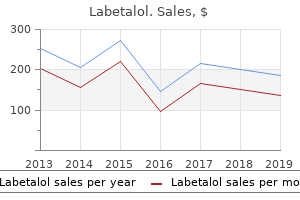
Labetalol
Kenichi Ta naka, MD, MSC - Associate Professor
- Anesthesiology
- Emory University School of Medicine
- Atlanta, Georgia
Discount 100 mg labetalolBiopsy specimens of paraneoplastic pemphigus show suprabasilar acantholysis and dyskeratotic keratinocytes with basal cell vacuolization blood pressure information labetalol 100 mg low cost. Whereas direct immunofluorescence demonstrates cell floor deposits of IgG in patients with pemphigus vulgaris and foliaceus hypertension 3rd trimester cheap labetalol 100mg otc, oblique immunofluorescence reveals circulating IgG antibodies that recognize molecules on the epidermal cell floor blood pressure urgency purchase 100mg labetalol visa. Patients with paraneoplastic pemphigus have circulating and tissue-bound IgG antibodies that are indistinguishable from these in pemphigus vulgaris and that additionally recognize the cell floor of simple epithelia hypertension synonym buy 100 mg labetalol amex, including the liver and heart. Theduration of therapy with every of these medications varies according to the extent of illness exercise. Although using steroid-sparing agents is supported by clinical expertise, few managed research have demonstrated their profit. For paraneoplastic pemphigus attributable to benign tumors corresponding to Castleman disease(Chapter185),tumorremovalisoftencurative. Overall, nevertheless, the mortality fee is about twice that of the final population. The prognosis of sufferers with paraneoplastic pemphigus is expounded to the type of related neoplasm. Patients with benign tumors often expertise clearance of their lesions after tumor resection, but those with malignant tumors generally have a poor prognosis. Erythema multiforme main, also referred to as StevensJohnson syndrome, is a extra extreme mucosal and skin disease characterized by indicators and signs paying homage to serum sickness (Chapter 47). Toxic epidermal necrolysis is on the most severe finish of the erythema multiforme spectrum. The major lesions of erythema multiforme minor are erythematous macules and edematous papules with vesicular facilities that turn into dusky violet. The pores and skin lesions of Stevens-Johnson syndrome resemble those of erythema multiforme minor however are likely to be generalized and show confluent erythema with urticarial and purpuric lesions. Erosions of two or extra mucosal surfaces happen in Stevens-Johnson syndrome and will embrace hemorrhagic crusting of the lips, ulceration of the ocular mucosa, and genital involvement. Patients with erythema multiforme main have a 1- to 14-day prodrome that features fever, cough, sore throat, vomiting, and diarrhea. Patients with poisonous epidermal necrolysis could have an identical prodrome, quickly followed by generalized macular erythema that progresses to confluent erythema with skin tenderness. Large blisters observe quickly afterward, after which pores and skin sloughing happens as the massive blisters break and go away denuded pores and skin. The prognosis is good for patients with pseudoporphyria after the offending agent has been discontinued. In sufferers with continual renal failure treated by hemodialysis, true porphyria cutanea tarda or pseudoporphyria may develop and could be very troublesome to treat. Distal extremity blisters might occasionally develop in sufferers with diabetes mellitus (Chapter 229). Many patients with junctional epidermolysis bullosa have severe illness that can result in dying, often secondary to infection, and metastatic squamous cell carcinoma may develop in some sufferers with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa and can even lead to demise. Epidermolysis bullosa simplex is attributable to mutations of the genes coding for keratins 5 and 14. Junctional epidermolysis bullosa has a variable molecular etiology, and mutations in genes coding for laminin 5 subunits, bullous pemphigoid antigen I, 6 integrin, and 4 integrin have been demonstrated. No medicines are identified to right the underlying molecular defects, however gene remedy is being actively pursued. Erythema multiforme major takes three to 6 weeks to clear and has less than a 5% mortality price. Toxic epidermal necrolysis has a mortality price approaching 30%, and sufferers are best managed in an intensive care or burn unit. Healing of crusted erosions and blisters leaves scars, milia, and hyperpigmented and hypopigmented atrophic patches. Histology reveals a subepidermal blister with minimal dermal infiltrate, and direct immunofluorescence demonstrates immunoglobulin and complement deposition in dermal capillaries and at the basement membrane. Phlebotomy is the usual treatment, and the goal is to cut back serum ferritin to the lower limit of the normal range. Nonbullous impetigo is characterized by fragile vesicles or pustules that rupture and depart honey-colored crusted papules or plaques, particularly close to the nose and mouth and on the extremities. Lesions develop on normal or traumatized skin or are superimposed on preexisting circumstances, including scabies, varicella, or atopic dermatitis. Culture and sensitivity studies are really helpful if topical or oral treatment is ineffective. Oral antibiotics, including dicloxacillin (500 mg four times daily for 7 days) or cephalexin (500 mg thrice every day for 7 days), are used for extensive illness or in sufferers refractory to topical mupirocin. Acute glomerulonephritis (Chapter 121) develops in 2% to 5% of young children with nonbullous impetigo, often inside 10 days after the skin lesions seem. Staphylococcal scalded pores and skin syndrome is a blistering illness brought on by an exotoxin produced by S. Staphylococcal scalded pores and skin syndrome is manifested as a sudden onset of fever and tender, blanchable erythema. It begins on the central a part of the face, neck, and intertriginous areas and rapidly generalizes. If the patient is discovered to have methicillinresistant staphylococci, vancomycin, 1 g every 12 hours (with dose adjustment based on creatinine clearance), should be given for 10 to 14 days. Patients with delicate disease could additionally be treated with oral dicloxacillin, 500 mg 4 instances every day for 10 to 14 days, unless the staphylococcal isolate is methicillin resistant, in which case the choice of antibiotics should be guided by the results of sensitivity testing. For extreme methicillin-resistant gram-positive pores and skin infections, one dose of intravenous oritavancin (1200 mg)A5 or two doses of intravenous dalbavancin (1 g on day 1, 500 mg on day 8) is as efficacious as twice daily intravenous vancomycin for up to 7-10 days. Chronic erosive ulcers of the face and anogenital areas might develop in immunocompromised sufferers. Patients with main gingivostomatitis have excessive fever, regional lymphadenopathy, and malaise. Patients with primary genital herpes have fever, flulike symptoms, tender inguinal adenopathy, and aseptic meningitis. The prognosis is normally made clinically, but direct fluorescent antibody or culture confirmation is usually wanted. The main morbidity, which is ache throughout the affected dermatome, could be severe and persist after the skin lesions have resolved (postherpetic neuralgia). In patients with gentle to moderate disease, remedy with benzoyl peroxide is the most cost-effective remedy. Moresignificantdiseaseisoften treated with oral tetracycline (250-1000mg/day), doxycycline (200mg/day), orminocycline(200mg/day). Androgenic hormones,systemiccorticosteroids,lithium,phenytoin,phenobarbital,isoniazid, and endocrinologic situations corresponding to polycystic ovary illness and adrenal or ovarian tumors could produce acneiform eruptions or worsen preexistingacne.
