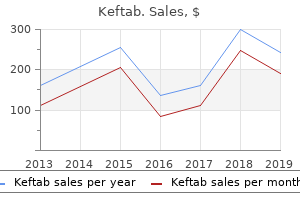
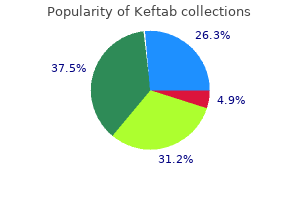
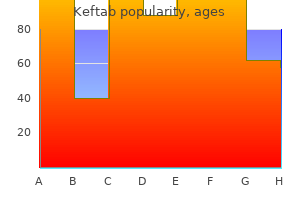
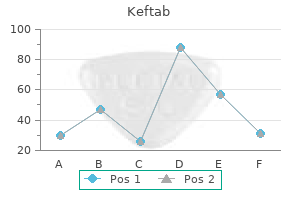
Keftab
Roger E. Stevenson, M.D. - Greenwood Genetic Center
- Greenwood, South Carolina
Keftab: 750 mg, 500 mg, 375 mg, 250 mg, 125 mg
Buy keftab 750mg overnight deliveryNeural crest migration is influenced by a selection of molecules residing in the extracellular matrix virus 20 generic keftab 125mg with amex. Overall zombie infection symbian 94 buy 250mg keftab visa, intrinsic elements are heavily involved in organizing the migrating streams of cells antimicrobial antibiotic purchase 750mg keftab fast delivery. During their migratory section infection 2 cure race best 375 mg keftab, neural crest cells are exquisitely sensitive to steering molecules, most of which are inhibitory. Among the most important of these steering molecules are the ligand/receptor pairs Robo/Slit, Neuropilin/Semaphorin, and Ephrin/Eph (see Table 11. Migratory neural crest cells extend protrusions that each check the setting and are a part of the propulsive mechanism. In a migrating stream of neural crest cells, contact with the cells behind additionally leads to the pulling on the trailing fringe of the cells, thus leading to a web ahead movement of the main cells. Specific examples of the environmental control of neural crest cell migrations are given later in this chapter. Much remains to be realized about what causes neural crest cells to cease migrating, but usually they stop migrating in areas the place repulsive alerts are low. What controls their differentiation is a principal question of neural crest biology. According to one, all neural crest cells are equal in developmental potential, and their final differentiation is decided by the environment through which they migrate and into which they finally settle. The different hypothesis suggests that premigratory crest cells are already programmed for different developmental fates, and that sure stem cells are favored, whereas others are inhibited from further growth during migration. More latest analysis signifies that the actual answer could be found someplace between these two positions. Increasing evidence suggests that amongst migrating neural crest cells is a mix of cells the fate of which has been predetermined inside the neural tube and cells the last word phenotype of which depends on environmental influences. A correlation exists between the time of migration of neural crest cells from the neural tube and their developmental potential. Many cells that first start to migrate have the potential to differentiate into a number of several sorts of cells. Crest cells that begin to migrate later are capable of forming solely derivatives characteristic of more dorsal areas. One kind of experiment entails the transplantation of neural crest cells from one part of the body to one other. For instance, many neural crest cells from the trunk differentiate into sympathetic neurons that produce norepinephrine because the transmitter. In the cranial region, nonetheless, neural crest cells give rise to parasympathetic neurons, which produce acetylcholine. If thoracic neural crest cells are transplanted into the pinnacle, some cells differentiate into cholinergic parasympathetic neurons as a substitute of the adrenergic sympathetic neurons normally produced. Conversely, cranial neural crest cells grafted into the thoracic region reply to their new environment by forming adrenergic sympathetic neurons. The subectodermal pathway of neural crest migration (asterisk) is comparatively cell free, however it contains a nice mesh of extracellular matrix molecules. Attachment to and migration over these substrate molecules are mediated by the family of attachment proteins known as integrins. Many of the regional influences on the differentiation of native populations of neural crest cells at the second are acknowledged to be interactions between the migrating neural crest cells and particular tissues that they encounter during migration. Examples of tissue interactions that promote the differentiation of particular neural crest derivatives are given in Table 12. The plasticity of differentiation of neural crest cells could be proven by cloning single neural crest cells in culture. In the identical medium, and apparently in the same environmental circumstances, the progeny of the one cloned cells frequently differentiate into neuronal and nonneuronal. Similarly, if individual neural crest cells are injected in vivo with a dye, more than 50% of the injected cells will give rise to progeny with two to four completely different phenotypes containing the dye. By exposing cloned neural crest precursor cells to specific environmental circumstances in vitro, one can begin to understand the mechanisms that decide phenotype in vivo. In one experiment, rat neural crest cells grown under commonplace in vitro situations differentiated into neurons, but after they have been uncovered to glial development issue, they differentiated into Schwann cells because the glial growth factor suppressed their tendency to differentiate into neurons. Some evidence means that native environmental influences effect Polycombmediated adjustments in chromatin structure, thus permitting the expression of position-specific genes. Not all forms of transformations amongst possible neural crest derivatives can occur. Most experiments suggest that early neural crest cells segregate into intermediate lineages that preserve the option of differentiating into several, however not all, forms of particular person phenotypes. During regular growth, the sympathetic neurons that innervate sweat glands are catecholaminergic till their axons truly contact the sweat glands. An essential current development in neural crest biology is the recognition in grownup tissues of neural crest�derived cells with multipotent stem cell properties. Such cells have been present in a wide selection of tissues, corresponding to ganglia, peripheral nerve sheaths, dental pulp. For many years, it was traditional to subdivide the neural crest into trunk and cranial elements. In more recent years, however, it has become increasingly apparent that the neural crest in the posterior rhombencephalic area, often known as the circumpharyngeal crest, represents another main subdivision seeding cells into the pharyngeal region, the outflow tract of the guts and nice vessels, and far of the gut-associated crest derivatives. Adrenal medullary chromaffin cells Glucocorticoids secreted by adrenal cortex Enteric neurons Sympathetic neurons Sensory neurons Pigment cells Gut wall Spinal wire, notochord, somites Peripheral target tissue Extracellular matrix alongside pathway of migration Trunk Crest the neural crest of the trunk extends from the extent of the sixth somite to essentially the most caudal somites. These pathways happen in several sequences and are subject to different controls. The first neural crest cells to leave the neural tube migrate round and between the somites, which are nonetheless in an epithelial configuration. Their migratory path follows the intersomitic blood vessels, and Many neural crest cells are bipotential, relying on alerts from their local environment for cues to their final differentiation. The first emigrating cells (pathway 1) follow the ventral (sympathoadrenal) pathway (red arrows). The second wave of emigrating cells (pathway 2) follows the ventrolateral pathway indicated by the purple arrow. The last cells to depart the neural tube (pathway 3) observe the dorsolateral pathway (green arrow) whereas they go on to differentiate into pigment cells. It may be that at this early stage no different pathway is out there to these migrating cells. Slightly later in improvement, the somites are differentiated into sclerotomal and dermomyotomal compartments. At this stage, the neural crest cells preferentially enter the anterior compartment of the sclerotome. Another necessary repulsion mechanism is predicated on the presence of EphB receptors on the migrating neural crest cells and ephrinB proteins on cells of the posterior sclerotome. Passage through the anterior sclerotome is facilitated by extracellular matrix molecules, particularly thrombospondin. They kind the ganglia in concert with the outgrowth of the motor axons from the spinal twine, which follow related environmental cues. In mammals, cells that follow this pathway depend on the Steel factor, produced by the dermomyotome, to be capable of use this pathway.
