Tetracycline
Donna D. Castellone, MS, MT(ASCP)SH - Clinical Projects Manager, Hemostasis/Hematology
- Medical, Clinical, and Statistical Affairs
- Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics
- Tarrytown, New York
Cheap tetracycline 500 mg without a prescriptionAs these lots enlarge virus zero reviews discount tetracycline 250mg free shipping, they increase from the normal parenchymal margins antibiotic virus discount tetracycline 500 mg with amex, either peripherally to the kidney or into the renal sinus virus yontooc buy 500 mg tetracycline amex, relying on the epicenter and primary path of growth natural treatment for dogs fleas buy tetracycline 500 mg otc. The kidney retains its bean form, and these infiltrative lesions are often referred to as beans, in distinction to the previously described balls. In addition, each ball- and bean-shaped lesions could also be solitary or a quantity of and the variety of lesions is commonly helpful in figuring out the right diagnosis. Alternatively, with geographic infiltrating lesions one should also consider the following three Is: 1. B, the tumor is even more conspicuous through the nephrogram part after contrast materials injection. Nowadays, these two subtypes of urothelial tumors are sometimes classified by pathologists as urothelial carcinomas because the tumors typically include parts of every subtype. Furthermore, excretory urography lacks sufficient specificity for accurately characterizing any renal plenty as benign. Plain Films A Commonly, the first trace of a renal mass may be discovered on an abdominal radiograph. Renal plenty could also be seen on a radiograph or a tomogram of the abdomen, often as ball-shaped lots extending from the kidney. Before the refinement of cross-sectional imaging techniques, a urology rule of thumb was a calcified renal mass is a surgical renal mass. Although cross-sectional imaging is required to better characterize and information management of a calcified renal mass, plain-film findings often present important info on the etiology of those lots. A, Prior to contrast materials infusion, this infiltrating mass in the best kidney (arrow) is barely discernable as an space of subtle low density. B, Following the intravenous injection of distinction materials, this geographic area of decreased enhancement (arrow) is quickly identifiable. A, this cone-down view of the left higher quadrant demonstrates irregular calcifications (arrows) extending from, and projecting over, the decrease pole of the left kidney. This mass accommodates numerous calcifications similar to those seen on the stomach radiograph. This uninfused computed tomography scan demonstrates a skinny rim of calcification within the wall of straightforward cysts (C). Some renal lots include each skinny, peripheral calcifications and focal, central calcifications. Cross-sectional imaging helps to distinguish between benign and malignant calcified renal lots in most sufferers. These lesions typically develop slowly and lead to bubbly lesions that focally broaden the bone. They can mimic different forms of bone lesions, including metastases, 70 GenitourinaryRadiology:TheRequisites major bone neoplasms, and myeloma. Multiple osteomas, or bone islands, are one other interesting kind of skeletal abnormality sometimes seen in affiliation with renal plenty. However, if a mass is detected by urography, then some imaging options may be useful to information additional analysis. Large masses lead to calyceal splaying, stretching, and draping, whereas infiltrating renal lesions normally produce little, if any, parenchymal mass impact. However, inside the infiltrated parenchyma, function is absent or significantly diminished, and therefore opacification in the involved region is diminished through the nephrogram phase. Because many of those lots come up or invade the calyces, calyceal filling defects, also recognized as an oncocalyx, could additionally be evident on the intravenous urogram. As mentioned earlier, excretory urography lacks adequate specificity for accurately characterizing any renal plenty as benign or malignant. Therefore every renal mass detected with or suggested by excretory urography must be imaged with another method. With this technique, 80% of detected renal masses are characterized as simple cysts, thus ending their diagnostic analysis. This cone-down view of the kidneys demonstrates a large strong mass extending from the upper pole of the proper kidney. This mass compresses and displaces calyces, and its margins (arrowheads) lengthen past the expected margins of the kidney. This mass is solid and enhances just like the density of the conventional renal parenchyma. A transitional cell carcinoma is present in the upper pole of this right kidney causing stricturing of the upper-pole infundibulum and calyceal amputation. Extensive infiltrating lesions often result in secondary abnormalities, including hydronephrosis and vascular encasement with diminished move to the realm of involvement. Expansile renal masses 5 mm or bigger are almost at all times detectable with these two modalities. When the kidneys are imaged through the portal venous phase of liver enhancement, renal enhancement is normally within the corticomedullary phase and may be inadequate for detection. In this phase, hypervascular cortical masses and hypovascular medullary tumors may be inconspicuous and undetectable. This sometimes occurs approximately eighty to a hundred and twenty seconds after the initiation of intravenous contrast material injection. Renal arteriography together with embolization could additionally be helpful within the therapy of some renal lots. Devascularization of a tumor may be carried out before excision or ablation to reduce intraoperative blood loss or to improve ablation efficacy, or to diminish symptoms from an inoperable renal malignancy. In uncommon cases, angiography may be useful in distinguishing amongst various renal masses. In specific, angiography could also be an various to open biopsy in the analysis of infiltrating renal neoplasms. Urothelial neoplasms, inflammatory lesions, and infarcts are practically always hypovascular or avascular. The fact that this tumor is normally very vascular distinguishes it from different infiltrating lesions. The classes are solitary expansile plenty, multiple expansile masses, and geographic infiltrating lesions. Ball-Shaped Masses Box 3-3 lists lesions that form expansile lots on the kidney. With cross-sectional imaging, these are seen in more than half of sufferers older than 50 years of age. Simple cysts may be seen on plain films of the stomach as massive, spherical, water-density masses extending from the kidney. Renal parenchyma draped across the edges of the cyst is often referred to because the beak or claw sign. Any variance from these standards suggests Angiography Renal angiography, as quickly as a primary factor in the analysis of renal masses, is of little worth in the evaluation of most renal masses.
