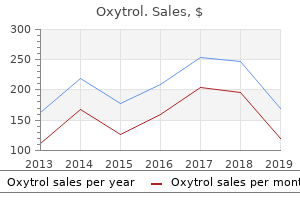
Oxytrol
Paul Stephen Kruszka, M.D. - National Human Genome Research Institute
- Bethesda, Maryland
Order 2.5 mg oxytrol with mastercardMost survivors have been of regular stature treatment solutions generic 5mg oxytrol with mastercard, although 6 of the 40 had been less than the third percentile for peak symptoms lupus purchase oxytrol 5 mg free shipping. The group of survivors from Australia is quite completely different from the roughly 300 survivors adopted in New York because the rubella epidemic of 1963 to 1965 treatment zinc poisoning buy generic oxytrol 5mg line. Neither the Australian nor the New York group is a representative pattern of all survivors of maternal rubella infection treatment juvenile rheumatoid arthritis order oxytrol 2.5mg without a prescription, but these groups do provide insight on long-term prognosis. Laboratory Diagnosis Timely, accurate prognosis of acute primary rubella infection in a pregnant girl and congenital rubella an infection in an infant is crucial if applicable administration is to be undertaken (see "Management Issues"). The diagnosis must be confirmed serologically or virologically as a outcome of medical prognosis of postnatal and congenital rubella is unreliable. In any suspected publicity of a pregnant lady, every effort must be made to confirm rubella an infection so that accurate counseling may be provided in regards to the risks to the fetus. Laboratory proof of congenital infection facilitates proper therapy, follow-up, and long-term administration. In addition, they want to be screened for rubella IgG antibodies on the first obstetric visit and examined further for IgM antibodies (see later on this section) if they give a history of rash or publicity to rash sickness earlier in being pregnant. Acute primary an infection can often be documented by exhibiting a significant enhance in rubella IgG antibody stage between acute and convalescent sera or the presence of rubella-specific IgM antibody. Appropriate timing of specimen collection with regard to rash onset (or publicity in the case of subclinical infection) is essential for correct interpretation of results. Diagnosis is significantly facilitated if the immune status is known before illness onset or exposure. From a sensible perspective, girls with a historical past of vaccination on or after the first birthday should also be thought of immune. With the arrival of enzyme immunoassay, the diagnosis may be primarily based on significant adjustments in optical density expressed as an index quite than a titer. The acute phase specimen must be obtained as quickly as attainable after onset of the rash, ideally within 7 days. If the first serum pattern is obtained more than 7 days after rash onset, some assays. In this example, measurement of antibodies that seem later in the course of an infection may be useful. Although rubellaspecific IgM testing is effective, numerous factors can have an result on check results. Results should be interpreted with cautious consideration to the timing of the specimens. Samples obtained throughout the first a quantity of days after onset of rash could have low or undetectable ranges of rubella-specific IgM, but a specimen obtained 7 to 14 days later invariably reveals higher titers of antibody. Many of the strategies previously described for detecting IgM have some limitations (see "Virus"). IgM antibody testing could involve pretreatment of the serum by varied techniques to separate IgM from IgG, similar to column chromatography, sucrose gradient centrifugation, or adsorption of IgG with staphylococcal protein A. The radioimmunoassay and enzyme immunoassay methods can detect particular IgM antibodies directly in unfractionated sera, but false-positive outcomes could also be produced by the presence of rheumatoid issue. Low titers have been proven to persist for a lot of months in a quantity of patients after natural infection and may be detected in some immune sufferers with subclinical reinfection. The diagnosis of subclinical an infection is more difficult if the immune status of the lady is unknown. If the first specimen lacks detectable antibody, continued close scientific observance and serologic follow-up are essential. A optimistic titer in a specimen obtained after this era signifies a necessity for additional serologic investigation. If test results of paired serum specimens are inconclusive, rubella-specific IgM testing could also be useful, however a negative check result may be difficult to interpret. Dried blood spots have been useful in the detection of IgM antibodies as a result of they show concordance with serum determinations. Where obtainable, avidity testing of rubella IgG may be used to help clarify the timing of an infection. When such low-avidity antibody is discovered within the presence of rubella-specific IgM, it helps a prognosis of current rubella an infection. Laboratories performing prenatal screening should retailer these specimens until delivery in case retesting is necessary. As with maternal rubella, congenital an infection must be confirmed by laboratory checks. In contrast to maternal rubella, attempting to isolate rubella virus in tissue tradition is a valuable device for diagnosing congenital rubella in newborns. In older kids in whom virus shedding has ceased from other websites, virus may be isolated from cataractous lens tissue. First, wire serum could be assayed for the presence of rubella-specific IgM antibody. False-positive outcomes may occur, nonetheless, because of rheumatoid issue or incomplete removal of IgG (largely maternal), depending on the strategies used. Persistence of IgG antibody at this age, especially in high titer, is presumptive evidence of intrauterine an infection with rubella virus. Sera ought to be drawn when the infant is 3 months and then 5 to 6 months of age, with a repeat specimen at 12 months of age if necessary. Important limitations of this method are the delay in analysis and the reality that rubella infections occurring after start may be mistaken for congenital infections. Confirming the analysis, counseling in regards to the dangers of an infection of and injury to the fetus, and discussing courses of action, including using immunoglobulin and consideration of termination of being pregnant, require a thorough understanding of the natural historical past and penalties of rubella in being pregnant. In the case of congenital an infection, the emphasis is on analysis and acute and longterm management. The quantity of antirubella antibody in industrial immunoglobulin preparations is variable and unpredictable; particular hyperimmunoglobulin preparations are unavailable. Fetal infection occurred when immunoglobulin was administered to the mother in what appeared to be adequate quantities quickly after exposure. Another drawback of immunoglobulin is that it could eliminate or �d References 2, thirteen, one hundred sixty five, 289-294, 296, 333, 334, 336, 338, 402, 405. If maternal blood is negative for IgM (IgM-), the IgG results determine if the woman is seropositive (immune) or seronegative (not immune). If not immune, the girl ought to be retested monthly for seroconversion until the end of the fifth month of pregnancy. If the maternal blood is constructive for IgM (IgM+) and IgG (IgG+), the next step would be an IgG avidity assay on the same blood pattern to estimate the time of infection. If the woman has seroconverted (IgM+ IgG+), latest main infection is confirmed, and a prenatal diagnosis must be made if the lady needs to proceed her being pregnant. Determination of IgM in twine blood is the preferred diagnostic methodology with the highest prognostic worth.
Buy 5mg oxytrol with mastercardAntigen-specific B cells that proliferate strongly throughout the B-cell follicle lead to medicine joji cheap 2.5 mg oxytrol free shipping the formation of germinal centers medications kidney failure order oxytrol 2.5 mg visa. The extra avidly the B cell binds antigen treatment lower back pain purchase oxytrol 5 mg without prescription, the stronger is the stimulus to proliferate medications joint pain generic oxytrol 2.5mg on-line. The effects of the mutator are centered on the variable area of immunoglobulin and its quick flanking sequences. The peak of somatic mutation is roughly 10 to 12 days after immunization with a protein antigen. Somatic mutation is an important means for growing antibody affinity, however it may also end result within the acquisition of autoimmunity. Most neonatal and fetal immunoglobulin heavy chain gene variable regions seem to not have undergone somatic mutation,806,808 in preserving with the predominance of antigenically-na�ve new emigrant B cells within the fetus and neonate. Memory B cells enter the recirculating lymphocyte pool, the place they preferentially colonize the skin and mucosa, websites which would possibly be likely to have direct contact with antigen. Once reminiscence B cells are generated, they seem to persist indefinitely even within the absence of any subsequent publicity to the inciting antigen. The IgG and IgA isotypes could be, respectively, divided into the IgA1 and IgA2 and the IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4 subclasses. With the exception of IgD expression, this switching normally entails isotype recombination, the genetic replacement of the IgM-specific portion of the constant area (C) of the heavy chain with a brand new isotype-specific gene phase. Isotype recombination is mediated by switch regions which are positioned immediately upstream of every of the isotype-specific C regions, aside from IgD. Successive multiple isotype switching by a single B cell can also happen, for instance, IgM to IgA to IgG to IgE. Switch recombination after main immunization is obvious in peripheral lymphoid tissue four days after immunization with protein antigen and peaks between 10 and 18 days. Plasma cells are concentrated in peripheral lymphoid tissue, liver, and bone marrow, as properly as in lymphoid tissue of the gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts. Generation of Plasma Cells and the Molecular Basis for Immunoglobulin Secretion Some activated B cells become plasmablasts and migrate to extrafollicular areas of the lymph node or spleen, the place they turn into short-lived plasma cells that mainly produce IgM. Memory B cells appear to have a low threshold to turn into comparatively longlived plasma cells in an antigen-dependent method, and this antigen-dependent conversion, as properly as antigen-independent division throughout the memory B-cell pool, seems to account for the sometimes lifelong maintenance of serologic (antibody) memory in people after pure infection. Such polyclonal activation of memory B cells has been proposed to preserve levels of specific antibody for a lifetime as soon as a memory B-cell response has been generated. The membrane-bound type of immunoglobulin is barely longer than the secreted form and contains a carboxy-terminal region that anchors the molecule in the cell membrane. Plasma cells, somewhat than mature B cells, account for most of the