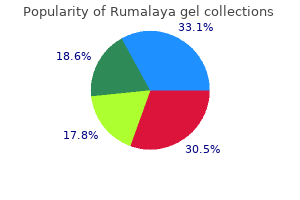
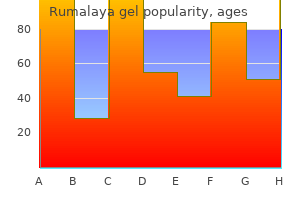
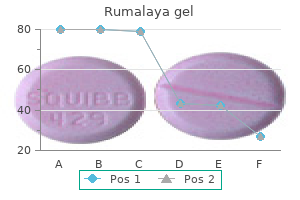
Rumalaya gel
C. James Corrall, M.D., MPH - Clinical Associate Professor of Pediatrics
- Clinical Associate Professor of EM
- Indiana University School of Medicine
- Indianapolis, IN
Buy rumalaya gel 30gr lineNerves the higher third of the oesophagus is equipped with parasympathetic fibres through the recurrent laryngeal nerve and sympathetic fibres from the center cervical ganglion by way of the inferior thyroid artery spasms colon order rumalaya gel 30 gr without prescription. Below the foundation of the lung the vagi and sympathetic nerves contribute to the oesophageal plexus muscle relaxant guardian pharmacy discount rumalaya gel 30 gr overnight delivery. Relations of the abdomen Clinical points There are three narrow factors in the oesophagus at which overseas our bodies could impression muscle relaxant bath buy 30gr rumalaya gel with mastercard. The abdomen lies in the epigastric and umbilical areas of the abdomen but muscle relaxant images rumalaya gel 30 gr without prescription, when distended, encroaches upon the left hypochondrium. Lymphatic drainage the arrangements of lymph nodes in relation to the abdomen is shown in. The space of the stomach supplied by the splenic artery drains by way of lymphatics accompanying that artery to the lymph nodes of the hilum of the spleen, then to these located alongside the higher border of the pancreas and finally to the coeliac nodes. The cardiac area of the abdomen drains along the left gastric artery to attain the coeliac nodes. The the rest of the stomach drains as follows: through branches of the hepatic artery by way of nodes along the lesser curve to the coeliac nodes and alongside the best gastroepiploic vessels to the subpyloric nodes and then to the coeliac nodes. Enlargements of these nodes may trigger exterior compression of the bile ducts to produce obstructive jaundice. The in depth and sophisticated lymphatic drainage of the stomach creates problems in coping with gastric most cancers. The stomach has such a rich blood provide that any three of the 4 major arteries may be ligated without any compromise of the arterial blood supply to the abdomen. The anterior vagus nerve lies close to the wall of the oesophagus and upper a half of the stomach, but the posterior nerve is at a little distance from it. The anterior vagus runs caudally and provides the anterior surface and lesser curve of the stomach. Before it reaches the abdomen, it provides off a hepatic department which passes in the lesser omentum to the liver and gall bladder and the pyloric branch to the pyloric sphincter. The posterior vagus nerve provides off a coeliac branch which passes to the coeliac plexus before sending a gastric department to the posterior floor of the abdomen. The gastric divisions of both anterior and posterior vagi reach the stomach on the cardia and descend alongside the lesser curve between the anterior and posterior peritoneal attachments of the lesser omentum. However, with the appearance of H2 receptor antagonists and proton pump inhibitors and the discovery of the function of H. The vagus nerve constitutes both the motor and secretory nerve provide for the stomach, i. When the nerve is divided in the operation of vagotomy, acid secretion is reduce down within the abdomen, but so is motility, in order that the stomach empties by way of an intact pylorus solely with issue. Because of this, complete vagotomy (truncal vagotomy) should all the time be accompanied by some form of drainage process: both a pyloroplasty to destroy the pyloric sphincter or a gastrojejunostomy to bypass the pyloric sphincter. Structure of the gastric mucosa the floor of the gastric mucosa is covered by columnar epithelial cells that secrete mucus and alkaline fluid that protects the epithelium from mechanical injury and from gastric acid. The floor of the mucosa is studded with gastric pits, every pit being the opening of a duct in to which the gastric glands empty. The cardiac gland area is the small segment located near the gastro-oesophageal junction. Histologically it incorporates principally mucus-secreting cells, though sometimes a couple of parietal (oxyntic) cells are current. The remainder of the stomach is split in to the acidsecreting region (oxyntic gland area) and the pyloric gland area. The oxyntic gland space is the portion containing the parietal (oxyntic cells) and the chief (zymogen) cells. The pyloric end space constitutes the distal 30% of the abdomen and accommodates G cells that produce gastrin. In this area there are few oxyntic and peptic cells, mucus-secreting cells predominating. Posterior nerve of Latarjet the first 2�3 cm of the primary a half of the duodenum is totally coated with peritoneum, but then the duodenum turns into retroperitoneal. As in the remainder of the gastrointestinal tract the muscular wall of the stomach consists of an internal circular layer and an outer longitudinal layer. The neck of the gland contains many mucus cells, oxyntic cells being most numerous within the midportion of the glands and chief cells predominating in the basal portion. This is approximately 5 cm long and it ascends from the pylorus, being directed superiorly, posteriorly and to the proper. Immediately posterior to it lie the portal vein, the widespread bile duct and gastroduodenal artery. The relationship of the gastroduodenal artery to the primary part of the duodenum is necessary because erosion of posterior duodenal ulcers in to the gastroduodenal artery will cause haematemesis and melaena. The bile ducts and main pancreatic ducts enter the second part of the duodenum collectively on the duodenal papilla on its posteromedial facet. The second a half of the duodenum is crossed by the transverse colon and lies anteriorly to the best kidney and ureter. Third part the third a half of the duodenum is roughly 10 cm lengthy and runs horizontally to the left. It is crossed anteriorly by the foundation of the mesentery and the superior mesenteric vessels. The mesentery contains the superior mesenteric vessels which enter the mesentery anterior to the third part of the duodenum, the lymph nodes draining the small intestine, and autonomic nerve fibres. At the duodenaljejunal flexure the small intestine leaves the posterior stomach wall and acquires a mesentery. At surgery the duodenojejunal flexure could also be recognized by the presence of the suspensory ligament of Treitz. This is a peritoneal fold descending from the right crus of the diaphragm to the termination of the duodenum. These two arteries both lie within the curve between the duodenum and the top of the pancreas, supplying each the duodenum and the head of the pancreas. In the mesentery of the jejunum the arteries kind one or two arcades a long way from the free fringe of the mesentery, and long straight branches from these arcades run to provide the jejunum. In the ileum the arterial supplies type a number of rows of arcades within the mesentery, and the ultimate straight arteries to the ileum are shorter than in the jejunum. In general, the jejunum is most likely to be found at or above the level of the umbilicus, whereas the ileum tends to lie below the extent of the umbilicus within the hypogastrium and pelvis. It consists of the caecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon and rectum. The caecum is a dilated blind-ended pouch situated in the best iliac fossa and is normally utterly lined with peritoneum. The ileocaecal valve lies on the left facet of the junction between the caecum and ascending colon. Tumours might grow to a large dimension within the caecum without inflicting any obstruction until they encroach on the ileocaecal junction.
