Kamagra Effervescent
Cynthia J. R. Curry, M.D. - University of California, San Francisco
- Genetic Medicine Central California
- Fresno, California
Purchase 100 mg kamagra effervescent overnight deliveryEye lotions are solutions for rinsing or bathing the attention impotence at 60 order 100mg kamagra effervescent, or for impregnating eye dressings what age can erectile dysfunction occur purchase kamagra effervescent 100mg without a prescription. Pulmonary Inhaled solutions are administered by pressurized metered-dose inhalers or by nebulizers for local or systemic effect erectile dysfunction caused by herpes cheap 100mg kamagra effervescent with mastercard. Rectal Solution enemas are usually administered for native or systemic drug motion impotence ginseng discount kamagra effervescent 100 mg with visa. Vaginal Vaginal options are administered for local impact, for irrigation or for diagnostic functions. Drugs are most commonly injected into the veins (intravenous), into the muscular tissues (intramuscular) and into (intradermal) and underneath (subcutaneous) the skin, although they can also be injected into arteries, joints, joint fluid areas, the spinal column, spinal fluid and the guts. Preservatives, such as benzyl alcohol, are included under sure circumstances corresponding to in multidose merchandise. Intravenous � the solution should be aqueous, as oil droplets can occlude the pulmonary microcirculation. Ideally, a parenteral aqueous resolution should have a pH close to physiological pH (which is 7. A broad pH range is tolerated because the administered answer is diluted on administration, most notably with the intravenous route. Parenteral options should be isotonic when large volumes are administered by intravenous infusion. When smaller volumes are used, a wider range of tonicity can be tolerated as dilution with physique fluids happens. The focus of ethanol must be limited as it exerts a pharmacological action following oral administration. Synthetic or naturally occurring flavourings similar to vanilla, raspberry, orange oil, and lemon oil are used for oral solutions. Certain flavours attraction to certain patient populations and certain parts of the world; this must be borne in thoughts by the formulator. Sucrose, sorbitol, mannitol, saccharin sodium, xylitol and high-fructose corn syrup are used to improve the palatability of oral solutions. Examples embrace benzalkonium chloride, benzyl alcohol, chlorobutanol, thimerosal and mixtures of parabens (methyl, propyl, butyl). Sodium metabisulfite, sodium sulfite, sodium bisulfate, ascorbic acid, used to stabilize options. Hypromellose, hydroxyethylcellulose, poly(vinyl alcohol), povidone, dextran, carbomer 940. Disadvantages of options the disadvantages of options compared with different dosage varieties embody: � Many medicine are inherently unstable, and instability is elevated when a drug is current in resolution. For different medication, stability may be enhanced by optimization of the formulation (see later). The packaging of pharmaceutical options requires supplies of upper quality (see Chapter 46). However, many drug molecules undergo chemical reactions, such as, hydrolysis, oxidation, decarboxylation, epimerization, and dehydration, with hydrolysis, oxidation and reduction being the most common. Pharmaceutical options are subsequently formulated on the pH favouring drug stability, and often embrace excipients to improve product stability. To scale back oxidation, antioxidants and/or metallic chelators (as heavy metallic ions catalyse oxidation) are used. Alternatively, oxygen could be excluded, by the purging of the solution with nitrogen and the creation of a nitrogen headspace inside the container. To inhibit microbial development during use, preservatives are used in multidose merchandise. All the excipients used inside a solution have to be of appropriate quality, unhazardous, suitable with the drug and with one another, and lively at the resolution pH. In addition, the excipient should stay within the resolution throughout the shelf lifetime of the product. That is, the concentration of the excipient should not lower, which might happen, for example, if the excipient degraded or was adsorbed onto (or absorbed into) the container walls. Further detailed information about drug and product stability may be present in Chapters 47, 48 and 49. Enhancement of drug solubility As talked about already, water is the most generally used vehicle in pharmaceutical options. Many medication are water soluble, solubility being outlined as the focus of the drug in an answer when equilibrium exists between dissolved and undissolved drug. That is, it must retain the same bodily, chemical, microbiological, therapeutic and toxicological properties that it possessed on the time of its manufacture. The nature of the solubility enhancer is dependent upon the drug molecule and the route of administration, in addition to the supposed patient inhabitants. Certain enhancers may be safely administered by way of the oral route, but not parenterally as a end result of their greater toxicity when administered parenterally. Different approaches to enhancing drug solubility are described within the following sections. Bioavailability of the drug also needs to not be compromised by a change in pH, un-ionized drug molecules being absorbed to a greater extent by way of biological membranes than their ionized counterparts. The pH of a pharmaceutical solution is thus a compromise between drug solubility, stability and bioavailability, the perform of excipients, and physiological acceptability of the product. That is, polar medication generally dissolve in polar solvents and nonpolar drugs typically dissolve in nonpolar solvents. This may be achieved by addition of a third component similar to a water-miscible organic liquid with a low polarity. Most water-miscible natural liquids are poisonous, and just a few are used as cosolvents in pharmaceutical options. Examples embody glycerol, propylene glycol, ethanol and the low molecular weight polyethylene glycols. The solubility of nonpolar drugs in water may be elevated by several orders of magnitude with cosolvents. Typically, a linear enhance in cosolvent fraction results in logarithmic will increase in drug solubility. The concentration of the cosolvent is, nonetheless, limited by its physiological acceptability. The cosolvent have to be nontoxic on the concentrations used, and for the route of administration. In resolution, an equilibrium exists between the undissociated drug molecules and their ions. Since ions are more soluble in water than neutral molecules, changing the pH of the medium to enhance ionization of the drug is a typical method for increasing drug solubility in an aqueous medium. The pH required to achieve drug ionization could be calculated using the Henderson�Hasselbalch equations (see Chapter 3), and the pH can be adjusted using acids or alkalis, or by utilizing buffers similar to citrate, acetate, phosphate and carbonate buffers. Extremes of pH ought to be avoided however so that the solution is physiologically acceptable; the pH ranges tolerated for the completely different routes are proven in Table 24. As talked about already, the rate of chemical reactions which lead to degradation can be pH dependent. The pH for optimum drug solubility may not be the identical as that for optimal stability.
