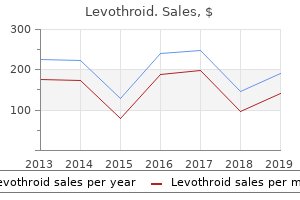
Levothroid
Kwesi Hankins, RN - Department of Emergency Medicine
- Methodist Hospital
- Peoria, IL
Order 100mcg levothroid amexSigns of vascular damage include endothelial cell swelling thyroid symptoms photos cheap levothroid 200mcg line, extravasation of erytluocytes thyroid gland t3 t4 cheap levothroid 50 mcg without a prescription, and thyroid gland removal recovery time generic levothroid 50mcg with mastercard, most importantly thyroid cancer essential oils cheap 200 mcg levothroid otc, fibrinoid necrosis of vascular partitions. These finding would possibly suggest neutrophilic hidradenitis; however, the medical scenario by which neutrophilic hidradenitis occurs is distinctive. In addition, the infiltrate of neutrophilic hidradenitis damages the eccrine duct epithelium as evidenced by duct necrosis and, later, syringometaplasia. The analysis is primarily medical Most authors finding out early lesions have reported a principally neutrophilic infiltrate that regularly involves follicular structures. A neutrophilic vascular response with limited vascular injury is typical, however vasculitis with fibrinoid necrosis or pustular vasculitis typically occur. Fully developed ulcers are surrounded by necrosis and a blended inflammatory infiltrate. If the deep reticular dermis and subcutis are concerned, the infiltrate may be primarily mononuclear or granulomatous. Differential Diagnosis the pathologist is usually confronted with the evaluation of a nondescript ulceration, often from the leg. Autoinflammatory pores and skin illness: a evaluate of ideas and functions to general dermatology. Most leg ulcers are related to trauma, peripheral vascular illness, diabetes, and an infection. Special stains for organisms are useful, and circumstances in tropical and subtropical regions warrant an acid-fast stain to exclude atypical mycobacterial infection. A myriad of different entities with nonspecific pathology can be considered, together with necrotic arachnidism and varied types of self-harm, together with cocaine-levarnisole injection. Inherited autoinflammatory syndromes Synonyms: Hereditary periodic fever syndromes, interleukinopathies, inflarnmasomopathies. Monogenic autoinflammatory issues may show cutaneous neutrophilic irritation as a distinguished syndromic function, providing insight into the pathogenesis of the neutrophilic dermatoses. The latter result in autoactivation of the innate immune system, some by way of the interleukin 1 beta-mediated response to pathogens (Table 9-13). Like the acquired neutrophilic dermatoses, these inherited syndromes may respond to interleukin blockade. These circumstances are mediated by a selection of proinflammatory pathways, illustrating an overlap between the neutrophilic dermatoses, granulomatous dermatitis, and acneiform folliculitis. Behset disease Clinical Features Beh~ disease is characterized by recurrent aphthous stomatitis and at least 2 of the following standards: genital aphthae, cutaneous lesions, ocular lesions, and, much less generally, arthritis, gastrointestinal ulceration, vascular lesions, or meningoencephalitis (Table 9-14). The scientific presentation is extraordinarily variable, though most cases present with aphthous stomatitis. A positive cutaneous pathergy test, as outlined by erythematous papules, or pustules appearing in response to a needle-prick have been long used in the analysis of Behcret illness. Cutaneous lesions may embrace pyoderma gangrenosum-like ulcerations, papulopustules, erythema nodosum-like lesions, or the sequelae of superficial thrombophlebitis. Deeper vascular lesions vary from varices to aneurysms or arterial and venous thrombosis. The situation is most typical from the Middle East through Asia and is uncommon in northern Europe and the United States. Several strains of evidence, enhanced inflammatory response to minor stimuli, response to an interleukin l beta inhibitor, and genetic susceptibility suggest that Behcret disease is a minimal of a partially inherited autoinflammatory dysfunction, resembling familial Mediterranean fever. The papulopustular lesions of Behcret disease clinically and histologically resemble acne vulgaris, suppurative folliculitis, perifolliculitis, or intrafollicular abscesses. The distribution differs from zits, however, with Behcret illness papulopustules occurring on the again and lower extremities, whereas zits is distributed throughout the face and back. Individual lesions may recommend vasculitis, various neutrophilic dermatoses, folliculitis, and pimples. The capillaries may present deposits of fibrinoid material or merely fibrous thickening. Many of the spindle cells have the immunohistochemical and electron microscopic options of macrophages. Neutrophils, nuclear dust, and fibrin owing to persistent vascular injury may be current, helping distinction from dermatofibromas or scars. However,vascularinjurymayplay a job in the pathogenesis ofthis lesion as a result of direct immunoduorescence information recommend an immune complex-mediated occasion with deposition of IgG in and round vessels. Frequently, the nuclei of a few of the neutrophils fragment especially near capillaries, forming nuclear mud Evidence of vasculitis with deposition of:fibrinoid material inside and round vessel partitions is common. In pimples and folliculitis, including eosinophilic pustular folliculitis, pilosebaceous models are invaded by intlammatory cells and may be destroyed or disrupted. Clear-cut evidence of vasculitis is indeniable if an inflammatory infiltrate coincides with fibrinoid necrosis of the vascular wall. Lymphocytic vasculitis, if rigidly defined, is uncommon; nonetheless, in most conditions categorized as lymphocytic vasculitis, �true vasculitis" is the exception rather than the rule. Regardless, a analysis oflymphocytic vasculitis may be rendered in the absence of:fibrinoid necrosis if a constellation of:findings suggests vascular damage. Features indicative of vascular damage embrace lamination of the adventitia of venules by concentric pericytes and basement membrane material, lymphocytic nuclear fragmentation, and subendothelial or intramural infiltration of arterioles by lymphocytes. Lymphocytic vasculitis happens with hypersensitivity reactions, including drug eruptions, autoimmune and connective tissue illnesses, infections, and numerous idiopathic circumstances (Table 9-17). The histologic differential prognosis typically parallels the superfidal to deep perivasatlar lymphocytic infiltrate; nonetheless, lymphocytic vascular reactions could replicate very early leukocytoclastic vasculitis or neutrophilic dermatoses. Clinical information and different histologic features are needed to decide the significance oflymphocytic vasculitis. Most of these entitles are discussed at larger size elsewhere on this textual content Pernlosls Synonyms: Chilblains, equestrian cold panniculitis, equestrian. Chronic viral infection, thrombo/ embolic phenomena, and hematopoietic neoplasms can produce related lesions, highlighting the significance of biopsy in this sc::enario. Lesions, variously described as orange-brown or bronze, are classically confined to the decrease limbs. Lichen aureus is a carefully related entity because the scientific lesion is purpuric and the histologic findings are the same as the opposite four variants. Telangiectatic puncta may mirror capillary dilatation, and pigmentation could result from hemosiderin deposition. In some cases, telangieetasia predominates (Majocchi disease), and in others, pigmentation predominates (Scharnberg disease). In Majocchi illness, the lesions normally are irregular in form and occur predominantly on the lower legs, in some cases mimicking persistent venous stasis. Frequently, scientific signs of inflammation are present, similar to erythema, papules, and scaling (Gougerot-Blum disease) or papules, scaling, and lichenification (eczematid-like purpura). The dysfunction often is proscribed to the lower extremities however often generalizes. There is a papillary dennal lymphocytic: perivasc:ular infiltrate and extravasation of red blood cells.
