Mectizan
Nicholas Lorenzo, M.D. - Neurology Consultants
- Papillion, NE
- Bayway Medical Services
- St. Petersburg, FL
3mg mectizan with mastercardIf the abnormalities persist for 6 to 12 months with out an obvious cause bacteria good and bad purchase mectizan 3mg without prescription, liver biopsy must be thought of antibiotic resistance database cheap 3mg mectizan with amex. Many sufferers with isolated elevation of the alkaline phosphatase level have nonhepatic causes antibiotics for dogs amoxicillin dosage safe mectizan 3mg, similar to being pregnant or bone illness bacteria brutal order 3mg mectizan with mastercard. Serologic studies should embody an antimitochondrial antibody take a look at; a positive result suggests main biliary cholangitis. A cautious historical past identifies sufferers at risk for intrahepatic cholestasis related to drugs or toxins. Essentially all different patients with persistently abnormal alkaline phosphatase ought to obtain a hepatobiliary sonogram or other noninvasive imaging check. Evidence of an intrahepatic mass ought to prompt thorough evaluation for attainable malignancy (Chapter 186). Biliary obstruction also can happen from malignant diseases, including lymphomatous involvement of the lymphatic tissue in the porta hepatis. Infiltrative ailments, including amyloidosis and granulomatous hepatitis (Chapter 142), should be considered. In the absence of proof of biliary obstruction or a trigger identifiable by noninvasive means, liver biopsy should be strongly thought of to complete the analysis of cholestatic liver test abnormalities. In specific, parenchymal issues that current with cholestatic liver take a look at abnormalities might mimic biliary obstruction. A cheap preliminary step is the usage of a noninvasive imaging research (Chapter 124) corresponding to ultrasonography or magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography to determine whether or not the intrahepatic or extrahepatic biliary system, or each are dilated, thereby implying mechanical obstruction. Because of its lesser expense, portability, and convenience, ultrasound is commonly the procedure of choice, particularly if gallstones are suspected. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography could present extra exact resolution, including stricturing of intrahepatic ducts attribute of primary sclerosing cholangitis. However, each of these methods can fail to identify dilated ducts, particularly in patients with cirrhosis. The selection of procedure relies on the suspected site of obstruction (proximal vs. AnA = antinuclear antibody; AmA = antimitochondrial antibody; AsmA = anti�smooth muscle antibody; AlKm = anti�liver/kidney microsomal antibody; ct = computed tomography; mr = magnetic resonance; mri = magnetic resonance imaging. Genetic variations in bilirubin metabolism genes and their affiliation with unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia in adults. Elevated liver enzymes and cardiovascular mortality: a scientific review and dose-response meta-analysis of multiple million members. These data meant that the autumn in plasma bilirubin concentration will must have resulted from a decrease in plasma bilirubin turnover, which, in fact, also declined by 75%. Thus, the fall in bilirubin focus precisely reflected the beneficial effects of steroids on red blood cell survival in this affected person with autoimmune hemolysis. Measurement of urinary coproporphyrin isomers Answer: E Heritable problems of bilirubin metabolism should be thought of within the setting of a mixed or predominately direct hyperbilirubinemia in the absence of evidence of cholestasis. The analysis of Dubin-Johnson syndrome could be established by the measurement of urinary coproporphyrin isomers; the coproporphyrin isomer 1 is generally greater than 80% of whole coproporphyrin focus. A 34-year-old Hispanic woman presents for the preoperative evaluation for cholecystectomy. For the past 3 months, she has experienced episodic, colicky, proper higher quadrant ache. Tests for chronic viral hepatitis and common genetic causes of continual liver illness are all adverse. Liver ultrasonography reveals increased echogenicity of the liver and cholelithiasis without thickening of the gallbladder wall. In addition to cholecystectomy, which of the following choices ought to be beneficial A 51-year-old man presents with 3 months of painless jaundice, pale stools, and darkish urine, in addition to spiking fevers. Abdominal ultrasound shows proximal dilation of the intrahepatic bile ducts, and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography reveals a constricting mass within the widespread bile duct a number of centimeters distal to the junction of the best and left hepatic ducts. After being began on intravenous broad-spectrum antibiotics, the affected person is taken to surgical procedure, where the mass is resected. Two weeks later his complete bilirubin is 14 mg/dL, direct-reacting bilirubin 10 mg/dL, alkaline phosphatase 225, and urine urobilinogen nonetheless undetectable. Because of the persistent direct-reacting hyperbilirubinemia and elevated alkaline phosphatase, the surgeon is contemplating taking the patient again to the operating room and re-exploring his biliary tract. Urine bilirubin Answer: E After successful relief of persistent bile duct obstruction, both the total bilirubin and the alkaline phosphatase might take several weeks to normalize. Although the absence of urobilinogen from the urine on the time of admission mirrored complete bile duct obstruction, its persistence after 2 weeks of broad-spectrum antibiotic remedy not reflects biliary obstruction, but quite elimination by the antibiotics of the micro organism necessary to convert bilirubin in the gut to urobilinogen. In this case, use of a dipstick that detects bilirubinuria might save the affected person from an unnecessary second surgical process. A 24-year-old nurse offered to the worker health division of her hospital complaining of arthralgias, weak point, and fatigue for 2 weeks. Her household history included relations with rheumatoid arthritis and lupus erythematosus. On physical examination, she was pale, with faintly icteric sclerae and a palpable spleen tip. A lupus erythematosus preparation was adverse, but as a outcome of a direct Coombs take a look at was strongly positive, the analysis of autoimmune hemolytic anemia was made. Based on her persistent anemia and reticulocytosis, a rheumatologist argued that the present remedy was ineffective and urged increasing her prednisone dose to 80 mg/day. The hematologist said that she was primarily cured and urged continuation of the current remedy with follow-up in 2 weeks. Which of the next test outcomes led the hematologist to that correct conclusion Other viruses might cause acute inflammatory liver illness, including members of the Herpesviridae household such as human cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, or herpes simplex virus. It is unclear to what extent other viruses, similar to parvovirus B19 or human herpesvirus 6, also can trigger acute hepatitis. Patients who current with an acute viral hepatitis syndrome however negative virologic checks are referred to as having non-A-to-E hepatitis, perhaps attributable to hepatotropic viruses which have but to be identified. Antiviral therapy is indicated just for the treatment of acute hepatitis C, due to the excessive danger (50 to 80%) of chronicity. The different causes of acute viral hepatitis are self-resolving in the vast majority of circumstances. Because not considered one of the hepatotropic viruses is cytopathic, liver damage is mediated by a robust cytotoxic T cell�mediated response towards contaminated hepatocytes that express viral antigens at their surface. Proinflammatory cytokines, natural killer cells, and antibody-dependent mobile cytotoxicity also appear to play a task in liver necroinflammation. Successful immune elimination could lead to viral clearance, which can or may not be associated with lifelong immunity, relying on the infecting agent. The immune response is sometimes so potent that the affected person develops subfulminant and even fulminant hepatitis that requires liver transplantation (Chapter 145). In some patients-the proportion varies, according to the virus liable for acute hepatitis-the immune response fails and persistent an infection is established (Chapter 140).