Generic keftab 750 mg onlineNeuroblasts migrate via the white matter to these layers by using radial glial cells as their guides antibiotics for acne keloidalis generic keftab 750 mg. Many congenital malformations of the nervous system are primarily based on incomplete closure of the neural tube or associated skeletal structures antibiotics for uti nausea keftab 750mg on-line. In the spinal cord antibiotics reduce bacterial biodiversity order keftab 500 mg without prescription, the spectrum of defects ranges from a extensively open neural tube (rachischisis) to relatively minor defects within the neural arch over the cord (spina bifida occulta) infection urinaire homme buy 250mg keftab fast delivery. Neural function seems in live performance with the structural maturation of varied parts of the nervous system. During successive weeks, the reflex movements turn into more advanced, and spontaneous actions appear. What molecule produced by the notochord is instrumental in inducing the floor plate of the neural tube An toddler with a tuft of hair over the lumbar area of the vertebral column undergoes surgery for a congenital anomaly in that area. During surgical procedure, it was discovered that the dura and arachnoid layers over the spinal wire were full, but that the neural arches of several vertebrae had been missing. Complete failure of the neural tube to close in the region of the spinal cord is a. Pregnant girls sometimes first turn out to be conscious of fetal movements during what month of pregnancy What is the likely look of the spinal twine and brachial nerves in an toddler who was born with the congenital absence of one arm (amelia) The cell biology of neurogenesis: toward an understanding of the development and evolution of the neocortex. Development of coherent neuronal activity patterns in mammalian cortical networks: frequent principles and native heterogeneity. Noses and neurons: induction, morphogenesis, and neuronal differentiation in the peripheral olfactory pathway. A homeodomain protein code specifies progenitor cell identification and neuronal fate in the ventral neural tube. Getting axons onto the proper path: the position of transcription factors in axon guidance. Pattern formation within the vertebrate neural tube: a sonic hedgehog morphogen-regulated transcriptional community. Parasympathetic neurons originate from nerve-associated peripheral glial precursors. Siah regulation of Pard3A controls neuronal cell adhesion during germinal zone exit. Morphogen to mitogen: the a quantity of roles of hedgehog signaling in vertebrate neural improvement. Slit-mediated repulsion is a key regulator of motor axon pathfinding within the hindbrain. Mechanisms regulating the development of the corpus callosum and its agenesis in mouse and human. The preliminary appearance of the cranial nerves and related neuronal migration in staged human embryos. The timing and sequence of appearance of neuromeres and their derivatives in staged human embryos. Hoxa2- and rhombomere-dependent growth of the mouse facial somatosensory map. Otx dose-dependent built-in management of anteroposterior and dorso-ventral patterning of midbrain. Oligodendrocyte precursors migrate along vasculature within the creating nervous system. Wnt won the warfare: antagonistic role of Wnt over shh controls dorso-ventral patterning of the vertebrate neural tube. Integrity of creating spinal motor columns is regulated by neural crest derivatives at motor exit points. How does Fgf signaling from the isthmic organizer induce midbrain and cerebellum growth Sonic hedgehog functions by way of dynamic adjustments in temporal competence within the creating forebrain. Among the model new transcription components upregulated in specified neural crest precursor cells are snail-1,-2 (formerly referred to as slug), Twist, and Foxd-3, that are instrumental in allowing the neural crest cells to undergo an epitheliomesenchymal transformation. These cells then break free from the neural epithelium and then migrate away as mesenchymal cells. Neural crest cells break away from the neural tube in the trunk at the degree of the last-formed somite or the neural plate within the head by altering their form and properties from these of typical neuroepithelial cells to those of mesenchymal cells. These molecules remain downregulated throughout migration, but after neural crest cells have accomplished their migrations and have differentiated into sure buildings. In the pinnacle, the place closure of the neural plate has not but occurred, neural crest cells must penetrate the basal lamina underlying the neural plate. This is achieved by the production of enzymes that degrade components of the basal lamina and by sending out processes that penetrate the basal lamina. The neural crest, the existence of which has been recognized for greater than a century, varieties an exceptionally wide range of cell varieties and structures, including a number of forms of nerves and glia, connective tissue, bones, and pigment cells. Its significance and prominence are such that the neural crest has usually been known as the fourth germ layer of the physique. Not until enough strategies of marking neural crest cells turned available-first with isotopic labels and subsequently with secure organic markers, monoclonal antibodies, intracellular dyes, and genetic markers-did the neural crest turn into one of the broadly studied components of the vertebrate embryo. More just lately, emphasis has shifted to research on the mouse, especially for dissecting molecular controls, but it seems that most of the info on the biology of the neural crest derived from birds may be utilized to mammalian embryos. Some important syndromes and malformations are based mostly on abnormalities of the neural crest. Tracing the history of the neural crest in any area involves consideration of the following: (1) its origin, induction, and specification; (2) epithelial-tomesenchymal transformation and emigration from the neural tube; (3) migration; and (4) differentiation. Each of these phases within the development of the generic neural crest is roofed before neural crest development in specific regions of the physique is taken into account. In addition to neural crest precursors, the neural plate border accommodates a number of kinds of progenitor cells, similar to progenitors of the ectodermal placodes in the anterior area. In response to these inductive indicators, cells on the border of the neural plate activate genes coding for a quantity of transcription factors, together with Msx-1,-2, Dlx-5, and Pax-3/Pax-7. They also activate another set of genes (Foxd-3, Sox-10, and Ets-1), which specify the neural crest progenitor cells inside the neural plate border. In this environment, the cells bear intensive migrations along several well-defined pathways. These migrations are determined by intrinsic properties of the neural crest cells and options of the exterior environment encountered by the migrating cells. One of its major features is to stop premature differentiation of the migrating cells.