secreted antibody throughout each primary and secondary immune responses. In this method, immunoglobulin manufacturing was low compared with that in adults, and mixing experiments advised that neonatal T cells acted as suppressors of immunoglobulin manufacturing by either adult or neonatal B cells. Between eight and 11 weeks of gestation, transcripts for IgA and IgG could be detected within the liver,879 and IgM and IgG synthesis have been detected as early as 12 weeks of gestation in fetal organ cultures. These findings in bone marrow contrast with a circulate cytometric research in which nonspecific binding was carefully excluded, and neonatal B cells expressing surface IgG or IgA have been below the limit of detectability. Important examples of such carbohydrate antigens are the capsular polysaccharides of pathogenic micro organism, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis, and Haemophilus influenzae. The white pulp space incorporates periarteriolar sheaths of lymphocytes, mainly T cells, in addition to periarteriolar follicles, which are mainly B cells. However, this is also because of the removal of other cell varieties and/or a specialised splenic microenvironment required for the response to purified polysaccharide antigens. Immunization with T-cell�independent antigens before human splenectomy maintains the capacity of the immune system to respond to these antigens subsequently. In mice, B-1 cells constitute the most important source of the low amounts of circulating "pure" IgM present at start and produced within the absence of antigenic stimulation, and animals lacking the power to secrete natural IgM have an increased susceptibility to acute peritonitis from endogenous micro organism. In addition to their position in host defense, pure IgM antibodies can also play a job in removing apoptotic cells. As discussed within the part "Immunoglobulin Synthesis by the Fetus and Neonate," total circulating IgM concentrations are very low within the fetus and healthy new child. The significance of pure IgM in human host defense in the fetus and neonate and its B-cell supply are unclear. Of importance, there was also considerably much less somatic hypermutation of the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene and decreased N-nucleotide addition within the antibody response of neonates in contrast with adults. This reduction might reflect a decreased ability of antigen-activated B cells to proliferate somewhat than a decreased precursor frequency of antigenspecific clones. In fetal sheep, the antibody response to bacteriophage X174 occurs as early as 40 days after conception,914 and again, isotype switching is obvious in the course of the fetal response. Together, these findings counsel that the B-cell response to protein antigens, together with isotype switching and, in all probability, memory-cell technology, are practical throughout fetal life. Second, these responses occur in a predictable, stepwise trend for particular antigens. No correlation exists between the physical or chemical traits of specific antigens and their immunogenicity during ontogeny. For instance, bacteriophage X174 and bacteriophage T4 both are particulate antigens that should work together in an analogous manner. In fetal sheep, nevertheless, bacteriophage T4 becomes immunogenic 60 days after X174 does so. In fact, with some infectious brokers, corresponding to Toxoplasma, IgA or IgE antibodies may be extra sensitive than IgM antibodies for analysis of congenital infection. The titers of IgA and IgE anti-Toxoplasma antibodies may be decrease at 20 to 30 weeks of gestation than after birth,925-927 however, indicating that their manufacturing could also be delayed within the context of congenital an infection. Whole-cell pertussis vaccine immunization of premature infants (born at 28-36 weeks of gestation) at 2 months of age elicited responses similar to these in 2-month-old time period infants,929 indicating that this putative tolerigenic interval wanes rapidly and is relatively impartial of gestational age. This low-level tolerance was restricted to the pertussis element of the wholecell pertussis vaccine as a end result of an inhibitory impact has not been observed after administration of diphtheria or tetanus toxoid928 or hepatitis B vaccine given inside forty eight hours of birth. Infants with tetanus-specific antibodies at delivery had enhanced secondary antibody responses after tetanus immunization, indicating that fetal antigen publicity was a priming event rather than a tolerizing one. Similarly, no fetal response to maternal immunization with inactivated trivalent influenza vaccine was noted. Congenital Toxoplasma an infection may result in detectable IgE and IgA anti-Toxoplasma antibodies at start or during early infancy. In distinction, and for unclear reasons, no such inhibition of pertussis-specific antibody responses was noticed when the acellular pertussis vaccine was administered alone shortly after delivery. The carbohydrate moiety of the conjugate is bound by floor immunoglobulin (sIg) on B cells, ensuing in the internalization of the conjugate. The response to some polysaccharide antigens can be demonstrated by 6 months of age, however the response to vaccination with Hib, most pneumococcal serotype polysaccharides, and Neisseria meningitidis kind C is poor till 18 to 24 months of age. Because the response to the unconjugated vaccine often is poor at this age, the conjugate vaccine acts by inducing Hib polysaccharide-specific B-cell reminiscence.
Diseases - Optic disc drusen
- Fas deficiency
- Congenital megacolon
- Schizencephaly
- Dyssegmental dysplasia glaucoma
- Ectrodactyly cleft palate syndrome
- Thanatophoric dysplasia cloverleaf skull
Buy oxytrol 5mg onlineWhen does mom to youngster transmission of hepatitis C virus happen symptoms 14 days after iui generic oxytrol 2.5mg with visa, Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal 90:F156-F160 treatment mononucleosis order oxytrol 5mg amex, 2005 spa hair treatment generic oxytrol 5mg with visa. Bortolotti F administering medications 7th edition ebook cheap oxytrol 5mg with mastercard, Iorio R, Resti M, et al: An epidemiological survey of hepatitis C virus infection in Italian children within the decade 1990�1999, J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 32:562-566, 2001. Wakita T, Pietschmann T, Kato T, et al: Production of infectious hepatitis C virus in tissue culture from a cloned viral genome. Himoto T, Masaki T: Extrahepatic manifestations and autoantibodies in patients with hepatitis C virus an infection, Clin Dev Immunol 871401:2012, 2012. European Paediatric Hepatitis C Virus Network: Three broad modalities in the natural history of vertically acquired hepatitis C virus an infection, Clin Infect Dis forty one:45-51, 2005. Mohan P, Colvin C, Glymph C, et al: Clinical spectrum and histopathologic features of persistent hepatitis C infection in children, J Pediatr one hundred fifty:168, e1�174. Bortolotti F, Verucchi G, Camm� C, et al: Long-term course of persistent hepatitis C in youngsters: from viral clearance to end-stage liver disease, Gastroenterology 134:1900-1907, 2008. Martinetti M, Pacati I, Cuccia M, et al: Hierarchy of baby-linked immunogenetic risk elements in the vertical transmission of hepatitis C virus, Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 19:369-378, 2006. Ruiz-Extremera A, Salmer�n J, Torres C, et al: Follow-up of transmission of hepatitis C to babies of human immunodeficiency virusnegative women: the function of breastfeeding in transmission, Pediatr Infect Dis J 19:511-516, 2000. Steininger C, Kundi M, Jatzko G, et al: Increased threat of mother-toinfant transmission of hepatitis C virus by intrapartum infantile exposure to maternal blood, J Infect Dis 187:345-351, 2003. Psichogiou M, Tzala E, Boletis J, et al: Hepatitis E virus an infection in individuals at high risk of transmission of non-A, non-B hepatitis and sexually transmitted illnesses, Scand J Infect Dis 28:443-445, 1996. Possibility of one other human hepatitis virus distinct from post-transfusion non-A, non-B kind, Am J Med sixty eight:818-824, 1980. Kumar A, Beniwal M, Kar P, et al: Hepatitis E in pregnancy, Int J Gynaecol Obstet eighty five:240-244, 2004. Ranger-Rogez S, Alain S, Denis F: Hepatitis viruses: mother to child transmission, Pathol Biol (Paris) 50:568-575, 2002. Buisson Y, Grandadam M, Nicand E, et al: Identification of a novel hepatitis E virus in Nigeria, J Gen Virol 81:903-909, 2000. Mjahed K, Charra B, Hamoudi D, et al: Acute fatty liver of being pregnant, Arch Gynecol Obstet 274:349-353, 2006. Aggarwal R, Krawczynski K: Hepatitis E: an summary and up to date advances in medical and laboratory analysis, J Gastroenterol Hepatol 15:9-20, 2000. Bendall R, Ellis V, Ijaz S, et al: Serological response to hepatitis E virus genotype 3 infection: IgG quantitation, avidity, and IgM response, J Med Virol 80:95-101, 2008. The improvement of viral typing strategies supplied the instruments required to make clear the epidemiology of those infections. This causal relationship was strengthened by detection of the virus in the maternal genital tract at the time of delivery, indicating that acquisition of the virus occurs by contact with infected genital secretions during start. A lipid envelope that incorporates viral glycoproteins surrounds the capsid and tegument. The nucleotide sequence of associated genes and the amino acid residues of the proteins they encode often differ considerably, nonetheless. These genes are transcribed in contaminated cells within the absence of viral protein synthesis. The onset of expression of genes coincides with a decline in the fee of expression of genes and an irreversible shutoff of host cellular macromolecular protein synthesis. Structural proteins, such as proteins that form the viral capsid, are usually of the, or late, gene. Assembly of the virus begins with formation of nucleocapsids in the nucleus, followed by egress across the nuclear membrane and envelopment at cytoplasmic places. Virus particles are transported to the plasma membrane, the place progeny virions are released. The biologic phenomenon of latency was first described at the beginning of the 20th century, when Cushing15 observed in 1905 that patients handled for trigeminal neuralgia by sectioning a department of the trigeminal nerve developed herpetic lesions in areas innervated by the sectioned branch. Clinically, silent viral reactivations are far more common than recurrent lesions which would possibly be clinically apparent. Primary infection in young adults has been related to pharyngitis only or with a mononucleosis-like syndrome. This is happening at a time when nearly half of youngsters 15 to 19 years of age and greater than 4 fifths of young adults 20 to 24 years of age have engaged in oral intercourse. The incidence of an infection in girls of higher socioeconomic class was 30% or larger in three large studies. However, infection during gestation might manifest in a quantity of scientific syndromes, the most extreme of which is broadly disseminated illness. As first reported by