Cheap 3 mg mectizan with amexIn new child infants antibiotics rash toddler generic mectizan 3 mg, a decreased capacity to conjugate bilirubin leads to virus free music downloads cheap mectizan 3mg on-line unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia (physiologic jaundice of the newborn) antibiotics for dogs home remedy cheap mectizan 3mg with amex. If extreme virus mutation buy mectizan 3 mg mastercard, this hyperbilirubinemia might then result in irreversible central nervous system toxicity. Phototherapy by exposure to gentle in the blue spectrum (390-470 nm) converts bilirubin to water-soluble photoisomers which are readily excreted in bile, thereby protecting the central nervous system from bilirubin toxicity. Enterohepatic Circulation and Excretion of Bilirubin Normal human bile incorporates an average of lower than 5% unconjugated bilirubin, 7% bilirubin monoconjugates, and 90% bilirubin diconjugates. Following canalicular secretion, conjugated bilirubin passes down the gastrointestinal tract with out reabsorption by either the gallbladder or intestinal mucosa. Although some bilirubin reaches the feces, most is converted to urobilinogen and to related compounds by micro organism within the ileum and colon, where the urobilinogen is reabsorbed, returns to the liver via the portal circulation, and is re-excreted into bile in a means of enterohepatic recirculation. Hemolysis will increase the load of bilirubin getting into the gut and due to this fact the amount of urobilinogen fashioned and reabsorbed. Liver illness decreases hepatic extraction of bilirubin; consequently, plasma urobilinogen levels rise and extra urobilinogen is excreted within the urine. Severe cholestasis, bile duct obstruction, or antibiotics that scale back or eliminate the bacterial conversion of bilirubin to urobilinogen markedly lower the formation and urinary excretion of urobilinogen. In these circumstances, unconjugated bilirubin is reabsorbed from the gut, thereby amplifying the hyperbilirubinemia. Increased Bilirubin Production Measurement of Bilirubin in Plasma the total plasma bilirubin focus in normal adults is less than 1 to 1. Modern analytic strategies show that ordinary plasma accommodates principally unconjugated bilirubin, with only a trace of conjugated bilirubin. Clinical laboratories usually quantify plasma bilirubin by a reaction in which bilirubin is cleaved by a diazo reagent, corresponding to diazotized sulfanilic acid, to azodipyrroles which are readily quantitated spectrophotometrically. Unconjugated bilirubin reacts slowly as a end result of the positioning of assault by the diazo reagent is protected by internal hydrogen bonding. Accordingly, accurate measurement of the entire plasma bilirubin concentration requires addition of an accelerator, similar to ethanol or urea, to disrupt this inner hydrogen bonding and to guarantee full reaction of any unconjugated bilirubin. An elevated production of bilirubin and a ensuing unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia could be caused by hemolysis, an accelerated destruction of transfused erythrocytes, resorption of hematomas, or ineffective erythropoiesis owing to lead poisoning, megaloblastic anemias associated to deficiency of both folic acid or vitamin B12, sideroblastic anemia, congenital erythropoietic porphyria, or myeloproliferative or myelodysplastic ailments. In these settings, other liver checks are usually normal and the hyperbilirubinemia is modest, rarely exceeding 4 mg/dL; larger values imply concomitant hepatic dysfunction. However, after brisk blood transfusion or resorption of huge hematomas brought on by trauma, the increased bilirubin load could additionally be transiently adequate to lead to frank jaundice. Besides specific blood problems, mild hemolysis accompanies many acquired diseases. In the setting of systemic disease, which may embrace a degree of hepatic dysfunction, hemolysis may produce a element of conjugated hyperbilirubinemia along with an elevated unconjugated bilirubin concentration. Prolonged hemolysis might lead to the formation of pigmented gallstones that contain calcium salts of bilirubin (Chapter 146). Decreased hepatic bilirubin uptake additionally contributes to the unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia of Gilbert syndrome, though the principal molecular foundation for that syndrome is a reduction in bilirubin conjugation. The most frequent reason for decreased bilirubin clearance is a decrease in bilirubin conjugating exercise. The hereditary hyperbilirubinemias (Table 138-2) are a gaggle of five syndromes in which hyperbilirubinemia occurs as an isolated biochemical abnormality, with out proof of both hepatocellular necrosis or cholestasis. In CriglerNajjar type 1, basically no functional enzyme activity is present, whereas patients with Crigler-Najjar type 2 have as a lot as 10% of regular and patients with Gilbert syndrome have 10 to 33% of normal activity, leading to bilirubin concentrations of 18 to forty five, 6 to 25, and 1. Most cases of Crigler-Najjar varieties 1 and a pair of also come up from homozygous or double heterozygous structural mutations throughout the coding area. Jaundice represents probably the most seen signal of hepatobiliary illness of many causes (Table 138-1). Bilirubin in regular bile: <5% unconjugated bilirubin, with an average of 7% bilirubin monoconjugates and 90% bilirubin diconjugates. Crigler-Najjar kind 1 is characterised by hanging unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia that seems in the neonatal period, persists for life, and is unresponsive to phenobarbital. In Crigler-Najjar Syndrome Type 1 a smaller subset (type 1B), a mutation in the bilirubin-specific exon A1 limits the defect to bilirubin conjugation. Before the availability of phototherapy, most patients with Crigler-Najjar type 1 died of bilirubin encephalopathy (kernicterus) in infancy or early childhood. Optimal remedy for a neurologically intact affected person includes (1) approximately 12 hours/day of phototherapy from start all through childhood, perhaps supplemented by trade transfusion in the neonatal interval; (2) use of tin-protoporphyrin to blunt transient episodes of elevated hyperbilirubinemia; and (3) early liver transplantation, before the onset of mind damage. Bilirubin concentrations are usually decrease in Crigler-Najjar sort 2, and plasma bilirubin ranges may be reduced to 3 to 5 mg/dL by phenobarbital. Although much much less common in CriglerNajjar sort 2, kernicterus has occurred at all ages, usually related to components that quickly raise the plasma bilirubin concentration above baseline. For this reason, phenobarbital remedy is usually recommended; a single bedtime dose usually maintains clinically protected plasma bilirubin concentrations. Gilbert syndrome is the most common type of the hereditary hyperbilirubinemias, with a genotypic prevalence of approximately 12% and a phenotypic prevalence of roughly 7% in whites. Its excessive prevalence could explain the frequency of mild unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia in liver transplant recipients and why population-wide research of bilirubin ranges tend to skew towards greater levels. Plasma bilirubin concentrations are most often less than 3 mg/dL, although both higher and decrease values are frequent, with will increase of two-fold to three-fold commonly occurring with fasting and intercurrent sickness. The phenotypic distinction between mild Gilbert syndrome and a standard state is commonly blurred. Oxidative drug metabolism and the disposition of many, but not all, xenobiotics that are metabolized by glucuronidation seem to be regular in Gilbert syndrome. Peak bilirubin ranges are sometimes lower than 5 to 10 mg/dL, and levels return to normal inside 2 weeks as mechanisms fostering bilirubin disposition mature. Prematurity, with or without hemolysis, is associated with greater bilirubin levels which will require phototherapy.
