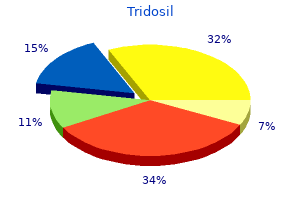
Tridosil
Phillip Fairweather, M.D. - Clinical Assistant Professor
- Mount Sinai School of Medicine
- New York, NY
- Department of Emergency Medicine
- Elmhurst Hospital Center
- Elmhurst, NY
Cheap 250mg tridosil visaWhen all these elements are thought-about virus yahoo order 250 mg tridosil amex, the optimum time for delivery of most diabetic pregnancies is between 39 and 40 weeks preferred antibiotics for sinus infection effective 100mg tridosil. However antibiotics for uti cause constipation cheap 100mg tridosil free shipping, coexisting maternal hypertension antibiotic resistance in campylobacter jejuni buy tridosil 500 mg cheap, suboptimal glucose management, or suspicious fetal biophysical testing outcomes are important cofactors that may affect decisions concerning 35. It could also be tempting to consider early supply in a diabetic being pregnant with "impending macrosomia" identified on ultrasonography. Fetal lung maturity ought to be verified in all patients delivered before 38 weeks by the presence of higher than 3% phosphatidylglycerol or the equivalent on an amniocentesis specimen. After greater than forty weeks, the advantages of continued conservative administration are less than the danger of fetal compromise. Induction of labor earlier than forty two weeks in diabetic being pregnant is prudent regardless of the readiness of the cervix. This could reduce the danger of shoulder dystocia to some degree for an individual patient, however the effect on the bigger obstetric inhabitants is less clear. Of the a hundred and fifteen undiagnosed macrosomic instances, 13 infants had been delivered by emergency cesarean and 86% had been delivered vaginally. The cesarean fee elevated barely after the protocol was initiated (25% versus 22%), but general, shoulder dystocia was less widespread (2. For an toddler from a normoglycemic being pregnant weighing 4500 g or more, routine obstetric management was the least costly alternative ($4014 per injury-free child) compared with elective cesarean ($5212) and induction ($5165). However, a sensitivity evaluation instructed that with a shoulder dystocia threat larger than 10% (as is the case with a fetus weighing more than 4500 g in a diabetic pregnancy), primary cesarean or early induction is somewhat more financially advantageous. Therefore, the current suggestion that cesarean delivery be thought-about when fetal weight is suspected to exceed 4500 g seems to confer a modest enchancment in neonatal end result. The decision to attempt vaginal delivery or perform a cesarean delivery is inevitably primarily based on restricted and considerably unreliable knowledge. Midpelvic operative deliveries should be prevented when macrosomia is suspected, and low pelvic and even outlet operative deliveries must be approached with extreme warning if labor is protracted. Most giant sequence of diabetic pregnancies have reported a rate of 30% to 50% for cesarean delivery. The finest means by which this price could be lowered is by early and strict glycemic management in being pregnant. Conducting lengthy labor inductions in sufferers with a big fetus and a marginal pelvis might increase, quite than lower, morbidity and costs. The use of a combined insulin and glucose infusion throughout labor maintains the maternal plasma glucose stage in a slim range (80 to one hundred ten mg/dL) and reduces the incidence of neonatal hypoglycemia. Typical infusion charges are 5% dextrose in lactated Ringer solution at a rate of 100 mL/hr and lispro or aspart insulin at 0. When cesarean supply is deliberate in a lady with diabetes, the procedure must be performed early within the day to keep away from prolonged intervals of fasting. Plasma/Capillary Glucose (mg/dL) <80 80-100 101-140 141-180 181-220 >220 Infusion Rate (U/hr) Insulinoff zero. A glucose-containing intravenous line should be established promptly on arrival on the hospital, with short-acting insulin given as intravenous boluses on a sliding scale as needed each 1 to four hours to keep the maternal plasma glucose degree in the vary of eighty to one hundred sixty mg/dL. The basal and bolus insulin doses required after delivery are sometimes 30% to 50% of the preprandial doses required throughout being pregnant simply before delivery. If greater quantities of glucose are required, bolus administration of 5 mL/kg of 10% glucose is beneficial, with progressively growing concentrations of glucose administered every 30 to 60 minutes, if needed. However, mounting proof indicates that breastfed infants have a much decrease risk of creating weight problems, cardiometabolic disease, and diabetes than do those exposed to the proteins in toddler formulation. This early separation of mother and neonate impedes breastfeeding and infant attachment, and it could delay the onset of lactogenesis in the diabetic mother. Delayed lactogenesis in girls with insulin-dependent diabetes tends to occur in these with poor metabolic control. Increased maternal calorie and fluid consumption is important to keep milk provide in all women. Studies of breastfeeding ladies with diabetes point out that lactation, even for a short period, has a useful impact on general maternal glucose and lipid metabolism. The diploma of hypoglycemia correlates roughly with the degree of maternal glycemic control in the course of the 6 weeks before start. Pancreatic hypertrophy and chronic fetal hyperinsulinemia-holdovers from the chronically glucose-rich intrauterine environment- can lead to significant hypoglycemia after the umbilical provide of vitamins is interrupted by delivery. Infants of diabetic moms additionally seem to have issues of catecholamine and glucagon metabolism and have diminished functionality to mount normal compensatory responses to hypoglycemia. The current recommendations specify frequent blood glucose checks and early oral feeding every time possible (ideally from the breast), with infusion of intravenous glucose if oral measures prove insufficient. Ordinarily, if neonatal blood glucose ranges fall into the hypoglycemic range, they are often controlled satisfactorily with 59 Diabetes in Pregnancy 1021. Standards of medical care in diabetes-2012, Diabetes Care 35(Suppl 1):S11�S63, 2012. Bartz S, Freemark M: Pathogenesis and prevention of sort 2 diabetes: parental determinants, breastfeeding, and early childhood diet, Curr Diabetes Rep 12:82�87, 2012. Mauricio D, de Leiva A: Autoimmune gestational diabetes mellitus: a definite scientific entity, Diabetes Metab Res Rev 17:422�428, 2001. International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups Consensus Panel: International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups recommendations on the analysis and classification of hyperglycemia in pregnancy, Diabetes Care 33:676�682, 2010. National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference: Diagnosing gestational diabetes mellitus conference, March 6, 2013. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists: Gestational diabetes mellitus. Matsuda M, DeFronzo R: Insulin sensitivity indices obtained from oral glucose tolerance testing, Diabetes Care 22:1462�1470, 1999. Schmitz O, Klebe J, Moller J, et al: In vivo insulin motion in kind 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic pregnant women as assessed by the insulin clamp technique, J Clin Endocrinol Metab 61:877�881, 1985. Basu S, Haghiac M, Surace P, et al: Pregravid obesity associates with elevated maternal endotoxemia and metabolic irritation, Obesity (Silver Spring) 19:476�482, 2011. Rossing K, Jacobsen P, Hommel E, et al: Pregnancy and progression of diabetic nephropathy, Diabetologia 45:36�41, 2002. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Network of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Units, Am J Obstet Gynecol 182:364�369, 2000. Sun F, Kawasaki E, Akazawa S: Apoptosis and its pathway in early post-implantation embryos of diabetic rats, Diabetes Res Clin Pract 67:110� 118, 2005. The National Institutes of Child Health and Human Development�Diabetes in Early Pregnancy study, Am J Obstet Gynecol 164:103�111, 1991. Langer O: Fetal macrosomia: etiologic factors, Clin Obstet Gynecol forty three:283�297, 2000. Radaelli T, Lepercq J, Varastehpour A, et al: Differential regulation of genes for fetoplacental lipid pathways in pregnancy with gestational and kind 1 diabetes mellitus, Am J Obstet Gynecol 201:209. Avon Longitudinal Study of Pregnancy and Childhood, J Clin Endocrinol Metab eighty five:4266� 4269, 2000.