Discount 100mg kamagra effervescent mastercardThe fee of drug input will lower steadily with time as the efficient drug focus on the site of absorption decreases (assumes first-order absorption) erectile dysfunction statistics india buy kamagra effervescent 100mg on-line. Other processes erectile dysfunction treatment mn discount kamagra effervescent 100mg with visa, corresponding to chemical degradation and motion of the drug away from the absorption site(s) impotence pills for men generic kamagra effervescent 100 mg without prescription, will also contribute to the gradual lower within the drug concentration with time on the absorption website erectile dysfunction doctor exam kamagra effervescent 100 mg discount. In the case of a one-compartment open model, the speed of drug output or elimination is a first-order process. Consequently, the magnitude of this parameter at any given time depends on the concentration of the drug in the body compartment at the moment. Immediately following administration of the first dose of an oral dosage kind, the speed of drug output from the body, i. However, as absorption proceeds, initially at the next price than the rate of drug output, the net concentration of the drug in the body will enhance with time. As the rate of drug output from the body compartment will increase while the speed of drug enter into the physique compartment decreases with time, there will be some extent at which the rate of drug enter is equal to the speed of drug 365 Rate of drug enter versus price of drug output In a one-compartment open model the overall kinetic processes of drug enter and drug output are described by first-order kinetics. Following administration of an oral dosage kind, the method of drug input into the physique compartment includes drug launch from the dosage form and passage of the drug (absorption) across the cellular membranes, in this case the gastrointestinal barrier. The shape of the curve is determined by the connection between the rate of absorption and the speed of elimination. The higher the speed of drug enter relative to the rate of drug output from the body compartment through the net absorption section, the upper would be the peak concentration achieved in the physique or plasma following oral administration of a single dose of the drug. This explains why will increase in dose dimension and formulation modifications in dosage types, which produce increases in the effective concentration of a drug on the absorption site(s), result in greater peak plasma and physique concentrations being obtained for a given drug. It also needs to be famous that any surprising decrease in the fee of drug output relative to the rate of drug enter, which may occur as the outcome of renal impairment or poor drug metabolism, can also be prone to end in higher plasma and physique concentrations of the drug than anticipated, and the potential of the affected person exhibiting toxic results of the drug. The adjustment of dosage regimens in patients with severe renal impairment is taken into account 366 later. Elimination price constant and organic half-life of a drug In the case of a one-compartment open model, the speed of elimination or output of a drug from the physique compartment follows first-order kinetics and is said to the concentration of the drug, C, remaining in the physique compartment at time t by the next equation: fee of elimination at time t = - keC (22. The apparent elimination fee fixed of a drug offers the proportion, or fraction, of that drug which is eliminated from the body per unit time. The apparent elimination rate constant of a given drug thus offers a quantitative index of the persistence of that drug within the physique. For example, the fraction of the drug remaining after time t is calculated from C = C0e- kt (22. It is defined as that volume of plasma during which the entire quantity of drug within the physique can be required to be dissolved to reflect the drug focus attained in plasma. Vd relates the whole amount of drug within the physique at any time to the corresponding plasma focus. If the drug has a big Vd, this implies the drug is very distributed in tissues. On the other hand, if Vd is much like the whole plasma volume, this implies the entire quantity of drug is poorly distributed and is especially in the plasma. If a drug has a clearance of two L h-1, this tells us that 2 L of the quantity of distribution is cleared of the drug per hour. Steady state Most medicines are given as a number of doses, hence offering sufferers are given a quantity of doses earlier than the preceding doses are eradicated, accumulation of the medication will happen until a gentle state is achieved. This occurs when the quantity of drug administered (in a given period) is the same as the quantity of drug eliminated in that same period. At the regular state, the plasma focus of the drug (Css) at any time during any dosing interval and the peak and trough are similar. The time to reach steady-state concentrations relies on the half-life of the drug under consideration. Half-life (t1/2) the time required to cut back the plasma focus to half of its preliminary value is outlined as the half-life (t1/2). This parameter can be used to estimate for the way long use of a drug should be stopped if a affected person has toxic drug ranges, assuming the drug displays linear one-compartment pharmacokinetics. Bioavailability (F) F is the fraction of an oral dose which reaches the systemic circulation, which following oral administration may be lower than 100 percent. Parenteral dosage varieties (intramuscular and intravenous) assume a bioavailability of 100 percent, and so F = 1 and is subsequently not thought-about, and is omitted from calculations. Salt factor (S) S is the fraction of the administered dose (which could additionally be within the type of an ester or salt) which is the lively drug. Aminophylline is the ethylenediamine salt of theophylline, and in this case S is zero. If the affected person has a starting plasma concentration of the drug, C0, of 20 mg L-1, then at four hours the fraction remaining within the body (C) is equal to C0e-kt C = 20e -0. An alternative parameter used is the organic or elimination half-life of the drug, t1/2. The organic half-life of a given drug is the time required for the body to get rid of 50% of the drug which it contained. Thus the bigger the biological half-life exhibited by a drug, the slower might be its elimination from the physique or plasma. For a drug whose elimination follows first-order kinetics, the value of its biological half-life is independent of the concentration of the drug remaining in the physique or plasma. Hence if a single dose of a drug with a organic half-life of 4 hours were administered orally, then after the height plasma focus had been reached, the plasma focus of the drug would fall by 50% every four hours until the whole drug had been eliminated or an extra dose was administered. The relationship between the numbers of half-lives elapsed and the share of the drug eradicated from the body following administration of a single dose is given in Table 22. An appreciation of the connection between the proportion of the drug eradicated from the physique and the variety of biological half-lives elapsed is beneficial when one is considering how much drug is eradicated from the physique in the interval between 368 Table 22. An understanding of this relationship can help in determining an appropriate dosing interval. There may also be important interpatient variability influenced by disease state and life-style. For the same drug, in a affected person who smokes will show a a lot shorter half-life; roughly 5 hours. For medication such as lithium, gentamicin or digoxin, the half-life varies with age and renal operate. This explains why elements corresponding to genetic variations between people, age and sure diseases can have an result on the biological half-life exhibited by a given drug. The organic half-life of a drug is a crucial factor that influences the plasma concentration�time curve obtained following oral administration of a multiple-dosage routine. Concentration�time curve of a drug in the body following the oral administration of equal doses of a drug at mounted time intervals In discussing how the design of multiple oral dosage regimens can affect the concentration�time course of a drug within the physique, the following assumptions have been made. The therapeutic vary expresses the vary of concentrations between which the drug will exhibit medical efficacy and minimal toxicity. In this case the plasma focus lies within the therapeutic range of the drug for only a relatively brief time following the administration of each dose and the patient stays undermedicated for relatively long periods. This enhance is a consequence of the time interval between successive doses being lower than that required for complete elimination of the earlier absorbed dose. Consequently, the entire amount of the drug remaining in the physique compartment at any time after a dose is equal to the sum of that remaining from all the previous doses.
