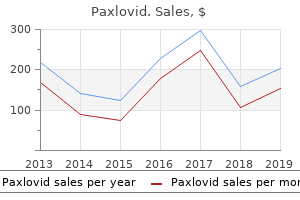
Paxlovid
Kosuke Izumi, M.D., Ph.D. - Research Center for Epigenetic Disease
- Institute for Molecular and Cellular Biosciences
- The University of Tokyo
- Tokyo, Japan
Order paxlovid 200 mg with visaAdverse events following acupuncture: Prospective survey of 32 hiv rates of infection in us paxlovid 200mg visa,000 consultations with docs and physiotherapists hiv infection through skin generic 200mg paxlovid amex. Patient reports of adverse events associated with acupuncture therapy: A potential national survey hiv symptoms of infection order 200 mg paxlovid visa. Rather hiv infection needle prick paxlovid 200 mg on line, injury or disease produces neural alerts that enter an active nervous system that (in the adult organism) is the substrate of past experience, culture, anxiety, and so forth. These mind processes actively participate within the selection, abstraction, and synthesis of knowledge from the entire sensory input. This article focuses upon 4 areas of curiosity to anesthesiologists and psychologists: (a) the major psychological contributions to pain; (b) theories of pain, which are based on psychological assumptions of the nature of perception, including the gate management and neuromatrix models; (c) the measurement of ache; and (d) labor ache, which is influenced by anesthetic blocks in addition to by manipulating psychological variables. Several topics surveyed in this chapter, because of their broad scope and special significance to pain administration, are explored in larger detail inside devoted chapters elsewhere on this quantity. Examples of the latter embrace social and cultural influences upon pain and incapacity (Chapter 29) and the placebo impact (Chapter 36). Cultural Determinants It is often asserted that variations in ache experience from particular person to individual are because of different "ache thresholds"; nonetheless, several thresholds are associated to ache, and it is important to distinguish amongst them. Typically, thresholds are measured by applying a stimulus, such as electrical shock or radiant warmth, to a small space of pores and skin and gradually increasing the depth. Four thresholds could be measured by this system: (a) sensation threshold (or lower threshold)-the lowest stimulus worth at which a sensation corresponding to tingling or heat is first reported; (b) pain perception threshold-the lowest stimulus worth at which the particular person reports that the stimulation feels painful; (c) pain tolerance (or upper threshold)-the lowest stimulus stage at which the subject withdraws or asks to have the stimulation stopped; and (d) encouraged ache tolerance-the identical as (c), however the particular person is encouraged to tolerate greater levels of stimulation. Evidence now suggests that that each one individuals, no matter cultural background, have a uniform sensation threshold. Sternbach and Tursky (2) made careful measurements of sensation threshold, using electrical shock because the stimulus, in Americanborn ladies belonging to 4 different ethnic teams: Italian, Jewish, Irish, and Old American. They found no variations among the many groups in the stage of shock that was first reported as producing a detectable sensation. The sensory conducting equipment, in different words, seems to be basically comparable in all people, in order that a given crucial level of input always elicits a sensation. Cultural background, nonetheless, has a robust effect on the pain notion threshold. For instance, levels of radiant heat which are reported as painful by individuals of Mediterranean origin (such as Italians and Jews) are described merely as warmth by Northern Europeans (3). Similarly, Nepalese porters on a climbing expedition are much more stoic than the Occidental visitors for whom they work. Even although each groups are equally delicate to changes in electric shock, the Nepalese porters require much larger intensities before they call them painful (4). The most putting effect of cultural background, nonetheless, is on pain tolerance ranges. But experiments and scientific observations show that ache is rather more variable and modifiable than many individuals have believed prior to now. Stimuli that produce insupportable pain in a single individual may be tolerated without a whimper by one other. Women of Italian descent tolerate less shock than women of Old American or Jewish origin. In an identical experiment (5) in which Jewish and Protestant ladies served as subjects, the Jewish, but not the Protestant, women increased their tolerance stage after they had been advised that their non secular group tolerated pain more poorly than others. These variations in ache tolerance mirror totally different ethnic attitudes towards pain. Zborowski (6) discovered that Old Americans have an accepting, matter-of-fact attitude towards pain and ache expression. Jews and Italians, on the other hand, are most likely to be vociferous in their complaints and brazenly seek help and sympathy. Jews tend to be involved about the which means and implications of the pain, whereas Italians normally specific a want for quick pain reduction. The main findings of those early studies on ethnic and cultural differences have been supported by more modern empirical work utilizing laboratory-induced pain in a variety ethnic groups, including African Americans, White Americans, White British, and South Asians. In distinction, warmth pain tolerance levels for depth and unpleasantness ratings present differences between ethnic teams (8�10). Differences in pain tolerance may be partially accounted for by different elements, corresponding to hypervigilance and daily levels of ache (8,9), but even after statistically controlling for these variables, ethnicity stays a major factor. Of forty six sufferers whose injuries had been limited to skin (lacerations, cuts, abrasions, burns), 53% had a painfree period. Of 86 sufferers with deep-tissue injuries (fractures, sprains, bruises, amputation of a finger, stabs, and crushes), 28% had a pain-free interval. The outcomes indicate that the relation between damage and pain is very variable and complicated. Hall and Stride (14) discovered that the simple look of the word "pain" in a set of directions made anxious subjects more likely to report a given level of electric shock as painful; the same stage of shock was hardly ever reported to be painful when the word was absent from the directions. Thus, the mere anticipation of pain is sufficient to increase the extent of tension and thereby the intensity of perceived pain. Similarly, Hill, Kornetsky and associates (15,16) have shown that if anxiousness is dispelled (by reassuring the topic that he has management over the pain-producing stimulus), a given level of electric shock or burning heat is perceived as considerably less painful than the same stimulus beneath conditions of high anxiousness. Distraction of attention, nevertheless, is often effective only when the pain is steady or rises slowly in intensity (17). If radiant warmth is targeted on the skin, for instance, the ache might rise so all of a sudden and sharply that topics are unable to control it by distraction. But when the ache rises slowly, folks may use various stratagems to distract their consideration from it. They often discover that the pain really levels off or decreases before it reaches the anticipated insupportable stage. Distraction stratagems are used effectively by some individuals to management ache produced by dental drilling and extraction (18). The scope of distracting and attentiondiverting strategies is in depth, masking direct intentional efforts to scale back ache awareness by way of strategies similar to relaxation and transformational imagery, in addition to indirect approaches that accomplish related goals without distraction being the first objective. Distraction and attention-diverting strategies are effective for many reasons (20). For example, leisure and related activities that require sustained, targeted attention may very well cut back ache depth, as well as ache awareness, by decreasing sympathetic nervous system activity (21). Engaging in distracting, social interactions with others might alter the frequency and use of maladaptive strategies, similar to catastrophizing and avoidance, in part due to response-incompatibility and partly because of improved mood. At the same time, socializing may lead to a decreased emphasis on the significance of ache. Meaning of the Pain-Producing Situation Considerable evidence shows that people connect variable that means to pain-producing conditions and that the that means greatly influences the diploma and quality of pain they really feel. Beecher (11) observed that troopers wounded in battle not often complained of pain, whereas civilians with related surgical wounds usually claimed that they had been in severe ache. Beecher (11) concluded the following from his examine: the frequent perception that wounds are inevitably related to ache, and that the extra intensive the wound the more severe the ache, was not supported by observations made as carefully as attainable within the fight zone. The ache is in very giant part decided by other components, and of nice significance here is the significance of the wound. In the wounded soldier [the response to injury] was aid, thankfulness at his escape alive from the battlefield, even euphoria; to the civilian, his major surgical procedure was a depressing, calamitous event.