Flewett and coworkers53 in 1969 and by others54,55 subsequently, disseminated infection during being pregnant has been documented to involve multiple visceral websites in addition to cutaneous ones. In a number of circumstances, dissemination after primary oropharyngeal or genital infection has led to severe manifestations of illness, together with necrotizing hepatitis with or with out thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, disseminated intravascular coagulopathy, and encephalitis. Earlier studies described an association of maternal major an infection earlier than 20 weeks of gestation,fifty six with spontaneous abortion in some ladies. Although the unique incidence of spontaneous abortion after a symptomatic major infection during gestation was thought to be 25%, this estimate was not substantiated by potential research and was faulty due to the small variety of ladies adopted. More precise knowledge obtained from a prospective analysis of susceptible girls confirmed that 2% or greater acquired an infection, however acquisition of infection was not related to a danger of spontaneous abortion. Overall, prospective investigations using cytologic and virologic screening point out that genital herpes happens with a frequency of about 1% in girls examined at any time during gestation. In a predominantly white, middle-class inhabitants, symptomatic recurrent an infection occurred throughout being pregnant in 84% of pregnant ladies with a historical past of symptomatic disease. Overall, these data indicate that the frequency of cervical shedding is low, which can scale back the danger of transmission of virus to the toddler when the maternal an infection is recurrent. These women often have neither a past history of genital herpes nor a sexual partner reporting a genital vesicular rash and account for 60% to 80% of all women whose infants turn into contaminated. Infections which are newly acquired, which have been referred to as firstepisode infections, are categorized further as both major or nonprimary based mostly on type-specific serologic testing. Because transmission has been studied utilizing type-specific serologic strategies, it has turn out to be obvious that attempts to distinguish primary and recurrent illness by scientific criteria are unreliable. These girls were experiencing genital symptoms, brought on by reactivation of latent virus, for the first time. The higher threat of transmission to the infant when the mom has a model new an infection could be attributed to differences within the quantity and period of viral shedding within the mom and within the switch of passive antibodies from the mom to the infant before supply. Primary infection is related to bigger portions of virus replication within the genital tract (>106 viral particles/0. In some moms, these infections trigger indicators of systemic sickness, including fever, malaise, myalgias, dysuria, and headache. In distinction, virus is shed for a median of only 2 to 5 days and at lower concentrations (approximately 102-103 viral particles/0. Asymptomatic reactivation can additionally be associated with short durations of viral replication, typically lower than 24 to forty eight hours.
Cheap oxytrol 2.5mg fast deliveryNo particular information exist on the performance of most checks in the new child because of small sample sizes in series; however symptoms pink eye discount oxytrol 2.5mg with visa, Hageman90 described optimistic cultures for Mtb in 10 of 12 gastric aspirates symptoms influenza purchase oxytrol 5 mg on-line, in all three bone marrow and all 3 lymph node biopsies medicine grapefruit interaction oxytrol 2.5mg overnight delivery, and in 2 of 4 bone marrow aspirates medicine wheel native american quality 5 mg oxytrol. One or extra of the next should be present: tuberculous lesions evident in the first week of life, major hepatic advanced or caseating hepatic granulomas, evidence of tuberculous infection of the maternal genital tract. In addition, the potential for postnatal transmission should be excluded by an intensive investigation of contacts. It must be pointed out that suggestions might differ in different nations, often dictated by local resources. All 4 drugs have glorious oral bioavaiIability and penetrate most tissues properly. Second-line therapy, which can be launched when opposed events happen or drug resistance is present (see later), mostly consists of fluoroquinolones and streptomycin (see Table 18-2). This length is often termed "quick course," based mostly on previous regimens that took longer to complete. Patients with cavitary lesions and a constructive sputum tradition at 2 months must be treated for 9 months as a end result of relapse rates after 6 months of remedy are high. In this setting, adherence should be assessed and drug resistance considered, whereas month-to-month sputum testing ought to proceed until the culture becomes unfavorable. In refractory instances of pulmonary disease or within the presence of complications, surgical removing of diseased lung may be indicated. The length of remedy for extrapulmonary disease is decided by the positioning of an infection. For lymphadenitis and most other websites of an infection, 6 months whole duration is enough. Table 18-3 Drug Regimens for Culture-Positive Pulmonary Tuberculosis Caused by Drug-Susceptible Organisms * 1. Although this adverse impact is uncommon, baseline and follow-up visual acuity and red-green colour discrimination testing is recommended. Drug susceptibility testing of the organism isolated from the mother or household contact, newborn, or both ought to be carried out and remedy adjusted if drug resistance is present (see later). If the source case is the mother and she or he is asymptomatic, the new child and mom should remain together. As for all treatment recommendations, completely different approaches could apply in different geographies. Separation of the mother or other supply case from the newborn is recommended until the diagnostic evaluation has been completed and prophylactic chemotherapy or treatment has been initiated, if required. Adherence of the mom or household contact to infection control measures could allow the newborn to be reintroduced to the family. Isoniazid-induced increases in hepatic aminotransferases during being pregnant are uncommon. There are comparable issues about neonatal deafness associated to use of other aminoglycosides (amikacin, kanamycin, and capreomycin) in pregnancy. Factors associated with infectiousness in adults embrace presence of a cough, lung cavities, acid-fast bacilli on sputum smear, disease of the lungs, airway or larynx, and fewer than 2 weeks of adherent therapy. Treatment success primarily depends on severity of illness, resistance pattern of the offending pressure, and patient adherence. In kids, complications resulting from lymph node obstruction of the big airways are comparatively common. It is estimated that the danger of recurrent illness in high-prevalence settings is a minimal of 5% throughout the first yr after completion of remedy; a high index of suspicion throughout the first 12 months of completion of therapy is therefore warranted. These vaccines include viral vectored constructs and adjuvanted subunits and comprise antigens thought to be necessary for management of mycobacteria. This differs from routine microbiologic laboratory procedures, which detect the Mtb complicated that includes each Mtb and M. Resistance is a laboratory analysis, primarily based on drug susceptibility testing during/after tradition. Newer sputum nuclear amplification checks, corresponding to Xpert, may detect resistance strains earlier by way of identification of common genotypic determinants of resistance. Aminoglycosides could trigger toddler deafness and ought to be avoided during being pregnant if potential. World Health Organization: Global tuberculosis report, 2013 (including supplement). Comas I, Coscolla M, Luo T, et al: Out-of-Africa migration and Neolithic coexpansion of Mycobacterium tuberculosis with trendy humans, Nat Genet 45:1176-1182, 2013. Human immunodeficiency virus, homelessness, and the decline of tuberculosis control programs, Am Rev Respir Dis 144:745-749, 1991. Koch R: Die Aetiologie der Tuberculose, Berliner Klinischen Wochenschrift 15:221-230, 1882. Lonnroth K, Raviglione M: Global epidemiology of tuberculosis: prospects for management, Semin Respir Crit Care Med 29:481-491, 2008. This assertion was endorsed by the Council of the Infectious Disease Society of America, September 1999, Am J Respir Crit Care Med 161(4 Pt 1):1376-1395, 2000. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Reported tuberculosis in the United States, 2012, Atlanta, 2013, U. Perry A, Angoulvant F, Chadelat K, et al: Neonatal exposure to active pulmonary tuberculosis in a maternity ward: screening and scientific course of a cohort of exposed infants, Arch Pediatr 19:396-403, 2012. Saengnipanthkul S, Jirapradittha J, Kiatchoosakun P: Outcome of neonates exposed to energetic pulmonary tuberculosis, J Med Assoc Thai ninety five:756-760, 2012. Saitoh M, Ichiba H, Fujioka H, et al: Connatal tuberculosis in an especially low birth weight infant: case report and administration of publicity to tuberculosis in a neonatal intensive care unit, Eur J Pediatr 160:88-90, 2001. Dubrulle S, Vervel C, Boutignon H, et al: Exposure of a cohort of new child infants to tuberculosis in a neonatology service, Arch Pediatr 17:1491-1494, 2010. Niederweis M, Danilchanka O, Huff J, et al: Mycobacterial outer membranes: looking for proteins, Trends Microbiol 18:109-116, 2010. Leung E, Minion J, Benedetti A, et al: Microcolony culture methods for tuberculosis analysis: a scientific review, Int J Tuberc Lung Dis sixteen:16-23, 2012. Thwaites G, Fisher M, Hemingway C, et al: British Infection Society tips for the diagnosis and therapy of tuberculosis of the central nervous system in adults and children, J Infect fifty nine:167-187, 2009. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Latent tuberculosis infection: a guide for major care suppliers, 2013. This statement was endorsed by the Council of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Uganda�Case Western Reserve University Research Collaboration, N Engl J Med 337:801-808, 1997. The controversy of the intracellular localization of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Tuberculosis (Edinb) 92:113-120, 2012. Di Pietrantonio T, Schurr E: Host-pathogen specificity in tuberculosis, Adv Exp Med Biol 783:33-44, 2013. Kothari A, Mahadevan N, Girling J: Tuberculosis and pregnancy- outcomes of a examine in a high prevalence space in London, Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 126:48-55, 2006. Pillay T, Adhikari M, Mokili J, et al: Severe, quickly progressive human immunodeficiency virus kind 1 disease in newborns with coinfections, Pediatr Infect Dis J 20:404-410, 2001. Abubakar I, Ariti C, Beynon R, et al: Systematic evaluate and metaanalysis of the present proof on the duration of protection by bacillus Calmette-Gu�rin vaccination towards tuberculosis, Health Technol Assess 17:1-372, 2013.
