Modafinil
Neda Zadeh, M.D. - Childrenĺs Hospital of Orange County
- Orange, California
Purchase modafinil 200 mg with visaSex differences and menstrual cycle dependent changes in cognitive strategies during spatial navigation and verbal fluency insomnia loss of appetite buy modafinil 200 mg without a prescription. The dynamic role of genetics on cortical patterning throughout childhood and adolescence insomnia 7 months postpartum order modafinil 100mg fast delivery. Boys do it the proper way: sex-dependent amygdala lateralization during face processing in adolescents sleep aid gift ideas order modafinil 100mg line. Functional anatomy of visuo-spatial working memory during psychological rotation is influenced by sex sleep aid vape juice order 200 mg modafinil with amex, menstrual cycle, and intercourse steroid hormones. Gender differences in major depressive disorder: outcomes from the Netherlands examine of despair and nervousness. Testosterone packages adult social conduct before and during, but not after, adolescence. The role of the amygdala in emotional processing: a quantitative meta-analysis of useful neuroimaging studies. Effect of estrogen on mind activation patterns in postmenopausal girls throughout working reminiscence duties. The Hunter-Gatherer theory of intercourse variations in spatial skills: information from 40 countries. Characterizing particular person differences in practical connectivity utilizing dual-regression and seed-based approaches. Intrinsic connectivity networks from childhood to late adolescence: effects of age and sex. Sex differences in handedness, asymmetry of the Planum Temporale and useful language lateralization. Age differences in persona traits from 10 to 65: huge 5 domains and facets in a large crosssectional sample. Mapping continued mind progress and grey matter density reduction in dorsal frontal cortex: inverse relationships during postadolescent brain maturation. Pubertal testosterone influences threatrelated amygdala-orbitofrontal cortex coupling. Evidence for a change within the sex ratio of youngsters referred for gender dysphoria: data from the center of experience on gender dysphoria in Amsterdam (1988e2016). Sex differences in mind activation to emotional stimuli: a meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies. Cognitive abilities in women with full androgen insensitivity syndrome and women with gonadal dysgenesis. Men and issues, ladies and people: a meta-analysis of intercourse variations in pursuits. Sex variations within the capacity to recognise non-verbal shows of emotion: a meta-analysis. Growth patterns within the growing mind detected by using continuum mechanical tensor maps. Widespread intercourse differences in gene expression and splicing within the adult human brain. Toy-playing habits, sex-role orientation, spatial ability, and science achievement. Exploring and enhancing spatial pondering: hyperlinks to achievement in science, know-how, engineering, and arithmetic Testing a dual-systems model of adolescent mind development using resting-state connectivity analyses. Neural activation throughout psychological rotation in full androgen insensitivity syndrome: the affect of intercourse hormones and intercourse chromosomes. Gender-specific gene expression in post-mortem human mind: localization to intercourse chromosomes. Evolutionary and developmental changes in the lateral frontoparietal community: somewhat goes a good distance for higher-level cognition. Hippocampal (subfield) volume and form in relation to cognitive efficiency across the adult lifespan. Valence, gender, and lateralization of functional brain anatomy in emotion: a meta-analysis of findings from neuroimaging. Nature needs nurture: the interaction of hormonal and social influences on the event of behavioral sex variations in rhesus monkeys. The organizational speculation: reflections on the 50th anniversary of the publication of Phoenix, Goy, Gerall, and younger (1959). Putative sex variations in verbal talents and language cortex: a important evaluation. Sex variations and menstrual cycle effects in cognitive and sensory resting state networks. Sex variations in mind activation sample throughout a visuospatial cognitive task: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study in wholesome volunteers. Brain activation sample during a verbal fluency test in wholesome male and female volunteers: a practical magnetic resonance imaging study. Typical growth of basal ganglia, hippocampus, amygdala and cerebellum from age 7 to 24. A cross-cultural analysis of the conduct of men and women: implications for the origins of intercourse variations. The effects of the X chromosome on intrinsic functional connectivity in the human mind: proof from turner syndrome patients. Sex differences of event-related potential results during three-dimensional mental rotation. Age-related intercourse differences in language lateralization: a magnetoencephalography study in kids. Effects of hormone therapy on brain volumes adjustments of postmenopausal ladies revealed by optimally-discriminative voxel-based morphometry. Mapping the effect of the X chromosome on the human brain: neuroimaging evidence from turner syndrome. Effects of cross-sex hormone therapy on cortical thickness in transsexual people. Sex differences in referral rates of children with gender identity disorder: some hypotheses. Growing together and growing aside: regional and sex differences in the lifespan developmental trajectories of functional homotopy. The reductive properties of the cellular setting present quite a few opportunities for oxygen to bear sudden univalent reduction. Regardless of little consideration received from the scientific neighborhood for Pathology. They can either donate an electron to , or settle for an electron from, other molecules, due to this fact behaving as oxidants or reductants, respectively.

Discount 200 mg modafinil mastercardAmong the psychological processes which are the idea for a lot of sociability and smooth social interplay insomnia by craig david order 200mg modafinil with visa, empathy performs a pivotal position insomnia karleusa buy 100mg modafinil fast delivery. Empathy-related responding insomnia history generic 200 mg modafinil fast delivery, including caring and sympathetic concern sleep aid dollar general buy discount modafinil 100 mg on-line, motivates bonding between people and some forms of prosocial behavior, inhibits aggression, and general facilitates group residing and cooperation. On the opposite hand, sure developmental issues are marked by empathy deficits, which influence the motivation to respond to others in misery or need, and take care of them. Understanding how these motivations and behaviors are implemented in the mind and downstream peripheral physiology, each in sometimes developing youngsters and kids with delinquent tendencies, can help elucidate the function of empathy in prosociality. It is necessary to notice that empathy can compete with moral judgment and justice ideas, for instance, by inducing partiality for in-group members (Cikara and Van Bavel, 2014; Decety and Cowell, 2014a). This article critically examines the current information concerning the growth of the mechanisms supporting empathy and its related behavioral responses corresponding to some types of prosocial behaviors including caring. We review the affective and cognitive elements that give rise to empathy, beginning first with the automatic proclivity to share have an result on and emotions with others, and then the cognitive processes of perspective-taking and government control, which enable individuals to deliberately adopt the subjective view level of another with out confusion between self and other. Based on conceptual and empirical proof from developmental psychology, cognitive neuroscience, and neurology, a quantity of distinct and interacting components contribute to the expertise of empathy: (1) affect sharing, a bottom-up course of grounded in affective arousal and neural circuits connecting the brain stem, amygdala, basal ganglia, and orbitofrontal cortex, (2) understanding emotion that relies on self- and other-awareness and critically involves the medial and ventromedial prefrontal