Metoprolol
Thomas F. Slaughter, MD, MHA, CPH - Professor and Head, Section on Cardiothoracic Anesthesiology
- Wake Forest University School of Medicine
- Winston-Salem, North Carolina
Purchase metoprolol 100mgDiagnostic paracentesis consists of obtaining a small quantity of peritoneal fluid for culture to rule out infection and to characterize the fluid as a transudate or exudate blood pressure calculator purchase metoprolol 50mg amex. Therapeutic paracentesis is a technique that removes a big quantity of ascites (typically in extra of 2 L) to scale back intra-abdominal stress and deal with the ensuing stomach discomfort and dyspnea blood pressure chart diabetes buy 50 mg metoprolol with visa. Ultrasound guidance for paracentesis in patients with ascites ends in higher success in acquiring fluid compared to hypertension and heart disease trusted metoprolol 50mg traditional methods blood pressure medication overdose symptoms order 50 mg metoprolol fast delivery, 95% versus 61%. The common space of the puncture web site is localized 2�3 cm medial and 2�3 cm cephalad to the anterior iliac spine within the left decrease quadrant. Skin preparation and sterile draping of the world and use of the ultrasound probe is performed adopted by insertion of the paracentesis needle. The paracentesis catheter is left in place to obtain elimination of the desired diagnostic sample or to reduce intraabdominal pressure. In the emergency department, the targeted ultrasound examination is more incessantly carried out to consider patients with suspected intra-abdominal inflammatory processes. Similarly, extra superior ultrasound techniques together with echocardiography are now being used to guide the resuscitation of critically sick patients. Of note, these surgeonperformed ultrasound examinations are presently thought of as normal care in many clinical settings. A potential research of surgeon-performed ultrasound as the first adjuvant modality for injured affected person evaluation. The standing of ultrasonography coaching and use generally surgical procedure residency applications. Ultrasound steerage improves the success price of inside jugular vein cannulation. Emergency center ultrasonography within the analysis of hemoperitoneum: a potential research. Early detection of hemoperitoneum by ultrasound examination of the best upper quadrant: a multicenter study. Focused abdominal sonogram for trauma: the educational curve of nonradiologist clinicians in detecting hemoperitoneum. Prospective proof of the prevalence of a sonography-based algorithm within the assessment of blunt abdominal injury. The utility of focused belly ultrasound in blunt stomach trauma: a reappraisal. Abdominal ultrasound is an unreliable modality for the detection of hemoperitoneum in patients with pelvic fracture. Blunt hepatic trauma: analysis with contrast-enhanced sonography: sonographic findings and clinical software. The role of ultrasound in sufferers with attainable penetrating cardiac wounds: a potential multicenter examine. A caveat to the efficiency of pericardial ultrasound in patients with penetrating cardiac wounds. Management of sufferers with anterior belly stab wounds: a Western Trauma Association multicenter trial. Role of ultrasonography in penetrating abdominal trauma: a prospective medical examine. Appraisal of early analysis of blunt chest trauma: improvement of a standardized scoring system for preliminary medical determination making. Diagnostic utility of cholescintigraphy and ultrasonography in acute cholecystitis. Revised estimates of diagnostic take a look at sensitivity and specificity in suspected biliary tract disease. Ultrasound, computed tomography, and laboratory findings within the analysis of appendicitis. Feasibility of emergency doctor prognosis of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis utilizing point-of-care ultrasound: a multi-center case sequence. Ultrasound steering decreases issues and improves the value of care amongst sufferers undergoing thoracentesis and paracentesis. A practical strategy to goal-directed echocardiography in the crucial care setting. Focused bedside echocardiography within the surgical intensive care unit: comparison of three methods to estimate cardiac index. Determination of cardiac output in critically sick patients by twin beam Doppler echocardiography. Pleural ultrasound in contrast with chest radiographic detection of pneumothorax decision after chest drainage. Chest sonography: a useful gizmo to differentiate acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema from acute respiratory misery syndrome. Prospective evaluation of a speedy trauma ultrasound examination performed by emergency physicians. Trauma ultrasound examination versus chest radiography within the detection of hemothorax. Sonographic screening of mass casualties for belly and renal injuries following the 1988 Armenian earthquake. Ultrasonographic functions after mass casualty incident brought on by Wenchuan earthquake. Screening ultrasonography of two,204 sufferers with blunt abdominal trauma within the Wenchuan earthquake. Ocular examination for trauma; medical ultrasound aboard the International Space Station. The utility of targeted assessment with sonography for trauma as a triage device in multiple-casualty incidents during the second Lebanon warfare. Portable ultrasound for remote environments, Part I: Feasibility of field deployment. A systematic evaluation and meta-analysis of diagnostic performance of imaging in acute cholecystitis. Diagnostic criteria and severity assessment of acute cholecystitis: Tokyo Guidelines. Comparison of accuracy of 99mTc-pyridoxylidene glutamate scanning with oral cholecystography and ultrasonography in diagnosis of acute cholecystitis. Ultrasound-guided central venous catheter placement decreases complications and reduces placement makes an attempt in contrast with the landmark technique in patients in a pediatric intensive care unit. Ultrasound guidance versus the landmark method for the placement of central venous catheters in the emergency department. Real-time ultrasonographically-guided inside jugular vein catherization in the emergency department increases success rates and reduces issues: a randomized, potential study. Real-time ultrasoundguided subclavian vein cannulation versus the landmark technique in crucial care patients: a prospective randomized research.