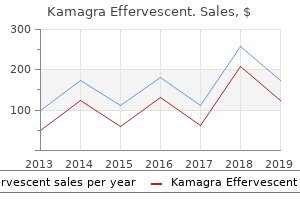
Kamagra effervescent 100mg on-lineThe condensed water additionally aids the process by hydrating microorganisms and making them extra delicate erectile dysfunction doctors albany ny cheap kamagra effervescent 100mg overnight delivery. The condensation of steam contracts it to a really small volume that creates a strain decrease into which more steam is drawn to reestablish the strain impotence newsletter order kamagra effervescent 100 mg with amex. Superheated steam is one other potential drawback that must be limited (see Chapter 15) erectile dysfunction 43 years old purchase kamagra effervescent 100 mg without a prescription. Principles of dry warmth sterilization Sterilization utilizing dry warmth is less efficient than sterilization utilizing moist warmth however is the preferred method for items which are thermostable however moisture sensitive or impermeable to steam (Sharp erectile dysfunction 20 years old order kamagra effervescent 100 mg online, 2000). In addition, temperatures larger than 220 �C are used for depyrogenation of glassware (in this case the method needs to demonstrate a 3-log reduction within the quantity of heat-resistant endotoxin). The primary benefit of dry heat sterilization over steam sterilization is its capability to penetrate objects and kill microorganisms via oxidation. The process is usually slower and the holding instances for dry heat sterilization are for much longer than these needed for steam sterilization (Table sixteen. Although some spores might survive the preliminary treatment, they then germinate and die, decreasing the numbers of organisms present as time passes (a course of referred to as autosterilization). This technique has been used within the meals industry with meat-based canned foods to avoid high-temperature sterilization. In addition, the mixture of warmth and hydrostatic stress is assumed to be synergistic. The steam is below atmospheric pressure (70 �C to 80 �C) and formaldehyde gasoline provides the sporicidal impact. Alternative means for heat delivery and control Systems for the supply of warmth via direct utility of flame, heating using alternating electric currents and microwave power have been developed and adopted in some components of the world. These embrace flexible pouches, polypropylene rigid containers, thermoformed containers, tin-free metal and foil-plastic combinations. Pharmacopoeias often suggest the use of ethylene oxide for gaseous sterilization of pharmaceutical preparations, although other chemical substances are available, such as formaldehyde, hydrogen peroxide, chlorine dioxide, peracetic acid and ozone. The chemical biocides are usually divided, in accordance with their mode of motion, into alkylating and oxidizing brokers. Alkylating gases Some alkylating gases can permeate through many polymeric supplies and are subsequently not limited to simply floor purposes. Ethylene oxide is extensively utilized in pharmaceutical manufacturing but less so in hospitals. Ethylene oxide has been shown to possess bactericidal, fungicidal, virucidal, sporicidal and protozoacidal properties (Dusseau et al. Penetration into porous supplies could be inhibited by the formation of polymers that cross-link, preventing additional sterilant entry (Chapter 15 supplies more information). Ozone as a disinfectant for water presently shows more promise, and commercial systems can be found for several purposes. Chlorine dioxide is a broad-spectrum biocide with a sporicidal activity and is principally used for the highlevel disinfection of medical units. Its functions are restricted due to its effect on materials such as uncoated aluminium foil, uncoated copper, polycarbonate and polyurethane (McDonnell, 2007). Peracetic acid exists as a liquid at room temperature and is used for high-level disinfection (discussed later). Vaporized peracetic acid can be used for the sterilization of surfaces and devices, although an extended contact time is required. Peracetic acid could cause corrosion of certain metals and rubbers and has low penetrating power. Formulations also contain excipients that cut back their adverse influence, such as scent and corrosiveness. Radiation sterilization There are two major types of radiation: electromagnetic and particulate. Hydrogen peroxide gas has been shown to be efficient against spores at a variety of temperatures. Water condensation on surfaces which would possibly be being sterilized can cut back local concentrations of hydrogen peroxide and therefore its exercise; decomposition by catalytic activity and absorption by cellulosic supplies. The mixture of hydrogen peroxide with chilly plasma, cupric or ferric ions, ozone or ultraviolet radiation has been shown to enhance activity (Dusseau et al. Both -rays and -particles are forms of ionizing radiation (Chapter 15 provides more information on the mode of motion and resistance). As with warmth sterilization, the dose�response curve to radiation can range (shoulders and tailing off can occur) but generally the exponential mannequin holds. It is used for disinfection of surfaces, together with isolators and security cabinets, and can be used as part of the remedy for drinking water (Lambert, 2013). Generally, solely membrane filters are thought to be suitable for the elimination of microorganisms. The types used for pharmaceutical functions are usually made from cellulose esters or other polymers and are extremely uniform with common areas or holes. When a liquid passes through the filter, all particles and microorganisms larger than the holes are retained. Membrane filters have the benefit of removing particles and microorganisms effectively whereas retaining little or no of the product of their holder or housing. High-level disinfectants are often thought of to be highly reactive against macromolecules and are typically divided into two main groups of highly reactive biocides: alkylating and oxidizing brokers (Table sixteen. Peracetic Filtration sterilization Thermolabile solutions can be sterilized by filtration by way of filters that remove bacteria. Filtration sterilization is the entire removal of microorganisms inside a particular size vary from liquids or gases. It is a nonterminal sterilization course of, and strict aseptic techniques have to be noticed. Items that might be filter sterilized include heat-sensitive injections and ophthalmic options, organic merchandise and air and other gases for provide to aseptic areas (Walsh & Denyer, 2013). This is an absolute mechanism since it ensures the exclusion of all particles above an outlined measurement. Oxidizing brokers additionally result in the formation of peroxyl radicals (fatty acids, lipids), hydroxyl radicals and different reactive species, although the role of these species within the lethality of those brokers at a excessive focus is subject to debate. Alkylating agents have been shown to react with macromolecules through a reaction with amino, carboxyl, thiol, hydroxyl and imino groups and amide substituents. Their interactions with proteins and enzymes and their cross-linking ability are thought to be answerable for their mechanisms of bactericidal motion. On event, the use of chemical biocides has been combined with elevated temperatures. For the disinfection of medical units corresponding to endoscopes, high-level disinfectants are sometimes utilized in automated washer disinfectors, that are designed for specific devices and guarantee automation of the process, although a precleaning stage is usually essential before disinfection takes place.