Purchase rumalaya gel 30gr amexArthrology Glenohumeral joint this is a ball-and-socket joint muscle relaxant g 2011 30 gr rumalaya gel otc, the relative form and dimension of whose articular surfaces make it completely reliant on delicate tissue structures for static and dynamic stability spasms while pregnant cheap 30 gr rumalaya gel with amex. The capsule is connected across the margin of the glenoid cavity of the scapula spasms right side abdomen cheap 30 gr rumalaya gel free shipping, extending on to the bottom of the coracoid superiorly to include the biceps attachment spasms just under rib cage purchase 30gr rumalaya gel fast delivery. The glenoid labrum, deepening the concavity of the glenoid fossa, is totally intracapsular. On the humerus, the capsule is hooked up around the anatomical neck besides where it passes on to the medial metaphysis inferiorly. The latter attachment brings the inferior capsule in to shut relation with the axillary nerve, rendering the nerve weak in anteroinferior dislocations. It additionally signifies that a metaphyseal osteomyelitic lesion of the proximal humerus may be intracapsular, leading to the chance of septic arthritis as a sequel. The capsule is strengthened by the tendons of the rotator cuff muscle tissue, which mix with it everywhere except inferiorly, and additionally by the coracohumeral ligament superiorly. The synovial sheath extends distally beneath the transverse ligament of the humerus in to the bicipital groove. The two main bursae related to the joint are the subacromial/subdeltoid bursa superiorly and the subscapular bursa anteriorly. The joint could additionally be aspirated or injected anteriorly or posteriorly, the posterior subacromial method being somewhat easier and also being that often used for arthroscopy. The widespread approach for open shoulder surgical procedure is anterior, passing between deltoid and pectoralis major. The muscle tissue attaching to the coracoid are displaced medially, protecting axillary neurovascular constructions, and the capsule is entered after dividing subscapularis. Movements and muscle tissue � flexion: anterior a half of deltoid, pectoralis major, biceps brachii, coracobrachialis; � extension: posterior deltoid, teres major, latissimus dorsi; � abduction: mid-part of deltoid, supraspinatus; � adduction: pectoralis main, latissimus dorsi, teres main, coracobrachialis, [gravity]; � medial rotation: subscapularis, anterior deltoid, latissimus dorsi, teres major; � lateral rotation: posterior deltoid, infraspinatus, teres minor; and � circumduction: the entire above. Long head of biceps Fibrous capsule Synovial sheath Glenoid cavity Long head of biceps Labrum glenoidale Major anatomical relations � anterior: brachial plexus; axillary vessels; � inferior: axillary nerve; circumflex humeral vessels; and � posterior: suprascapular nerve and vessels (on the neck of the scapula medial to the capsular attachment). The tendons of the rotator cuff muscles merge with the capsule anteriorly, superiorly and posteriorly. The muscles crossing the glenohumeral joint and their actions upon it are summarised beneath. The joint is innervated by the nerves which supply these muscle tissue, primarily by the axillary and suprascapular. The suprascapular artery, from the subclavian, and the subscapular and circumflex humeral arteries, from the axillary, are the primary participants within the anastomosis around the scapula and the pinnacle of the humerus. The glenohumeral capsule is said to be at its tightest when this can be a modified hinge joint between the humerus and the forearm bones. The primary a part of the joint is the humero-ulnar, between the trochlea of the humerus and the trochlear notch of the ulna. The trochlear articular floor of the humerus is steady laterally with that of the rounded capitulum, which is confined to the anterior aspect of the bone and which articulates with the concavity of the head of the radius. The trochlear articular surface of the ulna continues laterally and distally over the radial notch, which articulates with the circumferential a half of the radial articular floor. The humeral attachment of the capsule of the elbow joint leaves the articular margins of trochlea and capitulum anteriorly and posteriorly to include the coronoid, radial and olecranon fossae. The capsule is thin anteriorly and posteriorly but thicker medially and laterally where strengthened by the collateral ligaments. It attaches distally to the articular margins of the trochlear notch, then passes on to the superior border of the annular ligament, with which it becomes continuous. The collateral ligaments of the elbow differ in form: the radial is fan-shaped, radiating on to the annular ligament from the lateral humeral epicondyle, while the ulnar has three bands constituting a triangle between the medial epicondyle and the lateral sides of the coronoid and olecranon processes. The synovium of the elbow, lining the capsule, is steady with that of the superior radio-ulnar joint, and extends distally a little means below the annular ligament. The synovium is separated from the capsule anteriorly and posteriorly by fat pads, whose displacement can be utilized within the radiological analysis of small effusions or haemarthroses of the elbow. The arterial anastomosis around the elbow is made up of branches from the brachial, radial and ulnar vessels. The elbow is maximally secure in full extension, when the anterior capsule is tense. A swollen elbow is finest aspirated from the lateral facet, where no necessary neurovascular constructions cross the joint. A posterior method, lateral to the primary physique of the triceps tendon, can also be used. Open surgical approaches are mainly lateral or posterior, relying upon the size of publicity required. Movements and muscle tissue � flexion: brachialis, biceps brachii, brachioradialis, pronator teres; and � extension: triceps brachii, anconeus. Radio-ulnar joints the shafts of radius and ulna are strongly linked in all positions of the forearm by the interosseous membrane, whose fibres cross distally and medially, transmitting drive from radius to ulna. The distal ends articulate on the inferior radio-ulnar joint, between the cylindrical ulna and the concave ulnar notch of the radius. The capsule of this joint is weak, however the joint is strengthened by a triangular intra-articular fibrocartilage passing between the ulnar styloid and the distal margin of the ulnar notch of the radius. If intact, this fibrocartilage separates the synovial lining of the inferior radio-ulnar joint from that of the wrist joint. Movements and muscular tissues � supination: biceps brachii (especially when elbow flexed), supinator; and � pronation: pronator teres (especially when elbow flexed), pronator quadratus. Major anatomical relations � superior radio-ulnar joint: the posterior interosseous nerve runs in supinator near the distal capsular attachment; and � inferior radio-ulnar joint: the dorsal branch of the ulnar nerve passes near the joint posteriorly. The actions are produced by all of the named flexors and extensors of wrist and digits. Radial and ulnar deviation are produced by the respective flexors and extensors of the wrist working collectively. Major anatomical relations � � anterior: median nerve; ulnar nerve and vessels; radial vessels; and lateral: radial vessels; radial cutaneous nerve. This is a very cell saddle-shaped joint, giving the thumb much of its versatility and precision of movement. There are additionally the intercarpal joints, between the person carpal bones, and the midcarpal joint, between the 2 rows of carpal bones. The capsule of the radiocarpal joint is hooked up distal to the (distal) growth plates of radius and ulna, and is stronger in its palmar than in its dorsal component. There are two collateral ligaments, radial and ulnar, attaching to the respective styloid processes and fusing with the capsule. The synovium of the radiocarpal joint is often separate from the continual synovial lining of the intercarpal, midcarpal and carpometacarpal joints. It is usually approached, both surgically and for aspiration, from the dorsal facet. Note that, on clinical examination, most of the carpus lies distal to the distal wrist crease, i. Movements and muscular tissues the wrist complicated could be flexed, prolonged, adducted (ulnar deviated) and abducted (radially deviated).

