Keppra
Phillip Fairweather, M.D. - Clinical Assistant Professor
- Mount Sinai School of Medicine
- New York, NY
- Department of Emergency Medicine
- Elmhurst Hospital Center
- Elmhurst, NY
250mg keppra amexCardiovascular function Patients with liver disease are inclined to symptoms 8 dpo bfp buy generic keppra 500 mg be vasodilated and hypotensive treatment 7th feb bournemouth safe keppra 500 mg. This may be aggravated by lack of fluid from the circulation because of hypoalbuminaemia and low oncotic stress treatment upper respiratory infection purchase keppra 500mg visa. Respiratory function There may be respiratory compromise caused by diaphragmatic splinting secondary to ascites and/or pleural effusions medicine cups effective keppra 250 mg. I n extreme disease, intrapulmonary shunting could cause disproportionate hypoxaemia. Hypoalbuminaemia leads to oedema and ascites and predisposes to pulmonary oedema. S econdary hyperaldosteronism produces sodium retention (even though the plasma sodium focus may be low) and hypokalaemia. D iuretic remedy usually including spironolactone, may also affect the serum potassium, focus. I n hepatic failure a combined respiratory and metabolic alkalosis might occur, which shifts the oxygen dissociation curve to the left, doubtlessly impairing tissue oxygenation. Hepatorenal syndrome Hepatorenal syndrome is outlined as acute renal failure growing in patients with pre-existing persistent liver failure. Close cardiovascular monitoring is important, and measurement of cardiac output should be thought of. Gastrointestinal haemorrhage from gastro-oesophageal varices may trigger main management issues. Close liaison with the haematology service is crucial, and native protocols must be in place for the administration of main haemorrhage. Drug metabolism S ignificant impairment of liver operate will have an result on protein binding on account of decreased synthesis. D rug metabolism, cleansing and excretion are likely to be affected, resulting in extended drug half-lives. Propofol is secure to use, however sensitivity to its sedative and cardiorespiratory effects may be elevated. S uxamethonium may have a prolonged length of motion because of lowered plasma cholinesterase activity. O f the volatile anaesthetic brokers, desflurane is least metabolised, with minimal results on hepatic blood circulate (see Chapter 3). Hepatic failure the management of hepatic failure is past the scope of this chapter. The main points are recognition, assessment, a initial resuscitation and switch to a specialist centre. D uring anaesthesia, cardiovascular stability should be maintained so far as possible. I n the adequately volume-expanded affected person, hypotension could additionally be reversed by infusion of noradrenaline. However, within the unstable patient, skilled help should be sought, and monitoring ought to embody measurement of cardiac output. I n the presence of oesophageal varices, oesophageal D oppler monitoring is contraindicated, and different cardiac output screens must be used. D rugs that depress cardiac output or arterial pressure, including unstable anaesthetic agents and -blockers, must be used with warning to avoid reductions in hepatic blood move. O pioids must be administered with caution until ventilatory help is deliberate postoperatively. Renal disease Renal dysfunction has essential implications for anaesthesia, and a full evaluation is required before even minor surgical procedures are contemplated (see Chapter 19). I t can be inaccurate where muscle mass or creatinine consumption are at extremes, such as in cachectic patients or those on a vegetarian diet. I n this context the term persistent means two or more creatinine concentrations measured at least 90 days aside. Preoperative assessment Preoperative assessment ought to be directed to several specific problems that require correction earlier than anaesthesia. I n continual renal failure, overload may be controlled with diuretic therapy or dialysis. Pulmonary oedema and hypertension could end result from fluid overload and should be treated before induction of anaesthesia. I n patients with nephrotic syndrome, hypoalbuminaemia ends in oedema and ascites. Circulating blood quantity in these sufferers is often decreased, and care should be taken at induction of anaesthesia to keep away from hypotension. I nvasive monitoring and measurement of cardiac output should be considered in these sufferers. The renal tubules could have a decreased capability to preserve sodium, such as in pyelonephritis, analgesic nephropathy or recovering acute renal failure. Potassium Hyperkalaemia happens usually in renal failure, usually in affiliation with metabolic acidaemia, and causes delayed myocardial conduction; if that is untreated, it could lead to cardiac arrest due to asystole or ventricular fibrillation. The use of bicarbonate is controversial, and its use may be related to danger of sodium and fluid overload. Calcium Retention of phosphate and vitamin D depletion (1,25dihydroxycholecalciferol) in chronic renal failure lead to hyperparathyroidism. The improvement of a parathyroid adenoma results in hypercalcaemia (tertiary hyperparathyroidism). Cardiovascular effects Hypertension could occur for a quantity of causes: � Raised plasma renin concentration secondary to decreased perfusion of the juxtaglomerular apparatus ends in hypertension via increased secretion of angiotensin and aldosterone. Both pulmonary and peripheral oedema might happen from a combination of fluid overload, hypertensive cardiac illness and hypoproteinaemia. Uraemia may cause pericarditis and haemorrhagic pericardial effusion, which can reduce cardiac output and require aspiration, although that is now a rare occasion. Electrolyte disturbances and rapid fluid shifts, corresponding to throughout dialysis, can also have an result on level of consciousness by causing cerebral oedema. Morphine could additionally be an issue because renally excreted metabolites, particularly morphine-6glucuronide, accumulate. Patients are normally well compensated, with an elevated cardiac output, so preoperative blood transfusion is pointless. Conventional tests of coagulation are regular, however bleeding time is prolonged and correlates with the diploma of bleeding tendency. Drug therapy Drug treatment is important for several reasons: � Patients are often receiving concurrent medication for attendant issues. This may be important in septic or shocked sufferers, these with pre-existing renal dysfunction or these present process surgical procedure associated with major blood loss. Patients receiving these agents ought to be monitored carefully, and fluid must be replaced adequately to keep away from hypotension. It may be prudent to omit the quick preanaesthetic dose within the high-risk affected person. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors can also trigger hyperkalaemia, notably in patients with renal dysfunction. Anaesthesia � Minor procedures, such because the institution of vascular access for dialysis, could additionally be carried out satisfactorily underneath regional anaesthesia.
