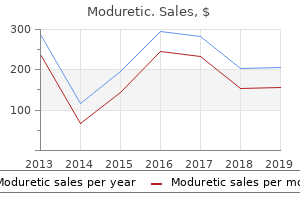
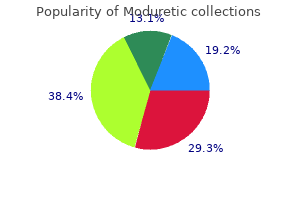
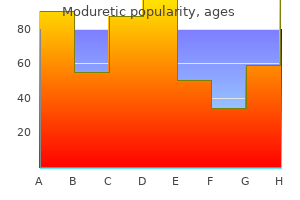
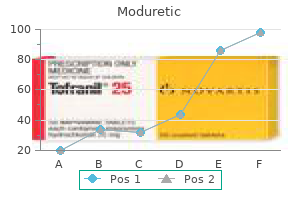
Moduretic
Judith G. Hall, M.D. - University of British Columbia
- Dept. of Pediatrics, BH Childrenĺs Hospital
- Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada
Generic moduretic 50 mg without a prescriptionSimilarly, one major spermatocyte gives rise to 4 daughter cells, two with 22 plus 1 X chromosomes and two with 22 plus 1 Y chromosomes blood pressure levels.xls discount 50mg moduretic mastercard. Chapter 2 ´┐Ż Gametogenesis; Conversi´┐Żn of Germ Cells into Male and Female Gametes V)´┐Ż ´┐Ż! These individu´┐Żis aiso have an increased chance of deveioping ieukemia, infections, th yro id dysfunction, and prem ature growing older heart attack vs panic attack purchase moduretic 50 mg amex. Furtherm ore, an increased frequency and earlier onse t of Aizheim er illness is noticed am ong individuals with Down syndrom arrhythmia word breakdown buy moduretic 50 mg without prescription. This danger increases with m aternal age to 1 in 3 zero zero a t age 35 and 1 in 100 a t age 40 blood pressure chart what is too low order moduretic 50 mg free shipping. Children with Down syndrome usualiy have a point of mental incapacity and lots of have cardiac defects. Another characteristic of these youngsters is a broad hand with a single transverse [simian] crease. Note the lowset ears, small mouth, poor mandible [micrognathia], flexi´┐Żn of the hands, and absent and/or hypoplasia of the radius and ulna. Note the loose skin on the posterior of the neck brought on by the stays of a cystic hygroma (fluid-filled cyst], the brief neck, malformed ears, and sweiling within the hand (B) and the foot (Cj caused by lymphedema. At 6 years of age, the webbed neck is prominent, and the nipples are extensively spaced with a broad chest. If the defect is inherited on the pater nal chromosome, Prader-Willi syndrome occurs. Two cells are superimposed on the lower proper, giving the impression of the presence of m´┐Żltiple probes. It is current on oniy one of many pairs of chro mosome 22 indicating the other has the 22q11 deletlon. Whereas all of the oogonia in one cluster are in all probability derived from a single cell, the flat epithelial cells, known as follicular cells, orig´┐Ż nate from surface epithelium overlaying the ovary. The majority of oogonia continu´┐Ż to divide by mitosis, but a few of them arrest their cell divi si´┐Żn in prophase of meiosis I and form prim ary oocytes. During the next few months, oogonia increase quickly in quantity, and by the fifth month of prenatal growth, the whole variety of germ cells within the ovary reaches its m´┐Żximum, estimated at 7 million. At this time, cell dying begins, and lots of oogonia as well as main oocytes degenerate and turn out to be atret´┐Żc. This prophase could last forty or extra years and finishes oniy when the cell begins its final maturation. All surviving primary oocytes have entered prophase of meiosis I, and most of them are individually surrounded by a layer of flat follicular epithelial cells. A primary oocyte, together with its surrounding flat epithelial cells, is named a prim ordial foUicle. Some show/ mitosis; others have differentiated into primary oocytes and entered prophase of the first m eiotic divisi´┐Żn. Almost all oogonia are rework ed into main oocytes in prophase of the first m eiotic divisi´┐Żn. Each prim ary oocyte is surrounded by a single layer of follicular cells, kind ing the prim ordial follicle. Primordial follicle consisting of a primary oocyte surrounded by a layer of flattened epithelial cells. Early major or preantral stage follicle recruited from the pool of primordial follicles. As the follicle grows, follicular cells become cuboidal and start to secrete the zona pellucida, which is seen in irregular patches on the floor of the oocyte. The whole number of main oo cytes at delivery is estimated to differ from 600,000 to 800,000. During childhood, most oocytes turn into atretic; only approximately forty,000 are present by the beginning of puberty, and fewer than 500 shall be ovulated. Some oocytes that reach maturity late in life have been dormant within the diplotene stage of the primary meiotic divisi´┐Żn for 40 years or more before ovulation. W hether the diplotene stage is probably the most suitable phase to protect the oocyte in opposition to environmental influences is unknown. The fact that the chance of getting youngsters with chromosomal abnormalities increases with maternal age indicates that primary oocytes are weak to break as they age. At puberty, a pool of rising follicles is established and repeatedly maintained from the availability of primordial follicles. Some of those die, whereas others start to accumulate fluid in an area known as the antnim, thereby coming into the antral or vesicular stage. Fluid contin´┐Żes to accumulate such that, instantly prior to ovulation, follicles are fairly swollen and are called m ature vesicular follicles or graaf´┐Żan follicles. The antral stage is the longest, whereas the mature vesicular stage encompasses approximately 37 hours prior to ovulation. As primordial follicles start to grow, surrounding foflicular cells change from flat to cuboidal and proliferate to produce a strati fied epithelium of granulosa cells, and the unit known as a prim ary follicle. Granulosa cells rest on a basement membrane separating them from surrounding ovar´┐Żan connective tissue (stromal cells) that kind the theca folliculi. Also, granulosa cells and the oocyte secrete a layer of glycoproteins on the surface of the oocyte, forming the zona pellu cida. As follicles continu´┐Ż to develop, cells of the theca folliculi organize into an inside layer of secretory cells, the theca interna, and an outer fibrous capsule, the theca externa. Also, small, finger-like processes of the follicular cells extend throughout the zona pellucida and interdigitate with microvilli of the plasma membrane of the oocyte. These processes are necessary for transport of supplies from follicular cells to the oocyte. The oocyte, surrounded by the zona pellucida, is off heart; the antrum has developed by fluid accum ulation between intercellular spaces. The antrum has enlarged significantly, is full of follicular fluid, and is surrounded by a stratified layer of granulosa cells. At maturity, the m ature vesicular (graa´┐Żan) follicle may be 25 mm or more in diameter. It is surrounded by the theca interna, which is composed of cells having characteristics of steroid secretion, wealthy in blood vessels, and the theca externa, which gradually merges with the ovarian connective tissue. With every ovarian cycle, numerous follicles begin to develop, however often, only one reaches full maturity. Meiosis I is accomplished, leading to formation of two daughter cells of unequal size, each with 23 double-structured chromosomes. One cell, the secondary oocyte, receives most of the cytoplasm; the other, the first polar body, receives virtually none. Chapter 2 ´┐Ż Gametogenesis; Conversi´┐Żn of Germ Cells into Male and Female Gametes between the zona pellucida and the cell membrane of the secondary oocyte within the periviteUine space. At delivery, germ cells in the male toddler can be acknowledged within the intercourse cords of the testis as giant, pal´┐Ż cells surrounded by supporting cells. Supporting cells, which are derived from the surface epithelium of the testis in the identical manner as follicular cells, turn into sustentacular cells, or Sertoli cells.