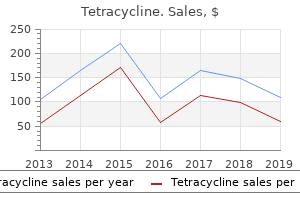
500mg tetracycline with amexA xyrem antibiotics generic tetracycline 250mg otc, Plain film demonstrates calculi within the pelvis (arrow) and the perineum (open arrow) of a 44-year-old man with bladder-outlet obstruction that required suprapubic cystostomy bacteria characteristics tetracycline 250 mg on line. B virus scan online cheap tetracycline 500 mg fast delivery, this coned-down antibiotic while breastfeeding generic tetracycline 500 mg with amex, magnified indirect view from a retrograde urethrogram demonstrates two filling defects (arrows) in the bulbar urethra proximal to a good stricture (curved arrow). A, Axial high-resolution T2-weighted picture reveals effacement of the conventional targetlike look of the urethra by an intermediate-signal-intensity mass (arrow). B, the mass shows diffuse enhancement and fills the urethral diverticulum, with solely a small quantity of residual fluid in the diverticulum (arrow). C, Coronal high-resolution T2-weighted picture exhibits extension of the urethral mass into the neck and base of the bladder (arrow). Carcinomas of the anterior urethra unfold to the superficial and deep inguinal nodes, with occasional involvement of the exterior iliac lymph nodes. Posterior urethral carcinomas sometimes spread to pelvic lymph nodes earlier than spreading to extra proximal nodal stations. Infused computed tomography of the pelvis exhibits a big hypodense mass within the perineum, which had invaded and obstructed the distal urethra. Tumors that originate from or that invade the distal third of the female urethra preferentially unfold to the inguinal nodes. Carcinomas that originate in the distal third of the female urethra preferentially unfold to the superficial and deep inguinal nodes, whereas these originating from the proximal two thirds spread to the exterior and inner iliac node groups preferentially. Carcinoma of the Male Urethra Carcinoma of the male urethra is kind of exclusively a disease of the older population, occurring predominantly in men over the age of fifty. The following two threat factors predispose to the event of urethral carcinoma: (1) a medical historical past of persistent urethral irritation or sexually transmitted infection, and (2) urethral stricture, which is seen in higher than 50% of patients. The onset of signs is insidious; preliminary scientific complaints embody poor urinary stream, serosanguinous discharge, or hematuria. Two thirds originate within the bulbar or membranous urethra, and nearly all of the remaining carcinomas are discovered in the anterior urethra, particularly the fossa navicularis. Urothelial carcinoma accounts for 15% of urethral carcinomas; in most patients it originates in the posterior urethra. An affiliation exists between urothelial carcinoma of the prostatic urethra and former transurethral resection of bladder carcinoma. Adenocarcinoma or undifferentiated carcinoma comprise the remaining 5% of urethral cancers. The diagnosis of urethral carcinoma could be made on urethroscopy and urethrography. At urethrography, carcinoma appears as an irregular filling defect, which may be eccentric or circumferential. This analysis must also be suspected when the margin of a stricture is irregular or poorly defined. Fibrous polyps normally are pedunculated, and the base of the stalk originates close to the verumontanum. The polyp itself appears as a well-defined, easy, fingerlike filling defect, approximately 1 to 1. Hence, sufferers may present with bladder-outlet obstruction or intermittent interruption of the urinary stream. Urothelial and squamous cell papillomas are benign mesenchymal growths which are lined by the urothelium and metaplastic squamous cells, respectively. Urothelial papillomas may be discovered within the prostatic urethra and could be associated with papillomas within the urinary bladder. At urethrography, papillomas can seem as single or a number of easy, sessile filling defects. Dermal papillomas of the genitalia and around the anus can unfold to the urethra, vagina, and rectum. As many as 5% of patients with penile condylomata also have urethral lesions, which are often restricted to the anterior urethra. The look of condylomata acuminata at urethrography is that of a number of, sessile filling defects of the anterior urethra. An related stricture, though typical of carcinoma, is atypical with condylomata acuminata. Metastases to the Urethra In female and male patients, bladder and colorectal carcinomas can involve the urethra through extensive local unfold. D, Bilateral superficial inguinal adenopathy (arrows) is present and was 18-fluoro-deoxyglucose avid on positron emission tomography-computed tomography (not shown). Urethral Outpouching or Tract Common and uncommon causes of paraurethral outpouching or tract are listed in Box 6-24. Acquired Urethral Diverticulum (Pseudodiverticulum) Urethral diverticulum may be either a congenital or an acquired lesion. Congenital saccular diverticulum is a rare lesion of the mid penile urethra that will trigger high-grade obstruction in children. It incessantly is difficult to distinguish congenital diverticulum from an anterior urethral valve. In contrast to the congenital urethral diverticulum, the acquired diverticulum presents in adults. A, Percutaneous cystogram shows a barely lobulated filling defect (arrowheads) near the bladder neck. B, Voiding cystourethrogram shows an oblong, polypoid filling defect in the posterior urethra. Fibrous polyps can be lengthy and pedunculated; the drive of the urinary stream may trigger antegrade prolapse and urethral obstruction. Axial high-resolution T2-weighted image exhibits a fluid-filled periurethral structure (arrow) typical of a diverticulum. The urethral diverticulum is most often located posterior to the midurethra in ladies and at the 244 GenitourinaryRadiology:TheRequisites with a urethral diverticulum, it is essential to seek a coexistent abnormality, corresponding to a stricture or carcinoma which will have incited fistula formation. Cowper Duct and Gland Paired Cowper ducts enter the ventral surface of the perineal portion of the bulbar urethra. The length of the duct varies from a few millimeters to 6 cm, and duct width varies from 1 to 6 to 8 mm. The ducts extend backward alongside the undersurface of the bulbar urethra way back to the urogenital diaphragm, during which the Cowper glands are embedded. M�llerian Remnants the paramesonephric or m�llerian duct system regresses in male sufferers because of an inhibiting substance produced by the creating testis. A cranial remnant of the duct could persist because the appendix testis and M�ller tubercle; the caudal tip of the duct remains because the verumontanum. Incomplete obliteration of the caudal part of the m�llerian ductal system might give rise to tubular, vaginalike buildings or cysts lying between the bladder and the rectum. The prostatic utricle has come to be viewed because the homolog of the uterus (utriculus masculinus), and subsequently a by-product of the caudal remnant of the paramesonephric ducts.