[newline]The progestational steroid 3,20pregnanediol and certain fatty acids that are present in breast milk (but not serum) of some mothers inhibit bilirubin conjugation and can cause extreme neonatal hyperbilirubinemia (breast milk jaundice). Two phenotypically similar however mechanistically distinct inherited disorders, Dubin-Johnson syndrome and Rotor syndrome, are characterized by conjugated or mixed hyperbilirubinemia with normal values for other commonplace liver exams (see Table 138-2). The process of secretion adopted by reuptake can be concerned within the disposition of drug metabolites and is believed to stop the local saturation of upstream hepatocytes with bilirubin and drug conjugates. Another distinguishing attribute is the gray to black pigment that accumulates in cytosolic lysosomal granules in Dubin-Johnson syndrome and offers the liver a characteristic black appearance. Jaundice is a typical sign of generalized hepatobiliary dysfunction, both acute and chronic. Liver illnesses could be categorized as those by which the first harm outcomes from inflammation and hepatocellular necrosis, inhibition of bile circulate (cholestasis), or a combination of the two. The cholestatic disorders could be further subdivided into those resulting from mechanical obstruction of the bile duct move and people from intrahepatic cholestasis, from a mess of conditions that embody a quantity of familial cholestatic syndromes; infiltrative disorders, inflammatory or neoplastic conditions; and drug-induced liver harm (see Table 138-1).
Cheap 3 mg mectizan with mastercardDieulafoy ulcers antibiotics zinnat buy mectizan 3mg low price, that are small mucosal defects over an intramural arteriole antimicrobial antibiotic discount 3mg mectizan free shipping, can result in bacteria helicobacter order mectizan 3mg line extreme bleeding antimicrobial qualities of silver buy mectizan 3mg visa. Although these lesions can occur all through the gastrointestinal tract, two thirds happen in the abdomen. Colonization with this bacterium is virtually always associated with persistent energetic gastritis, which persists so lengthy as an individual remains colonized and solely slowly disappears 6 to 24 months after bacterial eradication. In creating countries, high colonization rates result in a high prevalence of H. In Western nations, the colonization strain in children has decreased markedly in recent a long time, thereby resulting in a birth-cohort phenomenon for the prevalence of H. The incidence of peptic ulcer disease rose steeply in Western nations within the late 19th and early twentieth centuries and has decreased over the previous forty years; nevertheless, peptic ulceration remains a common disorder. The decline in incidence, associated with a decrease in hospital admissions and surgical procedure for ulcer disease, is believed mostly to mirror the reducing prevalence of gastric colonization with H. It additionally outcomes from the widespread software of eradication therapy, which strongly lowered recurrent ulcers in H. Nevertheless, hospital admissions for issues of ulcers and mortality from ulcer illness have shown a far less marked decline in each the United States and other international locations as a end result of the reduction in H. The predominant age at which duodenal ulcers happen is between 20 and 50 years, whereas gastric ulcers mostly occur in patients older than 40 years. The incidence of gastroduodenal ulcer disease is roughly 1 to 2 per one thousand inhabitants per year. Patients with suspected acid peptic disease are often first treated empirically with acid suppression. Patients with persistent or recurrent symptoms, with new-onset symptoms at an older age, or with alarm symptoms should have H. Treatment should be targeted to heal mucosal breaks, handle the underlying cause, and forestall recurrence. Peptic ulcer illness can be complicated by bleeding, perforation, and stenosis, each of which requires particular assessment and therapy by endoscopy, interventional radiology, or surgical procedure. In most circumstances, these initial information can be utilized to direct additional diagnostic studies (Table 130-1). Gastric mucosa colonized with Helicobacter pylori appearing as curved bacilli on the mucosal surface. More than 50% of patients have a recurrent ulcer within 12 months of therapeutic in the absence of treatment. Maintenance acid suppressive therapy reduces this recurrence price, however only therapeutic measures that take away the underlying reason for the ulcer can stop most ulcer recurrences. Malignant Ulcer Disease Most peptic ulcers are associated with colonization with H. Genome-wide association studies have identified a relationship between polymorphisms in the toll-like receptor gene and the interleukin-1 gene2 with the prevalence of H. Bacterial components that improve mucosal irritation improve the danger for ulcer embody: a high production of the VacA product, which reflects the presence of the s1m1 genotype; a excessive degree of cytokine induction, owing to the presence of genes within the cag pathogenicity island; and enhanced adherence to the gastric epithelium on account of bacterial expression of babA and oipA. At least 2 to 4% of the inhabitants in lots of nations use acetylsalicylic acid, acetic acid derivatives (diclofenac, indomethacin, sulindac), or propionic acid derivatives (ibuprofen, ketoprofen, naproxen) on a day by day basis. Within 14 days after the beginning of such remedy, about 5% of patients develop erosions or ulcers. In patients who continue remedy for 4 weeks or longer, this proportion increases to 10%, however many are clinically silent. Malignant ulcers within the duodenum may outcome from primary duodenal carcinomas or from penetrating pancreatic cancers. In both the stomach and the duodenum, ulcer disease additionally may be attributable to metastatic tumors, together with cancers of the breast, colon, thyroid, or kidney, or by melanoma, disseminated lymphoma, or Kaposi sarcoma. Malignant ulcers are characteristically irregular in form with heaped borders, but they also may be flat or depressed. Current highresolution and magnification endoscopes enable visualization of the altered mucosal construction surrounding an ulcer, together with modifications within the microvascular pattern. Primary gastric adenocarcinomas usually occur in mucosal areas with atrophic and intestinal metaplastic changes. For a particular analysis of malignancy, a number of biopsy specimens are needed, normally from the ulcer margins. A few gastroduodenal ulcers are caused by systemic inflammatory ailments, in particular, Crohn disease (Chapter 132). Patients with Crohn disease affecting the proximal gastrointestinal tract usually have multiple ulcers characterised by irregular longitudinal shapes. The demonstration of ulcerative inflammation elsewhere in the digestive tract, in particular in the terminal ileum and colon, strongly helps the diagnosis of Crohn disease, as do noncaseating granulomas on biopsy specimens. Other inflammatory issues that can trigger gastritis or gastroduodenal ulcers embody numerous types of vasculitis affecting the mesenteric system, specifically Beh�et illness (Chapter 254), Henoch-Sch�nlein purpura (Chapter 254), Takayasu arteritis (Chapters 69 and 254), polyarteritis nodosa (Chapter 254), systemic lupus erythematosus (Chapter 250), Churg-Strauss syndrome (Chapter 254), and granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Chapter 254). Lymphocytic gastroduodenitis, which is strongly related to celiac disease (Chapter 131), might lead to duodenal ulceration and subsequent stenotic internet formation. Ulcer illness additionally could happen in patients with polycythemia vera (Chapter 157), probably in relation to reduced mucosal blood flow. Vasculitis underlying ulcer disease ought to be considered in sufferers with persistent or recurrent ulceration in whom different causes have been excluded. Lymphocytic phlebitis, which is a rare vasculitic inflammatory disorder that impacts the mesenteric veins, could cause gastric ulcers. Systemic amyloidosis (Chapter 179) affecting the abdomen wall may result in gastric ulcers. Rare instances of duodenal ulceration have been described in the presence of annular pancreas or congenital bands obstructing the descending duodenum. The most necessary hypergastrinemic disorder is Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (Chapter 219), a condition of marked hyperacidity resulting in extreme peptic ulcer disease brought on by a gastrin-producing endocrine tumor. These sufferers often have a number of bulbar and postbulbar duodenal ulcers which are resistant to conventional acid suppressive therapy. The prognosis could be confirmed by the presence of a excessive fasting serum gastrin stage (often but not at all times 10-fold elevated and >1000 pg/mL). Similar gastrin ranges are generally seen in sufferers treated for persistent ulcer illness with high-dose proton pump inhibitors. For clarification, secretin testing can be carried out: in patients with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, the injection of secretin (1 U/ kg) will increase serum gastrin levels by greater than 50%, or one hundred twenty pg/mL or higher, in these with fasting gastrin ranges lower than 10-fold above normal. In some sufferers, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome happens as a part of the multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome (Chapter 218), significantly in affiliation with hyperparathyroidism. Other hypergastrinemic hyperacidity syndromes are the retained gastric antrum syndrome (see later) and antral G-cell hyperfunction. Pallor of the mucosa, consistent with decreased mucosal blood move, could additionally be noted at endoscopy. Upper mesenteric ischemia is often related to higher belly ache, which could be elicited by a meal or by physical exercise. These symptoms could cause patients to decrease their food intake, leading to weight reduction before their clinical presentation.