Diseases - Bannayan Zonana syndrome
- Eec syndrome without cleft lip palate
- Powell Buist Stenzel syndrome
- Bowing congenital short bones
- MLS syndrome
- XY Female
- Morphea scleroderma
Moduretic: 50 mg, 50 mg
Discount moduretic 50mg fast deliveryThe zinc-finger transcription issue Klf4 is required for terminal differentiation of goblet cells in the colon blood pressure yoga ramdev trusted moduretic 50 mg. Inactivation of the transcription factor Elf3 in mice results in dysmorphogenesis and altered differentiation of intestinal epithelium blood pressure medication rash order 50mg moduretic mastercard. Protein tyrosine kinase 6 negatively regulates growth and promotes enterocyte differentiation within the small intestine blood pressure medication and zoloft cheap moduretic 50mg line. Incidence of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus amongst white Americans by intercourse, stage, and age jugular pulse pressure moduretic 50 mg overnight delivery. Invasion and metastases in gastric most cancers: in vitro and in vivo models with scientific correlations. Identification of a metaplastic cell lineage associated with human gastric adenocarcinoma. E-cadherin deficiency initiates gastric signet-ring cell carcinoma in mice and man. Amphiregulin-deficient mice develop spasmolytic polypeptide expressing metaplasia and intestinal metaplasia. Carcinogenesis in mouse stomach by simultaneous activation of the Wnt signaling and prostaglandin E2 pathway. Chronic gastritis within the hypochlorhydric gastrin-deficient mouse progresses to adenocarcinoma. Haploid loss of the tumor suppressor Smad4/Dpc4 initiates gastric polyposis and most cancers in mice. Development of gastric carcinoma from intestinal metaplasia in Cdx2-transgenic mice. A transgenic mouse model of metastatic carcinoma involving transdifferentiation of a gastric epithelial lineage progenitor to a neuroendocrine phenotype. A dominant mutation that predisposes to multiple intestinal neoplasia within the mouse. The Min (multiple intestinal neoplasia) mutation: its effect on gut epithelial cell differentiation and interaction with a modifier system. The secretory phospholipase A2 gene is a candidate for the Mom1 locus, a major modifier of ApcMin-induced intestinal neoplasia. Genetic identification of Mom-1, a serious modifier locus affecting Min-induced intestinal neoplasia within the mouse. A focused chain-termination mutation within the mouse Apc gene results in multiple intestinal tumors. Colonic tumorigenesis in BubR11/-ApcMin/1 compound mutant mice is linked to premature separation of sister chromatids and enhanced genomic instability. Intestinal tumorigenesis in compound mutant mice of each Dpc4 (Smad4) and Apc genes. Reduction of p27 accelerates gastrointestinal tumorigenesis in Apc mutant mice, however not in Smad3 mutant mice. Genetic disruption of Ptgs-1, as properly as Ptgs-2, reduces intestinal tumorigenesis in Min mice. Suppression of intestinal polyposis in Apc(Min/1) mice by inhibiting nitric oxide manufacturing. Intestinal tumorigenesis is suppressed in mice lacking the metalloproteinase matrilysin. Molecular diagnostics of most cancers predisposition: hereditary non-polyposis colorectal carcinoma and mismatch repair defects. Progress in genetic testing, classification, and identification of Lynch syndrome. Inactivation of the mouse Msh2 gene results in mismatch repair deficiency, methylation tolerance, hyperrecombination, and predisposition to most cancers. Mouse MutS-like protein Msh5 is required for proper chromosome synapsis in male and female meiosis. MutS homolog four localization to meiotic chromosomes is required for chromosome pairing throughout meiosis in female and male mice. Classification of colorectal most cancers based on correlation of scientific, morphological and molecular features. Ink4a/Arf and oncogene-induced senescence stop tumor development during different colorectal tumorigenesis. Chapter 6 Gastrointestinal Peptides: Gastrin, Cholecystokinin, Somatostatin, and Ghrelin Celia Chao and Mark R. The stomach mucosa is functionally divided into two regions: (1) the corpus or oxyntic (acid secreting) mucosa, which covers roughly 80% of the abdomen, and (2) the prepyloric mucosa, which covers the remaining 20% of the decrease space often known as the antrum. Ghrelin is localized in distinct cells positioned within the mid portion of oxyntic glands characterized by X/A-like granules. In maintaining with previous editions of this e-book, this chapter is organized round displays of the person peptides. As such, each is discussed with respect to their molecular construction, mobile origins, regulation of expression, involvement with intra- and intercellular signal transduction pathways, physiology, and association with human pathology. Gastrin can be expressed to a limited extent in certain neurons, the pituitary,2 fetal pancreas,3´┐Ż6 and developing sperm,7 as well as in certain cancers. Secretion of acid by parietal cells, positioned within the gastric corpus, facilitates protein digestion, adsorption of iron, calcium, and vitamin B, and decreases the chance of bacterial infection. He confirmed that it stimulated gastric acid and pepsin secretion when injected systemically into the jugular veins of cats. In 1942, Komarov15 reported a technique for isolating a preparation of mucosal extract that was freed from histamine contamination. The lower antrum (Panel A) contains antral glands (Panel B), which possess the G and D sort endocrine cells (Panel C). Large yellow arrows indicate the main secretory product of the varied endocrine cell types. Thin black arrows determine the goal cell(s) of a secreted regulatory peptide or biogenetic amine. The plus () and minus () symbols indicate stimulatory and inhibitory results, respectively. Also recognized are marsupials, similar to North American opossum, Monodelphis domestica; birds, corresponding to chicken, Gallus gallus; fish, similar to dogfish, Squalus acanthias; reptiles, similar to turtle, Pseudemys scripta; and amphibians, similar to bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana. It should be famous that the numbering Signal peptidase 1 Preprogastrin -21 21 22 57-58 system of important amino acid residues concerned in peptide cleavage and post-translational modifications of gastrin varies within the scientific literature. This is because of the reality that the numbering system of some authors is predicated on the sequence of preprogastrin, which includes the 21 amino acids of the signal peptide sequence, whereas the numbering system of others is predicated on the sequence of progastrin. The numbers at the prime of the diagram represent the amino acid (aa) sequence for preprogastrin; the numbers on the bottom of the diagram characterize the aa sequence for progastrin. For instance, in adult humans, roughly half of the gastrin peptide synthesized in G cells of the antrum and duodenum and launched into the circulation is sulfated, whereas the entire gastrin peptide produced by the fetal pancreas appears to be sulfated. Following sulfation and/or phosphorylation, progastrin exits the trans-Golgi network and enters immature granules of the regulated secretory pathway.
