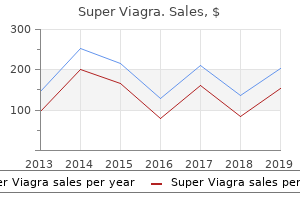
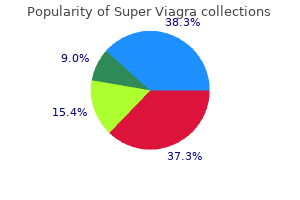
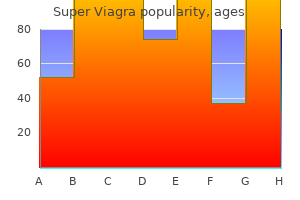
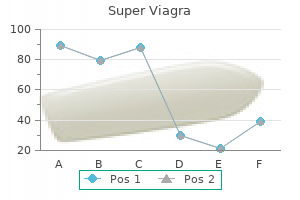
Super Viagra
Menachem Weiner, MD - Assistant Professor
- Anesthesiology
- Mount Sinai School of Medicine
- New York, New York
Cheap super viagra 160 mg onlineTwo distal interlocking screws are really helpful for comminuted or segmental fractures erectile dysfunction essential oils purchase 160 mg super viagra overnight delivery. If there are adjustments to be made impotence herbal remedies order super viagra 160 mg overnight delivery, these are finest made whereas the affected person is still beneath anesthesia erectile dysfunction oral medication discount 160mg super viagra with visa. Radiographs should reveal the entire fracture area erectile dysfunction injection medication purchase 160 mg super viagra with amex, together with the whole implant construct. Patients are mobilized to a chair upright place the day after the operative procedure. Ambulation with supervision is allowed, with weight bearing as tolerated with a walker or crutches and emphasis on heel-strike and upright steadiness workout routines. Patients are re-evaluated with an examination and ra diographs at 2 weeks after which month-to-month thereafter until fracture therapeutic is documented and the patients have maximized ambulatory capabilities, usually by 6 months after the injury. The surgeon ought to emphasize good vitamin and hip abductor exercises bilaterally. Patients have to be recommended to report any elevated swelling or respiratory distress as an emergency due to the excessive danger of thromboembolic illness. Functional recovery is poor in many patients, however, with more than 60% of patients failing to recover their preinjury level of operate. Many sufferers maintain progressive collapse of the hip into varus and shortening of the leg with the current era of sliding hip screw fixation. It is manifested by collapse of the screw and varus migration of the femoral head construct, with ultimate cutout failure within the worst circumstances. This happens to a small degree in all circumstances, because the sliding impaction was designed to reduce catastrophic cutout. Infection occurs in 1% to 2% of postoperative instances and is minimized by preoperative antibiotics, normally a cephalosporin class of antibiotic. In immunocompromised and malnourished patients, commonplace care entails isolation and sensitivity testing of the causative micro organism and acceptable intravenous antibiotics, in session with an infectious illness specialist, and commonplace d�bridement and irrigation for wound care. The lateral trochanteric wall: a key factor within the reconstruction of unstable pertrochanteric hip fractures. Reliability of classification systems for intertrochanteric fractures of the proximal femur in skilled orthopaedic surgeons. Dynamic hip screw compared with external fixation for treatment of osteoporotic pertrochanteric fractures: a potential randomized examine. Penetration of the distal femoral anterior cortex throughout intramedullary nailing for subtrochanteric fractures: a report of three circumstances. A important analysis of the eccentric place to begin for trochanteric intramedullary femoral nailing. Integrity of the lateral femoral wall in intertrochanteric hip fractures: an important predictor of a reoperation. Is there a gluteus medius tendon harm throughout reaming by way of a modified medial trochanteric portal Trochanteric versus piriformis entry portal for the remedy of femoral shaft fracture. Avoidance of malreduction in proximal femur fractures: minimally invasive nail insertion approach. Chapter 8 Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Peritrochanteric Hip Fractures Matthew E. These fractures happen after falls in a considerable variety of aged folks (estimated incidence of 250,000 fractures per year) and represent a rising percentage of healthcare expenditures yearly. These fractures require operative intervention to achieve stable fracture fixation to enable quick patient mobilization. However, owing to the pull of the musculature in this area, the fracture will heal in gross malalignment, resulting in subsequent practical limitations. Complaints of hip ache before falling could indicate a preexisting pathologic process that requires additional analysis. A thorough global musculoskeletal examination of the affected person is critical due to the high incidence of related fractures (especially of the wrist and proximal humerus) in the elderly inhabitants sustaining hip fractures from simple falls. Examination of the soft tissue overlying the lateral hip, sacrum, and heels is important to make sure that no stress ulcers or abrasions have occurred in these areas. The basic bodily finding in a patient with a peritrochanteric hip fracture is a brief, externally rotated affected extremity. Hip rotation assessment: Because of the muscular attachments and gravity, the lower extremity tends to rest externally rotated with a peritrochanteric hip fracture. Passive log-rolling of the leg will elicit ache (particularly with inside rotation, which tightens the hip capsule and causes ache as a outcome of the hemarthrosis). This could also be an particularly helpful discovering in occult hip fractures with no apparent fracture deformity. The angle subtended by the femoral neck and long axis of the femoral shaft in the coronal airplane (the neck�shaft angle) is often between one hundred twenty and one hundred thirty five degrees in adults. The common femoral neck is anteverted between 10 and 15 degrees (range 0 to 50 degrees) and slightly translated anteriorly (5 to eight mm) from the axis of the femoral shaft. Multiple muscle teams attach to this region of the femur: Iliopsoas: attaches to the lesser trochanter and exerts a flexion and external rotation drive to the hip Abductors and quick external rotators: attach to the greater trochanter Adductors: attach to the femoral shaft distal to the peritrochanteric area the blood provide to the peritrochanteric region of the femur is rich and ample. The medial and lateral femoral circumflex arteries supply the cancellous bone of the trochanteric area via muscle attachments at the vastus origin and the insertion of the gluteus medius. Numerous factors, similar to structurally weak bone, less subcutaneous padding, and slowed protecting reflexes, result in elevated forces on the hip with falls in the elderly population. The stability between medical optimization and early operative management in this principally elderly affected person population is delicate. Group 3 has a fracture geometry that runs in a more transverse or reverse oblique sample, with the fracture line exiting the lateral cortex beneath the vastus ridge. Implant selection for fracture fixation must be guided based on fracture pattern and patient age. Recent research have shown improved patient outcomes and better maintenance of fracture alignment with the use of intramedullary gadgets in this kind of fracture. Sliding hip screw devices are contraindicated in these fractures because of the excessive incidence of implant failure. A fixed-angle plate (such as a 95-degree blade plate or locked plate), as nicely as a reconstruction-type nail with a small proximal diameter, will allow for secure fracture fixation, together with preserved proximal femoral bone inventory, which is helpful in cases necessitating later revision open discount and inside fixation. Preoperative planning is significant for a passable consequence when a peritrochanteric fracture is fastened with a blade plate. Multiple views of the nonfractured, contralateral hip and femur, as nicely as a quantity of traction views of the fractured hip, are required to properly plan the surgical sequence for this kind of fixation. Positioning When fixing a peritrochanteric fracture with a sliding hip screw device, the affected person is positioned on a well-padded fracture table, with the nonfractured leg rigorously positioned in flexion and external rotation in a properly leg holder. Alternatively, the patient may be placed in the "scissor" position, with the nonfractured leg extended and supported with a boot. This place is useful in some patients (eg, weight problems, stiff contralateral hip, bilateral injuries) who might not be ready to flex and externally rotate the contralateral hip to allow use of a well leg holder. We favor to safe the affected foot to a well-padded heel cup with tape, leaving the posteromedial neurovascular bundle uncompromised.