Tridosil 500 mg without a prescriptionPatients with known coarctation of the aorta should be given prophylactic antibiotics in accordance with the recommended guidelines headphones bacteria 700 times 500 mg tridosil fast delivery. Mean arterial pressures within the decrease extremities must be a minimal of forty mm Hg to ensure sufficient blood flow to the kidneys and spinal twine antibiotic resistance malaysia cheap tridosil 250 mg fast delivery. Somatosensory evoked potentials are useful for monitoring spinal twine function and the adequacy of its blood flow during cross-clamping of the aorta antibiotic ear infection 100mg tridosil fast delivery. Excessive will increase in systolic blood strain throughout cross-clamping of the aorta could adversely increase the work of the guts and make surgical repair harder antibiotics for uti and chlamydia buy tridosil 250mg with mastercard. In this example, the utilization of unstable anesthetics is helpful for maintaining regular systemic blood pressures. If systemic hypertension persists, steady intravenous infusions of nitroprusside ought to be thought of. The disadvantages of lowering the systemic blood strain to normal ranges are excessively decreased perfusion pressure within the decrease a half of the body and insufficient blood flow to the kidneys and spinal wire. Although balloon dilation is a therapeutic different, the process is associated with the next incidence of subsequent aortic aneurysm and recurrent coarctation than is surgical resection. Blood circulate to the anterior spinal artery is augmented by radicular branches of the intercostal arteries and may be compromised during cross-clamping of the aorta for surgical resection of coarctation of the aorta. Paraplegia after surgical resection of coarctation of the aorta is a rare complication. Continuous monitoring of systemic blood strain above and below the coarctation is achieved by inserting Immediately postoperative complications embody paradoxical hypertension, attainable sequelae of a bicuspid aortic valve (infective endocarditis and aortic regurgitation), and paraplegia. Baroreceptor reflexes, activation of the renin-angiotensinaldosterone system, and excessive launch of catecholamines have been implicated as attainable causes of immediately postoperative systemic hypertension. Regardless of the trigger, intravenous administration of nitroprusside with or without esmolol successfully controls the systemic blood pressure through the early postoperative interval. If a thoracic epidural catheter has been positioned, local anesthetics or clonidine may be efficient adjuvants to management blood stress. Paraplegia manifesting through the immediately postoperative interval is assumed to replicate ischemic damage to the spinal twine during the aortic cross-clamping required for surgical resection of the coarctation. Left recurrent laryngeal nerve harm, manifesting as stridor or hoarseness, or left phrenic nerve injury could prolong the need for airway and respiratory help. Abdominal ache could happen through the postoperative period and is presumably as a end result of sudden increases in blood flow to the gastrointestinal tract, which finally ends up in elevated vasoactivity. Most of the patients who undergo surgical procedure throughout childhood are normotensive 5 years later, whereas those who undergo surgery after forty years of age typically manifest persistent systemic hypertension. Erythrocytosis secondary to persistent arterial hypoxemia leads to a risk of thromboembolism, particularly when the hematocrit exceeds 70%. Patients with secondary erythrocytosis might exhibit coagulation defects, most likely because of deficiencies of vitamin K�dependent clotting components within the liver and faulty platelet aggregation. Development of a brain abscess is a major threat in sufferers with cyanotic congenital coronary heart illness. Survival in the presence of a right-to-left intracardiac shunt requires a communication between the systemic and pulmonary circulations. Tetralogy of Fallot is the prototype of these defects and is included within the "5 Ts," or frequent cyanotic congenital coronary heart defects (tetralogy of Fallot, transposition of the good arteries, tricuspid atresia, complete anomalous pulmonary venous connection, and truncus arteriosus). Principles for the administration of anesthesia are the same for all the cyanotic congenital cardiac defects. Right-to-left intracardiac shunting occurs due to increased resistance to flow in the right ventricular outflow tract, the severity of which determines the magnitude of the shunt. Because the resistance to circulate throughout the proper ventricular outflow tract is relatively fixed, modifications in systemic vascular resistance (drug induced) may affect the magnitude of the shunt. Any event that will increase pulmonary vascular resistance or decreases systemic vascular resistance increases the magnitude of the shunt and accentuates arterial hypoxemia. Typically the infant with tetralogy of Fallot could also be pink (not cyanotic) as a neonate and develops cyanosis between 2 and 6 months of age. The most typical auscultatory discovering is a systolic ejection murmur heard along the left sternal border ensuing from blood circulate throughout the stenotic pulmonic valve or proper ventricular outflow tract. In distinction to pulmonic stenosis with an intact ventricular septum, the murmur of tetralogy of Fallot becomes shorter and less intense with growing severity of pulmonic stenosis. Chest radiographs show proof of decreased lung vascularity, and the center is boot formed with an upturned right ventricular apex and a concave primary pulmonary arterial segment. Arterial oxygen desaturation is present even when the patient breathes 100 percent oxygen (Pao2 is normally <50 mm Hg), indicating central cyanosis. Compensatory erythropoiesis is proportional to the magnitude of the arterial hypoxemia. It is speculated that squatting will increase the systemic vascular resistance by kinking the big arteries within the inguinal space. The ensuing increase in systemic vascular resistance tends to decrease the magnitude of the right-to-left intracardiac shunt, which ends up in elevated pulmonary blood circulate and subsequent improvement in arterial oxygenation. Hypercyanotic attacks are characterised by sudden spells of arterial hypoxemia associated