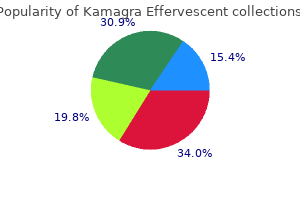
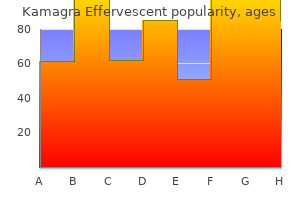
Cheap 100mg kamagra effervescent with mastercardEar powders usually need to erectile dysfunction blood flow order kamagra effervescent 100 mg overnight delivery comply with the pharmaceutical necessities for powders for cutaneous software erectile dysfunction treatment karachi buy generic kamagra effervescent 100mg on-line. Preparations requiring additional treatment at the time of dishing out Some preparations for oral use are ready from powders or granules to yield oral options or suspensions utilizing a suitable vehicle erectile dysfunction medicine in uae generic kamagra effervescent 100 mg otc. This could also be carried out on the dishing out stage or by the patient prior to erectile dysfunction doctors kansas city cheap kamagra effervescent 100mg without prescription administration. The car for any preparations for oral use is chosen with regard to the nature of the lively substance(s) and such that it provides organoleptic characteristics acceptable to the intended use of the preparation. Powders and granules for answer or suspension Powders and granules for the preparation of oral solutions or suspensions usually conform to the definitions within the regular pharmacopoeial requirements for oral powders or granules as acceptable. They could contain excipients, specifically to facilitate dispersion or dissolution and to forestall caking. After dissolution or suspension, the ensuing product should 482 taking capsules and tablets. Unfortunately, many antibiotics are bodily or chemically unstable when formulated as a solution or suspension. The method used to overcome this instability problem is to manufacture the dry components of the supposed liquid preparation in an appropriate container in the type of a powder or granules. When the product is allotted, a given quantity of water is added to reconstitute the solution or suspension. This permits enough time for warehousing and distribution of the product and storage at the pharmacy with out degradation. Amoxicillin Oral Suspension and Erythromycin Ethyl Succinate Oral Suspension are examples. Powders for oral drops Oral drops are solutions, emulsions or suspensions that are administered in small volumes, corresponding to in drops, by the means of an acceptable device. Powders for the preparation of oral drops must conform to the requirements of all different oral powders. After dissolution or suspension, they comply with the precise pharmacopoeial requirements for preprepared oral drops. If the dose is measured in drops, the label also needs to state the number of drops per millilitre or per gram of preparation. Powders for injection Injections of medicaments which are unstable in aqueous answer should be made immediately prior to administration. Powders for injection are most frequently manufactured by a freeze-drying process (see Chapter 29). The label for powders for injection should state (1) the quantity of energetic ingredient contained in the sealed container, (2) the directions for making ready the injection or intravenous infusion from the powder and (3) that when dissolved or suspended, the preparation is meant for parenteral use. After every container has been shaken, it must be emptied as fully as attainable; the test is carried out on the individual contents. As an instance, the British Pharmacopoeia defines an lively substance as one the place a single dose of powder or granules accommodates an quantity of energetic substance less than 2 mg, or lower than 2% of the entire mass of the single-dose preparation. Oral powders and granules equipped in multidose containers must adjust to this test. The strategies of manufacture of granules are mainly the same irrespective of the destiny of the granules. However, within the context of producing tablets, the mechanical properties of the granules and subsequently the means in which in which they deform and bond are crucial in the tableting process. Pharmacopoeial checks the pharmacopoeial checks for assessing the standard of most powdered and granular dosage varieties are very related. The function of those checks is indicated by its title; particulars of procedures and standards can be found within the newest applicable pharmacopeia. Single-dose oral powders should adjust to a pharmacopoeial test for uniformity of dosage units or, where justified and authorized, with the checks for uniformity of content and/or uniformity of mass. Pharmaceutical expertise of granule manufacturing Pharmaceutical granulation processes Granulation methods may be divided into two varieties: wet methods, which use a liquid in the course of, and dry strategies, by which no liquid is used. Single-dose oral powders have to adjust to a take a look at for uniformity of mass of single-dose preparations. The widespread types used are diluents, that are used to produce a unit dose weight of suitable size, and disintegrating agents, that are added to aid the break-up of the granule when it reaches a liquid medium. An adhesive (also known as a binder) within the form of a dry powder can also be added, significantly if dry granulation is employed. Dry granulation In the dry methods of granulation, the first powder particles are aggregated at excessive pressure. In each circumstances the intermediate product is damaged using a suitable milling approach to produce granular material which is normally sieved to separate the desired dimension fraction. Organic solvents are used as an alternative alternative to dry granulation when water-sensitive drugs are processed, or when a rapid drying time is required. In the traditional wet granulation method, the moist mass is pressured through a sieve to produce wet granules, that are then dried. A subsequent screening stage breaks agglomerates of granules and removes the fantastic material, which could be recycled. Variations of this conventional method are depending on the gear used, however the general principle of initial particle aggregation using a liquid remains in the entire processes. An alternative to the traditional moist granulation course of is soften granulation whereby thermosetting polymers are used to type the granules. Effect of the granulation technique on granule structure the sort and capability of granulating mixers considerably influence the work input and time necessary to produce a cohesive mass, enough liquid distribution and intragranular porosity of the granular mass. The method and situations of granulation affect intragranular pore construction by altering the degree of packing within particular person granules. It has been proven that precompacted granules, consisting of drug and binder particles, are held together by simple bonding formed during consolidation. Granules ready by moist massing consist of intact drug particles held together in a sponge-like matrix of binder. Fluidized-bed granules are similar to granules prepared by the wet-massing process but possess greater porosity, and the granule surface is covered by a film of binding agent. With spray-dried techniques, the granules consist of spherical particles composed of an outer shell with an inside core of particles or air. Wet granulation (involving moist massing) Wet granulation involves the massing of a mixture of dry main powder particles utilizing a granulating fluid. The granulating fluid accommodates a solvent that have to be volatile, so that it can be eliminated by drying, and nontoxic. Typical suitable liquids embrace water, ethanol and 2-propanol either alone or together. The granulation liquid may be used alone or, more often, as a solvent containing a dissolved adhesive (also referred to as a binder or binding agent), which is used to guarantee particle adhesion as soon as the granule is dry. The disadvantages of water as a solvent are that it could adversely have an result on drug stability, causing hydrolysis of vulnerable products, and it wants a longer drying time than natural solvents. This lengthy drying time will increase the period of the method and again might have an effect on chemical stability of the drug(s) due to the prolonged exposure to heat. The ones discussed subsequent are these which are most related to pharmaceutical granulations. Adhesion and cohesion forces in motionless films If enough liquid is present in a powder to type a very thin, immobile layer, there will be an effective lower in interparticulate distance and an increase involved space between the particles.