Levothroid 200mcg low costA determine of 30% is quite adequate for diagnosis if a great aspirate thyroid cancer early symptoms generic levothroid 50 mcg, not diluted with peripheral blood thyroid gland order 50 mcg levothroid visa, is obtained and if different options are typical thyroid cancer therapy buy levothroid 50mcg. In one research the per centage of lymphocytes in the aspirate showed independent prognostic significance [67] thyroid osteoporosis levothroid 50mcg with visa. Richter transfor mation sometimes occurs within the bone marrow however extra often happens initially at an extramedul lary site with bone marrow infiltration being a late event. Flow cytometric evaluation of peripheral blood lymphocytes has a role in detection of minimal residual illness. Cytogenetic and molecular genetic evaluation A normal karyotype has been reported in from 40% to 72% of instances in numerous sequence of sufferers [76�78]. Other abnormalities embody: deletion of 6q21, 11q2223 or 17p13; different abnormalities of 17p; and 14q+. A normal karyotype, del(13q) and most cases with an isolated trisomy 12 are related to classical morphology and a good prognosis. The nuclear out line seems considerably irregular in sections of paraffin and resinembedded specimens. In addi tion to the predominant small lymphocytes there are small numbers of prolymphocytes and para immunoblasts. The latter are mediumsized cells with plentiful cytoplasm and a big nucleus with a prominent nucleolus. The cytoplasm of para immunoblasts is much less intensely basophilic than that of immunoblasts. A combined pattern rep resents a combination of nodular and interstitial infiltration. Most investigators have demonstrated a statistically significant distinction between the finish result in circumstances with a diffuse pattern (poor prognosis) and those with nondiffuse (nodular and interstitial) patterns (good prognosis) [4,85,87]. Some staff have additional discovered circumstances with a mixed pattern to have a prognosis intermediate between that of the above two groups [4]. Somewhat divergent findings have been reported by Frisch and Bartl [88]; additionally they discovered the shortest survival in those with diffuse infiltra tion, but those with an interstitial pattern had a shorter survival than those with a nodular infil trate. Attempts have been made, with some suc cess, to correlate the medical staging techniques with patterns of bone marrow infiltration. In basic, inside a single stage, sufferers in whom the bone marrow is diffusely infiltrated do worse than those with nondiffuse patterns of infiltration [85,87]. The trephine biopsy is also of significance in assessing response to treatment since there may be residual lymphoid nodules when the share of lymphocytes within the aspirate is not elevated [67]. When assessing response to remedy, immunohistochemical staining is essential in helping distinguish low level residual illness from reactive T cells forming residual lymphoid nodules. Pangalis and Kittas [92] found a nodular sample in all of six sufferers with bone mar row infiltration however others [6,12,68] have observed focal, interstitial and occasionally diffuse patterns. Expression of the proliferation marker, Ki67, is confined to the proliferation centres and scattered paraimmunob lasts. Cyclin D1 is often adverse but is occasionally expressed in cells of proliferation centres [61]. The lymphocytosis is usually delicate and there are typical morphological abnormalities including binuclearity and deeply lobed nuclei. Correct analysis requires correlation of cytological options, immunophenotype and, in some circumstances, molecular genetic evaluation. With care ful evaluation of cytological options and immu nophenotype, distinction from other small Bcell lymphoproliferative problems is normally not a prob lem. Monoclonal Bcell lymphocytosis this designation indicates a clonal lymphocyte depend of less than 5 � 109/l without lymphade nopathy, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly or different proof of extramedullary involvement. Smaller cells are inclined to have a considerably greater nucleocytoplasmic ratio and the nucleolus is less distinguished. Bone marrow cytology the bone marrow is infiltrated by cells of similar appearance to those in the peripheral blood. In the past, circumstances with similar cytology to that described above with t(11;14)(q13. The mitotic rely is much decrease than in diffuse giant Bcell lymphoma, with which it could be confused. The widespread medical fea tures are splenomegaly and indicators and symptoms ensuing from anaemia and neutropenia. The prognosis can typically be suspected from peripheral blood examination and confirmed by a bone marrow aspirate. However, bushy cells can be infrequent in the blood and the attribute bone marrow reticulin fibrosis commonly renders aspiration difficult. Examination of trephine biopsy sections subsequently performs an necessary role in prognosis. Peripheral blood Hairy cells are normally current in the peripheral blood only in small numbers and in some circumstances none are detected. Bone marrow cytology the bone marrow is often troublesome or inconceivable to aspirate. When an aspirate is obtained, the charac teristic cell has the identical morphological features as the few circulating neoplastic cells. Aspirates are sometimes aparticulate but, when fragments are present, mast cells are sometimes very prominent within them. Rarely large cell transformation occurs, particu larly in belly lymph nodes [109]. Cytological options are more useful than histological features in making this distinction. Flow cytometric immunophenotyping the cells show strong SmIg expression which, in about one third of instances, is IgM with or with out IgD and, in the remaining two thirds, is IgA or IgG. Expression of annexin A1 has been found to have a excessive diploma of sensitivity and specificity for this analysis. Nuclei differ in each size and shape and may embrace round, oval, indented, dumbbell shaped and bilobed types. In some circumstances there are foci of furry cells with spin dleshaped or fusiform nuclei giving the cells a fibro blastic appearance; nonetheless, a fibrous or fusiform sample may be because of accompanying clusters of fibroblasts [117]. Red blood cells could also be seen in infiltrated areas, both apparently extravasated or surrounded by a layer of hairy cells; this look resembles the red blood cell lakes seen in the spleen and liver [116,117]. Reactive plasma cells, lympho cytes and mast cells are also often distinguished in areas of infiltration. Haemopoietic ele ments are scattered among the infiltrating furry cells and consist of isolated erythroid clusters and megakaryocytes; granulocyte precursors are par ticularly sparse [117,118]. The neoplastic clone is derived from a postgerminal centre B cell with hypermutated immunoglobulin variable area genes in about 80% of patients [114]. Bone marrow histology the diploma of marrow involvement could be very exten sive in all but the earliest of circumstances [115�118]. Infiltration is normally both random focal or diffuse; focal involvement is generally in depth with giant confluent patches involving up to 50% of the mar row. A third sample of infiltration is that of interstitial infiltration in a severely hypoplastic marrow [117,119].
Cheap levothroid 200 mcg amexMature plasma cells are usually elevated thyroid gland releases discount levothroid 100mcg on line, as are macrophages thyroid cancer in pregnancy buy levothroid 200 mcg cheap, mast cells and thyroid nodule biopsy purchase levothroid 100 mcg without a prescription, sometimes thyroid lymphoma cheap levothroid 50 mcg fast delivery, eosinophils. Trephine biopsy sections sometimes show infiltration when the bone marrow aspirate is normal. Immunohistochemistry Immunohistochemical features range between and inside cases, relying on the degree of plasmacytic differentiation. Cytogenetic and molecular genetic analysis Nonspecific cytogenetic abnormalities include 6q�, 13q�, trisomy three and trisomy 4. Other syndromes related to secretion of a paraprotein A number of different, comparatively unusual, syn dromes are associated with the secretion of a paraprotein. Clinical options can even include hepato megaly, autonomic and peripheral neuropathy, carpal tunnel syndrome, macroglossia and a bleed ing tendency [158]. In a small minority of sufferers no paraprotein is detect ready in the serum or urine however, in this group also, the illness outcomes from a neoplastic proliferation of plasma cells, albeit occult. Peripheral blood the peripheral blood could additionally be normal or could show the options often related to myeloma or lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma. Occasionally, fea tures of hyposplenism are current, indicating that the spleen is infiltrated by amyloid and has become hypofunctional. Thrombocytosis, observed in 9% of cases in a single giant series, could additionally be indicative of hyposplenism [156]. Using sensitive immunophe notyping strategies, monoclonal plasma cells can be detected within the peripheral blood in a major minority of sufferers, their presence indicating a worse prognosis [159]. Bone marrow cytology the bone marrow aspirate varies from normal via elevated numbers of plasma cells of regular morphology to overt myeloma or lymphoplasma cytic lymphoma. In a large sequence of sufferers, 40% had at least 10% bone marrow plasma cells [156]; the presence of increased numbers is indicative of a worse prognosis [159]. These, and different con ditions associated with the presence of a paraprotein, are summarized in Table 7. Neoplastic lymphocytes and plasma cells, when present in increased numbers, present the expected patterns of reactivity. Light chain restriction is demonstrable within the great majority of those with a minimal of 6% of plasma cells and in two thirds of these with 5% or much less [157]. Numerical abnormalities, both monosomies and trisomies, are widespread as are complex cytogenetic abnormalities. Some such sufferers have heredi tary amyloidosis [163] and, in different patients additionally, the association could also be coincidental. Bone marrow histology Bone marrow biopsy sections could also be regular or show elevated plasma cells, amyloid deposition or each. Patients with increased plasma cells can also have lymphoid aggregates and occasional sufferers have granulomas [157]. Sometimes, characteristic options of myeloma or lymphoplasmacytic lym phoma are present. Amyloid was detected in bone marrow sections in 56% of 1 massive collection of sufferers [160]. In another examine of a hundred patients, amyloid was detected in bone mar row sections in 60%, in 39% in blood vessels and in 21% interstitially [157]. In the same collection, a neoplastic plasma cell infiltrate was detected in 83% when histology was supplemented by immunohistochemistry [157]. Congo pink fluorescence microscopy has been discovered to be more sensitive than microscopy with polar ized light, with each techniques being extremely spe cific [161]. Amyloid stains metachromatically with crystal violet and methyl violet and fluoresces after staining with thioflavineT [162]. Light chain and heavy chain deposition diseases Light chain deposition disease [162,168�170] describes a syndrome of organ harm consequent on the systemic deposition of free mild chains. There is an associated neoplastic proliferation of plasma cells, which can be occult or overt. Rarely the association is with a lymphoplasmacytic neoplasm, marginal zone lymphoma or persistent lymphocytic leukaemia [1]. About 70% of sufferers have related scientific features, most frequently of plasma cell myeloma but occasionally of solitary plasmacytoma, lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma or different nonHodgkin lymphoma. The predominant organ damage is renal, with glomerular and tubular deposition causing the nephrotic syndrome, renal failure or both. In a sequence of 69 patients with coex isting a number of myeloma, impaired renal function was found in 84% and cardiac involvement in 32%; light chain amyloidosis and cast nephropathy had been current in 17% and 13%, respectively [172]. Occasional sufferers have offered with clinical features of hepatic or adrenal involvement. In these sufferers in whom the bone marrow is outwardly regular it could be possible to reveal a mono clonal inhabitants of plasma cells by circulate cytometry. Rarely, mild chains are deposited within the bone mar row, either in the interstitium or in the partitions of blood vessels [162,169]. The nature of sunshine chain deposits could additionally be confirmed by immunohistochemis attempt with anti or anti antiserum but this is techni cally tough due to background staining. In a couple of quarter of patients, cryoglobulinaemia is a manifestation of myeloma or of Waldenstr�m macroglobulin aemia. In these circumstances the clone of cells secreting the paraprotein is too small to produce any pathological manifestations aside from these as a result of the traits of the cryoglobulin. Some hepatitis Cassociated cases have oligo clonal lymphoid infiltrates within the bone marrow while a smaller proportion of patients have overt low grade nonHodgkin lymphoma [174]. In a minority of patients, a cryoglobulin precipitate is current, often as weakly basophilic globular plenty, much less typically as crystals or a fibrillar deposit. Peripheral blood Unless it has been prepared from warmed blood, the blood film exhibits red cell agglutinates. If there has been a latest episode of haemolysis a number of sphero cytes could also be present together with polychromatic macrocytes. Some patients have lymphocytosis, with the cells both having the morphology of nor mal mature lymphocytes or showing some plasma cytic options. Bone marrow cytology and histology the bone marrow appearances differ from normal to those of an overt lymphoproliferative disorder. The histology has previously been reported as lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma or marginal zone lymphoma but is now thought to be distinct from both [176]. Most sufferers have a nodular infil trate of small lymphocytes with scattered clonal plasma cells exterior the nodules [176]. It often affects predominantly the small bowel and is asso ciated with the secretion of a truncated IgA heavy chain into the serum or into the bowel lumen. This disease has been acknowledged notably in rela tively younger persons living in poor socioeconomic conditions around the Mediterranean region, the Middle East, the Far East and Africa. Peripheral blood and bone marrow cytology the peripheral blood often shows no particular abnormality. The bone marrow is usually regular but could also be infiltrated by plasma cells or lymphoplasmacytoid cells that synthesize chain in the absence of or. Many patients have related autoimmune illness, most frequently rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus erythematosus [179,181].