Purchase mectizan 3mg with mastercardHemoglobin concentration and hematocrit could not accurately replicate blood loss as a end result of equilibration with extravascular fluid requires 24 to 72 hours treatment for dogs back legs buy 3mg mectizan with mastercard. A low platelet rely suggests persistent liver disease bacteria in bloodstream discount mectizan 3mg free shipping, dilution bacteria resistant to antibiotics order mectizan 3 mg free shipping, drug reaction virus yardville nj cheap 3 mg mectizan with mastercard, or a hematologic dysfunction. However, this phenomenon could be deceptive in the setting of renal insufficiency or rapid transit of blood. Large-bore (14- or 16-gauge) intravenous catheters are recommended, with normal saline infused as fast as essential to preserve hemodynamic stability. General pointers are additionally to use blood products as needed to maintain the platelet count above 50,000/�L and the international normalized ratio below 2. To forestall aspiration, which might trigger considerable morbidity and mortality, endotracheal intubation must be thought of in sufferers with lively hematemesis or altered psychological standing. Endoscopy can identify the positioning of bleeding and supply therapeutic hemostasis in most patients. Patients with proof of active bleeding (hematemesis red blood by nasogastric lavage, or hemodynamic instability) ought to endure emergency endoscopy as soon as possible (within 12 hours) after medical resuscitation. An intravenous prokinetic agent (either erythromycin, 250 mg, or metoclopramide, 10 mg) 30 to 60 minutes earlier than endoscopy may assist move blood out of the stomach and into the small gut, enhancing endoscopic visualization. In addition to localization of the bleeding supply, endoscopic analysis can present prognostic info and stratify the chance of rebleeding on the basis of the presence or absence of stigmata of recent hemorrhage (Table 126-2). Retroflexed endoscopic image of a Mallory-Weiss tear on the gastroesophageal junction. Other lesions had been surgical anastomoses, Cameron ulcers, aortoenteric fistulas, and hemobilia. No cause present in esophagus, abdomen, or duodenum, however 2% had mouth, nostril, or pharyngeal bleeding websites. Recurrent bleeding after endoscopic therapy immediately will increase mortality, raises transfusion requirements, and prolongs hospitalization. Independent predictors of recurrent hemorrhage after successful endoscopic therapy embrace: hemodynamic instability, comorbid sickness, posterior duodenal location, and enormous ulcer dimension. Persistence of a positive Doppler signal after endoscopic remedy correlates with rebleeding, and Doppler probe� guided endoscopic hemostasis significantly reduces 30-day rebleeding rates compared with commonplace, visually guided hemostasis. Clinical scoring systems, such as the Rockall score (Table 126-3), use medical information and endoscopic findings to predict clinical outcomes. The objective of endoscopic remedy is to cease acute bleeding and to scale back the risk of recurrent bleeding. Available therapies embrace injection (epinephrine or sclerosants), thermal coagulation (with multipolar/bipolar or heater probe), and mechanical compression (hemostatic clips). When epinephrine injection is mixed with both thermal coagulation or hemoclips, hemostasis is achieved in additional than 95% of sufferers with lively bleeding, and rebleeding charges are decreased by more than 50%. A2 A system with a bigger, over-the-scope-clip may be helpful for re-treating patients who rebleed after initial hemostasis. Patients with documented Helicobacter pylori infection ought to be treated with combination antibiotics and a proton pump inhibitor (Chapter 130). Proton pump inhibitors (see Table 129-1) are the mainstay of medical remedy for hemostasis and therapeutic of peptic lesions. Acid suppression can promote platelet aggregation and clot formation in addition to reduce the chance of rebleeding. High-dose intravenous proton pump inhibitors (bolus adopted by continuous infusion [e. For patients with highrisk stigmata, either this similar routine or intermittent high-dose proton pump inhibitor therapy may be equally effective. A4 Patients with low-risk or no stigmata could be handled with an oral proton pump inhibitor. However, patients who proceed low-dose aspirin have a significantly lower mortality price in contrast with the placebo group due to lower charges of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular complications. Management of sufferers with severe hematochezia-with all current proof available. Patients are usually older and present with painless hematochezia, usually without orthostasis. The most typical explanation for extreme colorectal hemorrhage is from diverticulosis (Chapter 133). Other frequent causes include inner hemorrhoids (Chapter 136), ischemic colitis (Chapter 134), rectal ulcer (Chapter 136), and delayed bleeding from post-polypectomy ulcers at a median of 8 days (range, 5 hours to 17 days) after the process (Table 126-4). Colonoscopy is important for identifying a luminal supply of bleeding in addition to for potential hemostasis of amenable lesions. To cleanse the colon adequately and to visualize the colonic mucosa, a bowel purge with 6 L or more of a polyethylene glycol resolution must be administered before the procedure. If each are adverse, capsule endoscopy (Chapter 125), whether it is locally obtainable, may be the popular way to search for a small intestinal source of bleeding. The purple blood cell scan may help localize bleeding if it occurs at a fee of a minimal of 0. Angiography has the advantage that it might possibly treat the bleeding source with embolization of the bleeding vessel. Neither red blood cell scans nor angiography can establish nonbleeding stigmata, and usually neither yields an etiologic analysis. The primary indications for surgery are malignant lesions (Chapters 136 and 184), diffusely bleeding lesions that fail to reply to medical remedy (such as ischemia; Chapter 134), and recurrent diverticular hemorrhage (Chapter 133). If the bleeding supply may be localized preoperatively to a particular space of the colon, a segmental resection may be carried out somewhat than a subtotal colectomy. Iron deficiency (Chapter 150) has a prevalence of 2 to 5% amongst grownup men and postmenopausal girls. It must be suspected in patients with low mean corpuscular volume, low ferritin degree, or low transferrin saturation. If the first process is unremarkable, analysis ought to be undertaken from the other end. If the capsule endoscopy is unfavorable and rapid rebleeding recurs, a tagged pink blood cell scan or angiography could also be used to localize the bleeding website and help with subsequent intraoperative enteroscopy. Upper endoscopy and push enteroscopy should follow if the colonoscopy is unremarkable. Afterward, the algorithm is similar as for overt bleeding; however, if the capsule endoscopy is adverse, efforts ought to be focused towards providing supportive care somewhat than further evaluation. Doppler endoscopic probe monitoring of blood move improves risk stratification and outcomes of sufferers with extreme nonvariceal upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Intermittent vs steady proton pump inhibitor therapy for high-risk bleeding ulcers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Colonoscopy must be carried out first, followed by higher endoscopy and push enteroscopy if the colonoscopy is unfavorable.