375 mg keftab free shippingOne important operate of the Hox genes in hematopoiesis is the regulation of proliferation virus incubation period discount 250 mg keftab visa. The first wave begins with precursors throughout the yolk sac 3m antimicrobial filter cheap keftab 500 mg without prescription, which produce primitive nucleated erythrocytes that mature inside the bloodstream bacterial vaginosis symptoms discount keftab 125 mg overnight delivery. The second wave additionally begins within the yolk sac antibiotic japan discount keftab 750 mg on-line, however the precursor cells then colonize the embryonic liver and produce the first of a era of definitive fetal erythrocytes that are dominant during the prenatal period. Some of these definitive erythroid progenitor cells send progeny directly from the liver into the bloodstream as definitive fetal erythrocytes. Others seed the bone marrow and produce adult-type erythrocytes later within the fetal period. The earliest phases of erythropoiesis are acknowledged by the conduct of the precursor cells in tradition, somewhat than by morphological or biochemical differences. Later in growth, synthesis shifts to the kidney, which stays the location of erythropoietin manufacturing in adults. These pluripotent stem cells, generally referred to as hemocytoblasts, have nice proliferative capability. They produce huge numbers of progeny, most of that are cells on the next stage of differentiation, however they also produce small numbers of their unique stem cell type, which act as a reserve able to replenishing particular person strains of cells ought to the need come up. Very early in improvement, the line of lively blood-forming cells subdivides into two separate lineages. Lymphoid stem cells in the end kind the two traces of lymphocytes: B lymphocytes (which are responsible for antibody production) and T lymphocytes (which are responsible for cellular immune reactions). Myeloid stem cells are precursors to the other strains of blood cells: erythrocytes, the granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils), monocytes, and platelets. The second-generation stem cells (lymphoid and myeloid) are still pluripotent, although their developmental potency is restricted because neither lymphoid cells nor myeloid cells can form the progeny of the other type. For each lineage, the forming cell varieties should move through several levels of differentiation earlier than they attain their mature phenotype. From mesenchymal stem cells, a primitive wave of hematopoiesis that occurs in the early embryo is followed by a definitive wave of mature hematopoiesis. The first recognizable stage is the proerythroblast, a large, extremely basophilic cell that has not yet produced sufficient hemoglobin to be detected by cytochemical analysis. After the lack of the nucleus and most cytoplasmic organelles, the immature pink blood cell, which still accommodates a small number of polysomes, is a reticulocyte. Reticulocytes are launched into the bloodstream, the place they proceed to produce small amounts of hemoglobin for 1 or 2 days. The thickness of the tan background is proportional to the amount on the corresponding stages of erythropoiesis. The final stage of hematopoiesis is the mature erythrocyte, which is a terminally differentiated cell due to the loss of its nucleus and most of its cytoplasmic organelles. Erythrocytes in embryos are bigger than their adult counterparts and have a shorter life span (50 to 70 days within the fetus versus one hundred twenty days in adults). Hemoglobin Synthesis and Its Control Both the purple blood cells and the hemoglobin inside them endure isoform transitions throughout embryonic development. The grownup hemoglobin molecule is a fancy composed of heme and 4 globin chains: two and two chains. During the period of yolk sac hematopoiesis, embryonic globin isoforms are produced. The earliest embryonic hemoglobin, typically known as Gower 1, is composed of two (-type) and two (-type) chains. Fetal hemoglobin consists of two adult-type chains, which form very early in embryogenesis, and two chains, the main fetal isoform of the chain. The major adaptive value of the fetal isoform of hemoglobin is that it has a higher affinity for oxygen than the grownup kind. This is advantageous to the fetus, which depends on the oxygen focus of the maternal blood. During the early interval of somite formation, networks of small vessels quickly seem in many regions of the embryonic physique. The first is the specification of a population of vascular precursors, referred to as angioblasts. These cells turn out to be organized into a major capillary plexus via a course of known as vasculogenesis. To keep pace with the quickly growing embryo, the primary capillary plexus must quickly bear reorganization through the resorption of present vessels and the sprouting of new branches to assist the increasing vascular community. Angiogenesis continues not only within the prenatal period but additionally throughout adult life, as tissues and organs regularly adapt to changing conditions of life, whether or not regular or pathological. Detailed descriptive research and transplantation experiments involving intrinsic cellular labels or graft-specific monoclonal antibody labels have proven that angioblasts arise from most mesodermal tissues of the physique, except notochord and prechordal mesoderm (Table 17. Under additional stimulation by progress components, competent endothelial cells of the first capillary plexus kind vascular sprouts within the earliest levels of angiogenesis. This is adopted by the recruitment of surrounding mesenchymal cells to kind the mobile components of the vascular wall. Many of the bigger blood vessels, such as the dorsal aortae, are fashioned by the coalescence of angioblasts in situ. Other equally giant channels, such as the endocardium, are shaped by angioblasts migrating into the area from other websites. Other vessels, especially the intersegmental vessels of the principle body axis and vessels of the central nervous system, arise as vascular sprouts from existing larger vessels. Many of the angioblasts of the trunk are initially associated with the splanchnic mesoderm. The developmental processes resulting in the initial formation of the aorta are beginning to be understood. The endothelium of the early paired aortae is derived from splanchnopleure and requires an interaction with the underlying endoderm for its growth. While the aortae are still in the paired stage, somitederived cells contribute to their dorsal walls. Concomitantly, the ventral splanchnopleure�derived endothelium begins to give rise to clusters of hematopoietic stem cells. Then the dorsal somite� derived endothelial cells overgrow the ventral splanchnopleure� derived endothelial cells. All stages in the formation of the vascular system happen in response to the affect of highly effective progress components and their receptors. A sprouting issue, angiopoietin-1, interacts with its receptor, Tie-2, on the endothelial cells at sites the place endothelial sprouts will happen. Stalk cells, on the other hand, categorical high ranges of Notch and are mitotically lively. Whereas tip cells are migratory and make contact with tip cells from other areas to form incipient capillary loops, dividing stalk cells kind a lumen and differentiate into mature endothelial cells with a basement membrane surrounding them. The next step in building a blood vessel is formation of the vascular wall, which in the trunk and extremities is derived from native mesoderm that becomes related to the endothelial lining of the vessel. In the pinnacle and plenty of areas of the aortic arch system, mesenchyme derived from neural crest ectoderm is a major contributor to the connective tissue and clean muscle of the vascular wall.