Proven 50 mg modureticThe diploma of sign loss within the artery created by the stent is variable and to some extent associated to the anatomic location of the parent vessel and its anatomic configuration and tortuosity blood pressure medication guidelines generic moduretic 50mg fast delivery. In fact, after the diseased phase is reconstructed and the construct is absolutely endothelialized, the aneurysm and the diseased vascular section could be thought of definitively treated, with the everyday mechanisms of aneurysm recurrence or regrowth being essentially eliminated blood pressure 8959 discount moduretic 50mg online. In addition, as a purely extrasaccular treatment strategy, no direct catheterization or manipulation of the aneurysm sac is required, presumably reducing the probability of procedural rupture and potentially bettering the security of endovascular aneurysm treatment blood pressure normal low high purchase moduretic 50mg online. Moreover, the precise aneurysm sac in these circumstances was typically found to be not solely thrombosed but in addition atretic at follow-up blood pressure chart images 50mg moduretic amex. The rabbit aorta provides an animal mannequin for the intracranial vasculature and its perforator branches as a end result of the vessel approximates the caliber of human intracranial arteries and the lumbar artery branches approximate the dimensions of the cerebral perforators. Flow into the aneurysm is governed utterly by the geometry of the father or mother vessel´┐Żaneurysm complicated, the orientation of the inflow jet at the aneurysm neck, and the presence of an available, organized outflow. As such, with reconstruction of the parent artery´┐Żaneurysm complex, these influx and outflow pathways turn out to be disrupted, and the aneurysmal sac progresses to thrombosis. On the opposite, move into perforating vessels is governed nearly totally by the presence of a pressure gradient. Follow-up histology of those specimens sometimes demonstrated complete incorporation of the system into the vessel wall with contiguous circumferential neoendothelialization along the complete length of the construct. At 6-month follow-up, 93% (28 of 30) of the lesions demonstrated full angiographic occlusion. This unprecedented fee of full angiographic occlusion at follow-up surpasses any of the reported occlusion rates for aneurysms after endovascular therapy and far exceeds these reported for big or wide-necked lesions. Three such instances have been carried out by Fiorella and coworkers in North America under a U. Imagesfroma13-year-oldgirlwithagiant, 38-mm circumferential basilar trunk aneurysm,presentingwithheadache,leftupper extremity dysmetria, and mild nystagmus. Subtractedimagesinfrontal(A)andlateral (B) projections depict the giant aneurysm involvinga3-cmlongsegmentofthebasilar trunk. Curative reconstruction of an enormous mid-basilar trunk aneurysm with the Pipeline embolization gadget. Postprocedure ischemic events after remedy of intracranial aneurysms with Guglielmi detachable coils. Monorail snare method for the restoration of stretched platinum coils: technical case report. Usefulness of the Neuroform stent for the remedy of cerebral aneurysms: results at preliminary (3-6-mo) follow-up. Endovascular reconstruction with the Neuroform stent as monotherapy for the therapy of uncoilable intradural pseudoaneurysms. Preliminary expertise utilizing the Neuroform stent for the remedy of cerebral aneurysms. Strategies for the administration of intraprocedural thromboembolic problems with abciximab (ReoPro). Balloon in-stent approach for the constructive endovascular therapy of "ultra-wide necked" circumferential aneurysms. Neuroform in-stent stenosis: incidence, natural history, and treatment strategies. Definitive reconstruction of circumferential, fusiform intracranial aneurysms with the Pipeline embolization gadget. Profile and prevalence of aspirin resistance in sufferers with heart problems. A potential, blinded dedication of the natural historical past of aspirin resistance among steady sufferers with cardiovascular disease. In vitro research of the Neuroform microstent utilizing transparent human intracranial arteries. Histological postmortem research of an inside carotid artery aneurysm handled with the Neuroform stent. Treatment of a vertebral dissecting aneurysm with stents and coils: technical case report. Endovascular reconstruction of intracranial arteries by stent placement and combined techniques. Balloon-assisted coil embolization of wide-necked aneurysms of the internal carotid artery: medium-term angiographic and medical follow-up in 22 sufferers. Stent-supported coil embolization: the therapy of fusiform and wide-neck aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms. Treatment of inside carotid artery aneurysms with a coated stent: experience in 24 patients with mid-term follow-up results. Combined use of stents and coils to deal with experimental wide-necked carotid aneurysms: preliminary results. Self-expanding and balloonexpandable stents in the remedy of carotid aneurysms: an experimental study in a canine mannequin. Self-expanding nitinol stents in canine vertebral arteries: hemodynamics and tissue response. First and foremost, knowledge describing both the periprocedural and long-term security and efficacy of these gadgets remain quite preliminary. As a larger quantity of clinical expertise is accrued, the suitable medical applications of those devices (as well as their limitations) will turn out to be more evident. Second, as with all intracranial stent-like system, a course of twin antiplatelet medications is required for prophylaxis towards thrombosis while the construct is turning into endothelialized and incorporated into the father or mother artery. The optimum period of twin antiplatelet remedy remains unsure, but the present advice is for aspirin along side clopidogrel for six months and aspirin alone thereafter. Third, the efficacy and security of the system for the remedy of bifurcation aneurysms stays uncertain. In reality, the protection of crossing or jailing main bifurcation or department vessels with the system (regardless of the situation of the handled aneurysm) remains unsure. However, until a bigger knowledge set is out there, the quantity of protection that could be safely applied in these anatomic areas stays uncertain. Flow Diverters: Summary Flow diverting devices symbolize a brand new remedy paradigm for intracranial aneurysms. Many complex aneurysms that had been once regarded as untreatable or to require a deconstructive treatment with mother or father vessel occlusion may be amenable to reconstruction with these newer units. Moreover, the main shortcomings of endosaccular aneurysm therapies-incomplete aneurysm occlusion and aneurysm recurrence-may be lowered with this technique of circumferential reconstruction of the mother or father vessel. Further investigation will better define the security, efficacy, and ultimately the appropriate function for these gadgets in the armamentarium of gadgets used for endovascular aneurysm remedy. Flow adjustments caused by the sequential placement of stents across the neck of sidewall cerebral aneurysms. A novel endovascular treatment of a wide-necked basilar apex aneurysm through the use of a Y-configuration, double-stent technique. Lavine Hunterian ligation refers to one of the oldest profitable interventions for arterial aneurysms-ligation of the femoral artery to treat a popliteal aneurysm by John Hunter in 1785. Because refinements in the coiling expertise used to treat cerebral aneurysms have continued to broaden the scope of intracranial aneurysms that might be repaired by coiling, hunterian ligation is extra frequently relied on as a last resort to deal with solely the most surgically inaccessible and tough aneurysms. Historically, hunterian ligation has referred to the everlasting sacrifice of a parent artery to prevent entry of blood to the aneurysm.