Trusted 160mg super viagraRadiographs are evaluated at 1- to 2-week intervals over the primary month of remedy to verify maintenance of acceptable alignment erectile dysfunction from steroids super viagra 160mg cheap. The lateral radiograph is essentially the most accurate to use for measuring the appropriate nail size impotence guide buy cheap super viagra 160mg line. Orthogonal radiographs of the uninjured tibia can be used as templates for figuring out the appropriate size impotence bike riding cheap 160mg super viagra overnight delivery, alignment erectile dysfunction drugs research generic 160 mg super viagra amex, and rotation in comminuted fractures or open fractures with bone loss. A fracture desk can be utilized with boot traction, calcaneal traction, or an arthroscopy leg holder that supports the leg and offers mechanical traction when no assistants can be found. Several relatively well-accepted indications and contraindications have been established for the intramedullary nailing of tibia fractures (Table 2). Preoperative measurement of the intramedullary canal and the size of the tibia will help decide which measurement nail can be used. The fractured leg is positioned in calcaneal skeletal traction on the fracture table. This offers glorious mechanical traction however limits limb mobility, especially knee flexion. The knee is flexed over a positioning triangle in preparation for the surgical strategy. The tibial fracture is distracted and reduced using a mechanical distraction gadget with proximal and distal half-pins. A distal half-pin positioned just over and parallel to the plafond may be helpful for aligning the distal fragment and lies inferior to the projected end of the nail. The knee is maximally flexed over the triangle to permit for the right starting wire insertion angle. Typical setup for semi-extended nailing with a small bolster for restricted knee flexion and easy access to the limb for reduction and imaging. The semi-extended position permits for discount of the flexion deformity associated with these fractures. If the suprapatellar method is being carried out, a superomedial or superior midline is used and special instrumentation is required. All of the surgical approaches are carried out with the knee within the semi-extended place. Incise the pores and skin beginning at the inferior margin of the patella and continue distally in the midst of the patellar tendon. Incise the paratenon within the midline, and elevate medial and lateral flaps to identify the margins of the patellar tendon. Do not incise the capsule and keep away from injuring the menisci at the inferior margin of the incision. A formal full medial parapatellar method permits for straightforward patellar subluxation and start website localization however requires significant dissection. The distal portion of the quadriceps tendon is incised, leaving a 2-mm cuff of tendon medially for later restore. A formal medial arthrotomy is completed extending around the patella, leaving a 2-mm cuff of capsule and retinaculum for later restore, and persevering with alongside the medial border of the patellar tendon. Incise the quadriceps tendon within the midline, extending proximally from the superior pole of the patella, and make an arthrotomy. Standard Intramedullary Nailing Initial Guidewire Placement Suprapatellar Approach30 the suprapatellar strategy requires particular nail insertion instrumentation as properly as cannulas for guide pin placement and reaming. Draping the leg more distally can restrict knee flexion because of bunching of the drapes. Flex the knee over a bolster or radiolucent triangle A padded thigh tourniquet may be applied and inflated during the surgical method, but it should not be inflated throughout reaming due to the danger of thermal injury to the intramedullary canal. The knee is maximally flexed, and the guidewire is aligned with the anatomic axis of the tibia. Typically, attaining an acceptable insertion vector would require the wire to be pushed in opposition to the patella or the peripatellar tissues. The frontal plane wire place ought to be consistent with the anatomic axis and proximally ought to be just medial to the lateral tibial spine. Marking the skin alongside the crest can assist in aligning the guidewire with the path of the intramedullary canal and reduce the necessity for fluoroscopic steering. Ideal proximal extra articular begin web site as seen on lateral fluoroscopic picture; this is close to the articular margin. An best insertion vector approaches a parallel path with anterior cortex and minimizes the chance of fragment extension with seating of the nail. Place a 15-degree bend 2 cm from the distal extent of the ball-tipped guidewire to permit for directional management during wire advancement. Alternatively, a straight ball-tipped guidewire can be used with an intramedullary discount instrument (eg, a cannulated finger device), which can exactly direct the wire and simplify passage across the fracture. A ball-tipped guidewire is launched into the proximal section, and the knee is barely prolonged for fracture reduction and instrumentation. Creating and Reaming the Starting Hole the opening reamer (matching the proximal nail diameter) is introduced by way of a tissue sleeve and inserted while rigorously sustaining knee hyperflexion and biplanar alignment. Fracture Reduction Simple Middle Diaphyseal Fractures (Transverse or Short Oblique) Manual traction with gross manipulation will scale back easy transverse mid-diaphyseal fractures. Medially-based external fixation or distraction with a large common distractor is helpful for reduction when no assistants can be found, in giant patients, or when used for provisional fixation. Placement of percutaneous pointed reduction forceps can be helpful in oblique and quick oblique patterns to obtain anatomic or near-anatomic reduction. Highly Comminuted Middle Diaphyseal Fractures Have comparability radiographic photographs of the uninjured extremity obtainable to be used as a template for length and rotational discount landmarks. Use fluoroscopy to localize clamp place and decide perfect clamp incision locations. Percutaneous clamps can precisely reduce and stabilize indirect fractures before nail introduction. The intramedullary discount software available in most nail or reamer sets can be used to manipulate the proximal fragment so as to advance the device across the fracture which achieves fracture reduction and guidewire placement. If discount is troublesome, a small-fragment unicortical plate can be used to maintain the reduction throughout reaming and nail placement. Passing the Guidewire Open Middle Diaphyseal Fractures Large segmental and butterfly fragments that are fully devitalized and void of soppy tissue attachments should be eliminated and cleaned of contamination. These items can then be reintroduced into the fracture website and used to carry out anatomic open reduction following passage of the intramedullary rod and interlocking. In metadiaphyseal fractures, the wire must be centered within the metaphyseal phase. A half-pin placed simply above the ankle joint lies beneath the projected finish of the nail.