Cheap paxlovid 200mg with mastercardWhen conservative remedy by ergotamine tartrate hiv infection statistics australia paxlovid 200mg for sale, isometheptene antiviral plants buy paxlovid 200mg lowest price, triptans antiviral used for rsv paxlovid 200 mg amex, and oxygen inhalation fails stages of hiv infection video buy cheap paxlovid 200 mg, a trial of diagnostic sphenopalatine ganglion block through the attack is warranted. Apart from a quantity of case stories and critiques, just one large observational study was published (124). Radiofrequency lesions of the sphenopalatine ganglion had been made in 66 patients suffering from either episodic (56 patients) or chronic (10 patients) cluster headache. Nine patients complained of hypesthesia of the palate, which disappeared in all instances inside three months (124). Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia Radiofrequency lesioning of glossopharyngeal ganglion appears to be appropriate for the treatment of throat pain as a result of cancer or idiopathic glossopharyngeal neuralgia (125). The identical etiologies have been advised as for trigeminal tic, except that it apparently has not been acknowledged in a quantity of sclerosis. It tends to be less extreme than trigeminal tic, with 67% of sufferers suffering a single episode (29% in trigeminal tic) and 42% requiring no therapy (9% in trigeminal tic) (124�130). Like trigeminal tic, the condition could be diagnosed solely on the idea of the history of the ache with the absence of neurologic or imaging abnormalities, a tough exercise for the rationale that symptomatology is complicated. Apart from rare purely syncopal attacks, most sufferers complain of ache, though syncopal attacks, first described in 1942 by Riley, might accompany the ache (127,131). Even typical pain could additionally be preceded by itching, tickling, tingling, or a sense of sticking, choking, or scratching from a overseas physique and, as in trigeminal tic, could also be adopted by an after-pain. Both forms of ache begin both (a) within the ear, mandibular angle, eustachian tube, or entrance of the ear or (b) within the pharynx, tonsil, or posterior tongue, and may project from both to the other site. Triggering is sometimes seen, induced by swallowing (especially of cold fluids), yawning, chewing, coughing, sneezing, clearing the throat, blowing the nostril, talking, or turning the head, or by touching the gingivae, external canal of the ear, tongue, periauricular skin, tonsillar pillars, or pharynx; typically triggering happens from outdoors glossopharyngealvagal territory. It may be accompanied by tinnitus, by soreness in the cheek or mandible, and, like trigeminal tic, sometimes by sensory loss. There are a number of weirder signs: uncontrolled gestures, involuntary coughing, dyspnea, hoarseness, sweating, dryness of the mouth, salivation, choking, hiccups, flushing, mydriasis, and tearing. In 10% of sufferers, bradycardia, hypotension, asystole, syncopal fits accompany the ache, generally leading to sudden demise. In this condition, open surgery may be preferable to keep away from the indiscriminate damage to different lower cranial nerves that may follow the percutaneous approach, inflicting hoarseness and cardiovascular instability (105,one hundred twenty five,132�135). The percutaneous approach consists of introducing a needle into the exterior pars nervosa portion of the jugular canal during which the vein lies laterally. The foramen is located according to, however posterior to , the foramen ovale, behind the temporomandibular joint and anterior to the occipital condyle, medial to the carotid artery. The lesion is enlarged till the tonsillar pharynx is analgesic and the gag reflex is lessened. Since vocal twine paralysis might happen, the percutaneous technique is healthier suited to circumstances of cancer than to these of tic. Isamat and associates (125) used this process in four patients with glossopharyngeal tic. Tew and co-workers (105) and Lazorthes and Verdie (133) relieved ache in three patients, but dysarthria and dysphasia were noticed postoperatively. Tew and associates (105) handled nine sufferers with cancer in glossopharyngeal distribution, eight of whom have been relieved. Broggi (135) used the procedure in 5 patients with cancer, with two excellent outcomes and two recurrences successfully managed by reoperation. All sufferers introduced after surgery with some impairment in glossopharyngeal function (136). Sindou and colleagues (130) reviewed 15 circumstances from the literature and three of their own handled by thermocoagulation, discovering issues greater than in instances treated by open means. Complications affected 10 (56%) sufferers; along with the above-mentioned cardiac complications, seven sufferers suffered sensory loss; six, suppression of gag reflex; 5, transient dysphagia; one, persistent dysphagia; and one, deafness. Ori and colleagues (134) reported thermocoagulation in 9 patients, in considered one of whom two repetitions were required; six of 11 procedures caused cardiac dysrhythmia or over a 50% fall in blood pressure or coronary heart fee, causing syncope in two instances and seizures in one. A lateral cervical method is also obtainable, as described by Salar and associates (137). The needle is launched anterior to the mastoid process, below the external auditory meatus, perpendicular to the skin and is advanced till the styloid process is reached at a depth of 1. The needle is pulled back and pushed throughout the styloid posteriorly for two cm, until the tip lies tangential to and below the lateral a part of the jugular foramen. Vagal hyperactivity can also be seen with a fall in blood strain and heart rate, during which case the needle must be repositioned. Most doubtless, those who exhibit a pattern of mechanical and particularly chilly allodynia could benefit from a sympatholysis (143) (see also Chapter 46). Anatomy Cervical Level Preganglionic fibers to the top and neck depart the spinal canal with the ventral roots of T1 and T2, after which proceed as white rami communicans before becoming a member of the sympathetic chain and passing cephalad to synapse at the inferior, center, or superior cervical ganglion. All preganglionic nerves either synapse or pass through the inferior (stellate) ganglion; subsequently, the stellate ganglion must be focused to obtain sympathetic block of the head and neck (see Chapter 39). Thoracic Level Sympathetic fibers to the higher extremity exit with T2 to T8 ventral roots and journey as white rami communicans to the sympathetic chain before they synapse the second and, presumably, the third thoracic ganglion. Thus, a T2 and/or T3 lesion will reliably deprive the upper extremity from the sympathetic innervation (144) (see Chapter 39). Currently, the indications appear to embody hyperhydrosis, vascular insufficiency, and pain. In basic, sympathectomy is much less helpful in controlling intractable "nonmalignant" pain than that of cancer ache, though the sympathetic dystrophic changes that sometimes accompany deafferentation pain could also be relieved (138�140) with out affecting the underlying pain. The compelling evidence of efficacy as either a diagnostic or ther- Abdomen Innervation of the viscera originates in T5 to T11, with occasional T4 and T12 preganglionic fibers. T5 to T9 preganglionic fibers coalesce to construct the higher splanchnic nerve; T10 and T11 constitute the lesser and T12, the least splanchnic nerves (145). Lumbar Level Each lumbar sympathetic chain lies at the anterolateral facet of the vertebral bodies L1 to L4, whereas the L5 ganglion is situated extra dorsally at the stage of the L5�S1 intervertebral Chapter forty two: Percutaneous Neural Destructive Techniques 1021 disk. The sympathetic ganglia of the lumbar sympathetic chain are variable in each numbers and place. There tends to be fusion of L1 and L2 ganglia in most patients, and ganglia are aggregated on the L2�L3 and L4�L5 disks. Upper Thoracic Percutaneous Sympathectomy Thoracic sympathectomy has been used to handle numerous painful situations and vascular insufficiency of the upper extremities. Acute vascular occlusive events, similar to Raynaud syndrome, are often accompanied by excruciating pain refractory to systemic analgesics. Sympathetic block and sympathectomy can have main roles for both dietary blood circulate restoration and pain control (150) (see also Chapter 39). Despite the excessive rate of recurrence, when used in Raynaud syndrome, thoracic sympathectomy clearly produced a high success fee and confirmed potential for lowering the severity of refractory symptoms (151). Although chemical thoracic sympathectomy was one of the first described neural damaging procedures (4), it was ultimately deserted.