cortex and temporoparietal junction, and (3) executive features instantiated in the prefrontal cortex that function as a top-down mediator, allowing for perspective-taking; emotion regulation, and appraisal of social context (Decety and Jackson, 2004; Decety and Meyer, 2008). Drawing from multiple sources of knowledge and ranges of analysis offers a more full image of the phenomenological experience of empathy, as well as an understanding of the development and interaction between the mechanisms that drive the phenomenon. Furthermore, learning subcomponents of more complex psychological constructs similar to empathy may be significantly useful from a developmental perspective, because only some of its components or precursors may be observable. Until fairly recently, research on the development of empathy-related responding from a neurobiological degree of analysis has been relatively sparse. We believe that integrating this perspective with behavioral observations can shed mild into the neurobiological mechanisms underpinning the essential building blocks of empathy and sympathy and their age-related useful adjustments. Such integration helps us characterize the neurobiological processes that underpin interpersonal affective responding and prosocial behavior while also potentially informing interventions for people with atypical improvement, such as antisocial behavior problems. Empathy is implemented by a network of distributed, recursively connected, interacting neural systems and areas, including the superior temporal sulcus, insula, medial and orbitofrontal cortices, amygdala, and anterior cingulate cortex, as nicely as autonomic and neuroendocrine methods implicated in sociality. Prosocial habits is an umbrella term for actions that are benefiting one other person. This umbrella idea contains many various kinds of behaviors corresponding to helping, cooperating, sharing, comforting, rescuing, and informing. These numerous types of prosocial behaviors have distinct underlying motivations such as caring, equity, reputation administration, group loyalty, reciprocity, social rewards, and so forth. Morality refers to prescriptive norms concerning how individuals should deal with one another, together with ideas similar to justice, equity, and rights. All definitions of morality minimally include judgment of the rightness or wrongness of acts or behaviors that knowingly cause harm to people. Autonomic synchronization entails any associative pattern within the physiologies of interacting companion like a mom and her youngster, such as synchrony in coronary heart price, respiration rhythm, pupil diameter, and hormonal degree. Emotion contagion is the unconscious tendency to take on the sensory, motor, physiological, and affective states of others. Investigating dysfunction of the parts of empathy offers essential clues for understanding deviations that can lead to the dearth of concern for others in social decision-making and conduct. Some scholars more narrowly characterize empathy as one specific set of congruent A developmental neuroscience perspective on empathy Chapter 22 487 feelings, those feelings which are extra other-focused than self-focused, and make use of the notion of empathic concern (Batson, 2012), which is functionally linked with a motivation to look after the welfare of one other. The experience of empathy can lead to caring (an other-oriented motivation) or personal distress (an egoistic motivation to cut back stress by withdrawing from the stressor, thereby lowering the chance of prosocial behavior). Emotion regulation is considered to be a important part of empathy, because the modulation of emotional experience allows a person to remain conscious of an emotionally evocative scenario with out being overwhelmed or numbed by it. This is particularly necessary within the case of unfavorable arousal (Decety and Lamm, 2009). For instance, in 5- to 6-year-old youngsters, prosocial habits is significantly correlated with ratings of the emotional state of the protagonist but not with personal emotional state, suggesting that empathic concern quite than personal distress is the primary affect on prosocial conduct (Williams et al. These sides operate by the use of automatic and controlled processes and interact with one another. Yet they are often dissociated, as they depend on partially separable information processing systems and underlie different features (Shdo et al. Moreover, these sides have different developmental trajectories and phylogenetic roots (Decety and Svetlova, 2012). Functional imaging research reveal that the anterior insula and the anterior cingulate cortices are conjointly activated during the experience of negative emotion and in the course of the perception of negative emotion in others. The insula offers a foundation for the illustration of subjective bodily emotions, which substantiates emotional consciousness. For occasion, present temper states, relationship to the particular person, social standing, and the context by which the interplay occurs affect the way and the extent to which the observer will react. In the next sections, each of the parts of empathy (affect sharing, emotion understanding, perspective-taking, and emotion regulation) might be considered individually from a developmental neuroscience perspective. These components are dissociable as documented in sufferers with brain lesions (Shdo et al. In addition, both genetic and environmental factors contribute to the development of empathy and prosociality (Knafo et al. Both developmentally and evolutionarily, advanced types of empathy are preceded by and develop out of more elementary ones, such as the capability to specific and respond adaptively to emotional signals (Decety et al. Affective responsiveness is thought to be current at an early age, is involuntary, and relies on somatosensorimotor resonance between other and self (Decety and Meyer, 2008). This type of physiological linkage is shared by most mammals and represents the earliest type of emotional contagion that occurs between a mom and a child even earlier than start (Feldman, 2016). Infants implicitly pick up these subtle social alerts from their caregivers, and this in flip has an impact on their very own physiology and cognition (Prochazkova and Kret, 2017). The experience of synchrony through the first months of age demonstrates how crucial environmental input is for each the maturation of neural circuits that support social engagement (Johnson et al. In a cross-sectional research, 6- and 9-month-old infants were offered with schematic depictions of eyes with smaller and bigger pupils whereas their own pupil sizes have been recorded (Fawcett et al. Similarly, another examine demonstrated that 6- and 12-month-old infants had greater pupil dilation whereas viewing videos of other infants laughing and crying than whereas viewing videos of impartial babbling (Geangu et al. This spontaneous transfer of internal states is prime for survival, social group cohesion and, we contend, the event of empathy. Pupil mimicry modulates belief decisions through the activation of the theory-of-mind community (precuneus, temporoparietal junction superior temporal sulcus, and medial prefrontal cortex). This demonstrates that pupil mimicry is regulated by the theory-of-mind network and informs selections of trust. The outcomes revealed that infants in all age categories mimicked crying, with distress reactions highest in response to cries of pain. Thus, it appears that infants are endowed with an early capacity for differentiating among elemental distress indicators. Complementing the aforementioned behavioral findings, neurophysiological approaches doc that neonates seem to possess prewired neural mechanisms for discriminating vocal affect. Differential responding was noticed, listed by an increase in eye opening habits in response to the presentation of joyful speech patterns. More importantly, differential responding was observed solely when the infants listened to emotional speech spoken by speakers of their maternal language. The emotional and physiological synchrony with others (mostly caregivers) permits for dynamic transactions on which intersubjectivity and empathy develop.