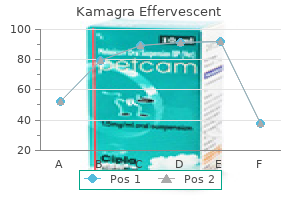
Buy kamagra effervescent 100 mg on lineAll of the required elements for the syrup could also be manufactured and saved in the dry powdered or granular state and then reconstituted (usually by the addition of water alone) on the time of dishing out or administration erectile dysfunction natural treatment kamagra effervescent 100 mg visa. After dissolution impotence kidney disease kamagra effervescent 100 mg generic, the ensuing syrup should adjust to the conventional pharmacopoeial requirements for syrups erectile dysfunction caused by performance anxiety buy 100mg kamagra effervescent visa. Ear powders Powders containing lively components may additionally be administered to the ear erectile dysfunction treatment san francisco generic kamagra effervescent 100 mg on-line. The bond energy between the particles might be elevated because of this, as the van der Waals forces of attraction are proportional to the particle diameter and inversely proportional to the square of the distance of separation. This scenario will arise with adsorbed moisture and accounts for the cohesion of barely damp powders. In dry granulation, nonetheless, the pressures used will increase the contact space between the adsorbed layers and reduce the interparticulate distance, and it will contribute to the final granule strength. Thin, motionless layers can also be formed by highly viscous solutions of adhesives. The resulting bond power will be higher than that produced by the cell films discussed next. The use of starch mucilage in pharmaceutical granulations may produce this sort of film. Sufficient liquid is often added to exceed that needed for an immobile layer and this produces a mobile film. At low moisture ranges, termed the pendular state, the particles are held collectively by lens-shaped rings of liquid. These trigger adhesion because of the floor rigidity forces of the liquid�air interface and the hydrostatic suction pressure in the liquid bridge. When all the air has been displaced from between the particles, the capillary state is reached, and the particles are held by capillary suction at the liquid�air interface, which is now solely on the granule floor. The funicular state represents an intermediate stage between the pendular and capillary states. Moist granule tensile strength increases by approximately three times from the pendular state to the capillary state. It might appear that the state of the powder mattress relies upon the total moisture content of the wetted powders however the capillary state may be reached by lowering the separation of the particles. In the massing process throughout moist granulation, continued kneading/mixing of fabric initially in the pendular state will densify the wet mass, lowering the pore volume occupied by air and finally producing the funicular or capillary state with out further liquid addition. In this state the strength of the droplet is dependent upon the surface tension of the liquid used. These wet bridges are only short-term buildings in wet granulation as a end result of the moist granules shall be dried. They are, however, a prerequisite for the formation of strong bridges shaped by adhesives present within the liquid, or by materials which dissolve within the granulating liquid. Attractive forces between stable particles In the absence of liquids and strong bridges shaped by binding brokers, there are two kinds of attractive force which may operate between particles in pharmaceutical methods. Electrostatic forces may be of significance in inflicting powder cohesion and the preliminary formation of agglomerates. Van der Waals forces, however, are roughly 4 orders of magnitude stronger than electrostatic forces and contribute significantly to the strength of granules produced by dry granulation. The magnitude of those forces will improve as the distance between adjacent surfaces decreases, and in dry granulation that is achieved with use of pressure to pressure the particles together. Solid bridges these may be fashioned by: � partial melting; � hardening binders; or � crystallization of dissolved substances. When the strain is relieved, crystallization will occur, binding the particles collectively. Mechanisms of granule formation In the dry strategies, adhesion of particles occurs because of utilized strain. A compact or sheet is produced which is larger than the granule size required and therefore the required measurement could be attained by milling and sieving. In moist granulation strategies, liquid added to dry powders has to be distributed throughout the powder by the mechanical agitation produced within the granulator. The particles adhere to each other due to liquid movies, and additional agitation and/or liquid addition causes more particles to adhere. The exact mechanism by which a dry powder is reworked right into a mattress of granules varies for every sort of granulation tools but the mechanism mentioned in the following sections serves as a useful broad generalization of the process. The proposed granulation mechanism can be divided into three stages: nucleation, transition and ball progress. This is the widespread mechanism in pharmaceutical wet granulations when an adhesive is included in the granulating solvent. The liquid will form liquid bridges, as mentioned earlier, and the adhesive will harden or crystallize on drying to form solid bridges to bind the particles. Adhesives such as polyvinylpyrrolidone, the cellulose derivatives (such as carboxymethylcellulose) and pregelatinized starch perform in this method. When the granules are dried, crystallization of this material will occur and the dissolved substance then acts as a hardening binder. The size of the crystals produced in the bridge will be influenced by the speed of drying of the granules; the longer the drying time, the bigger the particle measurement of the drug crystals. The Nucleation Granulation starts with particle�particle contact and adhesion as a outcome of liquid bridges. Further agitation densifies the pendular our bodies to type the capillary state, and these our bodies act as nuclei for additional granule progress. This stage is characterised by the presence of a massive number of small granules with a reasonably wide size distribution. Larger granules may give rise to problems in small-diameter dies because of bridging across the die and uneven fill. Ball progress Further granule progress produces massive, spherical granules, and the imply particle size of the granulating system will improve with time. If agitation is continued, granule coalescence will continue and produce an unusable, overmassed system, although that is dependent on the amount of liquid added and the properties of the material being granulated. When a second batch of powder combine is added to a bed of granules, the powder will adhere to the granules, forming a layer over the floor and thus increasing the granule measurement. This mechanism is only of relevance to the production of layered granules utilizing spheronizing tools. There will be some degree of overlap between these stages, and it is going to be very tough to establish a given stage by inspection of the granulating system. With quicker granulation equipment, the period of granulation can solely be used as a control parameter when the formulation is such that granule progress is gradual and occurs at a reasonably uniform rate. In many cases, however, the transition from a nongranulated to an overmassed system is very fast and monitoring tools is critical to stop the granulation at a predetermined point.