Mectizan 3mg without a prescriptionIn the inpatient setting antibiotics for acne and eczema order mectizan 3 mg otc, intravenous magnesium sulfate (1 to 2 g every 6 hours) can be used for repletion antimicrobial uniforms discount mectizan 3 mg with amex. Because the redistribution of magnesium from extracellular to intracellular compartments is relatively slow bacteria 7th grade cheap 3mg mectizan overnight delivery, the serum magnesium focus may normalize earlier than complete physique magnesium shops are replete infection trichomoniasis 3 mg mectizan with amex. It is subsequently prudent to proceed intravenous magnesium for a further 1 to 2 days after restoration of normomagnesemia. In patients with regular renal function, any extra magnesium is just excreted renally. Adverse effects from intravenous magnesium administration are primarily because of transient hypermagnesemia and embrace flushing, hypotension, and flaccid paralysis. However, in patients with persistent magnesium losing, corresponding to in Gitelman syndrome (Chapter 119), it might be difficult to sustain with the continued losses with oral therapy. Fortunately, these people are inclined to adapt to their continual hypomagnesemia and tolerate it fairly well. Transient hypermagnesemia can happen in patients given massive doses of intravenous magnesium, for instance, in the setting of preeclampsia. Phosphate is frequently depleted in alcoholism (Chapter 30) because of the consumption of a carbohydrate-rich, phosphate-poor food plan, as properly as renal phosphate wasting. Divalent cation-containing antacids bind phosphate in the intestinal lumen to kind insoluble salts, thereby stopping their absorption. Vitamin D deficiency also leads to decreased intestinal phosphate absorption and therefore to hypophosphatemia. Respiratory however not metabolic alkalosis (Chapter 110) may cause transient hypophosphatemia. In this disorder, intracellular pH is increased, thereby stimulating glycolysis, which depletes the intracellular inorganic phosphate pool and results in a shift of phosphate into cells. The reason for hypophosphatemia is commonly evident from the historical past and physical examination. Similarly, in malnourished sufferers (Chapter 203), whose complete physique phosphate stores may be depleted, overzealous intravenous refeeding with carbohydrate-rich fluids could stimulate insulin release and cause acute hypophosphatemia. The tyrosine kinase inhibitors imatinib, sorafenib, and nilotinib, which are used within the treatment of various cancers (Chapters 169 and 175), can cause profound hypophosphatemia, which appears to be due both to inhibition of bone resorption or a partial Fanconi syndrome. Renal phosphate losing is normally due to impaired proximal tubule phosphate reabsorption. In major hyperparathyroidism (Chapter 232), hypercalcemia is often related to hypophosphatemia. Phosphaturia can also happen with diuretics, notably carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, and with antimicrobial brokers such as pentamidine and foscarnet. Oncogenic osteomalacia is a paraneoplastic syndrome (Chapters 169 and 231) related primarily with mesenchymal tumors that secrete quite lots of phosphaturic factors collectively generally identified as phosphatonins. A comparable phenotype is present in X-linked and autosomal dominant hypophosphatemic rickets; these inherited disorders are characterized by an increase in a circulating phosphatonin known as fibroblast growth factor-23. Phosphatonins inhibit each renal tubular phosphate reabsorption and 1-hydroxylation of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol, thereby resulting in hypophosphatemia, rickets, or osteomalacia (Chapter 231) and inappropriately low serum ranges of 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol. Finally, patients undergoing renal alternative remedy by steady venovenous hemodiafiltration often turn into phosphate-depleted and wish ongoing replacement. Manifestations of extreme hypophosphatemia embrace encephalopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy, generalized muscle weak point that may lead to respiratory failure, rhabdomyolysis, and hemolysis. Hypophosphatemia also impairs renal ammoniagenesis and reduces the provision of urinary buffer, thereby impairing renal acid excretion and causing metabolic acidosis. Oral repletion can be achieved with sodium or potassium phosphate salts (1 to 2 g/day) or with skimmed milk. Hypophosphatemia in patients on continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration may be ameliorated by way of phosphate-containing dialysate and substitute solutions. The phosphorus in some laxatives and enemas may be absorbed and trigger hyperphosphatemia. Intoxication with vitamin D or its analogues increases intestinal absorption of each calcium and phosphorus. Patients with diabetic ketoacidosis (Chapter 216) are sometimes hyperphosphatemic at initial evaluation because of the redistribution of phosphate out of cells in the insulin-deficient state. Decreased phosphate excretion is most commonly as a result of acute or persistent renal failure (Chapter 121). With a normal diet, serum phosphate levels may be maintained throughout the normal range until the glomerular filtration price falls under 25 mL/ minute. Finally, because parathyroid hormone stimulates proximal tubule phosphate excretion, main hypoparathyroidism (Chapter 232) is often associated with gentle hyperphosphatemia together with hypocalcemia. Acute hyperphosphatemia will increase the chance for precipitation of calcium phosphate and subsequent metastatic calcification in gentle tissues, together with the kidney, during which it can cause acute renal failure. In the continual hyperphosphatemia of persistent renal insufficiency, sufferers with a serum phosphate concentration higher than 6. Hyperphosphatemia on this setting is a danger factor for coronary and different vascular calcification, which is associated with elevated mortality. In symptomatic sufferers and people with impaired renal perform, phosphate ought to be eliminated by extracorporeal remedy. Because of the gradual fee of phosphate mobilization from intracellular shops, steady venovenous hemodiafiltration is significantly simpler than intermittent hemodialysis. Chronic hyperphosphatemia (Chapter 121) may be managed by minimizing dietary phosphorus intake8 and administering oral phosphate binders such as calcium salts. Data recommend that non�calcium-based phosphate binders A1 and particularly sevelamer A2 might cut back all-cause mortality compared with calcium-based binders in patients with chronic kidney illness. Severe acute hyperphosphatemia could be life-threatening owing to metastatic calcification and multiorgan failure, but it generally responds properly to prompt therapy. Chronic hyperphosphatemia in sufferers with persistent kidney failure (Chapter 121) is usually pretty resistant to remedy, significantly in poorly compliant individuals, and is related to elevated long-term mortality. Effect of calcium-based versus non-calcium-based phosphate binders on mortality in patients with continual kidney illness: an up to date systematic review and meta-analysis. Magnesium and well being outcomes: an umbrella evaluate of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational and intervention research. Serum magnesium concentrations and all-cause, cardiovascular, and most cancers mortality among U. Phoxilium() reduces hypophosphataemia and magnesium supplementation during continuous renal substitute therapy. Admission hyperphosphatemia increases the danger of acute kidney damage in hospitalized sufferers. Routine laboratory examination revealed the following: serum sodium 133 mEq/L, potassium 2. Answer: B this patient has hypophosphatemia, hypokalemia, a possible hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis, hypouricemia, and glycosuria with out hyperglycemia. Tenofovir can also cause acute tubular necrosis and acute kidney harm, but these medical syndromes would are likely to enhance the serum phosphate focus.