Buy keftab 125mg on lineEach secondary spermatocyte produces two immature haploid gametes antibiotics used for cellulitis buy keftab 375 mg without prescription, the spermatids virus 2014 usa generic 500mg keftab mastercard. The 4 spermatids produced from a main spermatocyte progenitor are nonetheless linked to each other and sometimes to as many as a hundred different spermatids as properly infection high blood pressure quality keftab 375 mg. The strategy of transformation from spermatids to spermatozoa is called spermiogenesis or spermatid metamorphosis will antibiotics for uti help kidney infection generic keftab 375mg visa. One is the progressive discount within the dimension of the nucleus and super condensation of the chromosomal materials, which is associated with the replacement of histones by protamines. Along with the changes in the nucleus, a profound reorganization of the cytoplasm occurs. Cytoplasm streams away from the nucleus, but a condensation of the Golgi apparatus on the apical finish of the nucleus ultimately offers rise to the acrosome. The acrosome is an enzyme-filled structure that plays a vital position in the fertilization process. At the opposite finish of the nucleus, a prominent flagellum grows out of the centriolar area. Type B spermatogonia, that are simply getting into the preleptotene stage of the first meiotic division and turning into primary spermatocytes, are located outside (basal to) the blood-testis barrier. Latestage spermatids are attached to the apical surface of Sertoli cells by aggregates of tight-junction proteins, known as surface adhesion complexes. At a selected stage in spermatid growth, the floor adhesion complexes break down, and the mature spermatids are launched into the lumen of the seminiferous tubule. Biologically lively laminin fragments, originating from the degenerating surface adhesion complexes, make their way to the tight-junction complex that constitutes the blood-testis barrier. These fragments, along with certain cytokines and proteinases, degrade the tight-junctional proteins of the blood-testis barrier, and the blood-testis barrier, situated apically to the preleptotene major spermatocyte, breaks down. Then testosterone, which is 50 to 100 times more concentrated within the seminiferous tubule than in the general circulation, stimulates the synthesis of new tight-junction proteins on the basal side of that preleptotene spermatocyte, thus reestablishing the integrity of the blood-testis barrier. In parallel, a new set of spermatids turns into adherent to the apical surface of the Sertoli cells by way of the formation of recent surface adhesion complexes. The spectrum of anomalies ranges from double heads or tails to defective flagella or variability in head measurement. A widespread number of sperm abnormality is globozoospermia, which is characterized by a rounded head resulting from the absence or malformation of the acrosome. If the proportion of faulty spermatozoa increases to greater than 20% of the whole, reduced fertility may end result. These domains endure numerous adjustments as the sperm cells mature in the male and at a later level when the spermatozoa are traveling through the feminine reproductive tract. Many of the subtler features of this adaptation are underneath hormonal control and are cyclic. This section briefly reviews the aspects of feminine reproductive construction which might be of biggest importance in understanding gamete transport and embryonic development. Ovaries and Uterine Tubes the ovaries and uterine (or fallopian) tubes kind a useful complex dedicated to the production and transport of eggs. In addition, the uterine tubes play an necessary position as a conduit for spermatozoa and in making ready them to be fully practical through the fertilization process. The uterine tube consists of three anatomically and functionally recognizable segments: the ampulla, the isthmus, and the intramural segments. The uterine tube is characterised by a complex internal lining, with a excessive density of distinguished longitudinal folds within the higher ampulla. These folds turn into progressively less complicated in components of the tube nearer to the uterus. The lining epithelium of the uterine tubes incorporates a mix of ciliated cells that help in gamete transport and secretory cells that produce a fluid supporting the early growth of the embryo. Layers of easy muscle cells all through the uterine tubes present the basis for peristaltic contractions. The amount and performance of many of those parts are under cyclic hormonal control, and the overall impact of these changes is to facilitate the transport of gametes and the fertilized egg. The two segments of the uterine tubes closest to the uterus play significantly necessary roles as pathways for sperm transport towards the ovulated egg. The intramural segment, which is embedded in the uterine wall, has a really skinny lumen containing mucus, the composition of which varies with phases within the menstrual cycle. This segment serves as a gateway regulating the passage of spermatozoa into the uterine tube, however it also restricts the entry of micro organism into the tube. The middle isthmus section serves as an important web site of momentary sperm storage and participates within the final phases of practical maturation of sperm cells (see Chapter 2). Uterus the principal functions of the uterus are to receive and keep the embryo throughout pregnancy and to expel the fetus on the termination of being pregnant. The first operate is carried out by the uterine mucosa and the second by the muscular wall. Under the cyclic effect of hormones, the uterus undergoes a series of distinguished adjustments all through the course of each menstrual cycle. The mucosal lining, called the endometrium, has a structure that modifications day by day throughout the menstrual cycle. The endometrium could be subdivided into two layers: a useful layer, which is shed with every menstrual period or after parturition, and a basal layer, which stays intact. All these constructions participate within the implantation and nourishment of the embryo. The cervical epithelium produces glycoprotein-rich cervical mucus, the composition of which varies considerably throughout the menstrual cycle. The differing bodily properties of cervical mucus make it easier or harder for spermatozoa to penetrate the cervix and find their way into the uterus. Vagina the vagina is a channel for sexual intercourse and serves because the birth canal. It is lined with a stratified squamous epithelium, however the epithelial cells contain deposits of glycogen, which vary in amount all through the menstrual cycle. The low pH of the upper vagina serves a bacteriostatic function and prevents infectious brokers from entering the upper genital tract via the cervix and in the end spreading to the peritoneal cavity by way of the open ends of the uterine tubes. Note the massive number of small projections which are collectively involved in capturing an ovulated oocyte. New York: Parthenon Publishing; 2001) Hormonal Control of the Female Reproductive Cycle Reproduction in girls is governed by a complex sequence of interactions between hormones and the tissues that they affect. Hormones concerned principally in the proliferative phase of the menstrual cycle are represented by dashed arrows; these involved principally in the secretory section are represented by stable arrows. The hypothalamus influences hormone manufacturing by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. The pituitary hormones are unfold by way of the blood throughout the complete physique and act on the ovaries, that are stimulated to produce their very own sex steroid hormones. During being pregnant, the placenta exerts a robust effect on the mother by producing several hormones. The final degree of hormonal management of female reproduction is exerted by the ovarian or placental hormones on different reproductive goal organs. Hypothalamic Control the first stage of hormonal control of replica is in the hypothalamus.