Moduretic 50mg free shippingTranscriptional mechanisms have been suggested in regulating these developmental changes blood pressure 9862 cheap moduretic 50mg with visa. The roles of extrinsic and intrinsic indicators during pancreas development are variable and depend on the actual competence of every progenitor cell blood pressure in pregnancy buy discount moduretic 50mg on-line. Interruption of genes for Pdx1, Hlb9, Isl1, or Hex results in an arrest of pancreas growth at a very early stage (embryonic day 8´┐Ż9) hypertension word parts purchase 50 mg moduretic with visa. Disruption of genes encoding for the Notch signaling pathway, for example, Hes1 or neurogenein-3, abrogates improvement of the endocrine pancreas (islets of Langerhans) prehypertension stage 1 order moduretic 50mg without a prescription. Knockout transcriptional issue genes expressed more downstream within the development cascade. Pax genes encode key regulators, that are involved in the embryonic development of many organs including the eyes, brain, kidney, thyroid gland, immune system, and pancreas. A variety of murine Chapter 14 Molecular Physiology of Gastrointestinal Function during Development 419 E10. This is the transcription issue requirement during the specification of duct (green), acinar (blue) and endocrine and exocrine pancreas (yellow). The Pdx1 is a grasp regulator of each pancreatic development and the differentiation of progenitor cells into the -cell phenotype. The degree of Chapter 14 Molecular Physiology of Gastrointestinal Function throughout Development 421 intestinal maturation also plays a serious position in affecting absorptive function throughout ontogeny. Thus, the mechanisms and ranges of intestinal transport of nutrients and electrolytes differ throughout early postnatal growth. Nutrient transport within the neonatal gut happens along the whole crypt´┐Żvillus axis, whereas solely enterocytes alongside the higher villus have an absorptive phenotype after weaning. Changes in transport activity can additionally be related to alterations in mucosal surface space, proliferation and differentiation of epithelial cells, membrane fluidity, and paracellular permeability. Enterocyte amplification additionally occurs to increase the absorptive floor space of microvilli. During early postnatal life, growth factors, immunoglobulins, food antigens, other macromolecules, and micro organism may be absorbed from colostrum and milk by adhering to the intestine epithelium. This transport happens through enterocytes and specialised M cells that appear early in fetal development. The high permeability of the neonatal intestine for macromolecules decreases after delivery, a course of labeled "intestine closure," but the exact timing of this event is species dependent. In some rodent species and in pigs, transport capacity decreases a quantity of days after start, whereas transport ceases utterly around weaning in rats and rabbits. Only molecules that adhere to the microvillous membrane are transported across the cells, whereas soluble molecules in the fluid phase are largely degraded. This process is essential for the event of passive immunity, which is involved in regulating the expression of development-specific genes within the neonatal gut. The transcytotic pathway can be observed in some mammals and involves non-selective endocytosis, the place endocytosed molecules are both partially destroyed or partially transported into the interstitial fluids. IgA dimers bind to the receptor on the basolateral membranes and are endocytosed and transported throughout the cellular cytoplasm the place the complexes are secreted into the intestine lumen. The principal target of those milk-borne substances seems to be the intestinal epithelium, the place they affect proliferation and differentiation of enterocytes. The postnatal ontogeny of nutrient transporters displays the want to absorb rising quantities of nutrients for speedy growth and excessive metabolic activity. The developmental adjustments in transport capacities are as a end result of a quantity of factors: modifications in intestinal mass, physicochemical properties of the cell membranes, and forms of transporters expressed and their kinetic properties. In sucklings, even the colon participates in nutrient absorption, which may be a compensatory mechanism for decreased transport capability within the small bowel and less developed colonic bacterial fermentation. Total intestinal transport capability increases with age predominantly because of increased intestinal mass, however surprisingly, the absorptive capability for lots of carbohydrates and amino acids decrease in proportion to intestinal mass. Decreased absorptive capability could additionally be related to the smaller proportion of enterocytes that specific numerous active transporter processes during early ontogeny. These transporters play a pivotal function in shifting monosaccharide throughout epithelial cell layers in the intestine. The absorption course of mediated by these transporters is regulated by many developmental and dietary elements. Only the developmental regulation of those transporters shall be discussed within the following sections. Kinetic studies of sugar absorption in intact animals and in brush border membrane vesicle preparations indicate the present of a low-affinity Physiologic results Hormone shown to be absorbed from formula-fed, glucocorticoiddeficient rats. Transforming progress factor- given orally can cross the intestinal epithelium and can be detected in varied tissues. In the perinatal interval, only high-affinity receptors are expressed, whereas later in postnatal development, high- and low-affinity receptors are expressed in rats. Chapter 14 Molecular Physiology of Gastrointestinal Function throughout Development 425 glucose transporter in the apical membrane of the epithelial cells. In assist of this supposition, lactose absorption has been detected within the proximal colon of newborns. In addition to lipid absorption through pinocytosis,202 the neonatal gut can absorb fatty acids and cholesterol from dietary sources. In the neonatal gut, lysine and alanine are absorbed in a manner independent of Na, whereas alanine, 14. In suckling rats, water transport in the colon is fourfold greater than in the small intestine, but colonic water transport decreases during early postnatal improvement. On the opposite hand, water absorption within the colon can also be mediated by paracellular pathways, as instructed by the observation that an artificially created osmotic gradient leads to water secretion. It is usually thought that Na transport will increase the local osmotic stress within the lateral intercellular areas, and in flip, generates osmotic water move across the epithelium. At least six aquaporin isoforms (aquaporin 1, three, 4, 5, eight, and 9) have been identified within the digestive system. It can additionally be current in the duct system within the pancreas, liver, and bile duct in addition to in colonic crypts. Thus, a significant perform of the gastrointestinal tract is to soak up virtually all water and Na to take care of overall body water and Na homeostasis. High Na absorption occurs in the neonatal interval and reduces later in postnatal life in the rat, rabbit, and human colon213,226,227 and in the rat small intestine. In rabbits, colonic Na transport persists until adulthood,227 whereas in rats, colonic Na transport ceases after weaning228,229 and is replaced by Na/H change. Brush border membrane vesicles have been purified by the Mg 2 precipitation methodology from rats and pH-dependent uptake of radiolabeled sodium was assayed. The lowest activity is seen in suckling rats, and the best activity is seen in adolescent rats.
BNADH (Nadh). Moduretic. - What is Nadh?
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Nadh work?