Labetalol 100 mg with visaOpening pressures should be measured as a outcome of elevated intracranial pressure can occur with all types of viral encephalitis and may have extra treatment prehypertension 2014 proven labetalol 100mg. However heart attack 4sh generic labetalol 100 mg without a prescription, a polymorphonuclear predominance is seen in some cases of West Nile encephalitis and cytomegalovirus ventriculitis blood pressure medication for anxiety order labetalol 100mg. For instance heart attack diagnosis order labetalol 100 mg otc, herpes simplex encephalitis has a attribute pattern involving the mesiotemporal, inferofrontal, and insular cortices, often unilateral or asymmetrically bilateral. Other types of infectious non-viral causes mimicking viral encephalitis embrace bacterial cerebritis, meningovascular syphilis, and cerebral cysticercosis. In the United States, the most typical explanation for nonepidemic encephalitis is herpes simplex encephalitis, which is attributable to herpes simplex virus type 1 (Chapter 374). The most common epidemic virus within the United States is now West Nile virus (Chapter 383), which is a mosquito-transmitted Flavivirus related to St. If frank necrosis and purulence are present, the correct pathologic time period is brain abscess (Chapter 413). Encephalitis, nonetheless, may be related to substantial necrosis, and sufferers with severe acute viral encephalitis frequently have microscopic evidence of necrosis. Certain viral encephalitides, corresponding to herpes simplex encephalitis, could be both focal and hemorrhagic. Viruses that cause acute encephalitis may usually also trigger meningitis (Chapter 412). Indeed, sufferers with encephalitis virtually at all times have some microscopic inflammatory adjustments within the leptomeninges. Conversely, patients with viral meningitis will inevitably have some element of microscopic encephalitis. The diploma of inflammatory change current in the brain is set by the person viral pathogen and by host immune elements, which are liable for the response to the invading virus. As the encephalitis progresses, signs of elevated intracranial pressure, lethargy, and coma are ordinary. Spinal fluid evaluation is important within the analysis of herpes simplex encephalitis. Because herpes simplex kind 2 could cause encephalitis in neonates and meningoencephalitis in adults, this distinction may information therapy. Radiographically detected involvement of the mesiotemporal quite than the lateral temporal areas and involvement of the grey matter rather than the white matter suggest herpes simplex encephalitis as the prognosis. Electroencephalography is an adjunctive test that can show periodic lateralized epileptiform discharges ipsilateral to the concerned temporal lobe. Furthermore, main demyelinating disease (Chapter 411), significantly in the type of acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, overlaps clinically with viral encephalitis. The encephalitis can strike older children however is most commonly a disease of adults. Herpes simplex encephalitis often happens in immunocompetent patients, however immunosuppressed sufferers may be affected. Herpes simplex virus sort 1 infects and establishes latency within the majority of the inhabitants. Whether herpes simplex encephalitis arises from reactivation of a latent viral an infection in the trigeminal ganglion or is a primary nasopharyngeal an infection that ascends into the olfactory nervous system is unsure. The pathology of herpes simplex encephalitis is a necrotizing hemorrhagic inflammatory encephalitis in a characteristic sample affecting the mesiotemporal, inferofrontal, and insular cortices, with gray matter predominance. Even if the brain is affected bilaterally, the pathologic features are often asymmetrical, a sample that helps distinguish herpes simplex from other types of limbic encephalitis. Focal neurologic deficits, corresponding to hemiparesis or aphasia, seem early and can be mistaken for stroke. Intravenous acyclovir (10mg/kg each 8 hours for 14 to 21 days) is the therapyofchoice. It produces a fatal encephalitis, although the latency between animal chew exposure and occurrence of neurologic symptoms might sometimes obscure the prognosis. Rabies virus variants in bats at the moment are accountable for almost all of latest human cases within the United States and Canada. Raccoon rabies has extended from Florida into Georgia, Alabama, and South Carolina. Because the disorder tends to be a mind stem encephalitis, the bulbar cardiovascular and respiratory centers are affected. Human rabies normally develops 20 to 90 days after a bite, although hardly ever disease develops after only a few days or after a year or more following bite exposure. Nonspecific prodromal signs embody fever, chills, malaise, fatigue, insomnia, anorexia, headache, and irritability. In the vast majority of sufferers, pain or paresthesias will develop in the limb that was affected by the bite. Following the prodromal illness, an encephalitic form develops in about 80% of sufferers and causes behaviors ranging from episodes of agitated arousal to quiet lethargy. Disinhibition of brain stem reflexes leads to hydrophobia with laryngospasm and an incapability to cope with salivation, swallowing of water, or other oral intake. When the brain stem encephalitis affects the bulbar, cardiovascular, and respiratory facilities, autonomic dysfunction, cardiopulmonary issues, and respiratory failure may occur. Another form of rabies that affects as much as a 3rd of patients is known as paralytic rabies. This type of rabies is manifested as acute flaccid paralysis, which can be multifocal and affect each the limbs and the bulbar musculature, thereby resembling poliomyelitis (Chapter 379) because of its multifocality. A lymphocytic pleocytosis, normally lower than one hundred white cells/�L, is discovered in more than 50% of sufferers within the first week of sickness. Involvement of mind grey matter, including the hippocampus and basal ganglia buildings, signifies the grey matter predilection and infrequently bilateral involvement of supratentorial structures. Serum antibodies may also be present in spinal fluid, however their absence is unreliable in excluding the analysis. Classically, staining a skin biopsy pattern taken from an space near the nape of the neck for rabies antigen within the sensory nerves can verify the prognosis of rabies. A constructive result confirms the analysis, however the exclusionary value of negative results is unknown. Fluid-attenuated inversion restoration (FlAir) Mri scan of the mind, showing elevated signal(A)intherightmesiotemporallobe(includingtheamygdala,hippocampus,and uncus), and (B) in the bilateral inferofrontal lobes (cingulate gyrus and orbital frontal cortex)andtherightinsularcortex. Dog rabies got here underneath management within the United States during the 1950s and was related to a marked reduction within the number of human instances transmitted by dogs. Much of the dog-related scientific rabies seen in the United States is the outcomes of canine bites that occurred in growing nations, before the patient migrated to the United States. Rare instances of transmission of rabies to transplant organ recipients have occurred in the United States.
Diseases - Pilonidal cyst
- Ichthyosis linearis circumflexa
- Lymphangiomatosis, pulmonary
- Congenital hepatic fibrosis
- Sharp syndrome
- Faulk Epstein Jones syndrome
- Bahemuka Brown syndrome
- Camurati Engelmann disease
- Troyer syndrome
- Cold antibody hemolytic anemia
100 mg labetalol otcExcept in probably the most extreme instances blood pressure lowering discount 100 mg labetalol with mastercard, nonetheless blood pressure heart attack discount labetalol 100 mg without prescription, warning is warranted in communicating a hopeless prognosis before aggressive efforts have been made to resuscitate victims of intracerebral hemorrhage heart attack in 30s discount labetalol 100mg without a prescription. Physicians are probably to pulse pressure 66 order 100 mg labetalol amex underestimate the probabilities of a good end result, and plenty of poor outcomes end result from self-fulfilling prophesies of doom. Mortality after intracerebral hemorrhage is lower amongst sufferers in specialty neurologic intensive care items, presumably due to adherence to greatest medical practices, early transition to rehabilitation, and cautious optimism when setbacks happen. Brain vascular malformations are space-occupying congenital anomalies that may typically exist for a lifetime without signs. The most feared and harmful complication is rupture, which could be manifested as intracerebral hemorrhage, as intraventricular hemorrhage, or much less usually as subarachnoid hemorrhage. About 10% of intracerebral hemorrhages however only about 1% of strokes are caused by vascular malformations. Hemorrhage from an arteriovenous malformation is most typical in the course of the second through fourth a long time. For the following 5 years, the chance of bleeding is about 2% per yr, and it then falls to about 1 to 2% yearly thereafter. Over a lifetime, a younger person due to this fact has a 50 to 60% chance of another hemorrhage, each of which carries a 10 to 15% danger of acute death. Cerebrovascular malformations are characterised on the premise of their histologic appearance and the intervening neural parenchyma. The most frequent kind of vascular malformation is an arteriovenous malformation, by which a core or nidus of dysplastic vessels is fed by arteries and drained by veins without intervening capillaries. Bleeding from a feeding artery aneurysm usually results in subarachnoid hemorrhage, bleeding from the nidus itself usually results in intracerebral hemorrhage, and bleeding from a draining vein normally is manifested as intraventricular hemorrhage. The next most common vascular malformations are cavernous angiomas or hemangiomas. Dural arteriovenous fistulas are usually acquired lesions that outcome from the formation of small arteriovenous shunts within the wall of a cavernous sinus as a consequence of dural sinus thrombosis. Over time, move via the fistula increases, resulting in pulsatile growth of regional veins and subsequent rupture. About 50% of arteriovenous malformations are manifested with intracranial hemorrhage, about 30% initially are manifested as seizures, and about 20% could additionally be manifested with progressive neurologic incapacity. An increasing proportion, however, are actually detected by mind imaging as a part of the analysis of complications (Chapter 398), to which arteriovenous malformations may or may not be causally related. Because an arteriovenous malformation can bleed into the subarachnoid area, the mind parenchyma, or the ventricular system, symptoms and indicators depend upon the situation and severity of bleed. Post-bleeding cerebral vasospasm, which is much less common than aneurysmal bleeding, occurs in lower than 5% of cases and is often linked to thick cisternal clot or intensive intraventricular hemorrhage. Patients who develop seizures as a result of these arteriovenous malformations usually have focal seizures (Chapter 403). Even with out seizures, sufferers can develop focal neurologic deficits because of vascular thrombosis or the shunting of blood through the malformation quite than allowing it to perfuse regular brain tissue. Even if an arteriovenous malformation is discovered by unilateral carotid injection, four-vessel angiography is indicated as a end result of malformations may be multiple and can be associated with saccular aneurysms. The low move price via these lesions makes them tough to detect by angiography. Options embrace selective embolization of the feeding arteries, surgicalresection,andradiation-inducedthrombosis,aloneorsometimesin combination. In a randomized trial, medical management emphasizing management of hypertension, avoidance of