Cheap 30gr rumalaya gel free shippingHere it turns forward and medially and emerges on to the surface of the hyoglossus muscle muscle relaxant m 58 59 order 30 gr rumalaya gel. It runs forward deep to the mucosa of the ground of the mouth between the mucosa and the sublingual gland and the geniohyoid muscle to open in to the floor of the mouth on both aspect of the frenulum of the tongue muscle relaxant stronger than flexeril purchase rumalaya gel 30gr without prescription. As it goes forward it crosses medial to the nerve to lie above the nerve after which crosses back spasms in colon 30gr rumalaya gel free shipping, this time lateral to it to reach a place once again below the nerve muscle relaxant 551 discount rumalaya gel 30 gr online. Four nerves are intently associated to the submandibular glands and hence are weak throughout its removing. The right half of the mandible and part of the submandibular and sublingual glands have been eliminated. The glossopharyngeal nerve, stylohyoid ligament and lingual artery pass deep to the posterior border of hyoglossus; the lingual nerve, submandibular duct and hypoglossal nerve are superficial to hyoglossus. Sublingual gland the sublingual gland lies in the floor of the mouth and raises the sublingual fold of the oral mucosa. The gland is medially associated to the genioglossus muscle and laterally to the sublingual fossa of the mandible. The parasympathetic supply of the submandibular and sublingual glands is from the facial nerve through its chorda tympani department. The chorda tympani joins the lingual nerve and the preganglionic fibres synapse within the submandibular ganglion. The postganglionic fibres rejoin the lingual nerve to be distributed to the glands. It has three parts: � � � Nerve supply of the salivary glands the secretomotor provide to the parotid gland is from the glossopharyngeal nerve, the parasympathetic fibres nasopharynx opening anteriorly to the nasal cavities; oropharynx opening to the oral cavity; and laryngopharynx or hypopharynx opening in to the larynx and persevering with downwards because the oesophagus. The cartilaginous finish of the tube has a prominence on the postero-superior a part of the opening. The roof and the posterior wall has lymphoid accumulation within the mucosa forming the adenoids. Examination of the nasopharynx can be done by placing a small angled mirror within the oropharynx. The following may be visualised: � � � � � � opening of the Eustachian tube; the tubal elevation; the pharyngeal recess; nasopharyngeal tonsils or adenoids � seen as vertical ridges separated by clefts; the posterior choanae; and the posterior finish of inferior concha or turbinate. There are extra branches from the lingual, ascending palatine and ascending pharyngeal arteries as properly. The troublesome paratonsillar vein which regularly bleeds during tonsillectomy extends from the taste bud to lie on the lateral surface of the tonsil earlier than piercing the superior constrictor. The lymphatic drainage is to the jugulo-digastric lymph node situated behind the angle of the mandible. The sensory nerve provide of the tonsillar fossa is through the glossapharyngeal nerve with minor contribution from the lesser palatine nerve. Laryngopharynx this a half of the pharynx which is also known as the hypopharynx has the inlet of the larynx and the piriform fossa. The inlet of the larynx which is vertical is bounded by the epiglottis, aryepiglottic fold and the arytenoids. It is a standard site for lodging international our bodies such as fish bones and likewise infamous for malignant tumours which may be silent in the early levels. The internal laryngeal nerve which provides the laryngopharynx and a lot of the larynx can additionally be discovered within the piriform fossa. As this half has a wealthy lymphatic drainage the tumour rapidly spreads in to the deep cervical nodes. The nasopharyngeal tonsils are prominent in youngsters but like all lymphoid tissues undergo atrophy after puberty. Infection from the nasopharynx can easily spread in to the center ear via the Eustachian tube. Oropharynx and the anatomy of the tonsil an important structure within the oropharynx is the palatine tonsil or the tonsil. It lies in the tonsillar fossa bounded by the anterior and posterior pillars of the fauces. The anterior pillar is the palatoglossal arch produced by the palatoglossus muscle and the posterior pillar is the palatopharyngeal arch by the palatopharyngeus muscle. Pharyngobasilar fascia lining the internal floor of the constrictor types the capsule of the tonsil and lies between the tonsil and the muscle. Its oral floor is lined by mucous membrane having stratified squamous epithelium. Structure of the pharynx the pharyngeal wall consists of the: � � � � � the mucosa; submucosa; pharyngobasilar fascia; muscle; and buccopharyngeal fascia (areolar tissue). Blood supply the primary arterial supply is derived from the tonsillar branch of the facial artery which pierces the superior the mucosa has pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium (respiratory epithelium) within the nasopharynx and stratified squamous epithelium in the remainder of the pharynx. The pharyngobasilar fascia lies deep to the mucosa and features the muscle tissue of the pharynx. It is thick in the upper part and its attachment to the base of the skull provides agency anchorage to the pharynx. These are strengthened by a lot smaller longitudinal muscles: � � � stylopharyngeus; salpingopharyngeus; and palatopharyngeus. Cartilages There are 5 major cartilages: Each constrictor muscle begins from a limited origin anteriorly and broadens out laterally and posteriorly to insert in to a posterior midline raphe � the pharyngeal raphe. The gap between the inferior and center are occupied by the thyrohyoid ligament and associated structures. The stylopharyngeus muscle accompanied by the glossopharyngeal nerve enters the pharynx by way of the gap between the center and superior constrictors. The gap between the higher border of the superior constrictor and the base of the skull is bridged by the thick pharyngobasilar fascia. Anteriorly the superior constrictor is attached to the pterygomandibular raphe and the middle constrictor to the larger horn of the hyoid bone. The thyropharyngeus part of the inferior constrictor is fan-shaped like the opposite constrictors and is connected to the lamina of the thyroid cartilage. The cricopharyngeus part of the inferior constrictor is circular and acts like a sphincter. The weakest area of the pharyngeal wall is the hole between the thyropharyngeus and the cricopharyngeus posteriorly within the midline. Cricoid cartilage Shaped like a signet ring, the cricoid cartilage has a narrow arch anteriorly and a broad lamina on the again. Thyroid cartilage the thyroid cartilage is the biggest of the laryngeal cartilages and has two laminae meeting within the midline anteriorly. This cartilage articulates inferiorly with the cricoid at the cricothyroid joints and is connected to the hyoid bone by the thyrohyoid ligament. Epiglottis this could be a leaf-shaped cartilage forming the anterior wall of the inlet of the larynx. Its slender lower end is connected to the thyroid cartilage by the thyroepiglottic ligament.