100 mg modafinil overnight deliveryAnosognosia A disorder of govt operate by which a person lacks insight into his or her deficits insomnia music buy modafinil 200mg cheap. Anterior (ventral) corticospinal tract A nerve tract that originates in the motor and premotor areas of the frontal lobe after which courses ipsilateral down the spinal twine insomnia funny purchase 200 mg modafinil free shipping, inputting on the ventral horn insomnia 9 dpo cheap modafinil 100mg fast delivery. Anton syndrome A uncommon condition during which patients have visual loss and visual anosognosia insomnia 55 modafinil 100mg low cost. Axodendritic synapse A synapse that entails the axon of 1 neuron connecting and sending a chemical signal to the dendrite of one other neuron. Axosomatic synapse A synapse that includes the axon of one neuron connecting and sending a chemical signal to the soma of one other neuron. Apraxic agraphia A problem in writing as a result of injury to the superior parietal lobe, premotor cortex, and supplementary motor area that results in people not being in a position to call up the motor plans for writing. Arachnoid area An actual area under the arachnoid mater and above the pia mater. Aspiration Penetration of food or liquid beneath the vocal cords, providing a clear path to the lungs. Astereognosis Difficulty recognizing three-dimensional types by way of touch, often as a result of harm to the primary sensory cortex. Astrocyte A star-shaped nervous system cell that nourishes neurons and helps to maintain the neuronal environment. Ataxic dysarthria A type of dysarthria caused by cerebellar harm and characterised by harsh voice, monopitch, loud voice, imprecise consonants, and irregular breakdown in articulation. Attentional alexia A condition in which the particular person can learn single phrases, however when there are a quantity of phrases on a page the person turns into distracted and unable to read. Audition the process of listening to whereby acoustic or sound power waves are turned into neural impulses. Auditory association cortex An space in the superior temporal lobe concerned in auditory processing and attaching meaning to spoken words. Autism A neurological developmental dysfunction that occurs in 1 in sixty eight youngsters in the United States and is characterized by problems in social interaction, communication issues, and stereotyped behaviors, all of which are diagnosed earlier than a baby is 3 years of age. Autonomic nervous system That a part of the motor nervous system concerned in body functions that occur automatically and without acutely aware management. In a wholesome grownup, a traditional (negative) Babinski sign occurs when the toes curl and withdraw from the scratching. An abnormal (positive) Babinski happens when the massive toe extends and the opposite toes flare out, indicating upper motor neuron injury. Basal ganglia A group of subcortical gray matter structures including the caudate nucleus, globus pallidus, and putamen. Benedikt syndrome A condition caused by damage to the midbrain, resulting in contralateral hemiparesis and ataxic tremor. Binaural hearing Hearing with two ears that enables us to determine the placement of a sound. Brain dying A state in which a person has no purposeful responses to stimuli, no brainstem reflexes, and no sleep´┐Ż wake cycle, and there are flat electroencephalographic patterns. It consists of the medulla, pons, and midbrain, which collectively control many fundamental life features and reflexes. Brodmann map A map of the human mind by which the cerebral cortex is split into 52 areas primarily based on variations in gross anatomy and mobile structure with the thought that every of those areas is answerable for certain capabilities. Carotid arteries the primary arteries that run up the anterolateral a part of the neck and feed the mind blood. Cell concept A concept that states that each one organic beings (humans, animals, and plants) are composed of particular person cells. Central agraphia A reading downside involving impairment in the underlying linguistic studying system. Central auditory system the auditory system that entails hearing buildings found centrally within the head, together with areas in the brainstem, the thalamus, and the cerebral cortex. Central fissure A deep groove in the mind that separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe. Centrosome A cell structure that directs the expansion of the cell via cell division. Cerebellar circuit A neural circuit involving the cerebellum, premotor cortex, and precentral gyrus that integrates proprioceptive and kinesthetic info into motor activity in order that motor actions are easy and exact. Cerebellar hemispheral syndrome A condition of the cerebellum that might be caused by stroke, tumor, and multiple sclerosis that primarily affects the ipsilateral limbs, causing tremor, dysmetria, and dysdiadochokinesia. Cerebellar peduncles Nerve tracts that make communication between the cerebellum and different nervous system buildings possible. Cerebellum A structure that lies just posterior to the pons and is concerned within the coordination and precision of fantastic motor movement. Cerebral hemispheres the areas of the mind, divided into left and proper cerebral hemispheres, that management greater cortical functions such as cognition and language as nicely as planning motor perform and interpreting sensory experiences. Cerebral refers to the brain and palsy refers to paralysis or uncontrolled actions. Cerebral peduncles Portion of the midbrain that includes everything besides the tectum. Cerebral spinal rhinorrhea A condition brought on by trauma to the nose resulting in cerebral spinal fluid leaking through the nostril. Chorea Means "like a dance"; quick actions of the hands or feet which have a dance-like quality. Choroid plexus A construction located in each ventricle that produces cerebrospinal fluid. Cingulate cortex An space located in the medial floor of the mind between the corpus callosum and the cingulate sulcus. Circle of Willis A circular array of blood vessels on the base of the mind that helps to equalize blood circulate and strain. Claustrum A sheet-like membrane of neurons under the cortex that seems to provide some level of cortical control of swallowing. Clonus Involuntary muscle contractions, which can have a rhythmic high quality; one frequent instance is hiccups. Closed head harm A kind of traumatic brain injury that includes forces that trigger injury to the mind, but with out penetrating the skull; examine to open head injury. Cricopharyngeus A muscle on the high of the esophagus that relaxes, permitting the bolus to enter the esophagus. Cytoskeleton A cell construction made up of microtubules that transport molecules across the cell. Cognition the psychological means of knowing by which we purchase and act upon knowledge.
Order modafinil 100 mg free shippingInterestingly insomnia zyprexa generic modafinil 100 mg online, these alterations have been reversed after 6-month remedy with metformin insomnia 4 days discount modafinil 200mg amex. Nevertheless insomnia 2015 line up cheap 100 mg modafinil free shipping, regardless of the ample literature on this topic sleep aid alteril purchase modafinil 100 mg on line, the evidence relating to pediatric populations remains scarce. Neaton, Is relationship between serum cholesterol and risk of untimely dying from coronary heart disease continuous and graded Relationship of baseline serum cholesterol levels in three large cohorts of younger males to long-term coronary, cardiovascular, and all-cause mortality and to longevity. Atherosclerosis of the aorta and coronary arteries and cardiovascular risk factors in persons aged 6 to 30 years and studied at necropsy (The Bogalusa Heart Study). Accumulation of extracellular cholesterol-rich liposomes within the arterial intima and cardiac valves of the hyperlipidemic rabbit. Tracking of serum lipids and lipoproteins from childhood to maturity: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Association between multiple cardiovascular threat elements and atherosclerosis in kids and young adults: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Expert Panel on Integrated Guidelines for Cardiovascular Health and Risk Reduction in Children and Adolescents; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Expert panel on built-in guidelines for cardiovascular well being and danger discount in kids and adolescents: abstract report. Proatherosclerotic events: pathobiochemical adjustments occurring within the arterial wall earlier than monocyte migration. Subendothelial lipoprotein retention because the initiating course of in atherosclerosis: replace and therapeutic implications. Lipoprotein modification and macrophage uptake: function of pathologic ldl cholesterol transport in atherogenesis. Multiple substrates for paraoxonase-1 during oxidation of phosphatidylcholine by peroxynitrite. Paraoxonase polymorphism Met-Leu54 is related to modified serum concentrations of the enzyme. A possible link between the paraoxonase gene and increased risk of cardiovascular disease in diabetes. Paraoxonase-1 deficiency in mice predisposes to vascular inflammation, oxidative stress, and thrombogenicity within the absence of hyperlipidemia. Human paraoxonase gene cluster transgenic overexpression represses atherogenesis and promotes atherosclerotic plaque stability in ApoE-null mice. Quantitative evaluation of the influence of paraoxonase 1 exercise and coronary heart disease risk. Serum paraoxonase-1 exercise in kids: the results of weight problems and insulin resistance. The impact of ´┐Ż lifestyle change and metformin remedy on serum arylesterase and paraoxonase exercise in obese children. ´┐Ż Human paraoxonase-1 exercise in childhood obesity and its relation to leptin and adiponectin ranges. Q192R polymorphism of paraoxonase 1 gene associated with insulin resistance in Mexican youngsters. Paraoxonase genotype and carotid intima-media thickness in children with familial hypercholesterolemia. Paraoxonase-1 activities in kids and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Paraoxonase 1 polymorphisms (L55M and Q192R) as a genetic marker of diabetic nephropathy in youth with sort 1 diabetes. Modulation by blood glucose ranges of activity and focus of paraoxonase in younger sufferers with sort 1 diabetes mellitus. Paraoxonase gene cluster is a genetic marker for early microvascular issues in sort 1 diabetes. Relationship between paraoxonase-1 and butyrylcholinesterase activities and nutritional standing in mexican youngsters. Serum paraoxos nase/arylesterase activity and oxidative stress standing in youngsters with metabolic syndrome. Effects of paraoxonase, s arylesterase, ceruloplasmin, catalase, and myeloperoxidase activities on prognosis in pediatric sufferers with sepsis. Paraoxonase 1 polymorphism and prenatal pesticide publicity related to opposed cardiovascular danger profiles at college age. Activity of the antioxidant enzyme paraoxonase in Argentinean kids residing at excessive altitude. Physical activity and cardiometabolic danger in male kids and adolescents: the Balcarce research. Paraoxonase-1 activity in sufferers with cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The driving forces for these biochemical reactions are several intracellular free radicals. These free radicals are produced as a byproduct of those biochemical reactions involving oxygen and localized in numerous mobile compartments, similar to mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and peroxisomes. Mitochondrion, being probably the most reactive mobile organelle, is considered the most important source of reactive radicals. These biochemical reactions facilitate the metabolism and development of a living system. Several stories recommend that in mitochondria, roughly 2% of the consumed oxygen is converted into superoxides via redox reactions. They primarily act as secondary messengers in numerous signaling cascades and regulate virtually every essential life course of. Functioning of the mitochondrial electron transport chain mostly contributes to the intracellular technology of superoxide. A schematic diagram representing the damaging impact of free radical accumulation in numerous cellular compartments. Accumulation of free radicals lead to injury the intracellular biomolecules similar to proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids. It causes structural and useful adjustments in biomolecules and impairs several signaling cascades. Apart from these, the mobile activity involving immune responses just like the activation of macrophages and manufacturing of cytokines generate totally different reactive radicals, including superoxide, nitric oxide, hydroxyl radical, and hydrogen peroxide. Recent analysis reports have recognized several different antioxidant enzymes similar to thioredoxins, peroxynitrite reductases, thioredoxin reductases, methionine sulfoxide reductase, and others. The panel on the right represents probably the most predominant intracelular antioxidant machinary and its functioning.