anticoagulants, and use of anticonvulsants to control seizures was superior to multimodality intervention with surgery, embolization, or radiotherapy, with a 10% fee of death or stroke at 33 months compared with a 30% danger within the intervention group. Antifibrinolytic remedy in the management of aneurismal subarachnoid hemorrhage revisited. Calcium antagonists in sufferers with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a systematic evaluate. Intensive blood strain discount in acute intracerebral hemorrhage: a meta-analysis. The explanation for Parkinson disease is believed to be a variable mixture of poorly understood genetic1 and environmental factors. The protein -synuclein, which is the chief constituent of the hallmark cytoplasmic inclusion, the Lewy physique (Chapter 402), is important in the pathogenesis of Parkinson disease. Abnormal aggregation of the protein, either from mutations within the -synuclein gene or on account of extreme manufacturing of the traditional protein due to gene duplications or triplications, is associated with varying disease phenotypes. This knowledge, combined with recognition of the significance of dopamine (see later), has implicated oxidative stress within the pathogenesis of Parkinson illness. Other proposed pathogenetic elements include mitochondrial dysfunction, protein misfolding or aggregation, excitotoxicity, irritation, apoptotic cell death, and lack of trophic help. Approximately 60% of those dopaminergic neurons could have degenerated before clinical options of the illness develop. Indeed, it has been advised that Parkinson illness might start within the decrease mind stem and the olfactory system, where it causes early loss of the sense of scent and only later includes the substantia nigra. Studies suggest the potential of cell-to-cell transmission of a type of -synuclein which will then induce abnormal folding and aggregation of the traditional protein in a "permissive templating" style similar to prion illnesses (Chapter 415). It is generally current with the limb in full repose and usually subsides when the limb strikes and takes up a model new place, though the tremor may reemerge ("reemergent tremor") within a brief time after sustaining the new position (Video 4091). Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a suggestion for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Difference in aneurysm traits between ruptured and unruptured aneurysms in patients with multiple intracranial aneurysms. Guidelines for the management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a tenet for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Outcome after conservative management or intervention for unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations. Rigidity is "activated" or accentuated on examination by asking the affected person to transfer the limb reverse the one being tested. Non�motor Akinesia Akinesia or bradykinesia includes a variety of disturbances in movement, together with slowness, reduced amplitude, fatiguing, and interruptions in ongoing motion. This disabling side of parkinsonism interferes with all voluntary actions and accounts for many of the well-known options of parkinsonism: lack of facial features with lowered blinking (hypomimia or masked facies-the "reptilian stare"), delicate monotonous speech (hypophonia), impaired swallowing leading to drooling (sialorrhea), small handwriting (micrographia), lowered arm swing whereas walking, shortened stride and shuffling gait, problem arising from a low chair, and issues turning over in mattress. Bradykinesia is obvious on inspection and elicited by testing rapid repetitive and alternating movements: finger tapping, opening and shutting the fist, pronating and supinating the wrist, and toe and heel tapping. Patients could complain of being unable to stop themselves from going ahead (propulsion) or backward (retropulsion). Clinical evaluation of postural instability includes the "pull take a look at," in which the examiner abruptly pulls the affected person off stability while being able to catch the affected person in the occasion of a fall. In addition to the motor options of parkinsonism, a selection of non�motorrelated features are extraordinarily frequent. These include ache and different sensory disturbances; dysautonomic complaints, corresponding to urinary urgency and frequency; orthostatic faintness; constipation; male erectile dysfunction; sleep abnormalities, together with rapid eye movement behavioral disorder (Chapter 405); anxiety; fatigue; melancholy; and cognitive disturbances, together with dementia. Accordingly, sufferers exhibit a mixture of the traditional options of parkinsonism, which can enhance significantly in response to medication; signs that persist despite the peak good factor about medicine; and symptoms that occur as a complication of dopaminergic medicine Table 409-2).

Buy 100mg labetalolCessation of smoking blood pressure and age buy labetalol 100 mg without prescription, management of blood sugar blood pressure by age chart discount labetalol 100mg online, management of blood lipid ranges blood pressure ranges and pulse order labetalol 100mg amex, and management of systemic blood stress are significantly essential behavioral modifications blood pressure zinc order 100mg labetalol fast delivery. Hemorrhage is accompanied by acute, and normally permanent, loss of central visible acuity. Drusen are current in the posterior pole round a big space of geographic atrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium. In sufferers with type 2 diabetes (Chapter 229), the prevalence of diabetic retinopathy is about 23% after 12 years and 60% after sixteen years. Tight control of blood glucose greatly reduces the chance for the event of diabetic retinopathy. A10 With acute hyperglycemia, accumulation of sorbitol could result in lenticular swelling; secondary refractive errors could persist for six to eight weeks. TaySachs and Niemann-Pick diseases (Chapter 208) are associated with a foveal cherry-red spot owing to the buildup of gangliosides inside perifoveal ganglion cells. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (Chapter 260) is commonly related to attribute angioid streaks of the retina. The main vessels of the retina enter the eye at a point of relative constriction in the tissues of the lamina cribrosa of the optic disc. Partial occlusion of either the artery or vein is associated with less visible loss but nonetheless will increase the risk for creating neovascular glaucoma. The ischemic posterior retina generally has a pale grey look besides at the fovea, the place the conventional color is preserved (cherry-red spot). The retina, nonetheless, is characterized by excessive, generalized hemorrhages, which resolve very slowly and are sometimes associated with opaque areas of focal retinal ischemia (cotton-wool spots). Moderately sclerosed arterioles have a "copper wiring" appearance, whereas severely sclerosed vessels reveal "silver wiring. Hypertension retinopathy with narrowed arterioles whose sclerosed partitions create the appearance of "nicking" when the arterioles cross venules. Central retinal vein occlusion with diffuse intraretinal hemor- Amiodarone Thiabendazole Isotretinoin* remedy, but intravitreal ranibizumab can present significant and sustained visual enchancment. A11 Central vein occlusion is associated with a major danger for creating secondary neovascular glaucoma. Giant cell arteritis (temporal arteritis [Chapter 271]) is occlusion of the blood provide of the optic disc by irritation of the brief posterior ciliary arteries. Presenting symptoms earlier than visible loss often include a imprecise sensation of fatigue, scalp tenderness, or jaw claudication. Diagnosis is suspected by classic traits and by an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate or elevated C-reactive protein level. Histologic affirmation is offered by a biopsy showing granulomatous irritation in the area of the internal elastic lamina of the temporal artery. Nonarteritic optic neuropathy is caused by occlusion of the posterior ciliary arteries and infarction of the optic disc, resulting in acute, normally unilateral, painless lack of vision. Occlusion is thought to be due to atherosclerosis or some other lumen-compromising mechanism. Scleritis, which presents as severe pain and redness, is related to infectious or autoimmune connective tissue disease in about 50% of cases. Diagnostic evaluation includes ultrasonography or magnetic resonance imaging and laboratory exams to establish potential underlying situations. Treatment might require topical or oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or corticosteroids. Bandage contact lenses and conjunctival recession or advancement have additionally been used with variable success. Orbital Pseudotumor Nonspecific, idiopathic orbital inflammation involving the lacrimal gland (dacryoadenitis), extraocular muscular tissues (myositis), orbital fat, sclera, or optic nerve sheath (optic perineuritis) may be attributable to orbital pseudotumor. Some of the circumstances of idiopathic orbital inflammation have been just lately associated with immunoglobulin G4 autoimmune disease. Patients might present with proptosis, limited ocular actions, or decreased acuity. Patients reply dramatically to systemic corticosteroids inside 24 hours, however the steroids should be tapered slowly over months to forestall recurrence. Ocular or periocular tissues will be the main focus of isolated idiopathic or autoimmune irritation. Symptoms embrace gritty, overseas physique sensations, burning, photophobia, and decreased visible acuity. Iritis Iritis presents with ache, photophobia, and blurred vision, with about 50% of cases associated to systemic disease. Slit lamp examination shows inflammatory cells and protein exudate within the anterior chamber. Symptomatic treatment is with prednisolone acetate 1% suspension 4 instances a day and cycloplegic medication (cyclopentolate 1 or 2% twice daily) is usually effective, however repeated episodes require analysis for autoimmune and infectious causes. Rheumatoid Arthritis Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (Chapter 264) is the most typical specific childhood entity related to uveitis. In adults, the ocular manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis mainly have an result on the anterior part of the attention, cornea, and sclera. Scleromalacia perforans, which is aseptic necrosis of the sclera, is related to rheumatoid arthritis about 46% of the time. Oral or topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines similar to flurbiprofen or diclofenac may hasten resolution. The retina could present a retinal vasculitis, and the optic nerve an optic neuritis, ischemic or nonischemic. Sarcoidosis About 25% of sufferers with sarcoidosis (Chapter 95) develop persistent uveitis. Sarcoid also can contain the lids, conjunctiva, optic nerve, cranial nerves, and lacrimal glands. Anterior uveitis is handled topically with prednisolone acetate in decreasing doses, relying on degree of inflammation, and with daily cycloplegics (cyclopentolate 2%, atropine 1%). Sympathetic Ophthalmia Sympathetic ophthalmia is an autoimmune illness characterized by bilateral, granulomatous uveitis following trauma to one eye. The situation could be very rare, occurring in less than 1 per 10,000 instances of ocular surgical procedures and 1 per a thousand cases of unintended trauma. The illness is recognized clinically by indicators of irritation in the uninjured eye, usually 2 weeks or longer after the injury. When sympathetic ophthalmia is established, the patient will require antiinflammation treatment. In the untimely toddler, vessels of the immature retina might leave the aircraft of the retina and grow into the adjoining vitreous physique, the place tractional forces could cause total, irreversible retinal detachment.