Best 200mg paxlovidThe latest developments in regional anesthesia hiv infection onset cheap paxlovid 200mg otc, such as longer-acting hiv infection process in the body cheap paxlovid 200 mg visa, safer native anesthetics and improved strategies hiv infection leads to depletion of buy 200 mg paxlovid fast delivery, ought to end in improved outcomes in orthopedic surgical procedure hiv infection rates in zimbabwe discount paxlovid 200 mg overnight delivery, including lowered postoperative ache and optimized patient rehabilitation. The effects of clonidine added to mepivacaine for paronychia surgery underneath axillary brachial plexus block. Chlorhexidine versus povidone iodine in preventing colonization of steady epidural catheters in kids: A randomized, controlled trial. Evaluation of continuous femoral nerve block in hemophiliacs after total knee substitute. Neuraxial anesthesia and low-molecularweight heparin prophylaxis in main orthopedic surgery within the wake of the most recent American Society of Regional Anesthesia guidelines. Worsening of neurologic signs after epidural anesthesia for labor in a Guillain-Barr� affected person. Is there a spot for interscalene block carried out after induction of general anaesthesia Small risk of significant neurologic complications related to lumbar epidural catheter placement in anesthetized sufferers. Neurologic complications after placement of cerebrospinal fluid drainage catheters and needles in anesthetized sufferers: Implications for regional anesthesia. The feasibility and efficacy of brief axillary catheters for emergency upper limb surgery: A descriptive collection of one hundred twenty cases. Infraclavicular brachial plexus block versus humeral block in trauma sufferers: A comparison of patient consolation. Pre-operative analgesia for patients with femoral neck fractures using a modified fascia iliaca block approach. The use of regional anaesthesia in patients susceptible to acute compartment syndrome. Transient neurologic symptoms after spinal anesthesia: An epidemiology research of 1. A comparison of minidose lidocaine-fentanyl spinal anesthesia and local anesthesia/propofol infusion for outpatient knee arthroscopy. Minidose bupivacaine-fentanyl spinal anesthesia for surgical repair of hip fracture within the aged. Small-dose intrathecal lidocaine versus ropivacaine for anorectal surgery in an ambulatory setting. Effects of regional anesthesia medical pathway techniques on process effectivity and recovery profiles in ambulatory orthopedic surgery. Ambulatory discharge after long-acting peripheral nerve block 2382 blocks with ropivacaine. Early but no long-term advantage of regional compared with general anesthesia for ambulatory hand surgery. Interscalene brachial plexus block with a continuous catheter insertion system and a disposable infusion pump. Continuous infraclavicular brachial plexus block for postoperative ache management at residence: A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled examine. Continuous popliteal sciatic nerve block for postoperative pain control at home: A randomized, doubleblinded, placebo-controlled study. Continuous interscalene brachial plexus block for postoperative pain control at house: A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled examine. Ambulatory continuous interscalene nerve blocks lower the time to discharge readiness after total shoulder arthroplasty: A randomized, triple-masked, placebo-controlled study. Total knee arthroplasty as an overnight-stay process using continuous femoral nerve blocks at house: A prospective feasibility research. Infraclavicular brachial plexus block utilizing a multiple injection method and an approach in the cranial course in a patient with anticipated difficulties in tracheal intubation [Spanish]. Ankylosing spondylitis: Lateral method to spinal anaesthesia for decrease limb surgical procedure. Effects of intravenous patientcontrolled analgesia with morphine, continuous epidural analgesia, and continuous three-in-one block on postoperative pain and knee rehabilitation after unilateral total knee arthroplasty. Introducing anesthesia clinical pathways to enhance processes and outcomes and to cut back nursing labor depth in ambulatory orthopedic surgical procedure. Spinal versus basic anesthesia for orthopedic surgery: Anesthesia drug and supply prices. A comparative study of basic anesthesia, intravenous regional anesthesia, and axillary block for outpatient hand surgery: Clinical consequence and value analysis. A retrospective comparison of prices for regional and basic anesthesia methods. Postoperative analgesia after major backbone surgical procedure: Patient-controlled epidural analgesia versus patientcontrolled intravenous analgesia. Complications related to lumbar laminectomy: A comparability of spinal versus common anesthesia. Preemptive epidural morphine for postoperative ache aid after lumbar laminectomy. Analgesic impact of low-dose intrathecal morphine after spinal fusion in youngsters. Intrathecal morphine: Dosage and efficacy in youthful sufferers for management of postoperative pain following spinal fusion. A prospective analysis of anesthesia for posterior lumbar backbone fusion: the effectiveness of preoperative epidural anesthesia with morphine. Preemptive analgesia for postoperative ache reduction in lumbosacral backbone surgeries: A randomized controlled trial. Double epidural catheter with ropivacaine versus intravenous morphine: A comparison for postoperative analgesia after scoliosis correction surgery. The efficacy of surgically placed epidural catheters for analgesia after posterior spinal surgery. Sedation with target-controlled propofol infusion throughout shoulder surgery underneath interscalene brachial plexus block in the sitting position: Report of a sequence of a hundred and forty patients. The effect of exogenous epinephrine on the incidence of hypotensive/bradycardic occasions during shoulder surgery in the sitting place throughout interscalene block. The use of metoprolol and glycopyrrolate to prevent hypotensive/bradycardic events during shoulder arthroscopy within the sitting position under interscalene block. Intraarticular morphine and bupivacaine reduces postoperative pain after rotator cuff restore. Anesthetic methods for discount of acute shoulder dislocations: A potential randomized study comparing intraarticular lidocaine with intravenous analgesia and sedation. Total elbow arthroplasty as an outpatient process utilizing a steady infraclavicular nerve block at home: A prospective case report. Single, double or a quantity of injection methods for axillary brachial plexus block for hand, wrist or forearm surgery. A systematic evaluation of adjuncts for intravenous regional anesthesia for surgical procedures. Hemodynamic results of spinal anesthesia in the elderly: Single dose versus titration by way of a catheter. Spinal anesthesia utilizing single injection small-dose bupivacaine versus continuous catheter injection strategies for surgical restore of hip fracture in elderly patients.
Quality paxlovid 200 mgThese neurons receive convergent input from large-diameter afferents being activated by stimulation of low-threshold rapidly conducting fibers hiv infection through needle prick paxlovid 200mg on line, as nicely as by mild touch hiv infection from dried blood paxlovid 200mg generic, hair movement hiv infection symptoms cdc cheap paxlovid 200mg on-line, and vibration hiv infection in zambia generic paxlovid 200 mg on-line. Rather, such observations would suggest that fibers decussating inside the brainstem have been interrupted. It has been estimated that the visceral afferents account for about 10% of the fibers that run within the dorsal roots. Yet these visceral afferents serve an organ floor space equivalent to about 25% of the body floor, which suggests that visceral sensitivity shall be poorly localized. To understand visceral ache, one should recognize that these afferents appear to converge onto somatotopically organized dorsal horn systems, which receive cutaneous enter. Gallbladder and urinary bladder stimulation serves to excite cells which have a corresponding cutaneous dermatomal subject. Such segments correspond with the cutaneous innervation of that particular spinal section. With regard to thoracic enter, subsequently, sensory info from thoracic viscera will serve to activate sensory afferents traveling with sympathetic fibers that terminate in cord segments T1�T4. Similarly, sensory enter that ends in exercise in visceral sympathetic afferents will enter the spinal wire at segments T5�T12/L1, touring through the splanchnic nerves via the celiac plexus. These afferents enter the dorsal horn of the spinal twine to terminate within the dorsal grey matter. At this level, convergence with somatic afferent input onto frequent postsynaptic neurons happens. As famous in earlier sections, both spinoreticular and spinothalamic projecting neurons confirmed such viscerosomatic and muscular somatic convergence as a typical property. Ascending Projections After the injection of horseradish peroxidase into the ventrobasal thalamus of the rat, retrogradely labeled neurons are discovered all through the entire trigeminal sensory advanced, with the attainable exception of the nucleus oralis of the spinal nucleus. Conversely, cold block of the nucleus caudalis decreases the responses of neurons in the nucleus oralis and major sensory nucleus to peripheral stimuli. Behavioral proof for such a facilitatory action of nucleus caudalis neurons on afferent impulse transmission within the nucleus oralis and main sensory nucleus has been obtained within the cat. Medullary Reticular Formation Given the ipsilateral spinopetal projections and the reticulothalamic projections from the medullary reticular neurons Chapter 32: Physiologic and Pharmacologic Substrates of Nociception after Tissue and Nerve Injury 719 to the intralaminar and ventrobasal nuclei of the thalamus, the medullary reticular formation has been suggested as a "relay" station for the rostrad transmission of nociceptive information. Retrogradely labeled neurons have been localized to neurons in the medullary reticular formation following the injection of horseradish peroxidase into the thalamus. Neurons of the lateral reticular nucleus,498 the nucleus gigantocellularis,574-578 the nuclei raphe magnus and pallidus,342 and the nucleus locus coeruleus579 are activated by noxious or innocuous stimuli, or both, utilized to their peripheral receptive fields. These receptive fields, each ipsilateral and contralateral, are massive, usually together with an entire limb or extending over the whole physique. Many of those neurons which would possibly be conscious of somatic enter are also activated by auditory and visual stimuli. Thus, stimulation of spinothalamic fibers could produce a direct drive of thalamic substrates in a manner unbiased of the system within the nuclei being stimulated. These syndromes might be disagreeable, and such sensations themselves might underlie the "aversive" characteristics of local stimulation. Parabrachial Nucleus the parabrachial nucleus is a inhabitants of neurons that can be discriminated into a variety of subnuclei, every with distinct input�output relationships. Singleunit recording has recognized nociceptive-responsive cells in the parabrachial region. Of particular interest are the large projections that connect the central grey matter with the subjacent tegmentum. Thus, cells that appear to be activated only by noxious tail pinch may be pushed by electrical stimulation of the coccygeal nerve at intensities that evoke only a fast-conducting (A) volley. Neurons of the mesencephalic reticular formation show a high degree of convergence with bilateral receptive fields that will include the entire physique. The stimulus intensity that evokes escape conduct can additionally be the minimal intensity that produces a maximum discharge rate in that neuron. The discharge frequency of thalamic neurons has been correlated with the depth of stimuli delivered to the nucleus gigantocellularis and the escape threshold in awake animals. Stimulation of the nucleus gigantocellularis could additionally be used to evoke realized escape conduct in rats and cats. Additionally, such stimuli can serve as an unconditioned stimulus in pavlovian conditioning paradigms. In unanesthetized animals, the activity of nucleus gigantocellularis neurons covaries with the intensity of somatic stimulation, and stimuli utilized to the nucleus gigantocellularis will drive thalamic neurons, evoke escape habits, and