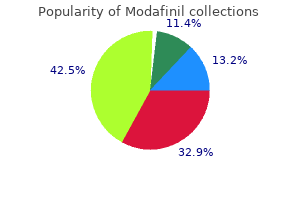
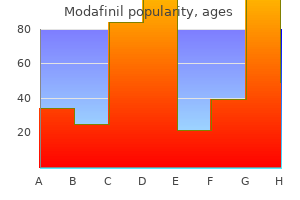
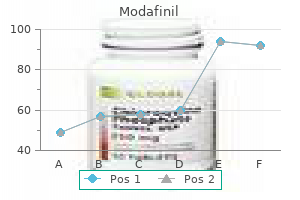
Modafinil: 200 mg, 100 mg
Buy cheap modafinil 200 mgDynamic transformation of Bergmann glial fibers proceeds in correlation with dendritic outgrowth and synapse formation of cerebellar Purkinje cells insomnia wheesung cheap modafinil 100 mg online. Development of stellate and basket cells and their apoptosis in mouse cerebellar cortex sleep aid belsomra modafinil 200mg with amex. The d2 glutamate receptor: a key molecule controlling synaptic plasticity and construction in Purkinje cells insomnia yale generic modafinil 200 mg without prescription. A important role for neurofascin in regulating action potential initiation through upkeep of the axon initial phase sleep aid toddler cheap modafinil 200mg without a prescription. The unfastened and uncritical use of the term in ways which are so generalized as to be unhelpful and even confusing 107 5. A lack of a common presence of sure columns within cortical areas, brains, and species is undermining the concept that comparable building blocks comprise all cortical circuits 108 5. Overlap between columnar entities within the similar constructions; combining physiological and anatomical definitions 111 5. General concept that the cortical column (even just an arbitrary unit column that includes the total depth of the cortex) has a common fixed variety of neurons related to it 112 5. Lack of correlation between the absence or presence of particular columns and a selected sensory or cognitive processing community (comparisons across the same mind and throughout close and extra distant species) 112 5. What is the correlation between the columnar improvement of the mind and future columns 119 5. Ontogenic units/columnsdthe fundamental building blocks in the creating neocortex119 5. The method forward 122 Acknowledgments 123 References 123 Columns are ubiquitous in the mind but by no means obligatory, and comprehensive descriptions of the various specific types of "columns" within the brain are nonetheless in progress. Pyramidal neurons are generated in "ontogenic models" and subsequently disperse radially. It has been proven that sibling cells have a stronger tendency to establish synaptic connections with each other within the cortical plate. However, the link between the embryonic and grownup columnar constellations is currently not identified. There are, due to this fact, a quantity of problems concerning the time period and concept of cortical column. Knowledge of the laminar and columnar organization of the cerebral cortex is constantly advancing, and with this, the conceptual particulars of the columnar group are also changing. The time may arrive when both the idea and the nomenclature may also should adapt to these adjustments. The hypothesis of the column as the elemental processing unit of the cerebral cortex was formulated by Mountcastle (1957) from studies of cells responding to a single modality of tactile stimuli (cutaneous or deep joint receptors) within the somatosensory cortex of the cat. By exploring the physiological, anatomical, genetic, and developmental properties of the cerebral cortex, more particulars of its group have been revealed, and lots of of those new entities were referred to as "column. There are references to practical columns, minicolumns, hypercolumns, ontogenetic or embryonic columns, ocular dominance columns, orientation columns, and barrel columns. The solely common theme linking these terms is that they refer to a structural, physiological, or developmental organization that transcends the laminar pattern and is perpendicular to it. None of these a number of forms of column are general to all cortical areas, and various other are restricted to main sensory areas. Mountcastle (1997) "The modular group of nervous techniques is a widely documented precept of design for both vertebrate and invertebrate brains of which the columnar group of the neocortex is an example. The classical cytoarchitectural areas of the neocortex are composed of smaller items, native neural circuits repeated iteratively within each space. Modules are mostly grouped into entities by units of dominating exterior connections. This unifying factor is most evident for the heterotypical sensory and motor areas of the neocortex. Columnar defining factors in homotypical areas are generated, partly, throughout the cortex itself. The set of all modules composing such an entity could also be fractionated into totally different modular subsets by completely different extrinsic connections. Linkages between them and subsets in other massive entities type distributed techniques. The neighborhood relations between related subsets of modules in different entities end in nested distributed techniques that serve distributed features. A cortical area outlined in classical cytoarchitectural terms might belong to a couple of and sometimes to several distributed techniques. Columns in cytoarchitectural areas positioned at a long way from one another, but with some frequent properties, could additionally be linked by long-range, intracortical connections. Neurons inside a minicolumn encode similar options, whereas a hypercolumn "denotes a unit containing a full set of values for any given set of receptive subject parameters. Various estimates recommend there are 50e100 cortical minicolumns in a hypercolumn, each comprising around 80 neurons. An important distinction is that the columnar group is useful by definition, and reflects the native connectivity of the cerebral cortex. Connections "up" and "down" throughout the thickness of the cortex are a lot denser than connections that spread from facet to aspect. They are ubiquitous within the mind however on no account obligatory, and a complete description of the various forms of "columns" in the brain is still missing. Beyond the cortical column: abundance and physiology of horizontal connections suggest a powerful role for inputs from the surround. Module Cortical column/ module Cortical area S1 Definition Penetrations parallel to the pial floor and crossing the vertical axis of the cortex move by way of 300- to 500-mm-sized blocks of tissue in every of which neurons with identical properties are encountered. Sharp transitions are observed from a block with one set of properties to the adjacent block with completely different properties. Most neurons arrayed in a column perpendicular to the cortical surface display the same aural dominance and binaural interplay. Summation columns occupy about two-thirds of the realm sampled; suppression columns, about one-third. Summation columns appear to be composed of smaller columns differing in aural dominance. Repeat interval of 500e550um, the parallel rows are 350 mm apart Livingston and Hubel (1984) Isofrequency bands A1 No wider than 200 mm, and 5e7 mm in size extending across the gyrus the sizes of binaural interplay columns vary considerably; some occupy a number of square millimeters of cortical floor. Dimension 300 mm extensive, separated by 100 mm cell-sparse zones 400e500 mm References Meyer et al. In this article, (1) we focus on the problems associated with our current nomenclature; (2) discuss the evidence for and towards the concept that columns are the common constructing blocks of the cortex; (3) look at the question of how constant the cell numbers are inside a column and the way homogeneous is the structure of the assorted columns; (4) examine the attainable functions of the columns; and (5) look at our present information of the columnar growth in the cortex. The cortex is organized horizontally into six laminae and vertically into teams of cells linked synaptically throughout and alongside the horizontal layers. The definitions of laminae and radial modules are each a historic conference, quite than a biologically or functionally related demonstrable reality.
