterior intermuscular septum is then identified and the anterior compartment crural fascia incised in a longitudinal course. There are sometimes two to three subcompartments organized in a volar-to-dorsal direction. The most superficial of those incorporates the flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, flexor carpi ulnaris, and superficial portion of the pronator teres. The subsequent division incorporates the flexor digitorum superficialis, and the flexor digitorum profundus and flexor pollicis longus make up the ultimate section. The main dorsal compartments are divided into the extrinsic finger extensors, thumb extensors with the index proprius, and the wrist extensors with the brachioradialis muscle. These anatomic divisions are necessary to contemplate throughout fasciotomy of the forearm. The resting place of the hand and wrist is slight wrist flexion, with metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joint flexion and forearm pronation. The presence of a compartment syndrome is normally associated with swelling within the flexor compartment, because that is probably the most incessantly involved compartment. The traditional findings of forearm compartment syndrome are disproportionate ache in view of the bodily exam, pain with passive stretch of the finger extensors, restricted finger and wrist motion, and paresthesias in the hand along the distribution of the median, the ulnar, and fewer typically the radial nerve. There could also be pallor in the terminal digits with extended capillary refill and decreased skin temperature. As this condition progresses, complete anesthesia happens, and the radial and ulnar pulses may be diminished in extreme circumstances. Ancillary studies ought to embrace radiographs as a end result of the fracture location may help pinpoint the site of severely injured muscle. In the obtunded or sedated patient, direct compartment stress measurements should be obtained. A compartment strain 30 mm Hg above the imply diastolic pressure, or an absolute stress between 30 and forty five mm Hg, is irregular. This therapy consists of elevation of the limb to the heart degree, software of an elbowto-finger splint, and avoidance of extra intravenous fluids. Surgical Anatomy and Technique the mainstay of treatment for confirmed compartment syndrome is decompressive fasciotomy. The volar compartment is most often concerned and is approached initially through an extensile anterior or Henry-type method. A carpal tunnel release is included if the swelling is critical in the distal forearm or palmar side of the wrist. The septae between the muscle groups can be incised to guarantee full decompression. The relationship of the median and ulnar nerves inside the compartments is such that the ulnar nerve lies adjoining to the flexor digitorum profundus muscle, and the median nerve is generally between the flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus muscles within the midforearm. The necessity for further surgical intervention is decided by the extent of muscle necrosis. Closure A clear and healthy muscle bed is necessary earlier than closure may be thought of. Skin staples with intervening vessel loops can be used to approximate the skin sequentially. The distal and proximal extents are primarily approximated, and the central defect is roofed with a split-thickness skin graft. Complications and nonclosure rates of fasciotomy for trauma and related threat elements. In the pressing situation the patient has unstable physiologic parameters and requires instant chest tube placement. In the semiurgent scenario the obligatory chest tube is needed "sooner somewhat than later," and has an acute problem or indication however seems hemodynamically secure. However, delay in placing the chest tube might result within the affected person turning into unstable and the need for an pressing process due to scientific deterioration. The nonurgent state of affairs is usually elective and occurs in patients with steady hemodynamics and a chronic or recurrent physiologic downside. In different elective conditions a chest tube is needed as part of a scheduled process, such as diaphragm restore or thoracotomy. Cross-sectional anatomy to visualize layers of the chest wall the primary necessary concept of inserting a chest tube or accessing the pleural area includes the flexibility to determine superficial anatomic landmarks. The key landmarks for accessing the pleural area are identification of the clavicular head; midclavicular line; the anterior, center, and posterior axillary lines; and intercostal areas with corresponding ribs. The capability to count ribs accurately will facilitate the position of chest