Discount tetracycline 250mgThis normally happens with tibial disease and is further confirmed by the presence of femoral and popliteal pulses and monophasic pedal indicators polyquaternium 7 antimicrobial buy tetracycline 500mg low cost. A 51-year-old diabetic man presents with a 1 cm � 1 cm ulcer over the plantar aspect of his proper great toe antimicrobial gorilla glass tetracycline 500 mg. The ulcer began as a blister after a chronic stroll sporting a brand new pair of footwear infection 1 game buy tetracycline 500 mg on line. Diabetic foot ulcers happen as result of continuous pressure at one spot within the setting of diabetic neuropathy anabolic steroids discount tetracycline 500mg otc. On bodily examination, he has a palpable pulsatile stomach mass on the level of the umbilicus. He stopped smoking 1 year ago, has well-controlled hypertension and is otherwise in good well being. A 59-year-old man presents with a historical past of a sudden onset of slurred speech related to weak point in his proper upper extremity 2 hours previously. He is a continual smoker and is known to have secure coronary artery disease for which he receives medical therapy. The best initial imaging modality for diagnosing asymptomatic abdominal aortic and popliteal aneurysms is duplex ultrasonography, due to its widespread availability, lack of radiation, low price and reproducible results. This makes an ulcerated carotid plaque high on the list of differential diagnoses. It refers to morphological and functional venous disorders with scientific manifestations various from simple superficial venous dilation to venous hypertension with continual skin changes and ulceration. Chronic venous disease often starts on account of venous valve dysfunction, venous pump failure or venous obstruction. Over time, a build-up of strain inside the venous system directs the blood circulate abnormally from the deep to the superficial venous system, which in turn may end in pores and skin fibrosis, local irritation and ulceration. There are many danger elements for the development of venous illness, including advancing age, a household history of venous pathology, an elevated body mass index, prolonged standing, smoking, prior venous thrombosis and being pregnant. Competent valves forestall retrograde circulate into the superficial venous circulation, and the venous strain of the superficial circulation is maintained at between 20 and 30 mmHg during ambulation. Presentation Chronic venous disease encompasses a large spectrum of useful and morphological venous issues, and as such its medical manifestations range significantly. Pain and oedema are usually worse when the patient is standing or when the ft are in a dependent place for prolonged periods of time; this often improves with limb elevation. Nevertheless, the symptoms are often more outstanding at evening when the affected person goes to bed. Numbness and tingling can also be current however are troublesome to differentiate from other causes of peripheral neuropathy within the leg. Some sufferers complain of cramping, itching and swelling, and this is usually associated with persistent skin adjustments. Skin ulceration and bleeding of varicose veins are usually late manifestations of severe venous reflux illness. The bodily findings are also variable and usually correlate with the severity of the symptoms. Telangiectasias, that are small dilated intradermal veins, are usually early manifestations of venous disease. Varicose veins, on the opposite hand, may represent a more superior stage of venous disorders. Venous ulcers are normally situated on the degree of the medial side of the ankle or along the course of the great or small saphenous veins. They are often tender and exudative with an Normal Venous Anatomy of the Lower Extremity There are three major venous pathways in the decrease extremity: � the deep system forms from the confluence of the anterior, posterior and peroneal veins of the leg. These be part of to form the popliteal vein, which in flip turns into the femoral vein because it accompanies the superficial femoral artery. The femoral vein joins the deep femoral vein slightly below the saphenofemoral junction to turn into the widespread femoral vein. These normally be a part of the deep system on the saphenofemoral and saphenopopliteal junctions, respectively. These characteristics help to differentiate them from different kinds of leg ulcer, primarily neurogenic and arterial ulcers. A mixture of those manifestations may be associated with marked disability and a diminished quality of life. This classification system is essential to stage the severity of the disease on presentation as properly as to document modifications over time. Diagnosis the analysis of chronic venous illness is usually a clinical one, established by taking an adequate medical history and performing a radical physical examination. This strategy can be helpful in ruling out some other systemic causes of venous hypertension corresponding to heart failure or fluid overload. The Trendelenburg check (also often recognized as the Brodie� Trendelenburg test) can be used to assess for the presence of venous reflux. Typically, the affected person is placed in a supine position and the leg in query is elevated. A tourniquet is positioned across the proximal thigh and the affected person is asked to rise up. The tourniquet must be tight sufficient to occlude solely the superficial system while preserving the deep system unobstructed. The veins are then rigorously inspected to assess the time taken for them to refill. In people without venous insufficiency, the veins need 3�5 seconds to refill normally from the capillaries. Earlier refill is indicative of reflux beneath the tourniquet from the speaking perforator veins or the saphenous vein itself. If it now refills in lower than 20 seconds, that is indicative of reflux originating proximal to the level of the tourniquet. With the patient supine, a compression bandage is utilized to the leg tightly sufficient to occlude the superficial venous system. If the patient develops extreme pain upon strolling, this means vital deep venous obstruction and means that the superficial venous system has been acting as an necessary collateral and contributor to the venous drainage of the lower extremity. Although the Trendelenburg and Perthes exams can be useful, the inherent inaccuracies of applying the tourniquet or elastic bandages and the presence of different extra direct goal testing modalities have led to a lower of their use. This shows distinguished skin bulges over the varicosities of the posterior arch vein, along with widespread venular dilatation and loss of ankle contour in a postphlebitic leg. Because the affiliation between the severity of the disease and its scientific signs and symptoms varies amongst patients, a scientific classification of the disease may be made utilizing the Clinical�Etiology�Anatomy�Pathophysiology standards (Table 32. This classification system allocates a special grade depending on the presence of sure findings on physical examination. Oedema, pores and skin modifications and healed or energetic ulcers signify more superior Duplex Ultrasonography this has turn out to be the imaging modality of selection for assessing the superficial and deep venous circulation of the decrease extremity.