Oxytrol: 5 mg, 2.5 mg

Discount oxytrol 2.5 mg visaFew individuals with uncomplicated sickness have immune complexes containing rubella virus symptoms pancreatitis oxytrol 2.5 mg, and virus has been isolated from concerned and uninvolved skin kapous treatment generic oxytrol 5 mg free shipping. These embrace chromosomal breaks treatment e coli cheap oxytrol 5 mg visa, elevated cellular multiplication time medicine while pregnant buy oxytrol 2.5 mg on-line, and elevated production of a protein inhibitor that causes mitotic arrest of sure cell sorts. A report by Bowden and associates476 signifies that rubella virus could interfere with mitosis by having an opposed impact on actin microfilaments. Observations of Yoneda and coworkers477 present that rubella virus may alter cell receptors to particular development factors. All of those abnormalities, if occurring in vivo, might result in decreased cell multiplication because of slow progress charges and limited doubling potential during the period of embryogenesis, when cell division and turnover are normally very fast. These observations have been offered to explain the elevated incidence of intrauterine progress restriction seen in infants with congenital rubella, however this explanation in all probability represents an oversimplification of the actual mechanisms involved. More just lately, it has been shown that rubella virus capsid protein interacts with host cell proteins to inhibit translation. Changes in lymphoreticular tissue have been limited-to-mild edema, nonspecific follicular hyperplasia, and some lack of normal follicular morphology. Examination of mind tissue has revealed diffuse swelling, nonspecific degeneration, and little meningeal and perivascular infiltrate. Cellular necrosis and secondary irritation are seldom obvious, though a generalized vasculitis predominates (see "Pathogenesis"). The pathologic findings of the placenta include hypoplasia, inflammatory foci in chorionic villi, granulomatous adjustments, gentle edema, focal hyalinization, and necrosis. The vessel lesions consist primarily of endothelial necrosis, with fragmentation of intraluminal blood cells. T�ndury and Smith462 postulated that emboli of contaminated endothelial cells originating from the chorion might seed goal organs within the fetus. These emboli may also contribute to organ injury by obstructing the fetal blood provide. Petechiae and the presence of hemosiderin-laden phagocytes in surrounding tissue are proof of practical vascular damage. This condition is characterised by cytoplasmic eosinophilia, nuclear pyknosis or karyorrhexis, and mobile necrosis. Specific nuclear and cytoplasmic cellular inclusion bodies are uncommon however have been observed. The necrotizing angiopathy of small blood vessels seen within the placenta is the most characteristic lesion in fetal organs. Cytolysis with tissue necrosis and accompanying inflammatory modifications can be far much less common however has been discovered within the myocardium, brain, spinal cord, skeletal muscle, viscera, and epithelial cells of the developing lens, inner ear (organ of Corti), and enamel. The general pathologic process of congenital rubella, in line with its continual nature, is progressive. Healing and new lesions could be found in specimens obtained in the later stages of gestation. As observed by Cherry,9 the histologic findings of tissues which were examined. Sheinis and associates486 reported the demise of a neonate with rash onset when 12 days of age; the mom developed rash on the day of delivery. The first signs of rubella happen after an incubation interval of sixteen to 18 days (range, 14-21 days). In adolescents and adults, the eruption is often preceded by a 1- to 5-day prodromal period characterised by low-grade fever, headache, malaise, anorexia, delicate conjunctivitis, coryza, sore throat, cough, and lymphadenopathy often involving suboccipital, postauricular, and cervical nodes. The constitutional signs often subside quickly with the appearance of the rash. All patients are seropositive for rubella, and intraocular antibody production of rubella (but not other pathogens) has been proven in adults and in a 13-year-old unvaccinated youngster. After the extensive studies within the mid-1960s, in which virologic and serologic strategies of assessment had been used, the pathologic potential associated with intrauterine rubella an infection had to be greatly expanded. Alternatively, extreme a number of start defects could additionally be apparent in the new child interval. The extensive spectrum of illness is mentioned later and summarized in Tables 29-3 and 29-4. Schiff and colleagues353 prospectively examined 4005 infants born after the 1964 rubella epidemic. Based on virologic and serologic strategies to detect infection within the newborns, the general rate of congenital rubella was higher than 2% in contrast with solely approximately zero. Among infants who have been adopted, 71% developed manifestations of an infection at various times in the first 5 years of life. Many important rubella defects may be undetectable or overlooked in the early months of life. Existing manifestations of an infection can progress, and new manifestations may appear throughout life. The silent and progressive nature of congenital rubella infection has essential implications for correct, timely prognosis and appropriate short-term and long-term management. It is useful to group the scientific features of congenital rubella into three categories: transient manifestations in newborns and infants; permanent manifestations, which may be current at start or become obvious during the first yr of life; and developmental and late-onset manifestations, c References 6, 13, 14, 111, 135, 136, 165, 289-294, 296, 311, 333-339, �c References 6, 9, 302, 305, 370, 485. More than 50% of infants with these transient findings often have evidence of intrauterine progress restriction and may proceed to fail to thrive during infancy. These situations often are self-limiting and clear spontaneously over days or perhaps weeks. They may be associated with different, extra severe defects; this is applicable particularly to thrombocytopenia and bone lesions. Extreme prematurity, gross cardiac lesions or myocarditis with early coronary heart failure, rapidly progressive hepatitis, extensive meningoencephalitis, and fulminant interstitial pneumonitis contributed to the mortality throughout infancy. It is unsure that the entire malformations listed in Table 29-5 are related to congenital rubella. The most typical lesions, in descending order, are patent ductus arteriosus, pulmonary artery stenosis, and pulmonary valvular stenosis. Cataracts and childish glaucoma is probably not present or detectable at birth, but usually turn out to be apparent during the early weeks of life. Other ocular abnormalities happen later in life (see "Developmental and Late-Onset Manifestations"). Table 29-5 Clinical Findings and Their Estimated Frequency of Occurrence in Young Symptomatic Infants With Congenitally Acquired Rubella Clinical Findings Adenopathies Anemia Bone Micrognathia Extremities Bony radiolucencies Brain Encephalitis (active) Microcephaly Brain calcification Bulging fontanelle Cardiovascular system Pulmonary arterial hypoplasia Patent ductus arteriosus Coarctation of aortic isthmus Interventricular septal defect Interauricular septal defect Others Chromosomal abnormalities Dermal erythropoiesis (blueberry muffin syndrome) Dermatoglyphic abnormalities Ear Hearing defects (severe) Peripheral Central Eye Retinopathy Cataracts Cloudy cornea Glaucoma Microphthalmos Genitourinary tract Undescended testicle Polycystic kidney Bilobed kidney with reduplicated ureter Hypospadias Unilateral agenesis Renal artery stenosis with hypertension Hydroureter and hydronephrosis Frequency* ++ + + + ++ ++ + Rare + ++ ++ + Rare Rare Rare Mental retardation and motor retardation are widespread and are directly associated to the acute meningoencephalitis in 10% to 20% of affected children at delivery. The incidence of deafness has been underestimated as a result of many cases had been missed in infancy and early childhood.