- Dosing considerations for Nadh.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96977
Cheap moduretic 50 mg fast deliveryKidneys had been absent, lum bar and sacral vertebrae had been missing, and the hind limbs were fused blood pressure kit cvs cheap moduretic 50mg otc. By the end of the embryonic period, the main organ systems have been estabhshed, rendering the m ajor options of the exterior body type recognizable by the end of the second month blood pressure reduction purchase 50mg moduretic visa. Appearance of the notochord and prechordal mesoderm induces the overlying ectoderm to thicken and type the neural p´┐Żate heart attack or stroke cheap moduretic 50 mg fast delivery. Cells of the p´┐Żate make up the neuroectoderm, and their induction represents the preliminary event in the means of neurulation blood pressure chart while exercising discount moduretic 50mg fast delivery. These three proteins are present within the organizer (primitive node), notochord, and prechordal mesoderm. Neurulation Neurulation is the method whereby the neural p´┐Żate varieties the neural tube. The process is regulated by sig naling by way of the planar cell polarity pathway (see Chapter 1, p. As the neural p´┐Żate lengthens, its lateral edges elevate to form neural folds, and the depressed midregion types the neural groove. Fusi´┐Żn begins within the cervical regi´┐Żn (fifth somite) and proceeds cranially and caudally. Until fusi´┐Żn is full, the cephalic and caudal ends of the neural tube communicate with the amniotic cavity by the use of the anterior (cranial) and posterior (caudal) neuropores. The embryo is pear-shaped, with its cephalic regi´┐Żn somew hat broader than its caudal end. Dorsal view of an embryo at approxim ately 20 days showing somites and kind ation of the neural groove and neural folds. Note the pericardial bulge on each side of the m idline in the cephalic part of the embryo. Closure of the cranial neuropore happens at approximately day 25 (18- to 20-somite stage), whereas the posterior neuropore closes at day 28 (25-somite stage). Neurulation is then full, and the central nervous system is represented by a closed tubular construction with a slim caudal portion, the spinal cord, and a a lot broader cephahc portion characterised by a number of dilations, the mind vesicles (see Chapter 18). Neural Crest Cells As the neural folds elevate and fuse, cells on the lateral border or crest of the neuroectoderm start to dissociate from their neighbors. Mesenchyme refers to loosely organized embryonic connective tissue no matter origin. Neural crest cells additionally type and migrate from cranial neural folds, leaving the neural tube before closure in this regi´┐Żn. These cells contribute to the craniofacial skeleton in addition to neurons for cranial ganglia, glial cells, melanocytes, and other cell types (Table 6. Evolutionarily, these cells appeared at the dawn of vertebrate improvement and expanded this group extensively by perfecting a predatory lifestyle. Molecular Regulatlon of Neural Crest Induction Induction of neural crest cells requires an interaction at the junctional border of the neural p´┐Żate and surface ectoderm (epidermis). After migration, crest cells contribute to a heterogeneous array of structures, Including dorsal root ganglia, sympathetlc C hain ganglia, adrenal medulla, and other tissues (Table 6. These cells go away the crests of the neural folds prior to neural tube closure and m´┐Żgrate to form buildings In the face and neck [blue area). By the time the neural tube is closed, two bilateral ectoderm al thicken´┐Żngs, the otic placodes and the lens placodes, becom e visible in the cephalic regi´┐Żn of the embryo. During further growth, the otic placodes Chapter 6 ´┐Ż Third to Eighth Weeks: the Embryonic Period Neural Crest Derivatives C onnective tissue and bones of th e face and skuli Cranial nerve ganglia (see Table 18. These placodes additionally invaginate and, through the fifth week, type the lenses of the eyes (see Chapter 20). By approximately the seventeenth day, however, cells ci´┐Żse to the mid line proliferate and kind a thickened p´┐Żate of tissue known as paraxial m esoderm. M ore laterally, the mesoderm layer remains skinny and is called the lateral p´┐Żate. With the appearance and coalescence of intercellular cavities within the lateral p´┐Żate, this tissue is split into two layers. The thin mesodermal sheet gives rise to paraxial mesoderm (future somites), inter med´┐Żate mesoderm (future excretory units], and the lateral p´┐Żate, v^hlch Is spilt Into parietal and visceral mesoderm layers lining the intraem bryonic cavity. A layer steady with mesoderm masking the yolk sac, generally identified as the splanchnic or visceral mesoderm layer. Paraxial Mesoderm By the beginning of the third week, paraxial meso derm begins to be organized into segments. Part I ´┐Ż General Embryology segments, often recognized as somitomeres, first appear in the cephalic regi´┐Żn of the embryo, and their formation proceeds cephalocaudally. Each somitomere consists of mesodermal cells arranged in concentric whorls across the middle of the unit. In the head regi´┐Żn, somitomeres form in association with segmentation of the neural p´┐Żate into neuromeres and contribute to mesenchyme within the head (see Chapter 17). The first pair of somites arises in the occipital regi´┐Żn of the embryo at approximately the twentieth day of development. There are four occipital, eight cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 8 to 10 coccygeal pairs. The first occipital and the last 5 to seven coccygeal somites later disappear, whereas the remaining somites form the axial skeleton (see Chapter 10). Because somites seem with a specified periodicity, the age of an embryo may be accurately decided during this early time interval by counting somites (Table 6. The improve in Notch protein prompts different segment-patterning genes that set up the somite. Som ite Differentiation When somites first type from presomitic meso derm, they exist as a ball of mesoderm (fibroblastlike) cells. These cells then undergo a means of epithelization and prepare themselves in a donut form round a small lumen. Cells from the ventral and medial walls of the som ite lose their epithelial arrangem ent and migrate across the neural tube and notochord. Both groups of muscle precursor cells become mesenchymal and migrate beneath the dermatome to kind the derm omyotom e (B,C), whereas some cells from the ventrolateral group aiso migrate into the parietal layer of lateral p´┐Żate mesoderm. Eventually, derm atome cells aiso become mesenchymal and migrate beneath the ectoderm to kind the dermis of the again (D). Collectively, these cells form the sclerotome that will differentiate into the vertebrae and ribs (see Chapter 10). Cells at the dorsomedial and ventrolateral edges of the upper regi´┐Żn of the somite form precursors for muscle ceUs, whereas cells between these two teams type the dermatome. Cells from both muscle precursor groups become mesenchymal once more and migrate beneath the dermatome to create the dermomyotome. In addition, cells from the ventrolateral edge migrate into the parietal layer of lateral p´┐Żate mesoderm to type a lot of the musculature for the physique wall (external and inside indirect and transversus abdominis muscles) and most of the limb muscle tissue. Cells within the dermomyotome finally form dermis for the pores and skin of the again and muscular tissues for the back, body wall (intercostal mus cles), and some limb muscle tissue (see Chapter 11).
Discount moduretic 50 mg amexFinally, we consider that spinal vascular malformations are so complicated that some lesions will defy any proposed classification system blood pressure medication numbness cheap 50mg moduretic with visa. Because their specific characteristics match no existing class, a new one was created fetal arrhythmia 36 weeks order moduretic 50 mg mastercard. B, Posterior view showing that engorgement of epidural veins can produce a symptomatic mass impact on adjacent nerve roots and spinal cord blood pressure medication problems order 50mg moduretic. In addition, shunting of large amounts of arterial blood into the venous system can steal blood circulate from the spinal cord with resultant ischemia and worsening myelopathy blood pressure kiosk machines buy moduretic 50mg. Types B and C have increasingly larger shunts, which often result in a markedly distended coronal venous plexus. As flow through the fistula increases, progressive vascular steal and spinal cord compression take place and result in worsening myelopathy. A glomerular community of tiny branches of the radicular artery coalesces at the fistulous web site, which is within the dural sleeve of the nerve root. Arterialization of the coronal venous plexus leads to myelopathic venous congestion and subsequent myelopathy. Such obstruction leads to arterialization of the coronal venous plexus, which finally ends up in venous hypertension and myelopathy. As their old name implies, they are typically most typical in youngsters but can also occur in adults. Typically, they respect no tissue boundaries and might contain bone, muscle, skin, spinal canal, spinal wire, and nerve roots alongside a complete spinal stage. These lesions are usually low-resistance, high-pressure, and high´┐Żblood flow vascular malformations. The glomerular network of tiny branches coalesces on the site of the fistula along the dural root sleeve. In addition to venous outflow obstruction (not shown), arterialization of these veins produces venous hypertension. Focal disruption of the purpose of the fistula by endovascular or microsurgical strategies will obliterate the lesion. C, Illustrative case of a 55-year-old man with progressive myelopathy and bowel and bladder incontinence. A sagittal T2-weighted magnetic resonance image of the thoracic backbone reveals serpiginous vessels dorsal to the spinal cord. E, Intradural intraoperative photograph revealing a quantity of dilated vessels over the dorsal facet of the spinal cord. F, A single feeding arterial pedicle is isolated exiting at the right T7 nerve root sleeve as anticipated. B, Anterior view displaying the fistula alongside the anteroinferior facet of the spinal cord. These treacherous lesions can