assist pavlovian conditioning. Lesions of the nucleus gigantocellularis have been proven to attenuate the response to otherwise aversive stimuli within the absence of any important signs of motor impairment. Several cautionary notes ought to be thought-about in these and other studies in which the behavioral results of stimulating and lesioning of supraspinal methods are used to look at the involvement of a given construction in a pain occasion. The observation that electrical stimulation of the mesencephalic reticular formation would excite spinothalamic cells suggests that pathways either originating in, or passing through, the mesencephalon could exert an excitatory effect on the exercise of spinothalamic neurons in any other case evoked by noxious peripheral stimuli. Note the midline and intralaminar projections into the limbic forebrain (anterior cingulate) and inferior insula and the ventrolateral thalamus into the somatosensory cortex. Populations of neurons in the posterior nuclear advanced respond to noxious stimuli. Electrical activation of A afferents from tooth pulp, presumably noxious in nature, additionally evokes exercise in neurons of the posterior thalamic complex. Input to these nuclei is contributed primarily by the spinothalamic tract481,504,612,613 and the nucleus reticularis gigantocellularis. These reticulothalamic projections are thought to be a serious supply of input to the intralaminar advanced. The medial areas receiving ascending input are composed of a number of nuclear teams, together with the centromedian and parafascicular area. The centromedian and parafascicular are stated to receive enter from the nucleus reticularis gigantocellularis (medulla). The mediodorsal is of particular curiosity, because it receives enter primarily from spinothalamic tract neurons originating in lamina I (high-threshold marginal cells). Populations of neurons in the medial and intralaminar nuclei reply to noxious stimuli and encode the stimulus intensity within the period and frequency of patterned discharges. Two courses of neurons have been described: these activated with a brief latency to response and those activated with a long latency. The former class of neurons is discovered predominantly in the basomedial parts of the parafascicular nucleus, and the latter group is localized to the dorsal centromedian and parafascicular regions. Limbic System Although these feedback document those pathways which are part of the traditional somatosensory projection system, it has become increasingly apparent that different areas play an necessary role. These systmes have been proven to play a profound position in modulating the ache response. In addition to the somatosensory cortex, different areas have additionally been proven to be activated. As reviewed earlier, these areas receive enter from medial features of the thalamus (as opposed to the basic relay centers of the lateral thalamus).
Quality 200mg paxlovidA 2 to 5 mL quantity of local anesthetic is injected close to quinolones antiviral order paxlovid 200mg with amex each of those branches (preferably starting with the posterior department antivirus windows xp paxlovid 200 mg online, then the anterior branch on elimination of the block needle) to anesthetize all obturator nerve fibers (see additionally Chapter 14) hiv infection rates us 2012 200mg paxlovid with visa. Metatarsal and Transthecal Blocks the ideas sustaining metacarpal and transthecal blocks are legitimate for anesthetizing the toes hiv infection prevalence worldwide generic paxlovid 200 mg line. However, performing a transthecal block is comparatively more difficult than at the level of the hand in small infants. Conversely, metatarsal blocks are simpler (but painful in awake children): A normal needle is inserted at the dorsum of the foot, close to the medial then the lateral border of the bottom of the primary metatarsal bone till the tenting produced by the tip of the needle is perceived by palpation on the sole of the foot (225). Sciatic Nerve Blocks Popliteal Sciatic Nerve Blocks the sciatic nerve can be simply and safely blocked in the upper portion of the popliteal fossa, where its two constitutive branches separate from each other. All techniques used in adults are applicable to children; however, the only one consists of inserting the kid in the semiprone place (Sim position) with the unblocked side down (221). The needle insertion site lies at the point the place the tendons turn out to be adjacent at the upper summit of the popliteal fossa. The landmarks are the mid-axillary line and the lower borders of the ribs, corresponding to the intercostal nerves to be blocked. The insertion websites are identified barely under (2 mm) the crossing of the midaxillary line with the decrease border of the related ribs. The Tuohy needle is then inserted posteriorly and cephalad at every insertion website, at an 80-degree angle to the chest whereas continuous strain is exerted on the barrel of the syringe (as for an epidural). A lack of resistance is felt because the intercostal house is entered: the local anesthetic is then injected slowly (1 mL of zero. Longer period of pain relief can be obtained by inserting a catheter into the intercostal space, centering on the realm to preserve anesthetized (this catheter can also be put in beneath visible management by the surgeon on the end of the surgery) (227,228). Chapter 27: Neural Blockade for Pediatric Surgery 621 the method has a quantity of limitations. It requires a number of punctures, thus increasing the failure rate and danger of pleural penetration. Only diluted native anesthetic should be injected and, if epinephrine is added, care must be taken to not inject greater than four g/kg to avoid vital hemodynamic adjustments (see Chapter 16). When a large quantity of native anesthetic is injected in a single intercostal space, the solution can unfold to adjacent ipsilateral but in addition contralateral intercostal areas (via the paravertebral space). This unpredictable unfold of native anesthetic, along with the danger of pneumothorax, requires that the kid stays hospitalized. Rectus Sheath/Periumbilical Block the rectus sheath/periumbilical block process consists of injecting native anesthetic within the substance of the rectus abdominis muscle, where the terminal department of the tenth intercostal-which provides sensory innervation to the periumbilical area-courses (241,242). The approach is really helpful for intra- and postoperative analgesia of periumbilical surgical procedure, especially umbilical hernia repair. It could be tailored by moving the insertion site to the relevant level to present analgesia to any restore of hernias of the linea alba. An grownup examine (gynecologic surgery) reported good postoperative analgesia after laparoscopic surgical procedure (243) (see Chapter 16). A short-bevel needle is inserted medially at a 60-degree angle to the skin, in the path of the higher border of the umbilical ring, until the rectus sheath is contacted (a robust resistance is felt), then penetrated. A typical "crack" is usually perceived at the identical time as a loss of resistance is felt. Some authors recommend injecting half the dose at the higher border and half at the decrease border of the umbilical ring, then injecting a small amount (1 mL) subcutaneously while the needle is withdrawn (242). An ultrasound-guided method was lately reported (244); it permits exact identification of the rectus aponeurosis and visual spread of the local anesthetic, but has no different advantage when it comes to reliability or security as compared to the "blind" technique. The success fee of the method is extraordinarily high and, until a pointy needle is used, the morbidity is minimal as a outcome of the internal part of the rectus fascia provides the same resistance because the Interpleural/Intrapleural Block the technique of interpleural (or intrapleural) block consists of injecting an area anesthetic between the two sheaths of the pleura-that is, within the interpleural space-without making a pneumothorax. This technique elicited some curiosity a decade ago, in an attempt to present ache reduction following thoracotomy, however contradictory outcomes had been reported. Paravertebral Thoracic Space Block During the final 20 years, thoracic paravertebral blocks have elicited numerous purposes, together with in the pediatric inhabitants (231,232). The benefits of this approach are that it avoids thoracic approaches to the epidural space and it supplies unilateral analgesia of the chest that may be extended for days following catheter placement and infusion of a local anesthetic. The method is basically the identical in children and in adults (see Chapters 14 and 16). The needle is inserted at right angles to the skin until contact is made with the related transverse process. It is then "walked" upward along the surface of this course of till the costotransverse ligament is pierced, which supplies a loss-of-resistance feeling, and a motor response is elicited in related intercostal muscle tissue. A catheter may be inserted for 2 to three cm (with some difficulties most of the time), and the native anesthetic is injected (starting dose of 0. As in adults, the endothoracic fascia most likely performs a significant role within the spread of the native anesthetic (233,234). Spread to the lumbar paravertebral house and in addition to the belly cavity (through the medial and lateral arcuate ligaments) (235), the epidural space, and the contralateral thoracic paravertebral area (236) is frequent. Complications include pleural penetration, dural puncture, seizures as a outcome of unintentional vascular injection, and thoracic epidural spread inflicting Horner syndrome (238,239). Occasionally, especially when the method is first introduced, the surgeon might complain of "edema" at skin incision however, with expertise, will see this as an assist to the identification and dissection of the completely different fascial planes. Block of Ilioinguinal, Iliohypogastric Nerves and Genital Branch of Genitofemoral Nerves Blocking these three nerves offers complete analgesia of the inguinal space including the spermatic cord, thus providing anesthesia and analgesia for virtually all surgeries in this region, particularly inguinal hernia, hydrocele of the wire, and undescended testis. The classical approach requires three injections, two at the degree of the anterior superior iliac spine and one on the stage of the pubic backbone. Many pediatric anesthesiologists only carry out a twoinjection technique near the anterior superior iliac backbone, aiming to block the ilioinguinal and the iliohypogastric nerves only. Not surprisingly, the quality of analgesia produced is usually unsatisfactory, as sensory provide by the genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve remains unchanged. The contribution of the genitofemoral nerve may be very limited; in these circumstances, more or less, an ilioinguinal/iliohypogastric nerve block successfully reduces postoperative ache. A simplified technique takes advantage of the close proximity, in the identical fascial aircraft, of the three nerves near the subcutaneous inguinal ring shaped by the aponeurosis of the external indirect muscle and giving passage to the spermatic cord (round ligament in girls). With the affected person in the dorsal decubitus position, the umbilicus and ipsilateral anterior superior iliac backbone are localized. A short-beveled needle (a 22- or 20-gauge 50-mm long epidural needle is the most effective option) is inserted posteriorly and caudally in the direction of the midpoint of the inguinal ligament, till the superficial layer of the aponeurosis of the external indirect muscle (which provides sturdy resistance) is pierced with a clearly identifiable "crack. Bupivacaine is extra quickly absorbed from the injection website than ropivacaine (247). A catheter can simply be inserted by way of the Tuohy needle to present extended analgesia (see additionally Chapter 16). If the surgeon exerts too vigorous a traction on the wire, then autonomic reactions are elicited. Pudendal Nerve Block In latest years, the pudendal nerve block has been more and more performed in each adults and youngsters present process perineal surgical procedure. The approach is especially indicated to complement an ilioinguinal/iliohypogastric nerve block in case of orchidopexy with scrotal incision. Blocking the pudendal nerves is straightforward near the ischial tuberosity, in the ischiorectal fossa, the place they give off their terminal branches.