Cheap oxytrol 5 mg amexAssociated with epidemiologic investigations treatment with chemicals or drugs generic oxytrol 5 mg otc, they seem to be the only means to gather information in precise clinical settings and allow doctors to provide parents-to-be with unbiased data and help coverage makers to take the suitable selections symptoms bipolar buy generic oxytrol 2.5 mg on-line. In the meantime medicine 44 159 discount 5 mg oxytrol, working teams ought to concern standardized pointers on which doctors can rely for counseling pregnant ladies treatment meaning generic 5mg oxytrol mastercard, initiate data campaigns for each the public and docs, and implement networks with referral laboratories and referral physicians, who could be obtainable for face-to-face interviews with sufferers whenever requested. Acknowledgments the authors are grateful to Marie Laure Dard�, Valeria Meroni, and Eskild Petersen for his or her recommendation and assist. They also thank Jane Mitchell and Monique Billaud for providing technical assistance, Jack Remington for his helpful ideas, and Christopher Wilson for help in enhancing the manuscript. Kaneko Y, Takashima Y, Xuaun X, et al: Natural IgM antibodies in sera from numerous animals however not the cat kill Toxoplasma gondii by activating the classical complement pathway, Parasitology 128(Pt 2): 123-129, 2004. Unno A, Suzuki K, Xuan X, et al: Dissemination of extracellular and intracellular Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites within the blood flow, Parasitol Int 57:515-518, 2008. Ajzenberg D, Cogne N, Paris L, et al: Genotype of 86 Toxoplasma gondii isolates associated with human congenital toxoplasmosis, and correlation with medical findings, J Infect Dis 186:684-689, 2002. Wallon M, Peyron F, Cornu C, et al: Congenital Toxoplasma infection: monthly prenatal screening decreases transmission price and improves medical consequence at age three years, Clin Infect Dis 56:1223-1231, 2013. Kirby T: Calls for more detailed studies on toxoplasmosis, Lancet Infect Dis 12:912-913, 2012. Peyron F: When are we going to rejoice the centenary of the invention of environment friendly therapy for congenital toxoplasmosis Nicolle C, Manceaux L: Sur un protozoaire nouveau du gondi, Arch Inst Pasteur Tunis 2:97-107, 1909. Janku J: Pathogenesa a pathologicka anatomie tak nazvaneho vrozeneho kolobomu zlute skvrny v oku normalne velikem a mikrophtalmickem s nalezem parasitu v sitnicio, Cas Lek Cesk 62:1021-1027, 1923. Wolf A, Cowen D, Paige B: Human toxoplasmosis: prevalence in infants as an encephalomyelitis verification by transmission to animals, Science 89:226-227, 1939. A new case of granulomatous encephalomyelitis because of a protozoon, Am J Pathol 15:657-694, 1939. Bautista G, Ramos A, Fores R, et al: Toxoplasmosis in twine blood transplantation recipients, Transpl Infect Dis 14:496-501, 2002. Derouin F, Pelloux H: Prevention of toxoplasmosis in transplant patients, Clin Microbiol Infect 14:1089-1101, 2008. Aubert D, Ajzenberg D, Richomme C, et al: Molecular and biological characteristics of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from wildlife in France, Vet Parasitol 171:346-349, 2010. Ajzenberg D, Yera H, Marty P, et al: Genotype of 88 Toxoplasma gondii isolates associated with toxoplasmosis in immunocompromised sufferers and correlation with clinical findings, J Infect Dis 199:1155-1167, 2009. Mercier A, Ajzenberg D, Devillard S, et al: Human influence on genetic range of Toxoplasma gondii: instance of the anthropized setting from French Guiana, Infect Genet Evol 11:1378-1387, 2011. Carme B, Demar M, Ajzenberg D, et al: Severe acquired toxoplasmosis brought on by wild cycle of Toxoplasma gondii, French Guiana, Emerg Infect Dis 15:656-658, 2009. Delhaes L, Ajzenberg D, Sicot B, et al: Severe congenital toxoplasmosis because of a Toxoplasma gondii pressure with an atypical genotype: case report and evaluation, Prenat Diagn 30:902-905, 2010. Sobanski V, Ajzenberg D, Delhaes L, et al: Severe toxoplasmosis in immunocompetent hosts: pay consideration to atypical strains, Am J Respir Crit Care Med 187:1143-1145, 2013. Pomares C, Ajzenberg D, Bornard L, et al: Toxoplasmosis and horse meat, France, Emerg Infect Dis 17:1327-1328, 2011. Dunn D, Wallon M, Peyron F, et al: Mother-to-child transmission of toxoplasmosis: threat estimates for scientific counselling, Lancet 353:1829-1833, 1999. Romand S, Chosson M, Franck J, et al: Usefulness of quantitative polymerase chain reaction in amniotic fluid as early prognostic marker of fetal infection with Toxoplasma gondii, Am J Obstet Gynecol one hundred ninety:797-802, 2004. Thouvenin M, Candolfi E, Villard O, et al: Immune response in a murine mannequin of congenital toxoplasmosis: elevated susceptibility of pregnant mice and transplacental passage of Toxoplasma gondii are sort 2-dependent, Parassitologia 39:279-283, 1997. Biedermann K, Flepp M, Fierz W, et al: Pregnancy, immunosuppression and reactivation of latent toxoplasmosis, J Perinat Med 23:191-203, 1995. Senegas A, Villard O, Neuville A, et al: Toxoplasma gondii-induced foetal resorption in mice involves interferon-gamma-induced apoptosis and spiral artery dilation on the maternofoetal interface, Int J Parasitol 39:481-487, 2009. Suzuki Y, Sa Q, Gehman M, et al: Interferon-gamma- and perforinmediated immune responses for resistance in opposition to Toxoplasma gondii within the brain, Expert Rev Mol Med 13:e31, 2011. Guglietta S, Beghetto E, Spadoni A, et al: Age-dependent impairment of useful helper T cell responses to immunodominant epitopes of Toxoplasma gondii antigens in congenitally contaminated individuals, Microbes Infect 9:127-133, 2007. Garweg J, Boehnke M, Koerner F: Restricted applicability of the polymerase chain response for the diagnosis of ocular toxoplasmosis, Ger J Ophthalmol 5:104-108, 1996. Wallon M, Kodjikian L, Binquet C, et al: Long-term ocular prognosis in 327 youngsters with congenital toxoplasmosis, Pediatrics 113: 1567-1572, 2004. Webber A, Hirose R, Vincenti F: Novel methods in immunosuppression: points in perspective, Transplantation ninety one:1057-1064, 2011. De Lalla F, Sampieri L, Bechelli G, et al: [Relations between the resistance to reinfection and serum antibodies in mice utilized in isolation checks of human Toxoplasma], Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper forty:297-298, 1964. Werner H, Janitschke K, Masihi M, et al: the impact of Toxoplasma antibodies after reinfection with T. Fortier B, Aissi E, Ajana F, et al: Spontaneous abortion and reinfection by Toxoplasma gondii, Lancet 338:444, 1991. Dao A, Fortier B, Soete M, et al: Successful reinfection of chronically infected mice by a special Toxoplasma gondii genotype, Int J Parasitol 31:63-65, 2001. Kodjikian L, Hoigne I, Adam O, et al: Vertical transmission of toxoplasmosis from a chronically infected immunocompetent lady, Pediatr Infect Dis J 23:272-274, 2004. Valdes V, Legagneur H, Watrin V, et al: Congenital toxoplasmosis due to maternal reinfection throughout pregnancy, Arch Pediatr 18: 761-763, 2011. Dzitko K, Staczek P, Gatkowska J, et al: Toxoplasma gondii: serological recognition of reinfection, Exp Parasitol 112:134-137, 2006. Bodaghi B, Touitou V, Fardeau C, et al: Toxoplasmosis: new challenges for an old disease, Eye (Lond) 26:241-244, 2012. Barragan A, Hitziger N: Transepithelial migration by Toxoplasma, Subcell Biochem 47:198-207, 2008. Djurkovic-Djakovic O, Milenkovic V, Nikolic A, et al: Efficacy of atovaquone combined with clindamycin towards murine an infection with a cystogenic (Me49) strain of Toxoplasma gondii, J Antimicrob Chemother 50:981-987, 2002. Esterre P: Immune reactions in the brain, Arch Inst Pasteur Madagas automotive sixty three:24-30, 1996. Neghme A, Thiermann E, Pino F, et al: Toxoplasmosis in Chile; preliminary communication, Bol Inf Parasit Chil 7:6-8, 1952. Sarrut S: Histological study of the placenta in congenital toxoplasmosis, Ann Pediatr (Paris) 14:2429-2435, 1967. Mellgren J, Alm L, Kjessler A: the isolation of Toxoplasma from the human placenta and uterus, Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand 30:59-67, 1952. Immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study of a case, Ann Pathol 17:337-339, 1997.
Cao Ma-Huang (Ephedra). Oxytrol. - How does Ephedra work?
- Dosing considerations for Ephedra.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Improving athletic performance, allergies, asthma and other breathing disorders, nasal congestion, colds, flu, fever, and other conditions.
- Is Ephedra effective?
- What is Ephedra?