Rumalaya gel 30 gr free shippingThe breast is actually a conglomerate gland consisting of 15�20 lobes that are pyramids of glandular tissue with an apex pointing in the direction of the nipple and a base peripherally muscle relaxant pregnancy category buy rumalaya gel 30 gr amex. Secretions drain centripetally in course of the nipple and every lobe drains by way of a system of branching ducts in to a lactiferous sinus and in turn in to a collecting duct which opens at the tip of the nipple spasms under ribs cheap rumalaya gel 30 gr line. Individual lobes are composed of tubuloalveolar buildings by which several acini or alveoli open in to a standard duct � the terminal duct infantile spasms 8 month old order rumalaya gel 30gr line. The terminal ducts drain in to subsegmental and in flip larger segmental ducts that are interwoven within any single lobe muscle relaxant medication 30gr rumalaya gel fast delivery. The epithelial elements are supported by connective tissue which surrounds the gland and extends as collagenous and inelastic septa between the lobes and lobules. On the deep floor of the breast, fibrous processes from the ligamenta move in to the aponeurosis over pectoralis main. Thus the breast is slung between pectoral fascia and skin by a complex structure of fibrous tissue. C the glandular construction of the breast which is supported by the ligamenta suspensoria. The deeper layer of the superficial fascia covers the posterior surface of the breast and forms the anterior wall of the retromammary bursa. Fibrous thickenings shaped of collagenous bundles move from the superficial mammary fascia to the dermis of the skin. These suspensory ligaments of Astley Cooper type projections which spread out to kind a white, firm irregular surface of folds between the pores and skin and the glandular tissue. The breast consists of 6�12 branching glands radiating from the periphery towards the nipple. Arteries, veins, nerves and lymphatics lie inside this layer and are distributed throughout the construction. Nipple and areola the nipple is probably the most outstanding part of the breast and protrudes forward and outwards to a variable diploma. It is a cylindrical construction, receives the connecting ducts from particular person lobes of the breast and incorporates blood vessels and nerves united by fibrous and cellular tissue. The nipple is covered with small papillae which impart a tough texture and will aid suckling. The pores and skin of the nipple bears neither hair nor sweat glands, however contains quite a few sebaceous glands whose secretions are protecting. Both sebaceous and sweat glands are present alongside the margin of the areolar along with accent areolar glands. They can become outstanding during pregnancy when typically the areolae turn into bigger and extra pigmented. There are strands of easy muscle fibres beneath the areola that are primarily circumferential but in addition happen radially along the lactiferous ducts. These contract when stimulated by touch or cold and render the nipple extra protruberant for ease of suckling. There is much variation within the physical characteristics of particular person breasts; some patients have lumpy (or nodular) breasts which can make it harder to palpate a discrete or separate lump. Superimposed on this bodily spectrum are the adjustments influenced by age and hormonal status. The breast undergoes reversible proliferative modifications throughout each menstrual cycle which might exacerbate any pre-existing lumpiness. During lactation, the glands separate in to smaller bodies with indentations around them i. This lobulation have to be distinguished from a discrete lump, significantly malignancy. The formal evaluation of a breast lump or lumpiness now entails a combination of clinical examination with breast imaging (mammography; ultrasound) and attainable percutaneous biopsy. Beyond the menopause, lobulation turns into less obvious because of atrophy of glandular parenchyma and deposition of adipose tissue. By distinction, the glandular tissue undergoes marked proliferation and hypertrophy during pregnancy with an increase in blood provide. Perforating branches of the inner mammary artery pierce the 2nd, 3rd, 4th (and often 5th) intercostals areas and traverse the pectoralis major muscle to supply the medial and deep parts of the gland. These vessels can produce troublesome bleeding at operation should they retract in to the chest wall as quickly as divided. These branches anastomose with these of vessels entering from the superolateral aspect of the breast arising from the axillary artery; the lateral thoracic artery supplies branches which sweep across the lateral border of pectoralis main to reach the gland. Branches from the thoracoacromial trunk together with some intercostals vessels provide the deeper aspects Applied anatomy the structure and form of breasts differ tremendously with age, hormonal standing, pregnancy and lactation. The nulliparous breast tends to be hemispheric in form whilst those of multiparous ladies are larger and more pendulous. The bases of the pyramids for individual lobes of the breast lengthen outwards to unequal lengths. The medial side of the breast has an irregular outline and superolaterally in the region of the axillary tail, the sting of the breast is turned up like a hem. There is a wealthy anastomotic community between these totally different sources of blood supply and during being pregnant the medial perforators enhance considerably in diameter. Veins beneath the areola type an anastomotic circle (circulus venosus) which along with deeper veins carry blood to the periphery of the gland where venous outflow is via the internal thoracic, lateral thoracic and upper intercostals veins. Breast most cancers can unfold haematogenously through these venous routes and also by the use of the vertebral venous plexus which is linked to veins of the chest wall by valveless conduits. Lymphatic drainage Axillary nodes nearly all of invasive breast cancers can potentially metastasize via the lymphatic system, and axillary lymph nodes are a major route of lymphatic unfold. There is a few confusion in designation of nodal groupings, however an understanding of nodal anatomy is important within the surgical management of breast most cancers. The lymphatics of the breast pores and skin and parenchyma are inter-connected and circulate throughout the valveless vessels is passive. This results in a level of plasticity which is relevant to malignant infiltration whereby uni-directional lymph move could additionally be diverted due to blockage at proximal websites by tumour emboli. The lymphatics of the pores and skin of the breast characterize part of the superficial system of the neck, thorax and stomach. From this subareolar and a related circumareolar plexus, lymph flows principally to the axillary nodes through a lateral lymphatic trunk. This together with the minor inferior and medial lymphatic trunks drain along the surface of the breast to penetrate the cribriform fascia and attain the assorted teams of axillary nodes. Lymph drains medially from the circumareolar plexus in to lymphatics accompanying the internal mammary vessels to enter the inner mammary (parasternal) nodes. Approximately 75% of lymph flow passes to the axillary nodes and 25% to the interior mammary nodes. Sentinel lymph node biopsy is a model new staging process which may precisely decide the pathological status of axillary nodes. Clearance of nodal tissue is confined to clinically node constructive sufferers and people clinically node unfavorable sufferers found to have nodal illness on sentinel node biopsy. A the lymphatics of the nipple are massive and numerous and drain along the surface of the breast beneath the skin. B the deeper lymphatics of the breast interconnect and drain mainly in to main channels directed towards the axilla.
Safe rumalaya gel 30grWhat Not To Do: Do not overlook infectious causes presenting as torticollis muscle relaxant klonopin discount 30 gr rumalaya gel mastercard, particularly the pharyngotonsillitis of younger youngsters spasms feel like baby kicking discount rumalaya gel 30 gr otc, which can soften the atlantoaxial ligaments and allow subluxation muscle relaxer 800 mg order 30gr rumalaya gel amex. Do not fail to think about the unusual disk herniation or bony subluxation that spasms throughout my body generic rumalaya gel 30 gr without prescription, once in a while, can present as acute wryneck or torticollis. Do not confuse torticollis with a dystonic drug response (see Chapter 1) from phenothiazines or butyrophenones. Discussion Torticollis is an involuntary twisting of the neck to one facet, secondary to spasm and contraction of the neck muscular tissues. The ear is pulled toward the contracted muscle while the chin is dealing with in the reverse direction. The term torticollis is derived from the Latin words tortus ("twisted") and collum ("collar" or "neck"). Twisting of the neck may also be accompanied by the elevation of 1 shoulder up towards the contracted neck muscle tissue. Torticollis could be a symptom in addition to a disease, with a host of underlying issues. Abnormalities of the cervical spine can vary from fracture, subluxation, and osteomyelitis to tumor. Infectious causes embody retropharyngeal abscess, cervical adenitis, tonsillitis, and mastoiditis. Head tilting can occur to compensate for an essential head tremor, and idiopathic spasmodic torticollis and cervical dystonia ought to be suspected when symptoms are extended. When examined for stability, it may show various degrees of joint widening towards the radial (or palmar) side more than the metacarpophalangeal joint of the opposite thumb. What To Do: Obtain a history of the mechanism of damage, and study the thumb, hand, and wrist completely. Tenderness to palpation should be biggest along the ulnar border of the proximal thumb. Stress testing of the primary metacarpophalangeal joint should be carried out whereas the joint is in 30 levels of flexion and the thumb is held in full extension. The affected person may not have the ability to tolerate this a half of the examination due to pain, and it could possibly consequently