Cheap 200 mg paxlovid with visaRecently hiv infection rates in poland order paxlovid 200 mg with mastercard, Ilfeld and colleagues have shown hiv infection timeline trusted paxlovid 200mg, in a randomized hiv infection cure buy 200mg paxlovid amex, double-blinded research time between hiv infection and symptoms buy paxlovid 200mg low price, that native anesthetic infusion through a portable pump via a popliteal sciatic perineural catheter is protected and supplies efficient analgesia (170). By distinction, within the placebo group, solely 7% of sufferers delayed their first opioid consumption till after infusion discontinuation, and the average resting ache score was three to 4. In addition to improved ache management, decreases in opioid consumption, and fewer side effects, they reported a big decrease in sleep disturbances within the ropivacaine group. A comparison of neuraxial block versus common anesthesia for elective complete hip replacement: A meta-analysis. The effect of anesthetic technique on postoperative outcomes in hip fracture restore. Spinal anesthesia versus common anesthesia for hip fracture repair: A longitudinal remark of 741 elderly patients throughout 2-year follow-up. Epidural infusion of bupivacaine and fentanyl reduces perioperative myocardial ischaemia in elderly sufferers with hip fracture: A randomized controlled trial. Preoperative cardiac events in elderly patients with hip fracture randomized to epidural or conventional analgesia. Combined lumbar and sacral plexus block compared with plain bupivacaine spinal anesthesia for hip fractures in the elderly. Intravenous however not perineural clonidine prolongs postoperative analgesia after psoas compartment block with zero. Effect of postoperative epidural analgesia on rehabilitation and pain after hip fracture surgical procedure: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Intraoperative epidural anesthesia and postoperative analgesia with levobupivacaine for main orthopedic surgical procedure: A double-blind, randomized comparison of racemic bupivacaine and ropivacaine. Subarachnoid sufentanil for early postoperative ache administration in orthopedic patients: A placebocontrolled, double-blind research using spinal microcatheters. Postoperative analgesia with 3-in-1 femoral nerve block after prosthetic hip surgery. Lumbar plexus block reduces ache and blood loss related to total hip arthroplasty. Continuous psoas compartment block for postoperative analgesia after total hip arthroplasty: New landmarks, technical pointers, and scientific evaluation. Intrathecal morphine provides higher postoperative analgesia psoas compartment block after major hip arthroplasty. A procedure-specific systematic review and consensus suggestions for analgesia after complete hip alternative. A complete anesthesia protocol that emphasizes peripheral nerve blockade for total knee and complete hip arthroplasty. Femoral-sciatic nerve blocks for complex outpatient knee surgery are related to much less postoperative pain earlier than same-day discharge. Analgesia after whole knee arthroplasty: Is continuous sciatic blockade wanted in addition to steady femoral blockade The value of including sciatic block to continuous femoral block for analgesia after whole knee replacement. Plasma concentrations of bupivacaine following combined sciatic and femoral 3 in 1 nerve blocks in open knee surgical procedure. Post-operative analgesia following whole knee substitute: An evaluation of the addition of an obturator nerve block to combined femoral and sciatic nerve block. Patient satisfaction and effectiveness of lumbar plexus and sciatic nerve block for total knee arthroplasty. Continuous versus singleinjection lumbar plexus blocks: Comparison of the consequences on morphine use and early restoration after complete knee arthroplasty. Unilateral spinal anesthesia using low-flow injection via a 29-gauge Quincke needle. Lateral popliteal sciatic nerve block compared with ankle block for analgesia following foot surgical procedure. Popliteal sciatic nerve block aided by a nerve stimulator: A reliable method for foot and ankle surgical procedure. A comparability of the posterior versus lateral approaches to the block of the sciatic nerve in the popliteal fossa. Ultrasound guidance for a lateral method to the sciatic nerve in the popliteal fossa. Does the sciatic nerve approach influence thigh tourniquet tolerance throughout below-knee surgery Continuous lateral sciatic blocks for acute postoperative pain administration after main ankle and foot surgical procedure. Continuous popliteal sciatic nerve block for postoperative ache management at residence: A randomized, 171. Postoperative analgesia by sciatic nerve block after foot surgery: Continuous versus patient-controlled strategies. Continuous popliteal sciatic nerve block: An original approach to provide postoperative analgesia after foot surgical procedure. Continuous subgluteus sciatic nerve block after orthopedic foot and ankle surgical procedure: Comparison of two infusion methods. Continuous psoas compartment block for anesthesia and perioperative analgesia in patients with hip fractures. Nerve blocks (subcostal, lateral cutaneous, femoral, triple, psoas) for hip fractures (Cochrane Review). Outpatient surgical procedure has grown to roughly 65% of all surgical procedures performed within the United States, and using regional anesthesia in the outpatient setting also can enhance effectivity and cost effectiveness, improve restoration, provide postdischarge analgesia, and shorten discharge time. Although regional anesthesia may reduce the need for opioids in such sufferers, commonplace pointers for monitoring and postoperative remark however should be observed (7). The indications and contraindications for regional methods additionally stay the same: the presence of coagulopathy, infection, lack of cooperation, and neurologic disease should be thought of. Ambulatory patients are regularly interviewed by the anesthesiologist solely on the morning of surgery, and a detailed explanation of a regional approach and acceptance by the patient can consume treasured time. Preferably, a preoperative analysis could be scheduled in advance, or a cellphone name can at least provoke the tutorial process. Ideally, the surgeon might be an advocate of regional methods and start the acceptance process throughout her preoperative counseling. As with all regional techniques, the smallest quantity of the native anesthetic drug in an answer of the bottom attainable concentration that will give the specified effect should be used. Because of the danger of toxicity, as properly as the more widespread danger of respiratory melancholy from sedative medicines, a devoted observer skilled in superior life assist should be available to monitor psychological status, especially with local anesthesia and sedation offered by the surgeon. Multiple research have shown these advantages, particularly with extremity surgery (4), though quicker discharge has been elusive.