Purchase metoprolol 12.5 mg with mastercardConsistent with a postulated function of copper in initiating A2M fibrillogenesis heart attack songs videos trusted metoprolol 50 mg,sixty six copper-free dialysis membranes appear to reduce the incidence of illness arrhythmia ketosis cheap metoprolol 25mg on-line. Patients undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis usually have decrease plasma levels of 2-microglobulin than do sufferers undergoing hemodialysis and may not develop amyloid deposits as rapidly arteria iliaca comun purchase metoprolol 100mg with amex. Symptoms of arthropathy are frequent blood pressure chart runners discount metoprolol 50 mg visa, and prevalence could approach 100 percent of people undergoing dialysis for longer than 15 years. Within each family, disease begins at practically the identical age, and signs normally embrace neuropathy, cardiomyopathy, or each. Peripheral neuropathy begins as a lower extremity sensory and motor neuropathy and progresses to the higher extremities. Autonomic neuropathy is manifested by gastrointestinal symptoms of diarrhea with weight loss and orthostatic hypotension. Definitive identification of the amyloid precursor protein is crucial for appropriate remedy, and amyloid referral facilities can present specialised diagnostic methods and entry to clinical trials. An understanding of the biophysical properties of amyloid proteins and of the mechanisms of protein misfolding and tissue damage will allow the further improvement of extra specific and fewer poisonous antiamyloid therapeutics. Report from the Nomenclature Committee of the International Society of Amyloidosis. The first step is recognition of a clinical syndrome according to amyloidosis, adopted by an acceptable biopsy or fat aspirate to determine tissue fibrils. Johan K, Westermark G, Engstrom U, et al: Acceleration of amyloid protein A amyloidosis by amyloid-like artificial fibrils. Kluve-Beckerman B, Manaloor J, Liepnieks J: A pulse-chase research tracking the conversion of macrophage-endocytosed serum amyloid A into extracellular amyloid. Skinner M, Anderson J, Simms R, et al: Treatment of a hundred sufferers with major amyloidosis: a randomized trial of melphalan, prednisone, and colchicine versus colchicine only. Bergethon P, Sabin T, Lewis D, et al: Improvement in the polyneuropathy associated with familial amyloid polyneuropathy after liver transplantation. Sarcoidosis occurs worldwide and impacts folks of all racial and ethnic backgrounds, but prevalence and severity are increased in African-American sufferers. The pathogenesis of sarcoidosis involves the interaction of various cells, cytokines, and other inflammatory mediators in a vulnerable host. Rheumatologic manifestations are common in sarcoidosis but are often ignored or misdiagnosed. Food and Drug Administration for extrapulmonary manifestations, including sarcoid arthritis. However, the American Thoracic Society, the European Respiratory Society, and the World Association of Sarcoidosis and Other Granulomatous Disorders counsel a diagnosis of sar coidosis if the following criteria are fulfilled: (1) a compat ible medical picture, (2) histologic demonstration of noncaseating granulomas, and (3) exclusion of different dis eases capable of producing an analogous medical picture. Because of its medical hetero geneity and variable diagnostic standards in several coun tries, the worldwide prevalence and incidence of sarcoidosis have been troublesome to calculate. In Northern Europe, up to 40 cases per one hundred,000 individuals have been reported,three,4 whereas in a research from Eastern Europe, only three. In the United States, the annual incidence of sarcoidosis is greater than thrice larger in black people (35. The fact that it impacts barely more ladies than males has been confirmed in studies from around the world; estimates indicate that 57% of patients with sarcoidosis are girls. People of any age could acquire the illness, but the median age of onset is round 40 years. Its trigger has yet to be recognized, however environmental, genetic, and infectious causes have been suggested. The hallmark of sarcoidosis is the development and accumulation of noncaseating granulomas in any organ system. Organ system involvement, which is unpredictable and varies between sufferers, is the main determinant of morbidity and mortality in sarcoidosis. Any organ system can be concerned, but the lungs are affected in more than 90% of instances. Given the variability of sarcoidosis manifesta tions, diagnosing this disorder is commonly difficult. Patients may be asymptomatic or current with a variety of nonspecific symptoms, or particular signs similar to cough, dyspnea, burning of eyes, or a rash could suggest the diagnosis. Both inorganic and natural environmental components with antigenic capabilities have been implicated in the patho genesis of sarcoidosis. Early studies on the causes of sar coidosis instructed a hyperlink between sarcoidosis and brokers associated with a rural way of life, such as the lumber business and burning wooden. Because of clinical and histologic similarities, numerous methods have been used to search for an infectious agent as a cause of sarcoidosis, with most research specializing in Mycobacterium tuberculosis or Propionibacterium acnes. When in situ hybridization was used, Mycobacterium tuberculosis catalaseperoxidase protein (mKatG) was found in practically 40% of tissue samples from sufferers with sarcoidosis. Recombinant mKatG protein was then used to measure mKatG antibodies in sufferers with sarcoidosis, which have been current in 50% of sufferers studied. Because several forms of micro organism have been associated with sarcoidosis, some clinicians have attempted to use antibiotics or antimycobacterial agents to handle the disease. Although pores and skin sarcoidosis has on occa sion responded to these remedies,24,25 their usefulness in treating different forms of sarcoidosis seems to be minimal. In considering collectively a quantity of of the factors postulated to trigger sarcoidosis, a compelling argu ment may be made for a genetic factor that predisposes people to the disease and a subsequent environmental exposure that triggers the onset of sarcoidosis. The underlying immunologic events embody (1) exposure to a quantity of (unknown) antigens, (2) activation of antigenpresenting cells (macrophages and/or dendritic cells), (3) a T cell response in an effort to get rid of the antigen, and (4) granuloma formation. Physiologically, granulomas act as shields, protecting tissues from pathogens and thereby preempting inflamma tory reactions. Granuloma formation happens in several phases, divided into the initiation, accumulation, and effector phases and determination. At this level within the disease process, lymphocyte ranges are typically elevated at the sites of inflammation, however peripheral blood lymphopenia could occur as a end result of sequestration. Although granulomas spontaneously resolve with out causing injury typically, this cycle results in fibrosis in up to 25% of sufferers with sarcoidosis. Fewer than 5% of sufferers die of sarcoidosis, but fibrosis resulting in respiratory failure is a contributing consider many sarcoidosisrelated deaths. Additional signs are sarcoidosis related fatigue (present in about 50% to 70% of patients),forty nine smallfiber neuropathy (44%), which is troublesome to diagnose and treat,50 and cognitive dysfunction. In patients with sarcoidosis, arthritis could be acute or continual; the acute form is most typical. In a study of patients with acute sarcoid arthritis, Visser and colleagues53 prospectively evaluated patients and pub lished criteria to assist in analysis. Of 579 individuals, 55 sufferers (9%) eventually had been recognized with sarcoid arthritis. From the findings of their research, investigators established standards with 93% sensitivity and 99% specificity to information physicians in dif ferentiating between sarcoid and different causes of arthritis (Table 1172). Therefore, it may be very important rule out different situations that affect the nails, similar to pso riatic arthritis, when making sarcoid arthritis diagnoses. Other skeletal areas that may be affected by sarcoidosis embody nasal bones, pelvic girdle buildings, ribs, and the cranium.