be deferred until specialist follow-up. Obtain radiographs, which may be unfavorable or present a small avulsion fracture of the proximal phalanx on the insertion of the ulnar collateral ligament. Treat with ice, elevation, relaxation, acetaminophen, or anti-inflammatory drugs, for consolation. A delicate dressing with an immobilizing elastic bandage that incorporates the thumb could additionally be adequate for sprains or delicate partial tears. A thumb spica provides support to the wrist and thumb for the more important ligament accidents. Explain to the affected person with a significant partial or an entire ligament tear that this explicit injury may not heal with closed immobilization and typically requires operative restore. Complete tears that require surgical repair must be carried out 1 to three weeks after the harm. Surgical intervention is often reserved for Stener lesions and complete undisplaced tears with laterolateral instability, because conservative therapy leads to continual instability and arthrosis. Avulsion fractures involving more than 20% of the articular floor may require pinning. Note any darkened areas of pores and skin crush, and study for underlying areas of bony tenderness by making use of indirect stress and/or axial loading to the metatarsals and malleoli. Provide any tetanus prophylaxis required (see Appendix H), and apply a quick lived normal saline/povidone-iodine dressing. Apply ice to the affected area to reduce pain and swelling while awaiting radiographs. Incorporate a bulky compressive dressing consisting of gauze fluffs, knitted cotton curler gauze (Kerlix), and a mildly compressive Ace wrap (or equal dressing material). Have the patient maintain the foot strictly elevated above the extent of her coronary heart over the following 24 hours, after which schedule her for a wound examine within forty eight hours. They should perceive that a slow-healing sore might end result or pores and skin grafting may be required, and due to this fact close follow-up is necessary with surgical referral if warranted. Encourage the patient and the parents to wear correct closed-toe footwear when driving a bicycle to minimize the prospect of future injuries. Consider modifications to the bicycle to reduce the possibility of harm, including bicycle chain and spoke guards. Take advantage of time with mother and father to emphasize the importance of wearing a helmet whenever riding a bicycle. What Not To Do: Do not assume that the injury is merely a simple abrasion as a outcome of the radiographs are negative. Discussion Bicycle spoke accidents are similar to however not as critical as historic wringer injuries. Consequences of a crush damage could be minimized by the use of compression dressings, elevation, and early follow-up. Though the preliminary ache has subsided, there continues to be level tenderness, swelling, ecchymosis, hematoma, or pain with use. Common sites of painful bruising are the shin, iliac crest ("hip pointer"), and anterior thigh (quadriceps). Patients often seek medical attention for trivial injuries after being struck by an object due to preliminary extreme pain, rising discoloration of the pores and skin, worsening swelling, concern of an underlying fracture, or secondary achieve after an altercation. What To Do: Take an intensive historical past to ascertain the mechanism of injury, and carry out a whole examination to document structural integrity and intact perform. Ecchymosis and/or swelling out of proportion to the mechanism of injury warrant an investigation of possible bleeding issues. Patterned bruises can be caused by coining and cupping, that are innocent cultural cures employed by conventional Asian households. Suspected domestic, elder, or youngster abuse must be reported immediately to the appropriate authorities. With an extensive muscle contusion, consider in search of secondary rhabdomyolysis. Pain out of proportion to the damage of a muscle or severe pain rising over time within a muscle compartment warrants immediate measurement of the compartment stress to rule out the ischemic pain of compartment syndrome. One dependable intracompartmental stress monitoring system is the Stryker Intra-Compartmental Pressure Monitor System (Stryker Surgical, Kalamazoo, Mich. Fractures are uncommon after a direct blow but are advised by ache with distant percussion, stressing of bone. The yield may be very low when radiographs are ordered on the basis of ache and swelling alone. Explain to the patient that swelling will peak in 1 day and then resolve gradually.
Sweet Mary (Lemon Balm). Rumalaya gel. - Cold sores.
- Colic in breast-fed infants.
- How does Lemon Balm work?
- Upset stomach (dyspepsia), when a combination of lemon balm and several other herbs is used.
- What other names is Lemon Balm known by?
- Improving the quality of sleep, when taken with valerian.
- What is Lemon Balm?
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96446
Rumalaya gel 30 gr low priceGrafting carries added dangers because the graft might occlude muscle relaxant brand names cheap 30gr rumalaya gel amex, slim muscle relaxant that starts with the letter z discount 30 gr rumalaya gel with visa, dilate spasms after urinating generic 30gr rumalaya gel amex, or rupture yawning spasms cheap rumalaya gel 30gr free shipping. He may have a urinary catheter in place to enable correct output measurement. Evaluate the power and sound of the blood move and the symmetry of the pulses, and notice bruits. Record the temperature of the extremities, their sensitivity to motor and sensory stimuli, and pallor, cyanosis, or redness. Rate peripheral pulse volume and power on a scale of zero (pulse absent) to 4 (bounding pulse), and check capillary refill time by blanching the fingernail or toenail; regular refill time is lower than three seconds. Keep your guard � If the affected person is awaiting surgical procedure for aortic aneurysm restore, be on guard for indicators and signs of acute dissection or rupture. Especially notice sudden, extreme, tearing ache within the chest, abdomen, or decrease back; severe weakness; diaphoresis; tachycardia; or a precipitous drop in blood strain. Check all extremities bilaterally for muscle strength and motion, shade, temperature, and capillary refill time. Administer antithrombotics, as ordered, and monitor acceptable laboratory values to consider effectiveness. To promote good pulmonary hygiene, encourage the affected person to cough, turn, and deep-breathe frequently. Valve surgery Types of valve surgery embody valvuloplasty (valvular repair), commissurotomy (separation of the adherent, thickened leaflets of the mitral valve), and valve alternative (with a mechanical or prosthetic valve). Attention to prevention Valve surgical procedure is often used to stop heart failure in a patient with valvular stenosis or insufficiency accompanied by extreme, unmanageable signs. Pressure points Because of the high pressure generated by the left ventricle during contraction, stenosis and insufficiency most commonly have an result on the mitral and aortic (c) 2015 Wolters Kluwer. Complication Pulmonary an infection Signs and symptoms � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � Fever Cough Congestion Dyspnea Abnormal lung sounds Fatigue Malaise Redness Warmth Drainage Pain Fever Increased coronary heart fee Hypertension or hypotension Malaise Microalbuminuria Infection Renal dysfunction � Low urine output � Elevated blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine levels � � � � � � � � � � � � Reduced or absent peripheral pulses Paresthesia Severe ache Cyanosis Loss of Doppler sign in bypass graft Hypotension Tachycardia Restlessness and confusion Shallow respirations Abdominal ache Increased stomach girth Lethargy Occlusion Hemorrhage (c) 2015 Wolters Kluwer. It will get sophisticated Although valve surgery carries a low threat of mortality, it can trigger severe complications. Hemorrhage, for instance, may outcome from unligated vessels, anticoagulant therapy, or coagulopathy resulting from cardiopulmonary bypass throughout surgery. Stroke could end result from thrombus formation caused by turbulent blood flow through the prosthetic valve or from poor cerebral perfusion (c) 2015 Wolters Kluwer. In valve substitute, bacterial endocarditis can develop within days of implantation or months later. Frequently assess heart sounds; report distant coronary heart sounds or new murmurs, which can point out prosthetic valve failure. Such disturbances may sign harm of the conduction system, which may happen during valve replacement from proximity of the atrial and mitral valves to the atrioventricular node. Arrhythmias can also end result from myocardial irritability or ischemia, fluid and electrolyte imbalance, hypoxemia, or hypothermia. If you detect serious abnormalities, notify the physician and be ready to assist with short-term epicardial pacing. Evaluate tissue oxygenation by assessing breath sounds, chest excursion, and symmetry of chest growth. Assess chest tubes regularly for signs of hemorrhage, excessive drainage (greater than 200 ml/hour), and a sudden decrease or cessation of drainage. Monitor intake and output, and assess for electrolyte imbalances, especially hypokalemia. Start the affected person on incentive spirometry, and encourage him to splint the incision, cough, turn incessantly, and deep-breathe. In a surgical procedure, blood is diverted from a ventricle to a man-made pump. An influx cannula drains blood from the left ventricle in to a pump, which then pushes the blood in to the aorta through the outflow cannula. A steady flow pump fills continuously and returns blood to the aorta at a continuing rate. Other complications might embody coronary heart failure, bleeding, cardiac tamponade, or infection. Evaluate oxygen saturation or blended venous oxygen saturation ranges, and administer oxygen as needed and as ordered. Percutaneous balloon valvuloplasty enlarges the orifice of a stenotic coronary heart valve. Percutaneous balloon valvuloplasty Percutaneous balloon valvuloplasty may be carried out in the cardiac catheterization laboratory. A small balloon valvuloplasty catheter is introduced via the