Diseases - Asphyxia neonatorum
- Hennekam Beemer syndrome
- Francois dyscephalic syndrome
- Hydronephrosis
- Retinal telangiectasia hypogammaglobulinemia
- Barrett syndrome
- Hyperphenylalaninemia due to GTP cyclohydrolase deficiency
Paxlovid: 200 mg
Buy paxlovid 200mg overnight deliverySimilar analgesia was offered by a bolus of 50 mg of bupivacaine alone and by smaller bolus doses of bupivacaine (25 or 12 general symptoms hiv infection order 200 mg paxlovid with visa. In one examine hiv infection muscle pain effective paxlovid 200 mg, the diploma of hypotension after a thoracic epidural bolus was considerably less when a decreased dose of native anesthetic was utilized in mixture with fentanyl (441) hiv infection statistics 2014 cheap paxlovid 200mg fast delivery. In the examine by Kopacz and colleagues (440) anti muslim viral video generic paxlovid 200 mg free shipping, hypotension occurred in all therapy groups, including patients receiving opioid alone. Hypotension might have been a residual impact of the big dose of intraoperative native anesthetic, as a result of the timing of the hypotension was not reported. In the remaining research, hypotension was not observed in any remedy group (439,442). A important reduction in the diploma of motor and sensory block was reported by Cooper and colleagues (439) when the dose of native anesthetic was decreased by combination remedy, however many patients in both the local anesthetic and the mix teams had problem mobilizing. In other research, no vital difference in the diploma of motor block was seen in the local anesthetic or mixture groups (438,442,443). One examine reported a discount in sedation with mixture remedy compared with sufentanil alone (443). These research offered no proof for the flexibility of combination therapy to scale back the side effects of nausea, vomiting, or pruritus in contrast with opioid alone (438,440), despite reductions in opioid necessities with mixture therapy (439,442,443). This failure to discern differences in unwanted effects associated with dosage sparing may in part relate to the comparatively small numbers of sufferers in each therapy arm (10�24 patients) and consequent underpowering. In the study by Kopacz and colleagues (440), the pattern measurement was based on estimates of the primary efficacy end-point (time to first rescue analgesia). The study by Torda and colleagues (441) included calculations based mostly on adjustments in ache scores, in addition to adjustments in one chosen aspect effect (hypotension). In abstract, 4 research help improved analgesic efficacy with the mix of a local anesthetic and an opioid in contrast with either drug administered alone. However, in two other studies, no distinction in analgesic efficacy was found between the combination and the opioid alone (439) or the mix versus both single drug (441). Most studies point out that combination therapy reduces dose necessities for either the native anesthetic or the opioid compared to their administration as single medicine. This dose discount was associated with decreased native anesthetic-related unwanted facet effects (hypotension and motor block) however little (sedation) or no (vomiting and pruritus) reduction in opioid-related adverse effects. Chronic and Cancer Pain Spinal coadministration of a local anesthetic and an opioid has been used extensively for the administration of chronic ache. In fifty one patients with most cancers pain, 17 proceeded from a morphine-only to a morphine + bupivacaine spinal infusion. Pain depth subsequently improved in 10 patients, with only reasonable enchancment in four patients, whereas 11 patients required continuation of oral morphine supplementation (447). In these case collection, bupivacaine was added when ache management was inadequate with the opioid alone. Interpretation of those data is hampered by lack of randomization, variable inclusion standards (particularly source and sort of pain), and variable definitions of passable ache aid. Two prospective studies have proven improvement in analgesia with bupivacaine and morphine combos compared with opioid alone, though there was neither blinding nor randomization in a single examine (449) and there was incomplete blinding in the other (437). As required clinically, infusions were titrated to impact in every affected person, but the resultant variation in dosing makes evaluation of the efficacy and side-effect profile of combination versus single-drug therapy difficult. A discount in opioid-related side effects was reported in a single examine after the initiation of mixture therapy (450), but in most series the numbers studied are too few to determine any distinction in the incidence of unwanted effects with single or mixture therapy. In summary, only one trial satisfied the selection criteria applied in this systematic evaluation for using opioid-local anesthetic mixtures within the chronic ache setting. However, as a end result of infusions had been titrated to effect in individual sufferers who had progressive disease, no assessment of analgesic efficacy with combination therapy was possible. Similarly, many sufferers had preexisting opposed results associated to analgesic regimens, the underlying disease, or both, thus rendering direct comparability of the incidence of unwanted aspect effects unimaginable. Clonidine can also profit sympathetically maintained pain, which is commonly a part of chronic neuropathic ache as a end result of cancer or nonmalignant causes. The absence of medical experience with dexmedetomidine for spinal analgesia leaves clonidine, a "line 2" agent in accordance with the newest Polyanalgesic Consensus Conference suggestions (30), as the only clinically available 2 agonist for this purpose. Seven randomized, managed trials involving clonidine glad our selection standards. These trials investigated the analgesic effect produced by combos of opioids. In aggregate, 461 patients enrolled in seven medical trials have been randomized to receive an opioid with clonidine, the same opioid alone, or clonidine alone. Clonidine was mixed with morphine in five research, sufentanil in one examine, and fentanyl in one examine. Morphine and Clonidine Carabine and colleagues (453) compared bolus epidural injections of clonidine (150 g) followed by continuous epidural infusion of clonidine 25 or 50 g/h, with a bolus injection of morphine (1 mg) followed by epidural infusion of morphine (0. At both 30 and 60 minutes after the injections, all three groups had significantly decrease values for ache intensity in contrast with the morphine group. Hypotension was significantly more pronounced in the combination group compared with the opposite teams from 5 till 20 minutes after injection. At 18 and 24 hours after surgical procedure, arterial blood strain was considerably less in each clonidine teams than within the morphine and mixture groups. Rockemann and coworkers (455) showed that the mix of a minimally effective epidural morphine dose (2 mg) with a marginally effective clonidine dose (280 g, based on patient weight) produced analgesia that was not considerably totally different from that produced by morphine alone (3. It is noteworthy that the investigators rightly excluded six of 15 patients within the morphine group from information analysis due to requests by these sufferers for supplemental analgesia. The study demonstrates that the mixture of clonidine and morphine is healthier in contrast with morphine alone only because of the quicker onset of pain reduction. Van Essen and colleagues (456) in contrast clonidine (70 g), morphine (3 mg), and a mix of the 2 given as bolus epidural injections 60 minutes after surgical procedure in 28 patients for postoperative ache management. The authors discovered no difference in ache intensity (verbal analog ache score) in any of the three treatment teams. Statistically significant reductions in blood pressure were noticed within the morphine-with-clonidine group however had been thought of of no scientific importance by the authors. No vital variations have been noticed in other unwanted aspect effects (urinary retention, nausea, vomiting, and pruritus) after the mix as compared with morphine alone. No supplemental opioid was administered to any of the patients in this study, though it was out there. Acute Pain Pain management after abdominal, orthopedic, or obstetric operations or during labor was investigated in five studies (453� 457). Finally, one examine in contrast the mix of epidural fentanyl and clonidine with every drug alone for the management of labor pain (454). This was the one examine in this group that evaluated the analgesic interplay by using the isobolographic approach (458).