Buy generic keftab 125mg lineThis new foramen preserves the direct connection between the proper and left atria infection z movie buy keftab 125mg free shipping. Shortly after the looks of the foramen secundum antimicrobial jewelry 375 mg keftab mastercard, a crescentic septum secundum begins to type simply to the best of the septum primum antibiotic kidney damage 500 mg keftab free shipping. This construction antibiotics for uti philippines buy cheap keftab 375mg, which grows out from the dorsal to the ventral a part of the atrium, types a foramen ovale. The place of the foramen ovale permits a lot of the blood that enters the proper atrium via the inferior vena cava to pass directly by way of it and the foramen secundum into the left atrium. Because of the orientation of the orifice and its pressure, blood getting into the best atrium from the inferior vena cava passes principally through the interatrial shunt and into the left atrium, whereas blood getting into from the superior vena cava and the coronary sinus flows through the tricuspid valve into the proper ventricle. This accounts for the partial spiraling of the aorta and the pulmonary artery in the grownup heart. Before and through the partitioning course of, the neural crest�derived cells of the wall of the outflow tract start to produce elastic fibers, which provide the resiliency required of the aorta and other great vessels. Elastogenesis follows a gradient, first via the outflow tract, then into the aorta itself, and in the end into the smaller arterial branches off the aorta. These valves, each of which has three leaflets, forestall ejected blood from washing back into the ventricles. Cranial neural crest cells and cardiac mesoderm contribute to the formation of the semilunar valves. As beforehand acknowledged, essentially the most proximal extensions of the truncoconal ridges contribute to the formation of the interventricular septum. Just previous the aortic facet of the aortic semilunar valve, the 2 coronary arteries join the aorta to provide the guts with blood. Development of the Ventricular Myocardium While the guts is undergoing partitioning, essential changes are also going down in the ventricular walls. In addition to cardiomyocytes, the ventricular wall accommodates connective tissue cells, largely derived from the epicardium, and branches of the coronary circulation (see p. The compact layer develops in close communication with the epicardium and receives molecular signals from it. Contraction of the cardiomyocytes of the compact layer provides most of the pressure in ventricular pumping, however the trabecular layer additionally contributes to the overall effort. The trabecular layer is spongy and the individual trabeculae appear ropelike on the internal surface of the ventricles. This overall arrangement facilitates the change of nutrients and gases from the interior of the heart chambers to the myocardium, especially earlier than the institution of the coronary circulation. Trabeculae first appear as ridges along the inside partitions of the ventricular Partitioning of the Outflow Tract of the Heart In the very early tubular heart, the outflow tract is a single tube, the bulbus cordis. Closest to the heart, the wall of the outflow tract consists largely of cells derived from the secondary coronary heart subject; extra distally, cells derived from the neural crest predominate. Although initially a single channel, the outflow tract is partitioned into separate aortic and pulmonary channels by way of the appearance of two spiral truncoconal ridges, that are derived largely from neural crest mesenchyme. Initially, the trabecular layer could be very spongy, but it undergoes compaction whereas development proceeds. The compact layer of the ventricular myocardium develops later than the trabecular myocardium. In contrast to most cells of the myocardium, these of the conducting system are characterized by a very low proliferative rate. Left ventricular noncompaction is a situation characterized by a prominence of trabeculae in relation to the compact layer of the ventricular wall. The general morphology of this situation resembles that of early embryonic hearts. A genetic basis is suspected for some instances, but a quantity of etiologies are probably involved. A fundamental problem with this condition is inefficient pumping of blood, resulting in coronary heart failure. In addition, arrhythmias or sudden cardiac death can result from this defect in improvement. Sympathetic (adrenergic) nerve fibers, which act to pace up the heartbeat, arrive as outgrowths from sympathetic ganglia of the trunk. Parasympathetic (cholinergic) innervation is derived from the cardiac neural crest. Neurons of the cardiac ganglia, which are the second-order parasympathetic neurons, migrate on to the heart from the cardiac neural crest. These synapse with axons of firstorder parasympathetic neurons that gain entry to the heart through the vagus nerve. If the cardiac neural crest is removed in the early chick embryo, cholinergic cardiac ganglia still type. Experiments have decided that the nodose placodes compensate for the lack of neural crest by supplying neurons that exchange the traditional parasympathetic ones. The left and proper bundle branches emanate from this structure and ultimately spread out alongside the ventricular walls as the Purkinje fibers. The beat is gradual (<40 beats/min), and pacemaking activity begins close to the inflow region of the center and spreads towards the outflow tract via spontaneous depolarization of the cells. While the atrial and ventricular chambers take form, the differentiating cardiomyocytes are unable to generate or propagate beats in the same method because the cells of the primary myocardium. To coordinate the beat of the expanding chambers, the mammalian coronary heart should develop a specialized conducting system that takes advantage of some components from the first myocardium in the atrial area and provides to them a phylogenetically newer conducting system throughout the ventricular myocardium. Pacemaker cells have just lately been proven to come up individually from a discrete space of lateral plate mesoderm behind the posterior finish of the first and secondary coronary heart fields. Terminals of sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve fibers grow into the world to modulate the heartbeat. The contractile stimulus then passes to the atrioventricular node through mechanisms nonetheless not well understood. From early growth, the atrioventricular node, which can additionally be a direct spinoff of the first myocardium, features to decelerate the conductive impulse to separate the contractions of the atrial and ventricular chambers. Activity of the transcriptional repressor Tbx-3 prevents the first myocardial cells destined to kind the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes from differentiating into the extra highly contractile and extra poorly conducting cells that characterize the ventricular chambers. From the atrioventricular node, the pacemaking impulse then passes with growing velocity down the atrioventricular bundle and into left and right bundle branches before spreading out over the ventricular myocardium because the Purkinje fibers. Branches from this ring ultimately move alongside both aspect of the interventricular septum after which arborize along the ventricular partitions as Purkinje fibers. The part of the conducting system consisting of bundle and Purkinje fibers represents a network of highly modified cardiac muscle fibers, the structural and useful traits of which have been highly modified during improvement by paracrine influences. Umbilical twine Umbilical arteries from the endocardium, stimulates the transformation of early cardiomyocytes into conducting cells of the Purkinje system. Purkinje cells elaborate connexins, which facilitate speedy conduction from one cell to another. Very fast conduction is necessary to guarantee a virtually simultaneous beat throughout the ventricle. The embryo should prepare for the second, however, when it all of a sudden shifts to a completely different sample of oxygenation of blood by way of the lungs, quite than the placenta, thus making the modifications of the fetal plan of circulation important. Poorly oxygenated blood flowing within the inferior vena cava could be backed up because of the power of the umbilical blood circulate.