500 mg tetracycline with mastercardB antibiotic resistance scientific journal discount 250mg tetracycline with visa, Retrograde pyelogram shows that the dilated ureter inserts directly into the urethra bacteria diagram order 250 mg tetracycline amex. Radiographically bacteria large intestine discount 500mg tetracycline otc, it is essential to antibiotics and yogurt purchase tetracycline 500 mg with amex distinguish orthotopic ureteroceles from pseudoureteroceles. Pseudoureteroceles suggest underlying pathology similar to infiltrating transitional cell carcinoma, or ureteral stone impaction. With an orthotopic ureterocele, the radiolucent line surrounding the ureterocele shall be no thicker than 2 mm and shall be uniform all through. When evaluating congenital anomalies of the urinary tract, corresponding to duplications, it is important to keep in thoughts that up to one third of sufferers have a second coexisting vital congenital abnormality of the urinary tract. A, A view of the pelvis demonstrates a big oval calcification close to the midline in this patient with chronic proper flank pain. Although duplication anomalies of some extent are seen generally in on a daily basis follow, other supernumerary anomalies of the ureter and pelvocalyceal system are distinctly unusual. Because of the rarity of these anomalies, little is known about their association with reflux, ureteroceles, and different urinary tract abnormalities. Another uncommon type of ureteral duplication happens when incomplete growth leads to a congenital ureteral diverticulum. Computed tomography urography shows a blind-ending section of the ureter (arrow) arising from the lower proper ureter, a congenital anomaly attributed to interrupted improvement of a duplicated ureteral bud. Coronal computed tomography picture shows marked pelvocaliectasis with a normal-caliber ureter and not using a mass or stone. These typically go unnoticed until maturity and are found after subclinical an infection and worsening stricture or because of elevated urine production. Although this anomaly is of little clinical significance, the ureteral diverticulum can kind a reservoir for relatively static urine, thereby increasing the chance of an infection and stone illness. Congenital abnormalities of the ureter, which usually end in hydronephrosis or ureteral dilatation, embrace congenital strictures, retrocaval ureter, main megaureter, prune-belly syndrome, and vesicoureteral reflux. When hydroureteronephrosis is detected, consideration must be directed to identify the purpose for dilatation. A search must be made to define the transition level from dilated ureter to normal ureter. Congenital strictures of the ureter are the commonest congenital anomalies of the ureter. However, it has been postulated that in utero ureteral ischemia results in the formation of a focal stricture. The degree of hydroureteronephrosis varies, as does the medical significance of these strictures. The combination of those two abnormalities encourages clinicians to select percutaneous nephrolithotomy and endopyelotomy for therapy. In these cases, renal calculi could be removed and endopyelotomy may be carried out percutaneously during the same procedure. Detection of those contralateral anomalies could additionally be significantly significant and should affect therapy. Other abnormalities of the ureter can be categorized into a quantity of teams in accordance with radiologic pattern. Deviations of the Ureter the ureter may be deviated medially or laterally, and deviation can happen alongside its complete course or segmentally. Abnormalities of ureteral course are rarely as a end result of primary ureteral disease however normally outcome from abnormalities extrinsic to the ureter. In addition, retroperitoneal fibrosis can contain one ureter and spare the contralateral ureter. Cross-sectional imaging is commonly helpful to affirm the abnormality or guide biopsy in these patients. It is more commonly seen in younger, African-American men, and it might possibly lead to bilateral hydroureteronephrosis. Often, the rectum can also be involved, and concentric narrowing and straightening of the rectosigmoid colon could occur. A, An intravenous urogram demonstrates the standard appearance of a retrocaval, or circumcaval, ureter with abrupt medial deviation of the right ureter. The medial portion of the ureter (arrowheads) is within the ipsilateral vertebral pedicle. B, A computed tomography scan on this similar patient demonstrates the proper ureter (arrow) as it courses behind the vena cava (V). The ureter will then course medially to the vena cava and passes back laterally over the ventral floor of the cava. A, A single film from a urogram demonstrates marked medial deviation of the best ureter and mild medial deviation of the left ureter at the L4 degree. B, Diagram of the typical medial deviation of the ureters sometimes seen with retroperitoneal fibrosis. A, An intravenous urogram demonstrates medial deviation of the pelvic ureters (arrowheads) and a pear-shaped bladder in affiliation with increased lucency in the pelvis across the bladder. B, Computed tomography scan by way of the pelvis in this same affected person demonstrates marked proliferation of perivesical and perirectal fats diagnostic of pelvic lipomatosis. C, Diagram of lower ureteral deviation seen in association with pelvic lipomatosis. There is loss of the conventional lateral curvature of the ureteral course in patients following this type of surgical procedure. Typically, upon getting into the pelvis, the ureters course directly inferior to the bladder. A history, or radiographic proof, of considerable previous belly surgical procedure is usually evident. Atherosclerotic calcifications of the aorta are sometimes seen in affiliation with this type of deviation. A major path of lymphatic drainage of the left testicle parallels the left testicular vein and empties to nodes close to the left renal vein. If the psoas muscle is wider than 8 cm from the edge of a vertebral body to its lateral edge, at the higher edge of the iliac bone, then psoas hypertrophy is prone to be the purpose for ureteral deviation. Often the pelvic ureters are also medially deviated in these muscular individuals because of large iliacus and obturator internus muscle tissue, with ensuing displacement of the ureters. A, the pelvic ureters, as seen containing ureteral stents, are medially deviated with loss of the conventional lateral curvature of the pelvic ureters. B, Diagram of the typical course of the ureters following abdominoperineal resection. Atherosclerotic calcifications are seen inside the wall (arrows) of this aneurysm.