with worsening cyanosis, increasing rate and depth of respirations (hyperpnea), and, in some instances, loss of consciousness, seizures, cerebrovascular accidents, and even dying. These attacks can occur with out obvious provocation but are sometimes associated with crying, defecation, feeding, or exercise. They can happen any time between 1 month and 12 years of age, however the peak incidence is at 2 to three months. Treatment of hypercyanotic assaults is influenced by the trigger of the pulmonary outflow obstruction. When symptoms reflect a dynamic infundibular obstruction (spasm), applicable therapy is administration of -adrenergic antagonists similar to esmolol or propranolol. If the cause is decreased systemic vascular resistance, treatment is intravenous administration of fluids and/or phenylephrine. Recurrent hypercyanotic attacks point out the need for surgical correction of the abnormalities associated with tetralogy of Fallot. They may also have issues of persistent cyanosis, together with erythrocytosis, hyperviscosity, abnormalities of hemostasis, cerebral abscess or stroke, and infective endocarditis. Cerebrovascular thrombosis or extreme arterial hypoxemia may be the rationalization for these antagonistic responses. A cerebral abscess is typically recommended by the abrupt onset of headache, fever, and lethargy adopted by persistent emesis and the looks of seizure activity. The more than likely cause is arterial seeding into areas of earlier cerebral infarction. Infective endocarditis is a constant danger in patients with tetralogy of Fallot and is related to a excessive mortality fee. Antibiotics must be administered to defend in opposition to this critical possibility each time dental or surgical procedures are planned in these sufferers in preserving with normal tips. Pulmonic regurgitation attributable to an incompetent pulmonic valve usually outcomes from surgical correction of the cardiac defects characteristic of tetralogy of Fallot however poses no major hazard unless the distal pulmonary arteries are hypoplastic, in which case quantity overload of the proper ventricle secondary to regurgitant blood flow might end result. Platelet dysfunction and hypofibrinogenemia are widespread in these patients and may contribute to postoperative bleeding problems. Right-to-left intracardiac shunting typically develops by way of the foramen ovale during the postoperative period.
Buy tridosil 100 mg with mastercardHowever infection 2 months after surgery discount 500 mg tridosil overnight delivery, distal embolization should still happen to any downstream vascular bed antibiotics for acne on back generic tridosil 250 mg with visa, including to the bowel or kidneys antibiotic 30s ribosomal subunit buy tridosil 250 mg with amex. This reversal of flow diverts blood from the mind to provide the arm (subclavian steal syndrome) can antibiotics for acne delay your period buy tridosil 500 mg amex. Left ventricular thrombi could develop after myocardial infarction or in the setting of dilated cardiomyopathy. Other cardiac causes of systemic emboli are valvular heart illness, prosthetic coronary heart valves, infective endocarditis, and paradoxical emboli from a patent foramen ovale. Noncardiac causes of acute arterial occlusion embody atheroemboli from an upstream artery, plaque rupture, and hypercoagulability derangements. Aortic dissection and trauma can acutely occlude an artery by disrupting the integrity of the vessel lumen. There is lack of a palpable peripheral pulse, cool skin, and sharply demarcated pores and skin color changes (pallor or cyanosis) distal to the arterial occlusion. Large embolic fragments often lodge at an arterial bifurcation such because the aortic bifurcation or the femoral artery bifurcation. Arteriography could additionally be used to define the site of acute arterial occlusion and the appropriateness of revascularization surgical procedure. Extreme neck movements or train of the ipsilateral arm might accentuate these hemodynamic modifications and should cause neurologic symptoms. There is commonly an absent or diminished pulse within the ipsilateral arm, and systolic blood pressure is often found to be 20 mm Hg decrease in that arm. Stenosis of the left subclavian artery is liable for this syndrome in most sufferers. Coronary-Subclavian Steal Syndrome A uncommon complication of utilizing the left inner mammary artery for coronary revascularization is coronary-subclavian steal syndrome. This steal syndrome is characterised by angina pectoris and a 20-mm Hg or more lower in systolic blood strain within the ipsilateral arm. Angina pectoris associated with coronarysubclavian steal syndrome requires surgical bypass grafting. Surgical embolectomy is used to deal with acute systemic embolism, usually thromboembolism, to a big peripheral artery. However, if the first supply of atheroembolism is identified and amenable to surgical publicity, it might be resectable. Once the analysis of acute arterial embolism is confirmed, anticoagulation with heparin is initiated to forestall propagation of the thrombus. Intraarterial thrombolysis with urokinase or recombinant tissue plasminogen activator could restore vascular patency in acutely occluded arteries and synthetic bypass grafts. Vasodilation with hyperemia is usually seen after rewarming and reestablishment of blood circulate. The disorder is categorized as Acute Arterial Occlusion Acute arterial occlusion differs from the gradual growth of arterial occlusion brought on by atherosclerosis and is frequently the end result of cardiogenic embolism. Pharmacologic intervention including calcium channel blockade or -blockade may be useful in some sufferers. In rare cases, surgical sympathectomy is taken into account for therapy of persistent, extreme digital ischemia. Increasing the ambient temperature of the working room and maintaining normothermia are fundamental concerns. Noninvasive blood strain measurement techniques could additionally be strongly considered to keep away from any arterial compromise of probably affected extremities. The most necessary related complication of deep vein thrombosis is pulmonary embolism, a quantity one explanation for perioperative morbidity and mortality. Associated diseases embrace many immunologic issues, most frequently scleroderma or systemic lupus erythematosus (Table 8-4). Most of those