Generic mectizan 3 mg onlineIn sufferers whose response is equivocal virus chikungunya discount mectizan 3mg on line, an extended proton pump inhibitor trial of 4 to 8 weeks antibiotics for acne and probiotics 3mg mectizan visa, endoscopy infection quality control staff in a sterilization unit of a hospital buy discount mectizan 3 mg on-line, or 24-hour pH testing could be thought-about antimicrobial agents generic mectizan 3 mg visa. Esophageal motility issues (Chapter 129), similar to high-amplitude contractions ("nutcracker esophagus") or diffuse esophageal spasm, can be recognized by highresolution esophageal manometry, but the low concordance between signs and manometric findings means that such testing ought to be performed only in extremely chosen patients primarily based on the recommendation of a gastroenterologist. For each useful chest ache and functional heartburn, low-dose tricyclic antidepressants. Even in the absence of a particular psychiatric diagnosis, belly breathing, mindfulness-based stress reduction, or cognitive-behavioral therapy could additionally be of profit. In the affected person with practical chest ache, hypervigilance and fears of cardiac illness must be addressed explicitly, and the importance of a negative cardiac analysis have to be reinforced. If the practical chest pain is conscious of a proton pump inhibitor trial, patients ought to be continued on such remedy or handled with various acid-suppressing medications. However, each practical chest ache and practical heartburn have a benign prognosis, although signs might persist and continue to diminish quality of life. Low fermentable, oligo-, di-, mono-saccharides and polyol food plan in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: a scientific review and meta-analysis. Interactions between the microbiota, immune and nervous techniques in well being and illness. Doctor-patient relationship and high quality of life in irritable bowel syndrome: an exploratory research of the potential mediating function of illness perceptions and acceptance. Effect of antidepressants and psychological therapies in irritable bowel syndrome: an updated systematic evaluation and meta-analysis. Effects of antidepressants on gastric perform in patients with useful dyspepsia. It also relaxes transiently throughout regular features, similar to belching and vomiting. The vagus nerve, acetylcholine, and nitric oxide affect tone, but the lower esophageal sphincter tone is influenced by the crural diaphragm as the esophagus traverses the diaphragmatic hiatus. The mucosa is a stratified squamous nonkeratinized epithelium that transitions to a columnar epithelium on the gastroesophageal junction. The muscular layer of the esophagus is composed of striated muscle in the higher one third and smooth muscle in the decrease two thirds. These muscular components are organized as an inner round and an outer longitudinal layer. Located between the round and longitudinal muscle layers is Auerbach (myenteric) plexus, whereas Meissner plexus is positioned inside the submucosa and innervates the muscularis mucosae. The esophagus is sure by an upper esophageal sphincter proximally and the decrease esophageal sphincter distally. The upper esophageal sphincter contains useful contributions from the inferior pharyngeal constrictor proximally and the cricopharyngeus distally. By distinction, the decrease esophageal sphincter is anatomically and histologically indistinguishable from the lower esophagus. Blood provide for the cervical portion is derived from branches of the inferior thyroid artery. The intrathoracic section of the esophagus receives its blood supply from bronchial arteries and direct branches from the aorta, and the left gastric and the inferior phrenic arteries provide the belly portion of the esophagus. Venous drainage follows the arterial supply in the cervical and stomach parts, whereas the thoracic esophagus drains into the azygous and hemiazygos system. Likewise, the lymphatic drainage of the esophagus is segmental, with the cervical portion draining into deep cervical lymph nodes, the thoracic portion into the superior and posterior mediastinal lymph nodes, and the stomach portion into the gastric and celiac lymph nodes. The motor capabilities of the esophagus are to transport a meals bolus from the oropharynx into the abdomen and then to maintain food from returning to the esophagus after it has entered the stomach. The upper esophageal sphincter and the proximal third of the esophagus compose the primary portion of the esophagus. The recurrent laryngeal nerve inferiorly and a pharyngeal plexus superiorly provide the higher esophageal sphincter, which is roughly 2 to 4 cm in size. The muscle layers shut the esophageal lumen and shorten the esophagus to facilitate forward transport via the proximal esophagus. After meals traverses the proximal esophagus, it strikes into the distal two thirds of the esophagus, where peristalsis is achieved by sequential muscular contraction mediated via an interaction of inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmitters. Although native mechanisms control most esophageal motor operate, vagal input is necessary within the distal esophagus, where clean muscle myopathies and autonomic neuropathies could cause dysfunction. The distal esophagus is separated from the stomach by the decrease esophageal sphincter, which is four to 5 cm in size and is functionally distinct as a outcome of it maintains a tonic high-pressure zone. Barium esophagography (Chapter 124) reveals both anatomic and physiologic details about luminal lesions, similar to malignancies, ulceration, diverticula, hiatal hernia, and strictures; intramural lesions, such as leiomyomas; and extrinsic lesions, such as happen from vascular (aorta, proper atrium, subclavian artery) impingement or solid lesions (pulmonary malignancy, adenopathy) that compress the esophagus. Radiography can also be a wonderful software for finding out motility patterns, corresponding to peristalsis with either liquid or solid distinction materials, while exactly visualizing how the esophagus handles a bolus rather than by implying perform from pressure or impedance changes. High-resolution esophageal manometry measures stress adjustments generated by esophageal wall contraction and changes in tone using multiple sensors that concurrently measure pressure from the pharynx to the lower esophageal sphincter. Air, which is a poor conductor of electrical current, will yield excessive impedance, whereas swallowed or refluxed liquids, that are excellent conductors of electrical energy, will generate a low impedance sign. From these measurements, the course and velocity of the transport of air and bolus may help assess peristaltic function and the reflux of acid and nonacid gastric contents. Impedance can also mirror site-specific esophageal mucosal permeability, thereby offering further insight into mucosal integrity and disease in inflammatory or metaplastic conditions. Symptoms of Esophageal Disease the commonest symptom of esophageal disease is heartburn, which is outlined as a sensation of substernal burning. Chest pain without typical heartburn may occur in quite lots of esophageal disorders, including gastroesophageal reflux and motor issues such as in achalasia. However, esophageal ache and even heartburn could be indistinguishable from cardiac angina (Chapter 45), so care should be taken when a patient at risk for coronary artery illness complains of heartburn for the first time. Dysphagia, or problem swallowing, is one other cardinal symptom of esophageal disease. Dysphagia with solely strong food tends to occur with structural lesions, which trigger esophageal constriction, whereas dysphagia with each liquids and solids occurs extra often with motility issues. Patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia will commonly complain of a feeling of meals "sticking" in the throat or the shortcoming to propel the bolus from the mouth to the pharynx; they might also complain of the necessity for multiple swallowing motions to clear the bolus. Since the cranial nerves that generally control the initial phases of swallowing are answerable for different features as properly, symptoms that could be associated with oropharyngeal dysphagia embrace drooling, dysarthria (due to tongue dysfunction), nasal regurgitation (due to failure to seal off the nasal passage), or coughing and aspiration (due to failure to elevate and canopy the laryngeal vestibule). Dysphagia can also lead to a selection of behavioral accommodations, together with maneuvers corresponding to sluggish eating, meals aversion, avoidance of exhausting solid meals, and consuming of enormous quantities of liquids with stable meals. Regurgitation, which is one other typical esophageal symptom, may be described as the sensation of meals developing into the chest or, extra dramatically, into the mouth. Regurgitation later in the meal suggests a motility abnormality similar to achalasia. When impaction occurs in the oropharynx, patients may develop a "steakhouse" syndrome, by which an impacted food bolus results in tracheal impaction or compression.