Generic tetracycline 500 mg without a prescriptionImpingement syndrome is ache ensuing from strain on the supraspinatus tendon because it passes by way of the outlet between the acromion and the humeral head antibiotics for deep sinus infection 500mg tetracycline with visa. In rotator cuff tears virus 69 tetracycline 250mg on-line, the supraspinatus is the tendon mostly implicated treating uti quickly discount tetracycline 500mg otc, and large rotator cuff tears can current with a constructive drop arm check antibiotics for acne dry skin cheap tetracycline 500mg with amex. Calcium deposits within the rotator cuff muscle which are seen on X-ray mirror an inflammatory process that may result in a frozen shoulder. Clavicular fractures are widespread, and the overwhelming majority may be handled conservatively by immobilization in a sling. Humeral fractures can potentially be difficult by axillary nerve harm at the humeral neck or radial nerve harm on the shaft of the humerus. Posterior shoulder dislocations require a excessive index of suspicion and tend to be missed on first presentation. After a primary dislocation, the shoulder is weak to repeat episodes, resulting in shoulder instability. Which one of the following statements in regards to the clavicle is wrong: a Most birth fractures involve the clavicle b Most clavicular fractures happen within the proximal third of the bone c Birth fractures of the clavicle heal rapidly d Brachial plexus injuries, vascular injuries and pneumothorax are potential problems e Clavicular fractures are often attributable to a direct blow to the shoulder 2. Which statement in regards to the supraspinatus muscle is inaccurate: a Its origin is the supraspinous fossa b Its insertion is the superior side of the higher tuberosity c It is innervated by the axillary nerve d It is essentially the most generally involved tendon in rotator cuff tears. The supraspinatus muscle is equipped by the suprascapular nerve (C5 and C6), which arises from the superior trunk of the brachial plexus. For each of the next circumstances, select the most likely finding from the list below. Posterior shoulder dislocation is rare and sometimes related to particular injuries similar to lightning strikes, electrical accidents and seizures. This sort of dislocation can sometimes occur with minimal harm in the aged, and the analysis could additionally be missed the primary time the affected person presents for analysis of the shoulder pain. Ehlers�Danlos syndrome is a heterogenous group of inherited connective tissue disorders marked by a number of joint laxity, skin extensibility and tissue fragility. Impingement syndrome of the shoulder is mechanical irritation of the rotator cuff tendon underneath the anteroinferior portion of the acromion, particularly when the shoulder is positioned in the kidnapped, forward flexed and internally rotated place. Multidirectional shoulder instability is excessive vary of movement of the glenohumeral joint in all directions � anterior, posterior and inferior. The sulcus signal demonstrates the inferior instability, while the load shift check reveals anterior and/or posterior instability. Humeral shaft fractures are related to radial nerve palsy in as much as 18 per cent of cases. The nerve is especially at risk on the junction of center and distal thirds of the humeral shaft the place is emerges from the spiral groove. Injury to the nerve leads to weak point of the wrist extensor muscles, resulting in wrist drop. For each of the following circumstances, select the most likely association from the list under. Each option may be used once, more than as quickly as, or not at all: 1 Radial nerve palsy 2 Axillary nerve palsy three Suprascapular nerve palsy 4 Long thoracic nerve palsy 5 Ulnar nerve palsy a Humeral surgical neck fracture b Mid-clavicular fracture c Humerus shaft fracture d Atrophy in the supraspinatus fossa e Medial winging of the scapula Answers a 2 Axillary nerve palsy. The nerve winds around the surgical neck of the humerus approximately 7 cm distal to the tip of the acromion. Loss of sensation over the shoulder space and/or or lack of arm abduction is a possible complication ensuing from denervation of the deltoid muscle. On rare events, medial cord harm and ulnar nerve palsy, for example, can happen. Fractures of the humeral shaft, especially at the junction of the center and distal thirds of the humerus, endanger the radial nerve because it emerges from its spiral groove. Atrophy within the supraspinatus fossa may be appreciated by seeing and palpating a melancholy over the fossa of the scapula when analyzing the higher again. It may end up from overtension of the nerve secondary to a torn and retracted rotator cuff tendon. Medial winging of the scapula presents with shoulder and scapular pain, weakness when lifting objects and discomfort when sitting on a chair. It is more commonly seen in young athletes because of lengthy thoracic nerve damage from repetitive stretch or chest compression injuries during sports activities. The serratus anterior muscle is then denervated and the scapula elevates off the chest wall and migrates medially. The tip of the olecranon and the medial and lateral epicondyles type an equilateral triangle when the elbow is flexed. This relationship is preserved in supracondylar fractures but lost in dislocations. Effusions are seen as a bulge emphasizing the