Generic 200 mcg levothroid amexWhen there are complicating conditions corresponding to megalo blastic anaemia thyroid cancer male vs female discount 50mcg levothroid amex, pure purple cell aplasia or bone marrow necrosis thyroid cancer powerpoint purchase levothroid 100 mcg on line, the appropriate morphological options are superimposed on these of the underly ing illness thyroid zyprexa order 100 mcg levothroid amex. Macrophages are generally increased and each Bone marrow histology Sections of bone marrow trephine biopsy cores often show normal cellularity thyroid symptoms come and go buy 50 mcg levothroid fast delivery. There may be increased lymphoid nodules, plasma cells, mast cells and macrophages. Problems and pitfalls An iron stain may be falsely negative, if a trephine biopsy specimen has been decalcified, resulting in a mistaken assumption that the affected person has iron deficiency anaemia. Other forms of sickle cell illness include the compound heterozygous states, sickle cell/haemoglobin C disease and sickle cell/ thalassaemia. Haemoglobin S comprises almost all the whole haemoglobin, hae moglobin A being absent. Bone marrow aspiration is often solely indicated to detect suspected com plications such as megaloblastic anaemia, pure pink cell aplasia or bone marrow necrosis. Bone marrow histology Trephine biopsy sections present hypercellularity due to erythroid hyperplasia. Blood vessels could also be distended by sickle cells and perivascular fibrosis is common [39]. Foamy macrophages and small fibrotic scars might mark the sites of previous bone marrow infarction. Pure red cell aplasia (including Blackfan� Diamond syndrome) Pure pink cell aplasia has been defined as severe anaemia with the reticulocyte rely being lower than 1% and mature erythroblasts in a normocellular bone marrow being less than 0. Pure purple cell aplasia could be either constitutional or acquired and either acute or chronic. Constitutional pure red cell aplasia, also referred to as the Blackfan�Diamond syndrome, is a persistent situation which usually becomes manifest in the course of the first 12 months of life. It appears to be a trilineage dis order, consequent on an inherited stem cell defect, rather than a purely erythroid dysfunction. Inheritance is usually autosomal dominant, with variable penetrance, however some instances are autosomal reces sive. Red cell adenosine deaminase is elevated within the nice majority of sufferers with Diamond� Blackfan anaemia and in some relations this can be the one signal of the underlying genetic abnormality [43]. It can also occur as the presenting feature of childhood coeliac disease, an aetiological relation ship being suspected [52]. In older kids and adults, probably the most generally acknowledged explanation for acute aplasia is parvovirus B19 infection; the aplasia is usually of temporary duration and therefore causes symptomatic anaemia solely in sub jects with a preexisting intrinsic red cell defect or with an extrinsic cause of shortened red cell life span. However, in certain circumstances, parvovirus B19 an infection is persistent and thus results in chronic pure red cell aplasia. This occurs particu larly, but not exclusively, in sufferers with evident causes of immune deficiency, both congenital or acquired. Occasionally parvovirusinduced chronic pure red cell aplasia is seen in sufferers with no apparent defect in immune responses [60]. A associated virus, erythrovirus V9, has been reported in affiliation with acute anaemia (plus neutropenia) in a single affected person [62]. Pure red cell aplasia is a relatively widespread complication of Tcell massive granular lymphocytic leukaemia [64]; the lymphoproliferative disorder could also be occult. In one sequence, nearly 20% of cases of pure pink cell aplasia have been attributed to giant granu lar lymphocytic leukaemia [65]. Immunotherapy with medicine directed on the programmed death ligand 1 pathway (such as pembrolizumab), and doubtless also medication directed on the cytotoxic Tlymphocyte related protein 4 pathway (such as ipilimumab), can induce autoimmune phenomena including pure purple cell aplasia (and autoimmune haemolytic anaemia) [69]. In sufferers with an underlying lym phoproliferative disorder, neoplastic cells may be present. In transient erythroblastopenia of childhood, granulopoiesis could also be left shifted, and in sufferers with neutropenia there may be obvious arrest of maturation at the myelocyte stage [47]. Iron stores are generally increased since the iron usually in erythroid cells has been deposited in the shops. There is an entire absence of polychromatic cells and the reticulocyte count is zero or virtually zero. In transient erythroblastopenia of childhood the purple cells are of regular size and lack fetal traits. Neutropenia, which can be reasonably severe, occurs in a couple of quarter of cases and thrombocytosis in about a third [45,46]. Since symptomatic anaemia fol lowing parvovirusinduced aplasia is largely con fined to patients with an underlying purple cell defect, the blood film reveals options of the related dis ease, most frequently hereditary spherocytosis or sickle cell anaemia. In such cases the absence of polychro masia, regardless of marked anaemia, is diagnostically necessary and should result in a reticulocyte rely being carried out. Neutrophil and platelet counts are only occasionally reduced in sufferers with par vovirusinduced purple cell aplasia. Patients with pink cell aplasia related to thymoma or with auto immune disease sometimes also have neutropenia or thrombocytopenia. There could also be nonspecific inflammatory changes including elevated lymphocytes (including haem atogones), plasma cells, macrophages (which may be ironladen) and mast cells [71]. In immunocompetent sufferers, the bone marrow is hypercellular and megakaryocytes are elevated [70]. In transient erythroblastopenia of childhood, there are giant proerythroblasts, which can have small cytoplas mic vacuoles but lack the intranuclear viral inclu sions discernible in parvovirus an infection [47]. A lack of matur ing erythroblasts should alert the observer to the true nature of these cells, which can be confirmed by immunohistochemistry. Careful examination of the blood movie and immu nohistochemistry of the bone marrow will assist to exclude purple cell aplasia secondary to Tcell large granular lymphocytic leukaemia. Disorders of leucocytes Congenital neutropenia Severe congenital neutropenia is a heterogeneous group of problems with either autosomal domi nant, autosomal recessive or Xlinked recessive inheritance. Congenital neutropenia could be cyclical with variation, over a interval of 3 weeks or extra, from very low to regular or above regular levels. All these inherited circumstances are associated with erythroid hyperplasia without other abnor mality. Peripheral blood In extreme congenital neutropenia the peripheral blood shows severe neutropenia and infrequently mono cytosis, eosinophilia, thrombocytosis and the consequences of continual or recurrent an infection similar to anaemia and increased rouleaux formation. This has been reported in affiliation toxic changes, whereas myelokathexis, an autoso mal dominant condition attributable to accelerated apoptosis in neutrophil precursors, is characterised by neutropenia with particular cytological abnormali ties in neutrophils [79,80]. Some circumstances present a extreme discount of all granulopoietic cells with residual cells sometimes being morphologi cally atypical. An association between extreme congenital neutropenia and osteopo rosis has been noticed [92]. In Barth syndrome, obvious maturation arrest at the myelocyte stage has been described. Congenital neutropenia associated with hyperimmu noglobulin M syndrome is characterised by matura tion arrest and vacuolated promyelocytes [81]. In the Shwachman�Diamond syndrome, the bone marrow might present granulocytic hypoplasia, left shift or obvious maturation arrest [93,94]; with illness development, generalized bone marrow hypoplasia develops [94]. Phagocytosis of neutrophils has been described in continual benign neutropenia of child hood [97].