Super Viagra: 160 mg
Super viagra 160mg with visaRandomized prospective research evaluating operative and nonoperative remedy of preliminary patellar dislocation found no profit from instant medial retinacular restore erectile dysfunction drugs with the least side effects generic super viagra 160 mg on-line. As a result impotence 101 cheap super viagra 160 mg visa, nonoperative management relies on brace protection throughout early progressive moblization and useful rehabilitation causes of erectile dysfunction in 20 year olds buy super viagra 160mg mastercard. After an acute dislocation erectile dysfunction at the age of 24 buy 160 mg super viagra otc, patients initially are positioned in knee immobilizers for comfort and weight bearing as tolerated. Patients are inspired to proceed wearing the patellastabilizing brace throughout participation in pivoting actions and sports activities. Surgical administration normally is indicated for any affected person with a minimal of two documented patellar dislocations and a physical examination demonstrating excessive lateral patellar laxity. A superolateral portal is used to facilitate viewing of the patellar articular floor and passive patellar tracking and mobility. Specifically, the patellofemoral compartment is assessed for the severity of articular cartilage harm and the presence of degenerative modifications. After dissection by way of the subcutaneous tissue, the superficial medial patellar retinaculum (layer 1) is recognized. The deep synovial layer (layer 3) may be dissected off the deep floor of the ligament to assist in inspection. The knee is then flexed to 30 degrees with the patella manually decreased in the trochlear groove. With the knee prolonged, a laterally directed force ought to reproduce a firm endpoint ("check rein" sign). Patellar mobility is assessed by applying medial and lateral forces of about 5 kilos with the knee flexed to 30 levels. If lateral displacement is lower than 5 mm or greater than 10 mm, then the medial restore is retensioned. Alternatively, the origin could additionally be approached through a separate posterior incision centered between the medial epicondyle and the adductor tubercle. The dissection is carried down through the subcutaneous tissue, and the injured medial retinacular tissue is recognized. Augmented restore of avulsion-tear sort medial patellofemoral ligament damage in acute patellar dislocation. Identify and isolate both the gracilis (proximal) and semitendinosus (distal) tendons from their deep facet, ie, from throughout the bursal layer. Apply pressure to the semitendinosus while liberating it from the crural fascia at the posteromedial nook with tissue scissors. Once all tendinous slips have been freed, harvest the semitendinosus tendon utilizing a closed (preferred) or open tendon stripper. Baseball stitches are placed on both free ends for later graft passage throught the two patellar tunnels. The graft is prepared on the back table by first sizing the graft to 240 mm, then folding it in half, leaving a doubled graft of a hundred and twenty mm. Patellar Tunnel Placement A longitudinal incision the length of the patella is made on the junction of the medial and middle thirds of the patella (in line with the medial border of the patellar tendon on the distal patellar pole). The medial 8 to 10 mm of the patella is exposed by subperiosteal dissection with a no. Again, a corresponding drill gap is positioned on the anterior floor of the patella about eight mm from the medial border, and the two holes are linked with a curved curette. The knee is flexed slightly to facilitate palpation of this landmark (flexion strikes the hamstrings posteriorly away from the medial epicondyle). If the affected person is obese and the landmarks are difficult to palpate, a small pores and skin incision is made and palpation is finished via the wound to identifty the ridge. Using a protracted, curved clamp, the chosen interval is developed (again, preferably between layers 2 and 3) from the patellar incision anteriorly to the medial femoral epicondyle posteriorly. With the tip of the clamp overlying the ridge between the medial epicondyle and adductor tubercle, layers 1 and 2 are incised utilizing a no. The tip of a Beath pin is placed at some extent 9 mm proximal and 5 mm posterior to the medial epicondyle; the pin is then handed towards the lateral side of the femur. If lengthening happens in flexion, a second Beath pin is positioned more distally towards the medial epicondyle. The first pin is left in place to facilitate repositioning while drilling the second Beath pin. If lengthing occurs in extension, a second Beath pin is placed more proximally toward the adductor tubercle. Again, the primary pin is left in place to facilitate repositioning while drilling the second Beath pin. Once the femoral pin web site is accepted, a blind tunnel is reamed into the femur the size of the doubled graft. The femur is reamed to a depth of no much less than 20 mm, with a preferred depth of 25 mm. Fixation to the femur may be achieved reliably with a 20-mm absorbable interference screw. The free graft arms are passed individually by way of their respective patellar tunnels using double 22-gauge chrome steel wire or a curved suture passer. The free graft arms are then doubled back and sutured on themselves simply medial to the patella using two determine 8 mattress sutures of no. After appropriate placement of the femoral attachment web site is confirmed using the isometry suture, the semitendinosus graft has been mounted to the femur utilizing an interference screw. The isometry suture is used to shuttle the graft anteriorly out the medial patellar incision. Schematic diagram demonstrating fixation of the graft posteriorly into a blind femoral tunnel, and anteriorly to two patellar tunnels. At the patella, every limb of the graft enters into respective medial drill gap, exits the anterior drill hole, then is sutured back to itself medial to the patella. Adjust the tunnel placement to guarantee appropriate graft conduct during flexion and extension, recreating isometry. The patella ought to enter the trochlea from the lateral facet because the knee is flexed. May occur during preparation of the two patellar tunnels or during passage of an oversized graft by way of a good patellar tunnel. If this happens, then drill a second exit hole more laterally on the anterior patellar floor or drill the tunnel transversely across the patella, exiting on the lateral patellar margin. The graft can be secured by tying the sutures over a button or suturing the end of the graft to the gentle tissues on the lateral patellar border. Bracing may be continued for up to 6 weeks during ambulation to stop falls until quadriceps control is restored.
