Nebivolol
Michael L. Cunningham, M.D., Ph.D. - Seattle Childrenĺs Hospital Craniofacial Center
- Seattle, Washington
Generic nebivolol 2.5 mg onlineAlthough these medication all activate descending pain-inhibitory mechanisms within the central nervous system, they bind to five distinct molecular sites blood pressure yahoo health buy discount nebivolol 2.5 mg online. Thus, we had been surprised to discover a remarkably excessive degree of genetic correlation among them (r = zero pulse pressure deficit buy nebivolol 2.5mg without prescription. In a follow-up research, an identical genetic correlation was noticed between acetylsalicylic acid and indomethacin analgesia, but acetaminophen analgesia seemed to be genetically distinct (Wilson et al 2003a) hypertension blood pressure readings nebivolol 2.5 mg with mastercard. A related genetic correlation is the repeatedly noted correlation between baseline nociceptive sensitivity and subsequent sensitivity to inhibition of the stimulus by analgesics (Mogil et al 1996a, Elmer et al 1998, Wilson et al 2003b) blood pressure spikes 2.5mg nebivolol with amex. That is, mouse strains initially sensitive to nociception are additionally proof against analgesia, and vice versa. This principle works within a quantity of nociceptive modalities and means that the "grasp" analgesia gene or genes referred to above may in reality be ones with a major action on nociception, which can subsequently affect analgesia as nicely. Elmer and colleagues (1998) hypothesized that this can be explained when it comes to genetic variations in efficient stimulus intensity affecting fractional receptor occupancy of the analgesic. Qualitative Strain Differences the overwhelming majority of documented strain differences of relevance to pain are quantitative in nature, variations in diploma somewhat than in sort. In a few intriguing cases, however, qualitative pressure variations have been uncovered, thus suggesting that totally different genotypes could be processing ache by way of from false positives. We just lately performed a meta-analysis of the primary 20 revealed continual pain´┐Żrelevant microarray studies (LaCroix-Fralish et al 2011). Findings from Animal Pain Genetics As mentioned, the major goal of this chapter is to evaluate the genetics of particular person differences because the molecular genetics of ache is addressed elsewhere on this quantity. Interested readers are directed to other evaluations as properly (Mogil 1999, 2004; Mogil et al 1996b; LaCroix-Fralish and Mogul 2009). Heritability (h2; see later for further discussion) is the proportion of trait variance attributable to genetic inheritance. Heritability may be estimated in laboratory animals both through the use of panels of inbred strains or by assessing the response to artificial selection (see Crabbe et al 1990). In the only systematic inbred strain surveys to date, the heritability of response to 22 common algesiometric assays has been found to range from h2 = zero. This vary of heritability is very similar to that obtained in large human twin studies of experimental ache published in latest years (Norbury et al 2007, Nielsen et al 2008). Using the same set of strains, the heritability of the efficacy of eight analgesics was discovered to be barely decrease, h2 = zero. The three present selective breeding studies of relevance to ache (see earlier) have yielded heritability estimates of h2 = 0. Genetic Correlations One interesting use of each chosen traces and inbred strains entails the investigation of genetic correlations (see Crabbe et al 1990). If choice or probability has fixed the alleles of a gene right into a homozygous state, that fixation will probably affect multiple traits. Genetic correlation is demonstrated if lines chosen for his or her efficiency on one trait are observed to vary on one other or if the same distribution of phenotypic responses on two traits is observed among a panel of inbred strains. As may be anticipated, the sensitivity of inbred strains and chosen lines on sure nociceptive assays is genetically correlated with sensitivity on other nociceptive assays, however not all other nociceptive assays. Rady and Fujimoto (1999) demonstrated that heroin produces analgesia by way of -, -, or -opioid receptors, depending on the mouse pressure in query. There even exists proof of genetic effects on the anatomy of the painrelevant neurocircuitry. A recent examine has demonstrated pressure variations in rat and mouse sciatic nerve anatomy, together with even the variety of lumbar vertebrae (Rigaud et al 2008). Finally, people however not rodents can describe essential phenomena similar to pain quality, ongoing or stimulus-independent pain (see Mogil 2009, Mogil et al 2010; but see additionally Sufka 1994, King et al 2009, Langford et al 2010), and relationships between pain and mood. The following discussion suggests several ways that medical researchers can solve a few of these issues. One may be in a position to prioritize this half of the genes on a rodent-derived ache candidate gene listing by finding out the effects of the genetic variants on a medical ache consequence. Such a study, somewhat analogous to transgenic and linkage mapping studies in animals, is much inexpensive than developing a new drug after which finishing up toxicology studies and a clinical trial. Some Definitions Disease Genes versus Pain Genes If one searches PubMed or Medline for the phrases "ache," "human," and "polymorphism," most of the ensuing stories will describe genes that trigger a visual harm that offers rise to pain-a herniated lumbar disc, occluded coronary artery, or a tumor. The prevalence in the basic inhabitants is low, and heritability follows a simple mendelian mannequin: one (dominant) or two copies (recessive) of the altered gene, without the need for some other mutations, alter the phenotype. The mouse researcher can also rigorously control the environment and the pain-provoking stimulus. However, this abundance of riches presents new issues that human studies might help solve. First, how should one prioritize these targets for physiological examine or for the development of recent drugs that mimic or antagonize them Location in centimorgans (cM; roughly 1 million base pairs) from the proximal end of the chromosome of the peak statistical proof for genetic linkage. The 95% confidence intervals in this sort of research are typically very giant, however, and average greater than 10 cM. These findings have all led to the speculation that migraines are associated to dysfunction of ion transport. One might chorus from calling any of these "pain genes," however, as a end result of the encoded channel abnormalities in all probability initiate the migraine assault quite than affecting processing of the nociceptive enter in the course of the attack. Non-parametric linkage methods utilizing affected sibling pairs have proved effective in examining the genetic contribution to suspected mendelian disorders (McPeek 1999). It is possible that other mendelian ache issues are ready to be found by a pain researcher who brings a ache questionnaire and a thermal probe right into a genetics clinic. However, we speculate that virtually all such robust single-gene results have been reported already. The varied features of ache processing are extra doubtless to be "advanced genetic traits," phenotypes decided by small contributions from many genes (independently or by way of gene´┐Żgene interactions) and genetic´┐Ż environmental interactions. The the rest of this chapter discusses approaches that one might take to point out that ache problems are advanced genetic traits and to identify the genetic polymorphisms accountable. Table 10-3 shows heritability values for bodily characteristics, some well-studied medical diseases, and several pain traits. Apart from the well-replicated migraine knowledge, most of those pain traits have been examined in only one study every. Advantages of Twin Studies of Heritability ´┐Ż For traits that may be assessed by questionnaire or phone, twin research could be conducted rapidly and easily. Groups in plenty of nations maintain registries of as a lot as a hundred,000 twin pairs every (MacGregor et al 2000), and one can readily enroll a number of thousand fascinated pairs, which is usually sufficient to estimate heritability. For example, a twin examine of particular person variations in experimental ache sensitivity revealed that more than 50% of the variance in chilly pressor pain, however only 26% of the variance in heat ache, was genetically mediated (Nielsen 2008) and that these pain phenotypes are distinct phenomena from a genetic perspective. For example, twin designs are nicely suited to the research of laboratory ache stimuli or the lifetime prevalence of the symptoms of migraine or multisomatoform issues (Kroenke et al 1998) corresponding to fibromyalgia, irritable bowel syndrome, or persistent tension-type complications, which seem to develop in many patients and not using a dramatic precipitating environmental insult. One may also research the same pain stimuli experienced by most youngsters, such as vaccinations, and the interplay of genes and parenting on future ache conduct (Rocha et al 2003). In complicated problems involving genes with small effects, one wants association studies, whose optimal design may be different. More than 9000 twin pairs were studied with a survey and examination of hospital records. However, if the more severe criterion of hospital admission was used, solely eight pairs had both suffered sciatica, which is inadequate for a comparability.