Discount keftab 500mgThe current study revealed that 7 nmol/mL cyclic Pro-Hyp brought on a major enhance in the growth rates of pores and skin fibroblasts on collagen gel compared with the same concentration of linear Pro-Hyp bacteria living or nonliving discount 125mg keftab with visa. This result instructed that the increase in cyclic Pro-Hyp in human blood after ingestion of collagen hydrolysate could effectively improve wound therapeutic process in damaged skin tissues systemic antibiotics for acne vulgaris cheap 750mg keftab. Similarly antibiotics for uti for cats cheap 125mg keftab fast delivery, earlier reports have proven that quick peptides with excessive hydrophobicity exhibit excessive uptake by cells [40] bacteria die when they are refrigerated or frozen discount 500 mg keftab with visa, and cyclic peptide formation could improve cell incorporation of Pro-Hyp. However, the concentration of cyclic Pro-Hyp detected in human blood was significantly decrease than that of linear Pro-Hyp after ingestion of collagen hydrolysate. Fermentation or therapy of food-derived enzymes might improve the prevalence and absorption of cyclic Hyp-containing peptides in human blood. Additional research on the formation of cyclic dipeptides using food-derived enzymes and the examination of its absorption in human blood at the moment are in progress. Conclusions In abstract, cyclic Pro-Hyp was detected in human plasma from 5 volunteers after ingestion of collagen hydrolysate. The most stage was reached 2 h after ingestion of collagen hydrolysate, and the average focus was 0. Cyclic Pro-Hyp enhanced the expansion price of mouse skin fibroblasts on collagen gel. These results advised that the rise in cyclic Pro-Hyp in human blood after ingestion of collagen hydrolysate might effectively enhance the wound healing course of in damaged pores and skin tissues. Funding: this work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) (No. Tomoaki Kawaguchi of Fukuoka Industrial Technology Center, for his technical recommendation on getting ready cyclic Pro-Hyp. Effects of collagen peptide ingestion on skin properties-placebo-controlled double-blind trial. Oral intake of particular bioactive collagen peptides reduces pores and skin wrinkles and increases dermal matrix synthesis. Oral supplementation of particular collagen peptides has beneficial results on human pores and skin physiology: A double-blind, placebo-controlled research. A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, scientific examine on the effectiveness of collagen peptide on osteoarthritis. Collagen peptide supplementation in combination with resistance coaching improves physique composition and increases muscle strength in aged sarcopenic males: A randomised managed trial. Effects of Pro-Hyp, a collagen hydrolysate-derived peptide, on hyaluronic acid synthesis utilizing in vitro cultured synovium cells and oral ingestion of collagen hydrolysates in a guinea pig mannequin of osteoarthritis. Identification of food-derived collagen peptides in human blood after oral ingestion of gelatin hydrolysates. Chondroprotective effect of the bioactive peptide prolyl-hydroxyproline in mouse articular cartilage in vitro and in vivo. Effect of prolyl-hydroxyproline (Pro-Hyp), a food-derived collagen peptide in human blood, on development of fibroblasts from mouse skin. Identification of a novel food-derived collagen peptide, hydroxyprolyl-glycine, in human peripheral blood by pre-column derivatisation with phenyl isothiocyanate. Identification of Collagen-Derived Hydroxyproline (Hyp)-Containing Cyclic Dipeptides with High Oral Bioavailability: Efficient Formation of Cyclo(X-Hyp) from X-Hyp-Gly-Type Tripeptides by Heating. Prolylhydroxyproline in urine: Its dedication and observations in muscular dystrophy. Dose-dependent adjustments within the ranges of free and peptide forms of hydroxyproline in human plasma after collagen hydrolysate ingestion. Changes in composition and content material of food-derived peptide in human blood after daily ingestion of collagen hydrolysate for 4 weeks. Assessment of effectiveness of oral administration of collagen peptide on bone metabolism in rising and mature rats. Cyclic dipeptides from lactic acid bacteria inhibit proliferation of the influenza a virus. Cyclic dipeptides from lactic acid bacteria inhibit the proliferation of pathogenic fungi. Efficient Absorption of X-Hydroxyproline (Hyp)-Gly after Oral Administration of a Novel Gelatin Hydrolysate Prepared Using Ginger Protease. Effects of the properties of brief peptides conjugated with cell-penetrating peptides on their internalization into cells. Subsequently, this byproduct was freeze-dried, hydrolysed at 50 C utilizing Protease N to get hold of C. Systolic blood strain and diastolic blood strain had been lowered 20 and 21 mm Hg, respectively, in spontaneously hypertensive rats after 6 h of oral administration with a dose of 171. Keywords: chlorella protein hydrolysate; angiotensin I-converting enzyme; spontaneously hypertensive rat; antihypertensive effect 1. Introduction Hypertension has been recognized as a cardiovascular risk issue and is usually referred to as a "silent killer" because individuals with hypertension can remain asymptomatic for years [1]. The prevalence of hypertension has reached epidemic ranges, affecting 15 to 20% of adults worldwide [2]. However, such therapy can produce opposed effects, together with coughing, lack of style, angioedema, and pores and skin rashes [7]. Among these protein sources, protein from algae has acquired explicit attention because of its probably helpful results associated to hypertension [24�26]. After 2 to four h, this tripeptide achieved the identical blood pressure-lowering effect as captopril at the same dose [30]. Green algae are composed of roughly 60% protein and have carbohydrate and lipid contents of 12 to 17% and 14 to 22%, respectively [31]. After hot water extraction, a substantial quantity of green algae residue containing approximately 50% protein remains. This byproduct is a relatively cheap protein supply compared with most bioactive peptides deriving from costly animal and plant proteins [1]. Protease N with a nominal exercise stage of one hundred fifty,000 U/g was provided by Amano Pharmaceutical Co. Next, this powder was homogenised with deionised water at a ratio of 1:10 for 2 min and boiled for 10 min to produce C. After this combination had cooled to ambient temperature, the enzyme (Protamex or Protease N) was added to the substrate at ratios of 1:one hundred (w/w) and a pair of:one hundred (w/w). This response mixture was incubated at 50 C for five h, and the protease was subsequently inactivated by incubation at 98 C for 10 min. Measurement of Peptide Content the peptide content material of the samples was measured by an ortho-phthaldialdehyde reagent with dipeptide (Leu-Gly) (Sigma, St. Prior to the measurement, the pattern solution (30 mg/mL) was filtered via a 0.