Purchase super viagra 160mg with visaUsing a beneficiant amount of lubricant gel erectile dysfunction foundation buy 160 mg super viagra fast delivery, the gloved index finger is inserted into the rectum and then turned to face the anterior floor erectile dysfunction doctor sydney buy 160 mg super viagra mastercard, where the lobes of the prostate may be palpated through the rectal mucosa erectile dysfunction doctor boston discount 160 mg super viagra with amex. The seminal vesicles and vasa erectile dysfunction drugs buy order super viagra 160 mg online, neither of which is palpable in the normal individual, lie cranial to the prostate. It is important to assess the scale of the prostate, document the utmost transverse distance between the lobes, as well as the consistency, and check for the presence of tenderness, nodules and asymmetry. If the prostate feels boggy, this implies the presence of a prostatic abscess, and radiological imaging should be requested. If the affected person is systemically unwell, prostatic massage for bacteriology is contraindicated and only the midstream urine is collected for urine culture. Urinary retention should be managed utilizing a suprapubic catheter to keep away from instrumentation of the prostatic urethra. Severe instances of acute bacterial prostatitis require antimicrobial agents first intravenously and then followed by a 3�4 week oral course. About 5 per cent of circumstances of acute bacterial prostatitis progress to continual bacterial prostatitis, which is characterized by recurrent genitourinary and again pain with associated urinary frequency, urgency and dysuria. In contrast to acute bacterial prostatitis, the bodily findings in persistent bacterial prostatitis are sometimes normal. The diagnosis is commonly made by the culture of urine samples taken earlier than and after prostatic therapeutic massage. The prostatic therapeutic massage ought to be carried out through the rectal examination and often requires agency palpation to get hold of prostatic secretions from the urethral meatus. Bacilli can unfold into the decrease urinary tract from renal granulomas that erode into the calyceal system. Involvement of the bladder normally initially manifests within the area of the ureteric orifices with fibrosis and obstruction or ureteric reflux. In severe cases of infection of the scrotal contents, a discharging sinus may type. Schistosomiasis It is estimated that over 200 million individuals worldwide are infected with organisms of the genus Schistosoma, with 97 per cent of instances of centred round North and West Africa and the Middle East. Urinary tract schistosomiasis is attributable to infestation with a trematode fluke, the most common species being Schistosoma haematobium, S. Travel to endemic areas and swimming, bathing and wading in contaminated water may find yourself in an infection. Schistosomiasis is the outcomes of direct penetration of the skin by free-swimming cercariae released from freshwater snails. The cercariae enter the venous system, traverse the pulmonary circulation and migrate to the perivesical veins. On their method, they induce a granulomatous response resulting in ulceration of the mucosa on the release of the eggs into the lumen. However, most contaminated patients exhibit haematuria and, on cystoscopic examination, have typical perioval granulomas visible on the mucosal floor. Lower ureteric involvement is a feature of heavy or prolonged an infection and leads to obstruction and hydronephrosis. Epididymitis and Orchitis Epididymitis and orchitis are irritation, usually secondary to an infection, of the epididymis and testicle, respectively. Infection of the epididymis that progresses to the adjoining testicle is referred to as epididymo-orchitis. Both pathologies usually current with scrotal ache and swelling, which develop over a few days, in contrast to torsion of the spermatic cord, which presents inside hours. Associated signs embody dysuria, urinary frequency, urgency and occasionally fever and urethral discharge. A common cause of isolated orchitis is mumps, by which testicular ache is often preceded by fever, malaise and parotiditis. On examination, orchitis and epididymitis are characterised by swelling and tenderness of the respective tissue with erythematous and oedematous overlying scrotal pores and skin. In advanced circumstances, a reactive hydrocele might happen, making scrotal examination tougher. The most common presenting features are urinary frequency, nocturia, dysuria, fever, suprapubic ache, flank pain, haematuria and pyuria. Delayed analysis and intervention often ends in vital morbidity and sometimes demise. The supply of the an infection is often the big bowel, urinary tract or skin of the genitalia. Patients often have multiple comorbidities that compromise the immune system, which precipitates and augments the an infection. Sexually Transmitted Infections Gonorrhoea Gonorrhoea is a common infectious condition attributable to the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Approximately 10 per cent of infected males and 50 per cent of contaminated girls are asymptomatic. The latter is usually brought on by an infection with Chlamydia trachomatis, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Mycoplasma hominis or Trichomonas vaginalis. In primary genital herpes, the affected person sometimes starts to expertise constitutional signs (fever, headache, malaise) and local signs (pain, dysuria, itch, urethral and vaginal discharge) after an incubation interval between 1 day and 3 weeks. Recurrent genital herpes is common, occurring in as much as 90 per cent of sufferers within the first 12 months. Infection has been related to changes within the cervical epithelium that will progress to cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and later to invasive carcinoma. The primary route of infection is thru sexual contact, however it might also be transmitted from mom to fetus in utero or at delivery (congenital syphilis). During the latent part, which may last a few years, affected people are often asymptomatic. The manifestations of tertiary syphilis include symptoms of neurosyphilis and cardiovascular syphilis. The highest incidence of urinary tract stones happens in the 20�50-year-old group, however sufferers of all ages, including children, may be affected. More commonly, if the stone partially or totally obstructs the higher urinary tract, it induces renal ache, often referred to as a renal colic. Renal ache is attributable to acute distension of the renal capsule, and the discomfort radiates from the flank anteriorly in the direction of the umbilicus. Typically, patients with renal pain normally roll around holding their loin, whereas those with ache due to intraperitoneal illness favor to lie nonetheless to limit irritation of the peritoneum. Note the two dense white shadows at the identical degree within the dilated amassing system of the best kidney. On rectal examination, prostatic calculi in the peripheral aspect of the gland can often be felt as small hard nodules and could be confused with prostatic adenocarcinoma. Bladder most cancers is the fourth and eleventh most common cancer prognosis in women and men, respectively. This male:feminine ratio is partially due to the distinction in exposure to occupational carcinogens and cigarette smoking.