skin at the femoral vein. Balloon bungles Unfortunately, aged sufferers with aortic disease commonly expertise restenosis 1 to 2 years after present process balloon valvuloplasty. Patient preparation � Describe the procedure to the patient and his family, and tell them that it takes 1 to 4 hours to full. The doctor uses a balloon-tipped catheter to dilate a coronary artery that has turn out to be narrowed due to atherosclerotic plaque. Patients with a historical past of lower than 1 year of disabling angina make good candidates because their lesions are inclined to be softer and more compressible. To stop restenosis, such procedures as stenting, atherectomy, and laser angioplasty may be performed. Also, vascular brachytherapy and new drug-eluting stents may lower the incidence of restenosis. The illustration beneath shows the doorway of a guide catheter in to the coronary artery. When angiography exhibits the information catheter positioned at the occlusion site, the doctor fastidiously inserts a smaller double-lumen balloon catheter through the information catheter and directs the balloon via the occlusion. The physician then inflates the balloon, inflicting arterial stretching and plaque fracture, as proven under. The balloon may need to be inflated or deflated several instances until successful arterial dilation occurs. Plaque Catheter in place; balloon deflated Balloon inflated Catheter Patient preparation � Describe the procedure to the affected person and his family, and tell them that it takes 1 to 4 hours to full. Preventing restenosis Standard angioplasty is performed to remove the plaque blockage within the coronary artery. However, restenosis of the vessel is a frequent complication that happens from scar tissue formation quite than plaque buildup. Vascular brachytherapy Vascular brachytherapy is using radiation in the coronary vessels to inhibit the development of this scar tissue, thus stopping restenosis of the vessel. The radiation and catheter are then eliminated, with no radiation source being left within the physique. Coronary drug-eluting stents Stents are used to open arteries that feed the heart, thereby bettering circulation to myocardial tissue. Drug-eluting stents open the artery and in addition release a drug to the implantation web site that helps scale back restenosis. Placement of drug-eluting stents throughout a cardiac catheterization or angioplasty process is the same as for regular stents.
Syndromes - Making special proteins, called antioxidant enzymes, which play a role in preventing cell damage
- Muscles on the weak side of the body may be very tight.
- Corticosteroid injections
- Blood chemistry tests (basic or comprehensive metabolic panel)
- Fever
- Abdominal distention
Order rumalaya gel 30 gr without a prescriptionUsing the simple approach described muscle relaxant yellow pill v rumalaya gel 30 gr otc, linear foreign bodies muscle relaxant vicodin purchase 30gr rumalaya gel otc, similar to needles muscle relaxant menstrual cramps cheap rumalaya gel 30 gr without a prescription, may be faraway from the only real of the foot without extensive dissection muscle relaxant cyclobenzaprine dosage generic rumalaya gel 30gr, complicated or cumbersome tools, or repeated radiographic research. This ache is accompanied by a really pink, tender swelling of the nail fold, or this swelling could also be much less purple and tender and seem chronic in nature. Fluctuance which could be tough to detect, together with local purulence on the nail margin, could occur, and infection may lengthen beneath the nail margin to involve the nail bed. This also occurs with people whose palms are regularly exposed to moisture and minor trauma. Alternatively, use a large-gauge needle with the bevel all the way down to elevate the lateral nail fold. When this separation or puncture of the cuticle occurs, pus will often unexpectedly drain from the eponychial cul-de-sac. The patient can remain fairly cellular if he uses a disposable cup to soak his finger while performing his daily routine. Under nail C If no pus was obtained, present shut follow-up and consider prescribing an antibiotic: In uncomplicated circumstances, without likely oral flora publicity: cephalexin 250 to 500 mg qid � 7 days or dicloxacillin 250 to 500 mg qid � 7 days. In instances involving more vital disease, or immunosuppression: amoxicillin/ clavulanate (Augmentin), 875 mg/125 mg bid or clindamycin (Cleocin), 300 mg qid � 7 days. There must be no deliberate invasion in to the dermis (although there could also be an inadvertent stick); due to this fact it could nonetheless be pointless to carry out a digital block. Most important, instruct the affected person (as described above) to perform heat soaks for 10 to 15 minutes at least qid for 1 to 2 days. Chronic Paronychia When signs and findings are minimal, consider conservative therapy or temporizing the condition by sliding a cotton wedge or waxed dental floss beneath the corner of an ingrown nail to raise the nail edge from its embedded position. When candidiasis is suspected, the world should be saved dry and handled with local functions of nystatin or a topical antifungal treatment combined with a topical steroid. Also, instruct the patient to lower actions similar to operating or different sports that put strain on the toes. Inform him that it may take three months for an embedded toenail to grow past the lateral nail fold and that a cotton wedge must be repeatedly replaced till this happens. First cleanse the toe with an iodine-povidone solution, after which elevate the outer edge of the nail plate by inserting a nice straight hemostat beneath the nail. The patient is instructed to soak the toe in heat water for 20 minutes twice per day and arrange for multiple follow-up visits. Subungual Abscess (When Pus Is Visible beneath the Nail) Consider conservative therapy not requiring a digital block. Merely carry out a trephination utilizing the same "scorching paper clip" technique used for a subungual hematoma (see Chapter 156). The affected person should carry out frequent warm soaks over the next 36 hours to stop recurrence. A extra aggressive approach, requiring digital block, is to excise a portion of the nail. After performing a digital block, cleansing with iodine-povidone and performing a bloodless subject, insert a fantastic straight hemostat between the nail and the nail bed, and push and unfold until you enter the eponychial cul-de-sac. Using a pair of robust fine scissors, minimize away the one quarter to one third of the nail plate bordering the paronychia. A nonadherent dressing is required over the exposed nail bed, in addition to an early dressing change (within 24 hours). Inform the affected person that extensive damage to the germinal matrix by the infection could preclude wholesome nail regrowth. The cuticle needs solely to be separated from the nail to release any assortment of pus. When coalescing vesicles with surrounding erythema are current, assume that the infection is attributable to herpes simplex virus. Treatment includes inhibition of viral replication with acyclovir (Zovirax), valacyclovir (Valtrex), or famciclovir (Famvir) (see Chapter 54). The more intensive the an infection is, the extra aggressive the surgical approach have to be. Ingrown toenails (onychocryptosis) occur most regularly within the early to midadolescent period. Subsequent development causes a spicule of the nail, often in the lateral sulcus, to penetrate the pores and skin. This spicule introduces bacteria and infection in to the encompassing tissue with formation of pus and granulation tissue. Whenever conservative therapy is instituted, the patient should be advised of the advantages and drawbacks of that method. No single antibiotic will present complete coverage for the array of bacterial and fungal pathogens cultured from paronychias. In concept, amoxicillin/clavulanate clindamycin ought to be essentially the most applicable antibiotics, but as a outcome of most paronychias are easily cured with simple drainage, systemic antibiotics are normally not indicated. In immunocompromised patients, those with peripheral vascular disease, and those in whom unusual pathogens are suspected, cultures and antibiotics are certainly warranted. Remain alert to the possible problems of neglected paronychia, similar to osteomyelitis, septic tenosynovitis of the flexor tendon, or a closedspace infection of the distal fingerpad (felon). Recurrent infections may be brought on by a herpes simplex an infection (herpetic whitlow) or fungus (onychomycosis). Tumors corresponding to squamous cell carcinoma or melanoma, cysts, syphilitic chancres, warts, or international physique granulomas can sometimes mimic paronychia. Failure to remedy paronychia inside 4 or 5 days ought to immediate specialized culture techniques, biopsy, or referral. If the puncture wound is palpated, an underlying pencil level may give the affected person a international physique sensation. Pencil "leads" are manufactured from clay and graphite, which is primarily carbon and unhazardous. Conduct a full examination, including sensory and motor function of the affected area. If uncertain, get hold of a radiograph or ultrasonogram to rule out the presence of a foreign body. Always administer native anesthesia utilizing lidocaine (1% with or with out epinephrine) before scraping wound. Discussion It is unwise to excise the complete wound, as a outcome of the resultant scar might be extra unpleasant than the tattoo. If a superficial pencil tip international physique exists, see Chapter 154 for an easy elimination technique. If tattooing is present and of beauty concern, the affected person might profit from a referral to a dermatologist for removal. Rarely, deep punctures or foreign bodies might require exploratory surgery within the operating room. There could additionally be ache and swelling, but often the affected person is simply asking for a tetanus shot. He can often be found in the emergency department with his foot soaking in a basin of povidone-iodine (Betadine) solution. The wound entrance normally seems as a linear or stellate tear in the cornified epithelium on the plantar surface of the foot.