Discount 250mg keftab overnight deliveryIn addition bacteria que come el cerebro cheap keftab 500mg fast delivery, they lead to bacteria jokes for kids cheap keftab 125 mg visa the absence of the sleek muscle part of the anal sphincter bacteria lower classifications buy discount keftab 250 mg online. According to traditional embryology infection urinaire generic keftab 375 mg mastercard, the urorectal septum fuses with the cloacal membrane, thus dividing it into an anal membrane and a eight 9 eleven sixteen 20 the caudal limb of the intestinal loop (with the yolk stalk attachment and superior mesenteric artery as reference points) around the cephalic limb from its ventral aspect. Behind the colon, the small intestine undergoes nice elongation and becomes packed in its characteristic position within the abdominal cavity. Other research suggests that the cloacal membrane undergoes apoptosis and breaks down without its fusion with the urorectal septum. The area where the urorectal septum and lateral mesodermal ridges fuse with the cloacal membrane turns into the perineal body, which represents the partition between the digestive and urogenital techniques. The actual anal canal consists of a craniocaudal transition from columnar colonic (rectal) epithelium to a transitional area of cloacally derived endodermal epithelium leading into a zone of squamous epithelium that merges with the exterior perianal pores and skin. Histogenesis of the Intestinal Tract Shortly after its initial formation, the intestinal tract consists of a simple layer of columnar endodermal epithelium surrounded by a layer of splanchnopleural mesoderm. Three major phases are involved within the histogenesis of the intestinal epithelium: (1) an early section of epithelial proliferation and morphogenesis, (2) an intermediate interval of cellular differentiation during which the distinctive cell sorts characteristic of the intestinal epithelium appear, and (3) a last phase of biochemical and functional maturation of the various sorts of epithelial cells. The mesenchymal wall of the gut also differentiates into a quantity of layers of extremely innervated easy muscle and connective tissue. An overall craniocaudal gradient of differentiation is current throughout the developing intestine. The endoderm of the early foregut is capable of producing cell sorts aside from these of the intestine tube itself, such as liver cells. In (C) the shaded areas characterize regions where the mesentery is fused to the dorsal body wall. Descending colon Small gut Sigmoid colon One of crucial features of intestinal growth is the event of an absorptive floor massive enough to accommodate the digestive needs of the individual. Several mechanisms are concerned in the means of changing an basically smooth bore tube to one replete with folds and projections, specifically villi and microvilli. The larger dimensions of mucosal irregularities kind in relation to the sequence of clean muscle growth within the intestinal wall. While the muscle fibers inside this layer begin to contract, they drive the intestinal mucosa into a parallel series of longitudinal folds. Contractions of the longitudinal muscles lead to the formation of transverse folds, referred to as plicae. The third layer to form is the muscularis mucosae, and it might play a task in the formation of intestinal villi. In mammals, villus formation begins when endodermal shh and Ihh (Indian hedgehog) signals cause small clusters of mesenchymal cells to accumulate beneath areas of epithelium. The patterning of those clusters appears to be primarily based on a self-organizing principle first proposed by Alan Turing, the daddy of recent computer science. This sequence of sample formation begins in the anterior intestine and proceeds posteriorly. Presently unidentified alerts from these clusters trigger the conversion of the overlying pseudostratified epithelium of the intestine lining to a more readily deformable easy columnar selection. The mesodermal cell clusters then ship indicators back to the overlying endodermal cells, inflicting them to shorten and to cease proliferating. Changes in the shape of the epithelial cells along with contractions of underlying smooth muscle cells trigger the mucosa to begin to pucker into fingerlike villi. The gut grows in size by enlargement of the intervillous areas through cell proliferation, and new villi start to emerge in these spaces. While the villi elongate, the epithelial cells overlaying them further increase the entire absorptive area by forming numerous microvilli on their apical surfaces. Starting on the finish of the third month, pitlike intestinal crypts form on the bases of the villi. Despite the presence of four to six stem cells per crypt, it has been proven that every crypt is monoclonal. It counteracts the effects of Wnt and thus retains proliferation deep within the crypt, and it additionally facilitates mobile differentiation. Human intestinal epithelial cells develop the intrinsic capability for apoptosis by 18 to 20 weeks of gestation. Further biochemical differentiation of the intestine occurs after delivery, usually in response to specific dietary patterns. During the early embryonic period and generally into postnatal life, the epithelial and mesodermal components of the intestinal wall talk by inductive interactions. In regionspecific manners, these interactions involve hedgehog signaling (shh for the foregut and midgut and Ihh for the hindgut) from the endodermal epithelium. Interspecies recombination experiments present that the intestine mesoderm exerts a regional affect on intestinal epithelial differentiation. When regional willpower is ready, however, the controls for biochemical differentiation of the epithelium are inherent. This sample of inductive influence and the epithelial reaction are similar to these outlined earlier for dermal�epidermal interactions in the developing skin (see Chapter 9). The time scale shows the standard course of migration of daughter cells beginning with their generation from the stem cell inhabitants to their being shed from the villus into the intestinal lumen. Final enzymatic differentiation of intestinal absorptive cells is strongly influenced by glucocorticoids, and the underlying mesoderm appears to mediate this hormonal effect. In a converse inductive affect, the intestinal endoderm, through the action of shh signaling, induces the differentiation of clean muscle from mesenchymal cells within the wall of the intestine. Although the intestine develops many useful capabilities during the fetal period, no main digestive function happens until feeding begins after start. They are absent from the connective tissue of the submucosa because of the inhibiting effects of shh, secreted by the epithelial cells. During the migration, certain cells undertake a detour and head toward the mucosa, the place they colonize the submucosal mesenchyme to kind the submucosal plexuses. As they migrate via the intestine, the inhabitants of neural crest cells undergoes a massive enlargement until the number of enteric neurons finally exceeds the variety of neurons present in the spinal cord. Glial cells additionally differentiate from neural crest precursors in the intestine, but the environmental components that contribute to the differentiation of neural crest cells in the intestine wall remain poorly understood. Formation of Enteric Ganglia As outlined in Chapter 12, the enteric ganglia of the intestine are derived from neural crest. Pax-3�expressing cells from the vagal neural crest migrate into the foregut and unfold in a wavelike fashion all through the complete size of the intestine. Slightly later, cells from the sacral crest enter the hindgut and intermingle with cells derived from the vagal neural crest. A small subset of Schwann cell precursors also enters the intestine and contributes to the enteric nervous system.