Generic 160mg super viagra visaRestoration of limb "anatomy" have to be accomplished and permit early range of motion erectile dysfunction protocol video quality super viagra 160 mg. Radiographs of the harm can be templated with implant templates to make positive that proper lengths are available erectile dysfunction treatment nasal spray buy cheap super viagra 160 mg on-line. Additionally erectile dysfunction treatment dallas texas super viagra 160 mg with visa, "preop planning" of the working room must be carried out; this features a dialogue with the operative team in regards to the positioning and tools wanted for the procedure erectile dysfunction treatment ppt cheap super viagra 160 mg overnight delivery. The need for bone grafting ought to be assessed (eg, iliac crest bone graft versus allograft or bone graft substitutes). A longer plate could additionally be wanted to tackle each injuries, or consideration to overlap implants could also be warranted to keep away from a stress riser. A extra lateral incision incorporating a lazy S incision for the proximal tibia damage may be required. This allows for knee flexion, enjoyable the gastrocsoleus complicated and facilitating the reduction. The incision may curve distally toward the tibial tubercle, and osteotomy may be performed. Newer approaches include a lateral inverted U to permit better entry to the joint and to permit for plate placement. The minimally invasive lateral method can be utilized for sure fractures and implants. The placement of the plate on the shaft is completed submuscularly, and reduction and fixation are accomplished percutaneously beneath fluoroscopic guidance. A modified anterior approach (the swashbuckler) has been described by Starr et al. A lateral parapatellar arthrotomy is finished with elevation of the vastus lateralis as in the lateral method. Positioning A radiolucent table should be used to permit enough visualization with a C-arm. The rotation of the proximal phase of the fracture (hip) should be aligned earlier than patient preparation. The injured hip is imaged and internally rotated by the hip bump so that duplication of the profile of the traditional side is achieved. The size of the bump may be adjusted as wanted for the amount of rotation required. This is adopted by imaging of the ipsilateral hip to get hold of the lesser trochanter profile (outlined). Positioning of the C-arm relative to the flexed knee to acquire a notch view to evaluate for guide pin penetration within the posterior facet. Guide pin penetrating into notch and back into medial femoral D condyle A medial parapatellar arthrotomy can be utilized for retrograde intramedullary nailing or limited screw fixation. It can be used in kind C3 fractures if a second plate is getting used (in conjunction with a lateral approach). It is used for plates however can be utilized for retrograde intramedullary nailing as quickly as the articular floor is reconstructed. A midline incision with a lateral parapatellar arthrotomy is my most well-liked publicity for kind C fractures. Proximal extension is made into the quadriceps tendon, sufficient to restore to itself. This allows exposure of the condyles for articular discount and simpler lateral plate insertion. Two or three 5-mm Schanz pins are positioned within the tibia in an anterior-to-posterior course simply medial to the crest to guarantee intramedullary placement. Two or three 5-mm Schanz pins are placed in the femoral shaft in an anterior-to-posterior course. In my experience plates have typically overlapped with pin sites and there has not been an associated drawback with infections. The bars could be configured in many ways, all of which offer short-term stabilization across the knee joint. Reduction of the Metaphyseal Component Gross reduction of the metaphyseal element of the fracture should be carried out with traction and manipulation of the pins. Although the knee could also be considerably flexed, the scanogram can nonetheless be obtained and the femoral length decided as opposed to the entire leg size. The rotation must be checked as quickly as once more earlier than locking the external fixator construct, as described above beneath positioning. This may be done through the use of the Bovie wire intraoperatively and assessing the mechanical axis of the limb by fluoroscopically evaluating from the hip to the ankle with the cord centered on the femoral head all the way to the ankle. The point at which the twine crosses the knee permits one to decide the varus�valgus alignment. Bridging knee external fixation in patient with associated acetabular fracture; the tibial pin was used for traction functions as well. Variations in plate utility as nicely as reduction instruments and strategies are distinctive to each system. The surgeon then does an alcohol preparation, adopted by iodine for the fixator, adopted by alcohol and iodine on the pores and skin. This has been profitable in our practice and permits for upkeep of traction in the course of the preparation and aids in the actual surgery, functioning as a femoral distractor. Additionally, a blunt Hohmann retractor could be positioned on the medial facet on the degree of the condyle to retract the patella. The capsule is subperiosteally elevated off the lateral femoral condyle to enable for placement of the plate. The lateral collateral ligament is preserved as a outcome of the dissection is proscribed to the anterior two thirds of the lateral femoral condyle and plate placement is usually proximal to the lateral epicondyle. Arthrotomy is started after which extended proximally into the quad tendon (dashed line). The arthrotomy is completed and the condyles are visualized with medial subluxation of the patella. C D the medial facet in the metaphyseal area is left undisturbed as a lot as attainable. Reduction of the Articular Surface the joint is evaluated to determine comminution. Each condyle is fully assessed first for smaller fracture fragments, with the objective of restoring each condyle anatomically. Each fragment could be rotated relative to one other; this should be addressed as discussed earlier than. The greatest method to assess that is under direct visualization and evaluating the reduction at the trochlear area of the patellofemoral joint. Additionally, preoperative evaluation assessing the lateral radiograph can information the surgeon. Definitive Fixation of the Condyles this could be achieved exterior the plate first and supplemented with screws via the plate.
Garden Lavender (Lavender). Super Viagra. - What is Lavender?
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Lavender work?
- What other names is Lavender known by?
- Hair loss in a condition called alopecia areata when applied to the scalp in combination with other oils.
- Dosing considerations for Lavender.