Trusted levothroid 100mcgThey have regulatory roles in haemopoietic differentiation and in immune cell interactions thyroid symptoms uti cheap 50mcg levothroid visa, and are presumed to be the origin of fibrosis happen ring in inflammatory myelopathies and myelopro liferative neoplasms thyroid cancer anemia order levothroid 50mcg without prescription. However thyroid symptoms difficulty breathing trusted 50 mcg levothroid, their function in fibrosis occurring in reaction to metastatic solid tumours thyroid energy discount levothroid 50 mcg visa, lymphomas and a few granulomatous disease processes is unclear. Occasionally they may be identifiable as bipolar or tripolar cells, with longer cytoplasmic processes than the uncommon endothelial cells that will even be found. Histology Stromal dendritic cells form a meshwork by way of out the bone marrow stroma with accentuated density at trabecular margins and round bigger blood vessels. They are typically invisible without immunohistochemical demonstration as they intercalate between adipocytes and their lengthy, interconnecting dendritic processes are too fantastic to visualize readily. They are also mimicked by a com pletely separate inhabitants of highly dendritic resident histiocytes. Megakaryopoiesis and thrombopoiesis Cytology Megakaryocytes arise from haemopoietic stem cells by way of a common megakaryocyte�erythroid progeni tor cell that gives rise to erythroid precursors and megakaryoblasts. The latter are small, proliferative cells with diploid nuclei, not usually recognizable in regular bone marrow. In normal marrow, the earliest morphologically recognizable cell in the megakaryocyte lineage is the megakaryocyte itself though, when haemopoiesis is abnormal, megakaryoblasts of similar size and morphology to myeloblasts can sometimes be recognized. It is promoted by upregulation of cyclin D3 and is believed to contribute to the excessive produc tive capability of megakaryocytes for platelet elements [59]. In normal marrow they range from 4 N (tetraploid) to 32 N with the dominant ploidy class being 16 N. Megakaryocytes can also be classified on the idea of their nuclear and, more notably, their cytoplasmic characteristics into three phases of maturation [60]. There is a few correlation between the three levels of maturation and ploidy level. The nuclei of the good majority of normal polyploid megakaryocytes form irregular lobes joined by strands of chromatin. The latter are then shed directly into bone marrow sinusoids in a extremely coordinated means of cyto plasmic fragmentation. An elevated demand for platelets, for example as a result of peripheral destruction, results in an increase in ploidy stage and cell measurement, apparent in a bone marrow film as an elevated quantity of cyto plasm and a large, usually welllobated nucleus. It ought to be famous that whether or not or not megakaryo cytes appear to be producing platelets exhibits little correlation with the number of platelets being produced. In films of an aspirate this will only be a subjective assessment � that megakaryo cytes are decreased, regular or elevated. A extra correct evaluation could be created from histological sections of aspirated fragments or from sections of tre phine biopsy specimens. This course of differs from phagocytosis in that the engulfed cells have entered dilated cavities within the demarcation membrane system rather than being in phagocytic vacuoles; on examination of bone marrow movies the cells inside the megakaryocyte are noticed to be intact and morphologically normal. Serial sections present that, in normal marrow, all megakaryocytes abut on sinusoids [62]. Megakaryocytes lie instantly outdoors the sinusoid and discharge platelets by protruding cytoplasmic processes via endothelial cells; such processes break up into platelets. Intact megakaryo cytes and bare nuclei can even enter the circulation and are seen within vessels in histological sections of lung, spleen, liver and different organs. It is subsequently not possible to decide the scale or diploma of nuclear lobation of single megakaryocytes. Megakaryocytes of haematologically normal neonates and infants, as much as the age of 10 months, are smaller and more homogeneous in size than these of older kids and adults [63]. Larger clusters of megakaryocytes are seen in regenerating marrow, following chemotherapy and bone marrow transplantation, and also in various pathological states; this feature is diagnos tically useful. Depending on the processing and marking tech niques employed, estimates of imply megakaryo cyte number in regular marrow vary from 7 to 15 per mm2 [64]. In bone marrow movies they seem as oval or elongated cells varying in dimension from 5 to 25 �m. The cytoplasm is packed with granules that stain deep purple with Romanowsky stains. Mast cells are distrib uted irregularly within the medullary cavity however are most numerous close to the endosteum, within the perios teum, in association with the adventitia of small blood vessels and at the periphery of lymphoid nod ules or aggregates [65]. Osteoblasts and osteoclasts Osteoblasts and osteoclasts differ in their origin but have complementary functions. Osteoblasts have a standard origin with different mesenchymal cells and are responsible for bone deposition. Osteoclasts are formed by fusion of cells of monocyte lineage and are answerable for dissolution of bone. Osteoblasts can be distinguished from plasma cells, to which they bear a superficial resemblance, by the lesser degree of chromatin condensation and the separation of the Golgi zone from the nucleus. Osteoblasts are unusual in bone marrow aspirates of healthy adults however, when present, typically appear in small clumps. Their nuclei tend to be clearly separate, uniform in look and slightly oval with a single lilac staining nucleolus. The voluminous cytoplasm incorporates numerous azurophilic granules, which are coarser than these of megakaryocytes. Histology Osteocytes, osteoblasts and osteoclasts in histo logical sections are recognized by their position and their morphological features. A decline in number per unit space of bone happens through the second and third many years [66]. Golgi zones are very clearly shown; the nuclei are oval and a few include a small nucleolus. Fat cells Fat cells are virtually all the time recognizable in bone marrow specimens, exceptions being found in very younger infants and when the bone marrow is markedly hypercellular. Histology In sections of bone marrow, the fats cells appear in clusters, separated by haemopoietic tissue. The bone marrow contains mature cells and precursor cells of each T and Blymphoid lineages. T cells are extra quite a few amongst mature cells whereas among pre cursor cells those of B lineage are more frequent. Cytology Bone marrow lymphocytes are small cells with a excessive nucleocytoplasmic ratio and scanty, weakly basophilic cytoplasm. The nuclei show some chro matin condensation however the chromatin typically seems more diffuse than that of peripheral blood lymphocytes. The bone marrow of healthy youngsters could show significant numbers of immature cells with a cyto logical resemblance to leukaemic lymphoblasts, referred to as haematogones (see pages 357�358); these are Blymphocyte precursors. Lymphocytes appear to concentrate round arterioles near the centre of the haemopoietic cords.