Discount metoprolol 100 mg free shippingIn the past blood pressure danger zone cheap metoprolol 100mg online, one indication for thoracotomy was presence of a thoracoabdominal damage arteria transversa colli buy discount metoprolol 100mg online, and a thoracoabdominal incision across the costal margin was recommended blood pressure up pulse down purchase metoprolol 50 mg with visa. Neither this indication nor this incision is now thought of the standard arrhythmia mayo clinic generic metoprolol 100mg without a prescription, because it creates more issue in exposure in addition to complications than the extra normal incisions for the thoracic and stomach cavities. In addition, literature continues to increase considerations in regards to the quantity of radiation publicity for patients. Older scanners with fewer slices produce inconsistent results and infrequently create pointless confusion. Pericardiocentis Virtually each resuscitation course teaches and recommends the technique of pericardiocentesis to relieve hemopericardium and cardiac tamponade following harm. Trauma surgeons routinely describe clotted blood between the pericardium and heart at emergency thoracotomy for hemopericardium. Additionally, surgeons often describe iatrogenic cardiac penetration following an tried pericardiocentesis for acute trauma. For such instances, emergency thoracotomy, pericardiotomy, and cardiorrhaphy are indicated. Thoracic harm control strategies are, philosophically, a easy method to a fancy downside. Damage management techniques for the affected person with thoracic trauma shall be cited in different chapters of this guide and embrace: 1. With extra exact diagnostic techniques for pericardial fluid, a directed thoracic incision could possibly be used to expedite relief of pericardial tamponade and any cardiac harm. It is logical to apply a thoracic incision to a thoracic damage when an open procedure is indicated. As a screening modality, it joins the plain chest x-rays in aiding the clinician. Furthermore, rigidity pneumothorax is undoubtedly harder to decide than has been presumed, particularly in a shifting ambulance. In sufferers with no pneumothorax or with a pleural symphysis, insertion of a large-bore needle into the lung in an intubated affected person can contribute to fatal systemic air embolism and in addition cause a pulmonary hematoma with subsequent pulmonary insufficiency. In the current endovascular era, proximal vascular control can be obtained with an intravascular balloon, adopted by either endovascular or open repair via a supraclavicular incision. Ultrasound of the Chest Wall for Pneumothorax and Hemothorax Use of various types of ultrasound has found software for some specialists. Ultrasound has been investigated for use in chest trauma to evaluate quantity standing, cardiac function, hemopericardium, and pneumothorax (and hemothorax). In the emergency department, aside from hemopericardium, ultrasound has little or no sensible worth in guiding the clinician in therapeutic interventions. Trocar Chest Tubes Up to 25% of the population has some degree of pleural symphysis between the visceral and parietal pleura secondary to an earlier an infection or inflammation. Consequently, it is suggested that following the pores and skin incision and muscle spreading for a tube thoracostomy, the pleura be entered with the exploring finger rather than an instrument. If percutaneously inserted, the commercially available chest tube system with a Trocar-tipped steel rod in the center of the chest tube has the potential for causing an iatrogenic harm (stab) to the lung or other thoracic or higher abdominal organs transdiaphragmatically. Potentially life-threatening circumstances include acute pericardial tamponade, acute and big blood loss, disruption of ventilation, and decreased cardiac output. These situations are the premise for the standard A-irway, B-reathing, C-irculation of resuscitation. Infection, sepsis, pulmonary insufficiency, and different useful impairments may happen secondarily, and all or any contribute to the timing and determination to function. Alternatively, thoracotomy for evacuation of a clotted hemothorax, management of a late presenting complication or beforehand missed harm could also be delayed. In the chest, as elsewhere within the physique, following vital trauma, staged procedures are a part of present method to management. Clamping of Chest Tubes Large-bore chest tubes improve drainage of blood, fluids, air, and purulent material, from the pleural cavity. Chest tubes are broadly used for each penetrating and blunt thoracic trauma with concomitant pneumothorax, hemothorax, or both. An appropriately placed chest tube often precludes the necessity for a formal thoracotomy and may forestall retained clotted hemothorax. Once the pathology that necessitated chest tube insertion has resolved, the tube is eliminated. With a clear understanding of pleural anatomy and physiology, problems at chest tube elimination are rare. Some clinicians concerned in the care of trauma sufferers advocate that chest tubes be clamped previous to removal to guarantee appropriate timing of removing. Pledgets in Cardiorrhaphy Cardiorrhaphy is routinely achieved throughout cardiac surgery without the use of adjunctive pledgets within the suture line. Trap Door Thoracotomy this combined anterolateral, partial sternotomy, and supraclavicular ("trapdoor" or "book") incision that was in style Chapter 24 Trauma Thoracotomy: General Principles and Techniques 477 Tube thoracostomy is the most common procedure following thoracic injury. Many of these specific issues shall be cited and discussed in the organ-specific injury chapters. It is also well acknowledged that the contused lung is extra vulnerable to barotrauma, pneumonia, and fluid overload than is the unhurt lung. Trauma can even cause pulmonary venous air embolism, which turns into systemic air embolism. From there, air can go to the left atrium, producing system air embolism, seizures, and ventricular fibrillation due to air in the coronary (mostly proper coronary given its anterior location when affected person lays supine) and cerebral arteries. The insertion of a nasogastric or feeding tube into the pharynx of a totally awake patient with a abdomen filled with meals is conducive