Buy paxlovid 200mg mastercardHowever hiv infection rates in prisons generic 200 mg paxlovid with mastercard, when patients are taught abilities to cope with their pain antiviral drip purchase 200 mg paxlovid with mastercard, corresponding to rest or distraction strategies hiv infection latency cheap paxlovid 200 mg with visa, their ache is much less extreme (38) hiv infection and seizures buy generic paxlovid 200mg online. Other research have proven that postsurgical ache intensity is immediately proportional to the amount of hysteria perceived by the affected person (39). Suggestion and Placebos the influence of suggestion on the depth of perceived pain is clearly demonstrated by research of the effectiveness of placebos. Chapter 36 by Finniss and Benedetti surveys these research intimately and discusses their implications for neural blockade, so the present description is intentionally concise. As Beecher carefully documented within the 1950s (11), extreme pain, similar to postsurgical pain, could be relieved in some sufferers by giving them a placebo instead of morphine or different analgesic drugs. About 35% of the sufferers report marked reduction of pain after being given a placebo. This is a strikingly excessive proportion as a outcome of morphine, even in large doses, relieves severe pain in only about 75% of sufferers. However, in a current evaluation of controlled trials, 38% of patients obtained more than 10% of maximum potential pain reduction after placebo, whereas 16% obtained higher than 50% aid (50% of maximum with a potent agent). Thus, there was appreciable variation amongst patients in placebo response, within a given examine (41). There are massive particular person differences in susceptibility to placebos, and research have been carried out to decide some of the factors concerned (42). Recent work has documented variations within the neurobiology related to placebo responders and nonresponders. Interestingly, responders and nonresponders differ in the brain areas activated by the ultrashort-acting opioid remifentanil (44). Placebo responders however not nonresponders present activation of the rostral part of the anterior cingulate cortex, a construction associated with attentional processing of pain expertise (45), suggesting that placebo responders may have a simpler endogenous opioid system than nonresponders (46). Two placebo capsules, for instance, are more practical than one capsule, and large capsules are better than small ones. A placebo is more effective when injected than when given by mouth, and is more potent when accompanied by a strong suggestion that a strong analgesic has been given. In short, the higher the implicit and express suggestion that pain will be relieved, the larger is the relief obtained by the patient. Unfortunately, nevertheless, sufferers are inclined to get progressively much less reduction during repeated administration of placebos. We know very little about the extent to which placebo effects actually contribute to pain aid within the clinical setting (47). The placebo effect is no longer considered as a nuisance factor or artifact to be managed, parcelled out, or discounted, however a phenomenon worthy of research in its personal right (48). This curiosity has increased in part as a outcome of we now know that the opioid antagonist naloxone reverses placebo analgesia, implying that endogenous opioids mediate placebo analgesia (49,50). Moreover, the neurobiology of the placebo response is now higher understood because of fashionable imaging techniques (46,51). Consistent with this suggestion, a current functional magnetic resonance imaging study of patients with irritable bowel syndrome discovered that decreases in the exercise of pain-related brain areas, together with thalamus, somatosensory cortex, insula, and anterior cingulate cortex accompanied placebo analgesia induced by verbal suggestion (52). Expectation usually is generated by verbal recommendations, but may also involve implicit, nonverbal cues. Conditioning results operate by classical or Pavlovian conditioning and sometimes involve the pairing of an lively drug with a particular context or contextual cues. The sensitivity to naloxone of the placebo response following conditioning depends, partially, on the opioidergic standing of the unconditioned stimulus (drug). For example, naloxonereversible placebo responses develop after conditioning with the -opioid agonist morphine but not the nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug ketorolac (49). The neurobiology of the placebo impact has progressed to the point at which we now know that some medicine act particularly to improve placebo analgesia. This fascinating discovering was first shown by Benedetti and colleagues (53) in a randomized, double-blind managed trial of sufferers following posterolateral thoracotomy. After patients had recovered from the overall anesthetic, they have been randomly assigned to obtain a hidden or open injection of saline or proglumide, a cholecystokinin antagonist. Patients within the open injection group acquired the injection by a doctor in full view of the infusion pump and have been told that it was a potent analgesic. Patients receiving the hidden injection (by way of an infusion pump that was out of sight) had been unaware that an injection had been administered. Not surprisingly, the results confirmed that sufferers who received the hidden injection of saline reported no pain aid in any respect. In comparability, patients who acquired the open injection of saline confirmed considerably more pain relief. These findings appear to be simple and suggest that proglumide is an efficient analgesic because it produces more pain relief than both a placebo injection and no treatment. However, this interpretation is clearly incorrect since sufferers receiving the hidden injection of proglumide confirmed a complete lack of analgesic effect, equal to that of the management group that acquired the hidden injection of saline. These putting findings recommend that proglumide produces pain relief only within the context of a placebo process. Context performs an extremely necessary role in the expression of the placebo response. By context we mean the environmental cues and situations that co-occur with a treatment, together with concurrent phrases, and previous and present meanings attributed to these words. One of the most profound contextual cues known to produce a placebo response consists of the phrases spoken by a physician to her affected person, and specifically, the degree of certainty with which the message is conveyed (54�56). In addition to the background saline infusion, patients in all three teams obtained zero. Patients in group 2 (double-blind placebo) have been advised that the infusion was both buprenorphine or saline and thus had been uncertain as to the contents of the infusion. Patients in group 3 (deceptive placebo) had been told the infusion contained a robust painkiller. From their perspective, group three patients were certain they were receiving a potent analgesic agent. The results showed that the number of doses of buprenorphine acquired by the three teams differed significantly as a perform of the directions they got and, by implication, the certainty with which sufferers believed they were receiving an lively drug infusion. Patients who have been told that the saline was a strong drug (deceptive placebo) demonstrated the largest placebo impact, a 33. Being much less certain concerning the analgesic properties of the saline infusion (double-blind placebo) produced a 20. Under sure circumstances, it has been noticed that verbal suggestion, conditioning, or expectation can improve pain (57). The term nocebo hyperalgesia has been coined to describe the rise in pain that happens after administration of an inert substance (58).
Purchase paxlovid 200mg without prescriptionThe systemic administration of local anesthetics produces a selective despair of C-afferent fiber-evoked activity within the spinal twine antiviral medication for hiv buy paxlovid 200 mg amex. The effects of intravenous lidocaine on nociceptive processing in diabetic neuropathy hiv infection rates melbourne purchase paxlovid 200mg. Systemic lidocaine blocks nerve injury-induced hyperalgesia and nociceptor-driven spinal sensitization within the rat early hiv symptoms sinus infection cheap paxlovid 200 mg mastercard. Intravenous lidocaine infusion: A new remedy for chronic painful diabetic neuropathy Comparative local anaesthetic blocks within the diagnosis of cervical zygapophysial joint pain kleenex anti viral tissues discontinued discount 200 mg paxlovid visa. Treatment of chronic arthritis: Results of vaccine therapy with saline injections as controls. An experimental study of the placebo response underneath three totally different conditions of pain. Oral analgesic research: Pentazocine hydrochloride, codeine, aspirin, and placebo and their influence on response to placebo. Peak B endorphin focus in cerebrospinal fluid: Reduced in chronic ache patients and increased during the placebo response. The placebo impact in healthy volunteers: Influence of experimental situations on the adverse occasions profile throughout section I trials. The intersegmental anastomoses of posterior spinal rootlets and their significance. The anatomy of (A) the lumbosacral nerve plexus: Its relation to variations of vertebral segmentation, and (B), the posterior sacral nerve plexus. The brachial plexus of nerves in man, the variations in its formation and branches. Vasomotor innervation of the skin of the hand: A contribution to the study of human anatomy. Abnormal and collateral innervations of sympathetic and peripheral sensory fields associated with a case of causalgia. Neuronal mechanisms of ache with particular emphasis on visceral and deep somatic ache. The innervation of the veins: Its role in pain, venospasm and collateral circulation. The sympathetic nervous system affect on sensibility to heat and chilly and to certain types of ache. Afferent ache paths in man running from the spongiosa within the femoral head and passing by way of the lumbar sympathetic ganglia. Nerve provide to the posterior longitudinal ligament and the intervertebral disc of the rat vertebral column as studied by acetylcholinesterase histochemistry. Needle position for paravertebral and sympathetic nerve blocks: Radiologic affirmation is required. Correct placement of epidural steroid injections: Fluoroscopic guidance and contrast administration. Mechanical hyperalgesias in neuropathic ache patients: Dynamic and static subtypes. A comparison of the sensory dissociation produced by procaine and by limb compression. Sympathetic pores and skin nerve discharges in relation to amplitude of skin resistance responses. Use of pulse-wave monitor as a measurement of diagnostic sympathetic block and of surgical sympathectomy. Stellate ganglion block with bupivacaine: Minimum effective concentration of bupivacaine and the effect of added potassium. Interactions between sympathetic vasoconstrictor outflow and C nociceptor-induced antidromic vasodilatation. The use of electromyography and muscle palpation in the diagnosis of tension-type headache with and with out pericranial muscle involvement. The myofascial trigger point area: Correlation between the degree of irritability and the prevalence of endplate noise. The concept of main fibromyalgia (fibrositis): Clinical worth, relation and significance to different musculoskeletal ache syndromes. Pain on intramuscular injection of bupivacaine, ropivacaine, with and with out dexamethasone. Implications of the failure of nerve resection and graft to treatment persistent pain produced by nerve lesions. The sacroiliac joint in mild of anatomical, roentgenological, and clinical research. Macroscopic and microscopic anatomy of the sacroiliac joint from embryonic life until the eighth decade. Sacroiliac joint: Pain referral maps upon making use of a new injection/arthrography method. Diagnosis of sacroiliac joint ache: Validity of particular person provocation exams and composites of checks. Provocative sacroiliac joint maneuvers and sacroiliac joint block are unreliable for diagnosing sacroiliac joint ache. Morphologic evaluation of bipolar radiofrequency lesions: Implications for therapy of the sacroiliac joint. Immunohistochemical demonstration of nociceptors in the capsule and synovial folds of human zygapophyseal joints. Silver impregnation and immunohistochemical study of nerves in lumbar facet joint plical tissue. Computed tomography and fluoroscopy-guided anesthesia and steroid injection in side syndrome. Medial department blocks are specific for the analysis of cervical zygapophyseal joint pain. A controlled trial of corticosteroid injection into aspect joints for continual low back pain. Lumbar side joint injection: Indication, technique, clinical correlation, and preliminary outcomes. Apophyseal injection of native anesthetic as a diagnostic assist in main low-back pain syndromes. Distribution of pain provoked from lumbar facet joints and associated buildings throughout diagnostic spinal infiltration. Facet joint arthrography in lumbar spondylolysis: Anatomic foundation for spread of contrast medium.