- Weight loss. Ephedra can produce modest weight loss when used with exercise and a low fat diet, but it can cause serious side effects, even in healthy people who follow product dosage directions.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96822
Order 2.5 mg oxytrol free shippingA spectrum of organisms much like symptoms joint pain and tiredness discount oxytrol 2.5mg otc these inflicting neonatal sepsis has been isolated from the peritoneal fluid treatment 6th nerve palsy order 2.5mg oxytrol amex. More recently medications used for migraines generic 2.5mg oxytrol with mastercard, preliminary remedy with meropenam or -lactam and -lactamase inhibitor combinations treatment borderline personality disorder generic oxytrol 5mg fast delivery. Gentamicin and vancomycin dosages should be modified as needed on the basis of serum ranges. After immediate treatment has been began, follow-up research must be instituted. These embody serial examinations with measurement of belly girth; testing of stools for blood; ranges of serum electrolytes, blood glucose, and arterial blood gases; complete blood cell rely and platelet rely; urine-specific gravity; and supine and left lateral decubitus belly radiographs. Attention to very important features must be provided as needed on the premise of scientific, laboratory, or radiographic research. Parenteral nutritional support through a central or peripheral vein must be began as soon as potential. Early recognition and prompt initiation of medical therapy may reduce the need for surgical procedure. Generally accepted criteria for surgical exploration are a deteriorating clinical situation regardless of applicable medical remedy, indicators of peritonitis, presence of free air throughout the abdomen, or a optimistic paracentesis outcome. The ideas of surgical preparation and administration have been mentioned by a number of investigators. Umbilical catheters must be eliminated whenever attainable, oral feedings must be stopped, and nasogastric tube drainage should be instituted. Fluid and electrolyte deficits and maintenance require rigorous attention; blood, plasma, or colloid infusions are often necessary for quantity enlargement and upkeep of tissue perfusion. After appropriate cultures are obtained, broad-spectrum parenteral antibiotic remedy ought to be began. About 60 instances that meet medical and bacteriologic standards adequate to set up this analysis were reported within the literature earlier than the mid-1980s. In a 35-year evaluation of seventy six cases of endocarditis in youngsters, 10% of sufferers were youthful than 1 year; the youngest affected person was 1 month old. At the Mercy Hospital for Women in Melbourne, of greater than 12,000 infants admitted to the particular care nursery, 8 infants with endocarditis had been recognized; gestation less than 32 weeks, delivery weight less than 1500 g, thrombocytopenia and neutropenia, or elevated neutrophil depend were common features. The tricuspid valve (8 cases) and mitral valve (2 cases) were most frequently concerned. Among these sufferers, 10 had coagulase-negative staphylococci identified from blood cultures, 1 had Streptococcus sanguinis, and 1 had C. Usually found at sites of ischemia and necrosis in terminal ileum or colon,268 these strictures often turn out to be apparent inside a couple of weeks however could also be delayed 18 months. In contrast to older youngsters, in whom congenital coronary heart disease is often related to endocarditis,283 cardiac anomalies are extra uncommon in neonatal an infection. Damage to the intracardiac endothelium with formation of a sterile platelet-fibrin thrombus at the website of the harm are often the initiating occasions in a affected person with endocarditis. Endocardial trauma caused by placement of cardiac catheters, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and numerous nonspecific stresses associated with prematurity, similar to hypotension and hypoxia, has been implicated in the genesis of thrombi. Whether this mechanism or direct bacterial invasion is primarily answerable for valvulitis is unknown. A related pathogenesis has been postulated for formation of mycotic aortic aneurysms in newborns. When these findings are accompanied by persistent bacteremia, or by indicators of congestive heart failure without underlying coronary heart disease, the diagnosis have to be thought of seriously. Multiple septic emboli with involvement of the skin, bones, viscera, and central nervous system are frequent findings, nonetheless. Despite detection of vegetations 2 mm in diameter with echocardiography, the number of false-negative examinations is significant. Use of transesophageal echocardiography, which offers detailed views of the mitral and tricuspid valves, and utility of colour circulate Doppler imaging, which might establish areas of turbulence as blood passes over vegetations or by way of narrowed valve leaflets, improves diagnostic accuracy. Because blood drawn from a central catheter usually contains organisms colonizing the line however not present in the systemic circulation, no less than two peripheral venous blood cultures should be obtained before antimicrobial therapy is initiated. Routine laboratory studies are useful in supporting a prognosis of endocarditis in the newborn. The leukocyte count, differential depend, and platelet depend are often indicative of sepsis, rather than cardiac valve infection particularly. A chest radiograph should be obtained to determine signs of cardiac failure or pulmonary or pleural house infection. Baseline determinations of inflammatory markers are useful and can be utilized for assessing the efficacy of the therapy; erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein level have been used. Intravenous therapy with a penicillinase-resistant penicillin and an aminoglycoside must be began after applicable cultures have been obtained. After the infecting organism is isolated and antibiotic susceptibilities have been determined, specific antimicrobial therapy could be instituted. Four to 8 weeks of parenteral treatment is normally adequate, depending on the susceptibility of the organism, response to therapy assessed clinically by reduction or elimination of the noticed vegetations, and laboratory response. C-reactive protein stage usually normalizes 2 to three weeks before erythrocyte sedimentation price, and blood cultures are usually sterile after 3 to 5 days of effective remedy. Dosage and efficacy ought to be monitored weekly with scientific and bacteriologic response with or without serum antibiotic and bactericidal ranges. Extremely large or cell vegetations occluding an outflow tract or posing a excessive threat of embolism may have to be eliminated surgically. With the supply of echocardiography, improved clinical awareness, and early analysis, prognosis has improved. Although there have been rare survivors before 1973, the primary survivors with proven endocarditis were reported in 1983. Death is often the results of overwhelming sepsis, typically at the aspect of cardiac failure. Early reconstructive surgery for infants who fail medical management could also be useful but has been reported in only some instances. The tricuspid valve was concerned in 12 infants, the pulmonary valve in 7, the aortic valve in 6, contaminated mural thrombi in 12, and an unspecified web site in 3. Microscopic examination of valve cusps has revealed the attribute lesions of endocarditis, with multiple small, confluent, friable vegetations composed principally of bacteria and thrombi surrounded by inflammatory exudate. Cases described as fetal endocarditis in the literature are almost certainly examples of these sort of lesions. Approximately 20 cases of confirmed infectious origin have been reported throughout the previous 60 years. Virtually every infant with pericarditis has related septic foci; pneumonia and multiple pulmonary abscesses are the most typical websites.
Generic 2.5 mg oxytrol with mastercardBacteria which were isolated from blood or joints of newborns in two sequence are listed in Table 8-2 medicine 773 buy oxytrol 5 mg without a prescription. Exceedingly uncommon in neonates symptoms of dehydration buy generic oxytrol 5 mg, unlike its anticipated presence in older kids symptoms of high blood pressure buy cheap oxytrol 2.5mg, group A Streptococcus was isolated from the elbow joint of a neonate in India symptoms 10 dpo purchase oxytrol 5 mg on-line. Data are insufficient to provide any meaningful comparability between the skeletal distribution of septic arthritis and that of osteomyelitis. Infants with sources of an infection, corresponding to skin abscesses or omphalitis, represent a small minority. In some cases, osteomyelitis is believed to result from extension from a contiguous focus of infection within the maxillary antrum. Alternatively, organisms could additionally be bloodborne, establishing infection within the wealthy vascular plexus surrounding tooth buds. Shortly thereafter, redness and swelling of the eyelid appear and are regularly accompanied by conjunctivitis with a purulent discharge. Thrombosis of nutrient vessels and rising edema could cause a proptosis or chemosis of the affected eye. The alveolar border of the superior maxilla on the affected facet is swollen and gentle, as is the adjoining onerous palate. In most infants, the sickness pursues a comparatively chronic course characterized by discharge of premature tooth or quite a few small sequestra of necrotic bone through multiple palatal and alveolar sinuses that have shaped. The whole course might evolve over several days in severe circumstances, or it may prolong for several weeks in gentle or partially handled instances. Neonatal maxillary osteomyelitis is incessantly confused with either orbital cellulitis or dacryocystitis. Neither �d References orbital cellulitis nor lacrimal sac infection is related to a unilateral purulent nasal discharge. The early onset, restricted area of involvement, and Gram stain attribute of ophthalmia neonatorum ought to be sufficient, in most cases, to permit diagnosis of this condition. The need for or desirability of instillation of antibiotics into the maxillary antrum is unsure. Before the appearance of antibiotic remedy, the mortality fee for maxillary osteomyelitis was high, ranging from 15% to 75% in varied collection. Later studies260,262,267 confirmed a mortality rate of closer to 5%, though sequelae corresponding to stenosis of the lacrimal duct, ectropion, permanent loss of enamel, malocclusion, and facial hemiatrophy are nonetheless seen. Contzen H: Die sogennante Osteomyelitis des Neugeborenen, Dtsch Med Wochenschr 86:1221, 1961. Korakaki E, Aligizakis A, Manoura A, et al: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis and septic arthritis in neonates: diagnosis and administration, Jpn J Infect Dis 60:129, 2007. Matic A, Gajdobranski D, Petkovi L, et al: Acute osteomyelitis and septic arthritis of the shoulder in premature neonates: report of two circumstances, Med Pregl 65:59, 2012. Sandal G, Uras N, Akar M, et al: Iliac osteomyelitis in the newborn: a case report, J Pediatr Orthop 21:404, 2012. Bergdahl S, Ekengren K, Eriksson M: Neonatal hematogenous osteomyelitis: danger factors for long-term sequelae, J Pediatr Orthop 5:564, 1985. Bamberger T, Gugler E: Die akute Osteomyelitis im