to aspiration of vomited gastric contents. Aspiration of water-soluble distinction material, corresponding to gastrograffin, into the lungs produces a chemical pneumonitis much more severe than that produced by aspiration of a barium-based contrast material. The insertion of a feeding tube into the bronchus, lung substance, or even the pleural cavity, and then subsequent introduction of liquid feedings produces devastating outcomes. Controversy persists on the short- and long-term radiologic damage from the various radiologic studies, usually unnecessary and duplicative, in the course of the initial analysis of a trauma affected person. Unfortunately, high quality evaluate of medical data hardly ever reveals a preimaging progress note indicating why the check was ordered, what the clinician wanted to learn from the research, or how outcomes of picture might alter determination making. Such progress notes undoubtedly would be beneficial in defending excessive radiation that could be related to growth of lymphoma or leukemia a few years later. Double jeopardy: thoracoabdominal accidents requiring surgical procedure in each chest and abdomen. Urgent thoracotomy for penetrating chest trauma; evaluation of 158 patient of a single middle. Emergency department thoracotomy for gunshot wounds of the guts and great vessel. Timing of pressing thoracotomy for hemorrhage after trauma; a multicenter examine of the American Association of the Surgery of Trauma. The cardiac pendulum: blunt rupture of the pericardium with strangulation of the heart. Overcoming challenges of endovascular therapy of advanced subclavian and axillary artery 20. Blunt thoracic accidents are responsible for approximately 8% of all trauma admissions within the United States, with motorized vehicle crashes being the most common mechanism.
Order metoprolol 12.5mg amexThe biomechanics of this damage contains (1) direct transmission of elevated intrathoracic strain to the chambers of the heart; (2) a hydraulic effect from a large pressure applied to the belly or extremity veins blood pressure medication plendil generic metoprolol 100mg with mastercard, causing the pressure to be transmitted to the proper atrium; (3) a decelerating force between fastened and cell areas heart attack or heartburn cheap metoprolol 25mg amex, explaining atriocaval tears; (4) a direct pressure inflicting myocardial contusion blood pressure 50 over 70 cheap metoprolol 12.5 mg free shipping, necrosis hypertension jokes cheap metoprolol 12.5mg visa, and delayed rupture; and (5) penetration from a broken rib or fractured sternum. In distinction, in sufferers that arrive alive to the hospital, proper atrial disruption is more widespread. Blunt rupture of the cardiac septum occurs most incessantly near the apex of the heart. Multiple ruptures as properly as disruption of the conduction system have been reported. Traumatic rupture of the thoracic aorta can also be associated with deadly cardiac rupture in virtually 25% of cases. Pericardial tears secondary to elevated intra-abdominal stress or lateral decelerative forces can happen on either side, often parallel to the phrenic nerve; to the diaphragmatic surface of the pericardium; and finally to the mediastinum. Cardiac herniation with cardiac dysfunction can happen in conjunction with these tears. The heart may be displaced into both pleural cavity and even into the abdomen relying on the tear. In the circumstance of right pericardial rupture, the guts can turn out to be twisted, preventing venous return, resulting in the shocking discovery of an "empty" pericardial cavity at resuscitative left anterolateral thoracotomy. With a left-sided cardiac herniation via a pericardial tear, a trapped apex of the guts prevents the center from returning to the pericardium and the time period "strangulated heart" has been applied. One clue to the presence of cardiac herniation in a patient with blunt thoracic injury is sudden loss of pulse when the affected person is repositioned, corresponding to when moved or placed on a stretcher. Cardiac accidents caused by central venous catheter placement usually occur with insertion from both the left subclavian or the left internal jugular vein. Even optimum technique carries a discrete price of iatrogenic injury secondary to central venous catheterization. Common sites of injury include the superior vena caval�atrial junction and the superior vena Chapter 26 Heart and Thoracic Vascular Injuries 495 cava�innominate vein junction. Drainage by pericardiocentesis is commonly unsuccessful, and evacuation by way of subxiphoid pericardial window or full median sternotomy is sometimes required. At operation, when the pericardium is opened, the site of harm has typically sealed and may be troublesome to discover. Complications from coronary catheterization together with perforation of the coronary arteries, cardiac perforation, and aortic dissection could be catastrophic and require emergency surgical intervention. A more priceless and reproducible sign of pericardial tamponade is narrowing of the coronary heart beat pressure. An elevation of the central venous strain usually accompanies overaggressive cyclic hyper-resuscitation with crystalloid solutions, however in such cases, a widening of the heart beat pressure occurs. Gunshot wounds to the heart which have a larger pericardial defect are extra regularly related to hemorrhage than with tamponade. The kinetic power is bigger with firearms, and the injuries to the guts and pericardium are usually more extensive. Damage from electrical damage is due to direct results on the excitable tissues, warmth generated from the electrical present, and accompanying related injuries (eg, falls, explosions, fires). Septal rupture and valvular dysfunction (leaflet tear, papillary muscle, or chordal rupture) can initially seem with out symptoms however later show the delayed sequela of coronary heart failure. Blunt cardiac harm can also present as a dysrhythmia, mostly untimely ventricular contractions, the exact mechanism of which is unknown. Ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and supraventricular tachydysrhythmias can also occur. It is best to describe these injuries, as "blunt cardiac trauma with"-followed by the medical manifestation, such as dysrhythmia, or coronary heart failure. Patients with cardiac damage can present with a medical spectrum from full cardiac arrest to asymptomatic with normal important indicators. As pericardial fluid accumulates, a decrease in ventricular filling occurs, leading to a decrease in stroke quantity. A compensatory rise in catecholamines leads to tachycardia and elevated proper coronary heart filling pressures. The limits of right-sided distensibility are reached because the pericardium fills with blood and the septum shifts towards the left side, additional compromising left ventricular perform. As little as 60�100 mL of blood in the pericardial sac can produce the clinical picture of tamponade. Because it has a thicker wall, wounds to the ventricle seal themselves more readily than wounds to the atrium. Patients with freely bleeding injuries to the coronary arteries current with fast onset of tamponade combined with cardiac ischemia. The total mortality of those who are handled at trauma centers with such harm stays as high as 64%. When the center returns to its regular position in the pericardium, venous return resumes. Positional hypotension is the hallmark of cardiac herniation as a result of pericardial rupture,8 whereas pericardial tamponade is related to persistent hypotension until the pericardium is decompressed. Therefore, a high index of suspicion is useful when evaluating polytrauma patients with unexplained positional hypotension. On preliminary presentation to the emergency center, airway, breathing, and circulation beneath the Advanced Trauma Life Support protocol are evaluated and established. These findings recommend cardiac injury but are current in solely 10% of patients with cardiac tamponade. Patients in extremis can require emergency division thoracotomy for resuscitation. The clear indications for emergency department thoracotomy by surgical personnel embody the following17: 1. Severe post-injury hypotension (ie, systolic blood stress <60 mm Hg) as a result of cardiac tamponade, cardiac herniation, air embolism, or thoracic hemorrhage If, after resuscitative thoracotomy, important indicators are regained, the patient is transferred to the working room for definitive restore. Transthoracic echocardiography can have a restricted use in evaluating blunt cardiac trauma as a outcome of many patients also have important chest wall injury, thus rendering the take a look at technically tough to carry out due to limited windows. Ventricular dysfunction can often mimic cardiac tamponade in its clinical presentation. Echocardiography is particularly useful in older sufferers with preexisting ventricular dysfunction. However, most blunt cardiac injuries identified by echocardiography rarely require acute remedy. Electrocardiography In circumstances of blunt cardiac injury, conduction disturbances can occur. However, no relationship amongst serum assays and identification and prognosis of injury has been demonstrated with blunt cardiac damage. In a prospective examine, Meyer and coworkers24 in contrast the subxiphoid pericardial window with echocardiography in instances of penetrating heart harm and reported that the sensitivity and specificity of subxiphoid pericardial window were one hundred pc Chapter 26 Heart and Thoracic Vascular Injuries 497 and 92%, respectively, in contrast with 56% and 93% with echocardiography. They instructed that the difference in sensitivity may have been as a end result of the presence of hemothorax, which can be confused with pericardial blood, or as a outcome of the fact that the blood had drained into the pleura. Pericardiocentesis has had important historic help, especially years in the past when nearly all of penetrating cardiac wounds have been produced by ice picks and the (surviving) sufferers arrived a number of hours and/or days after damage. In such situations, there was a natural triage of the more severe cardiac accidents, and the intrapericardial blood had turn out to be defibrinated and was straightforward to take away.
Generic 12.5mg metoprolol amexHe might have been a hunter injured by firearm or animal arteria in english cheap metoprolol 12.5 mg without a prescription, a backcountry skier caught in an avalanche arteria zigomatico orbital metoprolol 25 mg lowest price, a rancher thrown from a horse blood pressure while pregnant metoprolol 25 mg for sale, or the motive force of a car on a remote rural highway arterial thrombosis order metoprolol 25mg free shipping. Remoteness, open farmlands, rugged beauty, and "nature" are powerful magnets for tourists, recreationists, and people looking for a quieter, less annoying lifestyle. Such guests are often shocked to discover that medical providers they take without any consideration at house are merely unavailable in a rural setting. The local weather could additionally be harsh, the terrain rugged and distant from companies, the roads badly engineered and maintained, communications rudimentary, and the financial system marginal. As a result, significant segments of the population are aged, poor, poorly educated, and in sick health. Population density (low) and private revenue (also low) are the strongest predictors of per capita trauma demise rates. Binge drinking and depression are strongly related comorbid elements, and suicide accounts for 10% of all rural trauma deaths. Group 1 states were rural, western, and below national averages for per capita revenue; group 2 states were urban, eastern, and financially well-off. The most typical causes of deadly damage are motorized vehicle crashes, suicide, murder, and falls. For these and the following 10 most frequent causes, rural demise charges exceed urban charges for all but poisonings. Some of the most hazardous occupations similar to mining, logging, and farming are almost completely rural by their very nature. Typical injuries are falls (horses), tramplings and gorings (bulls, wild game), and kicks (cows). As a mature moose weighs half a ton or more, a driver unfortunate enough to strike one dangers vital harm to the mind or dying. Crush damage between transferring logs and encounters with heavy equipment are different common mechanisms, and access to care is usually a problem. In Oregon, the rate of Chapter 9 Rural Trauma 141 such accidents and deaths doubled between 2002 and 2005. Most people really feel safe