Keppra 250 mg genericThis requires expenditure of approximately equal quantities of vitality to overcome the elastic recoil of the lung and chest wall and the non-elastic resistance of tissue movement and fuel circulate in the airway medications and pregnancy cheap keppra 500mg with visa. Energy overcoming elastic recoil is stored as potential power in the elastic tissue of the lungs and chest wall to be used during expiration; the rest is dissipated as warmth treatment of gout cheap 500 mg keppra amex. D uring slow and deep respiratory medicine ubrania keppra 250mg amex, the work carried out against elastic forces is increased treatment lung cancer generic 500 mg keppra mastercard, whereas throughout fast and shallow breaths, the work against airway and tissue resistance is increased. Respiratory system mechanics Elastic recoil the respiratory system has two major components, the lungs and the chest wall, which transfer together as a single unit. They are each elastic; on the finish of expiration the lung has inward elastic recoil, which is exactly balanced by the outward elastic recoil of the chest wall. Lung parenchyma and chest wall tissues include elastin, a molecule whose structure opposes efforts to stretch it and which instantly returns to its resting form when tension is eliminated. With ageing, repeated episodes of irritation cause alternative of elastin by the inelastic molecule collagen, so tissue elasticity reduces. This results in the gradual deterioration of respiratory function seen with age, adjustments that are accelerated by repeated molecular insults, such as by smoking. A lthough elastin accounts for a lot of the elasticity of the chest wall, an approximately equal contribution within the lung originates from floor forces between liquid and gasoline. S urface forces develop on the air�water interface of the alveoli and encourage alveoli to collapse, a scenario which is prevented from occurring by surfactant. Surfactant S urface forces in lung are reduced by the presence of a mixture of molecules often identified as surfactant. S urfactant reduces elastic recoil of the lungs general but also modifications floor forces within alveoli according to their size. A s alveoli become smaller, their surface forces scale back in order that they become more compliant � in consequence, gasoline will circulate from larger alveoli into small alveoli, so all alveoli have a tendency towards the identical dimension, stabilising the lung tissue. A spherical 90% of surfactant consists of phospholipid molecules, with the remaining 10% being 4 completely different surfactant proteins (A �D). The proteins are essential for organising the phospholipids into their functional layers in surfactant manufacturing and launch from epithelial cells, and have important immunological and antioxidant roles. A rtificial surfactant may be used to deal with situations the place surfactant is missing, such as neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. S urfactant proteins are required to facilitate spreading of the surfactant within the lung after intratracheal instillation, and pure surfactants are subsequently more practical as therapeutic brokers than artificial surfactants. The lung quantity at any given stress during deflation is bigger than throughout inflation because of time dependency. Endexpiratory and end-inspiratory no-flow factors occur when the trace is horizontal. At this level, airway stress and alveolar strain are equal, so the strain gradient is the difference between alveolar and atmospheric stress. Total respiratory system dynamic compliance is due to this fact the slope of the line between these points. Redistribution of gasoline happens in the lung on account of differing resistance and compliance of nearby lung areas. With an inspiratory pause, the quick alveoli will redistribute a few of their quantity to slow alveoli. Compliance D efined as the change in lung volume per unit strain change, compliance may be measured for the lungs, chest wall or each depending on which pressure gradient is used: � lung: alveolar�intrapleural (transpulmonary pressure); � chest wall: intrapleural�atmospheric; or � complete (respiratory system): alveolar�atmospheric. When measured together, lung and chest wall compliance are in series (analogous to capacitance) and subsequently addition of the reciprocals of lung and chest wall compliance equals the reciprocal of complete compliance. Compliance is measured when no gas is flowing, at which point mouth stress equals alveolar pressure. I ntrapleural strain is difficult to measure, so most compliance measurements are of the respiratory system. Static compliance is always higher than dynamic compliance as the la er removes the time dependency of the respiratory system. I ncreasing compliance with age and emphysema each end result from lack of total alveolar surface area, illustrating the importance of surface forces in lung recoil. I t can be lowered by weight problems or pathological skin situations similar to chest wall burns. Posture has a significant effect, with lowered chest wall compliance within the supine place (by 30%) and susceptible position (by 60%) in contrast with the sitting position. Static lung volumes S tatic lung volumes are volumes of gas contained within the lung when no fuel is flowing. These are tidal quantity, inspiratory reserve volume, inspiratory capacity, expiratory reserve volume and vital capability. The residual quantity, whole lung capability and useful residual capacity can solely be measured with more complex techniques. S tatic lung volumes are affected by height, sex, age and ethnicity, so calculating a normal worth for an individual requires inclusion of those components. Consequently, in medical use lung volumes are best expressed as a share of predicted value for the individual (see Table 10. Respiratory system resistance Resistance to move of fuel into the lungs outcomes from airway resistance, tissue resistance and inertance. Tissue resistance originates from the elasticity of lungs and chest wall and describes their reluctance to change shape with respiration. I nertance is the resistance brought on through the change in direction of fuel and tissues after they transfer with respiration. I nertance is negligible aside from the weird situation of high-frequency synthetic ventilation. A irway resistance outcomes from frictional resistance to gas flow through airways. Gas flow is generally turbulent within the upper airway and enormous bronchi, changing into laminar in bronchioles (1mm diameter, era 11) and past, but this varies with the pace of air move. With a doubling of the number of airways with every era beyond the trachea, the crosssectional space of the mixed airways will increase exponentially and so fuel velocity rapidly reduces, favouring laminar flow. Passive control of airway dimension Bronchioles lack cartilaginous help and rely completely on traction by elastic recoil of surrounding lung tissue to stay open. This explains why, in patients with continual small airway obstruction, hyperinflation of the lungs helps alleviate obstruction, however the hyperinflation also impairs respiratory muscle perform (see earlier). I n dependent lung regions, notably when upright, compression of lung by gravity might scale back airway size to the purpose that airway closure happens. I n addition to this volume-related collapse, excessive expiratory airway circulate rates may cause flow-related collapse. D uring regular resting respiratory or a rapid inspiration, chest expansion maintains a subatmospheric strain within the pleura while the airways are at atmospheric strain, so the transmural pressure gradient retains the airways open. However, with a compelled expiration the intrapleural strain turns into constructive, the transmural pressure gradient reverses and small airways close. Peak expiratory flow price (point A) is dependent upon effort, however circulate price soon turns into restricted by airway collapse, and the road becomes linear, nevertheless exhausting the topic tries to exhale. Neural pathways in the lung are primarily parasympathetic, with acetylcholine acting on M3 muscarinic receptors to cause bronchoconstriction. Stimulation of M3 receptors prompts a Gq protein to activate phospholipase to produce inositol triphosphate, which binds to sarcoplasmic reticulum, releasing calcium and causing smooth muscle contraction.