encompass soft tissues, bone, spinal canal, spinal wire, and spinal nerve roots along a complete spinal degree. Considerable involvement of multiple structures makes these malformations extraordinarily difficult to treat. A sagittal T1-weighted magnetic resonance image of the thoracolumbar spine exhibits flow voids in the vertebral bodies, pedicles, posterior components, and intradural and epidural spaces. Native (G) and subtracted (H) angiographic views of the right T12 spinal artery show the involvement of the posterior components and paravertebral musculature. C, Illustrative case of a 12-year-old boy with a history of subarachnoid hemorrhage. A sagittal T1-weighted magnetic resonance picture of the cervical backbone reveals abnormal vessels in the spinal wire. E, Intradural view by way of the working microscope showing the diffuse cervical intramedullary nidus. Most of the vessels are thrombosed from multiple classes of endovascular embolization. B, Posterior view recapitulating the complexity of the angioarchitecture of these lesions. C, Illustrative case of a 15-year-old boy who skilled an acute onset of back pain and subarachnoid hemorrhage. Color Atlas of Microneurosurgery: Microanatomy, Approaches, and Techniques, 2nd ed. Use of such a complete and anatomically primarily based system improves the efficacy of therapy. Classification of spinal arteriovenous malformations and implications for treament. Classification and therapeutic modalities of spinal vascular malformations in 80 sufferers. Aneurysms of spinal arteries associated with intramedullary arteriovenous malformations. Intradural extramedullary spinal arteriovenous malformations fed by the anterior spinal artery. The nidus is of the glomus type and is often extramedullary and pial based mostly, but it might possibly even have an intramedullary element. These lesions turn into symptomatic because of venous hypertension, ischemia, hemorrhage, and a mass effect from the vastly dilated venous system. Cavernous angiomas and arteriovenous malformations of the spinal epidural area: report of eleven circumstances. A dural spinal arteriovenous malformation with epidural venous drainage: a case report. La gliose ang´┐Żio-hypertrophique de la moelle ´┐Żpini´┐Żre (my´┐Żlite n´┐Żcrotique de Foix-Alajouanine). Neurological Surgery: A Comprehensive Reference Guide to the Diagnosis and Management of Neurosurgical Problems. Spinal epidural vascular malformation presenting in association with a spontaneously resolved acute epidural hematoma. Patel Vascular lesions of the spinal axis have engendered many classification schemes prior to now century. In the thoracic and lumbar area, nonetheless, the our bodies are predominantly fed by branches of the intercostal and lumbar radicular arteries, respectively. More distal branches of the radicular arteries circumscribe the vertebrae, thereby forming a vascular arcade anterior to the posterior longitudinal ligament, which in flip provides the posterior facet of the vertebral our bodies. Even additional radicular branches type an arcade in the posterior epidural area that provides the lamina and a portion of the posterior spinous process, in addition to the dorsospinal artery, which provides the outer floor of the lamina and the posterior spinous process. The anterior and posterior spinal veins are the 2 main midline longitudinal trunks and are crammed by sulcal veins. The ventral portion of the cord is drained by anteromedian and anterolateral veins, and posteromedian and posterolateral veins drain the posterior funiculi and dorsal horns. It is important to notice that the transition of a median vein into a radicular vein has the same "hairpin" turns because the arteries described earlier. Drainage of blood from the spine happens via the valveless internal and exterior venous vertebral plexus, which is related to the azygos and hemiazygos venous techniques. The most outstanding of those is the great anterior segmental medullary artery, referred to eponymously because the artery of Adamkiewicz, which usually arises from the left between T8 and L2.
Discount moduretic 50mg mastercardSonic hedgehog signaling regulates Gli2 transcriptional activity by suppressing its processing and degradation heart attack 36 purchase moduretic 50mg overnight delivery. Genetic elimination of Suppressor of fused reveals an essential repressor operate in the mammalian Hedgehog signaling pathway blood pressure of 100/60 discount 50 mg moduretic with amex. G protein Galphai features instantly downstream of Smoothened in Hedgehog signalling arteria znaczenie purchase moduretic 50mg amex. The kinesin protein Kif7 is a critical regulator of Gli transcription elements in mammalian hedgehog signaling blood pressure chart vertex buy moduretic 50mg with amex. Expression of three mouse homologs of the Drosophila phase polarity gene cubitus interruptus, Gli, Gli-2, and Gli-3, in ectoderm- and mesoderm-derived tissues suggests multiple roles throughout postimplantation improvement. Genetic deletion of sonic hedgehog causes hemiagenesis and ectopic growth of the thyroid in mouse. Involvement of Sonic hedgehog (Shh) in mouse embryonic lung development and morphogenesis. Essential perform of Gli2 and Gli3 within the formation of lung, trachea and oesophagus. Haploinsufficiency of the forkhead gene Foxf1, a goal for sonic hedgehog signaling, causes lung and foregut malformations. Arteries outline the place of the thyroid gland throughout its developmental relocalisation. The creating mouse thyroid: embryonic vessel contacts and parenchymal growth pattern during specification, budding, migration, and lobulation. Stomach development depends on fibroblast growth issue 10/fibroblast development issue receptor 2b-mediated signaling. Paracrine Hedgehog signaling in abdomen and gut: new roles for hedgehog in gastrointestinal patterning. Downregulation of Hedgehog signaling is required for organogenesis of the small intestine in Xenopus. Combined actions of hedgehog signaling inhibitors regulate pancreas improvement. A bipotential precursor inhabitants for pancreas and liver throughout the embryonic endoderm. Distinct populations of endoderm cells converge to generate the embryonic liver bud and ventral foregut tissues. Different thresholds of fibroblast progress factors sample the ventral foregut into liver and lung. Paneth cell differentiation within the creating gut of normal and transgenic mice. Indian hedgehog regulates intestinal stem cell destiny by way of epithelial-mesenchymal interactions during improvement. Tail intestine endoderm and gut/genitourinary/tail development: a model new tissue-specific role for Hoxa13. Anal atresia, vertebral, genital, and urinary tract anomalies: a main polytopic developmental area defect recognized via an epidemiological evaluation of associations. Vertebral defects, Anal atresia, T-E fistula with esophageal atresia, Radial and Renal dysplasia: a spectrum of related defects. A mouse mannequin of greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome: the extra-toesJ mutation incorporates an intragenic deletion of the Gli3 gene. Gastrointestinal anomalies related to esophageal atresia or tracheoesophageal fistula. Chapter 10 Hedgehog Signaling in Gastrointestinal Morphogenesis and Morphostasis 325 147. Germline mutations of the gene encoding bone morphogenetic protein receptor 1A in juvenile polyposis. Forced expression of E-cadherin in the mouse intestinal epithelium slows cell migration and supplies proof for nonautonomous regulation of cell fate in a self-renewing system. Hedgehog and epithelial-mesenchymal transition signaling in regular and malignant epithelial cells of the esophagus. Lf10-05-9780123820266(ve) stem cells drive selfrenewal in the abdomen and build long-lived gastric models in vitro. Identifying and counting epithelial cell varieties in the "corpus" of the mouse abdomen. Hedgehog sign activation in gastric pit cell and in diffuse-type gastric cancer. Diphtheria toxin-mediated ablation of parietal cells in the stomach of transgenic mice. Evidence that lack of sonic hedgehog is an indicator of Helicobater pylori-induced atrophic gastritis progressing to gastric most cancers. Down-regulation of a morphogen (sonic hedgehog) gradient within the gastric epithelium of Helicobacter pyloriinfected Mongolian gerbils. Reduced pepsin a processing of sonic hedgehog in parietal cells precedes gastric atrophy and transformation. Interleukin 1 beta and tumour necrosis factor alpha inhibit acid secretion in cultured rabbit parietal cells by multiple pathways. Sonic hedgehog: a link between inflammation, gastric atrophy, and acid suppression. Loss of parietal cell expression of Sonic hedgehog induces hypergastrinemia and hyperproliferation of floor mucous cells. Intracellular calcium release and protein kinase C activation stimulate sonic hedgehog gene expression during gastric Acid secretion. Identification of stem cells in small intestine and colon by marker gene Lf10-05-9780123820266. Depletion of the colonic epithelial precursor cell compartment upon conditional activation of the hedgehog pathway. Hedgehog pathway activity is required for the lethality and intestinal phenotypes of mice with hyperactive Wnt signaling. Conditional deletion of beta 1 integrins within the intestinal epithelium causes a loss of Hedgehog expression, intestinal hyperplasia, and early postnatal lethality. Loss of Indian hedgehog prompts multiple aspects of a wound therapeutic response within the mouse intestine. Hedgehog is an anti-inflammatory epithelial signal for the intestinal lamina propria. Sonic hedgehog is an endodermal signal inducing Bmp-4 and Hox genes during induction and regionalization of the chick hindgut. Akt-mediated liver growth promotes induction of cyclin E by way of a novel translational mechanism and a p21-mediated cell cycle arrest. Progressive fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: affiliation with altered regeneration and a ductular reaction. Sonic hedgehog is an autocrine viability factor for myofibroblastic hepatic stellate cells. Accumulation of hedgehog-responsive progenitors parallels alcoholic liver illness severity in mice and humans. Hepatic accumulation of Hedgehog-reactive progenitors will increase with severity of fatty liver injury in mice.