in rural setting as the chance of violent assault and penetrating trauma is very low as noted above. The low homicide charges, nonetheless, are negated by high suicide rates, significantly amongst adolescents and younger adults. It could be subtle, nonetheless, requiring experience and a excessive index of suspicion to keep away from missed injuries. In essence, the best problems confronting rural trauma care are entry to the system and lack of sources. The problem is to devise a system, guarantee entry, and take benefit of restricted resources. In rural methods of care, time of crash until time of arrival on the hospital is greater than an hour in 30% of instances, as opposed to 7% in urban systems. Retrieval is equally difficult and often relies on the particular skills of search-and-rescue volunteers equipped to go into swamps and tidal flats, excessive mountains, or dense forests and other wilderness areas. Population Shifts Population shifts within the coming years will have an impact on the issues of rural trauma. Although many elements of the Great Plains have gotten progressively depopulated, rural areas of the coastal regions, Rocky Mountains, Southwest, and Sunbelt states are experiencing an inflow of younger, energetic people who discover themselves bored with city life and eager for what small town America has to offer. Whether they are going to be keen to pay for it by way of taxes or user charges is another matter. An necessary mission for rural methods will be convincing constituents of the importance of financial support for trauma activities. In rural areas, the configuration of such techniques varies and will embrace hearth department� primarily based, hospital-based, or freestanding entities. The nomenclature for the assorted levels of coaching is in transition, which has been clarified by the publication of a scope of apply document. If the victim is inaccessible to an ambulance, varied strategies, all of them gradual, could additionally be employed to convey the affected person to a street. The ambulance might then have to negotiate a sequence of roads from unsurfaced or gravel to county or state highway. Response times, which include travel from the dispatch site to scene, extrication or retrieval, packaging, and travel to the hospital, are sometimes measured in hours, not minutes. Ambulance services could also be freestanding or, in some instances, an integral part of the native fireplace division. Funding may be via a particular ambulance district or as a half of the county price range, jealously guarded by county commissioners. If an ambulance is in service on a call or out of service for maintenance, the next call might need to be answered by a crew in a neighboring district by way of a mutual assist agreement. Aeromedical and ground transport systems that furnish critical care are becoming more frequent; nonetheless, their availability lags behind in many rural areas. Ideally, evacuation from the scene of damage on to the trauma middle should afford the affected person one of the best opportunity for restoration. Due to reimbursement adjustments, there has been a proliferation and related overutilization of helicopter services in some areas. Beyond that distance, the simultaneous dispatch of floor and air transport was probably the most efficient as ground personnel may extricate and resuscitate in advance of the arrival of the helicopter. For floor transports of greater than forty five miles, helicopter was quicker even when dispatched after the ground unit. In the rural setting, provided the scene is within the range of plane without the need to refuel, direct transport could also be worthwhile if the time to the native hospital by floor ambulance is greater than that of the helicopter flight. The downside is that such aircraft are expensive ($900,000�2,200,000 start-up; $500,000�2,000,000 annual maintenance), hazardous (fatal accident fee 4. Once the initial outlay for equipment and personnel has been made, an incentive exists to use it, even when surface conveyance may be an acceptable different. It would seem that continued refinement of triage standards is important to make positive that helicopters are used judiciously and effectively. Fixed-wing transfers are another option, but are restricted to interhospital transfer. These aircraft are fast and, when properly outfitted, can function as an airborne intensive care unit. Drawbacks embrace the 30 minutes or extra needed to get the airplane airborne and the necessity to transport the sufferer by ground ambulance between airport and hospital on both ends of the transfer. Transport techniques are one other space where expertise combined with a safe funding source could enhance outcomes for trauma victims. Helicopters are very expensive, however might have the best potential for eliminating delay and downtime in the process of getting the right patient to the best hospital at the proper time. Extended range, expanded capacity for onboard tools and entry to the affected person, safer landing areas, and inventive strategies of funding are all possible Chapter 9 Rural Trauma 143 areas for investigation.
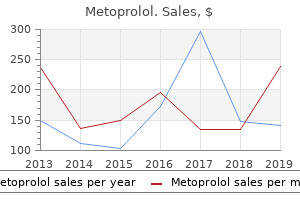
Metoprolol: 100 mg, 50 mg, 25 mg, 12.5 mg
Generic metoprolol 12.5 mgDespite these diagnostic strategies 5 purchase metoprolol 100 mg fast delivery, the analysis of gallbladder injury is most frequently secured at laparotomy blood pressure medication kinds discount metoprolol 12.5mg free shipping, at which period cholecystectomy is the advised therapy pulse pressure 55 mmhg buy generic metoprolol 50mg line. The patients with late presentation could develop jaundice heart attack risk assessment metoprolol 25mg sale, belly distention and ache, intolerance to enteral feeding, fever, or worsening base deficit as a outcome of bilious ascites or infection. There could additionally be some indication of pancreatic head fullness, duodenal thickening, or portal edema but these are nonspecific findings. In the presence of bile staining throughout an operative process and no obvious harm, a cholangiogram by way of the gallbladder can be useful. Ninety-seven percent of patients had concomitant injuries, thus illustrating the importance of full exploration and belly analysis. A generous midline incision ought to be made, followed