Cheap 500 mg keppra with amexThe current travels from the energetic electrode through the affected person and exits by way of the affected person plate medicine plies generic keppra 250 mg free shipping. Radiation X-rays X-rays are electromagnetic radiation produced when a beam of electrons is accelerated from a cathode to strike an anode (often made from tungsten) symptoms 6 months pregnant buy cheap keppra 250mg on line. Radiation safety Exposure to radioisotopes and X-rays ought to be stored to a minimal because of the risks of tissue injury and chromosomal adjustments medications that cause dry mouth buy keppra 500mg cheap. The aims of that document are to protect sufferers in opposition to pointless exposure to radiation and to set standards for practitioners using ionising radiation symptoms 6 week pregnancy buy keppra 500 mg low cost. The X-ray dose reduces based on the inverse sq. law � so shifting twice as distant from the beam reduces publicity fourfold. When placed in a powerful static magnetic area of 1�3 Tesla, the atoms align themselves longitudinally with the field. A pproximately half of the nuclei are aligned parallel to the field and the other half antiparallel to it. When such a population of nuclei is subjected intermi ently to a second magnetic subject which is oscillating on the Larmor frequency (usually within the radiofrequency range), at right angles to the static subject, they all flip to the higher power, antiparallel path, and so they precess in phase; this is magnetic resonance (Magee 2018). A fter 1ms the radiofrequency area is removed and the atoms relax and revert to their lower power, parallel alignment with the primary subject. A s they achieve this, they launch power, from which photographs are made at completely different phases of leisure generally identified as T1 and T2. To preserve such a big magnetic field, the magnets are supercooled to turn out to be superconductors of electrical present. An electrical sign input causes the crystal to deform (A), creating a strain wave. Air conducts ultrasound poorly, so coupling between probe and surface requires gel. In (B) the reverse course of happens and a reflected stress wave induces an electrical signal, which can be used to create a picture. The biggest penetration is achieved with the lowest frequency however with poor resolution, whereas the converse holds for high-frequency waves. The scientific compromise is to use a frequency that will give good resolution, with enough penetration of the tissues being investigated. I t is the reflection of the ultrasound wave on the interface between two tissues or at tissue�fluid (air) interfaces, which provides a diagnostic image. The identical piezo-electric crystal is often used as the receiver, with the transmission mode switched off. When an ultrasonic wave reflects off a stationary object, the mirrored wave has the same frequency because the transmi ed wave. When the object (such as a collection of purple blood cells) is moving in direction of the transmi er, nonetheless, it encounters extra oscillations per unit time than its stationary equivalent, so the frequency of the reflected wave is increased. Conversely, when the thing is transferring away from the ultrasound wave, the frequency of the reflected wave is lowered. This property can be utilized as a non-invasive method for measurement of blood velocity (not flow) inside the body. For a transmi ed frequency ft, of wavelength, and the rate of sound within the medium c: I f the beam hits an object which is transferring directly towards the transmi er at velocity v, the frequency of the waves arriving at the reflector (fr) will now be: the reflector will now act as a supply which is moving towards the transmi er, and the precise frequency sensed by the transmi er (in receiver mode) might be: the apparent enhance in frequency is given by: the frequency distinction could be transduced into an audible sign or used to calculate the velocity of the blood cells. N ormally the D oppler beam is utilized non-invasively, from outside the blood vessel, at an angle to it. Thus, rearranging the equations: Clearly the greatest accuracy in measuring blood velocity. Having measured imply velocity of the blood in a vessel to calculate blood flow, the mean diameter of the vessel should even be measured and its cross-sectional space calculated utilizing the method flow = velocity � space. Lasers A laser produces an intense beam of sunshine which ends up from stimulation of atoms (the laser medium) by electrical or thermal vitality. Laser light has three defining traits: coherence (all waves are in phase each in time and in space), collimation (all waves travel in parallel directions) and monochromaticity (all waves have the same wavelength). The term laser is an acronym for mild amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. Physical ideas of lasers When atoms of the lasing medium are excited from a standard floor state right into a high-energy state by a pumping supply, this is known as the excited state (Magee 2018). When the atoms return from the excited state to the traditional state, the vitality is commonly dissipated as gentle or radiation of a particular wavelength attribute of the atom (spontaneous emission). I n normal circumstances, when this change from greater to lower power state happens, the light emi ed is more more likely to be absorbed by an atom in the decrease power state somewhat than meet an atom in a better energy. These stages are summarised as follows: � Excitation: steady atom + vitality high-energy atom � Spontaneous emission: high-energy atom secure atom + a photon of light � Stimulated emission: photon of sunshine + high-energy atom secure atom + 2 photons of sunshine the sunshine emi ed is reflected back and forth many occasions between mirrored surfaces, giving rise to additional stimulation. This amplification continues as lengthy as there are extra atoms within the excited state than in the regular state. It also accommodates mirrors used to mirror mild to improve the energy of the stimulated emission. One of the mirrors is a partially transmitting mirror, which permits the laser beam to escape. The shorter the wavelength, the extra sca ered is the light, and the sunshine energy is converted to heat in deeper tissues. Lasers are categorised into four lessons in accordance with the degree of hazard they afford: class 1 is the least dangerous, and sophistication four essentially the most dangerous. Optical fibres O ptical fibres are used in the design of endoscopes and bronchoscopes to be able to see around corners. Fires and explosions A lthough the use of inflammable anaesthetic brokers has declined greatly during the last two to three decades, different inflammable brokers may be used in the working theatre, similar to alcohol for skin sterilisation. A hearth turns into an explosion if the combustion is sufficiently speedy to trigger pressure waves that, in flip, cause sound waves. I f these strain waves possess adequate power to ignite adjacent fuels, the combustion is extremely violent. Fuels the modern volatile anaesthetic agents are non-flammable and non-explosive at room temperature in both air or oxygen. I n the presence of excessive pressures of oxygen, nitrous oxide or compressed air, these fuels might ignite spontaneously, as within the diesel engine. Ethanol, used as a disinfectant (see Chapter 18), burns readily in air, and the risk is increased within the presence of oxygen or nitrous oxide. O ther nonanaesthetic flammable substances include methane within the gut (which could also be ignited by diathermy when the intestine is opened), paper dressings and plastics found in the operating theatre suite. The stoichiometric concentration of a gas and oxidising agent is the concentration at which all combustible vapour and agent are fully utilised. Sources of ignition the 2 major sources of ignition in the operating theatre are static electrical energy and diathermy. Electrostatic cost occurs when two substances are rubbed collectively and one of many substances has an excess of electrons while the other has a deficit. Electrostatic costs are produced on non-conductive materials, such as rubber ma resses, plastic pillowcases and sheets, woollen blankets, some synthetic materials, rubber tops of stools and non-conducting components of anaesthetic machines and respiration methods.