Discount 50 mg moduretic free shippingIncreasing the ramp velocity enhanced the magnitude of the depolarization and the chronotropic response blood pressure over 200 in elderly purchase moduretic 50mg amex. This was achieved either by blocking Kit receptors with neutralizing antibodies,17,18 by using animals carrying loss-of-function mutations in Kit or its ligand, stem cell issue,19,20,ninety three or by blocking downstream signaling molecules heart attack grill moduretic 50mg lowest price. Several motility disorders comply with bowel infections, and it could be potential to simulate some of these circumstances with infections in animals heart attack 40 year old female moduretic 50 mg without prescription. Slow waves produce a cycle of depolarization and repolarization that conducts to smooth muscle cells and changes the open probabilities of the various voltagedependent ion channels expressed by smooth muscle cells blood pressure chart dental treatment order moduretic 50 mg otc. Voltage-dependent ion channels form the backbone of the graceful muscle response to electrical rhythmicity, but metabotrophic and Ca2-dependent ion channels additionally contribute to the integrated responses of these cells. Many of the stereotypical motility responses of those cells additionally depend on modulations of ion channels. Two reviews41,107 ought to be helpful supplemental information together with the fabric described later. Slow wave depolarizations cause activation of voltage-dependent channels in easy muscle cells, corresponding to voltage-dependent (L-type) Ca2 channels. Ca2 entry via this pathway results in increases in global Ca2 and activation of the contractile equipment. Increases in open chance of Ca2 channels can result in the development of Ca2 action potentials superimposed on the sluggish waves (as shown within the trace). The magnitude of the response of smooth muscle cells is regulated by neural, humoral, and paracrine components. These are extraordinarily important mechanisms for determining the contractile performance of clean muscle cells and are addressed in different chapters of this text. In tonic muscles, hormonal or neuronal excitatory agonists could cause depolarization and activation of Ca2 channels. Rabbit and guinea pig gastric muscle cells from the gastric corpus had been used for their studies. Ca2 currents might be resolved in response to depolarizing steps optimistic to 30 mV. The current was inhibited by removing extracellular Ca2 and blocked by Co2, Cd2, or dihydropyridines. Another early article by Droogmans and Callewaert110 describes similar inward currents in longitudinal muscle cells of guinea pig ileum. A conductance apart from the L-type Ca2 present is clear from these recordings, and it was concluded that murine colonic myocytes also express a voltage-dependent, non-selective current. The inward present throughout depolarizations equal to gradual waves increases cell (Ca2) to at least 10 m. Direct measurements of modifications in free [Ca2]i with delicate Ca2 dyes in voltage-clamped, single smooth muscle cells reveal that Ca2 influx is enough to extend basal cytoplasmic Ca2 focus to levels excessive sufficient to perform excitation´┐Żcontraction coupling. Because L-type Ca2 channels provide an essential role in initiating excitation´┐Żcontraction coupling, regulation of these channels may present an efficient means of controlling motility. In reality, though there have been demonstrations of agonist regulation of L-type currents. Cat esophageal muscular tissues specific an inward present that prompts at negative potentials, producing a characteristic "hump" within the I-V curve between 50 and 20 mV. The authors conclude that the properties of the fast-activating present in human colonic cells had the properties of a T-type Ca2 current. Experiments on murine colonic muscles revealed a similar low-threshold present in these cells. Although the properties of the murine conductance had been much like a T-type present, the current´┐Żvoltage relation confirmed that the reversal potential occurred near zero mV. The low-threshold present in colonic cells had properties of a voltage-gated, nonselective cation current rather than T-type Ca2 present. These cells, in general, have resting potentials close to 60 mV, and at these potentials the low-threshold currents are substantially inactivated. This speculation was tested in murine colonic muscular tissues using blockers of the lowthreshold non-selective cation conductance. Thus, on the resting potentials of fundus muscular tissues (positive to 60 mV),1 little of this current is out there. These channels have been termed delayed rectifiers due to their comparatively slow time course of voltage-dependent activation. For example, there are significant differences in delayed rectifier conductances even in two adjacent muscle layers, such as the round and longitudinal muscular tissues of the canine colon. Benham and co-workers153 report an inwardly rectifying cation present in rabbit jejunal longitudinal muscle cells. Hyperpolarization negative to 70 mV evoked a time-independent present and a current that developed over a interval of a number of seconds. The time-dependent current reversed at about 30 mV and was blocked by cesium (1 mM). Others found hyperpolarization-activated cation channels (64 pS) in toad abdomen muscle cells, and this conductance was also activated by stretch. Functional channels kind as multimers of subunits and infrequently are associated with auxiliary subunits that participate in regulation. K channels fall into three major structural divisions: (1) pore-forming subunits with one ionic pore and six transmembrane segments. Outward currents were elicited by check potentials 70 and 20 mV from a holding potential of eighty mV. Peak K currents at check potentials have been transformed into permeabilities using the Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz present equation for voltage dependence of activation. Permeabilities have been normalized (P/Pmax), plotted as a perform of check potential (open circle), and fit with a Boltzmann function. The major -subunits are additionally associated with -subunits that modulate the properties of native channels. Inward rectifiers have the property of conducting ions higher at adverse membrane potentials. Thus, conductances of this sort are notably properly suited to contributing to membrane potential and stabilizing membrane potential. Activation of inward rectifier conductances would tend to reduce the amplitude of conducting slow waves and scale back the tendency of gradual waves to initiate Ca2 motion potentials in clean muscle cells. Inward rectifying K conductances have also been reported in feline esophageal smooth muscle cells. Ba2 (10 M) depolarized membrane potentials by about 6 mV, suggesting the inward rectifier conductance contributed to resting membrane potential. This class of K channels has been present in easy muscular tissues of the canine small and large intestine,187 and immunohistochemistry demonstrated expression of Kir3. Lemakalim triggered hyperpolarization of murine colonic muscular tissues;191 nevertheless, in contrast with other muscular tissues, glibenclamide alone caused depolarization (9 mV). Lemakalim induced outward current in murine colonic myocytes that was blocked by glibenclamide.