thromboses are subclinical and resolve completely when mobility is restored. Although deep and superficial venous thromboses may co-exist, isolated deep thrombosis could also be distinguished from superficial venous thrombosis primarily based on history, physical examination findings, and results of confirmatory ultrasonography. Venography and impedance plethysmography are also potential diagnostic modalities. Most postoperative venous thrombi come up within the lower legs, often in the low-flow soleal sinuses and in massive veins draining the gastrocnemius muscle. However, in roughly 20% of patients, thrombi originate in more proximal veins. Left untreated, deep vein thromboses can extend into larger and more proximal veins, and such extension is associated with subsequent fatal pulmonary emboli. The intense inflammation that accompanies superficial thrombophlebitis rapidly results in total venous occlusion. Typically, the vein may be palpated as a cordlike construction surrounded by an area of erythema, heat, and edema. Deep vein thrombosis is more usually associated with generalized ache of the affected extremity, tenderness, and unilateral limb swelling, but prognosis based on scientific indicators Assessment of scientific threat components identifies patients who can profit from prophylactic measures aimed toward lowering the chance of development of deep vein thrombosis (Table 8-6). Patients at low threat require only minimal prophylactic measures, such as early postoperative ambulation and the use of compression stockings, which increase propulsion of blood from the ankles to the knees. Subcutaneous heparin in doses of 5000 units administered twice or thrice daily reduces deep vein thrombosis risk, as does the usage of intermittent exterior pneumatic compression devices (see Table 8-6). The incidence of postoperative deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in sufferers undergoing complete knee or whole hip substitute could be substantially decreased (20% to 40%) by utilizing epidural or spinal anesthesia methods as a substitute of common anesthesia. Presumably, the beneficial results of regional anesthesia compared with general anesthesia are because of (1) vasodilation, which maximizes venous blood flow; and (2) the flexibility to present glorious postoperative analgesia and early ambulation. Therapy is initiated with heparin (unfractionated or low-molecular-weight heparin) as a outcome of this drug produces an immediate anticoagulant impact. Heparin has a narrow therapeutic window, and the response of individual sufferers can vary significantly. Advantages of low-molecular-weight heparin over unfractionated heparin embody an extended half-life, a extra predictable dose response without the need for serial assessment of activated partial thromboplastin time, and a decrease threat of bleeding complications. Disadvantages embrace elevated price and the dearth of availability of a rapid reversal agent. Therapy with warfarin, an oral vitamin K antagonist, is initiated during heparin therapy and adjusted to obtain a prothrombin time yielding a global normalized ratio between 2 and three. Inferior vena cava filters could additionally be inserted into patients who expertise recurrent pulmonary embolism regardless of enough anticoagulant therapy or in whom anticoagulation is contraindicated. Congenital resistance to activated protein C and increased levels of antiphospholipid antibodies are additionally related to venous thromboembolism. Frequent monitoring of activated partial thromboplastin time in patients receiving intravenous heparin is necessary as a end result of the variability in dose response. In addition, vasculitis is normally a characteristic of connective tissue ailments similar to systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis, which are mentioned in other chapters. It has alternative names corresponding to pulseless disease, occlusive thromboaortopathy, and aortic arch syndrome. Decreased perfusion of the mind because of involvement of the carotid arteries may manifest as vertigo, visible disturbances, seizures, or a stroke with hemiparesis or hemiplegia. Hyperextension of the top could lower carotid blood circulate further in these patients.
250mg tridosil otcAmerican College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists: Management of abnormal cervical cytology and histology: follow bulletin no antibiotic garlic order 100mg tridosil visa. Kiguchi K antibiotics for feline acne buy discount tridosil 100mg online, Bibbo M bacteria que come carne generic 250 mg tridosil visa, Hasegawa T antibiotics for uti penicillin order tridosil 250mg fast delivery, et al: Dysplasia during being pregnant: a cytologic follow-up study, J Reprod Med 26:66�72, 1981. Zemlickis D, Lishner M, Degendorfer P, et al: Maternal and fetal outcome after invasive cervical cancer in being pregnant, J Clin Oncol 9:1956� 1961, 1991. Kasamatsu T, Okada S, Tsuda H, et al: Early invasive adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix: standards for nonradical surgical remedy, Gynecol Oncol eighty five:327�332, 2002. Van Calsteren K, Heyns L, De Smet F, et al: Cancer during pregnancy: an analysis of 215 patients emphasizing the obstetrical and the neonatal outcomes, J Clin Oncol 28:683�689, 2010. Baloglu A, Uysal D, Aslan N, Yigit S: Advanced stage of cervical carcinoma undiagnosed throughout antenatal period in time period being pregnant and 948. Tewari K, Cappuccini F, Gambino A, et al: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in the remedy of locally advanced cervical carcinoma in being pregnant: a report of two cases and review of issues specific to the administration of cervical carcinoma in pregnancy including planned delay of remedy, Cancer eighty two:1529�1534, 1998. Caluwaerts S, Van Calsteren K, Mertens L, et al: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by radical hysterectomy for invasive cervical cancer identified during being pregnant: report of a case and evaluation of the literature, Int J Gynecol Cancer sixteen:905�908, 2006. Bernardini M, Barrett J, Seaward G, et al: Pregnancy outcomes in patients after radical trachelectomy, Am J Obstet Gynecol 189:1378�1382, 2003. Giles D, Hewitt D, Stewart A, Webb J: Malignant disease in childhood and diagnostic irradiation in utero, Lancet 271:447, 1956. Beeley L: Adverse results of drugs within the first trimester of pregnancy, Clin Obstet Gynaecol eight:261�274, 1981. Aviles A, Neri N: Hematological malignancies and pregnancy: a final report of 84 kids who obtained chemotherapy in utero, Clin Lymphoma 2:173�177, 2001. Zemlickis D, Lishner M, Degendorfer P, et al: Fetal outcome after in utero exposure to most cancers chemotherapy, Arch Intern Med 152:573�576, 1992. Akira S, Yamanaka A, Ishihara T, et al: Gasless laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy throughout pregnancy: comparability with laparotomy, Am J Obstet Gynecol 180(Pt 1):554�557, 1999. Mathevet P, Nessah K, Dargent D, et al: Laparoscopic management of adnexal masses in ninety seven. Lachman E, Schienfeld A, Voss E, et al: Pregnancy and laparoscopic surgery, J Am Assoc Gynecol Laparosc 6:347�351, 1999. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists: Avoiding inappropriate clinical choices based mostly on false-positive human chorionic gonadotropin test outcomes: Committee opinion no. Nettleton J, Long J, Kuban D, et al: Breast most cancers throughout being pregnant: quantifying the risk of therapy delay, Obstet Gynecol 87:414�418, 1996. Ishida T, Yokoe T, Kasumi F, et al: Clinicopathologic characteristics and prognosis of breast cancer sufferers related to pregnancy and lactation: evaluation of case-control examine in Japan, Jpn J Cancer Res 83:1143�1149, 1992. Garel C, Brisse H, Sebag G, et al: Magnetic resonance imaging of the fetus, Pediatr Radiol 28:201�211, 1998. Gwyn K, Theriault R: Breast most cancers throughout being pregnant, Oncology (Williston Park) 15:39�46, 2001; dialogue 46, 49�51. Reed W, Hannisdal E, Skovlund E, et al: Pregnancy and breast most cancers: a population-based examine, Virchows Arch 443:44�50, 2003. Societe Francaise de Senologie et de Pathologie Mammaire Study Group, Int J Cancer 72:720�727, 1997. Antypas C, Sandilos P, Kouvaris J, et al: Fetal dose analysis throughout breast most cancers radiotherapy, Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 40:995� 999, 1998. Fenig E, Mishaeli M, Kalish Y, et al: Pregnancy and radiation, Cancer Treat Rev 27:1�7, 2001. Cardonick E, Iacobucci A: Use of chemotherapy during human pregnancy (see comment), Lancet Oncol 5:283�291, 2004. Zemlickis D, Lishner M, Degendorfer P, et al: Maternal and fetal consequence after breast most cancers in being pregnant, Am J Obstet Gynecol 166:781� 787, 1992. Gadducci A, Cosio S, Fanucchi A, et al: Chemotherapy with epirubicin and paclitaxel for breast most cancers throughout pregnancy: case report and evaluate of the literature, Anticancer Res 23:5225�5229, 2003. Loibl S, von Minckwitz G, Gwyn K, et al: Breast carcinoma throughout being pregnant: international recommendations from an professional meeting (see comment), Cancer 106:237�246, 2006. Tretli S, Kvalheim G, Thoresen S, et al: Survival of breast cancer sufferers diagnosed throughout being pregnant or lactation, Br J Cancer 58:382� 384, 1988. Sankila R, Heinavaara S, Hakulinen T: Survival of breast most cancers sufferers after subsequent time period pregnancy: "wholesome mom effect. Helewa M, Levesque P, Provencher D, et al: Breast most cancers, pregnancy, and breastfeeding, J Obstet Gynaecol Can 24:164�184, 2002. Lens M, Bataille V: Melanoma in relation to reproductive and hormonal elements in girls: present evaluate on controversial points, Cancer Causes Control 19:437�442, 2008. Matthiesen L, Berg G: Malignant melanoma is the commonest type of most cancers occurring in being pregnant (in Swedish), L�kartidningen 35: 2845�2848, 1989. Stensheim H, Maller B, van Dijk, T, et al: Cause-specific survival for women diagnosed with most cancers during being pregnant or lactation: a registry-based cohort study, J Clin Oncol 27: 45�51, 2009. Lems M, Rosdahl I, Newton-Bishop J: Cutaneous melanoma during being pregnant: is the controversy over Korenaga D, Orita H, Maekawa S, et al: Relationship between hormone receptor levels and cell-kinetics in human colorectal most cancers, Hepatogastroenterology forty four:78�83, 1997. In Canellos G, Lister T, Young B, editors: the lymphomas, ed 2, Philadelphia, 2006, Saunders Elsevier, pp 536�541. Weisz B, Schiff E, Lishner M: Cancer in pregnancy: maternal and fetal implications, Hum Reprod Update 7:384�393, 2001. Juweid M, Stroobants S, Hoekstra O, et al: Use of positron emission tomography for response evaluation of lymphoma: consensus of the Imaging Subcommittee of international Harmonization Project in Lymphoma, J Clin Oncol 25:571�578, 2007. Ebert U, Loffler H, Kirch W: Cytotoxic therapy and being pregnant, Pharmacol Ther 74:207�220, 1997. Wiebe V, Sipila P: Pharmacology of antineoplastic brokers in being pregnant, Crit Rev Oncol Hematol sixteen:75�112, 1994. Zemlickis D, Lishner M, Degendrofer P, et al: Fetal consequence after in utero exposure to most cancers chemotherapy, Arch Intern Med 152:573�576, 1992. Dilek I, Topcu N, Demir C, et al: Hematological malignancy and being pregnant: a singleinstitution expertise of 21 cases, Clin Lab Hematol 28:170�176, 2006. Germann N, Goffinet F, Goldwasser F: Anthracyclines during being pregnant: embryo-fetal outcome in one hundred sixty patients, Ann Oncol 15:146� 150, 2004. Doll D, Ringenberg Q, Yarbro J: Anti-neoplastic agents and being pregnant, Semin Oncol 16:337� 346, 1989. Glantz J: Reproductive toxicity of alkylating brokers, Obstet Gynecol Surv forty nine:709�715, 1994. Kimby E, Sverrisdottir A, Elinder G: Safety of rituximab therapy in the course of the first trimester of being pregnant: a case history, Eur J Haematol seventy two:292�295, 2004. Amitay-Layish I, David M, Kafri B, et al: Earlystage mycosis fungoides, parapsoriasis en plaque, and being pregnant, Int J Dermatol forty six:160�165, 2007. Malik S, Oliver R, Odejinmi F: A uncommon association with hyperemesis: being pregnant and multiple myeloma, J Obstet Gynaecol 26:693�695, 2006. Niitsu N, Kohri M, Togano T, et al: Development of hepatosplenic gammadelta T-cell lymphoma with pancytopenia during early pregnancy: a case report and evaluation of the literature, Eur J Haematol seventy three:367�371, 2004. Maglione A, Di Giorgio G, Petruzzelli F, et al: Multiple myeloma recognized during early pregnancy: a case report, Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 111:214�215, 2003. Castelo-Branco C, Torne A, Cararach V, et al: Mycosis fungoides and being pregnant, Oncol Rep 8:197�199, 2001.