Syndromes - Chest x-ray
- Rinse your mouth with mild, over-the-counter mouthwashes or salt water.
- Receiving a blood transfusion or blood components
- Broken bones
- Draining fluid from the pericardial sac (pericardiocentesis) to prevent or treat cardiac tamponade
- Nonpapillary (sessile) tumors are flat. They are much less common. However, they are more invasive and have a worse outcome.
Modafinil 200mgFetal programming of brain growth: intrauterine stress and susceptibility to psychopathology sleep aid dementia order modafinil 100mg amex. Rearing environment and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal regulation in younger rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) insomnia university city discount 200 mg modafinil overnight delivery. Psychological and neuroendocrinological sequelae of early social deprivation in institutionalized children in Romania sleep aid supplements order modafinil 200 mg amex. Decreased adrenocorticotropic hormone and cortisol responses to stress in healthy adults reporting vital childhood maltreatment insomnia online cheap modafinil 200 mg line. Maternal corticosterone during lactation completely impacts mind corticosteroid receptors, stress response and behavior in rat progeny. The differential impacts of early physical and sexual abuse and internalizing issues on daytime cortisol rhythm in school-aged children. Mismatched pre-and postnatal vitamin leads to cardiovascular dysfunction and altered renal perform in maturity. Sex and the human placenta: mediating differential strategies of fetal growth and survival. An experimental test of the fetal programming hypothesis: can we scale back baby ontogenetic vulnerability to psychopathology by decreasing maternal despair Prenatal maternal cortisol concentrations predict neurodevelopment in center childhood. The timing of prenatal publicity to maternal cortisol and psychosocial stress is associated with human infant cognitive improvement. Prenatal remedy with glucocorticoids sensitizes the hpa axis response to stress among full-term infants. Corticotropin-releasing hormone during being pregnant is associated with infant temperament. Prenatal publicity to maternal depression and cortisol influences toddler temperament. Sexually dimorphic responses to early adversity: implications for affective problems and autism spectrum disorder. Prenatal maternal nervousness and depression predict adverse behavioral reactivity in infancy. Maternal care counteracts behavioral effects of prenatal environmental stress in feminine rats. Environmental stress as a developmental cue: corticotropin-releasing hormone is a proximate mediator of adaptive phenotypic plasticity in amphibian metamorphosis. Pubertal recalibration of cortisol reactivity following adolescence stress: a cross-sectional evaluation. Corticosteroid receptor polymorphisms: determinants of vulnerability and resilience. Acute stressors and cortisol responses: a theoretical integration and synthesis of laboratory analysis. Maternal psychological misery during being pregnant in relation to baby improvement at age two. Childhood cumulative threat and later allostatic load: mediating position of substance use. Physical development delays and stress dysregulation in stunted and non-stunted Ukrainian institution-reared youngsters. Longitudinal patterns of cortisol regulation differ in maltreated and nonmaltreated children. Stress in being pregnant: empirical proof and theoretical points to guide interdisciplinary analysis. Timing of fetal publicity to stress hormones: effects on new child bodily and neuromuscular maturation. Perceived early-life maternal care and the cortisol response to repeated psychosocial stress. Maternal stress starting in infancy could sensitize kids to later stress exposure: results on cortisol and conduct. Maternal postpartum conduct and the emergence of infantemother and infantefather synchrony in preterm and fullterm infants: the position of neonatal vagal tone. Effects of a poverty-alleviation intervention on salivary cortisol in very low-income kids. Early expertise in people is related to adjustments in neuropeptides important for regulating social behavior. Early developmental emergence of human amygdalaeprefrontal connectivity after maternal deprivation. Risk and resilience: genetic and environmental influences on growth of the stress response. The results of stress on early mind and behavioral development Chapter 26 581 Giurgescu, C. Relationships amongst neighborhood environment, racial discrimination, psychological distress, and preterm start in African American girls. Sex variations within the programming results of prenatal stress on psychopathology and stress responses: an evolutionary perspective. Giving delivery to a model new brain: hormone exposures of being pregnant affect human reminiscence. Gestational hormone profiles predict human maternal habits at 1-year postpartum. Prenatal maternal mood patterns predict youngster temperament and adolescent psychological well being. Maternal sensitivity moderates the impact of prenatal nervousness disorder on infant mental development. Disturbances in morning cortisol secretion in association with maternal postnatal melancholy predict subsequent depressive symptomatology in adolescents. Social assist and oxytocin work together to suppress cortisol and subjective responses to psychosocial stress. Prenatal stress will increase the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis response in younger and adult rats. Regulation of hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical responses to stressors by the nucleus of the solitary tract/dorsal vagal complicated. Reduced maternal corticosteroid-binding globulin and cortisol ranges in pre-eclampsia and gamete recipient pregnancies. Parent support is much less effective in buffering cortisol stress reactivity for adolescents compared to children. Psychobiological mechanisms underlying the social buffering of the hypothalamicepituitarye adrenocortical axis: a review of animal models and human studies across improvement. Fetal exposure to placental corticotropin-releasing hormone is associated with child self-reported internalizing symptoms. Fetal programming of hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal operate: prenatal stress and glucocorticoids. Early deprivation and residential basal cortisol levels: a examine of internationally adopted kids.