by evacuation of blood clot and hemoperitoneum with urgent packing of bleeding structures. Hematoma or bleeding around, or inside, the hepatoduodenal ligament or severe parenchymal injury leading to the porta hepatis should elevate suspicion of a portal triad harm. Bile staining also wants to be totally investigated, as 12% of bile duct accidents could also be missed at the preliminary operation. In order to get hold of adequate examination and publicity for restore, a large proper medial visceral rotation ought to be carried out, which includes mobilizing the ascending and hepatic flexure areas of the colon, thus exposing the duodenum. Similarly, a full Kocher maneuver should mobilize the duodenum and head of the pancreas medially to expose the inferior vena cava. However, there have been reports of laparoscopic cholecystectomy in penetrating trauma. Chapter 29 Liver and Biliary Tract 569 process should be accomplished with nice reserve, since many gallbladder accidents are associated with other intra-abdominal accidents in each penetrating and blunt trauma. Though the laparoscope may give an excellent superficial examination of the peritoneal cavity, visualization of the duodenum, pancreas, and porta hepatis is, in most palms, not sufficient. Minor gallbladder contusions can usually be managed nonoperatively,140,141 but could lead to cholecystitis or delayed rupture. Cholecystectomy also needs to be carried out on all sufferers with injury to the cystic duct or proper hepatic artery that might get rid of the blood supply to the gallbladder. In the patient who remains in shock and coagulopathic, packing and placement of drains within the area of the biliary damage is sufficient till reexploration is performed. Four broad categories of biliary duct harm have been described: (1) avulsion of cystic duct or small laceration, (2) transection without lack of tissue, (3) intensive defect within the wall, and (4) segmental loss of ductal tissue. A T tube with a limb underneath the restore can be used; nonetheless, this might be troublesome to insert in a affected person with a traditional sized duct. For avulsions during which major repair might slim the lumen, a bit of the cystic duct or proximal gallbladder wall can be utilized for the repair. One should make positive to perform minimal dissection across the duct or the lacerated ends to find a way to maintain sufficient blood provide for therapeutic. Ivatury et al reported a 55% stricture price in the end-to-end anastomoses that then required enteric conversion. Saphenous vein grafts have had difficulties with shrinking and fibrosis, which then required stenting. Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy with cholecystectomy and T-tube drainage is the most utilized approach to complicated harm. A retrocolic Roux limb of a minimal of 40 cm long is created and may be brought as much as the widespread hepatic duct or even to the hilar plate, much like the Kasai procedure. An avulsion of the hepatic ducts at the bifurcation could be managed by suturing the ducts collectively medially before the endto-side hepaticojejunostomy. However, the vascularity on this anastomosis is crucial and any sign of frequent bile duct vascular damage would lead the surgeon to assemble an anastomosis nearer to the common hepatic duct. Patterns of fluid accumulation on screening ultrasonography for blunt abdominal trauma. Ultrasound primarily based key medical pathway reduces using hospital resources for the evaluation of blunt belly trauma. Abdominal injuries with out hemoperitoneum: a possible limitation of centered stomach sonography for trauma. Blunt abdominal trauma: emergency contrast-enhanced sonography for detection of stable organ injuries. Appearance of strong organ injury with contrast-enhanced sonography in blunt abdominal trauma: preliminary expertise. Blunt stomach trauma patients: can organ damage be excluded with out performing computed tomography Nonoperative management reduces the general mortality of grades 3 and 4 blunt liver accidents. American Association for the Surgery of Trauma Organ Injury Scale I: spleen, liver, and kidney, validation based mostly on the National Trauma Data bank. The swinging pendulum: a national perspective of nonoperative management in extreme blunt liver damage. Damage-control resuscitation will increase profitable nonoperative administration charges and survival after extreme blunt liver injury. Angiointervention: an independent predictor of survival in high-grade blunt liver injuries. Hepatic arterial embolization within the administration of blunt hepatic trauma: indications and complications. This is a viable possibility especially in patients with small caliber ducts or instability. However, the surgical treatment of those injuries should be individualized to every state of affairs. Surgeons in favor of stenting report that stenting allows for decompression, when edema post-trauma could additionally be important, in addition to permits access for cholangiography. When ampullary or intrapancreatic bile duct damage is discovered, a pancreaticoduodenectomy may be appropriate if duodenal and pancreatic injury is also seen. Hepatic resection is critical solely within the case of combination damage to the liver parenchyma and hepatic duct traversing that phase. A current publication used an aggressive strategy of inserting an growing variety of stents till complete disappearance of the biliary stricture occurred. Though the authors did have a complication price of 9%, their imply period of remedy was 12 months with a forty eight. Nonoperative management of blunt hepatic trauma is the remedy of choice for hemodynamically secure patients. Sonographic detection of blunt hepatic trauma: hemoperitoneum and parenchymal patterns of harm. Risk components for hepatic morbidity following nonoperative administration: multicenter examine. Long-term follow-up after non-operative management of biloma as a end result of blunt liver injury. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography is an efficient remedy for bile leak after severe liver trauma. Biliary stenting is simpler than sphincterotomy within the decision of biliary leaks. Hemobilia presenting as lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage without pain or jaundice: a case report.