Buy 2.5 mg nebivolol amexIt can be unknown whether the mobile mechanisms underlying these alterations in synaptic efficacy are developmentally regulated, as has been reported previously in the hippocampus (Yasuda et al 2003) heart attack quizzes purchase nebivolol 2.5 mg with visa. Both results final into adulthood and are observed only if the unique inflammatory stimulus is applied throughout the first week of life (Ren et al 2004) arteria epigastrica cranialis superficialis commissura labiorum dorsalis purchase nebivolol 2.5mg. These persistent alterations in pain processing look like exacerbated in female pups (LaPrairie and Murphy 2007) blood pressure xanax purchase 2.5 mg nebivolol otc. Enhancement of ache responses with repeated harm at the identical website has been observed in other models blood pressure chart in pediatrics cheap 5mg nebivolol otc. A skin incision made throughout a crucial stage in neonatal pups leads to a larger pain response to subsequent damage in later life (Walker et al 2009b, Beggs et al 2012b). Thus, when an initial incision is performed in the first week of life, the diploma of hyperalgesia following a repeated incision in adulthood is bigger than in animals having a single incision on the identical age. This "priming" effect in young animals is blocked by perioperative native anesthetic blockade, thus highlighting the essential position of sensory activity on the time of the primary damage in triggering this phenomenon. Thus, mounting proof from both the somatic and visceral ache pathways suggests that neonatal inflammation can evoke both a widespread reduction in baseline ache sensitivity to acute noxious stimuli and site-specific enhancement of ache responses throughout extended noxious stimulation, which occurs with reinjury. Notably, these effects may by some means depend on the location and nature of the early injury. This turns into important when considering preterm infants in intensive care (Anand 2000). It is estimated that such infants experience a median of 10 painful procedures per day of hospitalization (Carbajal et al 2008). In help of a facilitatory effect of early noxious stimulation on future pain sensitivity, 4´┐Ż6-month-old infants who had undergone circumcision as neonates demonstrated elevated ache responses throughout inoculation (Taddio et al 1997), and prematurely born adolescents exhibited hypersensitivity to tactile stimulation (Buskila et al 2003). In distinction, different studies have reported unaltered and even decreased ache sensitivity in youngsters previously exposed to repeated painful procedures (Grunau et al 1994, Oberlander et al 2000). Animal models have helped to start unraveling the persistent results of early damage on nociceptive processing, partially by greatly emphasizing the significance of contemplating how. Effect of early hindpaw skin incision injury on the ache response to repeated damage in adulthood. Ipsilateral hindlimb mechanical withdrawal thresholds are expressed as the percent change from baseline for 4 weeks following damage. Importantly, recent human research have reached qualitatively comparable conclusions regarding the long-term effects of localized tissue damage during youth. No long-term changes in world mechanical ache sensitivity had been noted both in these children or in children born extremely prematurely (Walker et al 2009a), though persistent mechanical hypoalgesia has been reported in the area adjacent to neonatal thoracotomy scars (Schmelzle-Lubiecki et al 2007, Walker et al 2009a). This occurs independently of sensory neural activity (De Lima et al 1999) and will depend upon the discharge of neurotrophins from the damaged area (Constantinou et al 1994) or a site-specific down-regulation of factors that usually inhibit axonal progress into the skin (Moss et al 2005). Central Mechanisms Long-term modifications in pain sensitivity following neonatal harm are more doubtless to contain alterations within the central circuitry. The distinction in onset times between the worldwide hypoalgesia and the increased sensitivity to repeated harm means that distinct mechanisms might underlie these two persistent adjustments in pain sensitivity after early tissue harm. The local hyperalgesia arises from increased excitability and synaptic strengthening within the dorsal horn (Torsney & Fitzgerald 2003, Li et al 2009a). The delayed look of global hypoalgesia coincides with the gradual maturation of the descending pathways from the brain stem (Hathway et al 2009), thus elevating the likelihood that longterm adjustments within the supraspinal circuitry happen after early injury. Discovery of a critical period for the development of descending inhibition and the requirement for opioid exercise over this period (Hathway et al 2012) helps clarify how early publicity to pain and damage could have long-term effects on sensory processing in later life. Neonatal damage and stress affect future pain processing each on the website of injury and globally, throughout the entire physique. Interestingly, steady recording from single dorsal horn cells both earlier than and after pores and skin incision exhibits that the preliminary afferent-evoked spike exercise is bigger in young than in grownup animals (Ririe et al 2008). A transient barrage of sensory enter to the growing spinal twine may promote long-term alterations in the function of spinal nociceptive circuits inasmuch as brief inflammation of the neonatal hindpaw results in significant adjustments in gene expression inside the adult dorsal horn (Ren et al 2005). These changes may one method or the other "prime" the spinal wire in a somatotopically restricted manner such that segmental hyperexcitability is unmasked following a second harm later in life. Recent work has also recognized spinal microglia as critical mediators of the priming effects of early damage for the reason that dorsal horn neuroimmune response after grownup tissue harm is exaggerated in neonatally injured rats and the resulting hyperalgesia is decreased by intrathecal administration of the microglial inhibitor minocycline (Beggs et al 2012b). It has been speculated that harm and pain in early life may produce the continual pain patients of the lengthy run, and despite the shortage of direct biological evidence to support this principle, it stays an attention-grabbing possibility. Recently, this has additionally been shown in a younger animal mannequin of nerve damage by which mechanical hypersensitivity emerges solely later in life. Such novel findings might present clues to understanding the long-term results of early damage and the emergence of adolescent or adult chronic ache syndromes. The overlap between ache and reward pathways (Borsook et al 2007) means that neonatal ache expertise might affect reward-related pathways and behavior in adulthood, and recent proof in an animal model of motivational behavior helps this (Low and Fitzgerald 2012). Furthermore, surgery, medical situations, and intensive care treatment inevitably expose infants and youngsters to a massive number of stressors beyond the precise tissue harm that occurs throughout essential medical interventions, and emerging proof means that adolescence stress can also evoke long-lasting alterations within the function of nociceptive pathways. For instance, neonatal maternal separation alone can induce visceral hypersensitivity in grownup rats (Coutinho et al 2002, Gosselin et al 2010a). In addition, early life stress considerably prolongs muscle hyperalgesia following prostaglandin administration in the adult and increases the excitability of mature nociceptors innervating the muscle (Green et al 2011). The practical link between neonatal stress and the maturation of ache circuits represents an necessary space for future investigation. Anand P, Birch R: Restoration of sensory operate and lack of long-term chronic ache syndromes after brachial plexus damage in human neonates, Brain a hundred twenty five:113´┐Ż122, 2002. Andrews K, Fitzgerald M: the cutaneous withdrawal reflex in human neonates: sensitization, receptive fields, and the results of contralateral stimulation, Pain 56:95´┐Ż101, 1994. Andrews K, Fitzgerald M: Flexion reflex responses in biceps femoris and tibialis anterior in human neonates, Early Human Development fifty seven:105´┐Ż110, 2000. Andrews K, Fitzgerald M: Wound sensitivity as a measure of analgesic results following surgery in human neonates and infants, Pain ninety nine:185´┐Ż195, 2002. Behar T, Schaffner A, Laing P, et al: Many spinal twine cells transiently categorical low molecular weight types of glutamic acid decarboxylase during embryonic development. Borsook D, Becerra L, Carlezon J, et al: Reward-aversion circuitry in analgesia and ache: implications for psychiatric disorders, European Journal of Pain 11:7´┐Ż20, 2007. Boucher T, Jennings E, Fitzgerald M: the onset of diffuse noxious inhibitory controls in postnatal rat pups: a C-Fos study, Neuroscience Letters. Bourane S, Garces A, Venteo S, et al: Low-threshold mechanoreceptor subtypes selectively express MafA and are specified by Ret signaling, Neuron 64:857´┐Ż870, 2009. Buskila D, Neumann L, Zmora E, et al: Pain sensitivity in prematurely born adolescents, Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 157:1079´┐Ż 1082, 2003. Chen J, Sandkuhler J: Induction of homosynaptic long-term depression at spinal synapses of sensory A delta-fibers requires activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors, Neuroscience 98:141´┐Ż148, 2000. Cheunsuang O, Morris R: Spinal lamina I neurons that categorical neurokinin 1 receptors: morphological analysis, Neuroscience 97:335´┐Ż345, 2000.