200 mg modafinil with mastercardSigns of government operate issues are evident within the three classes presented earlier-restraint sleep aid gabapentin cheap 200 mg modafinil free shipping, initiative insomnia depression purchase modafinil 100 mg line, and order insomnia opposite discount modafinil 200 mg mastercard. More specifically insomnia quiz purchase 200 mg modafinil with visa, those with govt operate problems could have trouble planning initiatives and projecting the time wanted to full them, 314 Chapter 14 the Neurology of Cognition into linguistic and extralinguistic deficits. Linguistic deficits include rambling speech, poor coherence in producing and comprehending conversation and narratives, poor comprehension of abstract language and humor, and poor pragmatic expertise. Extralinguistic deficits embody aprosody and a scarcity of producing and decoding emotion. Logic would dictate that improvements in consideration would result in enhancements in episodic memory on this population. Under restraint, they could reveal poor judgment and lack foresight in how their actions have an effect on others. These deficits are classified under order, specifically involving organization, sequencing, and temporal order. Cognitive-Communicative Disorders 315 One day a lady was doing dishes within the kitchen. As Mikey begins to take a cookie, he loses his stability on the stool and is about to fall onto the floor. Mikey should apologize to his mom and be disciplined, however then all might be forgiven. There are even instances the affected person misperceives elements in the picture, like seeing a hat as an alternative of a plate. This give attention to the main points on the expense of the whole picture could be a important problem in telling tales to others or in having coherent and cohesive conversations. These problems can result in vocational and educational points, because a lack of consideration impairs each memory and government functions, and slowed pondering makes these pursuits frustrating. Retrograde amnesia is a lack of some or all memory before the brain injury, whereas anterograde amnesia is a lack of some or all memory between the mind damage and the present. Anterograde amnesia is the loss of the flexibility to make new memories post-accident, like in the case of H. These struggles can impair all three primary areas of govt function (restraint, initiative, and order). In terms of restraint, sufferers will generally have problem inhibiting socially inappropriate behaviors. For example, they could make sexually explicit statements or inordinately use foul language. Initiative and order deficits can particularly impair their capability to set, attain, and evaluate progress on goals. The injury sustained can contain penetration of the skull (open head injury) or the mind coming involved with the within of the skull (closed head injury). During the second Gulf War, many troopers died or have been injured by improvised explosive units. The secondary degree of injury results from flying shrapnel, causing open head accidents. The tertiary level of harm occurs when soldiers are knocked off their toes by the explosion. They could suffer a closed head harm as a end result of hitting their head on the group or on an object. Lastly, quaternary ranges of harm contain something not covered under the classes of primary through tertiary levels of harm. Some of this shrinkage is due to neuronal dying, but most of it is as a end result of of myelin breaking down, the thinning of dendrites, and the loss of synapses. Webster had suffered from amnesia, melancholy, and executive operate issues for years, and Dr. There has even been a big-budget movie starring Will Smith known as Concussion that dramatizes Dr. Top: Whole mind section from a 65-year-old control subject showing no irregular tau protein deposition. Bottom: Microscopic section displaying numerous tau-containing neurofibrillary tangles within the mind. Bottom: Microscopic part showing ample tau-containing neurofibrillary tangles. Dementia is a group of progressive neurological problems that result in cognitive decline. Patients with this logopenic variant may be each fluent when not having word retrieval issues and nonfluent when experiencing anomia. These plaques are toxic to neural cells, causing inflammation and impairing their function. The area most affected is the hippocampus and entorhinal area, crucial structures for declarative reminiscence. This impairment can show up practically in the lack of ability to resist distraction from competing stimuli. This condition is genetic, following an autosomaldominant inheritance sample by which children of these affected have a 50% chance of inheriting the disease. Initiative to talk can wain because the illness turns into worse, and after they do converse, their thoughts can lack order and be confusing to the listener. As a college scholar, your cognitive talents must be working at a excessive level. The different types of attention mentioned on this chapter are important for sophistication lectures, studying, and other actions. Memory is important for learning new info (declarative memory) and in studying new skills (nondeclarative memory). Executive capabilities are additionally important for the numerous exams, quizzes, papers, and tasks. In many ways, setting and reaching realistic targets is as important as acquiring data and expertise. The info that ought to have been realized is listed beneath each learning goal. The forms of consideration include focused, sustained, selective, alternating, and divided. Long-term memory consists of declarative or explicit reminiscence (includes episodic and semantic) and nondeclarative or implicit reminiscence (includes procedural memory). The learner will describe the neural basis of attention, reminiscence, and govt capabilities. By comparability, in Huntington illness the basal ganglia degenerate, leading to nondeclarative memory points. Draw an illustration that might explain the different sorts of consideration discussed on this chapter. List the several sorts of attention and provides illustrations of how you utilize these in on a daily basis life.
Purchase modafinil 200mg visaThe differential contributions of the parvocellular and the magnocellular subdivisions of the pink nucleus to skilled reaching in the rat insomnia zoloft withdrawal buy cheap modafinil 100mg on line. Projection on the motor cortex of thalamic neurons with pallidal enter in the monkey insomnia 3dpo purchase modafinil 100mg amex. Precentral cortical zones associated to flexion and extension in two hindlimb movements within the monkey insomnia 2013 generic 200mg modafinil with mastercard. Use-dependent alterations of movement representations in main motor cortex of grownup squirrel monkeys insomnia gaming festival order modafinil 100mg with visa. A comparative neuroanatomical study of the pink nucleus of the cat, macaque and human. Corticostriatal interactions during learning, memory processing, and determination making. Acetylcholine as a neuromodulator: cholinergic signaling shapes nervous system perform and habits. Intracellular potentials recorded from motoneurons following precentral gyrus stimulation in primate. The significance of combinatorial gene expression in early Mammalian thalamic patterning and thalamocortical axonal guidance. Individual cells within the nucleus basalis´┐Żdiagonal band advanced have restricted axonal projections to the cerebral cortex within the rat. Genetic evidence that Celsr3 and Celsr2, along with Fzd3, regulate forebrain wiring in a Vangl-independent manner. The exercise of primary motor cortex corticospinal neurons during device use by macaque monkeys. Monkey primary motor and premotor cortex: single-cell activity related to prior information about path and extent of an supposed motion. EphB receptor forward signaling regulates area-specific reciprocal thalamic and cortical axon pathfinding. Pathfinding errors of corticospinal axons in neural cell adhesion molecule-deficient mice. Peripheral afferent inputs to the forelimb area of the monkey motor cortex: input-output relations. Extensive spinal decussation and bilateral termination of cervical corticospinal projections in rhesus monkeys. Fezf2 directs the differentiation of corticofugal neurons from striatal progenitors in vivo. Direct lineage reprogramming of post-mitotic callosal neurons into corticofugal neurons in vivo. Compensatory position of the cortico-rubro-spinal tract in motor restoration after stroke. Semaphorin-6A controls steering of corticospinal tract axons at multiple choice points. Rescuing transient corticospinal terminations and selling development with corticospinal stimulation in kittens. Topographic sequence of outgrowth of corticospinal axons within the rat: a study using retrograde axonal labeling with Fast blue. Anatomical proof for functional diversity in the mesencephalic locomotor region of primates. Normal and pathological neuronal distribution of the human mesencephalic locomotor region. Control of posture by reticular formation and cerebellum in the intract, anesthetized and unanesthetized and within the decerebrated cat. Selective collateral elimination in early postnatal development restricts cortical distribution of rat pyramidal tract neurones. Excitation of pyramidal tract cells by intracortical microstimulation: effective extent of stimulating current. Synaptic termination of afferents from the ventrolateral nucleus of the thalamus in the cat motor cortex. Motor restoration and microstructural change in rubro-spinal tract in subcortical stroke. Differential laminar distribution of corticostriatal neurons in the prefrontal and pericruciate gyri of the dog. Skill learning induced plasticity of motor cortical representations is time and age-dependent. Organization and morphology of thalamocortical neurons of mouse ventral lateral thalamus. Corticospinal circuits from the sensory and motor cortices differentially regulate skilled movements via distinct spinal interneurons. Individual mind organoids reproducibly type cell range of the human cerebral cortex. Distribution of cerebellar and somatic lemniscal projections within the ventral nuclear complicated of the Virginia opossum. Cortical neurons require Otx1 for the refinement of exuberant axonal projections to subcortical targets. Specific patterns of intrinsic connections between representation zones within the rat motor cortex. Paw and limb use in skilled and spontaneous reaching after pyramidal tract, pink nucleus and mixed lesions in the rat: behavioral and anatomical dissociations. Morphology and synaptic connections of crossed corticostriatal neurons in the rat. Reconstruction of 1,000 projection neurons reveals new cell varieties and organization of long-range connectivity within the mouse brain. Somatotopic group of corticospinal and corticotrigeminal neurons within the rat. Ctip1 regulates the steadiness between specification of distinct projection neuron subtypes in deep cortical layers. Patterns of localization in precentral and "supplementary" motor areas and their relation to the idea of a premotor area. A genuine layer 4 in motor cortex with prototypical synaptic circuit connectivity. Combining optogenetics and electrophysiology to analyze projection neuron circuits. Instructing perisomatic inhibition by direct lineage reprogramming of neocortical projection neurons. Forward signaling mediated by ephrin-B3 prevents contralateral corticospinal axons from recrossing the spinal wire midline. Optimal parameters for microstimulation derived forelimb motion thresholds and motor maps in rats and mice. Specific basal forebrain-cortical cholinergic circuits coordinate cognitive operations. Chapter 9 Organization and development of hippocampal circuits Michele Pignatelli1, 2 and Kathleen S.