Purchase kamagra effervescent 100mg with amexFluid�fluid filtration Flavouring oils are generally added to liquid preparations within the form of a spirit erectile dysfunction drugs recreational use purchase kamagra effervescent 100mg online. When these spirits are added to aqueousbased formulations erectile dysfunction 18-25 cheap kamagra effervescent 100 mg on-line, a variety of the oil may come out of answer erectile dysfunction treatment in thailand purchase kamagra effervescent 100 mg amex, giving the product a degree of turbidity erectile dysfunction age 25 generic kamagra effervescent 100mg without a prescription. Removal of the oil droplets by passing them through an applicable filter (a liquid/liquid filtration process) is used to produce the desired product appearance. Before use, the compressed air must be filtered to ensure that any entrained oil or water droplets are removed. Filtration occurs on the surface of the filter on this case, and due to this fact the filter may be very skinny (typically approximately a hundred �m). Filters using the straining mechanism are used where the contaminant stage is low or small volumes have to be filtered. Examples of the use of membrane filters embody the removing of micro organism and fibres from parenteral preparations. There are two primary purposes of solid�gas filtration in pharmaceutical processing. One of specific significance in manufacturing is the removal of suspended solid material from air in order to supply air of the required standard for both processing tools or manufacturing areas. This includes the availability of air for gear such as fluidized-bed processors (see Chapters 28 and 29), film-coating equipment (see Chapter 32) and bottle-cleaning tools in order that product look and quality are maintained. The use of suitable filters also permits the particulate contamination of air in manufacturing areas to be maintained at an applicable level for the product being manufactured; for example, air free from microorganisms may be supplied to areas where sterile merchandise are being manufactured. This filter is used for solid�liquid filtration processes, however the identical fundamental rules are legitimate no matter filtration course of is being evaluated. Where the pores between filter fibres are larger than the material being removed, some particles may observe the fluid streamlines and miss the fibre, this being more doubtless if the particles are small (owing to their lower momentum) and as the distance from the centre of the fibre in the course of which they strategy will increase. To ensure the removing of all undesirable materials, filter media that use the impingement mechanism should be sufficiently thick so that material not trapped by the first fibre in its path is removed by a subsequent one. The fluid ought to circulate through the filter medium in a streamlined manner to make certain the filter works successfully, as turbulent flow may carry the particles previous the fibres. Depth filters are the main type of filter used for removal of fabric from gases. It is the Attractive forces Electrostatic and other surface forces might exert sufficient maintain on the particles to entice and retain them on the filter medium (as happens during the impingement mechanism). Air could be freed from dust particles in an electrostatic precipitator by passing the air between highly charged surfaces, which are a magnet for the mud particles. B�chner flask Autofiltration Autofiltration is the term used to describe the situation when filtered material (termed the filter cake) acts as its own filter medium. The difference between atmospheric stress and the decrease strain within the flask is added to the stress as a outcome of the unfiltered product to give the entire strain distinction. A viscous fluid will filter extra slowly than a cellular one owing to the larger resistance to movement offered by more viscous fluids (see Chapter 6). The total volume of filtrate flowing by way of the filter might be immediately proportional to the area of the filter, and therefore the speed of filtration may be elevated by using either bigger filters or a quantity of small models in parallel. Both of these approaches will also distribute the cake over a larger space and thus lower the value of L, thereby further growing the filtration fee. The contribution to resistance to filtration from the filter medium is often small in contrast with that of the filter cake, and might often be disregarded in calculations. The proportionality fixed K (m2) expresses the permeability of the filter medium and cake and can increase as the porosity of the mattress increases. It is clearly fascinating that K ought to be massive so as to maximize the filtration fee. If K is taken to characterize the permeability of the cake, it could be shown that K is given by K= e2 5(1 - e)2 S2 (25. If the stable materials is one that varieties an impermeable cake, the filtration price may be increased by adding a filter assist (discussed later), which aids the formation of open porous cakes. In practice, however, will in all probability be much less, as liquids will boil within the amassing vessel if the pressure is reduced to too low a price. One essential industrial filter, the rotary vacuum filter, also makes use of a vacuum; that is described later on this chapter. With industrial-scale liquid filtration, commonly used means of obtaining a high-pressure difference are both pumping the material to be filtered into the filter with an appropriate pump or using a pressurized vessel to drive the liquid through the filter. Most industrial filters have a positive-pressure feed; the strain used is restricted solely by the pump capability and the power of the filter to withstand the highpressure stress. Too high an applied stress might trigger the particles making up the cake to deform and due to this fact decrease the voidage (bed porosity). The effect of lowering K significantly outweighs any enhance within the filtration fee arising from a thinner cake. This is more than likely within the early levels before a continuous layer of cake has shaped. As a general rule, filtration ought to start at average pressure, which can be elevated as filtration proceeds and the cake thickness builds up. To increase the filtration fee, the viscosity of the filtrate can be lowered generally by heating of the formulation to be filtered. Care must be taken with this method when one is filtering formulations containing risky parts, or if the parts are thermolabile. In such circumstances, dilution of the formulation with water could additionally be an alternate technique of reducing the viscosity offering that the rise in the filtration rate exceeds the impact of increasing the total quantity to be filtered. Filter aids that are used embrace diatomite (a form of diatomaceous earth) and perlite (a sort of naturally occurring volcanic glass), which has been used in the filtration of, for example, penicillin and streptomycin. The use of filter aids is obviously not appropriate if the filtered materials is the meant end product. Filtration gear the filtration gear described on this chapter is that used for filtering liquids. The move via Equipment choice Ideally the equipment chosen should enable a quick filtration rate to decrease manufacturing costs, be low cost to buy and use, be simply cleaned and resistant to corrosion, and be able to filtering massive volumes of product earlier than the filter must be stripped down for cleaning or replacement. There are a number of product-related components that must be thought-about when one is deciding on a filter for a selected process. This effect is often noticed when one is filtering formulations within the laboratory utilizing filter paper in a funnel. In some instances, if the cake is allowed to construct up, the process slows to an unacceptable price, or may almost stop. In these situations, it might be necessary to take away the cake periodically or to preserve it at a relentless thickness, as occurs, for instance, with the rotary drum filter. As previously talked about, the cake thickness may be saved decrease by using a larger filter space. In addition, it might scale back the compressibility of the cake and/or stop the Interactions with the filter medium might result in leaching of the filter parts, degradation or swelling of the filter medium or adsorption of components of the filtered product onto the filter. All of these might affect the efficiency of the filtration process or the quality of the filtered product. These dictate the dimensions and sort of apparatus and the amount of time needed for the filtration course of. High operating pressures require that the gear is of sufficient energy and that acceptable safe operating procedures are adopted.