Nebivolol: 5 mg, 2.5 mg
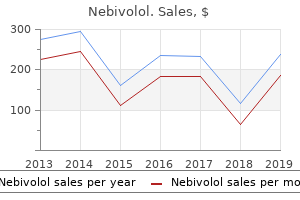
Purchase 5 mg nebivololWe additionally briefly talk about the pinprick methodology for punctuate hyperalgesia and approaches to measure deep strain blood pressure chart good and bad discount 2.5 mg nebivolol amex. In general, mechanical stimuli are difficult to use in a standardized fashion even when standardized equipment is used, and the nice number of units and protocols make it difficult to check outcomes reported in different publications blood pressure medication morning or evening discount nebivolol 5 mg on line. Von Frey Filaments and Similar Methods Von Frey filaments have been introduced within the nineteenth century to determine sensory thresholds in humans class 4 arrhythmia drugs buy nebivolol 5mg without a prescription. The method is based on the principle that a monofilament will bend at a definite drive when applied perpendicular to a surface arteria hypogastrica order nebivolol 5 mg overnight delivery. A vary of calibrated filaments can be utilized to calculate a response threshold or, alternatively, the response frequency (Chaplan et al 1994). When utilized in rodents, the animals are normally placed on a lined grid and probed from under, however in some cases the animals are restrained. Response is outlined as brisk withdrawal of the paw, however a "hyperalgesia-like" response during which the animal elevates the paw for a second or extra or shakes, grooms, licks, or chews the paw has been instructed to distinguish between aversive and non-aversive sensations when applied to neuropathic rats (Hogan et al 2004). Cold Cold stimuli are used primarily within the context of neuropathic pain fashions and in work aimed toward characterizing physiological and molecular mechanisms of chilly notion and chilly pain. Research on chilly transduction has made great progress within the last 10´┐Ż15 years, but the means in which that signaling in several afferent fiber varieties pertains to tissue temperature and sensory high quality is much less clear than that for warmth perception. Although 174 Section One Neurobiology of Pain Von Frey filaments are used extensively but are related to a quantity of drawbacks. Bove (2006) has provided a detailed analysis that may be summarized as follows: ´┐Ż the precise strain on the pores and skin will change during the software of a specific filament as a outcome of contact surface area and geometry depend upon the diploma of bending and compliance of the tissue. These components and the usage of discrete filaments of fixed nominal bending drive restrict accurate estimation of thresholds and comparison of data between laboratories. Bove (2006) further refers to anecdotal information suggesting a discrepancy between the impact of filament stimulation and a set of different, maybe more related mechanical stimuli, such as light or onerous stroking and vigorous rubbing of the affected paw. Some of these issues can be minimized by proper technique, similar to stopping stimulation immediately when the filament bends, but there are additional complications associated to the mechanical instability of typical filaments. They are normally made from hygroscopic material and their bending properties will change rapidly in response to normally occurring fluctuations in relative humidity; a No. As talked about earlier, contact space geometry performs a role in stimulus operate, and different factors being equal, probes of smaller diameter will be more effective (see ´┐Żngeby-M´┐Żller et al 1998 for references). Using filaments manufactured from non-hygroscopic material and with a set tip dimension can circumvent a quantity of of these issues (Song et al 1999, Fruhstorfer et al 2001). Standardized protocols that would minimize back inter- and intraobserver variability have been advised. Pinprick Mechanical hyperalgesia is regularly examined by the pinprick technique, which in its easiest form is performed by making use of a pointy object corresponding to a security pin or an injection needle to the pores and skin to cause an indentation however no penetration. The animals could additionally be restrained for the process or, more commonly, placed on a grid. The animal has simply been uncovered to a standardized mechanical stimulus applied by an electronic von Frey stimulator. In human experimental work, a extra standardized process has been devised in which weighted pinprick stimulators with a fixed flat contact area of 0. Deep Pressure Sensitivity to deep pressure may be examined by applying fixed or progressively rising stimuli, the later being extra frequent in animal research. The strain reached when the rat started to wrestle was taken as the behavioral readout. Since animals with an inflamed paw were used, the tactic could be proven to be delicate to non-narcotic analgesics similar to salicylates, in distinction to beforehand used deep strain strategies. Today, modified versions of the method are applied in fashions of neuropathic as nicely inflammatory hypersensitivity (Whiteside et al 2004, Pradhan et al 2010). Chemical Stimuli Irritants might cause pain by native administration to skin and other organs. In precept, they might act by direct activation of nociceptors and/or by inflicting inflammatory or poisonous effects within the tissue. In either case, this type of stimuli is fundamentally totally different from acute physical stimuli in that the impact is protracted and generally lasts for several minutes and longer. The hottest of those methods is undoubtedly the formalin take a look at, which is discussed in some detail. In humans, injection of formalin into the index finger or base of the hand was anecdotally reported to provide an intense, sharp, stinging, and burning ache (rated 3 out of 5 in intensity), which after about 5 minutes was changed by a gradual, throbbing ache that steadily disappeared over a interval of 30´┐Ż60 minutes and was followed by mild residual tenderness on the injection site (Dubuisson and Dennis 1977). The technique, as largely applied today, was first described in rats and cats and was developed to allow continuous painful stimulation (as opposed to commonly used transient stimuli similar to electrical shock and radiant heat) and to avoid restraint in the testing session, which could produce undue stress and interference with spontaneous habits (Dubuisson and Dennis 1977). Dilute formalin was injected subcutaneously right into a forepaw, and a ache depth index was calculated based on the period and weighting of protecting behavior. Formalin is often injected into the dorsum or plantar tissue of a hindpaw, which makes it easier to distinguish the response from grooming than when a forepaw is used. In either method, the injection causes licking, flinching, shaking, and favoring of the affected paw that typically happens in two phases, the early or first part lasting as a lot as 10 minutes after injection and the late or second phase for about 20´┐Ż60 minutes. Orofacial variations with injection into the higher lip of rats or mice have been developed to address mechanisms of the trigeminal system (Clavelou et al 1989, Luccarini et al 2006). Both the focus of formalin and the ambient temperature have an result on the time course of behavior. Conversely, larger ambient temperatures may enhance the behavioral activity in the quiet interval between the phases and make the biphasic pattern much less clear. These components also affect the tissue response and will affect the effect of pharmacological remedy (Rosland et al 1990, Tj´┐Żlsen et al 1992, Damas and Liegeois 1999, Munro 2009). Both phases of the behavioral response are related to a primary afferent C-fiber drive that might be expected to initiate and preserve activity-dependent sensitization at a spinal level (McCall et al 1996). The electrophysiological response to formalin within the rat has been additional characterized (Puig and Sorkin 1996). Single-fiber recordings of the sural nerve demonstrated exercise in A, A, and high-threshold C nociceptive afferent fibers in the course of the first phase. During the second phase, exercise was noticed in A fibers with receptive fields in hairy pores and skin and in mechanically sensitive C fibers, but in addition in mechanically insensitive fibers and A and C fibers with receptive subject facilities outdoors the injection site. Activity in the course of the second part was suppressed by the administration of lidocaine in doses that produced non-anesthetic, clinically relevant publicity. The human experience of changing ache quality and depth as a function of time after injection, in addition to the electrophysiological information cited earlier, might counsel that the phases differ with regard to pathology as properly as intensity. Usually, the test is completed within 1 hour of formalin injection, however hypersensitivity to mechanical and thermal stimuli culminating 1´┐Ż3 days after injection and lasting up to 4 weeks has been reported (Fu et al 2001). It appears that full-blown irritation comes later than the conduct normally quantified. There are many alternative implementations of the model in addition to those mentioned earlier, which hampers comparability of results throughout research (Capone and Aloisi 2004). The Writhing Test the writhing take a look at entails the intraperitoneal injection of an irritant that produces a behavioral response consisting of stretching and writhing, typically quantified as the number of episodes or the accumulated time that the behavior is displayed inside a certain time-frame. Agents used to induce the response embrace acetic acid (probably essentially the most incessantly used agent), hydrochloric acid, phenylquinone, and potassium chloride, along with substances that might be more mechanistically selective, such as acetylcholine, adenosine triphosphate, bradykinin, noradrenaline, and oxytocin. Historically, various implementations of this paradigm have shown good sensitivity to analgesics of different classes, however the specificity is poor (Taber 1974). The method is due to this fact rarely used however may have some utility in mechanistic research when agents that activate specific receptors are injected.