Levothroid 50 mcg for saleExtensive solar elastosis thyroid cancer types buy levothroid 200mcg, open comedones containing giant lots of keratin thyroid eye disease icd 9 cheap levothroid 50 mcg with amex, and small epidermoid cysts overactive thyroid symptoms yahoo cheap 50mcg levothroid mastercard, typically difficult by rupture and surrounding granulomatous inflammation and basophilic degeneration of surrounding connective tissue thyroid iodine purchase 200 mcg levothroid overnight delivery. Cyst formation follows, then rupture into the dermis, triggering inflammation, probably mediated by the innate immune system. Ongoing bouts of inflammation and fibrotic resolution result in follicular distortion. The end-stage of the persistent fibro-inflammatory response to continuous keratin extravasation is intensive fibrosis. The complexity of those lesions has prompted consensus research to outline sufficient nomenclature, producing phrases corresponding to "keratin-filled interconnected multi. Cutaneous infection ought to be excluded by tradition and particular stains for organisms. Squamous cell carcinoma may be difficult to differentiate from pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia, particularly when biopsies are too superficial. Rosacea and perioral dermatitis Ofnfeel Features the histopathology ofhidradenitis is just like that of dissecting cellulitis of the scalp, profiles exhibiting intensive dermal scar, deep dermal and subcutaneous abscesses, and sinuses partially lined with squamous epithelium. Sebaceous glands are decreased or absent, and this reduction seems to happen early within the illness process. Follicular-based papulopustules and exhausting red-brown to yellow papules and lesions arise on a background of a facial vascular abnormality with telangiectasias and transient although pers. The nostril, cheeks, and chin are sometimes affected, but extrafacial involvement not often happens. The pathogenesis of rosacea is poorly understood, but vascular flushing is one ofthe earliest phases, suggesting a neurovascular abnormality, presumably triggered by a genetic predisposition and environmental components: cold, psychological stress, sizzling or spicy foods and liquids, alcohoL certain vasodilatory medication, and sunlight, as the primary course of. Extensive dermal scarring is present with (B) a partially squamous�lined sinus tract and related suppurative infiltrates. Such circumstances, and different examples of atypical rosacea, warrant biopsy, the occasional case of suspected atypical rosacea reavealed to be a unique dermatosis or lymphoma. Granulomatous variants of perioral dermatitis, generally involving the eyelids and neck, are known, particularly in children. Papular lesion: Perifollicular and perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrates are characteristics of papular rosacea. Telangiectatic rosacea is characterized by ectatic venules surrounded by a sparse perivascular infiltrate in a background of solar elastosis and dermal edema. Lymphocytes and plasma cells may cluster to one facet ofa telangiectatic blood vessel or form an inflammatory nodule. Other options favoring rosacea embrace Demodex infestation and sebaceous hyperplasia. The folliculitis of rosacea could also be suppurative and entirely neutrophilic, with pustule formation, or ruptured with surrounding neutrophilic and lymphohistiocytic infiltrates, together with foreign-body large cells and occasional eosinophils. Demodex mites are virtually at all times present, and the adjoining dermis is commonly spongiotic. Infeaious folliculitis and various forms of zits can produce similar lesions, but evidence of acne-type folli. Loose to well-fonned granulomas comprised of histiocytes and multinudeate big cells are seen. Nonfollicular epithelioid granulomas that often exhibit caseating necrosis happen less regularly. Fungal and mycobacterial infections may be excluded with special stains and cultures. Histopathologically phyma is characterised by intensive hypertrophy of mature sebaceous glands, follicular dilatation, hyperkeratosis with variable inflammation, fibrosis, vascular ectasia. Perioral dermatitis show pathology like papular, pustular, and granulomatous rosacea. The lesions sometimes affect the face, trunk, and proximal extremities and could be pruritic. A drop in prevalence has been famous over the intervening a long time, a gift of antiretroviral therapies. Additional findings might embody sebaceous gland spongiosis, subcorneal eosinophilic pustules, and variably dense, perivascular, and interstitial Perforating folliculitis Clinical Features As defined as a clinicopathologic entity in 1968 by Mehregan and Coskey216, perforating folliculitis is a folliculocentric erythematous papule penetrated by a central hair shaft, generally encompassed by a keratotic plug. Histopathologic Features An eccentric infundibular perforation characterizes perforating folliculitis. Hyperkeratotic stratum corneum often plugs the intraepidermal section of the follicle acrotrichium). The dermis adjoining to the perforation incorporates a combined inflammatory infiltrate of neutrophils, lymphocytes, and plasma cells and will degenerate into basophilic and granular debris. Differential Diagnosis Infundibular perforation is a feature of a number of forms of folliculitis, including bacterial and fungal folliculitis, acne vulgaris, keratosis pilaris, and pustulofollicular types of alopecia such as folliculitis decalvans and acne keloidalis. Differential Diagnosis Histopathologic Features Peri and intrafollicular eosinophilic infiltration Occasional subcorneal eosinophilic pustules Follicular spongiosis usually Perivascular and interstitial lymphocytic infiltrates Flame figures rare Eosinophilic infiltrates also occur in papular urticaria, arthropod chunk reactions, the papular eruption of:tnV, scabies or Demodex infestation, dermatophyte infect. Severe paroxysmal pruritus initiated by emotional stimuli, bodily activity, and sexual exercise is usually reported. Both intrafollicular and perifollicular eosinophils are seen on this case of eosinophilic follic:ulitis. The microscopic presentation is usually nonspecific and can present vital variation, requiring examination of a number of serial sections. Hyperkeratotic plugging of the follicle on the level of apoc:rine duct entry is a more specific finding but a characteristic tougher to reveal in typical sections. Spongiosis and apoc:rine sweat retention are sometimes noticed within the distal apocrine duct. Perifollic:ular xanthomatosis that stains with the anti-human milk fat globulin immunostain could be the most distinctive feature of the condition. The scientific distribution ought to allow distinction between these entities and Fox-Fordyce disease. Hidradenitis suppurative can be intertriginous and may present similar histologic options but is generally more aggressively inflammatory, destructive, and neutrophilic. Infundibulofolliculitis (disseminate and recurrent infundibulofolliculitis) is a microscopic consideration since it exhibits spongiosis and lymphocyte exocytosis of the follicular infundibulum and ostia, but follicular hyperkeratosis is less distinguished, and, clinically, the infundibulofolliculitis is distinct, widespread, and not restricted to flexural surfaces; it tends to afflict younger black males. Lesions encompass tender erythematous macules, papules, and plaques, mimicking cellulitis. Histopathologic Features A sparse to dense neutrophilic infiltrate surrounds the eccrine models, favoring the secretory coils within the superficial subcutis and generally accompanied by eccrine epithelial vacuolization and necrosis269. The sweat ducts of profoundly neutropenic patients might degenerate Chromhidrosis (apocrine chromhidrosis) Clinical Features Chromhidrosis is a rare dysfunction characterized by colored perspiration that causes psychosocial dysfunction and stains clothing. The face and axilla are the most typical sites of apocrine chromhidrosis, though involvement of the areola and palms has been reported.
Diseases - Young Simpson syndrome
- Rocky Mountain spotted fever
- Triphalangeal thumb non opposable
- Chorioretinitis
- Orofaciodigital syndrome Thurston type
- Omsk hemorrhagic fever
- Gamstorp episodic adynamy
- Anemia
- Neuropathy ataxia and retinis pigmentosa
- Punctate inner choroidopathy
Levothroid: 200 mcg, 100 mcg, 50 mcg
Levothroid 200 mcg mastercardThere could be rete-ridge blunting and thickening of the stratum comeum thyroid nodules biopsy procedure generic 100mcg levothroid otc, emphasizing that in vitiligo histomorphologic changes additionally embody alterations to the epidermis thyroid gland images buy generic levothroid 50 mcg line. Differential Diagnosis the clinical differential prognosis of vitiligo is determined by the distribution and extent of hypopigmentation thyroid symptoms throat purchase levothroid 50 mcg with visa, in addition to on different factors thyroid nodules ct cheap levothroid 100 mcg without prescription, and consists of leukoderma from chemicals, trauma, and bums; halo nevi and melanoma; piebaldism; and Waardenburg syndrome, all of which may present an absence of epidermal melanocytes and melanin and thus be histologically indistinguishable from the end-stage lesion. Other entities that may be confused clinically with vitiligo embody lupus erythematosus, hypochromic mycosis fungoides, postinflarnrnatory hypopigmentation, tuberous sclerosis, pityriasis alba, tinea versicolor, leprosy, idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis, and nevus depigmentosus. In basic, the latter processes show basilar melanocytes, diminished epidermal melanin, and distinctive options in some sufferers. Various mutations of the tyrosinase gene on chromosome llq14-21 are responsible for these totally different medical phenotypes. However, the degree of skin pigmentation, corresponding to the ability to tan, is variable amongst both types depending on the mutant alleles. Due to an absence of melanin Histopathologic Features In all illness subtypes, basal melanocytes are observed, however the epidermal melanin content material is greatly diminished or absenL Electron microscopy proves the presence of regular melanocytes. Griscelli syndrome is a really rare situation whose hallmarks embrace diluted pigment of the skin, silver-gray hair, neurological impairment, and an accumulation of melanosomes. It is considered a form of partial albinism along with neurological and/or immunological defects. The merchandise of these 3 genes work intently together within the transport of melanosomes. Examination reveals large clumps of pigment in hair shafts because of accumulation ofmelanosomes in melanocytes. It is an autosomal recessive dysfunction that impacts primarily persons of Puerto Rican origin, though there have been a quantity of reported instances in Turkish, Pakistani, and Ashkenazi Jewish kindreds. In addition to decreased pigmentation, affected people even have severe immunologic defects (eg, impaired chemotaxis and abnormal natural killer cell perform, bleeding tendencies, and progressive neurologic dysfunction. They may also succumb to an "accelerated phase" throughout which a nonmalignant lymphohistiocytic infiltration of multiple organs resembling lymphoma occurs. Silver stains detect large melanin granules throughout the epidermis and in melanophages within the upper dermis; ultrastructurally, these granules are localized to membrane-bound large melanosomes in skin and hair. The traditional diagnostic characteristic of Chediak-Higashi syndrome is the presence of huge cytoplasmic granules and lysosomes within cells. These granules are formed by the fusion of irregular phagosomes incapable of regular bacterial killing. Multiple organ techniques might have hamartomatous involvement, including the central nervous system (with epilepsy being the commonest characteristic, kidneys, heart, and other viscera. By electron microscopy, the dimensions of melanosomes and degree of melanization are lower than the traditional counterparts, and their dendrites are less properly developed. The ash leaf macules are discriminated from piebaldism and vitiligo by the presence of melanocytes within the former. Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis differs from vitiligo and chemical and traumatic depigmentation by the presence of melanocytes and is discriminated from different leukodermas by its scientific features. The lesions ofpostinflammatory hypopigmentation are acquired and extra variable clinically. Hypomelanosil of Ito or lncontinentia pigmenti achromians Hypopigmented bands or streaks following Blaschko traces or exhibiting a block-like configuration on the trunk at delivery or during the first 12 months of life characterize hypomelanosis of Ito; the lesions are most conspicuous in trunk, head, and extremities. There is usually palm, sole, and/or mucosal involvement Repigmentation might happen in some instances and leukoderma might fade in adulthood. Karyotyping of blood lymphocytes, skin fibroblasts, or keratinocytes reveals nonuniform chromosomal abnormalities, together with mosaicism for tetruomy 12p and for trisomy 18, suggesting that somatic cell line mosaicism is liable for the hypopigmentation. Among the neurological manifestations are mental retardation, epilepsy, language disabilities, motor system dysfunction, psychiatric signs including autism, and cortical visual impairment. They can have a selection of structural abnormalities of the mind together with megalencephaly with Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis Relatively common amongst older (>50 years) African American women and men (Table 15-5). Numerous well-demarcated depigmented and hypopigmented (porcelain white) macules 2 to 10 mm in diameter are seen on the shins and, less incessantly. Treceptor and melanocyte differentiation antigens (Tyrp-1, tyrosinase, and gpl00/pmell7). On a Melan-A stain, the melano� cytes have a blunted appearance refiective of a marked attenua� tion within the dendrites. Differential Diagnosis the main circumstances to be thought-about are nevus depigmentosus and postinflammatory hypopigmentation. The scientific findings of symmetric swirled lesions in patients with seizures, psychological retardation, and different developmental abnormalities ought to facilitate this discrimination because the histology may be similar. Nevus depigmentosus Nevus depigmentosus manifests as a solitary congenital patch of hypopigmentation on the trunk, neck, and other places. Lesions may be circumscribed, irregular, oval or round, or a unilateral band or streak that may be arranged alongside 1 or more traces of Blaschk. Nevus depigmentosus could additionally be associated with both ipsilateral or contralateral segmental lentiginosis or with the acquired onset of a number of pigmented nevi within the hypopigmented area. The lack of pigmentation is due to decreased basal-layer melanin; the number of basilar melanocytes is normal or decreased, and these cells produce fewer and smaller melanosomes. Differential Diagnosis the major conditions to be thought of are postinflammatory hypopigmentation, tinea versicolor, vitiligo, and leprosy. In common, the medical features and identification of microorganisms ought to enable discrimination of pityriasis alba from different leukodermas. Postinflammatory leukoderma or hypomelanosis Hypomelanotic macular lesions could follow a diverse group of inflammatory dermatitides, similar to eczematous dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, psoriasis, drug eruptions, pityriasis lichenoides chronica, lupus erythematosus, lichen planus, alopecia mucinosa, sarcoidosis, and mycosis fungoides (Table 15-6). The medical lesions are usually off-white (not fully depigmented), often have vague margins, and show gradual repigmentation. Melanocytes may also be severely broken by varied bodily, chemical, thermal, and different pathologic injuries (Table 15-7). Repigmentation may happen rapidly on sun-exposed websites and in much less severely broken areas. Total destruction of melanocytes as seen within the setting of bums, exposure to certain chemical compounds, infectious ailments such as pinta or onchocerciasis, discoid lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, and halo nevi might go away a everlasting leukoderma. Histopathologic Features the number of basilar melanocytes is normal or decreased,75 and the amount of epidermal melanin is decreased in particular stains; electron microscopy reveals poorly developed, much less dendritic melanocytes with a tremendously lowered variety of otherwise regular melanosomes. In addition, some membrane-bound aggregated melanosomes may be seen in keratinocytes. Differential Diagnosis Conditions to be excluded embody piebaldism, segmental vitiligo, tuberous sclerosis, postinflammatory hypopigmentation, and hypomelanosis of Ito. Nevus depigmentosus is congenital and differs from the primary 2 issues histologically by advantage of having regular numbers of intraepidermal melanocytes and from the latter 3 entities primarily based primarily on scientific features as a end result of the histology may be fairly similar. Pityriasis alba Pityriasis alba causes hypopigmented patchy macules across the nose, cheeks, and eyebrow areas of children, particularly in In basic, reversible forms of leukoderma present basilar melanocytes usually in regular numbers however in some situations decreased in number or damaged in live performance with decreased epidermal melanin. Some pigment incontinence may be current as well as options of the antecedent dermatitis, corresponding to, for instance, lupus erythematosus. The melanocytes could or will not be detected with particular stains relying on the degree of melanocyte damage.

Generic levothroid 200 mcg mastercardGranular parakeratosis: pathologic and clinical correlation of 18 instances of granular parakeratosis thyroid gland health cheap levothroid 100 mcg with amex. Ultrastructural identification ofbasic abnormalities as clues to genetic disorders of the dermis thyroid gland joint pain buy 200 mcg levothroid with amex. Transgenic mice expressing a mutant keratin 10 gene reveal the doubtless genetic foundation for epidermolytic hyperkeratosis thyroid disease in cats buy cheap levothroid 100mcg on line. Epidermolytic hyperkeratosis and epidermolysis bullosa simplex attributable to frameshift mutations altering the v2 tail domains ofkeratin 1 and keratin 5 thyroid and iodine buy discount levothroid 50mcg on-line. Mutations within the rod domain of keratin 2e in sufferers with ichthyosis bullosa of Siemens. Phenotypic heterogeneity in bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma: attainable somatic mosaicism for keratin gene mutation within the mildly affected mother of the proband. Ultrastructural changes ensuing from keratin-9 gene mutations in two families with epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma. Identification of the keratin K9 R162W mutation in sufferers of Italian origin with epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma. Novel splice website mutation in keratin 1 underlies mild epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma in three kindreds. Hereditary epidermolytic palmo-plantar keratoderma (Vorner type)-report of a household and review of the literature. Insights into genotype-phenotype correlation in pachyonychia congenita from the human intermediate filament mutation database. Ito M, Fujiwara H, Maruyama T, et al Morphogenesis of the cornoid lamella: histochemical, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural examine of porokeratosis. Fuchs E, Coulombe P, Cheng J, et al Genetic bases of epidermolysis bullosa simplex and epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. Epidermolysis bullosa simplex in Scotland attributable to a spectrum of keratin mutations. Severe keratin 5 and 14 mutations induce down-regulation of junction proteins in keratinocytes. A site-specific plectin mutation causes dominant epidermolysis bullosa simplex Ogna: two equivalent de novo mutations. Inherited epidermolysis bullosa: updated recommendations on diagnosis and classification. Laminin 5 mutations in junctional epidermolysis bullosa: molecular basis of Herlitz vs. Insights into desmosome biology from inherited human skin illness and cardiocutaneous syndromes. Hailey-Hailey disease: the scientific features, response to treatment and prognosis. Atypical options and systemic associations in in depth cases of Grover illness: a scientific evaluate. Pseudoherpetic transient acantholytic dermatosis (Grover disease): case sequence and review of the literature. Loss of comeodesmosin results in extreme pores and skin barrier defect, pruritux, and atopy: unraveling the peeling skin disease. Familial reactive perforating collagenosis: a clinical, histopathological research of 10 instances. Elastosis perforans serpiginosa: a review of the literature and report of eleven cases. Elastosis perforans serpiginosa: a evaluation of the literature and our personal expertise. Disorders of Pigmentation the sources of pigment that cause hyperpigmentation of the skin range from endogenous merchandise such as melanin and hemosiderin to exogenous brokers similar to tattoo dyes, ingested metals, and drugs. When the dermis is closely melanized, pigment incontinence might lead to upper dermal melanization as nicely. The circulation of blood via the superficial capillary plaus may influence the pores and skin shade, as evidenced by information anemicus. Barnhill or hereditary, postinOammatory, or induced by chemical substances and overseas materials. Hyperactivity of melanocytes leads to various hyperpigmented situations, and in such disorders, lesions are once more more striking in dark than in mild skin. In some circumstances, the switch of melanosomes from regular melanocytes to the encompassing basal keratin. We use a hybrid Sox 1O/Melan A immunostain to beautify the nuclei with the previous and the cytoplasms and their dendritic processes with the latter reagent, enabling melanocyte enumeration and evaluation of morphology at the similar time. Epidermal melanocytes are either absent or inactive; accordingly, the epidermis is hypomelanized or totally depigmented. In stage three, melanin polymers become denser, and in stage 4, the elevated density masks the underlying construction of cristae. Piebaldism manifests congenital patches of depigmentation 0-eukodenna), a white forelock, orpoliosis (white hairs) in 85% of pati. Unlike vitiligo, the leukoderma is generally permanent as a outcome of melanocytes are largely absent within the lesion. Occasionally, repigmentation might happen on the periphery of a lesion or throughout the depigmented macule. The hwnan piebaldism gene locus has been mapped to chromosome 4q12, a website near the human Kl. Hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections of lesional and uninvolved pores and skin for basilar melanocytes, melanin, and other modifications, corresponding to irritation, granulomas 2. Electron microscopy to reveal quantitative and qualitative elements of melanosomes 7. Most other leukodermas are distinguished from piebaldism by the presence of melanocytes. Histopathologic Features Established (depigmented) lesions: absence of epidermal melanocytes and melanin Marginal (normal) skin Epidermal melanocytes and melanin present Basal-layer vacuolization often Sparse lymphocytic infiltrates Trichrome vitiligo: epidermal melanocytes and melanin present however often lowered Vitiligo and Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome Vitiligo is an acquired patchy pigment loss ofthe pores and skin and rarely the hairs that will develop at any age; rarely, it could be congenital (Table 15-3). Individual macules of established vitiligo typically measure several millimeters in diameter; are completely depigmented with a milk-white colour; and have well-defined, usually scalloped borders. Trichrome vitiligo refers to 3 sorts oflesions: white (established vitiligo), mild tan (transitional areas that can turn into depigmented), and regular brown areas. When serum IgG from vitiligo sufferers is injected into nude mice to which regular human pores and skin has been grafted, melanocytes of the grafted pores and skin are damaged and significantly decreased, suggesting an autoimmune mechanism within the etiology. There can also be evidence of modification of epidermal cytokine expression in sufferers with vitiligo. Differential Diagnosis Piebald ism Chemical, bodily depigmentation Postinflammatory hypopigmentation Lupus erythematosus Pityriasis alba Tinea versicolor Tuberous sclerosis Leprosy Melanoma-associated leukoderma Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis Nevus depigmentosus Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, fibroblast growth factor~. Histopathologic Features In well-established lesions, neither melanocytes nor melanin can be detected in the epidermis with hematoxylin and eosin or irnrnunohistochemical stains or electron microscopy.