100mg labetalol with visaBlows to the occipital or mastoid area are particularly prone to blood pressure diastolic high purchase 100mg labetalol fast delivery produce labyrinthine injury hypertension blood tests buy labetalol 100mg line. Transverse fractures of the temporal bone sometimes cross by way of the vestibule of the inside ear heart attack queen buy labetalol 100 mg online, tearing the membranous labyrinth and lacerating the vestibular and cochlear nerves pulse pressure 49 labetalol 100 mg on-line. Complete lack of vestibular and cochlear operate is the usual sequela, and the facial nerve is interrupted in roughly 50% of instances. As noted earlier, benign paroxysmal positional vertigo is also a standard sequela of head trauma. Fistulas of the oval and round windows may result from influence noise, deep-water diving, extreme bodily exertion, or blunt head harm without cranium fracture. The mechanism of the rupture is a sudden adverse or optimistic strain change within the middle ear or a sudden improve in cerebrospinal fluid stress transmitted to the internal ear via the cochlear aqueduct and internal auditory canal. Clinically, the rupture results in the sudden onset of vertigo or listening to loss, or both. Vertebrobasilar insufficiency is normally attributable to atherosclerosis of the subclavian, vertebral, and basilar arteries. On event, episodes of vertebrobasilar insufficiency are precipitated by postural hypotension, Stokes-Adams attacks, or mechanical compression from cervical spondylosis. Magnetic resonance angiography can identify occlusive vascular illness most commonly involving the vertebral-basilar junction. Vertigo is a typical symptom with infarction of the lateral mind stem or cerebellum (Chapter 407), or both. The diagnosis is normally clear, primarily based on the attribute acute history and pattern of associated signs and neurologic findings. On occasion, cerebellar infarction or hemorrhage arises with extreme vertigo, vomiting, and ataxia without associated mind stem signs and signs which may suggest the misguided analysis of an acute peripheral vestibular dysfunction. The key differential is the finding of clear cerebellar indicators (extremity and gait ataxia) and of direction-changing, gaze-evoked nystagmus. Such patients have to be watched rigorously for several days as a result of they may develop progressive brain stem dysfunction because of compression by a swollen cerebellum. Cerebellopontine Angle Tumors Postconcussion Syndrome the so-called postconcussion syndrome refers to a vague dizziness (rarely vertigo) associated with anxiety, difficulty in concentrating, headache, and photophobia induced by a head harm leading to concussion (Chapter 399). On event, related but less pronounced signs are related to gentle head harm judged to be trivial on the time. The cause is unknown, however animal studies point out that small multifocal mind lesions (petechiae) generally happen after concussive brain injury. On occasion, nonetheless, episodic vertigo or positional vertigo heralds the presence of a cerebellopontine angle tumor. In virtually all sufferers, retrocochlear listening to loss is current, best identified by audiometric testing. About two thirds of patients have antibodies directed in opposition to heat shock protein 70. The aminoglycosides streptomycin and gentamicin are remarkably selective for vestibular ototoxicity. Unfortunately, many sufferers being handled with ototoxic medication are initially bedridden and unaware of the vestibular impairment until they recuperate from their acute sickness and attempt to walk. The prognosis could be made at the bedside with a head-thrust take a look at (bilateral corrective saccades; see later). If the drug is discontinued early through the course of signs, the dysfunction might stabilize or enhance. Acute vertigo could be the first symptom of multiple sclerosis (Chapter 411), though only a small percentage of younger patients with acute vertigo eventually develop a quantity of sclerosis. Vertigo in multiple sclerosis is usually transient and often related to other neurologic indicators of mind stem disease, particularly, internuclear ophthalmoplegia or cerebellar dysfunction. Vertigo can also be a symptom of parainfectious encephalomyelitis or, rarely, parainfectious cranial polyneuritis. The Ramsay Hunt syndrome (geniculate ganglion herpes) is characterised by vertigo and listening to loss related to facial paralysis and, sometimes, pain in the ear. The typical lesions of herpes zoster (Chapter 375), which can comply with the looks of neurologic signs, are found in the external auditory canal and over the palate in some patients. Rarely is herpes zoster liable for vertigo in the absence of the fullblown syndrome. Granulomatous meningitis (Chapter 412) or leptomeningeal metastasis and cerebral or systemic vasculitis (Chapter 270) might involve the eighth nerve, producing vertigo as an early symptom. In these issues, cerebrospinal fluid analysis normally suggests the diagnosis (Chapter 396). Patients suffering from temporal lobe epilepsy (Chapter 403) often expertise vertigo as the aura. BedsideTests Hyperventilation Vascular Insufficiency Vertebrobasilar insufficiency is a typical reason for vertigo in older folks. Vertigo with vertebrobasilar insufficiency is abrupt in onset, usually lasting a number of minutes, and is incessantly related to nausea and vomiting. Associated symptoms resulting from ischemia in the remaining territory provided by the posterior circulation embrace visual illusions and hallucinations, drop assaults and weakness, visceral sensations, visible area defects, diplopia, and headache. Patients with compressive lesions of the vestibular nerve, corresponding to with an acoustic neuroma or cholesteatoma, or with demyelination of the vestibular nerve root entry zone could develop vertigo and nystagmus after hyperventilation. Presumably, metabolic adjustments associated with hyperventilation set off the partially broken nerve to hearth inappropriately. Vestibulospinal Function Bedside exams of vestibulospinal function are sometimes insensitive because most patients can use vision and proprioceptive alerts to compensate for any vestibular loss. Patients with acute unilateral peripheral vestibular lesions might past-point or fall towards the aspect of the lesion, but within a couple of days, balance returns to normal. In an alert human, rotating the top back and forth in the horizontal airplane induces compensatory horizontal eye actions which may be dependent on both the visible and vestibular methods. In this setting, conjugate compensatory eye actions point out normally functioning vestibulo-ocular pathways. Because the vestibulo-ocular reflex has a a lot larger frequency vary than the sleek pursuit system, a qualitative bedside check of vestibular perform could be made with the head-thrust test. Nystagmography can be helpful in figuring out a vestibular lesion and localizing it inside the peripheral and central pathways. Evaluatingthe"Dizzy"Patient Caloric Test the caloric test induces endolymphatic circulate in the horizontal semicircular canal and horizontal nystagmus by creating a temperature gradient from one aspect of the canal to the other. With a cold caloric stimulus, the column of endolymph nearest the center ear falls due to its elevated density. This causes the cupula to deviate away from the utricle (ampullofugal flow) and produces horizontal nystagmus with the fast section directed away from the stimulated ear. Because of its ready availability, ice water (approximately 0� C) can be utilized for bedside caloric testing. To bring the horizontal canal into the vertical aircraft, the affected person lies within the supine place with head tilted 30 degrees forward.
Syndromes - You have incontinence or have changed your lifestyle because of your symptoms
- Breathing too quickly (hyperventilation)
- Pancakes and waffles
- Infection in the lungs
- Red, irritated, and painful eye (looks like "pink eye")
- Shock
- Does the pain occur only with certain movements or positions?