Generic 250 mg keppra otcWork of breathing Work is outlined as the drive applied over a distance and is measured in J oules (N ewton metres (see Chapter 15)) symptoms multiple myeloma buy discount keppra 500 mg line. For breathing this equates to the amount of gas moved in response to the pressure utilized with items of litrekilopascal (volume � pressure) treatment jiggers discount keppra 250mg without a prescription. D uring resting respiration with passive expiration medicine 54 543 buy keppra 500 mg with amex, all the work of respiration is used for inspiration treatment 911 generic keppra 500mg free shipping. Humoral control outcomes from the presence of quite a few 2-adrenergic receptors on bronchial clean muscle that cause bronchodilatation in response to circulating adrenaline. Direct bodily and chemical stimulation of parasympathetic afferents in the respiratory epithelium induces reflex bronchoconstriction and may end up in laryngospasm or bronchospasm. Cellular mechanisms embrace activation of mast cells, eosinophils and different immune cells, releasing inflammatory mediators in response to bodily stimulation or pathogens. Histamine, leukotrienes, bradykinin and substance P may be released, and all trigger bronchoconstriction. The subject inhales to whole lung capacity after which exhales as quick and so long as possible. They act by binding to the transmembrane domains of the 2receptor, stabilising it in its active state. They act by competitively antagonising M3 receptors within the airway and by utilizing the inhaled route keep away from most of the systemic unwanted effects of anticholinergics. Their lack of specificity means many biological techniques are affected, inflicting a range of extreme unwanted effects. O ther bronchodilator medicine include leukotriene antagonists used to deal with chronic bronchial asthma caused by allergy as they antagonise some inflammatory, mediators. I nhaled anaesthetic brokers are good bronchodilators, performing by both suppressing the neural pathways usually lively in asthma and, at higher doses, by direct airway smooth muscle relaxation. Pulmonary blood volume can range broadly as changes in body position and systemic vascular tone displace blood to and from the chest. The former results from compression of the alveolar capillaries within the alveolar wall as the alveoli increase and the la er from kinking of nook capillaries between alveoli and presumably localised hypoxia. Humoral management in which the pulmonary vasculature is influenced by numerous molecules proven in Table 10. Hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction the hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction reflex represents a fundamental distinction between pulmonary and systemic circulations: the previous constricts when hypoxic; the la er dilates. The second, extra intense, section develops after 40min and is mediated by the discharge from endothelial cells of a paracrine peptide hormone, endothelin. Phase 1 of the response is full within a couple of minutes, and phase 2 occurs roughly 40min later. Processing of endogenous compounds by the pulmonary circulation Endothelial cells are metabolically energetic and course of a variety of compounds that pass by way of the lung by a mix of surface-bound enzymes and extremely selective uptake proteins importing compounds for intracellular metabolism. For instance, the pulmonary endothelium is very selective for the uptake of noradrenaline, whereas adrenaline passes via capillaries unchanged. The endothelial surface is rich in angiotensin-converting enzyme for activating angiotensin I into the vasoactive octapeptide angiotensin I. Many medication are also faraway from blood on passing by way of the lungs, though for many this occurs by retention of the drug in lung tissue rather than metabolism. The extremely specific uptake mechanisms seem to stop medication coming into endothelial cells the place the metabolic enzymes reside. Basic (pKa >8) and lipophilic medicine tend to be taken up in the pulmonary circulation, whereas acidic medication remain sure to plasma proteins. D rug binding within the pulmonary circulation may act as a drug reservoir inside the lung, with medicine then being launched slowly, or sometimes quickly returned to the plasma when binding websites both turn out to be saturated or when the drug is displaced by a molecule with greater affinity for the binding web site. There is also a smaller contribution to non-uniform air flow because of unequal branching pa erns of the airways inflicting preferential air flow of central versus peripheral lung regions. I nspiratory circulate price also impacts ventilation as different functional models have differing compliance and resistance and hence different filling rates, as described earlier. Perfusion Lung perfusion is affected by gravity in a similar approach to air flow, however to a fair larger extent due to the greater weight of blood relative to lung tissue. Compression of lung tissue in dependent areas additionally results in greater numbers of smaller alveoli per unit lung volume and so perfusion is elevated. A s for distribution of ventilation, perfusion of central regions is greater than in peripheral regions due to the branching pa erns of pulmonary arteries, irrespective of body place. I n zone three, dependent lung areas, both the pulmonary arterial and venous stress exceed alveolar strain; due to this fact flow is independent of alveolar stress (the S tarling resistor is absolutely open; the weir is completely submerged). Positive stress ventilation has profound results on these relationships by increasing alveolar strain throughout the lung, increasing the quantity of lung in zone 1. V/Q relationships O verall, air flow (V) and perfusion (Q) are intently matched within the lung, with typical values of four Lmin �1 for alveolar ventilation and 5 Lmin �1 for perfusion, giving a V/Q ratio of zero. However, as already described, each V and Q enhance progressively on transferring from non-dependent to dependent areas, more so for Q. I n healthy patients, most areas of the lung subsequently have comparable V/Q ratios, between 0. In reality the measured alveolar lifeless space consists of true alveolar useless space together with a component brought on by areas with excessive V/Q ratios, and the measured venous admixture consists of true venous admixture (shunt) together with a element caused by areas with low V/Q ratios. Note that perfect alveolar gas is all the time exhaled contaminated with alveolar lifeless space gas so unimaginable to sample. Thus a widening of the vary of V/Q ratios in a affected person rapidly results in inadequate gas trade. The alveolar air equation assumes that the alveolar concentration of any gas is expounded to its inspired focus and uptake/output between the alveolus and pulmonary circulation. O n this basis many variations of the alveolar oxygen equation exist, a easy version being: Shunt Shunt merely describes blood entering the left side of the systemic circulation with out passing via ventilated lung. Venous admixture is the amount of blending of venous blood with pulmonary end-capillary blood that might be required to produce the observed arterial oxygenation and so includes shunt and a part from blood passing through lung areas with zero > V/Q < 1 which is incompletely oxygenated. This is particularly important in the lateral place when the higher lung develops significant alveolar dead house, which will be further worsened by an open chest. I n scientific conditions adjustments in physiological lifeless space are usually as a outcome of altered alveolar dead area as anatomical dead house is approximately fastened offered any synthetic airway is unchanged. Facilitated mass motion by binding to haemoglobin, which is physically moved across the physique three. On the best is a summary of the elements influencing oxygenation at every website down the cascade. Equilibration of both gases is normally complete inside the time blood spends in a pulmonary capillary (0. A diffusion barrier only exists in elite athletes, at very high altitude or in diseased lung corresponding to with pulmonary oedema. O2 carriage in blood O xygen is carried within the blood in two forms � dissolved and bound to haemoglobin. Under normal circumstances this results in roughly 19ml dl �1, giving a total oxygen carriage in blood of about 20ml dl�1.