Buy generic keftab 125 mg on-lineCommon mechanisms for boundary formation in somitogenesis and mind development: shaping the "chic" chick bacteria names a-z buy 750 mg keftab with amex. Mechanism of cell fate alternative between neural and mesodermal growth during early embryogenesis antibiotic resistance wiki answers purchase keftab 750mg without a prescription. The patterning of progenitor tissues for the cranial region of the mouse embryo throughout gastrulation and early organogenesis antibiotics for acne not working buy keftab 375 mg on-line. Patterning the cranial neural crest: hindbrain segmentation and Hox gene plasticity antibiotics for acne topical cheap keftab 250 mg free shipping. The near-term period is marked by excessive manufacturing of fetal urine-as a lot as 25% of total physique weight (approximately 1000 mL) per day. Fetal swallowing accounts for a considerable share of fluid removing, however an important factor seems to be absorption by the amniotic membrane, which accounts for more than half of the quantity of fluid eliminated and could be adjusted to compensate for extra or deficient quantities of amniotic fluid. In the third trimester of being pregnant, the amniotic fluid turns over completely each three hours and at term, the fluid-exchange price may approach 500 mL/h. Although much of the amniotic fluid is exchanged across the amniotic membrane, fetal swallowing is a vital mechanism in late being pregnant, with approximately 20 mL/h of fluid swallowed by the fetus. Swallowed amniotic fluid finally enters the fetal bloodstream after absorption through the intestine wall. During the fetal interval, excreted urine from the fetus contributes to amniotic fluid. Traditionally, the amniotic membrane has been discarded along with the placenta and different extraembryonic tissues after the kid has been born. In newer years, nevertheless, essential medical uses have been found for amniotic membranes. Because of the antiinflammatory and antiangiogenic properties of amnion, sheets of amnion have been used to cover a big selection of wounds or burn surfaces, especially in ophthalmic surgical procedure. The amnion, amniotic fluid, and other placental tissues have confirmed to be a major supply of stem cells, which have the capability of differentiating into cell varieties from every of the three germ layers. One of essentially the most characteristic options of human embryonic improvement is the intimate relationship between the embryo and the mom. To survive and develop during intrauterine life, the embryo must maintain an essentially parasitic relationship with the physique of the mom for buying oxygen and vitamins and eliminating wastes. It must also avoid rejection as a overseas physique by the immune system of its maternal host. These exacting requirements are met by the placenta and extraembryonic membranes that surround the embryo and function the interface between the embryo and the mom. These embrace the next: the amnion (an ectodermal derivative), which varieties a protecting fluid-filled capsule across the embryo; the yolk sac (an endodermal derivative), which in mammalian embryos not serves a primary nutritive operate; the allantois (an endodermal derivative), which is associated with the removal of embryonic wastes; and much of the extraembryonic mesoderm, which varieties the bulk of the umbilical twine, the connective tissue backing of the extraembryonic membranes, and the blood vessels that offer them. The amniotic fluid serves as a buffer in opposition to mechanical damage to the fetus; in addition, it accommodates growth, permits normal fetal actions, and protects the fetus from adhesions. The thin transparent amniotic membrane consists of a single layer of extraembryonic ectodermal cells lined by a nonvascularized layer of extraembryonic mesoderm. In many respects, amniotic fluid can be viewed as a dilute transudate of maternal plasma, however the origins and exchange dynamics of amniotic fluid are complex and not fully understood. The first phase encompasses the first 20 weeks of being pregnant, throughout which the composition of amniotic fluid is sort of similar to that of fetal fluids. In addition, the amniotic membrane itself secretes fluid, and components of maternal serum pass through the amniotic membrane. While being pregnant advances (especially after week 20, when the fetal dermis begins to keratinize), changes happen within the source of amniotic fluid. In contrast to birds and reptiles, the yolk sac of mammals is small and devoid of yolk. Although vestigial by means of its authentic operate as a significant source of nutrition, the yolk sac remains vital to the embryo because of other features that have turn into associated with it. Some proof signifies that before the placental circulation is established, vitamins such as folic acid and nutritional vitamins A, B12, and E are concentrated in the yolk sac and absorbed by endocytosis. Because this form of histiotrophic nutrition happens in the course of the time of neurulation, it might play a role within the prevention of neural tube defects (see p. While the embryo grows and undergoes lateral folding and curvature alongside the craniocaudal axis, the connection between the yolk sac and the forming gut turns into attenuated within the form of a progressively narrowing stalk connected to a more spherical yolk sac proper at its distal finish. Cells found in every of those layers contribute vital components to the body of the embryo. Soon these cells migrate into the wall of the intestine and the dorsal mesentery while they make their approach to the gonads, the place they differentiate into oogonia or spermatogonia. Extraembryonic hematopoiesis continues within the yolk sac till approximately the sixth week, when blood-forming activity transfers to intraembryonic websites, particularly the liver. Such circumstantial evidence supports the necessary role of fetal swallowing in the overall balance of amniotic fluid trade. This condition is often related to bilateral renal agenesis (absence of kidneys) and factors to the role of fetal urinary excretion in amniotic fluid dynamics. Oligohydramnios can be a consequence of preterm rupture of the amniotic membrane, which occurs in roughly 10% of pregnancies. There are many parts, both fetal and maternal, in amniotic fluid; greater than 200 proteins of maternal and fetal origin have been detected in amniotic fluid. With the analytical tools out there, a lot may be discovered about the situation of the fetus by analyzing the composition of amniotic fluid. Because of the small quantity of amniotic fluid in early embryos, amniocentesis is normally not performed until the thirteenth or fourteenth week of being pregnant. Amniotic fluid has bacteriostatic properties, which may account for the low incidence of infections after amniocentesis is performed. Fetal cells current in the amniotic fluid can be cultured and examined for varied chromosomal and metabolic defects. Whether amniotic stem cells are capable of differentiate into such a wide variety of mature cell types as embryonic stem cells stays to be established. A high concentration of -fetoprotein (a protein of the central nervous system) in amniotic fluid is a powerful indicator of a neural tube defect. Fetal maturity can be assessed by figuring out the concentration of creatinine or the lecithin-tosphingomyelin ratio (which reflects the maturity of the lungs). The severity of erythroblastosis fetalis (Rh disease) can also be assessed by examination of amniotic fluid. Similar to the yolk sac, the allantois in a human retains solely a secondary perform, on this case respiration. In humans, this perform is served by the blood vessels that differentiate from the mesodermal wall of the allantois. Previously these cells were considered to be descendants of a stem cell population residing in the bone marrow.
References - Nguyen, B., Rivers, E., Abrahamian, F. et al. Severe sepsis and septic shock: Review of the literature and emergency department management guidelines. Ann Emerg Med 2006;48:28-54.
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Urinary Incontinence: The Management of Urinary Incontinence in Women. Clinical Guideline 40.
- Blinder D, Manor Y, Martinowitz U, Taicher S, Hashomer T. Dental extractions in patients maintained on continued oral anticoagulant: comparison of local hemostatic modalities. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 1998;88(2):137-40.
- Macdonald PS, Keogh AM, Marshman D, et al. A double-blind placebo-controlled trial of low-dose ganciclovir to prevent cytomegalovirus disease after heart transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant. 1995;14:32-38.
- Hassouna ME, Ghoniem GM: Long-term outcome and quality of life after modified pubovaginal sling for intrinsic sphincteric deficiency, Urology 53:287n291, 1999.
- Burstein DS, Mavroudis C, Michael DP, et al. Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformations in Heterotaxy Syndrome the Case for Early, Direct Hepatic Vein-to-Azygos Vein Connection; World Journal for Pediatric and Congenital Heart Surgery. December 30, 2010; 2(1):119-28.
|