Rumalaya gel 30 gr on-lineUnderstanding a balloon pump An intra-aortic balloon pump consists of a polyurethane balloon attached to an exterior pump console by means of a large-lumen catheter spasms calf muscles discount rumalaya gel 30 gr on line. This exterior pump works in exact counterpoint to the left ventricle spasms icd-9 buy rumalaya gel 30 gr without prescription, inflating the balloon with helium early in diastole and deflating it simply earlier than systole spasms caused by anxiety rumalaya gel 30gr without prescription. As the balloon inflates muscle relaxant parkinsons disease buy rumalaya gel 30gr on line, it forces blood towards the aortic valve, thereby raising strain within the aortic root and augmenting diastolic stress to improve coronary perfusion. It additionally improves peripheral circulation by forcing blood by way of the brachiocephalic, frequent carotid, and subclavian arteries arising from the aortic trunk. And pull the balloon deflates quickly at the end of diastole, creating a vacuum within the aorta. This vacuum action reduces aortic quantity and pressure, thereby reducing the resistance to left ventricular ejection (afterload). Ideally, balloon inflation should start when the aortic valve closes-at the dicrotic notch on the arterial waveform. Proper timing is crucial Early inflation can damage the aortic valve by forcing it closed, whereas late inflation permits many of the blood rising from the ventricle to flow past the balloon, reducing pump effectiveness. Late deflation increases the resistance in opposition to which the left ventricle should pump, possibly inflicting cardiac arrest. Inflation Early Normal Late Deflation Early Normal Late occludes the artery, you may see a diminished left radial pulse, and the affected person could report dizziness. Incorrect balloon placement can also trigger flank ache or a sudden lower in urine output. Quick response required � An alarm on the console might point out a fuel leak from a broken catheter or ruptured balloon. A minimum quantity or pumping ratio should be maintained to forestall thrombus formation. Most consoles have a flutter operate that strikes the balloon to prevent clot formation. Evaluate the location for bleeding and hematoma formation hourly for the following four hours. A great amount of electrical present is required for efficient monophasic defibrillation. Current flows to and fro Biphasic defibrillators have just lately been launched in to hospitals. The difference is that during biphasic defibrillation, the electrical current discharged from the pads or paddles travels in a optimistic direction for a specified duration after which reverses and flows in a adverse direction for the remaining time of the electrical discharge. The biphasic defibrillator delivers two currents of electrical energy and lowers the defibrillation threshold of the heart muscle, making it possible to efficiently defibrillate ventricular fibrillation with smaller quantities of power. The biphasic defibrillator is ready to regulate for differences in impedance (the resistance of the present via the chest). This performance reduces the number of shocks wanted to terminate ventricular fibrillation. With much less myocardial injury Because the biphasic defibrillator requires lower vitality ranges and fewer shocks, injury to the myocardial muscle is reduced. Biphasic defibrillators used at the clinically applicable vitality level could also be used for defibrillation and, in the synchronized mode, for synchronized cardioversion. If performing handbook exterior defibrillation, set the power stage at 200 joules (for a manual biphasic defibrillator) or 360 joules (for a monophasic defibrillator). Anterolateral placement For anterolateral placement, place one paddle to the right of the upper sternum, just under the proper clavicle, and the opposite over the fifth or sixth intercostal house on the left anterior axillary line. Anteroposterior placement For anteroposterior placement, place the anterior paddle immediately over the center on the precordium to the left of the decrease sternal border. Also, make a visible examine to make certain everyone is obvious of the affected person and the bed. Instruct somebody to reset the power stage on the defibrillator to 200 or extra joules (for a biphasic defibrillator) or 360 joules (for a monophasic defibrillator). The lead connects to a generator field, which is implanted in the right or left upper chest near the clavicle. The leadwires are inserted via the subclavian vein, threaded in to the center, and positioned involved with the endocardium. Pocket placement the leads are connected to the coronary heart beat generator, which is positioned beneath the pores and skin in a specifically prepared pocket in the right or left upper chest. Synchronized cardioversion Cardioversion (synchronized countershock) is an elective or emergency procedure used to correct tachyarrhythmias (such as atrial tachycardia, atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, and symptomatic ventricular tachycardia). Small shock In synchronized cardioversion, an electric current is delivered to the center to appropriate an arrhythmia. Thus, it reduces the chance that the present will strike in the course of the relative refractory period of a cardiac cycle and induce ventricular fibrillation. Cardioversion interrupts reentry circuits, allowing normal heart rhythms to regain management. Patient preparation � Describe this elective procedure to the affected person, and ensure an knowledgeable consent is obtained. Monitoring and aftercare � Turn on the defibrillator and select the ordered energy degree, normally between 50 and a hundred joules. Try, try once more Repeat this process till the arrhythmia is corrected or until the best vitality stage is reached. The monophasic vitality doses (or clinically equivalent biphasic vitality dose) used for cardioversion are: � a hundred, 200, 300, 360 joules for unstable ventricular tachycardia with a pulse � 50, a hundred, 200, 300, 360 joules for unstable paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia � one hundred, 200, 300, 360 joules for unstable atrial fibrillation with a speedy ventricular response � 50, 100, 200, 300, 360 joules for unstable atrial flutter with a fast ventricular response. Resetting document the this swap is important because rhythm earlier than most defibrillators automatically and after reset to an unsynchronized mode. Write it down � Document the use of synchronized cardioversion, the rhythm earlier than and after cardioversion, the amperage used, and the way the affected person tolerated the process. This implantation is usually performed in an working room or a cardiac catheterization laboratory. Permanent pacemakers are indicated for patients with: � persistent bradyrhythmia � complete heart block � congenital or degenerative coronary heart illness � Stokes-Adams syndrome � Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome � sick sinus syndrome. Setting the pace Pacing electrodes may be positioned in the atria, the ventricles, or both chambers (atrioventricular sequential or twin chamber). Biventricular pacemakers are additionally available for cardiac resynchronization therapy in some sufferers with coronary heart failure. To maintain the affected person wholesome and active, newer pacemakers are designed to enhance the guts price with exercise. Understanding pacemaker codes the capabilities of pacemakers are described by a five-letter coding system, though usually only the primary three letters are used. Here are the letters used to signify these options: � V Ventricle � A Atrium � D Dual (ventricle and atrium) � O None. Second letter the second letter signifies the center chamber the place the pacemaker senses the intrinsic activity: � V Ventricle � A Atrium � D Dual � O None. All collectively now It works by sending tiny electrical signals to the left and right ventricles on the identical time, ultimately inflicting the walls of the left ventricle to pump together. However, along with the two leads which would possibly be used in most pacemakers, a 3rd lead is placed in to a cardiac vein and paces the left ventricle.