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Losing interest in things previously enjoyed, flat mood

Buy labetalol 100 mg onlineMacrophage-mediated removal of mobile particles peaks at about three to 4 weeks after the infarct hypertension values cheap 100 mg labetalol with mastercard. Noninfectious aneurysms are typically situated at branch points of main cerebral arteries: anterior cerebral artery�anterior communicating artery blood pressure unstable buy 100 mg labetalol free shipping, inside carotid artery� posterior speaking artery pulse pressure decrease generic labetalol 100 mg without prescription, middle cerebral artery bifurcation heart attack sam order labetalol 100mg otc, basilar artery tip. Initial mind injury could be caused by an acute improve in intracranial stress, with delayed ischemic injury related to the event of vasospasm after 7 to 10 days. Interference with the absorption of cerebrospinal fluid though the arachnoid granulations can lead to speaking hydrocephalus. Clot throughout the third or fourth ventricle or cerebral aqueducts can cause obstructive hydrocephalus. The commonest causes of intracerebral parenchymal mind hemorrhages are hypertension (Chapter 67) and cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Myriad different potential vascular and nonvascular causes, together with vascular malformations, vasculitis (Chapter 270), venous sinus thrombosis, and coagulopathies (Chapters 172, 173, and 174), are much less common. Hypertension-related intracerebral hemorrhage happens in typical areas of the mind. In distinction, intracerebral hemorrhage associated to cerebral amyloid angiopathy is typically lobar and positioned closer to the cortical surface. Without sequential neuroimaging studies displaying an preliminary area of ischemic injury, lobar hemorrhages may be difficult to distinguish from a hemorrhagic infarction. Susceptibility-weighted brain magnetic resonance imaging sequences could reveal prior microhemorrhages at the graywhite junction in patients with cerebral amyloid angiopathy. When neurons and glia are injured by ischemia, vitality metabolism fails and the cells can not maintain regular ion gradients between the intracellular and extracellular compartments. Vasogenic edema, which may happen on account of disruption of the blood-brain barrier because of harm to the endothelium, permits massive molecules to move through the blood-brain barrier and to gain entry to the brain. In patients with ischemic stroke, the development of cytotoxic edema can lead to a rise in intracranial pressure and, when severe, herniation. In selected patients, craniotomy could be thought of to relieve the stress until the edema subsides. Neurons, glia, and endothelial cells are also broken in the setting of intracerebral hemorrhage. The hemorrhage itself is a space-occupying lesion that may additionally be related to both cytotoxic and vasogenic edema. Mass effect from cerebellar hemorrhages can compress the fourth ventricle (thereby resulting in obstructive hydrocephalus), compress the mind stem (thereby compromising the reticular activating system and impairing consciousness), or cause herniation. Calcium ions enter depolarized neurons and glia, where they activate second messengers, including lipases and proteases, thereby releasing free fatty acids and generating free radicals that degrade mobile organelles and membranes. Depolarized neurons also release excessive ranges of excitatory neurotransmitters, corresponding to glutamate into synapses, which finally ends up in further neuronal depolarization and calcium entry. Once this cascade has been initiated, neurons may still degenerate over time by apoptosis (programmed cell death) even when blood flow is restored. Although promising in the laboratory, all makes an attempt to block the ischemic cascade pharmacologically have failed in clinical trials to date. Global and regional burden of stroke throughout 1990-2010: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Heart illness and stroke statistics-2014 replace: a report from the American Heart Association. Which of the following circumstances is related to the highest population-attributable danger of stroke Sedentary life-style Answer: C Each of the listed circumstances and lifestyle factors is related to an increase within the danger of stroke. The left common carotid artery mostly arises from which of the following constructions Thyrocervical trunk Answer: C the left frequent carotid artery most commonly arises instantly from the aortic arch. In some individuals, it may arise from the proximal portion of the brachiocephalic trunk ("bovine" anatomy). Which of the following arteries is usually the first intradural department of the internal carotid artery The recurrent cerebral artery is usually a department of the anterior cerebral artery. The damage could also be focal (related to occlusion of a single artery), multifocal (related to occlusion of a quantity of arteries), or diffuse. In the absence of an inflammatory illness similar to vasculitis or different uncommon situations, simultaneous involvement of more than one vascular distribution suggests a proximal source of embolism. Involvement of a single vascular territory could additionally be as a result of both local steno-occlusive illness. Involvement within the distribution of a single penetrating artery suggests small-vessel sort intracranial disease, however ischemic strokes in this distribution can also be brought on by proximal arterial steno-occlusive disease or embolism. The definition of ischemic stroke is mind, spinal wire, or retinal cell dying attributable to ischemia with neuropathologic, neuroimaging, or medical proof of everlasting injury. Extracranial carotid artery stenosis is found in as much as 5 to 10% of people older than sixty five years and is associated with about 10% of all ischemic strokes. Untreated asymptomatic carotid stenosis carries solely a few 1 to 2% annual risk of stroke, and the chance may now be a lot decrease, maybe as low as 0. Stroke can also be a complication of sickle cell disease (Chapter 163), with danger dramatically decreased with transfusion remedy in high-risk children. Unlike with coronary coronary heart illness, the general association between excessive cholesterol concentration and the chance of stroke is less certain. Ischemic stroke danger is related to larger levels of complete ldl cholesterol, whereas the chance of hemorrhagic stroke is increased with decrease levels of cholesterol. Other components related to the danger of stroke embrace migraine headaches with aura (Chapter 398), notably in women who smoke and are receiving oral contraceptives; elevated homocysteine degree; high lipoprotein (a) degree; postmenopausal hormone substitute remedy (Chapter 240); coagulation issues (Chapter 176); systemic infection (Chapter 76); renal impairment (Chapter 130); low vitamin D levels (Chapters 218 and 244); and quite a lot of environmental elements, together with high levels of air air pollution. Sometimes bleeding into the plaque can lead to abrupt arterial occlusion, and generally a thrombus that has shaped on an ulcerated plaque may embolize and occlude a distal artery. Other arteriopathies, such as fibromuscular dysplasia (Chapters 67, 80, and 125), may also result in single, large-vessel distribution, ischemic stroke. Atherosclerosis of the ascending aorta or aortic arch can result in the formation of thrombus, which might then embolize to a cerebral artery. Paradoxical embolism of a venous clot throughout a congenital heart defect, similar to a patent foramen ovale or an atrial septal defect (Chapter 69), is another potential reason for embolic stroke. Classically, small-vessel strokes are caused by lipohyalinosis, which is a thickening of the vessel wall leading to a diminished luminal space, however in addition they can be attributable to atherothrombotic embolism. Symptoms of ischemic stroke might worsen during the first hours or days via varied mechanisms. For example, decreases in systemic blood pressure may decrease cerebral blood circulate to marginally perfused, ischemic brain. In the setting of atherothrombotic disease, a partially occluded artery might progress to complete occlusion. In addition to age, race or ethnicity, and family historical past, a selection of life-style factors and medical conditions enhance the chance of stroke (Chapter 406; Table 407-1). Of these, hypertension is the single most essential (Chapter sixty seven; Table 407-1), and the danger of stroke will increase with increasing blood pressure with no threshold impact.
Buy generic labetalol 100 mg onlineAll 11- to 12-year-olds must be vaccinated with meningococcal conjugate vaccine blood pressure chart new zealand generic 100mg labetalol, and a booster dose must be given at age sixteen years (Chapter 18) arrhythmia electrophysiology generic labetalol 100 mg on line. For adolescents who obtain the primary dose at age thirteen via 15 years arteria iliolumbalis generic 100 mg labetalol amex, a one-time booster dose ought to be administered arteria ulnaris generic labetalol 100 mg on-line, ideally at age 16 by way of 18 years, earlier than the peak in increased threat. Adher- Enterovirus An estimated 10 to 15 million scientific enteroviral infections (Chapter 379) occur annually in the United States, and these embody an estimated 50,000 to seventy five,000 cases of enteroviral meningitis. In temperate climates, enteroviral meningitis peaks through the summer and fall, particularly in kids. Eastern equine encephalitis happens sporadically or as focal outbreaks in the summertime within the japanese and Gulf coasts, most incessantly in youngsters and aged persons. Western equine encephalitis occurs predominantly within the western states, and Venezuela equine encephalitis is present in Florida. West Nile virus infections first appeared within the United States in 1999 and now account for about 3000 cases of meningitis and one other 3000 circumstances of encephalitis yearly. Mumps Mumps virus (Chapter 369) was the main identifiable cause of viral meningitis earlier than widespread immunization within the Sixties. LymphocyticChoriomeningitis Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus is transmitted to humans by rodents through direct contact, by way of ingestion of animal-contaminated meals, or via aerosol or an animal chunk. Currently, lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus is occasionally a cause of aseptic meningitis. Enteroviruses pass by way of the abdomen, the place they resist the acid pH, and proceed to the lower gastrointestinal tract. Some virus also undergoes replication in the nasopharynx and spreads to regional lymphatics. After presumably binding to specific enterocyte receptors, the virus breaches the epithelial lining and undergoes major replication in a permissive cell. From there, the virus progresses to Peyer patches, where additional replication happens. Following extensive replication at the latter websites, a serious viremia ensues, often accompanying the onset of medical sickness. Serotype-specific protective antibodies develop following infection, so subsequent episodes of enteroviral meningitis are unusual and are caused by a special serotype. Enteroviral an infection is spread predominantly by the fecal-oral route and infrequently by the respiratory route. Recurrences of genital herpes are widespread and are sometimes accompanied by aseptic meningitis. Herpesviruses also may be reactivated in patients taking immunomodulatory drugs, which are often used to deal with autoimmune diseases. Birds, that are vectors of mosquitoborne arboviruses, may not be clearly sick, though West Nile virus might cause distinguished die-offs of corvine species, particularly crows and blue jays, which may provide clues to an outbreak affecting humans. The geographic unfold of alphavirus infections (Eastern equine encephalitis, Western equine encephalitis, Venezuela equine encephalitis) within the the clinical features of enteroviral meningitis (Chapter 379) in older children and adults often begin abruptly with headache (85 to 100%), fever (80 to 100%), and stiff neck (50 to 80%). In some sufferers the course is biphasic, with the initial prodromal phase being characterised by low-grade fever and nonspecific symptoms (malaise, sore throat, diarrhea), followed by a second section at which era the meninges are seeded, with the event of higher fever, nausea, vomiting, myalgia, photophobia, and stiff neck. Other enteroviral syndromes may coexist, notably pleurodynia or pericarditis ensuing from