Kindesalter, Schweiz Med Wochenschr 113:1219, 1983. Bennet R, Eriksson M, Zetterstr�m R: Increasing incidence of neonatal septicemia: causative organism and predisposing risk components, Acta Paediatr Scand 70:207, 1981. Dan M: Septic arthritis in young infants: scientific and microbiologic correlations and therapeutic implications, Rev Infect Dis 6:147, 1984. Baitch A: Recent observations of acute suppurative arthritis, Clin Orthop 22:157, 1962. Wong M, Isaacs D, Howman-Giles R, et al: Clinical and diagnostic features of osteomyelitis within the first three months of life, Pediatr Infect Dis 14:1047, 1995. Narang A, Mukhopadhyay K, Kumar P, et al: Bone and joint an infection in neonates, Indian J Pediatr sixty five:461, 1998. Estienne M, Scaioli V, Zibordi F, et al: Enigmatic osteomyelitis and bilateral upper limb palsy in a neonate, Pediatr Neurology 32:fifty six, 2005. Lejman T, Strong M, Michno P: Radial nerve palsy related to septic shoulder in neonates, J Pediatr Orthop 15:169, 1995. Saez-Llorens X, Velarde J, Canton C: Pediatric osteomyelitis in Panama, Clin Infect Dis 19:323, 1994. Kienitz M, Schulte M: Problematik bakterieller Infectionen des Fr�hund Neuegeborenen, Munch Med Wochenschr 109:70, 1967. Bogdanovich A: Neonatal arthritis due to Proteus vulgaris, Arch Dis Child 23:sixty five, 1948. Peters W, Irving J, Letts M: Long-term effects of neonatal bone and joint an infection on adjacent growth plates, J Pediatr Orthop 12:806, 1992. Berant M, Kahana D: Klebsiella osteomyelitis in a newborn, Am J Dis Child 118:634, 1969. Brook I: Osteomyelitis and bacteremia brought on by Bacteroides fragilis: a complication of fetal monitoring, Clin Pediatr 19:639, 1980. Ladewig W: �ber eine intrauterin entstandene umschriebene Osteomyelitis des Sch�deldaches, Virchows Arch Pathol Anat 289:395, 1933. Trueta J: Three forms of acute haematogenous osteomyelitis, J Bone Joint Surg Br 41:671, 1959. Svirsky-Fein S, Langer L, Milbauer B, et al: Neonatal osteomyelitis attributable to Candida tropicalis: report of two circumstances and evaluation of the literature, J Bone Joint Surg Am 61:455, 1979. Gajzago D, Gottche O: Salmonella suipestifer infections in childhood, Am J Dis Child sixty three:15, 1942. Konzert W: �ber ein Salmonella-Osteomyelitis im Rahmen einer Salmonella typhimurium Epidemia auf einer Neugeborenen Station, Wien Klin Wochenschr 81:713, 1969. Steinwender G, Schimpl G, Sixl B, et al: Gut-derived bone infection in the neonatal rat, Pediatr Res 50:767, 2001. Lequier L, Robinson J, Vaudry W: Sternotomy infection with Mycoplasma hominis in a neonate, Pediatr Infect Dis J 14:1010, 1995. Gjuric G, Prislin-Muski M, Nikoli E, et al: Ureaplasma urealyticum osteomyelitis in a really low start weight infant, Perinat Med 22:seventy nine, 1994. Mallet R, Ribierre M, Labrune B, Breteaue C: Diffuse bony tuberculosis within the new child (spina ventosa generalisata), Semaine H�p Paris forty four:36, 1968. Lindblad B, Ekingren K, Aurelius G: the prognosis of acute hematogenous osteomyelitis and its problems during early infancy after the advent of antibiotics, Acta Paediatr Scand 54:24, 1965. Stone S: Osteomyelitis of the long bones in the newborn, Am J Dis Child 64:680, 1942. Greengard J: Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis in infancy, Med Clin North Am 30:a hundred thirty five, 1946. Obando I, Martin E, Alvarez-Aldean J, et al: Group B streptococcus pelvic osteomyelitis presenting as footdrop in a new child infant, Pediatr Infect Dis J 10:703, 1991. Ingelrans P, Fontaine G, Lacheretz M, et al: Les ost�oarthrites du nouveau-n� et du nourrison: particularite�s �tiologiques, diagnostiques et th�rapeutiques: � propos de 35 observations, Lille Med thirteen:390, 1968.

Generic 5mg oxytrol overnight deliveryThe length of the really helpful remedy course varies depending on the clinical presentation medications used to treat ptsd safe 2.5mg oxytrol, with a advised period of 7 days for scalp infections treatment 3 cm ovarian cyst proven oxytrol 2.5mg, 10 to 14 days for sepsis/meningitis symptoms 4 weeks 3 days pregnant purchase 2.5 mg oxytrol mastercard, 14 days for arthritis medicine cabinet home depot buy 2.5 mg oxytrol with visa, and 28 days for endocarditis. Prognosis With early recognition, effective antibiotic treatment and applicable management of the eye discharge, remedy charges for gonococcal ophthalmia and different neonatal manifestations of gonococcal infection within the newborn are close to 100 percent. By distinction, everlasting corneal harm after gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum was the standard clinical consequence in the preantibiotic period. Prevention Prevention of gonococcal an infection of the fetus and neonate is finest achieved by preventing gonococcal infection of the mother. Provision of accessible health care with available antibiotics which may be applicable and efficient in opposition to circulating strains of N. Women for whom a thirdgeneration cephalosporin is contraindicated ought to receive azithromycin at a dose of 2 g orally. Follow-up testing to guarantee eradication of the an infection and to detect reinfection is crucial. In addition, counseling associated to avoidance of further an infection is an important part of administration. Tracing and therapy of sexual contacts are necessary to scale back the danger of subsequent an infection. In one examine in Louisiana of 751 pregnant women whose charts have been reviewed retrospectively, 5. Retesting is most conveniently accomplished on the time of screening for group B streptococci. Since the late 1800s, eye prophylaxis has been the hallmark of prevention of gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum. Currently, many jurisdictions mandate the use of ocular prophylaxis for newborns through laws. In these conditions, the considerations concerning the issues of using the prophylactic brokers have to be balanced in opposition to the actual danger of the illness and the ability, or the want, to provide an alternative administration method involving shut statement of the infant with early remedy if necessary. Most brokers are properly tolerated, although a chemical conjunctivitis commonly is seen after instillation of silver nitrate. This response entails epithelial desquamation and a polymorphonuclear leukocytic exudate forty one and often appears inside 6 to eight hours and disappears inside 24 to 48 hours. A delicate chemical conjunctivitis may be seen in 10% to 20% of infants who *References 1, 2, 5, 6, 36, 37. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Sexually transmitted illness surveillance, 2011. Public Health Agency of Canada: Report on sexually transmitted infections in Canada, 2008. Rothenberg R: Ophthalmia neonatorum as a result of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: prevention and treatment, Sex Transm Dis 6:187-191, 1979. Tsirpouchtsidis A, Hurwitz R, Brinkmann V, et al: Neisserial immunoglobulin A1 protease induces specific T-cell responses in people, Infect Immunol 70:335-344, 2002. Marchini G, Lindow S, Brismar H, et al: the new child toddler is protected by an innate antimicrobial barrier: peptide antibiotics are present in the pores and skin and vernix caseosa, Br J Dermatol 147:127-134, 2002. Public Health Agency of Canada: Canadian pointers on sexually transmitted infections-updated January 2010. Studies accomplished to date present it to be promising, however the incidence of gonorrheal infection has been too low within the populations studied to assess its effectiveness towards this organism in the clinical context. If the sickness is established by the point of delivery, ocular prophylaxis is ineffective. In extremely uncommon cases, infection may be acquired after prophylaxis had been supplied. Some experts have suggested that irrigation of the eyes with saline too soon after silver nitrate software is the purpose for such therapy failures. Povidone-iodine additionally is taken into account to be a safe and efficient various in resource-poor international locations. Public Health Agency of Canada: Important notice-public health information replace on the therapy for gonococcal infection. Congenital syphilis results when the an infection is transmitted from a pregnant mother to her fetus. Syphilis has been known for an extended time to trigger severe infections in the newborn of an contaminated mother. Unfortunately, that is probably the most applicable name nonetheless, as a end result of a staggering variety of adults and newborn infants in each developed and growing nations are suffering and dying as a consequence of an infection with T. Syphilis is thus unlikely to be spread via informal contact or via contact with fomites. Horizontal transmission outcomes primarily from sexual exercise, though anecdotal reviews cite kissing as a possible route as properly. Although sexual transmission is dependent upon many components, such as stage of the disease, general, about half of those who have sexual contact with an infected partner will acquire the disease, with an estimated 50% infective dose of 50 bacteria. Such an entry level is identified as the location of the initial ulcerating sore, or chancre. It represents an approximately 1-Mb round chromosome with just more than 1000 predicted open studying frames encoding all factors necessary for replication, transcription, translation, and mobility. It is very sensitive to oxygen and temperature and thus not readily maintained in tradition. Such purified organisms retain their antigenicity but not their motility nor their virulence. The organism is isolated with increasing frequency throughout gestation from umbilical wire blood, amniotic fluid,43-47 and placenta. In contrast, in ladies with early latent syphilis, 20% to 60% of their infants had been wholesome at start, 20% premature, and 16% had been stillborn; 4% died as neonates, and 40% of these showing healthy at birth developed the stigmata of congenital syphilis later in life. In the case of untreated late syphilis, about 70% of the newborns appeared healthy, 10% have been stillborn, and roughly 9% have been premature; about 1% died as neonates, and about 10% of these showing healthy at birth developed indicators of congenital syphilis later in life. Infected infants and adults with infectious lesions must be placed in touch isolation for the primary 24 hours of therapy, and appropriate personal protective equipment. Once antimicrobial remedy has been initiated, the risk of transmission is just about nonexistent because penicillin in enough dosage causes an entire disappearance of viable treponemes from syphilitic lesions inside a few hours. Close unprotected contact is defined as skin (intact or abraded) contact with infectious bodily fluids. Serology in the uncovered should be assessed at time zero and once more at 1 month and three to 6 months postexposure, or sooner if signs happen. If the diploma of exposure is considered substantial, instant remedy ought to be thought of, as outlined later beneath postexposure prophylaxis within the "Therapy" part. Using this new surveillancebased case definition, till the year 2005, the rate of congenital syphilis within the United States had declined yearly over 14 consecutive years, with an overall reduction of 74. But between 2005 and 2006, for the primary time, the speed of congenital syphilis increased again (3.