Buy tridosil 500 mg on lineCurrent finest proof suggests no profit to intraoperative hypothermia in sufferers present process aneurysm clipping antibiotic mode of action 250 mg tridosil with amex. Traditionally antibiotics for dogs cost buy 250 mg tridosil otc, drug-induced managed hypotension has been used to decrease transmural pressure within the aneurysm and thereby decrease the chance of aneurysm rupture during microscopic isolation and clipping antibiotic chart buy cheap tridosil 250mg. Controlled hypotension is used less typically now than before due to considerations concerning the impairment of autoregulation that follows subarachnoid hemorrhage antibiotic resistance spread vertically by purchase 100 mg tridosil with mastercard, unpredictable cerebrovascular responses to drug-induced hypotension, and the risk of worldwide ischemia. As an alternative choice to drug-induced hypotension, regional controlled hypotension produced by putting a vascular clamp on the parent artery supplying the aneurysm provides protection against aneurysm rupture without incurring the chance of world cerebral ischemia. If longer periods of occlusion are wanted, the administration of metabolism-suppressing anesthetics, significantly barbiturates, might present safety in opposition to regional cerebral ischemia and infarction. During temporary clamping of the feeding vessel, systemic blood strain must be maintained towards the higher end of the conventional blood pressure range to encourage collateral circulation. At the conclusion of the surgical procedure, immediate emergence from anesthesia is fascinating to facilitate instant neurologic analysis of the affected person. The use of shortacting inhaled and intravenous anesthetic drugs makes immediate awakening more doubtless. However, incremental doses of antihypertensive drugs such as labetalol or esmolol could also be needed as the patient emerges from anesthesia. Lidocaine may be administered intravenously to suppress airway reflexes and the response to the presence of the endotracheal tube. Patients who had been obtunded preoperatively are likely to require continued intubation and mechanical ventilation in the course of the postoperative interval. Patients who experience intraoperative rupture of an intracranial aneurysm may recover slowly and benefit from postoperative airway and ventilatory assist. Neurologic standing is assessed at frequent intervals within the postanesthesia care unit or intensive care unit. Patients might manifest delayed emergence from anesthesia or focal neurologic deficits after intracranial aneurysm resection, and it might be troublesome to distinguish between drug-induced causes. The appearance of a model new focal deficit should increase suspicion of a surgical trigger, since anesthetic medicine can be expected to cause primarily global effects. Inequality of pupils that was not current preoperatively can be likely to reflect a surgical occasion. Successful surgical therapy may be adopted by delayed neurologic deficits (hours to days later) resulting from cerebral vasospasm. This, in turn, requires aggressive remedy, including hypertension, hypervolemia, passive hemodilution, or invasive radiographic interventions. The anesthetic objectives for sufferers present process angiographically guided cerebral aneurysm coil placement are much like those for sufferers undergoing aneurysm clip placement. Typically, coil placement procedures are carried out utilizing sedation or general anesthesia. The principal advantage of sedation is that intraprocedural neurologic assessment can be performed. However, affected person movement in the course of the procedure poses the risk of aneurysm rupture or coil dislodgment leading to coil embolization. These malformations are believed to be congenital and generally present in maturity as either hemorrhage or new-onset seizures. These low-flow, well-circumscribed lesions typically present as newonset seizures but occasionally manifest as hemorrhage. They are often found by the way at autopsy and are often related to other problems, including Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome and Sturge-Weber syndrome. Currently, treatment could contain a combination of surgical resection, highly targeted (Gamma Knife) irradiation, and/or angiographically guided embolization. They generally happen between meningeal vessels within the dura mater or between the carotid artery and venous sinuses inside the cavernous sinus. Many others are associated with a earlier traumatic harm or, in the case of carotid-cavernous fistulas, with earlier (presumably silent) rupture of an intracavernous carotid artery aneurysm. Dural arteriovenous fistulas generally current with pulsatile tinnitus or headache. An occipital bruit can be appreciated in 24% of those cases for the explanation that occipital artery is a common arterial feeder of an arteriovenous fistula. Treatment options embody angiographically guided embolization or surgical ligation. Patients with carotid-cavernous arteriovenous fistulas usually have orbital or retro-orbital ache, arterialization of the conjunctiva, or visible modifications. The nature of the malformation, including dimension, location, mechanism of venous drainage, presence of related aneurysms, and any prior treatment, must be elicited, since these factors may help in anticipating perioperative problems. Medications, together with antiepileptic medication if the affected person has a concurrent seizure disorder, ought to be administered preoperatively. Patients who underwent preoperative angiography might experience fluid and electrolyte abnormalities secondary to the administration of hypertonic distinction material. In addition to standard monitoring, an intraarterial catheter may be positioned before induction of anesthesia. Blood pressure control all through anesthesia, surgical procedure, and the postoperative interval is important, since hypotension may end in ischemia in hypoperfused areas and hypertension may improve the danger of rupture of an related aneurysm, exacerbate intraoperative bleeding, or worsen intracranial hypertension. For embolization or surgical resection of a vascular malformation in an eloquent area of mind, monitored anesthesia care is a beautiful choice. Techniques to blunt the hemodynamic responses to stimulating occasions similar to laryngoscopy, pinion placement, and incision ought to be used as wanted. These might embrace the administration of lidocaine, esmolol, or nitroprusside or deepening of the anesthetic state with either greater concentrations of volatile anesthetics, small doses of intravenous anesthetics, short-acting opioids, or intravenous lidocaine. Further, central venous entry could additionally be helpful in some circumstances to monitor volume status or to enable fast administration of huge volumes of fluids or blood merchandise. Monitoring via a pulmonary artery catheter or transesophageal echocardiography could be helpful in patients with cardiac disease. In cases of huge or high-flow vascular malformations, frequent communication with the surgeon is of paramount importance, as a result of impressions of the lesions and the surgical and anesthetic requirements for protected resection could change in the course of the operation. This is due, in part, to considerably less than definitive imaging evaluation preoperatively or changing surgical necessities throughout varied stages of resection of a large, complicated lesion. Hemodynamic stability, optimum surgical situations, and speedy emergence from anesthesia at the finish of surgical procedure are applicable objectives when selecting anesthetic upkeep medications. Hypotonic and glucose-containing solutions must be avoided, for the explanation that former can exacerbate cerebral edema and the latter can worsen the finish result of neurologic ischemia. Mild hyperventilation (Paco2 of 30 to 35 mm Hg) will help facilitate surgical exposure. Treatment of cerebral edema might embody average hyperventilation as a temporizing measure, administration of diuretics corresponding to mannitol and furosemide, and blood stress discount. In extreme cases, high-dose barbiturate or propofol anesthesia or short-term craniectomy with postoperative ventilatory assist may be helpful.