coxsackieviruses. Rash could also be a manifestation of infections brought on by echoviruses, significantly echovirus type 9, coxsackieviruses A9 and A16, and enterovirus 71; the latter three trigger hand-foot-and-mouth illness, which may happen alone or accompany aseptic meningitis. Echovirus 9 epidemics usually produce syndromes of exanthem, enanthem (small, grayish white lesions resembling Koplik spots on the buccal mucosa), and aseptic meningitis, both alone or together; a macular and petechial rash in the presence of a meningitic syndrome must be differentiated from meningococcal meningitis. Neurologic abnormalities affecting the cerebrum are not often observed as a outcome of such circumstances can be defined as encephalitis or meningoencephalitis rather than enteroviral meningitis. The scientific course of enteroviral meningitis is benign, even in the minority of patients in whom the onset is acute and even fulminant. Symptoms subside within per week in kids but could proceed for several weeks in adults. Clinical options of meningitis happen three to 12 days after the appearance of genital lesions and normally last for 4 to 7 days. Neurologic issues happen in as much as 37% of patients and embody dysesthesia or paresthesia within the perineum or sacral area, urinary retention, and constipation; evidence of transverse myelitis with motor weak spot in the lower extremities, hyporeflexia, and paraparesis often ensues. Recurrent vesicular lesions, paresthesia, or dysesthesia in areas of earlier genital herpes may or may not precede particular person recurrences of meningitis. Rarely, hypoglycorrhachia occurs in meningitis ensuing from mumps or lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus or in infants with enterovirus. When meningitis occurs in sufferers with mumps, it normally follows parotitis by 4 to 10 days, but it could precede parotitis by as a lot as 1 week. The typical options of viral meningitis (headache, fever, vomiting) are each present in 50 to one hundred pc of sufferers. Stiff neck (40 to 90%) is widespread, and abdominal pain (perhaps complicating pancreatitis or oophoritis) or orchitis (in 20% of males with mumps) may be current. Other issues of mumps might contain the nervous system (eighth nerve harm, transient facial nerve paralysis, and barely, fifth nerve palsy) however are often independent of mumps meningitis or meningoencephalitis. When meningitis complicates mumps, fever, which had been low grade, rises to 103� F or higher and persists at this level for three or 4 days. Most circumstances are uncomplicated, with roughly a 10-day duration of sickness and then full restoration. However, symptomatic mumps meningitis may persist for greater than 14 days in some sufferers. A four-fold rise in titer to mumps or lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus between acute and convalescent sera is also diagnostic. DifferentialDiagnosis an important course of to distinguish from viral meningitis is bacterial meningitis. Occasional micro organism and fungi cause meningitis with a predominantly lymphocytic pleocytosis just like that of most viral meningitides Table 412-9). Illness begins with a grippe-like syndrome of fever, rigors, malaise, myalgia, anorexia, and photophobia. This grippe-like sickness lasts 1 to three weeks in humans, but 15% of patients have a biphasic sickness consisting of transient enchancment after which recrudescence, 1 to 2 days later, of fever, photophobia, and extra distinguished headache. The length of meningitis caused by lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus, like that of mumps meningitis, tends to be longer than the 7 to 10 days for enteroviral meningitis. This acute sickness resembles mononucleosis, with fever, malaise, lymphadenopathy, arthralgia, myalgia, anorexia, nausea, headache, and morbilliform rash. A few patients with this initial syndrome have manifestations of aseptic meningitis (headache, photophobia, nausea, vomiting, and stiff neck). Occasionally, encephalopathy or cranial nerve palsies (seventh, eighth, and fifth) develop. Occasionally, manifestations similar to these of the preliminary infection could appear later in the midst of untreated infection.
Cheap labetalol 100 mg fast deliveryIn a patient with persisting headache prehypertension warsaw 2014 discount labetalol 100mg fast delivery, obtundation blood pressure chart throughout the day labetalol 100 mg with mastercard, and cerebral findings heart attack risk factors labetalol 100 mg mastercard, insufficient drug therapy or neurologic sequelae (cortical venous thrombophlebitis blood pressure 210110 100 mg labetalol, ventriculitis, subdural collections) are important considerations. Drug-induced fever (Chapters 254 and 280) must be suspected in patients who continue to show medical improvement in all different respects. Metastatic infection (septic arthritis, purulent pericarditis, thoracic empyema, endocarditis) could additionally be the reason for persevering with or recurrent fever. A syndrome, most likely immunologic, consisting of fever, arthritis, and pericarditis 3 to 6 days after the initiation of efficient antimicrobial therapy for meningococcal meningitis occurs in approximately 10% of patients (Chapter 298). Repeated episodes of bacterial meningitis usually point out a number defect, both in local anatomy or in antibacterial and immunologic defenses. Approximately 10% of episodes of pneumococcal meningitis in adults are recurrent meningitis, but only zero. Organisms may enter the subarachnoid house directly, by way of a defect within the cribriform plate (the most common site), in association with the empty sella syndrome, by the use of a basilar skull fracture, via an erosive sequestrum of the mastoid, through congenital dermal defects alongside the craniospinal axis (usually evident earlier than adult life), or as a consequence of penetrating cranial trauma or neurosurgical procedures. Any affected person with bacterial meningitis, notably if the meningitis is recurrent, ought to be evaluated fastidiously for congenital or post-traumatic defects. In adults older than 50 years and in high-risk teams, ampicillin can also be added because of the potential of the presence of L. Although resistance to chloramphenicol is uncommon in pneumococcal isolates from the United States, chloramphenicol has poor bactericidal exercise against penicillin-resistant isolates from kids with meningitis in South Africa. Consider intrathecal (or intraventricular vancomycin, 5 to 20 mg/day) if not responding to intravenous remedy. Notably,theriskforgastrointestinal bleeding was not increased in the dexamethasone-treated group. Chemoprophylaxis SupportiveCare Patients with acute bacterial meningitis should obtain constant nursing attention in an intensive care unit to ensure immediate recognition of seizures andtopreventaspiration. Prompt prophylaxis of close contacts (individuals who incessantly slept and ate in the same household with the patient, girlfriend, or boyfriend) is warranted because up to a third of secondary cases of meningococcal illness develop inside 2 to 5 days of illness in the preliminary case. Only hospital personnel who were in close contact with a patient (mouth-to-mouth resuscitation, preliminary examination earlier than establishment of respiratory precautions) are at particular danger. Commonly, oral rifampin is used for prophylaxis: for adults (other than pregnant women), 600 mg twice every day for two days; for kids, 10 mg/kg twice day by day for two days. Another selection is ceftriaxone intramuscularly as a single dose in adults (250 mg) or youngsters (125 mg). However, prophylaxis could be indicated for unimmunized shut household contacts of an index patient. The definition encompasses various processes that produce comparable clinical pictures and inflammatory responses: viral meningitis, atypical and nonpyogenic bacterial and fungal meningitis, chemically induced meningitis, druginduced meningitis, neoplastic meningitis, meningeal irritation caused by adjoining pyogenic infections, and meningitis related to autoimmune hypersensitivity ailments. Many of the viruses inflicting meningitis additionally might cause an infection of the mind parenchyma (encephalitis; Chapter 414) or spinal twine. Sometimes, parenchymatous involvement and meningeal involvement happen concurrently in the identical patient and are referred to as meningoencephalitis and meningomyelitis. Most instances of community-acquired aseptic meningitis are the outcomes of viruses, principally enteroviruses, which account for greater than 60% of viral meningitides and for 90% of those for which an etiologic agent is recognized Table 412-8). The most common serotypes implicated in viral meningitis from yr to year have been echoviruses four, 6, 9, eleven, sixteen, and 30 (most lately 13 and 33) and coxsackie B serotypes 2 to 5. Currently, poliovirus infections (Chapter 379) are restricted to elements of Asia and Africa, although uncommon circumstances happen secondary to attenuated vaccine strains. Persistent or late-onset obtundation and coma without focal findings suggest mind swelling, subdural effusion, hydrocephalus, loculated ventriculitis, cortical thrombophlebitis, or sagittal sinus thrombosis. The last three conditions are commonly associated with fever and continuing pleocytosis. The mortality price for community-acquired bacterial meningitis in adults varies with the etiologic agent and medical circumstances. The mortality fee for gram-negative bacillary meningitis, generally nosocomial in origin, has been 20 to 30% in adults, but may be decreasing. The mortality rate for recurrent community-acquired meningitis in adults (5%) is lower than the 20% price for nonrecurrent episodes. Poor prognostic components include advanced age, the presence of other foci of infection, underlying illnesses (leukemia, alcoholism), obtundation, seizures inside the first 24 hours, and delay in instituting appropriate therapy. Residual neurologic damage is seen in 10 to 20% of patients who get well from bacterial meningitis. Developmental delay and speech defects are each observed in roughly 5% of kids, and bacterial meningitis is associated with decrease subsequent educational achievement and economic self-sufficiency in maturity. Making a common vaccine in opposition to the B strains has been challenging as a result of there are numerous sorts that trigger illness in numerous parts of the world. Chronic enteroviral meningitis and meningoencephalitis in agammaglobulinemic patients have been managed by parenteral (even intrathecal) administration of immune globulin. Most viral meningitides are self-limited, however some cause continual or recurrent illness. Persistent meningitis or meningoencephalitis, typically deadly, can happen in individuals with hereditary (usually X-linked agammaglobulinemia or widespread variable immunodeficiency) deficiencies in B-lymphocyte operate. Nonviral infectious causes are uncommon or rare compared to viral or acute suppurative meningitis. Clinical manifestations embody fever and night sweats, sixth cranial nerve palsies, stroke associated to arteritis, or lesions on the chest radiograph. Parameningeal infections (Chapter 413) must be suspected when persistent meningitis with focal neurologic indicators develops in the setting of chronic otitis media or sinusitis, pleuropulmonary an infection, or right-to-left cardiopulmonary shunting. Meningitis may accompany the skin, mucous membrane, and lymph node features of secondary syphilis (Chapter 319), or it might occur alone. Lyme illness meningitis (Chapter 321) should be suspected on the idea of epidemiologic grounds (geographic location, season, tick exposure) and related clinical features (erythema migrans rash, Bell palsy, radiculopathy). The diagnosis is made by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with Western blot confirmation. Aspergillosis (Chapter 339) is angiocentric and can trigger associated cerebral infarcts. Mucormycocis (Chaper 340) is widespread in sufferers with poorly controlled diabetes mellitus. Flucytosine is superior to fluconazole when used with amphotericin B for remedy of cryptococcal meningitis (Chapter 336). A9 InfectiousCauses an infection may counsel aseptic meningitis due to its generally indolent onset and, often, an early predominantly lymphocytic response in younger youngsters. Patients with Rocky Mountain spotted fever (Chapter 327), an acute illness with a macular and petechial rash, may exhibit confusion. Epidemiologic factors are essential in elevating suspicion for nonviral aseptic meningitis.