Buy discount mectizan 3mg on-lineMild to reasonable chronic or intermittent signs that have been current for a long interval can be evaluated in a deliberate fashion antibiotics for uti how long does it take to work cheap mectizan 3 mg line. Complaints which have been ongoing for years rarely are attributable to readily remedied structural disorders antibiotics effective against strep throat purchase 3mg mectizan. A particular prognosis could be established in most sufferers after a focused history bacteria 2 in urine test 3 mg mectizan with visa, physical examination antibiotics for uti septra generic mectizan 3mg without prescription, and laboratory testing, in addition to acceptable radiographic and endoscopic imaging. The scientific historical past should focus on the acuity, severity, location, length, and pattern of signs, in addition to their relationship with meals and bowel movements. The previous medical historical past should elicit endocrine, cardiovascular, and neuromuscular disorders, together with drugs that may cause symptoms or improve the danger of diagnostic research (including endoscopy). The stomach examination contains inspection, percussion, and light and deep palpation to detect hernias, distention, abdominal tenderness, peritoneal irritation, an enlarged liver or spleen, abdominal masses, and ascites. Routine blood exams embody an entire blood depend, liver checks, and serum chemistries. Further analysis with radiologic imaging (commonly stomach ultrasound, computed tomography, or magnetic resonance imaging) and endoscopy (commonly upper endoscopy or colonoscopy) is guided by the suspected underlying disorder. For elderly, disabled, or marginally housed sufferers, it may be very important elicit how they acquire and put together their meals and the way they entry rest room services. A general survey must be carried out to assess for indicators of weight reduction (fat and muscle wasting), malnutrition (dry or thin pores and skin, hair loss, edema, anasarca), and vitamin deficiencies (pellagra, scurvy). An oral examination appears for mucocutaneous candidiasis (which might mirror immunosuppression), ulcerations (which might reflect inflammatory bowel disease, vasculitis, viral an infection, or vitamin deficiencies), and glossitis or angular cheilitis (which might reflect vitamin deficiencies). Examination of the lungs and cardiovascular system ought to give attention to evidence of circumstances which may improve the chance of moderate sedation in the event that endoscopy is required (respiratory insufficiency, coronary heart failure) and of circumstances that enhance the risk of intestinal ischemia (atrial fibrillation, valvular coronary heart disease, peripheral vascular disease) (Chapter 134). Superficial or deep lots ought to be assessed for dimension, location, mobility, content (solid, liquid, or air), and the presence or absence of tenderness. Superficial plenty embody hernias, lymph nodes, subcutaneous abscesses, lipomas, and hematomas. Neoplasms (liver, gallbladder, pancreas, abdomen, gut, kidney), abscesses (appendicitis, diverticulitis, Crohn disease), or aortic aneurysms may characterize deep abdominal lots. Examination of the best upper quadrant should assess the liver size, contour, texture, and tenderness. Liver size is crudely estimated by percussion of the upper and decrease borders of liver dullness within the midclavicular line. Liver contour and tenderness are finest assessed during held inspiration by deep palpation alongside the costal margin. The tip of an enlarged spleen could also be palpated throughout inspiration if the examiner supports the left costal margin with the left hand while palpating under the costal margin with the best hand. Ascites ought to be suspected in a affected person with a protuberant abdomen and bulging flanks. To display for ascites, percussion of the flanks ought to be carried out to assess the level of dullness. If the extent of flank dullness seems to be elevated, probably the most delicate take a look at for ascites is to examine for "shifting" dullness when the patient rolls from the supine to the lateral position. Digital Rectal and Pelvic Examinations the digital rectal examination is intrusive and uncomfortable and should be carried out solely when needed, such as in patients with perianal or rectal symptoms, incontinence, tough defecation, suspected inflammatory bowel disease, and acute belly pain. The perianal space must be visually inspected for rashes, soilage (suggesting incontinence or fistula), fistulas, fissures, pores and skin tags, exterior hemorrhoids, and prolapsed inner hemorrhoids (Chapter 136). After mild digital insertion, the anal canal should be assessed for resting tone and voluntary squeeze. The distal rectal vault should be swept circumferentially to palpate for mass lesions, tenderness, or fluctuance. Laboratory Studies Blood Tests Abdominal Examination the stomach examination begins with a visible inspection of the abdomen and inguinal area for scars (due to prior surgeries or trauma), asymmetry (suggesting a mass or organomegaly), distention (due to weight problems, ascites, or intestinal ileus or obstruction), outstanding periumbilical veins (suggesting portal hypertension), or hernias (umbilical, ventral, inguinal). The examination proceeds with auscultation adopted by percussion, and it ends with light and deep palpation. In sufferers without abdominal pain, auscultation of bowel sounds to assess intestinal motility has limited usefulness and may be omitted. Percussion could also be performed before or at the side of mild and deep palpation. Initial cursory gentle percussion across the higher, mid, and lower abdomen is beneficial to denote areas of dullness and tympany as well as to elicit unanticipated areas of ache or tenderness before palpation. More extensive percussion offers restricted however useful details about the dimensions of the liver and spleen, gastric or intestinal distention, bladder distention, and ascites (Chapters 137 and 144). Gentle, light palpation promotes stomach leisure and allows the detection of muscle resistance (guarding), stomach tenderness, and superficial plenty of the stomach wall or abdomen. A low platelet count could additionally be attributable to portal hypertension with splenic sequestration. Abnormal liver test results could additionally be because of acute or persistent liver ailments, issues of the pancreas or biliary tract, and medicines (Chapter 138). Serum amylase and lipase are obtained to display screen for pancreatitis (Chapter 135) in sufferers with acute stomach pain. Increased levels of inflammatory markers, similar to an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation fee and C-reactive protein, are nonspecific however useful in the administration of patients with inflammatory bowel illness (Chapter 132). Deficiencies in the fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) (Chapter 131) might mirror issues of malabsorption that result in steatorrhea. Serum B12 could additionally be decreased in sufferers with autoimmune gastritis (pernicious anemia), gastric bypass surgery, or malabsorption due to small bowel bacterial overgrowth or disease of the terminal ileum. In sufferers with acute diarrhea, assessment of fecal leukocytes or culture of widespread pathogens is routine, and in chosen patients, testing for parasites (Giardia, Entamoeba histolytica), Clostridium difficile, Escherichia coli O157:H7, or different specific organisms could also be warranted. In many medical settings, commercially available molecular diagnostic checks can display patients with acute diarrhea for a defined panel of micro organism, viruses, and parasites, and provide results within 1 to 5 hours. Esophageal manometry and esophageal pH and impedance monitoring could be helpful for the analysis of heartburn, reflux, and other esophageal signs (Chapter 129). Anorectal manometry could also be useful in some sufferers with fecal incontinence and defecatory dysfunction (Chapter 136). Thereafter, the emphasis should swap from finding a "cause" of the signs to implementing successful coping and adaptive behaviors. Abdominal ache, which is a frequent complaint among outpatients within the workplace setting and emergency division, may be benign and self-limited or the presenting symptom of severe, life-threatening illness. By distinction, most sufferers with severe acute abdominal ache require an intensive but emergent evaluation, which can shortly reveal an acute surgical illness (Chapter 133). Stimulation of hole belly viscera is mediated by splanchnic afferent fibers inside the muscle wall, visceral peritoneum, and mesentery which are delicate to distention and contraction. Visceral afferent nerves are loosely organized, innervate several organs, and enter the spinal twine at several ranges. Thus, visceral pain is vague or dull in character and diffuse; patients trying to localize the ache often move their whole hand over the upper, center, or decrease stomach.