- Depression, sleeplessness, agitation, general psychological well-being, loss of appetite, colic, headache, migraine, toothache, acne, nausea, vomiting, cancer, use as a mosquito repellent and insect repellent, and other conditions.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96813
Order super viagra 160 mg overnight deliveryThis technique erectile dysfunction pump.com buy generic super viagra 160mg on line, however muse erectile dysfunction wiki order super viagra 160 mg without a prescription, can doubtlessly provide further data concerning the status of the articular cartilage and identification of free bodies impotence tcm buy cheap super viagra 160mg on-line. Ultrasonography can even assist in the assessment of capitellar lesions erectile dysfunction pills over the counter buy super viagra 160 mg cheap, including early phases, but ultrasound is technician dependent. Activity modification consists of avoiding throwing activities and weight bearing on the concerned arm. Short-term immobilization (less than 2 to three weeks, depending on symptoms) could additionally be thought-about. Activity modification is continued till the radiographic look of revascularization and healing. The surgeon must assess the scale, stability, and viability of the fragment and resolve whether or not to remove the fragment or try and surgically reattach it. Arthroscopic abrasion chondroplasty or subchondral drilling could additionally be performed to encourage healing. Although signs often improve, about half of all sufferers will continue to have continual pain or limited vary of movement. Surgical indications for operative administration of steady lesions with intact articular cartilage include radiographic evidence of lesion development and failure of symptom resolution regardless of a 6-month trial of a conservative, nonoperative routine. Unstable lesions, characterized by overlying articular cartilage damage and instability in addition to collapse or disruption of the subchondral bone architecture, and people with free our bodies are often managed surgically. They characteristically present with extra superior radiographic changes (including a well-demarcated fragment surrounded by a sclerotic margin). There is controversy as to whether or not simple fragment excision or discount (open or arthroscopic) and inside fixation is the preferred treatment. Many authors advocate excision of displaced fragments, typically augmented by drilling or microfracture. Critical issues in operative planning embrace the scale and integrity (viability) of the fragment, the subchondral architecture on the fragment and the opposing bony bed, the poten- tial for anatomic restoration of the articular floor, and the strategy of fixation if tried. Internal fixation of the fragment may be performed utilizing metallic screws, bioabsorbable screws or pins, Kirschner wire, bone pegs, and dynamic staple fixation. There have been a number of reports of osteoarticular autograft or allograft plugs within the remedy of more advanced lesions, but experience with this methodology is restricted. This is the popular position, significantly because of the benefit of posterior elbow access. The setup of the room is the same and the relative place of the elbow for the surgeon is analogous between the susceptible and lateral positions. The elbow arthroscope is introduced in from the proximal anteromedial portal that provides a direct view of the anterior capitellum and radial head. Examination under anesthesia is performed to assess range of movement and ligamentous stability, significantly valgus laxity, as harm to the ulnar collateral ligament within the athlete may enhance the load on the radiocapitellar joint. Diagnostic arthroscopy of the elbow is carried out, utilizing a proximal anteromedial portal, a proximal anterolateral portal, and two posterior portals. Prone positioning is most well-liked because it permits easy access to the elbow, reduces the danger of sterility breaks if the arm must be in a finger-trap system, as wanted for supine elbow arthroscopy, and arthroscopy. The patient is positioned on chest rolls and padding under the knees and feet and ankles. Complete elbow examination is necessary to look for unfastened our bodies: Proximal anteromedial portal Proximal anterolateral portal Posterior central portal Posterolateral portal Direct lateral portal Loose our bodies tend to cover: In the proximal radioulnar joint anteriorly or the gutters In the olecranon fossa or gutters posteriorly, notably the lateral gutter When trying at the capitellum from the proximal anteromedial portal, instrumentation (shavers, burrs, graspers, and curettes) may be accomplished using the proximal anterolateral portal. Then the arthroscope is brought in from the posterior portals to search for unfastened bodies. This portal is necessary to absolutely evaluate the extent of the lesion and to enable for enough d�bridement of unfastened cartilage. View from the proximal anteromedial portal reveals a flap of cartilage from the capitellum (left) and a barely deformed radial head (to the right). This is achieved by complete d�bridement of all unstable and damaged cartilage within the lesion and the preservation of the subchondral layer for chondral lesions, based mostly on experience of the therapy of knee chondral injuries. All underlying bone is d�brided with an arthroscopic shaver or burr or manually with curettes or pituitary rongeurs. This portal is mandatory to totally evaluate the extent of the lesion and to enable for sufficient d�bridement of unfastened cartilage and may permit for a good path for microfracturing the bed. Abrasion is carried out from either anterolateral or direct lateral portals to the entire lesion. For chondral lesions, abrasion arthroplasty includes removal of the zone of calcified cartilage, then use of a burr to frivolously take away solely a partial thickness of the subchondral bone to expose subchondral arterioles to bring blood into the lesion. The bone is pierced every three to four mm for a 4-mm depth with an axe for microfracture or 0. Microfracture of the capitellum, making several small perforations inside the capitellum about 4 mm apart and 4 mm deep. Intraoperative arthroscopic photograph from the direct lateral portal with a microfracture axe at the fringe of the osteochondritis dissecans lesion after removing the zone of calcified cartilage. Elbow arthroscopy is begun in the inclined (my preference), lateral, or supine position, utilizing the proximal medial portal to visualize the capitellum. Complete elbow examination utilizing all 4 commonplace portals and the extra direct lateral arthroscopic portals is necessary to look for loose bodies. Drilling via the cartilage and thru the sclerotic subchondral bone is done in an effort to promote therapeutic. Attempts are made to limit the number of perforations through the intact cartilage, however the subchondral plate ought to be penetrated a number of times. This could additionally be achieved by redirecting the drill in numerous instructions from the identical single (or a few) perforations by way of the articular cartilage. The probe is deforming the intact cartilage owing to the dearth of subchondral assist. When looking on the capitellum from the proximal anteromedial portal, instrumentation (shavers, burrs, graspers, and curettes) may be accomplished using the proximal anterolateral portal. Flexion and extension of the elbow allow for enhanced visualization of the capitellum. The direct lateral ("gentle spot") portal is then used for full analysis of the capitellum. Using an anterior cruciate ligament tibial information or posterior cruciate ligament femoral guide can be helpful to assist aim the drill bit from outside the elbow towards the lesion. Depending on the location of the lesion, the drill is brought from proximal and barely anterior to the lateral epicondyle or posteriorly on the distal humerus. A small incision is made on the proposed drilling entry site and blunt dissection is completed to bone. Multiple passes with the Kirschner wire must be performed to enhance therapeutic all through the lesion. The precept is to stimulate therapeutic and to stabilize the fragment within the bony mattress. Complete elbow examination utilizing all 4 standard and the extra direct lateral arthroscopic portals is obligatory to look for unfastened our bodies. Next, the arthroscope is brought in from the posterior portals to look for loose our bodies. The direct lateral ("gentle spot") portal is used for complete evaluation of the capitellum.