Buy 12.5 mg metoprololPostinjury life threatening coagulopathy: is 1:1 contemporary frozen plasma:packed pink blood cells the reply Plasma restoration of endothelial glycocalyx in a rodent model of hemorrhagic shock blood pressure medication lotrel discount 50 mg metoprolol overnight delivery. Fresh frozen plasma resuscitation attenuates platelet dysfunction in contrast with normal saline in a large animal mannequin of multisystem trauma arteria lusoria discount metoprolol 12.5mg with mastercard. The ratio of fibrinogen to red cells transfused affects survival in casualties receiving large transfusions at a military fight help hospital arrhythmia originating in the upper chambers of the heart cheap metoprolol 100mg mastercard. Fibrinogen levels throughout trauma hemorrhage arrhythmia technology institute order 12.5mg metoprolol free shipping, response to substitute remedy, and association with patient outcomes. Management of bleeding and coagulopathy following major trauma: an updated European guideline. An analysis of the impact of apheresis platelets for massively transfused fight trauma patients. The association of blood component use ratios with the survival of massively transfused trauma sufferers with and with out mind damage. The impact of platelet and desmopressin administration on early radiographic development of traumatic intracranial hemorrhage. Refrigerated platelets for the remedy of acute bleeding: A evaluation of the literature and reexamination of current standards. Warm recent whole blood is independently related to improved survival for patients with combat-related injuries. Blood far forward-a whole blood research and coaching program for austere environments. Successful emergency reversal of phenprocoumon anticoagulation with prothrombin complicated concentrate: a prospective clinical research. Degree of anticoagulation, however not warfarin itself, predicts adverse outcomes after traumatic brain harm in elderly trauma patients. Heparin prophylaxis in patients with a quantity of injuries: an evidence-based method to a medical downside. Emergency surgery and trauma in patients handled with the brand new oral anticoagulants: dabigatran, rivaroxaban, and apixaban. The ex vivo reversibility of dabigatran-induced whole-blood coagulopathy as monitored by thrombelastography: mechanistic implications for medical apply. Pulmonary embolism with out deep venous thrombosis: de novo or missed deep venous thrombosis Incidence of asymptomatic pulmonary embolism in moderately to severely injured sufferers. Factors related to pulmonary embolism within seventy two hours of admission after trauma: A multicenter research. Hypercoagulability following blunt stable stomach organ damage: when to provoke anticoagulation. Obesity and clotting: body mass index independently contributes to hypercoagulability after damage. Postinjury hyperfibrinogenemia compromises efficacy of heparin-based venous thromboembolism prophylaxis. Is Fibrinolysis shutdown the missing hyperlink resulting in postinjury hypercoagulability. Failure of anticoagulant thromboprohylaxis: Risk components in medical-surgical critically ill patients. Prothrombin advanced concentrate (Beriplex P/N) in severe bleeding: expertise in a large tertiary hospital. Prothrombin complex concentrate vs contemporary frozen plasma for reversal of dilutional coagulopathy in a porcine trauma model. The impression of tranexamic acid on mortality in injured sufferers with hyperfibrinolysis. A controlled resuscitation strategy is possible and safe in hypotensive trauma patients: Results of a prospective randomized pilot trial. Effects of antiplatelet brokers on outcomes for elderly patients with traumatic intracranial hemorrhage. Predictors of mortality in trauma patients with intracranial hemorrhage on preinjury aspirin or clopidogrel. Standard prophylactic enoxapaparin dosing leads to insufficient anti-Xa levels and increased deep venous thrombosis rates in critically ill trauma and surgical sufferers. Safety and efficacy of pharmacologic thromboprophylaxis following blunt head damage: a systematic review. Safety and efficacy of early pharmacological thromboprophylaxis in traumatic mind injury: systematic evaluation and meta-analysis. Statins within the prevention of venous thromboembolism: A meta-analysis of observational studies. The effectiveness of prophylactic inferior vena cava filters in trauma sufferers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. This page deliberately left blank Emergency Department Thoracotomy Clay Cothren Burlew � Ernest E. Moore the variety of sufferers arriving at hospitals in extremis, somewhat than expiring within the prehospital setting, has elevated because of the maturation of regionalized trauma methods (see Chapter 4). In 1943, Blalock and Ravitch advocated the usage of pericardiocentesis quite than thoracotomy as the popular therapy for postinjury cardiac tamponade. With improvement in patient resuscitation and an ongoing evaluation of affected person outcomes, the indications for emergent thoracotomy shifted. The authors outline "no indicators of life" as no detectable blood stress, respiratory or motor effort, cardiac electrical activity, or pupillary exercise (ie, medical death). There is a high mortality rate in injuries to the pulmonary or thoracic great-vessel lacerations due to the lack of hemorrhage containment by adjacent tissue tamponade or vessel spasm (see Chapters 25 and 26). Therefore, a high scientific suspicion is warranted in sufferers with penetrating torso trauma, significantly in those with hemodynamic decompensation. Combined, these objectives attempt to handle the first problem of cardiovascular collapse from mechanical sources or extreme hypovolemia. Rising intrapericardial stress produces abnormalities in hemodynamic and cardiac perfusion that can be divided into three phases. In the intermediate phase of tamponade, rising pericardial strain further compromises diastolic filling, stroke quantity, and coronary perfusion, resulting in diminished cardiac output. Although, blood pressure may be maintained deceptively nicely, subtle indicators of shock (eg, anxiousness, diaphoresis, and pallor) become evident. During the final phase of tamponade, compensatory mechanisms fail as the intrapericardial pressure approaches the ventricular filling pressure.
References - Leitman IM, Virk CS, Avgerinos DV, et al: Early results of trans-oral endoscopic plication and revision of the gastric pouch and stoma following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery. J Soc Laparoendosc Surg 14:217, 2010.
- Huxley RL, Gaffney FA, Corbett JR, et al: Early detection of left ventricular dysfunction in chronic aortic regurgitation as assessed by contrast angiography, echocardiography, and rest and exercise scintigraphy, Am J Cardiol 51:1542-1550, 1983.
- Mulhall JP, Creech SD, Boorjian SA, et al: Subjective and objective analysis of the prevalence of Peyronie's disease in a population of men presenting for prostate cancer screening, J Urol 171(6 Pt 1):2350-2353, 2004.
- Wikstrom B, Backman U, Danielson BG: Ambulatory diagnostic evaluation of 38 recurrent renal stone formers: a proposal for clinical classification and investigation, Klin Wochenschr 61:85, 1983.
- Wainer BH, Mesulum MM. Ascending cholinergic pathways in the rat brain. In Steriade M, Biesold D, eds. Brain Cholinergic Systems. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1990 Edgar DM. Sleep-wake circadian rhythms and aging: potential etiologies and relevance to age-related changes in integrated physiological systems. Neurobiol Aging 1994;15(4):499-501.
|