500mg keppra with amexLocated instantly on the obex medicine quetiapine buy keppra 250 mg lowest price, medially dorsal of the central canal treatment 4 lung cancer order 500mg keppra, is the small Area postrema with right and left lateral offshoots that are in direct contact with the Nucleus tractus solitarii medications hyponatremia discount keppra 500mg online. The Area postrema accommodates vagal visceroafferents and is the central vomiting centre symptoms 9dpo bfp cheap keppra 500 mg fast delivery. Located dorsolaterally are the sensory Nuclei principalis and spi nalis nervi trigemini [V]. It forms a longitudinal rostrocaudal Pars compacta, which passes through the complete Medulla oblongata as the actual Nucleus ambiguus, as nicely as individual para-ambigualis nucleus groups ventral of this Pars compacta, including the exterior formation which incorporates parasympathetic neurons for the innervation of the center (> Table 12. Medial to the respiratory centre the nuclei of the medullary cardiovascular entre is positioned in the rostral ventrolateral Medulla oblongata, which, amongst others, sends adrenergic neurons to the sympathetic neurons of the spinal twine. The tapered caudal offshoots of the nuclear areas of the rostral Medulla oblongata are truncated (Nucleus ambiguus, Nucleus dorsalis nervi vagi, Nucleus tractus solitarii, Nucleus nervi hypoglossi), which partially lengthen to the spinal twine or proceed in tracts to/from the spinal twine. The transition from the caudal Medulla oblongata to the spinal twine is fluid and is called a transitional zone. However, the anterior and dorsal horn of the spinal twine are clearly delimited by the rostrally coming into and/or exiting spinal roots of the C1. The following tract methods go to or pass via the Medulla oblongata: Lemniscus medialis, Tractus tegmentalis centralis, Fasciculi longitudinales medialis and posterior, Tractus spinalis nervi trigemini, Tractus corticonuclearis and corticospinalis, Tractus spinothalamicus, Tractus spinocerebellaris. Axons from the posterior column nuclei pass ventrally and medially and cross in the midline, ventrally of the Nucleus nervi hypoglossi, within the Decussatio lemniscorum, and at last ascend. Clinical remarks Bilateral injury to the motor cranial nerve nuclei within the Medulla oblongata causes bulbar paralysis. The tongue and throat muscle tissue are paralysed by atrophy, in order that those affected clinically display slurred speech and difficulty swallowing. Brainstem reflexes Learning about brainstem operate, and particularly about primary configurations, helps with the orientation of brainstem reflexes and their afferent and efferent reflex limbs into the corresponding cranial nerves (> Table 12. It also derives from the precept that the primary central nervous configuration at all times takes place on the entry level level of the afferents, similar to controlling the respiratory movements on the degree of the Medulla oblongata (breathing reflex). An overview of the brainstem functions or brainstem reflexes and their configuration is shown in > Table 12. The space of the Formatio reticularis lies in the inside part of the brainstem (Tegmentum mesencephali, Pars dorsalis pontis, Medulla oblongata) between the median raphe and the outer adjoining nuclear areas and tracts. Characteristically, there are varying numbers of loosely-bundled groups of nerve cells of various sizes, as nicely as fibre bundles, which cross via the world of the Formatio reticularis in all instructions. From this it has been concluded that the Formatio reticularis is a diffuse network of multiple relay neurons, which passes via the complete brainstem, and based on some authors, additionally by way of the diencephalon and the cervical spinal cord. Under the affect of serotonergic Raphe nuclei, this causes an activation of the motor system ascending from the spinal twine, in addition to the central autonomous nuclear areas up to the hypothalamus and limbic system. With such a diffuse definition, the Formatio reticularis by its very nature resists this type of clear distinction. This lateral expansion marks the dorsal border between the pons and the Medulla oblongata. Additionally, this restrict is indicated by the Striae medullares ventriculi quarti which crosses the floor of the Fossa rhomboidea and belongs to the auditory system. In addition, there are relay nuclei for cerebellar afferents and nuclei of the monoaminergic neurotransmitter techniques (serotonin, noradrenaline, dopamine). The useful relationships are introduced in the respective chapters (sensory methods, cranial nerves, cerebellum, autonomic nervous system). Although the arterial vascular community of the brainstem could also be superficially extremely variable, in the horizontal part we are ready to distinguish three comparatively constant, pronounced supply areas: a posterior, a lateral and an anterior vascular territory. All of the fibres crossing in all directions over the midline are referred to as raphes. Depending on the section of the brainstem, a distinction is made between the mesencephalic, pontine and medullar raphes. In all raphe segments, there are serotonergic neurons embedded in numerous teams of nuclei, referred to as mesencephalic, pontine and medullar raphe nuclei. Typical of the serotonergic system (but additionally of different monoaminergic systems, such as the dopamine, histaminergic or noradrenergic methods, > Table 12. These terminals are often enlarged presynaptic boutons and are due to this fact referred to as varicose terminals. They release serotonin into the extracellular areas, from where it can act on postsynaptic serotonin receptors of the goal neurons. However, the effect is totally completely different: � Postsynaptic stimulation is also achieved very particularly at particular person goal cells by numerous, highly-varied and partly counteracting serotonin receptors. This will increase awareness of incoming (afferent) environmental stimuli and reinforces the somatic response, i. Clinical remarks Disorders of the arterial supply of the brainstem, due to the close proximity of probably the most various important nuclear areas and tracts, often result in wide-ranging signs of deficit and are incessantly life-threatening. This is a unilateral infarction of the dorsolateral Medulla oblongata because of a circulatory dysfunction within the A. In After working by way of this chapter, you should be succesful of: � use a macroscopic dissection or an anatomical model to describe the floor anatomy of the cerebellum and clarify its practical group � name the corresponding anatomic sections through the cerebellum, cerebellar nuclei and cerebellar peduncles, and explain their respective involvement in relay circuits or fibre methods � explain which medical neurological checks can be utilized to take a look at components of the cerebellum which have a functional-anatomical meaning 673 12 Special neuroanatomy 12. It is positioned within the posterior cranial fossa (Fossa cranii posterior), is positioned dorsally on the brainstem and is connected with it on each side by 3 stems (Pedunculi cerebellares). The pedunculi include afferent and efferent tracts by which the cerebellum is linked instantly or indirectly with different areas of the brain. Macroscopically the strikingly furrowed cerebellum is split into 3 sections: � the cerebellar vermis (Vermis cerebelli) within the center, � which is flanked by a cerebellar hemisphere (Hemispherium cerebelli) to the best and left. Grey matter is predominantly discovered within the triple-layered cerebellar cortex (Cortex cerebelli) as nicely as within the cerebellar nuclei (Nu clei cerebelli); white matter fills the Pedunculi cerebellares, surrounds the cerebellar nuclei (Corpus medullare cerebelli) and penetrates into the winding coils of the cortex. Functionally, the cerebellum is primarily responsible for the unconscious fine-tuning and coordination of movement, and the upkeep of muscle tone and steadiness. This nomenclature is based on the characteristic arrangement of grey and white matter, which is seen in this section. In the 14th week, due to the formation of another horizontal furrow within the cranial half, the Fissura prima, Lobus anterior arises (phylogenetically: paleocerebellum; in which the Vermis cerebelli is included) and the Lobus posterior (phylogenetically: neocerebel lum). Cranially, it borders the Lobus occipitalis and the posterior part of the Lobus temporalis of the cerebrum � separated by the cerebellar tentorium (Tentorium cerebelli) consisting of Dura mater; dorsocaudally, the Os occipitale or the Cisterna cerebellomedullaris. Clinical remarks An anatomical data of the positional relationships of the cerebellum plays a crucial function in the surgical remedy of tumours of the posterior cranial fossa. It consists mainly of the metencephalic part of the rhombencephalon and likewise partly of caudal parts of the mesencephalon. In this context, the dorsolateral elements of both alar plates are critical; from these the so-called rhombic lips are shaped. These superior sections present the vast majority of the unique neuroepithelial tissue of the 2 cerebellum systems (Primordia cerebellares), which merge with one another in the middle of their growth in the median aircraft and at last type a transversal dorsally-curved bulge, the cerebellum plate. Its lateral elements show the strongest progress and develop later into the Hemispheria cerebelli; the mid-section turns into the Vermis cerebelli.