Order nebivolol 2.5 mg without a prescriptionThis could additionally be appropriate if the concomitant somatic block is useful in addition to the sympathetic block blood pressure medication with alcohol buy 2.5 mg nebivolol. This could be a true placebo response however might also be caused by a counter-irritation impact, or peripheral enter that dampens a central component of a chronic ache condition pulse pressure 2012 generic 2.5mg nebivolol visa. Prognostic Blocks these blocks are supposed to indicate whether destruction of the peripheral nerve will give long-lasting pain relief blood pressure medication used for headaches order nebivolol 2.5mg with mastercard. Preventive Nerve Blocks (Not "Pre-emptive" Blocks) this concept acquired a lot of attention after the speculation was launched 2 decades ago that postoperative ache could probably be prevented by a nerve block established earlier than surgical procedure heart attack pathophysiology 2.5 mg nebivolol mastercard. However, a prophylactic block established earlier than surgical procedure and continued throughout and after surgery for so long as the patient has severe movement-triggered pain constitutes optimal postoperative pain management and will have extended helpful results, corresponding to facilitating lively rehabilitation after surgery and probably reducing danger for the development of persistent ache after surgical procedure (Breivik et al 1996). Therapeutic Local Anesthetic Blocks For acute ache after surgical procedure or trauma, an applicable nerve block can relieve the pain completely for the duration of the local anesthetic effect. The duration of ache relief may be prolonged by administering a dilute local anesthetic by continuous infusion or by patient-controlled bolus injections into a catheter placed near a nerve or a nerve plexus. However, skilled pain clinicians are satisfied that in some sufferers native anesthetic blocks may give ache relief that far outlasts the specific native anesthetic block of the peripheral nerve (Arn´┐Żr et al 1990). It additionally helps in explaining ache and ache mechanisms to sufferers, decreasing nervousness, and bettering coping. A profitable block could reinforce the effects of different measures taken to assist the patient. The physician have to be absolutely conscious of potential unwanted effects and complications of nerve blocks and have to be ready and expert at dealing with any that do come up. Nerves must be precisely focused with a nerve stimulator, ultrasound, or fluoroscopy. Initially, a short-acting local anesthetic such as lidocaine or chloroprocaine must be used. If a short-acting native anesthetic block relieves the pain for about an hour, the block ought to be repeated with a longer-acting agent similar to bupivacaine, which ought to give pain reduction for at least 2 hours, relying on the focus and volume injected. Chronic Pain Conditions When such conditions are localized, they can be relieved briefly with local anesthetic blocks, generally for prolonged intervals. Spontaneous ectopic discharges in a "set off point," in a painful scar after surgical procedure or trauma, or in an amputation stump could be suppressed by infiltration with a neighborhood anesthetic with a depot glucocorticoid added (Devor et al 1985). Depending on what is completed after the infiltration (stretching, cold, therapeutic massage, applicable exercises), the helpful effects may persist for longer periods. Patients with uncomplicated myofascial pain syndromes will benefit; patients with extra complicated persistent pain circumstances will want a comprehensive approach, together with appropriate cognitive remedy (Turk 2003). Arthritic ache may be relieved effectively by intra-articular injection of dilute native anesthetic with glucocorticoid added (Shipley and Morris 2008). All main limb joints, in addition to aspect joints of the spine, may be injected (Cooper 2008). The duration of pain reduction depends on the diploma and length of the arthritic adjustments. Topical software of local anesthetic medication can additionally be a form of native infiltration. Jellies or creams are useful for mucous membrane pain from the urethra, urinary bladder, and rectum. Ointments and concentrated options can quickly relieve the customarily excruciating ache from oral mucositis in most cancers patients and bone marrow transplant patients. Eutectic mixtures, ointments, and patches are used on the allodynic and painful skin of sufferers with, for instance, post-herpetic neuralgia (Garnock-Jones and Keating 2009). Systemic toxic concentrations can occur if patches are kept on the pores and skin for more than 12 hours. Initially a burning and tender inflammatory reaction occurs, followed by a numbing pain relief that peaks after a couple of days. Unfortunately, the duration of nerve impulse block with these neurolytic brokers is usually disappointingly temporary. Even worse, they induce a deafferentation´┐Żneuropathic kind of ache after a couple of weeks to months in as much as one-third of cases. In patients with localized ache from superior most cancers disease, the length of impact of such neurolytic blocks may be adequate (Campbell 2008). Denervation by heating the nerve to 70´┐Ż80´┐ŻC for brief durations with a radiofrequency probe that has a smaller dimension than the cryoprobe could trigger extra profound destruction in a localized area (Crul et al 2008). Some Useful Peripheral Nerve Blocks Agents ´┐Ż the local anesthetics most commonly used are short-acting lidocaine (lignocaine) and chloroprocaine and the longeracting bupivacaine, ropivacaine, and levobupivacaine. Adrenaline, being an 2-agonist, has analgesic effects of its own in the spinal wire (Collins et al 1984). Glucocorticoids appear to forestall and scale back the hyperexcitability of nociceptors and afferent nerve fibers and also to cut back secondary, central hypersensitivity (Warncke 2001, Romundstad et al 2004). In experimental animal studies, chronic neuropathic pain behavior may be decreased by local glucocorticoid remedy (Devor et al 1985, Takeda et al 2004). Peripheral Nerves and Regional Nerve Plexuses With good data of anatomy and a neuromuscular stimulator and/or an ultrasound device, most nerves may be blocked specifically (Hill 2008). Catheters can be positioned near peripheral nerves and nerve plexuses for steady infusion of local anesthetic medicine. With simple patient-controlled gadgets, these strategies can be utilized safely at house (Chelly and Williams 2004). Nerve Blocks of the Head and Neck ´┐Ż An occipital nerve block is indicated for analysis and treatment of occipital neuralgia (Kvarstein and H´┐Żgstr´┐Żm 2008). Nerve Blocks of the Upper Limb ´┐Ż A brachial plexus block is used for anesthesia and postoperative analgesia after shoulder, arm, and hand surgery. The excruciating pain from invasion of the brachial plexus by a tumor may be a sign for a neurolytic block. These blocks may be very helpful for facilitating physical therapy and giving patients a break from their ache. Nerve Blocks of the Thorax and Abdomen ´┐Ż A thoracic paravertebral block can be carried out at any stage and may be indicated for postoperative analgesia, fractured ribs, and acute herpes zoster. Nerve Blocks of the Lower Limb ´┐Ż the lumbar plexus could be blocked from the posterior approach, and such blocks are helpful for relieving ache after surgery on the hip, thigh, or upper a part of the leg and for most cancers ache in the identical space. Sympathetic Nerve Blocks Selective sympathetic blocks are possible as a end result of anatomically the autonomic nervous system is (in part) separated from the somatic nervous system within the pre- and paravertebral regions. The sympathetic efferent nerves arise from neurons in the intermediolateral column of the spinal wire, cross in the ventral roots from T1´┐ŻL2, and then, via the white rami communicantes, be part of the sympathetic chain of paravertebral ganglia on both sides of the vertebral bodies. The efferent sympathetic nerves then move a variable distance up or down the sympathetic chain of ganglia, where they may synapse (cholinergic) with the post-ganglionic (adrenergic) neurons or cross on to the prevertebral ganglia. Then they synapse with the adrenergic post-ganglionic neurons (cholinergic to the sweat glands and a few smooth muscular tissues of vessels). The paravertebral sympathetic ganglia consist of 3 cervical ganglia, the stellate ganglion, eleven thoracic ganglia, 5 lumbar ganglia, four sacral ganglia, and 1 coccygeal ganglion (the "ganglion impar").