tubes. Instead, the inframammary fold must be used to determine the 5th rib at the anterior axillary line. In a male patient the decrease border of the pectoralis main muscle is a good approximation for the site of tube insertion. The second key concept when accessing the pleural space is to acknowledge that the intercostal neurovascular bundles lie just below the inferior portion of the ribs. Thus it is important to place the chest tube over essentially the most superior portion of the rib to keep away from injuring the intercostal neurovascular bundle. Surface anatomy of the thorax Sternocleidomastoid muscle Sternal head Clavicular head Clavicle Jugular notch Deltoid muscle Body of sternum Nipple Cephalic vein Biceps brachii muscle Triceps brachii muscle Axilla Anterior axillary fold Posterior axillary fold Pectoralis main muscle Clavicular head Sternal head Latissimus dorsi muscle Xiphoid process of sternum Serratus anterior muscle Chest tube insertion website Linea alba Rectus abdominis muscle External oblique muscle Serratus anterior muscle Tendinous intersection Manubrium of sternum Common carotid artery Brachiocephalic trunk Subclavian artery and vein Brachiocephalic vein Internal thoracic artery and vein Anterior intercostal arteries and veins and intercostal nerve Internal intercostal muscular tissues Innermost intercostal muscular tissues B. Failure to recognize these boundaries can lead to misadventures in chest tube placement such as putting a tube into or below the diaphragm, which might trigger bleeding or injury to intraabdominal or main vascular buildings. The fourth critical anatomic concept is to understand the difference between the left and right chest. The key differences between the left and right chest should be appreciated when accessing the pleural space. The location of the horizontal fissure on the right and oblique fissure on the left is at roughly the 4th rib at the anterior axillary line. The fifth and last important anatomic detail is to perceive the cross-sectional anatomy of the chest wall and the layers that should be traversed to entry the chest.
10mg isogalen saleThe anterior and posterior limbs in the inner capsules are hypointense (a bit precociously) skin care before wedding order isogalen 40mg with amex. In addition acne quitting smoking order 40 mg isogalen fast delivery, hyperintensity is seen within the posterior putamina acne grading scale cheap 30mg isogalen with visa, one other attribute of this disorder acne gel 03 generic isogalen 5mg otc. This appearance could be extra typical of a neonate, though a neonate would have some hypointensity in the posterior limb of the inner capsule. Hypomyelination has been described in numerous chromosomal deletion syndromes, though the prevalence is tough to gauge. Note absence of seen caudate nuclei and corpus callosum along with the abnormal hyperintense sign of unmyelinated white matter. Examination of the hair underneath polarized light demonstrated attribute "tiger-tail" bands, and radiographs confirmed central osteosclerosis. I 1 48 (Left) Axial fractional anisotropy map from diffusion tensor imaging reveals restricted diffusion in the frontal white matter and enlarged sylvian cisterns in this 6 12 months old with glutaric acidemia kind 1. The appearance is brought on by central gliosis surrounded by hypointensity from iron deposition. Note the prominent subarachnoid areas, which may end result from malnutrition, medicines, or the illness course of itself. Hamazaki S et al: Mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes. Note the sparing of internal/external capsules and subcortical U-fibers, typical of early illness. The "tigroid" or "leopard" sample of strains and dots inside the cerebral hemispheric white matter is clear. Reduced diffusivity (cytotoxic edema) is typically seen in areas of energetic demyelination. Although less well evaluated within the sagittal airplane, dot-like areas of spared perivenular myelin could be identified. Although the subcortical Ufibers remain spared, the posterior limbs of the inner capsules are concerned. Although spared in this affected person, the subcortical Ufibers are often affected in late illness. Excepting gentle myelin maturation delay within the anterior limbs of the inner capsule, the standard photographs have been regular. Krabbe is 1 of the few leukodystrophies that has early cerebellar imaging findings. Udow S et al: Prolonged survival and serial magnetic resonance imaging/magnetic resonance spectroscopy modifications in childish Krabbe illness. Patel B et al: Optic nerve and chiasm enlargement in a case of childish Krabbe illness: quantitative comparison with 26 age-matched controls. McGraw