Buy kamagra effervescent 100mg lineAn opacifier erectile dysfunction young adults order 100mg kamagra effervescent with mastercard, normally titanium dioxide injections for erectile dysfunction forum purchase kamagra effervescent 100mg with amex, could additionally be added to produce an opaque shell when the fill formulation is a suspension or to prevent photodegradation of light-sensitive fill ingredients impotence at 19 purchase 100mg kamagra effervescent amex. Titanium dioxide can either be used alone to produce a white opaque shell or together with pigments to produce a coloured opaque shell erectile dysfunction treatment new orleans discount 100mg kamagra effervescent mastercard. Properties of soft gelatin shells Oxygen permeability the gelatin shell of a delicate gelatin capsule supplies an excellent barrier towards the diffusion of oxygen into the contents of the product. The oxygen permeability decreases with the relative humidity and the glycerol content in the gelatin shell formulation (Hom et al. For maximum protection against the ingress of oxygen, the gelatin shell must be dry and formulated to contain approximately 30% to 40% glycerol. The information present that minimum water content is found at glycerol ranges within the shell of between 30% and 40%. The residual water content of most pharmaceutical compounds saved at 20% relative humidity (the drying condition for softgels) is low and the water ranges in the fills of softgels subsequently are very low. Formulation of softgel fill supplies In terms of formulation necessities, the softgel must be thought of as a biphasic dosage form: a solid-phase capsule shell and a liquid-phase capsule fill matrix. The liquid-phase fill matrix is selected from parts with a wide range of different physicochemical properties. The selection of components is made in accordance with a quantity of of a quantity of criteria, together with the next: roughly 400 Da. Smaller hydrophilic molecules, corresponding to ethanol or indeed water, may be incorporated within the softgel fill matrix in low levels, usually below 10% by weight. The ensuing droplets allow rapid switch of the drug to the mucosa and subsequent drug absorption. Types of softgel fill matrices Lipophilic liquids/oils Trigylceride oils, similar to soya bean oil, are generally used in softgels. Nevertheless, active elements similar to hydroxycholecalciferol and different vitamin D analogues and steroids similar to oestradiol can be formulated into easy oily options for encapsulation in softgels. The drug may also be suspended in oils with acceptable excipients to ensure homogeneity during the manufacturing course of. Hydrophilic liquids Polar liquids with a sufficiently high molecular weight are commonly used in softgel formulation both to dissolve or to droop the drug. In addition, the microemulsion droplets have a high floor area, and are primarily surfactant micelles swollen with solubilized oil and drug. This excessive floor space facilitates the speedy diffusion of the drug from the dispersed oil section into the aqueous intestinal fluids, until an equilibrium distribution is established. Improved pharmacokinetic traits may be achieved with this formulation approach. Lipolysis systems In addition to selling the solubility of drug compounds, lipid formulations can also facilitate dissolution by benefiting from the pure strategy of lipolysis. Lipid parts of a softgel fill matrix, which comprise triglycerides or a partial glyceride (monoglyceride/diglyceride), are often topic to intestinal fats digestion or lipolysis. Lipolysis is the action of the enzyme pancreatic lipase on triglycerides and partial glycerides to type 2-monoglycerides and fatty acids. These 2-monoglycerides and fatty acids, known as lipolytic products, then work together with bile salts to type small droplets or vesicles. These vesicles are damaged down into smaller and smaller vesicles, ultimately resulting in the formation of combined micelles which are roughly three nm to 10 nm in measurement. In this fashion the method of lipolysis promotes the formation of a superb dissolution medium for the drug, particularly lipolytic merchandise. On the opposite hand, the absorption of a drug compound may be adversely affected by the presence of bile salts, and in such a case it might be advantageous for lipolysis to be lowered or blocked completely. It has been found that sure hydrophilic and lipophilic surfactants have the flexibility to block or promote lipolysis (MacGregor et al. These hydrophilic and lipophilic surfactants are sometimes used in softgel fill matrix formulations. Measurement of the rate and extent of lipolysis for a softgel fill matrix formulation can be achieved by an in vitro pH stat measurement technique. In this, lipolysis is quantified by the quantity of free fatty acids liberated by enzymatic digestion of the 622 lipids within the softgel fill matrix. The mixed intestinal micelles produced as a result of this lipolysis process are of physiological significance as a result of these buildings can transport excessive concentrations of hydrophobic molecules throughout the aqueous boundary layer which separates the absorptive membrane from the intestinal lumen. In distinction, the floor of the micelles stays hydrophilic, and this facilitates fast micellar diffusion throughout the aqueous boundary layer to the intestinal membrane. In the microclimate adjoining to the intestinal membrane, the pH is lower than in the intestinal lumen. This promotes demicellization, leading to the formation of a supersaturated answer of lipolytic merchandise (and hydrophobic drug, if present) near the enterocyte surface. These materials are then readily absorbed across the cell membrane by passive diffusion. Mixed intestinal micelles comprising bile salts and lipolytic merchandise can improve the bioavailability of hydrophobic medicine whose absorption is generally dissolution-rate restricted. This is because mixed intestinal micelles could be very potent solubilizing agents for a extensive range of hydrophobic drugs, much more so than easy bile salt micelles shaped in the absence of lipolytic products. For example, underneath simulated physiological situations, the aqueous solubility of cinnarizine in easy bile salt micelles is four �g mL-1, compared with 0. However, in the presence of blended micelles, the solubility of cinnarizine is additional enhanced to approximately 44 �g mL-1 (Embleton et al. Taking cinnarizine for instance, it will be advantageous to formulate a softgel fill matrix that allows lipolysis to happen in the intestinal lumen due to the high drug solubility in lipolytic merchandise. Formulation A was ready as a lipolysing formulation and formulation B was prepared as a nonlipolysing formulation, as demonstrated by the in vitro mannequin. Formulation A was composed of a digestible triglyceride oil, a hydrophilic surfactant and a lipophilic surfactant, which was chosen on the basis of its capacity to overcome the inhibitory results of the hydrophilic surfactant on the in vitro triglyceride lipolysis. In vitro, this formulation exhibited 79% lipolysis after 60 minutes in contrast with the digestible oil alone. It was proposed that the oil in formulation A, which types a fantastic oil-in-water emulsion on aqueous dilution, is rapidly digested, forming mixed intestinal micelles with endogenous bile. These micelles transport the drug to the intestinal membrane, the place the pH of the microclimate promotes micellar breakdown, facilitating enterocyte transport to the systemic circulation. In contrast, on dilution with aqueous fluids, formulation B varieties a translucent microemulsion (as indicated by a blue tinge ensuing from the Tyndall effect). As a results of this formulation failing to endure lipolysis and thereby remaining unaffected by enzymic activity, the drug is maintained throughout the oil phase, inhibiting the production of blended intestinal micelles, hence restricting absorption of the drug. The significance of the lipolysis process in enhancing the bioavailability of hydrophobic medication was investigated further in an in vivo examine. This examine in contrast the bioavailability of cinnarizine (30 mg) orally administered as a lipolysing formulation (formulation A) or a nonlipolysing formulation (formulation B) to six beagle dogs with a commercially out there pill (formulation C). The area beneath the plasma concentration�time curve (0 h to 24 h) for formulation A in contrast with the tablet preparation was considerably elevated by 64% and for formulation A in contrast with formulation B was elevated by 48%. The outcomes of this study have given useful perception into the effect of the microemulsion formulation on absorption of a hydrophobic drug in the gastrointestinal tract, and information as to how the lipolysis course of might affect bioavailability (Lacy et al.