5 mg nebivolol with visaAfferent alerts are neural (primary afferent neurons), hormonal from the neuroendocrine techniques, generated by cytokines from the immune system, and physical (osmolality, core temperature, glucose concentration, and so forth blood pressure medication xanax 2.5 mg nebivolol amex. Box 13-1 Homeostasis and Allostasis Maintenance of physiological parameters such because the concentration of ions, blood glucose, arterial blood gases, body core temperature, and others in a narrow range is identified as homeostasis blood pressure elevated order nebivolol 5 mg fast delivery. Homeostatic regulation includes the autonomic, endocrine, and respiratory techniques pulse pressure 16 generic 2.5 mg nebivolol visa. Cannon (1929) primarily based on an thought formulated by Claude Bernard within the nineteenth century that the interior milieu of the body is constant blood pressure chart per age order nebivolol 2.5 mg overnight delivery. The strategy of sustaining stability of the interior milieu of the fluid matrix during modifications within the physique and within the environment requires methods which have a broad variety of exercise, such as the cardiovascular system, the thermoregulatory system, the metabolic system (gastrointestinal tract and endocrine systems corresponding to insulin, glucagon, leptin, and the thyroid axis), and the immune system. Adaptation of parameters of the interior milieu in response to inner and environmental challenges (exercise, hunger, temperature load, or physical threat) is described by the concept of allostasis. This kind of adaptive regulation is rapidly mobilized during internal or environmental perturbations after which turned off when not needed. Allostatic responses maintained in an energetic state over long durations result in put on and tear of the mechanisms involved, including neurons. The penalties of allostatic load could result in varied kinds of disease, corresponding to hypertension, myocardial infarction, weight problems, diabetes, atherosclerosis, and metabolic syndrome (McEwen 1998, 2001; Juster et al 2010). Efferent Signals from the Brain to Body Tissues Coordinated exercise in somatic motor neurons generates the appropriate protective habits. Neural signals that concentrate on tissues of the body are generated in the sympathetic and parasympathetic efferent pathways. These pathways are distinct with respect to their goal tissue and due to this fact with respect to their features (J´┐Żnig 2006; J´┐Żnig and McLachlan 1992, 2012). This applies to the traditional features of autonomic neurons and probably additionally to functions that are associated to protective body reactions. Endocrine signals are generated within the hypothalamic´┐Żpituitary´┐Żadrenal system and in the sympathoadrenal system (adrenal medulla) (Elenkov et al 2000, Elenkov 2008). Central Circuits Involved in Body Protection Protective reflexes are programmed on the level of the spinal cord. Elementary homeostatic regulatory mechanisms associated to the cardiovascular system, the respiratory system, or the gastrointestinal tract are represented within the lower mind stem. Complex homeostatic rules are represented in the higher brain stem and hypothalamus. These regulatory mechanisms embody endocrine, autonomic, and motor parts (Bandler and Shipley 1994, J´┐Żnig 2006). Homeostatic regulation of body functions is adapted to the internal state of tissues and environmental perturbations. This strategy of adaptation has been referred to as allostasis (Box 13-1; McEwen 2001). The central control circuits include neural systems that powerfully control transmission of nociceptive impulses in the spinal twine. These endogenous neuronal control techniques are represented within the mind stem (periaqueductal grey; dorsolateral pontine tegmentum, including area A5; ventromedial medulla; caudal raphe nuclei) and are beneath the affect of the forebrain (cortex and limbic system). They can attenuate or enhance the transmission of nociceptive impulses, thereby leading to analgesia or hyperalgesia, respectively, and are carefully linked with different control systems, such as regulation of body temperature, regulation of sexual operate, and regulation of protection conduct (Mason 2001). They are responsible for generating responses enabling the organism to cope with external and inner tense challenges. They work continuously under normal organic circumstances and are important for survival of the organism. However, as soon as these allostatic rules are pushed to their extreme or not switched off, they could turn out to be deleterious to the organism and result in systemic ailments. These molecules can be synthesized and launched by all cells and are triggered by all types of stressors that endanger the integrity of tissues. Cells of the immune system are significantly specialised to make use of cytokines as signaling molecules in a paracrine and autocrine method. Cytokines are primarily involved in producing host responses to a wide range of stimuli and conditions that will endanger body tissues (during disease, an infection, or tissue inflammation). Synthesis plus launch of cytokines in response to pathogenic stimuli is fast and happens in minutes; the half-life of cytokines released into the circulatory system can additionally be on the order of minutes. This distinguishes cytokines from hormones, which are constitutively expressed, continuously launched, and concerned in classic homeostatic regulation (Dinarello 1999). Here we summarize the role of pro-inflammatory cytokines released by inflammatory cells in peripheral tissues-such as macrophages, leukocytes, Schwann cells, endothelial cells, and others-in the era of ache and hyperalgesia, both of that are necessary parts of illness habits. Illness responses (including hyperalgesia and pain) are elicited by pathogenic stimuli in the viscera. Pathogens (bacteria, viruses, and others) activate phagocytic immune cells (macrophages, Kupffer cells within the liver). The cytokines activate vagal afferents projecting through the hepatic department of the belly vagus nerve (probably via paraganglia, however probably additionally impartial of the paraganglia). Illness responses are generated by activation of the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus and structures within the limbic system. Specifically, ache and hyperalgesia are generated by facilitation of the transmission of nociceptive impulses within the spinal cord (and probably elsewhere). These functional characteristics are typical for further recuperation of the organism. This protective conduct organized by the mind evolves during noxious occasions, including invasion 202 Section One Neurobiology of Pain essential neural interface between the immune system and the brain. The physiology of the vagal afferents concerned in communication between the immune system of the gastrointestinal tract and the brain, and the mechanisms by which activation of vagal afferents results in pain, have to be labored out. It is hypothesized that activation of hepatic vagal afferents is followed by facilitation of nociceptive impulse transmission. These hepatic vagal afferents should be completely different from vagal afferents passing through the celiac branches of the abdominal vagal nerves since activation of the first is followed by hyperalgesia and activation of the latter by hypoalgesia (see the later section entitled Neuroendocrine Modulation of Hyperalgesia). Communication between the peripheral (innate) immune system and central neurons by the use of cytokines occurs by way of circumventricular organs. Transmission from the immune system to the mind is fast through peripheral afferent pathways and slow by way of the humoral and transport pathways. In the mind, notably at ports of entry such as the hypothalamus, nucleus of the solitary tract, and spinal dorsal horn, microglial cells and astrocytes are activated. Thus, peripheral pro-inflammatory cytokines reaching the brain swap on cytokine networks throughout the mind that activate and sensitize the neuronal pathways concerned within the era of sickness habits, which includes pain and hyperalgesia. The pain and hyperalgesia that happen following activation of the innate immune system by intraperitoneal injection of lipopolysaccharide are suggested to be produced by activity within the subdiaphragmatic vagal afferents, specifically these running within the hepatic department. These results suggest that vagal afferents, in all probability these innervating the liver, are activated by pro-inflammatory cytokines released by activated macrophages (Kupffer cells), dendritic cells, and leukocytes. The pro-inflammatory cytokines both activate the vagal afferents immediately or bind specifically to glomus cells in the abdominal paraganglia which are innervated by vagal afferents.
Northern Schisandra (Schisandra). Nebivolol. - Dosing considerations for Schisandra.
- Vision problems, preventing premature aging, preventing motion sickness, diabetes, high blood pressure, and other conditions.
- Improving concentration, coordination, and endurance.
- How does Schisandra work?
- Improving liver function in patients with hepatitis.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- What is Schisandra?
- What other names is Schisandra known by?