Tridosil: 500 mg, 250 mg, 100 mg
Discount tridosil 250 mg lineIt is essential to maintain management of the airway and of glucose and electrolyte balance antibiotics for uti didn't work tridosil 500 mg lowest price. The results are sometimes troublesome to consider because of the restricted variety of circumstances reported; the shortage of comparative information on nonepileptic ladies attending the same establishments; differences within the severity of the epilepsy and the means it has been treated; differences in age antibiotic eye drops over the counter tridosil 100 mg mastercard, medical background virus 68 ny order 250 mg tridosil visa, and socioeconomic status of the patients reported; and the lack of knowledge concerning relevant social habits similar to cigarette smoking and alcohol ingestion antibiotic infusion buy generic tridosil 500 mg on-line. The incidences of vaginal hemorrhage and of toxemia throughout pregnancy amongst epileptic girls had been discovered to be elevated in some studies however not others. Whether preterm labor happens more commonly in epileptic women, as is sometimes reported, is unclear. Anticonvulsant medicine taken by the mom may be current in breast milk, but data as to whether or not they have any major impact on the toddler are limited. There is evidence that primidone, ethosuxamide, gabapentin, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, and topiramate enter breast milk in clinically significant portions; valproic acid, phenytoin, carbamazepine, and phenobarbital can also do so, but the proof is less clear. The explanation for this increased danger to the offspring of epileptic mothers is unknown. It may relate to genetic elements, seizures arising throughout pregnancy, or the metabolic and poisonous consequences of seizures or anticonvulsant drugs. A major drawback in administration of epileptic patients during being pregnant is the possibility that sure anticonvulsant medication may induce fetal abnormalities. Some patients could have a typical genetic predisposition to seizures and to fetal malformation. Environmental components may be important in the genesis of congenital abnormalities, and socioeconomic backgrounds have to be matched as much as is feasible when comparisons are made from the incidence of malformations in different affected person populations. All the commonly used older antiepileptic medicine are in all probability teratogenic to some extent, and malformation rates are higher for the offspring of mothers taking drug mixtures. Animal studies lend help to the belief that some anticonvulsants are teratogenic. The mechanism involved is unclear but may embody folate deficiency or antagonism. Low blood folate ranges earlier than or early in being pregnant are considerably related to spontaneous abortion and the occurrence of developmental anomalies. Although most youngsters born to epileptic mothers are cognitively regular, prenatal antiepileptic drug exposure could also be associated with developmental delay, notably when more than one drug has been taken by the mother. Among infants uncovered to phenytoin in utero, 11% have sufficient medical features to be classified as having this syndrome, and virtually three times as many could show lesser levels of impairment of efficiency or morphogenesis. They include restlessness, constant crying, irritability, tremulousness, issue in sleeping, and vasomotor instability but not seizures. Clinical or subclinical coagulopathy may happen in the neonate whose mom obtained anticonvulsants throughout being pregnant. As a outcome, some specialists advocate maternal ingestion of vitamin K1 (10 mg daily) over the past month of pregnancy. Epilepsy should be treated with the smallest effective dosage of an anticonvulsant drug, and monotherapy is preferable to polytherapy. Drug selection is based on seizure type, scientific standing, and the maternal and fetal dangers. Because many pregnancies are unintended and congenital malformations may have already occurred by the point a woman realizes she is pregnant, consideration could be given to present folate supplementation for any woman of childbearing age taking antiepileptic drugs. Similar reasoning suggests that it could be advisable to keep away from valproate in epileptic girls of childbearing age. Data in regards to the relative security and therapeutic effectiveness of various anticonvulsant medicine within the management of pregnant epileptic sufferers are inadequate to information the physician responsible for the care of those sufferers. If valproic acid should be used, prenatal testing for maternal serum -fetoprotein levels or with ultrasound is advisable to detect neural tube defects, so that therapeutic abortion could be thought-about if essential. Substitution of 1 anticonvulsant drug for another in epileptic girls whose first medical visit is after the first trimester must be avoided, because if a serious malformation of the fetus is going to happen, it has in all probability occurred already. The ideas of drug management of a seizure disorder in the pregnant woman are the same as within the nonpregnant girl. Anticonvulsant drugs are as necessary to epileptic sufferers throughout being pregnant as at different occasions. A detailed account of the medicine used within the treatment of epilepsy is pointless here, but several factors are worthy of remark. Only time will inform whether a person who has a single seizure goes to have further assaults, thereby justifying a analysis of epilepsy and necessitating prophylactic anticonvulsant drug remedy. Although some physicians begin a affected person on anticonvulsant medicine after one convulsion, others choose to withhold medicine until the patient has had at least two seizures, a minimal of within the nonpregnant state. During pregnancy, many physicians provoke anticonvulsant remedy after even a single seizure and arrange for neurologic reevaluation after delivery. This method deserves emphasis as a end result of many patients with so-called gestational epilepsy have solely a single convulsion, and continued treatment in such circumstances may be unnecessary. If the findings of such investigations are unremarkable, discuss the controversial issue of anticonvulsant drug therapy with the affected person however usually suggest that remedy be withheld until a future assault occurs. Pregnant ladies experiencing two or extra seizures benefit prophylactic anticonvulsant drug remedy. Treatment is began with a small dosage of one of the anticonvulsants, depending on the sort of seizure experienced by the patient and the issues outlined earlier. The dosage is elevated till seizures are controlled, blood concentrations reach the upper finish of the optimal therapeutic vary, or side effects limit further increments. If seizures continue despite optimal blood levels of the anticonvulsant drug selected, a second drug must be substituted for the primary. Patients usually respond higher to one or another of the assorted medication that are available. Patients should take treatment as prescribed, and therapy must be managed by frequent monitoring of the plasma concentration of the anticonvulsant drug. Monthly follow-up visits during being pregnant often allow satisfactory supervision of the affected person. At the preliminary go to, trough values of complete and free concentrations of each drug must be measured. Total ranges should then be measured each month in sufferers whose seizures are well controlled; free levels must be monitored month-to-month in those with poor seizure management, seizures during being pregnant, or a marked (>50%) decline in whole stage. Poor compliance with an anticonvulsant drug routine can often be improved by encouragement and by explaining the significance of taking medicine regularly. Simplifying the dosage schedule so that medicine is taken simply once or twice every day may be helpful. As the being pregnant continues, the dosage of the anticonvulsant drug may must be elevated if seizures turn into extra common, or the free stage of the anticonvulsant drug declines by greater than about 30%. In some instances, the required dosage could reach a degree that would most likely trigger poisonous side effects in a nonpregnant patient. If the anticonvulsant dosage is elevated in the course of the pregnancy, reductions will in all probability be essential within the puerperium to stop toxicity, but this change should be based mostly on scientific analysis and measurement of the plasma focus of the drug, as a result of the interval over which drug requirements decline varies considerably.