Super viagra 160 mg without prescriptionInflammation may end result from infectious (purulent erectile dysfunction over 65 buy super viagra 160mg without prescription, faeculent) or chemical (bilious) irritation of the peritoneal cavity erectile dysfunction questions to ask super viagra 160 mg cheap. Depending on the illness goal of erectile dysfunction treatment purchase super viagra 160 mg visa, the peritonitis may be diffuse (from a perforated viscus) or focal (with cholecystitis or an intraabdominal abscess) erectile dysfunction injection dosage quality super viagra 160mg. Torsion is an acute twist of the organ (such as the bowel or ovary) around its axis, often the vascular pedicle. Initially, the stomach is soft and the tenderness is localized to the affected organ. Torsion of a phase of the gastrointestinal tract (volvulus) sometimes leads to bowel obstruction. Whereas a rotation of lower than 180� across the axis could result in partial obstruction, a rotation of over 360� leads to complete visceral obstruction and interruption of the blood supply (one of the causes of ischaemia). Bowel obstruction is related to nausea, vomiting, constipation and distension as material fails to pass normally by way of the gastrointestinal tract. The belly ache is of a visceral type and is due to intestinal distension and peristalsis. With overdistension of the bowel, ache and belly tenderness could turn out to be extreme and constant. With ongoing distension (as in full bowel obstruction), bowel wall ischaemia could develop. With advancing ischaemia, signs of parietal peritoneal irritation and physical findings of guarding develop. Full-thickness ischaemia of the bowel wall could lead to its necrosis and perforation. During the period of remark, a change from a previously imprecise ache to a sharp, fixed, parietal peritoneum irritation pain implies a surgical emergency until proven otherwise. Any associated symptoms are normally non-specific but could additionally be useful in figuring out the severity of the illness and the differential diagnosis. Constitutional signs, together with fever, chills, malaise and anorexia, might accompany any inflammatory process. Gastrointestinal symptoms corresponding to nausea, vomiting and alterations in bowel habit might accompany numerous surgical and medical conditions. Certain scientific traits (bilious vomiting, haematemesis, melaena) might assist to narrow the differential analysis. Always ask about genitourinary signs of dysuria, pyuria and haematuria, and procure a cautious menstrual historical past in girls. Therefore always assess haemodynamic and respiratory stability early and continue to monitor it. In the early phases of an acute surgical situation, systemic indicators may be minimal and stomach symptoms predominate. As the pathological course of evolves, the systemic inflammatory response and sepsis develop. Patients with a delayed presentation have apparent indicators of peritoneal irritation and indicators of progressing shock. Classically, patients with advanced peritonitis or bowel ischaemia, no matter its aetiology, are tachycardic and have a thready pulse and labile blood pressure. They are tachypnoeic and will have altered mental standing and poor tissue perfusion, manifested by a low urine output and funky and cyanotic pores and skin. Tachycardia is a very important sign of an early physiological response to the acute illness. In morbidly overweight patients, it might be the earliest sign of an intra-abdominal catastrophe. Always remember that sufferers receiving beta-blockers might not manifest modifications in coronary heart rate. As the intra-abdominal course of progresses, the stomach becomes extra distended secondary to paralytic ileus. During evaluation, pay attention to the place of the affected person, their facial expression and their general comfort stage. Patients with intra-abdominal sepsis look unwell and lie still to have the ability to protect a young stomach. Note the respiratory movements, and whether or not the patient can draw in or blow out the abdominal wall without discomfort. A degree of abdominal distension may be arbitrarily assigned relative to the extent of the costal margin. In a non-obese affected person within the supine place, the abdomen is described as scaphoid, mildly distended (distension on the degree of the costal margin) or considerably distended (the distension protrudes above the costal margin). On auscultation, bowel sounds could additionally be diminished or absent in peritonitis or ileus from other causes, or hyperactive and highpitched in early mechanical bowel obstruction. Auscultation of the chest might reveal consolidation of the decrease lobe mimicking an acute stomach. Start palpation away from these areas, thus creating the least discomfort and obtaining a extra correct evaluation. Assess the stomach wall for asymmetry, and always examine for hernias, especially when bowel obstruction is current. Voluntary guarding is contraction of the stomach wall muscle tissue by the affected person because of concern, an anticipation of feeling ache or the chilly hands of the examiner. Involuntary guarding is reflex rigidity of the abdominal wall muscle because of inflammation of the underlying peritoneum. It is a cardinal sign of peritoneal irritation produced by belly wall movement. A rough examination might scare the patient, cause voluntary guarding and make subsequent analysis tough. Deep palpation, while often helpful in sufferers with continual pain and abdominal masses, is normally not possible in sufferers with an acute abdomen. An examination could also be very difficult in kids, and the clinician have to be particularly affected person and careful. Attempt to distract the kid with dialog and questions, while simultaneously gently palpating to differentiate voluntary from involuntary guarding. Ask the patient to point the area of maximum ache, and begin palpation away from this. If the world pointed to can also be the location of most tenderness, the underling viscus is extremely prone to be the offender. Localization of ache to the abdomen throughout coughing signifies irritation of the parietal peritoneum. As their names indicate, these manoeuvres might reproduce ache in the areas of peritoneal irritation. Tenderness upon light percussion suggests irritation of the timeless peritoneum and will avoid the need for distressing palpation. Percussion may assist to differentiate gaseous distension (tympanic) from ascites (dull). A sudden release of a deeply palpating hand produces pain in instances of peritoneal irritation.