Order 500 mg keppra mastercardAround 5% of people aged 60�80 years are survivors of stroke symptoms uti discount keppra 500 mg on-line, increasing to 15% of those aged older than eighty years medications on airline flights buy generic keppra 500mg online. Subclinical (micro) infarcts are found in around one-third of cognitively intact older people medicine 0027 v buy 250 mg keppra otc. Reported rates are dependent on the diploma of case ascertainment but are around 5%�10% in these aged older than 65 years; the danger may be decreasing (those born extra recently may be at a lower risk) medicine 360 discount 250 mg keppra with visa. There is broad interindividual variability, in part due to association with risk elements such as diabetes, smoking, arterial hypertension and so on. Although creatinine clearance declines, so does muscle mass (and therefore creatinine excretion). Around 10% of communitydwelling individuals aged older than 65 years are anaemic; round 50% of nursing house residents are anaemic. Ageing: multimorbidity Multimorbidity is the presence of two or more concurrent chronic circumstances that collectively have an adverse impact on health status, function or quality of life and require complicated healthcare administration, decision making and coordination. A persistent situation is one which lasts a yr or more, requires ongoing medical a ention or limits activities of daily dwelling. These continual situations generally coexist because: � one is attributable to the opposite. The complexity of managing multimorbidity is compounded by the related polypharmacy and inevitable drug interactions. I n the perioperative se ing, because the surgical inhabitants ages, multimorbidity is extra generally encountered, conferring increased perioperative danger by way of morbidity and mortality. Ageing: geriatric syndromes Geriatric syndromes are a group of extremely prevalent age-related situations which share frequent danger components and confer opposed consequence but have illdefined pathophysiological aetiology. Frailty Frailty is a distinctive well being state related to the ageing process by which a number of body methods steadily lose their in-built reserves. This results in the frail individual being vulnerable to a fair seemingly minor exterior stressor corresponding to an uncomplicated an infection. With the ageing of the surgical inhabitants, frailty is encountered more usually; some studies report frailty in up to 50% of patients presenting for surgery. A cross cardiac and non-cardiac surgical procedure frailty is constantly reported as an unbiased danger factor for opposed postoperative outcome, together with morbidity, mortality, longer length of hospital keep and new institutionalisation at hospital discharge. Two main fashions of frailty exist: the Frailty Phenotype described in 2001 from data from the Cardiovascular Health S tudy and the Frailty I ndex described in 2005 from the Canadian Study of Aging. The Frailty Phenotype describes a model of 5 criteria: � weak point; � sluggish gait velocity; � low activity stage; � exhaustion; and � weight reduction. Those displaying three or more standards are described as frail and people with one or two criteria current are described as prefrail. I n distinction the Frailty I ndex is a measure of the variety of deficits a person has accrued across multiple domains. These domains embrace physical indicators, known medical diagnoses, cognitive or mood points, falls and so forth. For example, if a person has accrued 11 of a possible 33 deficits, she or he has a Frailty I ndex of zero. S ome tools measure a single area, corresponding to gait velocity, while others are area based mostly, such as the Edmonton Frail S cale. Choosing the most applicable software to measure frailty will rely upon the surgical se ing during which the sufferers is being assessed. I n unwell emergency sufferers, a pictorial scale which avoids functional assessment could additionally be most acceptable, whereas in preoperative assessment of deliberate surgical procedure a domain-based device incorporating practical measures could be used. This software uses routinely collected information from major care digital records and calculates a Frailty I ndex. The Edmonton Frail Scale could be employed in clinical practice to determine vulnerabilities, to direct assessment and modification and how to make sure the patient is provided to deal with the day-to-day consequences of the frailty syndrome. Patients with hip fracture are often reported as the best danger group with an incidence greater than 30%. D elirium has severe consequences, together with greater rates of postoperative morbidity, 12-month mortality and institutionalisation. Evidence is rising of the opposed impression of an episode of delirium on long-term cognitive trajectory and psychological sequelae, including anxiousness and melancholy. I n terms of management of delirium, no single intervention successfully reduces the incidence, severity or duration of delirium, however evidence does help the position of multicomponent interventions. These multicomponent interventions are non-pharmacological, with an emphasis on proactively figuring out and managing precipitating components (see Table 31. These interventions described in medical populations have been translated to surgical se ings with similar proof of profit. This is especially useful in hyperactive delirium when patients are a hazard to themselves or others, including by way of the refusal of essential investigation or remedy. The use of medications to treat a non-capacitous affected person with delirium must all the time be thought of throughout the relevant authorized framework. Current guidance differentiates between using dopamine antagonists for nearly all of postoperative delirium with benzodiazepine utilization reserved for delirium secondary to alcohol withdrawal and those with movement disorders. A ge, pre-existing cognitive impairment and prevalence of delirium are essentially the most constant associations. There is considerable debate as to how much of a decline in cognition after surgery is solely the progression of pre-existing or subclinical neurocognitive problems (mild cognitive impairment and dementias). Using Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment within the preoperative setting Comprehensive Geriatric A ssessment and optimisation is an established and evidenced-based methodology which has been utilized by geriatricians in various medical se ings during the last 30 years. I t entails a multidomain (medical, useful, psychological and social) assessment, which is normally interdisciplinary and is followed by the planning and implementation of individualised investigations, therapy, rehabilitation and longer-term follow-up. Comprehensive Geriatric A ssessment has been found to improve mortality at 18-month follow-up, increase the chance of dwelling independently at home and confer a optimistic effect on bodily operate when undertaken in medical inpatients and community-dwelling older folks. Physiological homeostasis in the perioperative interval could subsequently be more durable to obtain. I n broad phrases, this means utilizing decrease doses of medicine, given more slowly, and proactive management of blood pressure and temperature. The nadir in blood strain after induction of anaesthesia is delayed compared with youthful adults and infrequently coincides with shifting into the operating room or positioning. Blood stress readings are simply missed or ignored except the anaesthetist is vigilant to this danger. Postoperative care in older surgical sufferers O lder surgical sufferers are more doubtless than younger people to develop postoperative complications. These complications are a consequence of agerelated physiological decline, multimorbidity and geriatric syndromes corresponding to cognitive impairment and frailty. These medical points can contribute to practical deterioration resulting in longer duration of stay sluggish, rehabilitation and elevated care needs at hospital discharge. D espite the medical nature of these complications, postoperative ward care has traditionally been delivered by surgical groups with a reliance on on-call medical input.