concavity between the olecranon and the lateral epicondyle. The triangular sulcus is a landmark for access to the elbow joint because it lies between these two buildings and the radial head. An elevated angulation is called cubitus valgus, and decreased angulation as cubitus varus, a typical deformity in the malunion of supracondylar fractures. Flexion and extension happen on the elbow joint, the range of movement being 0�150� degrees. Supination and pronation happen as the radial head rotates, the vary of motion being 80�. The radial head, and its rotatory motion, is palpable l cm distal to the lateral epicondyle. There is pain along the lateral border of the elbow, which radiates proximally and distally. Grasp the decrease forearm within the left hand and, whereas the affected person continues to try to maintain the Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) this may be a frequent overuse situation, typically provoked by heavy repetitive physical exercise involving rotation at the elbow. Radial Tunnel Syndrome this situation causes lateral elbow and radial forearm pain. The drawback is produced by radial nerve compression as it passes through the radial tunnel. The maximal point of tenderness is 2�3 cm anterior and distal to the lateral epicondyle. The pain can be provoked by extension of the center finger towards resistance and by supination of the forearm against resistance. There is pain, aggravated by throwing, and tenderness located on the medial epicondyle on the widespread flexor origin. In the neighborhood of this landmark are different potential compression sites together with the medial intermuscular septum proximally and the flexor carpi ulnaris aponeurosis distally. Cubitus valgus or varus deformities, burns and occupational or athletic overuse also predispose to creating this situation. There may be wasting of the muscular tissues of the hypothenar eminence, as nicely as of the intrinsic muscle tissue of the hand.
Tetracycline: 500 mg, 250 mg
Cheap tetracycline 250mg on lineIn the presence of disc degeneration antibiotic treatment for acne generic 500 mg tetracycline mastercard, this leads to antibiotic resistance for uti purchase 250 mg tetracycline free shipping ache and is an indicator of painful segmental dysfunction antibiotic resistant infections order 500mg tetracycline. Bowstring Test this is carried out in an analogous method to the straight leg raising check antibiotics for sinus infection penicillin tetracycline 250mg fast delivery. Once the affected person is experiencing signs throughout leg elevating, the knee is flexed by approximately 20�. If such a manoeuvre recreates ache radiating down the again of the leg, the take a look at is considered constructive and signifies stretching of the dura mater or a compressed nerve, primarily at the L5, S1 and S2 ranges. Limited knee flexion/hip extension with pain radiating down the anterior aspect of the thigh is because of stretching of the femoral nerve and is indicative of a lesion at L2, L3 or L4. As with the straight leg raising take a look at, contralateral ache is of appreciable significance. Muscle bulk or girth, tone, power, reflexes and sensation are sequentially assessed (Table 10. The girth of the thigh or quadriceps must be in contrast with that on the contralateral side; it might be decreased secondary to an L4 lesion or to disuse. With lesions of the fourth lumbar root, the quadriceps could also be weak and tender to palpation. Lesions of the fifth lumbar root may trigger weak spot of the extensor hallucis longus previous to any demonstrable ankle dorsiflexor weak spot. Alternatively, wasting of extensor digitorum brevis is another sensitive sign of an L5 lesion. Ankle dorsiflexion should be examined with the knees flexed, as resisting plantar flexion with the hip and knee prolonged might exacerbate sciatic pain. In early lesions, the fatiguability of the gastrocnemius ought to be compared with that of the other aspect by asking the affected person to repeatedly rise on tiptoe. Ultimately, the patient could also be unable to stand on tiptoe at all, although this will also be difficult within the presence of quadriceps weakness. With first sacral root irritation, the calf muscular tissues could also be tender and the ankle jerk may also become deficient. Sensory testing, including light touch, pinprick and vibration sense, must be performed in those beneath 50 years of age. Difficulty with micturition, urinary retention, loss of anal sphincter tone or faecal incontinence, progressive motor loss and saddle anaesthesia are all suggestive of central wire compression and require pressing imaging and decompression. Absence of the superficial belly reflex may be the solely abnormality famous within the preliminary presentation of syringomyelia. At the tip of the neurological assessment, the history, general examination findings and motor and sensory findings ought to be collated to determine the anatomical level of any spinal pathology. This can then be confirmed by radiological investigation before any intervention is planned. A transmitted impulse can be detected from the swelling to the anterior fontanelle. An evaluation of the diploma of paralysis and anal tone reveals the extent of the neurological injury. A basic examination of these infants may reveal hydrocephalus in relation to the Arnold�Chiari malformation during which cerebellar herniation obstructs the cerebrospinal fluid outflow. Spina bifida occulta � a failure of spinal arch fusion, which is often associated with a local patch of hair, skin dimples, sinuses or lipomas, is found in practically 15 per cent of the inhabitants and is asymptomatic. It is incessantly an incidental finding when radiographic investigation of the back is undertaken. It could also be related to an abnormal filum terminale or spinal wire tethering, which becomes important if later operative intervention is planned. Back pain in children ought to never be dismissed as non-organic and will always be promptly investigated, especially