Buy labetalol 100 mg overnight deliveryOther medical manifestations include bradykinesia hypertensive urgency guidelines order labetalol 100mg amex, chorea blood pressure medication sweating generic 100mg labetalol with mastercard, dystonias pulse pressure 40 purchase 100mg labetalol, dysphagia blood pressure yoga asanas 100mg labetalol with amex, dysarthria or aphonia, seizures, and tremor. The severity of rhabdomyolysis correlates with the creatine kinase degree and with the presence of myoglobinemia, myoglobinuria, metabolic acidosis, and azotemia. The electroencephalogram shows nonspecific slowing in slightly more than half of sufferers. The time lag from starting of the drug to the onset of neuroleptic malignant syndrome is usually quick, with 30% of instances growing within forty eight hours and 96% within the first month of treatment. The exception appears to be clozapine-associated neuroleptic malignant syndrome, which has a median time lag of 50 days. Neuroleptic syndrome is typically confused with severe catatonia (Chapter 397), however the catatonic signs in neuroleptic malignant syndrome are often restricted to mutism and akinesia. Untreated, neuroleptic malignant syndrome has a mortality fee of 10% on account of acute renal failure, aspiration pneumonia, grownup respiratory distress syndrome, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and cerebellar neuronal degeneration. Most fatalities are avoidable if the analysis is made early, the neuroleptic agent is discontinued quickly, and the affected person is straight away transferred to an intensive care setting for supportive and particular therapy. The skeletal muscle relaxant dantrolene (starting with a dose of 1 mg/kg intravenously and titrated to a maximal dose of 10 mg/ kg/day divided into three intravenous or oral doses) should be added to bromocriptine or amantadine in patients with fulminant hypermetabolic options and those with persistent muscle rigidity despite treatment with dopamine agonists. Severe circumstances of the syndrome have been extra regularly reported in patients handled with monoamine oxidase inhibitors who took over-the-counter dextromethorphan or the illegal methylenedioxymethamphetamine (Ecstasy) or who started treatment with serotonin reuptake inhibitors, meperidine, or atypical antipsychotics similar to aripiprazole. Potentially life-threatening, the syndrome is characterised by changes in psychological standing (ranging from agitation to confusion and coma), autonomic instability (tachycardia, labile or high blood pressure, diaphoresis, and diarrhea), neuromuscular abnormalities (myoclonus, mydriasis, ocular clonus, rigidity, hyperreflexia, tremors, and shivering), and hyperthermia. The signs happen inside the first 24 hours and sometimes within minutes after the preliminary use of medicine, a change in dose, addition of a new drug, or overdose try. Death might occur as a consequence of rhabdomyolysis with renal failure, hyperkalemia, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and acute respiratory distress syndrome. The differential analysis includes neuroleptic malignant syndrome, viral or bacterial meningitis or encephalitis, warmth stroke (Chapter 109), anticholinergic toxidrome (Chapter 110), and drug (Chapter 34) or alcohol (Chapter 33) withdrawal. General administration contains quick discontinuation of serotonergic medicine, comprehensive supportive remedy, and benzodiazepines for management of agitation and myoclonus. Cyproheptadine should be started at a dose of 12 mg administered orally or by way of a nasogastric tube, with further 2-mg doses given each 2 hours until signs improve or the maximal dose of 32 mg has been reached. Chlorpromazine (50 mg intramuscularly; might repeat three or 4 times every day and increase steadily to four hundred mg/day in divided doses) is indicated in patients with extreme signs who have to be handled parenterally. Rapid improvement has also been noticed after single doses of olanzapine (10 mg administered sublingually). Chlorpromazine and olanzapine ought to be used only after the risk of neuroleptic malignant syndrome has been excluded. In sufferers treated with prolactin-raising antipsychotic medications, hormone levels are above the conventional restrict in 60% of women and 40% of males. Excess prolactin leads to dysfunction of target tissues (galactorrhea, oligomenorrhea and amenorrhea, infertility, sexual impairment, and gynecomastia) as nicely as an increased threat for breast most cancers, osteoporosis, and cardiovascular disease. The mechanism of antipsychotic-related hyperprolactinemia is suppression of dopamine inhibition of lactotroph cells within the hypothalamus. Brain imaging is required in symptomatic patients and people with significant elevated prolactin levels to exclude tumors of the pituitary and hypothalamus. Patients with psychogenic polydipsia typically have serum hypo-osmolality and a maximally dilute urine (urine osmolality <100 mOsm/L). Urinary incontinence and nocturnal enuresis may be part of the clinical manifestation. The differential analysis includes diuretic effect, renal insufficiency, glucocorticoid deficiency, and hypothyroidism. Stringent measures to limit fluid consumption are usually effective in patients with average hyponatremia, and clozapine limits polydipsia and improves water intoxication in refractory instances. Elderly sufferers, patients with a decrease physique mass index, and those with a baseline plasma sodium level of less than 138 mEq/L are at higher risk. Urinary excretion of sodium often is greater than 20 mEq/L, and urine osmolality is higher than 300 mOsm/L. The procedure requires a quick period of general anesthesia with sodium pentothal, etomidate, or propofol as nicely as muscle paralysis with succinylcholine, throughout which the patient receives bagvalve-mask air flow with supplemental oxygen and is monitored with steady electrocardiography and pulse oximetry. Bronchospasm may follow induction of anesthesia, notably in patients already at risk for respiratory compromise. During electrical stimulation of the mind, parasympathetic activation can lead to bradycardia or a number of seconds of asystole, which may be prevented by premedicating the patient with intravenous glycopyrrolate. The parasympathetic effect lasts until onset of the akinetic seizure, when sympathetic tone increases and produces tachycardia, an elevation in blood stress, and elevated myocardial demand for oxygen. At the identical time, due to the improved neuronal metabolic price, augmented blood move to the brain will increase intracranial strain. The elevated intracranial stress could lead to brain herniation in sufferers with a space-occupying lesion. Effects of adjunctive metformin on metabolic traits in nondiabetic clozapine-treated sufferers with schizophrenia and the impact of metformin discontinuation on body weight: a 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Metformin addition attenuates olanzapine-induced weight acquire in drug-na�ve first-episode schizophrenia patients: a double-blind, placebo-controlled examine. Effects of switching from olanzapine, quetiapine, and risperidone to aripiprazole on 10-year coronary heart illness danger and metabolic syndrome status: results from a randomized managed trial. Double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial of a vasopressin V2-antagonist in sufferers with schizophrenia and hyponatremia. An proof synthesis of care fashions to enhance general medical outcomes for individuals with severe psychological illness: a scientific evaluation. Embedding integrated mental health assessment and management in general hospital settings: feasibility, acceptability and the prevalence of widespread mental disorder. A systematic evaluation of the ability of urine focus to distinguish antipsychotic- from psychosis-induced hyponatremia. Medical deterioration throughout psychiatric admissions could lead to lifethreatening problems, interrupt biobehavioral interventions, and require transfer to medical facilities. Older age and a diagnosis of dementia with behavioral disturbance are nonmodifiable correlates of an elevated fee of acute changes in medical conditions in psychiatric sufferers. Which of the following is an independent threat factor for medical deterioration in psychiatric settings Substance use dysfunction Answer: A Among a thousand adults consecutively admitted to a free-standing psychiatric hospital, 14% were transferred to a common hospital for acute medical deterioration. The impartial predictors of medical deteriorations have been higher blood urea nitrogen focus (odds ratio, sixty three. Risk elements for medical deterioration of psychiatric inpatients: opportunities for early recognition and prevention. The 27-year-old with clozapine-treated schizophrenia admitted for suicidal ideation is prescribed venlafaxine 37. The following morning, the affected person has good behavioral control and is allowed to play basketball on the out of doors court for forty five minutes.