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96390
Buy nebivolol 5mg lineMore comparative research 490 Section Three Pharmacology and Treatment of Pain remedy with different analgesics is usually necessary, and new medication and approaches are needed arrhythmia greenville sc cheap nebivolol 5 mg without a prescription. References Alcoff J, Jones E, Rust P, et al: Controlled trial of imipramine for persistent low again ache, Journal of Family Practice 14:841´┐Ż846, 1982 prehypertension yahoo cheap nebivolol 5 mg. Bansal D, Bhansali A, Hota D, et al: Amitriptyline vs pregabalin in painful diabetic neuropathy; a randomized, double-blind scientific trial, Diabetic Medicine 26:1019´┐Ż1026, 2009 arrhythmia ketosis nebivolol 2.5mg fast delivery. Blumer D, Zorick F, Heilbronn M, et al: Biological markers for depression in persistent pain, Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 170:425´┐Ż428, 1982 pulse pressure usmle buy cheap nebivolol 2.5 mg on-line. Effectiveness and relationship of antimigraine and antidepressant results, Neurology 26:121´┐Ż127, 1976. Descombes S, Brefel-Courban C, Thalamas C, et al: Amitriptyline remedy in continual drug-induced headache: a double blind comparative pilot examine, Headache forty one:178´┐Ż182, 2001. Dickens C, Jayson M, Sutton C, et al: the connection between ache and depression in a trial using paroxetine in sufferers of chronic low back ache, Psychosomatics 41:490´┐Ż499, 2000. Gingras M: A clinical trial of Tofranil in rheumatic ache in general practice, Journal of International Medical Research 4(Suppl 2):41´┐Ż49, 1976. Goldenberg D, Schmid C, Ruthazer R, et al: A randomized double-blind crossover trial of fluoxetine and amitriptyline in treatment of fibromyalgia, Arthritis and Rheumatism 39:1852´┐Ż1859, 1996. Changes in pattern of assaults throughout a controlled scientific trial, Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 36:684´┐Ż690, 1973. Keskinbora K, Aydinli I: A double-blind, randomized, controlled trial of topiramate and amitriptyline either alone or in combination for the prevention of migraine, Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery a hundred and ten:979´┐Ż984, 2008. Kim H, Lee H, Rowan J, et al: Genetic polymorphisms in monoamine neurotransmitter systems show only weak association with acute post-surgical ache in people, Molecular Pain 2:24, 2006. Kirchheiner J, Grundemann D, Schomig E: Contribution of allelic variations in transporters to the phenotype of drug response, Journal of Psychopharmacology 20(Suppl 4):27´┐Ż32, 2006. Kityama S, Sogawa C: Regulated expression and function of the somatodendritic catecholamine neurotransmitter transporters, Journal of Pharmacological Science 99:121´┐Ż127, 2005. Leijon G, Boivie J: Central post-stroke ache: a controlled trial of amitriptyline and carbamazepine, Pain 36:27´┐Ż36, 1989. Martucci N, Manna V, Porto C, et al: Migraine and the noradrenergic control of vasomotoricity: a study with alpha-2 stimulated and alpha-2 blocker medicine, Headache 25:95´┐Ż100, 1985. Hale M, Upmalis D, Okamoto A, et al: Tolerability of tapentadol immediate release in patients with lower again pain or osteoarthritis of the hip or knee over ninety days: a randomized, double-blind study, Current Medical Research and Opinion 25:1095´┐Ż1104, 2009. Hannonen P, Malmiiniemi K, Yli -Kerttula U, et al: A randomized double blind placebo-controlled examine of moclobemide and amitriptyline within the treatment of fibromyalgia in females without psychiatric disorder, Br J Rheumatol 37(12):1279´┐Ż1286, 1998. Harati Y, Gooch C, Swensen M, et al: Double-blind randomized trial of tramadol for the treatment of the pain of diabetic neuropathy, Neurology 50:1842´┐Ż1846, 1998. H´┐Żuser W, Petzke F, Sommer C: Comparative efficacy and harms of duloxetine, milnacipran, and pregabalin in fibromyalgia syndrome, Journal of Pain 11:505´┐Ż521, 2010. McCleane G: Topical application of doxepin hydrochloride, capsaicin and a mixture of each produces analgesia in chronic human neuropathic ache: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled examine, British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology forty nine:574´┐Ż579, 2000. A randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled trial, Journal of Rheumatology 36:398´┐Ż409, 2009. Meier T, Wasner G, Faust M, et al: Efficacy of lidocaine patch 5% in the remedy of focal peripheral neuropathic ache syndromes. Mercadante S, Arcuri E, Tirelli W, et al: Amitriptyline in neuropathic most cancers pain in sufferers on morphine therapy: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, crossover research, Tumori 88:239´┐Ż242, 2002. Monro D, Swade C, Coppen A: Mianserin within the prophylaxis of migraine: a double-blind study. Norregaard J, Danneskiold-Samsoe B, Volkmann H: A randomized managed trial of citalopram in the treatment of fibromyalgia, Pain 61:445´┐Ż 449, 1995. Puozzo C, Lens S, Reh C, et al: Lack of interaction of milnacipran with the cytochrome p450 isoenzymes regularly involved in the metabolism of antidepressants, Clinical Pharmacokinetics forty four:977´┐Ż988, 2005. Raferty H: the administration of post herpetic ache using sodium valproate and amitriptyline, Journal of the Irish Medical Association 72:399´┐Ż401, 1979. Rafinesque J: Emploi du Tofranil a titre antalgique dans les syndrome douloureux de diverses oringines, Gazette Medicale Fran´┐Żais 70:2075, 1963. Thorpe P, Marchant-Williams R: the role of an antidepressant, dibenzepin (Noveril), in the reduction of ache in the chronic arthritic states, Medical Journal of Australia 1:264´┐Ż266, 1974. Vandel S, Bertschy G, Baumann P, et al: Fluvoxamine and fluoxetine: interplay studies with amitriptyline, clomipramine and neuroleptics in phenotyped patients, Pharmacological Research 31:347´┐Ż353, 1995. Vrethem M, Boivie J, Arnqvist H, et al: A comparability of amitriptyline and maprotiline in the remedy of painful diabetic neuropathy in diabetics and nondiabetics, Clinical Journal of Pain 12:313´┐Ż323, 1997. Yucel A, Ozyalcin S, Koknel Talu G, et al: the impact of venlafaxine on ongoing and experimentally induced ache in neuropathic ache sufferers; a double blind placebo-controlled research, European Journal of Pain 9:407´┐Ż416, 2005. Sharav Y, Singer E, Schmidt E, et al: the analgesic effect of amitriptyline on persistent facial pain, Pain 31:199´┐Ż209, 1987. Skljarevski V, Desaiah D, Liu-Seifert H, et al: Efficacy and safety of duloxetine in sufferers with chronic low again ache, Spine 35:E578´┐ŻE585, 2010. Skljarevski V, Ossanna M, Liu-Seifert H, et al: A double-blind, randomized trial of duloxetine versus placebo in the management of persistent low back ache, European Journal of Neurology sixteen:1041´┐Ż1048, 2009. Stein D, Floman Y, Elizur A, et al: the efficacy of amitriptyline and acetaminophen within the management of acute low back ache, Psychosomatics 37:63´┐Ż70, 1996. Sternback H: the serotonin syndrome, American Journal of Psychiatry 148:705´┐Ż713, 1991. Tammiala-Salonen T, Forssell H: Trazodone in burning mouth ache: a placebo-controlled, double-blind examine, Journal of Orofacial Pain thirteen: 83´┐Ż88, 1999. Tasmuth T, Brita H, Kalso E: Venlafaxine in neuropathic ache following therapy of breast most cancers, European Journal of Pain 6:17´┐Ż24, 2002. Taub A: Relief of postherpetic neuralgia with psychotropic medicine, Journal of Neurosurgery 39:235´┐Ż239, 1973. Chapter 35 Mechanism of Action of Anticonvulsants as Analgesic Drugs Valerie Morisset, John B. Many anticonvulsants, however, exhibit polypharmacology, which can help their total efficacy in treating each epilepsy and ache. The range of anticonvulsants working by way of different mechanisms may be seen as an advantage for sufferers with persistent pain. It will increase the options for clinicians, who can switch medication when a drug focusing on one explicit mechanism has not shown efficacy or has been related to an unacceptable aspect effect profile. With increasing numbers of molecular targets comes an increasing probability of figuring out priceless synergies between medication. The example of acetazolamide synergizing with midazolam is an excellent example of two mechanisms of motion reinforcing one another in the same pathway. Unfortunately, the useful properties of anticonvulsants for pain relief should be counter-balanced by the well-known side effects of this class of molecules, including dizziness, ataxia, nausea, and different central nervous system´┐Ż and cardiovascular-related occasions. Often, these well-described unwanted effects are managed by careful dose titration regimens specific for every anticonvulsant drug. The huge funding in primary analysis for voltagegated sodium and voltage-gated calcium channels has provided invaluable perception into their functional properties and highlighted their key position in ache physiology.