if it has lasted for more than per week. The most probably causes of again ache in childhood are infections similar to discitis or osteomyelitis, and spinal/paraspinal tumours. As in adults, the most typical reason for back pain in children is disc disease in the type of disc degeneration or disc herniation, facet arthroses and different mechanical situations as spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. In adolescence, inflammatory issues corresponding to ankylosing spondylitis or juvenile persistent arthritis should be considered. Painful scoliosis must be rigorously assessed as many instances have a sinister trigger. In addition, any medical situation that would present itself as back pain must be excluded. This requires a common examination of the affected person and an evaluation of the stomach, the pelvis, the lower limbs and the peripheral vascular system to exclude circumstances similar to peptic ulcer disease, renal or perirenal infections, renal stone illness, gallstones, pancreatitis, intrapelvic tumours, gynaecological infections (pelvic inflammatory disease), arthritis of the hip, an abdominal aortic aneurysm or vascular claudication. Discitis this is usually a childhood affliction, though it can happen as a complication after disc area surgical procedure in adults. The common age of presentation is 2�6 years, with boys and girls being equally affected. The baby classically complains of again ache growing in intensity over 2�4 weeks. On examination, the kid exhibits some spinal rigidity and maintains a hard and fast hyperlordosis. Patients usually current with both pain or cosmetic deformity without neurological signs or indicators. It is the most common explanation for persistent/recurrent again pain in childhood and adolescence. Examination reveals localized lumbar again ache, minimal tenderness and some paraspinal muscle spasm. Radiological evaluation is often with plain films, together with indirect radiographs. As for spondylolisthesis, the severity is graded in accordance with the share slip of 1 vertebra on the opposite, or the angle of rotation of the slip. Symptoms are also often severe at night time as a outcome of the supine posture decreases the area in the spinal canal. Moreover, combined causes may be famous in some instances, such as degenerative adjustments on a background of a congenitally slim canal. The Disc Herniation Disc herniation refers to herniation of the central disc materials, the annulus pulposis, into the spinal canal. Disc herniation can cause a compression of neural components, which, depending on the placement, can be compression of the spinal cord, dural sac or nerve roots: � Compression of the spinal wire (cervical or dorsal spine) gives rise to the signs and symptoms of higher motor disease, including hyperreflexia, a Babinski reflex and/or clonus; at a later stage, the anal and bladder sphincters might be affected. The initial modifications are seen within the sacroiliac joints and extend upwards to the lumbar and infrequently the thoracic backbone. The articular cartilage, synovium and ligaments all show continual inflammatory adjustments and ultimately turn out to be ossified. The prognosis is normally made on the premise of decreased spinal motion and chest expansion with potential sacroiliac or costochondral tenderness. Typical radiographic options embrace fuzziness of the sacroiliac joints and squaring or bridging of the lumbar vertebrae. In the early stages, a raised erythrocyte sedimentation price and elevated uptake at the sacroiliac joints on bone scan will be the solely constructive options.
Purchase 500mg tetracycline amexIntracerebral abscesses may be secondary to lung abscesses antibiotics for uti in horses cheap 500mg tetracycline amex, bronchiectasis or other pyaemic states virus test purchase tetracycline 250 mg without a prescription. The signs result from elevated intracranial pressure and a mass impact related to fever treatment for dogs with fits buy tetracycline 250mg overnight delivery. Subdural Empyema A surgical empyema is a collection of pus between the dural and arachnoid membranes secondary to cardio antibiotic treatment for acne cheap tetracycline 500 mg with amex, anaerobic or tubercular infections. Coexisting signs and signs of meningitis, paranasal sinusitis, mastoiditis, otitis, cranial osteomyelitis and trauma may give a clue to the supply of infection. Neoplasms Primary brain tumours can come up from the brain tissue, meninges, nerves, pituitary gland and various embryonic tissues and developmental abnormalities (Table 19. In adults 80 per cent of tumours are supratentorial, whereas in children infratentorial lesions are the most common. Symptoms of raised intracranial tension, headache, an altered sensorium, focal neurological deficits, endocrine disturbances and seizures may happen. Malignant tumours develop fairly quickly and due to this fact lead to rising intracranial stress. Headache Headache is among the most commonly encountered symptoms and has a long listing of differential diagnoses. In secondary headaches, an underlying structural, vascular, metabolic or infective cause could be detected. The related signs and signs typically provide a clue to the cause, for instance vomiting (migraine or increased intracranial pressure), fever (infections), visible signs (blurring of imaginative and prescient, photophobia), an infection, acute closed-angle glaucoma, migraine, cluster headaches, space-occupying lesions, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, preceding aura (migraine), focal neurological deficits (intracerebral haemorrhage, subdural haematoma, a mass lesion or infection) or seizures (epilepsy, infection or mass lesions). Epilepsy can be idiopathic/cryptogenic with no identified aetiology, or symptomatic with a known structural abnormality. Syncope, breath-holding spells, pseudoseizures, panic assaults and paroxysmal fast eye motion sleep can all mimic epilepsy. Tumours in the posterior strip of the frontal lobe � the motor strip � may