Cheap 5 mg oxytrol free shippingThe main milk elements identified to date exhibit antimicrobial 606 treatment syphilis cheap oxytrol 2.5mg online, antiinflammatory schedule 8 medicines buy oxytrol 5 mg line, proinflammatory medications mothers milk thomas hale buy generic oxytrol 5mg on-line, and/or immunoregulatory functions; cytotoxicity for tumor cells; capacity to mature and restore tissue damage; and receptor analogue features medications known to cause pill-induced esophagitis oxytrol 2.5 mg fast delivery, as properly as different metabolic effects. Milk antibodies seem to present protection against many intestinal pathogens, similar to Campylobacter, Shigella, E. Milk antibodies also effectively neutralize toxins and quite lots of human viruses. The passive transfer of the variety of maternal biologic experiences to the neonate via the process of breastfeeding represents a vital part of the survival mechanism in the mammalian neonate. For hundreds of thousands of years, maternal products of lactation delivered by way of breastfeeding have been the sole source of diet and immunity during the neonatal and early infancy period for all mammals, together with the human toddler. During the previous few centuries, nonetheless, human societies have undergone outstanding changes which have had a major impression on fundamental maternal-infant interaction, breastfeeding, and on our environment. Such modifications embody introduction of sanitation and nonhuman milk and formula feeds for neonatal diet, use of antimicrobial brokers, introduction of processed foods, and publicity to newer environmental macromolecules and dietary antigens. These changes have had a profound impression on human homeostatic mechanisms that, at the identical time, are opening up new insights into the importance of breastfeeding in the developing human neonate. Comparative analysis of natural (traditional) types of breastfeeding and artificial feeding modalities has demonstrated clearly that pure breastfeeding is associated with significant discount in toddler mortality and morbidity, protection towards acute infectious illnesses, and potential protection against allergic disorders and autoimmune illness; acute and chronic inflammatory issues; obesity, diabetes mellitus, and other metabolic disorders; and improvement of sure malignancies later in life. This data has been reviewed by Hanson342 in a chic monograph and by others. Nevertheless, we conclude that the development of lactation, an indicator of mammalian evolution, is designed to enhance the survival of the neonate of the species through a remarkable spectrum of instant and long-term protecting functions. Sakakura T, Suzuki Y, Shiurba R: Mammary stroma in improvement and carcinogenesis, J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 18: 189-197, 2013. Macias H, Hinck L: Mammary gland growth, Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol 1:533-557, 2012. Kratochwil K: Experimental analysis of the prenatal development of the mammary gland, vol. Vorherr H: the breast: morphology, physiology and lactation, New York, 1974, Academic Press. In Kretchmern N, Rossi E, Sereni F, editors: Milk and lactation, fashionable problems in paediatrics, vol. Fidler N, Koletzko B: the fatty acid composition of human colostrum, Eur J Nutr 39:31-37, 2000. Stuebe A: the dangers of not breastfeeding for mothers and infants, Rev Obstet Gynecol 2:222-231, 2009. Sann L, Bienvenu F, Lahet C: Comparison of the composition of breast milk from mothers of term and preterm infants, Acta Paediatr Scand 70:115-116, 1981. Bauer J, Gerss J: Longitudinal evaluation of macronutrients and minerals in human milk produced by moms of preterm infants, Clin Nutr 30:215-220, 2011. Saarela T, Kokkonen J, Koivisto M: Macronutrient and power contents of human milk fractions during the first six months of lactation, Acta Paediatrica ninety four:1176-1181, 2005. L�nnerdal B: Nutritional and physiologic significance of human milk proteins, Am J Clin Nutr seventy seven:1537S-1543S, 2003. Savino F, Sorrenti M, Benetti S, et al: Resistin and leptin in breast milk and infants in early life, Early Hum Dev 88:779-782, 2012. Distribution characteristics and concentrations of immunoglobulins at different times after the onset of lactation, J Pediatr 92:546-549, 1978. Fate and absorption of cellular and soluble elements in the gastrointestinal tract of the new child, J Immunol 119:245-248, 1977. Haneberg B: Immunoglobulins in feces from infants fed human or bovine milk, Scand J Immunol 3:191-197, 1974. Weemaes C, Klasen I, Goertz J, et al: Development of immunoglobulin A in infancy and childhood, Scand J Immunol 58:642-648, 2003. Renz H, Brandtzaeg P, Hornef M: the influence of perinatal immune growth on mucosal homeostasis and continual inflammation, Nat Rev Immunol 12:9-23, 2012. Kunz C, L�nnerdal B: Re-evaluation of the whey protein/casein ratio of human milk, Acta Paediatr 81:107-112, 1992. A important appraisal from the nutritional viewpoint, Pediatr Clin North Am 24:17-36, 1977. Spik G, Brunet B, Mazunier-Dehaine C, et al: Characterization and properties of the human and bovine lactoferrins extracted from the faeces of newborn infants, Acta Paediatr Scand 71:979-985, 1982. Wakabayashi H, Yamauchi K, Takase M: Inhibitory effects of bovine lactoferrin and lactoferricin B on Enterobacter sakazakii, Biocontrol Sci 13:29-32, 2008. Blanc B: Biochemical elements of human milk-comparison with bovine milk, World Rev Nutr Diet 36:1-89, 1981. Lindquist S, Hernell O: Lipid digestion and absorption in adolescence: an replace, Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 13:314-320, 2010. L�nnerdal B: Bioactive proteins in breast milk, J Paediatr Child Health 49(Suppl 1):1-7, 2013. Penttila I: Effects of transforming growth factor-beta and formulation feeding on systemic immune responses to dietary beta-lactoglobulin in allergy-prone rats, Pediatr Res 59:650-655, 2006. Soder O: Isolation of interleukin-1 from human milk, Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 83:19-23, 1987. Sarfati M, Vanderbeeken Y, Rubio-Trujillo M, et al: Presence of IgE suppressor components in human colostrum, Eur J Immunol 16: 1005-1008, 1986. Munoz C, Endres S, van der Meer J, et al: Interleukin-1 beta in human colostrum, Res Immunol 141:501-513, 1990. Skansen-Saphir U, Linfors A, Andersson U: Cytokine manufacturing in mononuclear cells of human milk studied at the single-cell degree, Pediatr Res 34:213-216, 1993. Bocci V, von Bremen K, Corradeschi F, et al: Presence of interferon- and interleukin-6 in colostrum of regular women, Lymphokine Cytok Res 12:21-24, 1993. Takahata Y, Takada H, Nomura A, et al: Detection of interferongamma-inducible chemokines in human milk, Acta Paediatr 92:659665, 2003. Korhonen H, Pihlanto A: Food-derived bioactive peptides- alternatives for designing future foods, Curr Pharm Des 9:1297-1308, 2003. Pihlanto A, Korhonen H: Bioactive peptides and proteins, Adv Food Nutr Res 47:175-276, 2003. Mellander O: the physiological significance of the casein phosphopeptide calcium salts. Pennsylvanicus growth selling activity of human milk casein and its derivatives, Int J Biochem thirteen:585-590, 1981. Tomita M, Bellamy W, Takase M, et al: Potent antibacterial peptides generated by pepsin digestion of bovine lactoferrin, J Dairy Sci 74:4137-4142, 1991. Schmidt-Sommerfeld E, Novak M, Penn D, et al: Carnitine and improvement of newborn adipose tissue, Pediatr Res 12:660-664, 1978. Maldonado J, Navarro J, Narbona E, Gil A: the influence of dietary nucleotides on humoral and cell immunity within the neonate and lactating toddler, Early Hum Dev 65(Suppl):S69-S74, 2001.
References - Hornick JL, Fletcher CD. Intestinal perineuriomas: clinicopathologic defi nition of a new anatomic subset in a series of 10 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2005;29(7):859-865.
- Reiner L, Jimenez FA, Rodriguez FL. Atherosclerosis in the mesenteric circulation. Observations and correlations with aortic and coronary atherosclerosis. Am Heart J 1963;66:200.
- Barrett DM, Parulkar BG, Kramer SA: Experience with AS800 artificial sphincter in pediatric and young adult patients, Urology 42:431, 1993.
- Tam J, Loeb C, Grajower D, et al: Neuromodulation for chronic pelvic pain, Curr Urol Rep 19(5):32, 2018.
- Wemmie JA. Neurobiology of panic and pH chemosensation in the brain. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 2011; 13: 475-483.
- Dahlman-Ghozlan K, Hedblad MA, von Krogh G. Penile lichen sclerosus et atrophicus treated with clobetasol dipropionate 0.
- Hai CM, Murphy RA: Ca2+, crossbridge phosphorylation, and contraction, Annu Rev Physiol 51:285n298, 1989.
- Spruance SL, Freeman DJ. Topical treatment of cutaneous herpes simplex virus infections. Antiviral Res 1990;14:305-21.
|