Cheap 160 mg super viagra with amexAn acute dissection of the aorta is strongly associated with systemic hypertension erectile dysfunction pump rings super viagra 160 mg sale. Dissection mostly occurs in the ascending thoracic aorta causes of erectile dysfunction in 20 year olds discount super viagra 160 mg without a prescription, presents with excruciating chest and again ache and leads to erectile dysfunction doctors in sri lanka buy generic super viagra 160 mg online acute aortic valve insufficiency erectile dysfunction exam what to expect purchase super viagra 160 mg otc, occlusion of the coronary arteries or cardiac tamponade. Dissection of the descending aorta could extend into the stomach, producing back and stomach ache. After assessing the very important signs and degree of shock, carry out a complete vascular examination. Assess the carotid, brachial, radial, femoral, popliteal and pedal pulses for his or her presence and symmetry, and observe the findings for subsequent comparison. If the pulses are faint because of hypotension or peripheral vascular illness, a hand-held Doppler probe ought to be used to assess them. Many of those situations could also be treated non-operatively, and an accurate analysis may require confirmatory tests. Ultrasonographic examination of the pelvic organs, both transvaginally or transabdominally, is an invaluable device. Some ladies with sure psychological and social circumstances could not report an accurate sexual history or just may not be aware of a recent conception. Thus, a being pregnant check is obligatory for girls of childbearing age with belly ache. Around 95 per cent of all ectopic implantations occur in the segments of the fallopian tube, and the remaining may be found within the ovary, peritoneal cavity and cervix. The major risk factors for this situation are a previous ectopic pregnancy, tubal pathology and pelvic surgical procedure. Among different elements are previous genital infections, infertility, assisted reproductive applied sciences, the utilization of the intrauterine devices and smoking. After ectopic implantation, the fertilized ovum initially develops usually, with typical physiology-related signs and signs of early being pregnant: morning sickness, breast tenderness and urinary frequency. Amenorrhoea is the cardinal sign of pregnancy and, along with some vaginal spotting or bleeding, is present in the majority of tubal pregnancies. This bleeding is expounded to the pathophysiology of ectopic implantation and outcomes from the breakdown of thickened uterine endometrium. Profuse vaginal bleeding is unusual and usually suggests an incomplete abortion. Current serum and urine checks for beta-human chorionic gonadotropin are invaluable tools and are positive in ninety nine per cent of ectopic pregnancies. Placental separation results in the extrusion of all or components of the merchandise of conception into the peritoneal cavity. After all of the tubal products have been both extruded or resorbed, the hormone ranges return to baseline and the vaginal bleeding stops. Tubal rupture outcomes once the scale of the rising trophoblast exceeds the elastic capacity of the lumen where implantation has occurred. It often happens spontaneously in the first few weeks, or could observe coitus or pelvic examination. There is a growth of vasomotor signs starting from feeling faint to sometimes precise syncope. The affected person complains of severe sharp or stabbing pain from the blood irritating the peritoneum, which is exacerbated by coughing and movement. In the supine place, referred ache from diaphragmatic irritation may cause neck and shoulder pain. Since these sufferers are typically young and have good compensatory mechanisms, the heart beat and blood pressure could initially be regular even with important blood loss. Sinus tachycardia and hypotension are the disturbing indicators of impending decompensation. The location of the tenderness is determined by the positioning of the intraperitoneal blood. Since pelvic examination might exacerbate the bleeding, it should be carried out with nice care and solely by an skilled clinician. Extension of the an infection could end in peritonitis, perihepatitis and tubo-ovarian abscess. The infection is most frequently as a outcome of sexually transmitted illness, however may develop as a post-operative or pregnancy-related pelvic infection. Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis and normal vaginal flora have been implicated. The ache, usually bilateral, may initially be gentle and progress to being extra extreme and constant over time. The ache frequently begins after the menstrual period and is aggravated by sexual activity and shaking actions. Abnormal uterine bleeding, new vaginal discharge and fever may be related signs. On bodily examination, the lower stomach is tender, with frequent indicators of peritoneal irritation. A important lateralization of the tenderness on pelvic examination is uncommon, not like in appendicitis or diverticulitis. Ovarian Cysts Ovarian cystic lesions are categorised as physiological (follicular and corpus luteum cysts) or pathological � benign, borderline or malignant ovarian tumours. These acute circumstances generally develop throughout strenuous physical exercise or sexual activity. It presents with non-specific symptoms of an acute onset of sharp, intermittent abdominal pain, frequently related to nausea and vomiting. A unilateral palpable adnexal mass is detectable on pelvic examination in many sufferers. Prompt recognition and surgical procedure is necessary to stop loss of the ovary and the risk to future fertility. Bleeding into the abdomen is often not significant however might produce signs of peritoneal irritation and mimic the indicators of an ectopic being pregnant. Rupture of dermoid cysts are uncommon, however their contents cause chemical peritonitis and vital pain. The ensuing mid-cycle ache in some women, generally known as Mittelschmerz, is usually unilateral and mild, lasting from a few hours to a few days. The peritoneal cavity extends from the diaphragm to the pelvic floor, the exterior landmarks being the nipple line anteriorly, the scapular tip posteriorly and the inguinal creases inferiorly. The primary outcomes of trauma to various abdominal organs are intraabdominal bleeding, contamination (faeculent, pancreatobiliary, urinary), disruption of the anatomy (wounds, traumatic ventral and diaphragmatic hernias) and combinations of these. Falls and incidental and direct violence-related impacts account for the remainder of the accidents. Powerful blunt forces towards the stomach wall (a seatbelt or foreign object) may crush the organs in opposition to the backbone and thoracic cage. Such abdominal accidents are regularly associated with spine, rib and pelvic fractures. Sudden deceleration during a high-speed impression creates shearing forces that will end result in the laceration and avulsion of each hole and solid organs from their vascular and ligamentous attachments. A sudden important rise in intra-abdominal stress might result in the rupture of a distended hollow viscus (diaphragm, abdomen, bladder).
References - Metcalfe PD, Cain MP, Kaefer M, et al: What is the need for additional bladder surgery after bladder augmentation in childhood?, J Urol 176(4):1801n1805, 2006.
- Dick P, Sabeti S, et al. Conventional balloon angioplasty versus peripheral cutting balloon angioplasty for treatment of femoropopliteal artery in - stent restenosis: initial experience. Radiology 2008; 248:297.
- Hulbert, J.C., Reddy, P.K., Hunter, D.W., Castaneda- Zuniga, W., Amplatz, K., Lange, P.H. Percutaneous techniques for the management of caliceal diverticula containing calculi. J Urol 1986;135:225-227.
- Berr F, Wiedmann M, Tannapfel A, et al. Photodynamic therapy for advanced bile duct cancer: evidence for improved palliation and extended survival. Hepatology. 2000;31:291-298.
- Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, et al: Sabiston textbook of surgery E-Book, 2015, Elsevier Health Sciences. Turnbull DK, Shepherd DB: Post-dural puncture headache: pathogenesis, prevention and treatment, Br J Anaesth 91(5):718-729, 2003.
- Tabak, M. H. (1995, February). Merging managed care and workersi compensation. Risk Management, 16n19.
- Verboven M, Ingels M, Delree M, et al: 99mTc-DMSA scintigraphy in acute urinary tract infection in children, Pediatr Radiol 20(7):540-542, 1990.
|