P et al: Krabbe illness treated with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: serial evaluation of anisotropy measurements-initial expertise. Symmetric corticospinal tract involvement is a trademark of globoid cell leukodystrophy. The infantile juvenile-onset kind is characterized by a extra protracted course with a slower price of progression. A unique function of this leukodystrophy is the occasional enlargement of optic nerves, described by Krabbe in his unique paper on the condition. Although nonspecific, this pattern is typical of Krabbe illness, and these alterations will worsen with out treatment. The outer layer consists of active destruction, the center layer of active irritation. Ratai E et al: Seven-Tesla proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging in grownup X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Note progressive myelin maturation of the subcortical U-fibers and (incomplete) improvement of periventricular white matter & corticospinal tracts. Note hypodensity in cerebellar white matter, dorsal pons, and 4 foci in the anterior and middle pons, that are paired pyramidal and tegmental tracts. Again seen are the paired tracts (4 bright pontine foci) superimposed on signal abnormality within the pons. Terek D et al: Diagnostic instruments of early brain disturbances in an asymptomatic neonate with maple syrup urine disease. Low sign of the concerned brainstem, cerebellar white matter, and subcortical cerebral white matter can also be current. They are also seen at longer echo times, a discovering that helps to confirm the analysis. The sylvian fissures are enlarged, and the basal ganglia are diffusely and symmetrically irregular in signal. Note the swelling and abnormally elevated sign intensity of the basal ganglia, including the heads of caudate nuclei, the putamina, and the globi pallidi bilaterally. Demographics I 1 86 � Age Generally manifests during 1st yr of life � Gender No predilection � Ethnicity 10% carrier rate in old order Amish 7. Abnormal sign is identified inside the globi pallidi, as anticipated, and in cerebral white matter. Normal signal depth is current inside the internal capsule, corpus callosum, caudates, and putamina. Normal diffusivity is seen in the myelinated inside capsule and corpus callosum. The cerebral white matter is diffusely hyperintense, greatest within the frontal lobes, where it extends from the ventricular margin to the subcortical Ufibers. The nodular, "rabbit ear" appearance of the frontal periventricular rim is typical of Alexander illness. Mignot C et al: Tumor-like enlargement of the optic chiasm in an toddler with Alexander disease. Pareyson D et al: Adult-onset Alexander disease: a series of eleven unrelated circumstances with review of the literature. Dinopoulos A et al: Discrepancy between neuroimaging findings and clinical phenotype in Alexander illness. Enhancement can be current over the surface of the caudate heads and within the putamina and fornix. Natural History & Prognosis I 1 96 � Early white matter swelling Swelling decreases over time Atrophy ensues � Clinical features progress slowly thirteen. Note the persistent hyperintensity of the cerebral white matter with involvement of the subcortical U-fibers. Gregory A et al: Clinical and genetic delineation of neurodegeneration with mind iron accumulation. Related Articles et al: Unraveling the Hallervorden-Spatz syndrome: pantothenate kinaseassociated neurodegeneration is the name. The appearance of the "eye" in "eye of the tiger" is variable, relying on the stage of the disease. Progressive iron deposition within the globus pallidus probably accounts for greater T1 shortening seen in later disease. Abnormal iron accumulation throughout the substantia nigra is more conspicuous on imaging as the illness progresses.
References - Schmidbauer, J., Remzi, M., Memarsadeghi, M. et al. Diagnostic accuracy of computed tomography-guided percutaneous biopsy of renal masses. Eur Urol 2008;53: 1003-1011.
- Strasburger JF. Cardiac Arrhythmias in childhood. Diagnostic considerations and treatment. Drugs. 1991;42:974-83.
- Norhona-Blob L, Kachur JF: Enantiomers of oxybutynin: in vitro pharmacological characterization at M1, M2 and M3 muscarinic receptors and in vivo effects on urinary bladder contraction, mydriasis and salivary secretion in guinea pigs, J Pharmacol Exp Ther 256:562, 1991.
- Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A, et al: Prospective identification of tumorigenic breast cancer cells, Proc Natl Acad Sci 100:3983n3988, 2003.
- Kunkle, D.A., Uzzo, R.G. Cryoablation or radiofrequency ablation of the small renal mass : a meta-analysis. Cancer 2008;113:2671-2680.
|