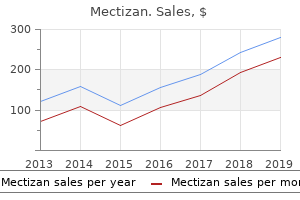
Mectizan: 12 mg, 6 mg, 3 mg
Order 3mg mectizan mastercardPatients require emergent endoscopy to decide the diploma of harm virus game online purchase 3 mg mectizan otc, which helps predict long-term prognosis virus lokal mectizan 3 mg low cost. Many sufferers will have lifelong disease marked by persistent strictures that require frequent dilation and even esophageal reconstruction virus definition discount 3mg mectizan fast delivery. In sufferers with a severe preliminary harm antibiotics for uti prevention order 3mg mectizan free shipping, the chance for esophageal most cancers is significantly elevated. The most typical neurologic cause of oropharyngeal dysphagia is a cerebrovascular accident (Chapter 379). Other neuropathic issues that may also affect function embody myasthenia gravis (Chapter 394), brain stem tumors (Chapter 180), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (Chapter 391), Parkinson illness (Chapter 381), Alzheimer illness (Chapter 374), postpolio syndrome (Chapter 355), Guillain-Barr� syndrome (Chapter 392), and botulism (Chapter 280). Myogenic problems that cause dysfunction embody paraneoplastic antibody-mediated syndromes (Chapter 169), thyroid illness (Chapter 213), main myopathies (Chapter 393) corresponding to dermatomyositis and inclusion body myositis, and medicines that trigger myopathy corresponding to statins and amiodarone. Patients with oropharyngeal abnormalities experience dysphagia, often accompanied by postprandial coughing, hoarseness, and aspiration pneumonia. Treatment focuses on the underlying myopathic or neurologic trigger and swallowing therapy, but prognosis is often poor owing to limited remedy choices. Achalasia Achalasia, which is the prototypic esophageal motility dysfunction, is characterised by inadequate relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter accompanied by loss of esophageal peristalsis. Achalasia can happen in sufferers of almost any age, from infants to nonagenarians, however it mostly presents between 30 and 60 years of age. The prevalence is 10 per 100,000 in the United States, with all races affected and an equal distribution in men and women. The pathophysiology of achalasia more than likely displays an antibody-mediated autoimmune myenteric plexopathy in the lower esophageal sphincter and a generalized neuropathy in the esophageal physique. Injury to the decrease esophageal sphincter neurons results in a relative selective deficiency of nitric oxide. With this loss of the primary practical inhibitory neurotransmitter, the sphincter loses its capability to chill out. The cardinal signs of achalasia are dysphagia to each liquids and solids, regurgitation, and chest pain. Some patients may have more delicate signs, including heartburn, presumably brought on by esophageal stasis of acidic meals content, weight loss, and aspiration pneumonia; in these settings, prognosis is often delayed. Whether classification methods primarily based on manometric findings can predict response is being studied. Endoscopy is really helpful to exclude secondary causes of achalasia, corresponding to gastroesophageal junctional cancer. Occasionally, sufferers current with a massively dilated esophagus and marked food retention. Radiographically, these sufferers develop a "sigmoid" esophagus with a radiographic image much like a sigmoid colon. Because extended contact is an essential part of the injury, predisposing factors for pill-induced harm embody anatomic limitations, similar to a stricture, a outstanding aortic arch that compresses the esophagus, or improper ingestion of the tablet because of inadequate fluid or improper positioning. The commonest medications are tetracycline and its derivatives, but different generally implicated medications include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, bisphosphonates, ferrous sulfate, quinidine, and potassium chloride. Radiographic or endoscopic findings could vary from discrete ulceration to diffuse esophagitis. Treatment is generally supportive with discontinuation of the treatment till the injury resolves. Patients should be given careful instructions to avoid mendacity down immediately after ingesting medication and to drink sufficient fluids to prevent harm. Barium esophagogram exhibiting a "corkscrew" esophagus in a affected person with diffuse esophageal spasm. In sufferers with underlying paraneoplastic malignancy, treatment of the tumor could additionally be useful, and botulinum toxin has been tried with anecdotal success. Achalasia may symbolize a paraneoplastic presentation of some malignancies, significantly small cell lung cancer (Chapter 182); in these patients, the tumor produces an antineuronal antibody (anti-Hu) that mediates the autoimmune lower esophageal sphincter plexopathy and produces a syndrome similar to major achalasia. Some tumors, corresponding to proximal gastric most cancers, may metastasize to or instantly prolong into the lower esophageal sphincter and produce an achalasia-like picture, probably owing to extrinsic compression or tumor infiltration. Recurrent signs could also be related to an incomplete myotomy, herniation or unwrapping of the fundoplication, esophageal strictures, Barrett esophagus, or simply the pure historical past of the illness. Classically, patients have symptoms of intermittent chest pain (Chapter 128), dysphagia, or both. On endoscopic ultrasound, patients may show thickening of the circular and longitudinal muscle layers. Diffuse esophageal spasm is outlined manometrically by premature fast contractions in a minimal of 20% of all swallows, accompanied by normal peristalsis. In pneumatic dilation, a 30- to 40-mm pneumatic balloon is placed fluoroscopically to straddle the decrease esophageal sphincter; the balloon is then inflated to tear the muscle fibers of the lower esophageal sphincter. In common, one pneumatic dilation will obtain 5 years of symptomatic remission in 70% of sufferers, and three dilations will succeed in 90% of sufferers. The downside of this procedure is the danger for perforation, which happens in as a lot as 2% of sufferers, even in skilled palms. The third method is a Heller myotomy, which is now usually carried out laparoscopically. This long myotomy begins at least 2 cm under the lower esophageal sphincter and extends for about 6 cm upward past the sphincter; a unfastened fundoplication is carried out to forestall gastroesophageal reflux. Randomized controlled trials recommend that both pneumatic dilation or Heller myotomy will present comparable scientific results over 2 years. Early outcomes together with 5-year follow-up knowledge are encouraging,20 however reflux is noticed in roughly 50% of sufferers. As a end result, sufferers should concentrate on this issue when selecting between the endoscopic and laparoscopic approaches. Empirical remedy may be tried with agents that loosen up smooth muscle or augment the nitric oxide content material, similar to hyoscyamine (0. Both are characterised by high-amplitude peristaltic contractions and are of unsure clinical significance. Antisecretory remedy with proton pump inhibitors (see Table 129-1) is usually warranted. Isolated incomplete leisure of the decrease esophageal sphincter, also called esophagogastric junction outflow obstruction, could represent a variant of achalasia and should be treated as such in patients with dysphagia. This entity also could also be seen with structural and vascular abnormalities within the vicinity of the gastroesophageal junction. The lower in cross-sectional area of the higher esophageal sphincter is likely brought on by fibrosis. This condition could additionally be asymptomatic or accompanied by signs of oropharyngeal dysphagia to solids.
References - Kaklamani VG, Kaklamanis PG: Treatment of Behcetis diseasenan update, Semin Arthritis Rheum 30:299n312, 2001.
- Lund KL. Menopause and the Menopausal Transition. Medical Clinics of North America. 2008;92:1253-71.
- Wilt TJ, Brawer MK, Jones KM, et al: Radical prostatectomy versus observation for localized prostate cancer, N Engl J Med 367(3):203n213, 2012.
- Ganguly N, Waller S, Stasik CJ, et al. Giant anal condylomatosis after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: a rare complication of human papilloma virus infection. Transpl Infect Dis. 2008; 10(1):56-58.
|