Moduretic 50 mg onlineY" gene on the Y chromo some, which encodes the testis-determining factor, the primitive intercourse cords continu´┐Ż to proliferate and penetrate deep into the meduUa to type the testis or medullary cords just started blood pressure medication generic 50mg moduretic visa. Toward the hilum of the gland, the cords break up right into a community of tiny ceU strands that later give rise to tubules of the rete testis hypertension recommendations purchase 50mg moduretic overnight delivery. During fiirther growth, a dense layer of ´┐Żbrous connective tissue, the t´┐Żnica albuginea, separates the testis cords from the floor epithe lium heart attack 4 blocked arteries order 50mg moduretic mastercard. In the fourth month, the testis cords turn out to be horseshoe-shaped, and their extremities are steady with those of the rete testis blood pressure 5020 discount 50 mg moduretic fast delivery. Testis cords are actually composed of primitive germ cells and sustentacular cells of Sertoli derived from the floor epithelium of the gland. Interstitial cells of Leydig, derived from the unique mesenchyme of the gonadal ridge, lie be tween the testis cords. By the eighth week of gestation, Leydig cells start production of testosterone and the testis is prepared to affect sexual differentiation of the genital ducts and external genitalia. Testis cords remain strong till puberty, once they acquire a lumen, thus forming the seminiferous tubules. Once the seminiferous tubules are canalized, they join the rete testis tubules, which in turn enter the ductuli efferentes. These e´┐Żferent ductules are the remaining parts of the excretory tubules of the mesonephric system. They link the rete testis and the mesonephric or Wolffian duct, which becomes the ductus deferens. These clusters, containing teams of primitive germ cells, occupy the medullary a part of the ovary. Later, they disappear and are changed by a vascular stroma that types the ovar´┐Żan meduUa. The floor epithelium of the female gonad, in contrast to that of the male, contin´┐Żes to proliferate. In the seventh week, it gives rise to a second technology of cords, cortical cords, which penetrate the underlying mesenchyme however stay ci´┐Żse to the surface. Cells in these clusters continu´┐Ż to proliferate and begin to encompass every oogonium with a layer of epithelial cells known as follicular cells. The paramesonephric duct arises as a longitudi nal invagination of the epithelium on the anterolateral floor of the urogenital ridge. Caudally, it first runs lateral to the mesonephric duct, then crosses it ventrally to develop caudomedially. In the midline, it comes in ci´┐Żse contact with the paramesonephric duct from the other facet. The caudal tip of the mixed ducts tasks into the posterior wall of the uro genital sinus, where it causes a small swelling, the sinus tubercle. The mesoneph ric ducts open into the urogenital sinus on both facet of the sinus tubercle. Genital Ducts within the Male Genital ducts in the male are stimulated to develop by testosterone and are derived from parts of the mesonephric kidney system. Except for essentially the most cranial portion, the appendix epididymis, the mesonephric ducts persist and form the primary genital ducts. Immediately under the entrance of the efferent ductules, the mesonephric ducts elongate and turn out to be extremely convoluted, forming the (ductus) epididymis. From the tail of the epididymis to the outbudding of the seminal vesicle, the mesoneph ric ducts obtain a thick muscular coat and form the ductus deferens. Initially, three elements can be recognized in every duct: (1) a cranial vertical portion that opens into the stomach cavity, (2) a horizontal part that crosses the meso nephric duct, and (3) a caudal vertical half that fuses with its companion from the other aspect. When the second part of the paramesonephric ducts strikes mediocaudally, the urogenital ridges progressively come to lie in a transverse pla´┐Że. After the ducts fuse within the midline, a broad transverse pelvic fold is established. This fold, which extends from the lateral sides of the fused parame sonephric ducts towards the wall of the pelvis, is the broad ligament of the uterus. The uterine tube lies in its upper border, and the ovary lies on its posterior floor. The uterus and broad ligaments divide the pelvic cavity into the uterorectal pouch and the uterovesical pouch. The fused paramesonephric ducts give rise to the corpus and cervix of the uterus and the upper portion of the vagina. The uterus is surrounded by a layer of mesenchyme that types each its muscular coat, the myometrium, and its peritoneal overlaying, the perimetrium. It appears to act at the aspect of the autosomal gene S0X9, a transcriptional regulator, that may also induce testes di´┐ŻFerentiation. Testosterone enters ceUs of goal tissues the place it might stay intact or be converted to dihydrotestosterone by a 5-ot reductase enzyme. Testosterone receptor complexes med´┐Żate differentiation of the mesonephric ducts to type the vas deferens, seminal vesicles, e´┐Żferent ductules, and epididymis. Dihydrotestosterone re ceptor complexes modulate di´┐Żferentiat´┐Żon of the male external genitalia. Estrogens are also concerned in sexual d´┐Ż´┐Żferentiation, and underneath their influence, the paramesonephric (M´┐Żllerian) ducts are stimulated to type the uterine tubes, uterus, cervix, and upper v ^ n a. In addition, estrogens act on the extemal genitalia on the indifferent stage to type the labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, and decrease vagina. Vagina Shortly after the stable tip of the paramesonephric ducts contacts the urogenital sinus. These evaginations, the sinovaginal bulbs, proliferate and kind a solid vaginal p´┐Żate. Proliferation contin´┐Żes on the cranial finish of the p´┐Żate, growing the space between the uterus and the urogenital sinus. The wing-like expansions of the vagina across the finish of the uterus, the vaginal fornices, are of paramesonephric origin. Thus, the vagina has a twin origin, with the higher portion derived from the uterine canal and the decrease portion derived from the urogenital sinus. The lumen of the vagina remains separated from that of the urogenital sinus by a thin tissue p´┐Żate, the hymen. The feminine might retain some remnants of the cranial and caudal excretory tubules within the mesovarium, where they kind the epoophoron and paroophoron, respectively. The mesonephric duct disappears apart from a small cranial portion discovered within the epoopho ron and sometimes a small caudal portion that might be discovered within the wall of the uterus or vagina. Caudally, the folds are subdivided into urethral folds anteriorly and anal folds posteriorly. In the meantime, one other pair of elevations, the genital swellings, turns into seen on each side of the urethral folds.
References - Makhdoom ZA, Komar MJ, Still CD. Nutrition and enterocutaneous fi stulas. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2000;31:195-204.
- Burns WC, Kantharidis P, Thomas MC: The role of tubular epithelialmesenchymal transition in progressive kidney disease, Cells Tissues Organs 185(1n3):222n231, 2007.
- Mishra PK. Management strategies for interrupted aortic arch with associated anomalies. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2009;35:569-76.
- Hagl C, Ergin MA, Galla JD, et al: Neurologic outcome after ascending aorta-aortic arch operations: Effect of brain protection technique in high-risk patients, J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 121:1107-1121, 2001.
- Koraitim MM, Marzouk ME, Atta MA, et al: Risk factors and mechanism of urethral injury in pelvic fractures, Br J Urol 77:876n880, 1996.
|