Buy modafinil 100 mg cheapMost necessary within the present context was that they may integrate visual-auditory stimuli insomnia janet jackson best 100 mg modafinil. But the cross-modal stimuli needed to insomnia types cheap modafinil 200mg online be spatially disparate in order to insomnia pms buy 100 mg modafinil simultaneously fall within their respective receptive fields sleep aid yahoo buy 200 mg modafinil mastercard. Collectively the data reveal that have is essential for the development of multisensory integration and that the character of the expertise directs the formation of the underlying neural circuits via which this integration is achieved. Chronic deactivation was accomplished by implanting muscimol-infused pledgets of Elvax (a polymer) over affiliation cortex. When the polymer is depleted or eliminated, cortical activity returns rapidly, and is once again aware of environmental stimuli. Behavioral and physiological research have been then accomplished when the animals had reached 1 year of age. Animals appeared normal in their capacity to reply to visual stimuli in each visual fields. They additionally benefited from visual-auditory cues in the ipsilateral hemifield as much as did normal animals. However, they have been severely compromised in their multisensory responses to cross-modal stimuli in their contralateral hemifield. That these deficits in multisensory integration were obvious lengthy after cortex was once again energetic (a period far longer than that required for its regular acquisition in early life) could possibly be interpreted as reflecting a "crucial" or "delicate" interval for instantiating this course of. This possibility was examined in some of the identical animals which have been retained for a quantity of years. These animals had been then retrained in the behavioral task and subsequently examined as before. They appeared to be normal, indicating that they acquired the ability to integrate visualauditory cues later in life. When visual-auditory stimuli have been spatiotemporally coincident and throughout the visual (left) or auditory (center) receptive fields, the multisensory response was no higher than that evoked by the best component stimulus. But, when the 2 stimuli have been disparate in house and concurrently introduced inside their respective receptive fields, they elicited a considerably enhanced multisensory response. Thus, the neuron built-in spatially disparate visual-auditory stimuli as normal animals integrate spatially concordant visualauditory stimuli, a seeming "reversal" of the spatial principle. This functionality of adults to purchase multisensory enhancement capabilities was immediately demonstrated in dark-reared and noise-reared animals that had been repeatedly uncovered in a "sensory coaching" paradigm to spatiotemporally concordant pairs of visual-auditory cues (Yu et al. This grownup growth was proven to be "site-specific": only neurons whose receptive fields encroached on the publicity areas developed multisensory enhancement capabilities. Normal levels of multisensory enhancement had been observed inside a few months of weekly exposure periods (Yu et al. This rapidity contrasts with the much longer time scale required for this adult growth in regular environments; nonetheless, the explanation for this distinction is presently unknown. For apparent reasons, technical limitations make conducting such studies in neonates quite troublesome, and especially of creating any direct correlations with the maturation of sensory properties in the primary sensory developmental mannequin, the cat. The target areas include the central grey overlying the oculomotor nucleus, an area into which oculomotor dendrites project, as properly as segments of the pontine and medullary reticular formation that connect to the abducens nucleus (Stein et al. This region is concerned in controlling head and limb movement, and these projections are described intimately in adults by Huerta and Harting (1982a,b). Such electrical stimulation elicits eye, ear, neck, whisker, and limb movements, albeit with higher threshold and decrease reliability than in adults. Thus, for example, the formation of topographic representations and the event of multisensory integrative capabilities have obvious implications for producing behavioral output and behavioral correlates in developing animals. A neural community model of multisensory integration also accounts for unisensory integration in superior colliculus. Multisensory integration within the superior colliculus requires synergy amongst corticocollicular inputs. Cortex mediates multisensory but not unisensory integration in superior colliculus. Rapid enhancement of visible cortical response discriminability by microstimulation of the frontal eye area. A direct projection from the retina to the intermediate gray layer of the superior colliculus demonstrated by anterograde transport of horseradish peroxidase in monkey, cat and rat. Intrinsic circuitry in the cat superior colliculus: projections from the superficial layers. The affect of stimulus properties on multisensory processing in the awake primate superior colliculus. Crossmodal integration within the primate superior colliculus underlying the preparation and initiation of saccadic eye movements. The effects of early postnatal modification of body shape on the somatosensory-visual group in mouse superior colliculus. Sensitive intervals for visible calibration of the auditory house map within the barn owl optic tectum. Postnatal improvement of retinogeniculate, retinopretectal and retinotectal projections in the opossum. Visual attention: linking prefrontal sources to neuronal and behavioral correlates. Responses in area V4 depend upon the spatial relationship between stimulus and a spotlight. Responses to visible stimulation and relationahip between visual, auditory, and somatosensory inputs in mouse superior colliculus. Neural maps of head motion vector and speed within the optic tectum of the barn owl. The deep layers of the superior colliculus: their reticular characteristics and structural group. The impact of rotatory stimulation on the actions of the pinnacle and eyes in new child and younger kittens. Effects of monocular lid closure on improvement of receptive-field characteristics of neurons in rabbit superior colliculus. Postnatal improvement of retinal projections in Syrian hamsters: a examine using autoradioagraphic and anterograde methods. Axon morphologies and convergence patterns of projections from different sensory-specific cortices of the anterior ectosylvian sulcus onto multisensory neurons within the cat superior colliculus. Cortex contacts each output neurons and nitrergic interneurons within the superior colliculus: direct and oblique routes for multisensory integration. Axonal patterns and sites of termination of cat superior colliculus neurons projecting in the tecto-bulbo-spinal tract. Anatomical group of retinotectal afferents within the cat: an autoradiographic examine. Descending pathways from the superior colliculus: an autoradiographic evaluation in the rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta). Anterograde degeneration study of the superior colliculus in Tupaia glis: proof for a subdivision between superficial and deep layers. Ascending pathways from the monkey superior colliculus: an autoradiographic analysis.