Buy tridosil 500 mg low costHydrocephalus is common after subarachnoid hemorrhage and is treated with ventricular drainage nebulized antibiotics for sinus infection buy cheap tridosil 100 mg on-line. Following subarachnoid hemorrhage with or without surgical or endovascular remedy of the aneurysm antibiotic resistance game purchase 100mg tridosil with amex, an essential aim is prevention of vasospasm (intracranial arterial narrowing) and its penalties bacteria water test kit purchase 250mg tridosil otc. Development of vasospasm may be triggered by many mechanisms virus fever purchase 100 mg tridosil with amex, an important of which is the contact of free hemoglobin with the abluminal surface of cerebral arteries. For this reason, day by day transcranial Doppler ultrasonographic examinations may be performed to detect vasospasm. If vasospasm is identified, triple H remedy (hypertension, hypervolemia, passive hemodilution) is initiated. Administration of nimodipine, a calcium channel blocker, has been proven to improve end result when initiated on the primary day and continued for 21 days after subarachnoid hemorrhage, which presumably reflects a protective effect from the consequences of vasospasm. This benefit of nimodipine occurs without angiographic proof of vessel luminal enlargement. Cerebral angiographic strategies can be employed to dilate vasospastic arteries mechanically (via balloons) or chemically (via intraarterial administration of papaverine). The goal through the induction of anesthesia is to prevent any increase in the transmural stress of the aneurysmal sac, which could improve the danger of aneurysm rupture. Patients with vasospasm also present a quandary as a outcome of systemic hypertension might improve circulate through vasospastic vessels but might increase the risk of aneurysm rebleeding. Aneurysm clipping during the period by which the patient is at high risk of vasospasm is related to elevated mortality. Monitoring of the blood pressure through an intraarterial catheter is fascinating to make certain the adequacy of blood stress control throughout direct laryngoscopy and at other instances of noxious stimulation. Prophylaxis towards significant hypertension during direct laryngoscopy could also be completed by administration of esmolol, lidocaine, propofol, barbiturates, or short-acting opioids. Loss of consciousness is achieved with intravenous administration of thiopental, propofol, or etomidate. Nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking medicine are most often selected to facilitate endotracheal intubation. A pulmonary artery catheter or transesophageal echocardiography could additionally be considered when sufferers have known cardiac disease. Drugs, fluid, and blood have to be immediately available to manage resuscitation ought to the aneurysm rupture intraoperatively. The danger of intraoperative rupture is approximately 7%, and rupture mostly happens in the course of the late levels of surgical dissection. Anesthetic administration of rupture consists of aggressive quantity resuscitation to preserve normovolemia mixed with controlled hypotension. If momentary clipping of the feeding vessel is used to acquire management of a ruptured aneurysm, the systemic blood strain may be returned to regular and even barely elevated levels to improve collateral blood move whereas the vessel is obstructed by the occlusion clip. Anesthesia is typically maintained with risky anesthetics (isoflurane, desflurane, sevoflurane) with or without the addition of nitrous oxide, which can be supplemented with intermittent (fentanyl) or continuous (remifentanil) infusion of opioids. Alternatively, a complete intravenous anesthetic approach (propofol and short-acting opioid) can be used. Intraoperative fluid administration is guided by blood loss, urine output, and measurement of cardiac filling pressures. Normovolemia is the objective, which is best achieved by intravenous administration of balanced salt options. Most sufferers reply quite well to surgical resection, and emergence from anesthesia ought to be clean and fast. Agents corresponding to -adrenergic antagonists as well as lidocaine or nitroprusside can be utilized to management short-term hypertension throughout emergence. Moyamoya Disease Progressive stenosis of intracranial vessels with the secondary development of an anastomotic capillary community is the hallmark of moyamoya illness. Moyamoya is the Japanese term for "puff of smoke" and refers to the angiographic discovering of a cluster of small abnormal blood vessels. There seems to be a familial tendency toward the event of this illness, however it could be seen following head trauma or in affiliation with other disorders similar to neurofibromatosis, tuberous sclerosis, and fibromuscular dysplasia. Since comparable pathologic findings may be present in other organs, central nervous system abnormalities may be manifestations of a systemic disease. Intracranial aneurysms happen with increased frequency in these with moyamoya illness. Symptoms of ischemia, such as transient ischemic assaults and cerebral infarcts, are common initial findings in youngsters, whereas hemorrhagic complications are often the presenting signs in adults. The prognosis is usually made by standard or magnetic resonance angiography, which demonstrates a cluster of small irregular blood vessels. Surgical choices include direct anastomosis of the superficial temporal artery to the middle cerebral artery (also known as an extracranial-intracranial bypass) or other indirect revascularization procedures, which can be combined with an extracranial-intracranial bypass. These strategies include laying the temporalis muscle instantly on the brain floor and suturing the superficial temporal artery to the dura mater. Anticoagulant or antiplatelet drug therapy must be discontinued, if attainable, to keep away from bleeding issues intraoperatively. The objectives of induction and maintenance of anesthesia embrace (1) guaranteeing hemodynamic stability, because hypotension could result in ischemia in the distribution of the abnormal vessels and hypertension might trigger hemorrhagic issues; (2) avoiding factors that result in cerebral or peripheral vasoconstriction, such as hypocapnia or phenylephrine, which may compromise blood flow in the feeding or recipient vessels; and (3) facilitating a fast emergence from anesthesia so that neurologic perform could be assessed. In addition to normal monitoring, intraarterial catheterization is important to rapidly assess modifications in blood pressure. If attainable, this must be accomplished before induction of anesthesia to help guarantee a hemodynamically secure induction sequence. Succinylcholine should be used with caution in sufferers with preexisting neurologic deficits ensuing from the chance of hyperkalemia. A volatile anesthetic� based approach might have the theoretical benefit of enhancing cerebral vasodilation. Excessive hyperventilation must be avoided due to its cerebral vasoconstrictive impact. Anemia must be avoided to prevent ischemia in already compromised mind regions. Associated injuries, including cervical backbone harm and thoracoabdominal trauma, incessantly accompany acute head harm. Brain harm can be further exacerbated by systemic situations associated to trauma, including hypotension and hypoxia related to excessive bleeding, pulmonary contusion, aspiration, or adult respiratory misery syndrome. Initial management of sufferers with acute head harm contains immobilization of the cervical backbone, establishment of a patent airway, safety of the lungs from aspiration of gastric contents, and maintenance of mind perfusion by therapy of hypotension. Delayed hematoma formation or cerebral edema is often liable for these adjustments. Delayed secondary harm at the cellular degree is a crucial contributor to brain swelling and subsequent irreversible mind damage.
References - Lamb AD, Vowler SL, Johnston R, et al: Meta-analysis showing the beneficial effect of alpha-blockers on ureteric stent discomfort, BJU Int 108:1894-1902, 2011.
- Hartman GS, Yao FS, Bruefach M III, et al: Severity of aortic atheromatous disease diagnosed by transesophageal echocardiography predicts stroke and other outcomes associated with coronary artery surgery: A prospective study, Anesth Analg 83:701, 1996.
- Arroyo EJ, Scherer SS. On the molecular architecture of myelinated fibers. Histochem Cell Biol. 2000;113(1):1-18.
- Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med 2003;9:669-676.
- Reinhardt GF, Myscofski JW, Wilkens DB, et al: Incidence and mortality of hypoalbuminemic patients in hospitalized veterans, JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 4(4):357-359, 1980.
- Moody TE, Vaughn ED Jr, Gillenwater JY: Relationship between renal blood flow and ureteral pressure during 18 hours of total unilateral uretheral occlusion. Implications for changing sites of increased renal resistance, Invest Urol 13(3):246n251, 1975.
- Routh JC, Cheng EY, Austin JC, et al: Design and methodological considerations of the centers for disease control and prevention urologic and renal protocol for the newborn and young child with spina bifida, J Urol 196(6):1728-1734, 2016.
- Vincent ME, Robbins AH. Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex enteritis: pseudo-Whipple's disease in AIDS. AJR 1985; 144:921-922.
|