Purchase levothroid 200mcg free shippingAppropriate documentation and coding have to be integrated into the method of offering care thyroid vasculature 50mcg levothroid visa, not added on as a further challenging task at the finish of a patient go to 5 thyroid gland supplements cheap levothroid 200 mcg on-line. Successful medical report designs incorporate all E/M necessities and guidelines into sophisticated documentation tools thyroid symptoms wrinkled fingers order levothroid 50mcg with amex, instead of demanding physicians to memorize lengthy lists of complex compliance guidelines thyroid visual symptoms discount levothroid 200mcg amex. Effective E/M methodology displays the perfect care process and workflow that physicians are taught throughout their training. Precise documentation of all E/M elements is critical to ensuring E/M compliance, significantly within the event of an exterior audit. This consists of documentation of the traditional H&P components: (a) full medical history, (b) normal and abnormal examination findings, (c) information reviewed, (d) assessment (differential diagnosis), and (e) plans (treatments and data ordered). This principle puts documentation and coding into correct perspective; patient care comes first, and rules and guidelines must conform to this framework to be thought-about credible. Effective H&P forms ought to be designed for usability and efficiency, with inclusion of E/M compliance rules to ensure acceptable care and documentation. On December 13, 1995, the New York Times published a report that despatched a compliance shock wave via the group of academic physicians. This substantial settlement followed a Government audit of 100 sufferers treated in 1993 � (45). The government had extrapolated the outcome of this restricted audit over all of the comparable information for multiple years, calculating a fine that was considerably larger than the ultimate settlement quantity. One involved submission of claims for E/M companies at ranges significantly exceeding the extent of care documented in the medical report by residents and physicians (the similar E/M points discussed above). The second issue highlighted a new idea that subsequently became generally identified as �physician presence. The audit concluded that this apply was evidence of billing twice for the same service. It is noteworthy that adhering to these more recent shortcut suggestions regularly leads once once more to imprecise documentation of the particular care that educating physicians perform. In the primary state of affairs, the educating doctor would personally perform, document, and code just for the weather of an E/M service that she or he accomplished unbiased of the resident (46); this approach requires more time for comprehensive care and documentation than optimum within the teaching state of affairs. In the second option, the resident performs the weather required for an E/M service in the presence of. The final compliant option luckily matches up extremely well with appropriate affected person care workflow for educating physicians. In this method, the resident supplies and documents the level of care medically indicated for the affected person, and "the teaching doctor independently performs the critical or keyportion(s) of the service with or with out the resident current and, as applicable. In this occasion, the teaching doctor must doc that she or he personally saw the affected person, personally carried out important or key portions of the service. Yes No Please record details below: List kind and the way a lot:: List sort and the way a lot. Chapter 200: Compliant Documentation, Coding, and Billing within the Practice of Otolaryngology Uate l l Account No. This additionally permits for the frequent apply the place attending physicians often communicate with and train their residents about these issues throughout regular educating rounds. There are two necessities for effective documentation instruments for educating physicians to obtain compliant documentation and coding in this setting. Fiat, the resident requires compliant documentation instruments similar to those described above (appropriate types for inpatient care can be found (48)) to ensure that his or her care and medical document documentation help the appropriate degree of service. This part Is based on the single organ system examination for "ear, nose, mouth, and throat:" introduced In the 1997 Documentation Guidelines. Physicians should document findings for all components examined as regular or abnonnal. Most of those software program packages also assign an assumed level of illness severity to numerous diagnosis codes as properly as medical necessity indicators for a lot of pairings of procedure and diagnosis codes. Note notably the Inclusion of a section for documentation of the three ranges of risk. Also note the documentation prompts, based on medically Indicated degree of care, located In every subsection. Claims for Multiple Procedures on Same Date of Service the magnitude of coding and billing challenges increases significantly when claims are submitted for 2 or more procedures, or for a process and an E/M service. Principle #1: the claims processing software ofMedicare Carriers and essentially all pri-vate insurers are programmed to authorize cost for only one se:Mce per day. Principle #2: Most surgical procedures embody a "surgical package deal" of additional care providers (50). The surgical package deal also includes anticipated E/M services associated to the procedure for a partirular time span. Principle #3: Many procedures include performance of other much less advanced procedures as "parts. Principle #7: Most non-public insurers use claims processing software program from a standard vendor. Commonly Used Modifiers for Multiple Procedures When submitting claims for two or more unbiased surgical procedures on the same date of service, the modifiers which might be mostly added to all procedure codes aside from the principle code are. A frequent instance of appropriate use of this modifier is � 31254 (endoscopic anterior ethmoidectomy), 31256. However, there are a number of outlined circumstances by which the E/M service is more in depth than usually anticipated. When these conditions arise, physicians are suggested to submit a code for the E/M service with an appropriate modifier. This state of affairs is mostly applicable when the process is performed for one diagnosis. Documentation should assist a special session, completely different procedure or surgical procedure, different site or organ system, separate incision/ excision, separate lesion, or separate damage" (55). An example of right use of this modifier is � 31255 (endoscopic total ethmoidectomy), 31254. However; it must only be used judiciously and accurately, as excessive use will likely trigger an audit and important monetary penalties if improper utilization is found. From the angle of insurer payments, sadly Medicare long ago decided that it might scale back payments by 50% for all secondary procedures (those submitted with a. Payment for a visit could be allowed along with cost for suturing a scalp wound if, in addition, a full neurologic exam is made for a affected person with head trauma. However, Medicare provides clarification that particularly differentiates appropriate use of the. A hypothetical instance for use of this modifier could be evaluation within the emergency department of an grownup affected person found to have a large parapharyngeal house abscess. There are, nonetheless, two circumstances underneath which an E/M code should be submitted with an attached. For instance, if a affected person who has undergone a superficial parotidectomy develops acute ethmoid sinusitis in the course of the 90-day international interval, the evaluation and administration of this episode should be coded. One such coverage concerns reimbursement for issues that happen during the world period of an operation.