Kamagra Effervescent: 100 mg
Discount kamagra effervescent 100 mg on-lineMushrooms and toadstools this group is characterized by the production of large reproductive fruiting our bodies of complex structure erectile dysfunction at 30 kamagra effervescent 100mg amex. Some of those fungi are edible and are used in cooking but others what is an erectile dysfunction pump buy kamagra effervescent 100mg line, such as Amanita phalloides (death cap) impotence use it or lose it buy 100mg kamagra effervescent with visa, produce potent mycotoxins that will end in death if eaten erectile dysfunction pill identifier order 100mg kamagra effervescent overnight delivery. Reproduction of fungi In the somatic portion of most fungi the nuclei are very small and the mechanism of nuclear division is unsure. Under the right environmental conditions, the organisms will swap from the somatic or vegetative progress section to a reproductive type, so that the fungus may propagate the species by producing new mycelia on contemporary food substrates. Each progeny is an exact duplicate of the parent and no species variation can happen. Schizosaccharomyces pombe) reproduce by binary fission in the same way as micro organism. The mother or father cell enlarges, its nucleus divides and, when a cross-wall is produced throughout the cell, two similar daughter cells kind. Budding happens within the majority of yeasts and is the production of a small outgrowth or bud from the mother or father cell. As the bud will increase in dimension, the nucleus divides and one of the pair migrates into the bud. A scar is left behind on the parent cell, and each parent can produce up to 24 buds. Fungi growing in a filamentous kind might employ hyphal fragmentation as a means of asexual propagation. The hyphal tips break up into component segments (called arthroconidia or arthrospores), every of which may disperse on the wind to different environments and fresh meals substrates. A limiting membrane surrounds the sporangium, and the spores contained within it are known as sporangiospores. This type of copy is discovered within the lower fungi possessing nonseptate hyphae. Separate spores produced on the ideas of specialized conidiophores are known as conidiospores. Sexual replica Sexual reproduction involves the union of two suitable nuclei and allows variation of the species. Some species produce distinguishable female and male intercourse organs on the same mycelium and are subsequently hermaphroditic, i. Others produce mycelia that are both male or female (called dioecious) and might due to this fact reproduce solely when two dissimilar organisms come together. Asexual reproduction Asexual reproduction is, normally, more important for the propagation of the species. Deuteromycetes Sometimes referred to as the Fungi Imperfecti, this group contains those fungi by which the sexual stage of reproduction has not been observed. Penicillium and Aspergillus are ascomycetes however are categorized among the Deuteromycetes as the proper stage is outwardly absent. Penicillium chrysogenum is necessary within the manufacturing of the antibiotic penicillin, whereas Aspergillus species have discovered widespread industrial use owing to their intensive enzymic capabilities. Some Aspergillus species additionally produce mycotoxins and may cause severe infections in humans. The Deuteromycetes comprise most of the human pathogens, similar to Blastomyces and Coccidioides, and some of the dermatophyte fungi. Zygomycetes these are terrestrial saprophytes possessing nonseptate hyphae and are generally referred to as the decrease fungi. Apart from their hyphae, they are often distinguished from different filamentous fungi by the presence of sporangia. Examples are Mucor and Rhizopus, which are essential in the manufacture of organic acids and the biotransformation of steroids. Ascomycetes Ascomycetes possess septate hyphae, and the sexual or perfect stage is characterized by the presence of a sac-like reproductive structure referred to as an ascus. An instance is Claviceps purpurea, which is a parasite of rye and is essential as a source of ergot alkaloids used to management haemorrhage and in treating migraine. The Ascomycetes embody the yeasts, such as Saccharomyces and Cryptococcus, together with Candida yeasts similar to Saccharomyces and Cryptococcus, together with Torulopsis and Candida. Basidiomycetes that is the most superior group, containing the mushrooms and toadstools. These are strategies used (1) to determine the efficiency or activity of antimicrobial chemical substances. In the latter class, for example, are procedures used to establish and enumerate microorganisms. These, together with staining and microscopical techniques, are described in Chapter 13. Measurement of antimicrobial activity In most of the methods used to assess the activity of antimicrobial chemical substances, an inoculum of the check organism is added to an answer of the chemical underneath take a look at, samples are eliminated over a time frame, the chemical is inactivated and the proportion of surviving cells is determined. Alternatively, culture medium is present together with the chemical, and the diploma of inhibition of growth of the test organism is measured. Because such considerations are widespread to several of the procedures described right here. A number of strains of a single species could usually be obtained from a culture collection. Different strains may happen in hospital pathology laboratories by isolation from swabs taken from contaminated sufferers or by isolation from contaminated meals, cosmetic or pharmaceutical products, and many different sources. Strains obtained in these methods are more probably to exhibit variations in resistance to antimicrobial chemicals. Strains from human or animal infections are frequently extra immune to antimicrobial chemical substances, notably antibiotics, than these from other sources. Similarly, strains derived from contaminated medicines could additionally be more proof against preservative chemical substances than those obtained from tradition collections. Many official testing methods now restrict the number of instances the tradition assortment specimen may be regrown in recent medium (called the variety of subcultures or passages) earlier than it should be replaced. This is as a result of the characteristics of the organism (including its resistance to antimicrobial chemicals) may progressively change on account of mutation and pure choice by way of the various generations that may arise during months or years of laboratory cultivation. Composition and pH of the tradition medium There are a number of strategies of assessing antimicrobial activity which all have in widespread the measurement of inhibition of growth of a test organism when the antimicrobial chemical is added to the tradition medium. The medium could comprise substances that antagonize the motion of the test compound. The antimicrobial actions of a number of teams of chemicals are influenced by the ease with which they Factors to be managed within the measurement of antimicrobial activity Origin of the check organism Although two cultures might bear the same generic and particular name, i. This, in flip, is influenced by the lipid solubility of the substance, as a end result of the membrane incorporates a high proportion of lipid and tends to allow the passage of lipid-soluble substances. Many antimicrobial chemical compounds are weak acids or weak bases, which are extra lipid soluble within the un-ionized type.
References - Cameron N, editor. Human Growth and Development. London's Academic Press, Elsevier Science; 2002; pp. 6-7, 85.
- Goodgame RW, Kimball K, Ou CN, et al. Intestinal function and injury in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome- related cryptosporidiosis. Gastroenterology 1995;108:1075.
- Ohayon MM. Interactions between sleep normative data and sociocultural characteristics in the elderly. J Psychosom Res 2004;56:479-86.
- Rutherford RB: Randomized EVAR trials and advent of level I evidence: a paradigm shift in management of large abdominal aortic aneurysms? Semin Vasc Surg 19(2):69-74, 2006.
|