Buy keppra 250mg mastercardWhen exposed to oxygen medicine 7253 pill buy 500 mg keppra mastercard, the lead is transformed to lead oxide treatment ibs proven keppra 500mg, producing a small voltage which can be measured and amplified medications used to treat bipolar quality keppra 250mg. Fuel cells are small medications you can crush buy discount keppra 500mg line, robust and dependable, although they require regular calibration. A fter around 6 months, they require substitute as a outcome of the lead becomes oxidised. The principle of the paramagnetic analyser is that oxygen molecules are a racted weakly to a magnetic subject (paramagnetic). I n the original analysers, a robust magnetic subject was handed throughout a chamber which contained two nitrogen-containing spheres suspended on a wire. When oxygen was introduced into the chamber, it tended to displace the spheres, inflicting them to rotate. A fast differential paramagnetic oxygen sensor makes use of the pneumatic bridge precept. The pattern and reference gasoline are drawn by a typical pump by way of two tubes surrounded by an electromagnet alternating at 110Hz. Pressure variations between the two tubes are related to the paramagnetic properties of the pattern and reference gases. The phasic adjustments in strain are extraordinarily small and measured with a miniature microphone. However, they overestimate oxygen focus when stress within the circuit is increased. Carbon dioxide and anaesthetic gases Absorption of radiation I nfrared radiation (1�15�m) is absorbed by all gases with two or extra dissimilar atoms in the molecule. Carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide and anaesthetic vapours absorb gentle at totally different wavelengths. Measurement of such gases is via an infrared gentle supply that emits gentle at totally different wavelengths in the direction of a photoelectric detector. The test gas absorbs the related wavelength of light, and any non-absorbed light passes to an optical filter. O nly mild with the wavelength comparable to the check gasoline passes by way of to the detector. The difference between light of the correct wavelength that reaches the detector and the sunshine emitted from the infrared source is a measure of infrared mild absorption by the take a look at gasoline. There are several sources of error with infrared evaluation: � Overlap of absorption spectra happens between different gases. For occasion, peak absorption for carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide and carbon monoxide is four. Whilst there are correction factors, calibration with a similar background gasoline mixture minimises error. Changes in atmospheric pressure, strain within the breathing system and adjustments in resistance of the sampling line can introduce error. Accuracy at normal breathing frequencies additionally requires a passable response time, typically a 90% or 95% rise time of less than 150ms. Slow response is usually attributable to blockage of the sampling line with condensation or sputum or by failure of the suction pump. Most analysers are facet stream systems: a small sample of gas is pumped into the analyser that necessarily entails some delay. I n most instances the sampled gas is handed into the scavenging system, however when low flows are required, it might be returned to the respiration system, although this can trigger errors because of the blending of inspiratory and expiratory gases. This association permits the sensing chamber to be housed within a monitor, making it more sturdy. The alternative major stream system places the sensing chamber in a connector throughout the patient respiration system and so reduces any delay in measurement. Carbon dioxide focus is normally displayed as a graph of concentration in opposition to time (capnograph). This provides visual confirmation that the airway is patent and that air flow is occurring. At the start of expiration, the carbon dioxide concentration is zero (dead area gas). The end-tidal value of carbon dioxide concentration approximates to alveolar, and subsequently arterial, carbon dioxide partial strain. However, when the respiratory rate is excessive, if tidal quantity is low, if the sampling point is distant from the airway or if the gases tend to combine within the circuit, the end-tidal value tends to be artificially low. This results in low end-tidal carbon dioxide readings and an increased arterial carbon dioxide rigidity. O ther strategies are used sometimes either for calibration or for complex analyses. Mass spectrometry Mass spectrometers separate the parts of complicated fuel mixtures in accordance with their mass and cost by deflecting the charged ions in a magnetic area. The ensuing positively charged ions are then accelerated by a negatively charged plate into a magnetic field. The magnetic subject causes the shifting particles to curve relying on their mass-to-charge ratio. A mass spectrum is produced by relating the detector output on the y-axis (calibrated to focus of gas) to the accelerating voltage on the x-axis (calibrated to molecular weight). S ome molecules could lose two electrons and become doubly charged � they behave like ions with half the mass. S ome fragmentation of molecules also happens in the ionisation process, resulting in the manufacturing of a mass spectrum rather than a single peak for each molecule. Mass spectrometers are expensive to purchase and keep but are extraordinarily correct, have a very quick response time, use very small sample move rates (approx. They may be sited centrally inside large theatre complexes as part of a calibration and high quality management system. Gas�liquid chromatography A gasoline chromatograph consists of two components: a column full of inert beads lined in a thin film of oil (the stationary phase) and a constant stream of inert gasoline which passes through the column. When a sample of gas is introduced at one end, the combination passes into the column and previous the oil. I nsoluble gases are inclined to stay within the provider gas and transfer by way of the column rapidly, whereas soluble gases are inclined to dissolve in the oil, slowing their progress. At the opposite finish of the column is a non-specific detector unit which yields an electronic signal proportional to the quantity of each substance present. Commonly used detectors include katharometers, flame ionisation and electron capture detectors. I dentification of a fuel is set by the duration of passage through the column and the amount measured by the detector unit.