Buy paxlovid 200 mg overnight deliveryThese afferent fibers convey pain impulses from the viscera and are just like hiv infection rates manchester buy paxlovid 200 mg on-line nociceptive afferents hiv infection cd4 purchase paxlovid 200 mg amex, except that they move without synapsing through sympathetic ganglia hiv infection in south korea discount paxlovid 200mg line. Part of the parasympathetic nervous system is indicated by the vagus nerve to and from the gut hiv infection rates uk 2013 generic paxlovid 200 mg with mastercard. The submucosal and the myenteric part of the enteric nervous system are indicated in the cross-section of the gut wall. Vascular nerves and filaments from these numerous sources are united round individual vessels in intensive "perivascular adventitial plexuses," which in turn ramify into plexuses between adventitia and media and between media and intima. The three primary levels of sympathetic blockade are proven together with main medical makes use of. Sympathetic fibers are generally found in a deep fascial airplane and are less accessible than segmental nerves. Interruption of sympathetic nerve fibers by neural blockade could be achieved within the following ways: at the sympathetic chain by anatomically specific sympathetic blockade, at peripheral nerves by a combined nerve block, at a vessel by perivascular infiltration, or to some extent by intradural or extradural injection of local anesthetic. Arterioles (in the pores and skin and in the splanchnic area), smaller arteries, and, in particular, peripheral veins, are usually beneath moderate vasoconstrictor influence. Pain, anxiety, and blood loss can provoke a really marked improve in arteriolar vasoconstrictor tone, mediated by the sympathetic nervous system. This enhance in resistance, particularly in skin vessels, influences the distribution of blood move. In addition, the related increase in venous vascular tone decreases the compliance of the venous system, lowering its blood content and rising venous pressure. Co-release of neuropeptide-Y from some sympathetic nerve endings increases and prolongs the vasoconstrictive impact of norepinephrine (8). Needle insertion is 3 cm from the midline, reverse cephalad facet of spinous course of. Needle is initially inserted perpendicular to skin in all planes to attain rib or transverse course of at a depth of about 2. Sometimes the needle might must be angled barely superiorly or inferiorly to find rib or transverse course of. Needle is then directed cephalad above the rib, and a lack of resistance could also be detected because the needle penetrates the costotransverse ligament. At this point, the needle tip lies within the paravertebral house where both sympathetic and somatic thoracic nerves are positioned. Careful aspiration must be carried out for air (intrapleural), blood (intravascular), or cerebrospinal fluid (intradural). In the gut and bladder, 2 -stimulation causes easy muscle leisure and sphincter contraction. Thus, sympathetic blockade leads to smooth muscle contraction (a small, contracted gut) and sphincter leisure. These effects present glorious surgical entry throughout procedures such as abdominoperineal resection. Sudomotor constructions (sweat glands) and hair follicles have the identical postganglionic efferents as do blood vessels; nevertheless, the neurotransmitter in sweat glands is acetylcholine. Phenoxybenzamine and phentolamine are nonspecific -blockers, acting on both pre- and postsynaptic receptors. Note that insertion of needle 10 cm from the midline permits the needle to attain the anterolateral angle of the vertebral physique. Insertion of needle nearer to the midline takes needle path near somatic nerve roots and lateral to sympathetic chain. This metabolic impact is widespread and in addition affects carbohydrate and lipid distribution and utilization (9). Uterine nociceptive input, as in labor pain, is transmitted by afferent fibers that traverse the lower thoracic sympathetic ganglia, whereas ache from upper stomach viscera and the intestine, as far distal as the descending colon, could be relieved adequately by celiac ganglion block. After nerve or tissue trauma, release of neurotransmitters similar to norepinephrine will increase discharge from peripheral major afferent nociceptors. Denervation hypersensitivity from augmented adrenoceptor exercise could increase discharge from major afferent nociceptors in the absence of elevated sympathetic efferent nerve exercise. Recently, J�rum and colleagues (13) documented direct stimulation of nociceptive fibers by sympathetic efferent discharge in a patient with sympathetically maintained pain (13). In a standard topic, this leads to dilatation of veins, selling an accumulation of blood in the veins, and dilatation of the arterial vessels, resulting in a fall in the peripheral resistance and, if the perfusion pressure has not been altered, to an elevated capillary blood flow. Skin capillary oxygen tension and venous oxygen rigidity and saturation are additionally elevated. A widespread block will trigger a peripheral pooling of blood, diminishing the venous return and decreasing cardiac output and blood pressure. Preganglionic (Pre) neurons within the thoracolumbar spinal wire project through the ventral roots and white rami communicantes to postganglionic neurons within the sympathetic trunk. The postganglionic neurons project with postganglionic fibres (Post) through the corresponding gray rami communicantes to the spinal nerves or alongside the arteries. Therefore, it seems logical to use sympathetic blockade to improve the blood move in a patient with insufficient peripheral superficial blood move due to vasospasm or arterial disease. As the regional resistance decreases in branch B, the move via this vessel will improve. A unilateral sympathetic blockade (in humans) is generally followed by a slight increase in vasomotor tone in the contralateral side, thus growing the regional resistance and reducing the blood flow via this a part of the vascular system. Such an obstruction will in itself diminish blood move by mechanically rising the regional resistance; nevertheless, decreased blood circulate across the obstruction may a minimum of be compensated by a rise in the collateral blood move. The blood move will be diverted into this a half of the vascular tree, and thus blood shall be shunted from the diseased part (branch B). Such "stealing" of blood is known to occur in sufferers with superior arterial illness. During irritation, vasodilatory components from inflammatory cells, calcitonin gene-related peptide, and substance P are launched from unmyelinated and thin myelinated fibres. Cold causes enhancement of neuroeffector transmission from vasoconstrictor fibers to pores and skin blood vessels. Only physiologic studies in patients and scientific experience will determine when a sympathetic block is indicated. Neuroeffector synapse of the postganglionic vasoconstrictor neuron and its blood vessel (A). The lengthy postganglionic axon varieties noradrenergic plexus and tons of thousand varicosities close to the smooth muscle cells of the blood vessel (B, C, D). Smooth muscle cells are coupled by junctional channels forming a practical syncytium (C). The varicosity types shut contact with the smooth muscle cells with out intervening Schwann cell cytoplasm and the basal laminae of clean muscle cell and varicosity fuse (D). Neuroeffector transmission to autonomic target cell, similar to clean muscle cells of arterioles or coronary heart. Subsynaptic receptors mediate the effect of transmitter launch during physiologic circumstances. Norepinephrine from small vesicles causes vasoconstriction of small arterioles by way of extrasynaptic receptors. Because of related coronary artery disease, pulmonary illness, and different bodily situations, many patients in this scenario are poor candidates for surgical procedure and are thus higher candidates for neurolytic sympathectomy (16).
References - Vickers AJ. Which botanicals or other unconventional anticancer agents should we take to clinical trial?. J Soc Integr Oncol. Summer 2007;5(3):125-129.
- Liu D, Zhou H, Chao M, et al: Transumbilical single-site multiport laparoscopic pyeloplasty for children with ureteropelvic junction obstruction in China: a multicenter study, J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 27:655, 2017.
- Kalantar-Zadeh K, Horwich TB, Oreopoulos A, et al. Risk factor paradox in wasting diseases. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2007; 10: 433-442.
- Killingsworth, L., Wheller T.L. 2nd, Burgio, K.L., Martirosian, T.E., Redden, D.T., Richter, H.E. One-year outcomes of tension-free vaginal tape (TVT) mid-urethral slings in overweight and obese women. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct 2009;20:1103-1108.
|