Order 100mg labetalol otcIndividuals with motion sickness and area illness usually develop perspiration prehypertension and anxiety discount labetalol 100mg amex, nausea heart attack causes order labetalol 100 mg with mastercard, vomiting blood pressure medication gout sufferers buy discount labetalol 100mg on-line, increased salivation blood pressure tracking chart printable buy cheap labetalol 100 mg, yawning, and generalized malaise. Hyperventilation is a common signal, and the ensuing hypocapnia leads to modifications in blood volume, with pooling within the decrease parts of the body predisposing to postural hypotension and syncope. An unusual variant of motion-induced dizziness happens when the topic returns to stationary conditions after prolonged exposure to movement (mal de d�barquement syndrome). Typically, affected patients report that they really feel the persistent rocking sensation of a ship long after returning to solid floor. Rarely, the syndrome can last for months to years after publicity to movement and might even be incapacitating. Physiologic vertigo can typically be suppressed by supplying sensory cues that assist to match the indicators originating from different sensory techniques. Thus, motion sickness, which is attributable to a mismatch of visible and vestibular alerts, is exacerbated by sitting in a closed space or reading (giving the visible system the miscue that the environment is stationary). Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo outcomes when otolith particles inadvertently enters one of the semicircular canals. It can happen after head trauma or inner ear an infection but mostly occurs spontaneously in older folks. The diagnosis rests on discovering characteristic positional nystagmus in the plane of the affected canal (see later). If the history or findings are atypical, the situation must be distinguished from other causes of positional vertigo that may happen with tumors or infarcts of the posterior fossa. Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (Canalithiasis) associated with auditory or neurologic symptoms. Pathologic studies displaying atrophy of a number of vestibular nerve trunks, with or without atrophy of their related sense organs, are evidence of a vestibular nerve website and, probably, viral trigger for many patients with this syndrome. Many sufferers report an higher respiratory tract illness 1 to 2 weeks before the onset of vertigo. This syndrome sometimes occurs in epidemics (epidemic vertigo), might have an effect on several members of the identical household, and extra often erupts within the spring and early summer time. Most affected patients steadily enhance during 1 to 2 weeks, but residual dizziness and imbalance can persist for months. Meniere illness (see earlier) accounts for about 10% of all patients with vertigo. Meniere Disease Acute Peripheral Vestibulopathy (Vestibular Neuritis) Migraine One of the most typical clinical neurologic syndromes at any age is the acute onset of vertigo, nausea, and vomiting lasting for a quantity of days and not Vertigo is a standard symptom with migraine (Chapter 398). It can happen with complications or in separate isolated episodes, and it may possibly predate the onset of headache. Practiceparameter:therapiesfor benign paroxysmal positional vertigo [an evidence-based review]: report of the quality Standards Subcommittee of the american academy of neurology. Infusion of 1 to 3 mL of ice water induces a burst of nystagmus often lasting a few minute. Greater than a 20% asymmetry in nystagmus length suggests a lesion on the aspect of the decreased response. The ice water caloric test is a helpful way to test the integrity of the oculomotor pathways in a comatose patient. In this case, ice water induces solely a slow tonic deviation toward the facet of stimulation. The history is essential because it determines the type of dizziness (vertigo, near-faint, psychophysiologic disequilibrium), associated symptoms (neurologic, audiologic, cardiac, psychiatric), precipitating factors (position change, trauma, stress, drug ingestion), and predisposing sickness (systemic viral infection, cardiac disease, cerebrovascular disease). The history supplies direction for both the examination and the diagnostic analysis Table 428-1). When focal neurologic signs are found, neuroimaging often results in a selected prognosis. When vertigo is current with out focal neurologic symptoms or indicators, head-thrust and positional testing are key to localizing the lesion to the labyrinth or eighth nerve. A detailed cardiac evaluation (including loop monitoring) typically identifies the cause of episodic near-fainting (Chapters 51 and 62). When attainable, therapy ought to be directed on the underlying disorder Table 428-2). A10 Endolymphatic duct blockage is a potential possibility for medically refractory Meniere disease. A11 In many circumstances, nonetheless, symptomatic remedy both is mixed with particular therapy or is the only therapy out there. Many totally different courses of medication have been found to have antivertiginous properties, and in most cases, the exact mechanism of motion is uncertain. All these brokers produce potentially disagreeable side effects, and the decision concerning which drug or mixture to use is based on their known issues and on the severity and length of the vertigo. An episode of extended, extreme vertigo is doubtless certainly one of the most distressing symptoms that a affected person can expertise. In more chronic vertiginous issues, when the affected person is trying to keep it up normal activity, much less sedating antivertiginous drugs, corresponding to meclizine (25 mg) or transdermal scopolamine (0. Vestibular rehabilitation exercises are designed to assist the patient compensate for everlasting lack of vestibular perform. A12 As the acute stage of nausea and vomiting subsides, the patient ought to attempt to focus the eyes and to transfer and maintain them within the direction that provokes probably the most dizziness. A helpful exercise involves watching a visible target whereas oscillating the pinnacle from side to side or up and down, sluggish at first and then fast. The patient ought to try to stand and stroll, at first in touch with a wall or with an assistant, and make gradual supported turns. Positional Tests Examination for pathologic vestibular nystagmus ought to include a search for spontaneous and positional nystagmus (see Table 424-5). Because vestibular nystagmus secondary to peripheral vestibular lesions is inhibited with fixation, the yield is elevated by impairing fixation with +30 lenses (Frenzel glasses) or infrared video recordings. Two forms of positional testing are usually performed: shifting the patient from the sitting to head-hanging-right and head-hanging-left positions (Dix-Hallpike test) and turning the pinnacle to the proper and left while the patient lies supine. Induced positional nystagmus may be paroxysmal or persistent, and it might be in the same direction in all positions or change instructions in several positions. The most typical explanation for positional nystagmus is otolith debris in the semicircular canals, either free floating (paroxysmal) or connected to the cupula (persistent). This type of nystagmus all the time happens within the aircraft of the affected canal-vertical torsional for the vertical canals and horizontal torsional for the horizontal canal. Nystagmography Nystagmography checks oculomotor control by inducing and recording eye movements. A commonplace take a look at battery contains (1) checks of visual ocular control tahir99 - vip. Diagnostic testing choices, which embrace fiberoptic examination, imaging, pulmonary function studies, and laboratory testing, are directed by history, symptoms, and physical findings. Oral vs intratympanic corticosteroid therapy for idiopathic sudden sensorineural listening to loss: a randomized trial.
Labetalol: 100 mg
References - Fujita T, et al. Influence of sex hormone disturbances on the internal structure of the mandible in newborn mice. Eur J Orthod 2006;28:190-194.
- Bottomley PA, Hardy CJ, Argersinger RE, Allen-Moore G. A review of 1H nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation in pathology: Are T1 and T2 diagnostic? Med Phys 1987;14: 1-37.
- Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese Classification of Gastric Carcinoma - 2nd English Edition. Gastric Cancer 1998; 1:10.
- Winfield, H.N., Donovan, J.F., Godet, A.S., Clayman, R.V. Laparoscopic partial nephrectomy: initial case report for benign disease. J Endourol 1993;7:521-526.
- Alimi YS, Chakfe N, Rivoal E, et al: Rupture of an abdominal aortic aneurysm after endovascular graft placement and aneurysm size reduction, J Vasc Surg 28:178-183, 1998.
|