Buy cheap nebivolol 5 mg onlinePsychophysical studies have proven that the reported depth of a given physical stimulus may be considerably elevated or decreased by a quantity of manipulations identified to alter spinal excitability and produce a state of hyper- or hypoalgesia, respectively blood pressure ranges hypotension buy nebivolol 5mg on line. In the following sections, components of the spinal and supraspinal systems that underlie such regulatory contributions are thought of hypertension research discount nebivolol 2.5mg overnight delivery. The presence of intervening segmental and suprasegmental interneurons linking the primary afferent input with the projecting neuron supplies additional opportunities for amplification or diminution of the excitatory state of the projection neuron blood pressure 200 100 purchase nebivolol 5 mg otc. Plasticity of Dorsal Horn Systems the complex neural linkages involving excitatory and inhibitory transmitters clearly permit considerable plasticity in the input´┐Żoutput relationships noticed in the dorsal horn prehypertension in your 20s buy cheap nebivolol 5 mg on line. The receptive area of these cells is typically advanced, with dermatomal regions responding to low-threshold input overlapping or contiguous with areas in which high-intensity thermal or mechanical stimulation is efficient in activating the neuron (Willis 1988). The response properties of such cells are, nonetheless, not merely defined by the nature of the afferent connectivity, but additionally by the affect of numerous pharmacologically distinct neuronal methods that modify the reaction of the cell to its afferent input. Two examples of the physiological response properties of these spinal neurons, which show positive and unfavorable regulation by convergent neuronal influences, are thought of under. This spinifugal activity reflects not only the monosynaptic excitatory input from major afferent fibers (which transduce the physical environment) but also the composite of polysynaptic excitatory/inhibitory elements activated by the afferent input. Thus, a dominant principle of 386 Section Three Pharmacology and Treatment of Pain behaviorally related results on physiological operate. These excitatory and inhibitory elements arise from a quantity of sources: (1) domestically organized segmental interneurons. These neurons in flip display synaptic terminations on each afferent and non-afferent terminals. The particular connectivity of these native interneurons is discussed in additional detail in Chapter 5. Importantly, the organization of these local methods is functionally organized to supply native inhibitory sculpting of native afferent-evoked excitation, notably from giant afferents (Khayyat et al 1975, Sivilotti and Woolf 1994). Conversely, the cascading group of glutamatergic neurons provides linkages which have the ability to amplify afferent enter. Non-neuronal Cells the spinal dorsal horn shows an abundance of astrocytes and microglia. This organization of pre- and post-synaptic neurons and astrocytes is usually known as the tripartite synapse. Astrocytes type hole junctions with adjoining astrocytes and collectively kind astrocytic nets over which they communicate for considerable distances by way of calcium waves (Scemes and Giaume 2006). Microglia are resident mind macrophages derived from circulating bone marrow´┐Żderived monocytes that enter the neuraxis at birth. These cells have been considered largely from the angle of immune surveillance and response to harm and an infection. Neurons may activate microglia by the precise release of a membrane chemokine (fractalkine) that binds to particular microglial receptors. This process is a part of a posh cascade referred to broadly as "neuroinflammation. Thus, intrathecal supply of brokers similar to minocycline (a second-generation tetracycline) and pentoxifylline has been reported to dam microglia activation and diminish hyperalgesic states. Similar metabolic inhibitors that block astrocyte activation (fluorocitrate) can likewise diminish hyperalgesia after nerve and tissue damage. Repetitive activation of small, sometimes high-threshold afferent enter results in a significant improve within the measurement of the receptive area of a given dorsal horn neuron. In contrast, different methods may decrease the dimensions or elements of the receptive field that activate a given dorsal horn neuron. Neuronal Response to Afferent Input the magnitude of the response could also be altered in the absence of a change in stimulus magnitude. Thus, as noted above, repetitive activation of C fibers will lead to an augmented response to subsequent afferent enter, a phenomenon known as "wind-up" (Mendell 1966). Conversely, agonists of specific dorsal horn receptor lessons, similar to those for the - and -opioid and 2-adrenergic receptors, induce highly effective suppression of the small afferent-induced excitation of these cells (see below). Furthermore, consistent with the results of activating these specific receptor techniques, considerable proof factors to a complex set of bulbospinal modulatory substrates that, by performing via these receptor systems, produce corresponding changes in dorsal horn output. Thus, mind stem stimulation can diminish the slope of the response (frequency of discharge)´┐Żversus´┐Żstimulus intensity curve of dorsal horn neurons, as properly as shift the intercept of the stimulus intensity´┐Żresponse curve to the left, indicative of a discount in the threshold stimulus intensity necessary to evoke activity within the cell (Gebhart et al 1983, 1984). Conversely, different enter facilitates the response of the dorsal horn to afferent visitors (Suzuki et al 2002). These bidirectional effects on the input´┐Żoutput relationships of the dorsal horn mediated by spinal and supraspinally organized techniques indeed type the core property of the unique "gate management" formalization proposed by Melzack and Wall (1965; see additionally Yaksh 1999). Importance of Spinal Plasticity to Supraspinally Mediated Functions Understanding the systems that regulate the output function of the spinal dorsal horn has specific relevance to the ache experience. Clearly, issues related to perception, although mediated by higher-order structures, are strongly influenced by the input encoded by the spinal techniques. Changes in spinal outflow usually lead to parallel alterations within the response of supraspinal goal nuclei to a given stimulus (see, for instance, Sherman et al 1997a, 1997b). That is to say, the nature of the experience is strongly driven by data arising from the spinal cord. Schematic define of currently thought of mechanisms whereby non-neuronal cells might work together with dorsal horn nociceptive processing. Primary afferent fibers release a wide selection of merchandise to directly activate second-order neurons. Astrocytes communicate over volumes of neural tissue by calcium waves via gap junctions. They work together reciprocally with native populations of microglia, which can be activated acutely as evidenced by the rise in phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases such as p38. Microglia can themselves be activated by neuronal products, notably the chemokine fractalkine, and in flip can launch quite so much of proinflammatory products, which by performing on eponymous receptors enhance the excitability of dorsal horn neurons. Finally, astrocytes and microglia, due to their proximity to the cerebral vasculature, can serve as sensors of circulating products and in this method permit these products to affect neural operate. Suprasegmentally Organized Bulbospinal Neuronal Projections Spinal projections originating in the mind stem and projecting into the spinal twine are characterised by being largely serotonergic and originating within the medullary midline raphe or by being noradrenergic and originating in several brain stem nuclei, including the locus coeruleus. Neurochemical research have proven that these neurons project into the dorsal horn and intermediolateral cell column. These bulbospinal projections could also be activated by spinifugal and supraspinal linkages. This linkage is mediated, in part, by spinal activation of lamina I neurons, which ship projections into the caudal brain stem, notably the caudal raphe nuclei within the rostroventral medulla (Todd et al 2000). Behavioral and electrophysiological studies have shown that the noradrenergic projections exert potent analgesic effects, as evidenced by reversal of those effects with intrathecal noradrenergic antagonists (Sagen and Proudfit 1984; see Jones 1991 for review). Direct help for the useful significance of these spinobulbospinal serotonergic methods on nociception is supplied by the observations that these therapies have been proven to decrease a wide range of hyperpathic states related to irritation and nerve harm (Porreca et al 2001, Rahman et al 2006, Zhang et al 2009; however see Leong et al 2011). It should be noted that elements of these descending pathways additionally project into the thoracic intermediolateral cell column synapsing onto preganglionic sympathetic neurons. These bulbospinal projections contribute to the sympathetic response initiated by spinal nociceptive enter. Supraspinal´┐ŻBulbospinal the mattress nuclei from which the bulbospinal projections arise receive robust enter from the rostral techniques.