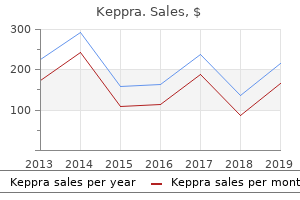
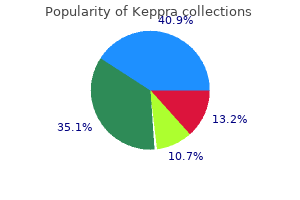
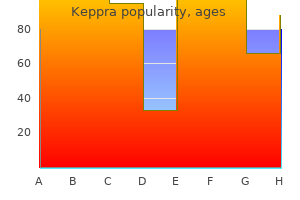
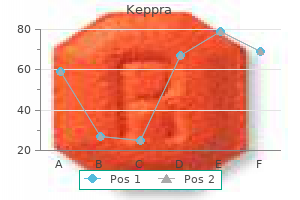
Keppra: 500 mg, 250 mg
Order keppra 500mgWith the affected person supine symptoms 7 dpo bfp generic keppra 500mg online, a linear array ultrasound transducer applied to the inguinal pores and skin crease can be utilized to identify the pulsatile femoral artery medicine 5e 250 mg keppra amex. Lateral to the artery can be recognized the echogenic fascia lata and fascia iliaca treatment 3 nail fungus keppra 500 mg otc, beneath which lies the hyperechoic symptoms ruptured spleen purchase 500mg keppra fast delivery, triangular or flat femoral nerve. I nadvertent vascular puncture may be identified by regular aspiration on the syringe through the injection. Therefore deviations from the norm should be recognised, and managed promptly and appropriately. Certain problems of anaesthesia manifest as emergencies during the intraoperative phase of surgery, similar to arrhythmias, hypotension, adverse drug effects and insufficient air flow of the lungs. The focus of this chapter is on problems that happen because of anaesthesia however which manifest within the postoperative interval. Causes of problems Human error Human error is a common contributor to anaesthetic complications, usually in association with inadequate monitoring, equipment malfunction and organisational failure. Human error is commonly associated with inadequate training, fatigue, insufficient experience and poor preparation of the affected person, environment or gear. These circumstances are usually avoidable and ought to be preventable by good organisation. When issues do occur, efficient monitoring and vigilance enable for a higher interval for action before the complication grows in severity. This may be facilitated by way of the use of action plans or drills which have been rehearsed beforehand. Communication failure Failure of communication is commonly implicated in the technology of complications in the perioperative interval. Poor working relationships, varying levels of training amongst staff and challenging working circumstances make such failure extra probably. Team training and simulation-based coaching are effective in reducing the incidence of this sort of error. Equipment failure Equipment failure might result in important danger to the affected person. I n explicit, failures of respiratory methods, airway gadgets and fuel provides have resulted in a quantity of deaths in current years. I n addition, malfunction of mechanical infusion pumps and infusion pressurising devices have also been responsible for patient morbidity and mortality. Typical examples embody diabetes mellitus, ischaemic heart illness, hypertension and asthma. Inevitable complications There is a subgroup of complications which could be classed as inevitable. D espite excellent surgical and anaesthetic apply, the affected person should still expertise a complication that brings morbidity or even death. Avoidance of issues the best steps in preventing hurt from issues are carried out earlier than the complication happens. Such preparation consists of: � preoperative evaluation, investigation and counselling of the affected person; � preoperative checking of equipment and the assurance of backup tools; � availability of an appropriately educated assistant; � preoperative session with extra skilled personnel, the place necessary, concerning essentially the most acceptable anaesthetic approach; and � use of applicable monitoring strategies. Experience Complications happen more generally in inexperienced (or incautious) hands. Redundant methods using redundant systems helps prevent complications; the availability of no much less than two working laryngoscopes illustrates this. O ther examples embrace the insertion of two or extra intravenous cannulae if significant blood loss is expected and monitoring of expired unstable agent focus in addition to depth of anaesthesia screens to minimise the danger of consciousness. Monitoring the A ssociation of A naesthetists has produced guidelines stipulating the suitable minimum stage of intraoperative monitoring (see Chapter 22). Modern monitoring methods have mechanically activated alarms, and the anaesthetist selects the values at which these alarms sound. Clearly that is totally different for every affected person, whose coexisting illness, age, anaesthesia and surgical procedure might range significantly. Management of problems Generic administration nearly all of issues that end in severe hurt to the affected person compromise the delivery of oxygen to tissues. O rgans which are damaged most rapidly by a deficiency in oxygen supply embrace the brain and heart. The liver and the kidneys are much less fragile but are probably at risk from even short interruptions in oxygen provide. Cessation of perfusion results in extra speedy injury to an organ than hypoxaemia whereas perfusion is maintained. Treatment should be offered quickly when organ perfusion is threatened or when arterial oxygenation is impaired. The administration of just about any vital complication ought to embrace the supply of a excessive impressed oxygen fraction and the assurance of an sufficient cardiac output. The evolving problem the early recognition of an evolving problem allows the anaesthetist time to handle the complication before it damages the patient. The first response to an rising complication ought to be to minimise the potential harm to the affected person. I n most situations by which complications turn out to be apparent, the analysis is straightforward and treatment might progress in a linear style. Where the differential diagnoses regarding an issue seem equally doubtless the, anaesthetist should treat the issue that threatens the most hurt to the patient. D uring the administration of problems throughout anaesthesia the anaesthetist must continuously be reconsidering the list of differential diagnoses, rearranging them mentally so as of likelihood and treating the most probably and most harmful possibilities first. Record maintaining Record preserving, while useful in preventing complications, can be important during problems. A ccurate report maintaining also allows safer sharing of care between anaesthetists, facilitating handover of care during lengthy operations and permitting be er teamwork in advanced circumstances by which two anaesthetists are required. Review of critical incidents and problems is vitally important in preventing future repetitions of the incident and in providing continuing schooling to individual practitioners and departments of anaesthesia. Finally, some problems lead to hurt to the affected person, and it is rather important for the practitioner and affected person that detailed information can be found for later evaluation. S uch practice aims to cut back the potential culpability of the anaesthetist should problems come up. The culture of blame by which we now practise mandates that anaesthetists should defend themselves as well as their sufferers. Meticulous document keeping, preoperative info and consent and frank dialogue of dangers with the affected person are very important. The anaesthetist should specific remorse and sympathy that the complication has occurred and explain why. A frank discussion of the difficulties that occurred throughout anaesthetic administration could provide the patient with sufficient data. I f human error has occurred, then the anaesthetist ought to apologise and reassure the affected person that additional information shall be offered when it turns into obtainable. I t could additionally be prudent that the scientific director accompanies the anaesthetist during their dealings with the patient.
References - Karthik S, Lisbon A. Low-dose dopamine in the intensive care unit. Semin Dial. 2006;19:465-471.
- Shatapathy P, Aggarwal BK, Kamath SG: Tricuspid valve repair: A rational alternative, J Heart Valve Dis 9:276-282, 2000.
- Kruse AL, Gratz KW. Oral carcinoma after hematopoietic stem cell transplantationoa new classification based on a literature review over 30 years. Head Neck Oncol 2009;1:29.
- Seiler L, Rump LC, Schulte-Monting J, et al: Diagnosis of primary aldosteronism: value of different screening parameters and influence of antihypertensive medication, Eur J Endocrinol 150(3):329n337, 2004.
- Le Trong I, Aprikian P, Kidd BA, et al: Structural basis for mechanical force regulation of the adhesin FimH via finger trap-like beta sheet twisting, Cell 141:645n655, 2010.
|