Cheap 50 mcg levothroid free shippingNote the collections of pink material around which the neuroblastoma cells are clustered thyroid cancer in dogs buy generic levothroid 50 mcg. Use of each antibodies considerably improves sensitivity and specificity in confirming the prostatic origin of metastatic most cancers thyroid symptoms goiter discount 200 mcg levothroid with mastercard. Expression of these antigens thyroid nodules icd 10 buy levothroid 100mcg overnight delivery, no matter exact tumour origin thyroid palpation generic 100mcg levothroid with amex, is important for choice of remedy. Immunohistochemical staining for thyroglobulin is useful in confirming the thyroid origin of meta static tumour cells. Thyroid transcription factor 1 is also normally constructive but it must be famous that positive reactions are usual in nonsquamous cell carcinoma of the lung, which is extra more likely to pre despatched as a metastasis of unknown origin. Cytokeratin expression is distinctive with an intracytoplasmic dotlike or perinuclear ring sample. In instances of metastatic melanoma, immunohisto chemical staining for S100 protein is often posi tive [44]. Spindle cell melanomas and spindle cell (sarcomatoid) carcinomas could be confused; the previous specific S100 protein and the latter cytokeratins. However, a significant minority of breast carcinomas categorical S100 in addition to cytokeratins. Use of vimentin immunostaining to distinguish such spindle cell tumours from true sar comas is unreliable, since many nonsarcomatous tumours with spindle cell morphology express vimentin. Apart from variants of angiosarcoma, however, metastatic sarcomas are exceptionally rarely seen in bone marrow biopsies. In rhabdomyosarcomas, immunohistochemical staining for desmin, myo genin and MyoD are normally positive [72] though staining for myoglobin, which is said to be extra specific, is variable [53]. The position of bone marrow examination within the staging of strong tumours Examination of the bone marrow by aspiration and trephine biopsy is a longtime a part of the staging of neuroblastoma in children in most large centres. The bone marrow biopsy is constructive at the time of initial prognosis in approximately half of all sufferers, most of whom have evidence of metastatic spread at other sites [76]. In one reported series, the trephine biopsy alone was constructive in 20% of instances whereas neoplastic cells have been seen within the aspirate films when trephine biopsy sections appeared regular in 7%. Taking bilateral bone marrow aspirates and trephine biop sies from the iliac crests increases the sensitivity of the staging process by approximately 10%. Particularly careful examination of aspirate movies and trephine biopsy sections is important because infiltration is usually extremely focal [77,78]. Immunohistochemical stain ing of paraffinembedded sections of trephine biopsies for neuronespecific enolase has not been found to increase the sensitivity of marrow biopsy as a means of detecting tumour cells [68]. It has been instructed that the appearances in publish remedy marrow trephine biopsy sections must be divided into 4 grades: grade 1, normal (or hypocellular) marrow; grade 2, marrow with retic ulin fibrosis as the only abnormality; grade 3, dis torted structure with collagen fibrosis; and grade four, marrow with obvious tumour cells, with or with out different abnormalities [52]. It stays unclear whether or not this is really true for grades 2 and three [87] and whether the different grades correlate with variations in medical end result. Ganglionlike cells may show superficial resem blance to megakaryocytes and neuropil requires differentiation from fibrous tissue. In small cell carcinoma of the lung, bone marrow tre phine biopsy is optimistic in 25�30% of cases [11,88,89]; the aspirate is simply barely much less delicate for detecting marrow involvement. It has been sug gested that bone marrow examination is indicated in patients with small cell lung carcinoma in order to identify sufferers who could additionally be appropriate for attempted healing remedy [90]. However, some studies have proven no difference in survival between patients with and with out detectable mar row involvement [11,81], and the worth of routine bone marrow examination has therefore been questioned [11]. Imaging techniques such as mag netic resonance imaging have been proposed as more sensitive various staging procedures [91]. Several research have evaluated the utilization of marrow aspiration and trephine biopsy within the staging of breast most cancers. Detection of subclinical metastatic disease may be helpful in figuring out patients with apparently localized illness who would possibly benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy. Bone marrow biopsy is optimistic in 25�55% of sufferers with positive radioisotope bone imaging, but solely 4�10% of patients with unfavorable radioisotopic imaging have tumour detected by bone marrow biopsy [9,92]. In one reported collection, 23% of all breast most cancers sufferers had optimistic bone marrow biopsies at the time of first recurrence [92]. In an try and improve the sensitivity of bone marrow examina tion as a staging process, some studies have used immunocytochemical staining to determine micro metastases that would not be detected by conven tional techniques. The method used has concerned aspirating bone marrow from multiple (up to eight) sites under common anaesthesia on the time of preliminary surgical procedure, pooling the fabric and prepar ing several films. Using this approach, micrometastases have been found in 27�35% of circumstances on the time of diagnosis and correlation has been proven between their presence and the size of the primary tumour [93,94]. The presence of bone marrow micrometastases is a pre dictor of early relapse in bone. Despite these find ings, software of immunocytochemistry to detect micrometastases in bone marrow aspirates per formed for staging of breast most cancers has not but turn into normal apply. A related approach has been advised for detection of oral, oesophageal and gastric cancers [97�100], pancreatic cancer [101,102], nonsmall cell lung most cancers [103], uro logical cancers [104] and malignant melanoma [105]. Information from all these kind of investigation needs to be integrated and interpreted in the light of the age and gender of the affected person. The clinical value of detecting occult bone marrow micrometastases in such tumours by these strategies stays unproven [109]. In all cases, together with breast carcinoma, technical problems with the immunocy tochemical strategy, together with falsepositive outcomes because of pores and skin contamination or nonspecific haemo poietic cell reactivity, at present limit its applicabil ity in routine follow [110,111]. Problems and pitfalls in identification of tumour infiltration of bone marrow Normal parts of bone marrow may be mistaken for nonhaemopoietic malignant cells in aspirate movies and biopsy sections. Awareness of the appearances of stromal elements in aspirate films is particularly essential in avoiding confusion with malignant cells. Care should be taken to avoid such inclusions by making a small pores and skin incision prior to insertion of the biopsy needle and utilizing disposable needles to guarantee a pointy leading edge. Carryover from other specimens into the paraffin block throughout tissue processing should be the function of bone marrow examination in figuring out the tissue of origin of metastases and markers of relevance to prognosis or therapy Sometimes the detection of a bone marrow metast asis supplies the first proof that a affected person has a neoplastic situation, with no main tumour being apparent. It is essential to ascertain the tissue of origin when a particular treatment could additionally be available, even in a patient with metastatic illness. It is due to this fact essential to recognize carcinoma of the breast, endometrium, ovary, prostate, lung and thyroid and small cell tumours of childhood. If carryover is suspected, it can be confirmed by molecular evaluation to demonstrate the totally different affected person origins of separate tissue frag ments in a single waxembedded block [112,113]. If such contamination is suspected, examination of the entire set of stained trephine biopsy sec tions should present that other sections are free of extraneous material. If doubt persists, new sections minimize from the trephine biopsy specimen shall be freed from contamination. Other pathological parts in trephine biopsy specimens might sometimes be mistaken for nonhaemopoietic malignant cells. These include macrophages (present singly or within granulo mas), lymphoid cells in some kinds of nonHodgkin lymphoma, Reed�Sternberg cells in Hodgkin lym phoma, neoplastic mast cells in systemic mastocy tosis and the cells of Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Malignant cells of nonhaemopoietic origin could additionally be confused with normal bone marrow con stituents or with neoplastic haemopoietic cells.
References - Jeske W, Hoppensteadt D, Callas D, et al: Pharmacologic profiling of recombinant tissue factor pathway inhibitor, Semin Thromb Hemost 22:213, 1996.
- Eicken H, Gildein C, Schreiber C, et al. Stenting of a restrictive foramen ovale in a patient with hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Internat J Cardiol. 2006;113:254A. 38.
- Fasano A, Uzzau S, Fiore C, et al: The enterotoxic effect of zonula occludens toxin on rabbit small intestine involves the paracellular pathway. Gastroenterology 112:839, 1997.
- Fraser JD, Aguayo P, Ostlie DJ, et al: Review of the evidence on the management of blunt renal trauma in pediatric patients, Pediatr Surg Int 25(2):125n132, 2009.
- Talley NJ, Janssens J, Lauritsen K, Racz I, Bolling-Sternevald E. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori in functional dyspepsia: randomised double blind placebo controlled trial with 12 months' follow up. The Optimal Regimen Cures Helicobacter Induced Dyspepsia (ORCHID) Study Group. BMJ 1999;318:833.
- Collins N. The difference between albumin and prealbumin. Adv Skin Wound Care 2001;14:235-236.
- Wyndaele M, De Winter BY, Pelckmans PA, et al: Exploring associations between lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and gastrointestinal (GI) problems in women: a study in women with urological and GI problems vs a control population, BJU Int 115:958n967, 2015.
- Kubitza D, Becka M, Mueck W, et al: Rivaroxaban (BAY 59-7939)-an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor-has no clinically relevant interaction with naproxen, Br J Clin Pharmacol 63:469-476, 2007.
|