Buy 200 mg modafinil with amexNote thin profiles (arrows) radiating from the blind spot in (C and D) insomnia new haven modafinil 100 mg generic, which symbolize shadows (angioscotomas) from retinal blood vessels sleep aid zma 200mg modafinil free shipping. M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors have a modular pattern equate sleep aid liquidcaps 96ct order modafinil 200 mg free shipping, which matches thalamic terminations from the lateral geniculate nucleus sleep aid od generic modafinil 200 mg on line. They show distinct practical specializations, not for ocularity, however somewhat for spatial or temporal acuity (respectively, the M2-rich and the M2-poor patches). Despite a long time of work, the organization of those modules and their connections, singly or in relation to one another, is just poorly understood. However, a few of these studies revealed no discrete anatomical arrangements that might clarify modularity of operate. As we discussed, the time period cortical "column" is ambiguousdit can refer to small-scale minicolumns (diameter 50 mm), to larger-scale macrocolumns (diametere300e500 mm), or to a quantity of totally different buildings inside each classes (Jones, 2000; Rakic, 2007; Rockland, 2010). It can additionally be generally accepted that the cortical surface areas vary much more than the radial thickness of the cortex. After quantification in selected species, it has been proposed that regardless of the thickness of the cortex inside an arbitrary (30-mm-wide, 25-mm-deep) vertical "column" between the pial floor and the white matter of the cortex, the number of neurons is a hundred and ten in all cytoarchitectonic areas (Rockel et al. Under such conditions, the neuronal number was claimed fixed in all mammalian species (mouse, rat, cat, Old World monkey, human) and for all cortical thicknesses, the numbers of cells in these arbitrary columns in prefrontal, major motor, somatosensory (posterior) parietal, and temporal neocortex (except the primary visible cortex in primates) all being the identical. There was just one area within the cortex that confirmed a difference from this constant quantity; in all primates studied (Galago, marmoset, squirrel monkey, macaque monkey, baboon, and human), the number per 30-mm-wide, 25-mm-deep column of visible cortex was increased to about 260e270. This improve is a reflection of the much larger packing density of cells in the true striate cortex. In a later research with Anita Hendrickson, Powell discovered that the neuronal number remained fixed throughout each the monocular and binocular segments of the macaque visual cortex (Powell and Hendrickson, 1981). The changes in packing density of neurons within the arbitrary unit columns had been inversely related to the volume of neuropil. Using related methods in marsupials, it has been established that the neuronal numbers are half the ones noticed in mouse in an identical arbitrary unit column (Cheung et al. Using a more recent "unbiased" stereology methodology, Herculano-Houzel and her colleagues showed that the density of neurons within the neocortex varies as much as thrice even among the highly related primate species (Herculano-Houzel et al. However, the idea that all mammalian cortices in most areas have a very comparable numerical fidelity has to be deserted. In fact, the differences may hold a key to understanding cortical specializations for specific functions. These could be from subtle microscopic patterns to macroscopically identifiable options. Some distinctive body components with homologously formed neuronal maps are even recognizable within the somatosensory cortex. Examples embody the barrel cortex of the mouse; representation of the nasal proboscis of the star-faced mole (Catania and Kaas, 1995); the representation of the raccoon hand (Welker et al. These macroscopically seen columns received particular standing in neurobiology as a outcome of they helped investigators to understand questions associated to synaptic plasticity and map formation. An arbitrary "unit column" (a 100-mm wide) spanning from layer 1 to 6) was marked within the major somatosensory/visual space (boxed areas in AeC, higher magnification in A0 eC0). The subventricular zone is the developmental milestone of a 6-layered neocortex: comparisons in metatherian and eutherian mammals. It is puzzling that barrel fields are current in rats, mice, squirrels, rabbits, possums, and porcupines, however not in raccoons, beavers, or cats (Woolsey et al. This pattern fashioned by thalamocortical axons may be current in the absence of the cytoarchitectonic pattern that was initially termed barrels (see L´┐Żpez-Bendito and Moln´┐Żr, 2003). In the barrel area of the rodent somatosensory cortex, dendritic bundles are principally positioned in the barrel walls and septa, avoiding hollows (mouse, Escobar et al. In rodent barrel cortex, dendrites of neurons in layer four conform to barrel limits (Harris and Woolsey, 1979), but this appears to be an distinctive case. The greatest documented example of two thalamic techniques in the identical layer is from rodent barrel cortex (Alloway, 2008). A similar segregation occurs extra usually but with a segregation in several layers. In this case, then, their column is of the kind outlined initially by Mountcastle and not a minicolumn, though it could contain minicolumns as outlined earlier. A second type of column outlined by the authors has its basis in the terminations of axons arriving from the posterior medial (Pom) nucleus of the thalamus and ending deep and superficial to the barrels and especially within the zones of lowered cell density or "septa" lying between them. Hollow barrels, with cell sparse cores, are typical of mice, young rats, and the anterolateral subfield of mature rats, however solid columns, with cell-dense cores, are typical of the main posteromedial field in rats (Rice, 1995). Short vertical clusters of cells are commonly noticed within the deep layers of marine mammals. The cortical structure could be lacking or significantly disrupted and yet apparently stays functionally intact. The diploma to which cortex is modifiable and, by what mechanisms, has been extensively investigated underneath varied environmental manipulations. Although we have no idea what the functional relevance (if any) of the barrel preparations could also be, this technique helped the understanding of varied elements of cortical circuit formation and plasticity. Study of the barrel area in various mouse mutants proved to be instrumental within the understanding of the molecular mechanisms of those interactions (Erzurumlu and Kind, 2001). The improvement of the periphery-related patterning of the thalamocortical projections and the induction of the cytoarchitectonic barrels require each pre- and postsynaptic interactions. With the event of finer techniques of clonal analysis and neuronal cell-type specification, one can anticipate a brand new era of genetic and molecular manipulations that can help us elucidate the underlying mechanisms of barrel formation. Innocenti and Vercelli (2010) distinguished minicolumns and bundles, whereas some investigators have used these phrases interchangeably. Minicolumns of radially aligned cell bodies can be demonstrated by normal Nissl preparations or different histological strategies that reveal cell bodies. Bundles comprise the apical dendrites of pyramidal neurons whose cell our bodies are in numerous layers and can be seen in materials prepared by the Golgi method, stained with osmium for electron microscopical evaluation or with markers of somatodendritic morphology. Innocenti and Vercelli (2010) demonstrated dendritic bundles utilizing retrograde transport of lipophilic tracers or intracellular injection of neurons in slice preparations. Myelinated axons are also organized in bundles; these bundles course close to these of the dendrites, and no less than some of them originate from neurons whose apical dendrites are in a bundle (monkey primary visible cortex: Peters and Sethares, 1996). Depending also on tangential location and depth, the minicolumns and bundles can be roughly distinct. Left panel: Schematic representation of the preparations of the apical dendrites of pyramidal cells. Right panel: Pyramidal minicolumns are represented adjacent to the dendritic bindles. In the monkey visual cortex, the microcolumns are estimated to consist of the dendrites of z142 pyramidal neurons. These modules are ´┐Ż30 mm in diameter and happen with center-to-center spacing that varies from 20 to 80 mm, the broader spacing occurring within the larger brains of the macaque monkey and man. In the visual cortex, the mean spacing between modules was found to be 60 mm in the rat, 56 mm within the cat, and 23 mm within the rhesus monkey (Peters, 1997).
References - Granick M, Boykin J, Gamelli R, et al: Toward a common language: surgical wound bed preparation and debridement, Wound Repair Regen 14(Suppl 1):S1-S10, 2006.
- Stacy GC. Recovery of oral opening following sagittal ramus osteotomy for mandibular prognathism. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1987;45:487.
- Doble A, Taylor-Robinson D, Thomas BJ, et al: Acute epididymitis: a microbiological and ultrasonographic study, Br J Urol 63:90n94, 1989. Doble A, Thomas BJ, Walker MM, et al: The role of Chlamydia trachomatis in chronic abacterial prostatitis: a study using ultrasound guided biopsy, J Urol 141:332n333, 1989. Drach GW, Fair WR, Meares EM, et al: Classification of benign diseases associated with prostatic pain: prostatitis or prostatodynia?, J Urol 120:266, 1978.
- Major outcomes in high-risk hypertensive patients randomized to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or calcium channel blocker vs. diuretic: The Antihypertensive and Lipid- Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT), JAMA 288(23):2981-2997, 2002.
- Huwyler M, Springer J, Kessler TM, et al: A safe and simple solution for intravesical tension-free vaginal tape erosion: removal by standard transurethral resection, BJU Int 102:582n585, 2008.
- Lu W, Tao Y, Wisniewski AB, et al: Different outcomes of hypospadias surgery between North America, Europe and China: is patient age a factor? Nephrourol Mon 4(4):609n612, 2012.
- Aikawa M, Rabkin E, Okada Y, et al: Lipid lowering by diet reduces matrix metalloproteinase activity and increases collagen content of rabbit atheroma: a potential mechanism of lesion stabilization, Circulation 97:2433-2444, 1998.
- Wang L, Yi L, Yang L, et al: Diagnosis and surgical treatment of nutcracker syndrome: a single-center experience, Urology 73:871-876, 2009.
|