Purchase 5mg nebivolol with visaAccordingly, there has been a lot analysis on the position of gonadal hormones in modulating pain, with nearly all of research focusing on the activational impact of hormones heart attack party tribute to trey songz nebivolol 2.5mg with mastercard. Somatic and visceral nociceptive processing has been reported to fluctuate in parallel with the estrous cycle, thus strongly suggesting hormonal modulation, but nociceptive sensitivity to circulating levels of estrogens and progesterone range with the tissue and check (estrogens are pro-nociceptive: Sapsed-Byrne et al 1996, Cason et al 2003, Okamoto et al 2003, Martin et al 2007, Ji et al 2008, Lu et al 2009b; estrogens are antinociceptive: Giamberardino et al 1997, Bradshaw et al 1999, Fischer et al 2008, Kramer and Bellinger 2009) nhanes prehypertension discount 2.5 mg nebivolol otc. Hormonal depletion by gonadectomy (ovariectomy or orchiectomy) alters nociceptive processing, but no consensus has been reached on the course of effect blood pressure medication edema order nebivolol 5 mg fast delivery. Ovariectomy decreases visceral sensitivity to colorectal distention (Bradesi et al 2003, Ji et al 2003, Fan et al 2009), bladder distention (Robbins et al 2010), and uterine cervix distention (Yan et al 2007) however increases responses to vaginal distention (Bradshaw and Berkley 2002) pulse pressure and map cheap nebivolol 5 mg free shipping. The pro- and antinociceptive effects of estrogens have been demonstrated with somatic stimuli as nicely. Ovariectomy decreased (Gaumond et al 2005, Hagiwara et al 2007) or elevated (Kuba et al 2006, Fischer et al 2008) behavioral responses to formalin (the path of change seems to depend on the focus of formalin). Estradiol 226 Section Two Assessment and Psychology of Pain or intramuscular glutamate than had been the afferents of male rats, an estradiol-dependent effect. In visceral tissues, ovariectomy had no effect on the excitability of colonic afferents from non-inflamed rats (Ji et al 2011), but estradiol substitute following ovariectomy elevated the excitability of uterine cervix afferents (Liu et al 2005). The excitability of vaginal/uterine afferents fluctuates throughout the estrous cycle, with excitability being larger throughout diestrus than throughout proestrus, although this can be extra associated to reproduction than to pain (Robbins et al 1992). Dorsal Horn Neurons Sex differences in response to noxious stimulation may be depending on differential processing of nociceptive stimuli on the degree of the spinal cord/medullary dorsal horn as properly. Estradiol decreased glycine-evoked currents in dorsal horn neurons (Jiang et al 2009). The response of spinal or medullary dorsal horn neurons to noxious stimulation of peripheral structures. Sex variations and fluctuating levels of sensitivity may also outcome from the differential expression of estrogen receptors. Proestrous rats expressed more estrogen receptor- in the superficial and deeper layers of the medullary dorsal horn than did males, with mixed expression ranges in diestrus females (Bereiter et al 2005a). In one examine, ovariectomy elevated the formalin response within the lip however not within the hindpaw (Pajot et al 2003). However, hyperalgesic priming (prolonged hyperalgesia to a noxious stimulus following a conditioning inflammatory stimulus) is suppressed by estrogens in females and males (Joseph et al 2003). In contrast to the predominantly pro-nociceptive effect of estrogens following injury in feminine rats, testosterone seems to be protecting in male rats. Gonadectomy in males elevated the formalin response that was decreased by testosterone substitute (Aloisi et al 2003, Pajot et al 2003, Gaumond et al 2005, Fischer et al 2007). There was a progressive decrease in response to repetitive formalin injections in intact males, however not following gonadectomy (Ceccarelli et al 2003). Antinociceptive mechanisms require testosterone in male rats and are lowered following gonadectomy (Stoffel et al 2005, Borzan and Fuchs 2006, Claiborne et al 2006, Thompson et al 2008). In contrast, estradiol will increase the formalin response in males (Aloisi and Ceccarelli 2000). The results of gonadal hormones will not be dependent on absolutely the focus of hormones in circulation however replicate altering levels throughout a standard estrous or menstrual cycle. It has been instructed that estrogen or progesterone withdrawal is more important in modulating nociceptive sensitivity than is upkeep of high ranges of either hormone (Ji et al 2003, Martin et al 2007, Martin 2008, Devall and Lovick 2010, Robbins et al 2010, Puri et al 2011). Ovariectomy decreases ache behavior in the course of the interphase of the formalin test, which is believed to reflect a rise in antinociceptive mechanisms (Gaumond et al 2005). An additional consideration is the impact of estrogens and testosterone on irritation and subsequent nociceptive processing. It is feasible that much less inflammation could lead to inflammatory mediators remaining at the web site of injury longer and thereby resulting in higher peripheral sensitization and an extended length of hyperalgesia. However, estrogens have anti-inflammatory as nicely as pro-inflammatory effects, depending on multiple components, together with the immune stimulus and response and the cell types affected (for evaluation see Straub 2007). Primary Afferents the mechanisms underlying gonadal hormone modulation of nociception happen at many ranges of the nervous system. Female craniofacial afferents, including masseter and digastric muscular afferents, had been more sensitive to subcutaneous Sex Differences in Neural Processing of Pain as Revealed by Human Neuroimaging Only a couple of dozen neuroimaging studies have addressed the question of sex variations in human pain processing (Table 15-2). Potentially associated to higher ache somewhat than intercourse variations per se Men had higher activation in the contralateral prefrontal, major and secondary somatosensory, parietal, and insular cortices; women had larger activation in the perigenual cingulate cortex Overall activation patterns larger in men than in women; the insula was activated (bilaterally) only in men For each stimulation and anticipation of rectal stimulation, ladies confirmed greater activation within the ventromedial prefrontal cortex, right anterior cingulate cortex, and left amygdala; men showed larger activation in the best dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, insula, and dorsal pons and/or periaqueductal grey Comparable ranges of activation in men and women. When comparing both activation and deactivation, there was larger insula activation in males. These investigators additionally discovered that the sex differences in temporal summation of heat-induced ache have been partially mediated by willingness to report ache (Robinson et al 2004). A related examine found that females viewed overt ache expression as extra acceptable than did males, and these beliefs predicted tolerance of cold-related ache, which was lower in females than in males (Nayak et al 2000). Another examine discovered that both women and men agreed that the ideal man ought to tolerate more ache than the best lady, thus additional supporting the conception that gender norms are related to ache tolerance. Furthermore, this examine demonstrated that robust identification with the male gender norm was related to greater electrical pain tolerance in men whereas gender norm identification was not related to ache tolerance in girls (Pool et al 2007). An related issue is the effect that the sex of the experimenter has on experimental ache sensitivity. Three research involving various sorts of psychophysical protocols reported that male members supplied results indicating much less pain sensitivity when tested by a female versus a male experimenter whereas female participants confirmed no difference (Levine and De Simone 1991, Gijsbers and Nicholson 2005, Aslaksen et al 2007). Another study reported that tolerance of coldrelated pain was higher in each men and women when examined by an experimenter of the opposite sex (Kallai et al 2004). In distinction, different investigators have failed to show an effect of experimenter gender on ache responses (Otto and Dougher 1985, Bush et al 1993, Myers et al 2001). It is in all probability going that the importance of this effect is related to numerous features of the interplay between the experimenter and subject, which is difficult to regulate for or specify fully. Psychological Distress Multiple psychological dimensions associated to pain demonstrate sex variations, including nervousness, depression, and coping/catastrophizing. Several studies have sought to determine whether or not sex differences in these psychological domains are associated to intercourse variations in ache. Among sufferers with musculoskeletal pain, ladies reported higher ranges of catastrophizing than did males, and better catastrophizing was associated with poorer perceived well being status in girls (Jensen et al 1994). In distinction, a telephone survey discovered no intercourse variations in catastrophizing regardless of women reporting extra intense ache and utilizing a wider range of coping strategies than males did (Unruh et al 1999). Among osteoarthritis patients, girls reported greater levels of pain and disability and exhibited extra pain habits than men did. When statistical adjustments have been made for catastrophizing, the sex variations in pain-related outcomes grew to become insignificant (Keefe et al 2000). Another examine found that adolescent women used more social support, optimistic statements, and internalizing/catastrophizing whereas boys relied extra on behavioral distraction. Furthermore, this study reported that internalizing/catastrophizing mediated intercourse variations in clinical ache (Keogh and Eccleston 2006). Multiple studies have reported higher ranges of catastrophizing in healthy ladies than in men. In one such study, catastrophizing mediated intercourse used, which evoked more intense pain in the women than in the men, thus leaving open the query of whether this was a intercourse difference or an intensity difference (Coghill et al 2003). Most subsequent studies applied stimuli that were perceived as being equally painful to the women and men, which frequently meant that the stimuli had been of lesser depth when utilized to women.
References - Carr RF, Halperin V: Malignant ameloblastomas from 1953 to 1966: review of the literature and report of a case. Oral Surg 1968;26:514-522.
- Whittemore AD, Clowes AW, Hechtman HB, et al: Aortic aneurysm repair: reduced operative mortality associated with maintenance of optimal cardiac performance, Ann Surg 173:940, 1971.
- Lo YM. Noninvasive prenatal detection of fetal chromosome aneuploidies by maternal plasma nucleic acid analysis: a review of the current state of the art. BJOG 2009; 116: 152-7.
- Balakirev M, Khramtsov VV, Zimmer G: Modulation of the mitochondrial permeability transition by nitric oxide. Eur J Biochem 1997;246:710-718.
- Costopanagiotou E, Spyrou S, Farantos C, Kostopanagiotou G, Smymiotis V. An unusual cause of massive gastric bleeding in a young patient. Am J Gastroenterol 2000;95:2400.
|