Rumalaya gel: 30 gr
Cheap rumalaya gel 30 grThe vowels are produced by altering the form of the oral cavity by adjusting the jaws spasms 24 generic rumalaya gel 30 gr on-line, cheek spasms pregnant belly generic rumalaya gel 30gr on line, tongue muscle relaxant options buy cheap rumalaya gel 30 gr, and palate muscle relaxant effects buy rumalaya gel 30gr cheap. Consonants are produced by exhalation via the mouth, isolating the nasal cavity by raising the taste bud. By blocking the exhaled air by lips labial consonants corresponding to P and B are articulated whereas T and D which are lingual consonants want approximation of the tongue towards the palate. In nasal sounds corresponding to M and N the soft palate is relaxed and air passes via each the nasal cavity and the oral cavity. Abnormalities in any structures concerned in articulation can produce a speech defect. In cleft palate, air always enters the nasal cavity giving nasal quality for the voice and affecting sounds which require contact between tongue and palate. Within a couple of days the alternative wire will cross the midline on phonation and approximate itself to the paralysed wire and the voice will return. However complete apposition of the two cords is impossible especially posteriorly. Bilateral recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis leads to aphonia due to lack of ability to adduct the vocal cords. External laryngeal nerve paralysis which not often happens in thyroid surgery paralyses the cricothyroid muscle resulting in inability to produce certain highpitched sounds. Disturbances in coordination of motor pathways as in cortical damages and extrapyramidal lesions produce dysarthria. In Parkinsons disease the tremor and muscular rigidity have an result on the muscles concerned in speech causing rapid and monotonous speech with slurring of consonants and repetition of syllables. Dysphasia results from lesions in the sensory cortex and a variety of the associated areas related with speech. They are unable to comprehend what was heard or seen and hence produce inappropriate responses and infrequently are unable to find acceptable words or formulate sentences. The visible pathway consists of: � � � � � � optic nerve; optic chiasma; optic tract; lateral geniculate body; optic radiation; and visual cortex. Optic nerve the optic nerve commences on the lamina cribrosa, the place the axons of the ganglion cells of the retina (page 432) pierce the sclera. The optic nerve coated by the dura, arachnoid and pia runs postero-medially in the orbit to enter the optic canal. The nerve which is longer than the gap it has to transverse lies loosely in the orbital fat surrounded by the four recti muscular tissues. The artery which is superolateral to the nerve posteriorly crosses above the nerve to its medial aspect. It offers off the central artery of the retina which sinks in to its inferomedial facet. More proximally the nerve has a short course in the middle cranial fossa earlier than uniting with the nerve of the other facet on the chiasma. Optic chiasma At the chiasma nerve fibres from the temporal half of the retina lie laterally and those from the medial half lie in the center. All the fibres that arise from the ganglion cells medial to a line passing through the fovea centralis cross from the optic nerve of that side to the optic tract of the opposite side. The left optic tract thus accommodates fibres from the temporal half of the left retina and nasal half of the proper retina. As the temporal half of the retina perceives light from the nasal half of the visible subject and the nasal half of the retina from the temporal visual subject, the left optic tract transmits data from the right half of the visible subject (and the right tract from the left half of the visible field). The upper half of the retina is represented on the higher lip of the calcarine fissure and the lower half on the lower lip. The macular area has a higher cortical illustration than the peripheral retina facilitating acuity of imaginative and prescient for the macular region. Lesions of the retina or optic nerve end in unilateral blindness of the affected section. Lesions of the optic tract and optic radiations produce controlateral homonymous hemianopia. Lesions of the center fibres of the optic chiasma, as attributable to a pituitary tumour, will trigger bitemporal hemianopia. Inferior to the optic chiasma lies the sella turcica containing the pituitary gland. A tumour of the hypophysis cerberi might bulge the diaphragma sellae or break by way of it and press on the optic chiasma. Aneurysm of the artery at this level will compress the lateral fibres within the chiasma. The tract varieties the anterolateral boundary of the interpenduncular fossa crossing the cerebral peduncle to terminate in the lateral genicualte body. Some enter the midbrain ending in the superior colliculus or the pretectal nucleus. Lateral geniculate body and optic radiation the great majority of the fibres within the optic tract finish in the lateral geniculate body. The six-layered lateral geniculate body has point-to-point illustration on the retina. From the lateral geniculate physique fibres of the optic radiation sweep laterally and backwards to the visible cortex within the occipital lobe. Alternate phases of condensation and rarefaction of molecules produce sound waves. The loudness of the sound is proportional to the amplitude of the wave and its pitch is correlated with the frequency. The ear converts sound waves in the air to motion potentials in the auditory (cochlear) nerves. The waves are transmitted by the tympanic membrane (ear drum) via the actions of the auditory ossicles in to the interior ear. These produce movements within the fluid within the inside ear which in turn produce waves of movement of hair cells of the organ of Corti which generate action potentials within the nerve fibres. The sound stress in the air as it passes through the middle ear must, due to this fact, be amplified. Because the tympanic membrane is a lot larger than the oval window the stress (force per unit area) is increased 15�20 occasions when transmitted from the bigger membrane to the smaller. The auricle collects the sound waves and so they move along the exterior auditory meatus to produce vibrations of the tympanic membrane. This is achieved by opening of the auditory tube which equalises the center ear air strain to that of the external auditory meatus. The vibrations of the tympanic membrane are transmitted to the malleus, incus, and stapes. When the deal with of the malleus strikes medially with the tympanic membrane, the pinnacle of the malleus and the body of the incus move laterally. Movements of the head of the stapes swings its foot-piece to and fro like a door hinge at the posterior edge of the oval window. The vibrations transmitted by the stapes produce displacement of the basilar membrane and actions of the hair cells and tectorial membrane of the organ of Corti which initiates nerve impulses in the auditory nerve.
References - Wingate JT, Erickson BA, Murphy G, et al: Multicenter analysis of patient reported outcomes following artificial urinary sphincter placement for male stress urinary incontinence, J Urol 199(3):785n790, 2017.
- Vanarsdall RL, Corn H. Soft-tissue management of labially positioned unerupted teeth. Am J Orthod 1977;72:53-64.
- Ozdemir E, Saliba R, Champlin R, et al. Risk factors associated with late cytomegalovirus reactivation after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for hematological malignancies. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2007;40:125-136.
- Gilja I, Radej M, Kovacic M, et al: Conservative treatment of female stress incontinence with imipramine, J Urol 132:909, 1984.
- Nardi PM, Ruchman RB: CT appearance of diffuse peritoneal endometriosis. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1989; 13:1075-1077.
- Tuttle TM, Haubermann EB, Grund EH, et al. Increasing use of contralateral prophylactic mastectomy for breast cancer patients: a trend toward more aggressive surgical treatment. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(33):5203-5209.
- Pohl HG, Rushton HG, Parl J-S, et al: Adjunctive oral corticosteroids reduce renal scarring: the piglet model of reflux and acute experimental pyelonephritis, J Urol 162:815-820, 1999.
|