cause focal motor seizures: Jacksonian epilepsy. Here the fit begins in a localized area of the contralateral half of the physique but then spreads to have an result on the entire half and will turn into generalized. The cerebral cortex is the organ most susceptible to hypoxic harm, followed by the brainstem. The myocardium is rather more resistant, so in any of the above crises the center and other physique organs survive preferentially. The brainstem survives so spontaneous respiration happens and the center continues to beat independently; this is termed a vegetative state. Death can subsequently be declared when brainstem demise is identified quite than when the heart stops. This has essential implications for the withdrawal of ventilatory support and for organ donation. Brain dying results from head injury in roughly 50 per cent of instances and from subarachnoid haemorrhage in about 30 per cent extra. It must be famous that alcohol, neuromuscular relaxants and hypothermia might trigger a temporary absence of brainstem operate so should be withdrawn or corrected earlier than the diagnosis could be made. A sagittal sequence demonstrating a sellar and suprasellar mass that showed contrast enhancement and was suggestive of a pituitary adenoma. Intracranial Conditions 331 � no motor response to ache; � an absence of laryngeal response to motion of the endotracheal tube; � no caloric or vestibulo-ocular response � syringing the exterior auditory meatus with ice cold water normally ends in vestibular nystagmus. Once these standards have been met, the ultimate test is that there should be no respiratory motion after disconnection of the ventilator for a length that permits the arterial Pco2 to exceed 60 mmHg when 6 L/min of oxygen is being delivered by way of the endotracheal tube. Features of raised intracranial stress embrace the entire following except: a Early morning headache b Vomiting c Papilloedema d Scalp swelling Answer b It is a retention cyst of a hair follicle. A sebaceous cyst is a closed sac underneath the skin, crammed with a cheese-like, oily material, that most often arises from a swollen hair follicle. All the opposite choices are examples of craniostenosis, the place the top dimension is normally small in some dimension, relying on the suture concerned. The triad of raised intracranial strain contains early morning headache, vomiting and papilloedema. The irregular respiration is because of decreased perfusion of the brainstem from swelling or attainable brainstem herniation. Brain contusion or middle cerebral artery damage may produce an intracerebral haematoma. Middle meningeal arteries are vessels in the dura mater; harm to these might produce an extradural haematoma. Seizures and intracerebral haemorrhage are common modes of presentation of which one of the following: a Dermoid b Arteriovenous malformations c Venous malformation d Telangiectasia 9. The commonest malignant major mind tumour is: a Pituitary tumour b Chordoma c Acoustic neuroma d Glioma 10. Arteriovenous malformations are an irregular cluster of vessels within the mind, and are usually congenital. They might rupture spontaneously, resulting in intracerebral haemorrhage or seizures. The commonest main brain tumour � people who begin in the mind and have a tendency to keep in the mind � is a meningioma. In the absence of any brainstem perform, the affected person is said mind useless, which is legally thought of to be dead. The ultimate confirmatory take a look at for declaring mind demise is the apnoeic take a look at, a check to observe for respiratory motion after increasing the Pco2 to above 60 mmHg. Abnormalities of eyes embody anophthalmos (absent eye), microphthalmos (small eye) and buphthalmos (congenital glaucoma). Defects of the pinna can vary in severity from microtia (a small rudimentary pinna) to anotia (complete absence of the pinna). Midfacial, jaw and palatal abnormalities embody micrognathia (mandibular hypoplasia) or macrognathia/megagnathia (large mandible), retrognathia (retracted hypoplastic mandible), cleft lip and cleft palate. The differential analysis of a congenital midline nasal swelling contains the following lesions: � Dermoids are strong, non-compressible and non-transilluminant. They are related to a constructive Furstenberg take a look at (enlargement on compression of the jugular veins). Some deformities may be a part of well-defined syndromes corresponding to Pierre Robin syndrome, during which the mandibular ramus is congenitally shortened. Down syndrome is characterised by a spherical face, microgenia (small chin), macroglossia (large tongue) and upslanting palpebral fissures. The facial options embody a generalized expansion of the skull at the fontanelles, outstanding brow protrusion, pronounced lower jaw protrusion and macroglossia. In infancy and childhood, there may be extensively spaced eyes with puffy eyelids, a broad depressed nasal bridge, thick lips and macroglossia. They usually begin at puberty and will continue to increase in quantity and size throughout maturity. Sinusitis of the frontal and ethmoidal sinuses usually happens secondary to maxillary sinusitis. Frontal sinusitis may cause ache or fullness within the brow or above the eyes, while ethmoid sinusitis can cause pain or strain ache between or behind the eyes, as nicely as complications.
References - Volkmer BG, Nesslauer T, Kraemer SC, et al: Prepubertal high flow priapism: incidence, diagnosis and treatment, J Urol 166:1018n1022, 2001.
- Gerig NE, Meacham RB, et al: Use of electroejaculation in the treatment of ejaculatory failure secondary to diabetes mellitus, Urology 49(2):239n242, 1997.
- Jules-Elysee K, Stover DE, Zaman MB, et al. Aerosolized pentamidine: effect on diagnosis and presentation of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1990;112:750-757.
- Woods M, Carson N, Norton NW, et al: Efficacy of the beta3-adrenergic receptor agonist CL-316243 on experimental bladder hyperreflexia and detrusor instability in the rat, J Urol 166(3):1142, 2001.
|