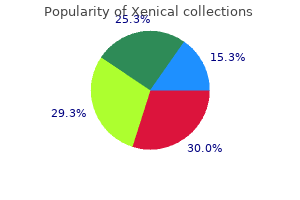
Xenical
Mark Franklin, M.D. - Department of Anesthesiology
- Northwestern University Medical School
- Chicago, IL
Purchase 60mg xenicalRefinement of Synaptic Connections Chapter 9 275 fiber over several months weight loss pills celebrity use buy xenical 120 mg otc, despite the fact that muscles are usually innervated by a single axon weight loss eating plan discount 120 mg xenical free shipping. The trick was to place the two motor terminals a number of millimeters from each other (Kuffler et al weight loss pills miranda lambert purchase xenical 60mg overnight delivery. In truth weight loss 4 2 day cleanse detox purchase xenical 60 mg with visa, some animals have muscle fibers that are usually innervated by a couple of motor axon. In one polyneuronally innervated muscle in chicks, the distance between terminals can be reduced when synaptic transmission is blocked, presumably because competition between energetic terminals normally keeps them separated (Gordon et al. This could clarify why terminal endings from a single axonal arbor typically innervate a continuous area of the postsynaptic cell (Forehand and Purves, 1984; Glanzman et al. For instance, when sensory neurons from the sea slug, Aplysia, are grown in culture together with a common target motor neuron, their terminals come to occupy separate areas of the postsynaptic cell. However, if the two sensory neurons are grown without a target, then they grow extensively along each other. Therefore, the antagonistic relationship between synapses must by some means be mediated by the postsynaptic neuron. However, the terminal zone remains wider within the eye-specific lamina at 3�4 weeks postnatal (arrows). This strategy additionally ends in more polyneuronal innervation, suggesting that the pattern of exercise governs which synapse might be eliminated. Together, these experiments present that synaptic transmission can influence the method of synapse elimination. This was demonstrated by grafting two motor nerve terminals onto the same muscle in grownup rats. Both nerves maintained functional connections to the muscle Use-dependent adjustments to grownup synaptic connections happen regularly, and are thought to help studying and reminiscence (see Box 9. To take an obvious example, we speak and comprehend the language to which we were exposed as kids, whether it was Tagalog, American Sign Language, or Farsi. Wiesel and Hubel (1963a, 1965) carried out a set of pioneering experiments that explored how visual experience impacts the maturation of connections. In these transgenic mice, motor neurons expressed both of two completely different fluorescent proteins. One of the motor terminals (blue) occupies a larger share of the postsynaptic territory at P11. It gradually withdraws from the junction (arrows) over the next four days, and the opposite terminal (green) takes over the postsynaptic web site. If it was pushed equivalently by each eye, then it was assigned to group four, and so forth. Notice that the majority cells are pushed by each eyes, and are assigned to classes 2�6. These histograms provide a sensitive measure of the innervation sample within the visual cortex. In distinction, a higher than normal number of synapses from the deprived eye were eradicated. Reasoning that disuse should have weakened the synapses from the disadvantaged eye, Wiesel and Hubel recorded from animals that had been deprived of imaginative and prescient in both eyes, anticipating to see a total absence of visually-evoked exercise. When the synapses are shut collectively (blue circles), synaptic elimination occurs within a quantity of weeks. When the synapses are far aside (red circles), synaptic elimination fails to occur. At the rat nervemuscle junction, polyneuronal innervation declines between 10 and 15 days postnatal (black line). Most rat soleus muscular tissues are polyneuronally innervated between postnatal days 8�10 (black line). Wiesel and Hubel wrote: "It was as if the expected ill results from closing one eye had been averted by closing the opposite. Taken collectively, these outcomes suggest that variations within the amount of exercise in the pathways from the left and right eyes determined the innervation pattern and energy of the projection from every eye. Thus, monocular deprivation creates a situation by which cortical neurons obtain a set of lively afferents from the open eye and a set of afferents with lowered exercise from the closed eye, putting the latter at an obstacle. In distinction, binocular deprivation evens the taking half in field because all afferents have an identical low degree of activity. In a pivotal test of the competitors speculation, kittens have been raised with an artificial strabismus (cf. This manipulation mimics a medical situation in humans, called amblyopia, which generally leads to the suppression of vision through one of many eyes. Following several months of strabismus, recordings had been produced from the visible cortex. Thus, this molecular mechanism may be an evolutionarily conserved type of synaptic plasticity. The influx of calcium prompts a quantity of kinases which, in flip, phosphorylate proteins at the synapse. A quite simple type of learning in Aplysia, long-term facilitation of transmitter launch, illustrates one other necessary molecular pathway. The facilitated transmitter launch includes new gene expression and protein synthesis (Kaang et al. Thus, when transgenic flies specific the activator, they keep in mind an odor with much much less coaching. However, flies that specific the repressor are unable to store long-term olfactory memories (Yin et al. This truth posed an interesting question: How is that this nuclear signaling-common to all synapses of a given neuron-restricted to only those synapses that undergo structural and practical modifications The cellular mechanisms answerable for adjustments of synaptic energy have been explored most thoroughly in adult animals because of their position in learning and memory. Synaptic plasticity has been studied in all kinds of neuronal methods, from molluscan ganglia to mammalian cerebral cortex, and the catalog of molecular and genetic mechanisms has grown steadily (Glanzman, 2010; Santini et al. This is good news for these thinking about developmental plasticity as a result of many of the ideas and methods have been imported successfully. The first experiments on synaptic plasticity demonstrated that intense stimulation of motor axons might enhance neurotransmission at a muscle cell for about one minute. This posttetanic facilitation occurred because extra neurotransmitter was launched from the presynaptic terminal (Larrabee and Bronk, 1947; Lloyd, 1949). For essentially the most half, modern electrophysiology studies nonetheless rely on intracellular recordings from a postsynaptic cell, usually at the side of medicine which may be designed to block the perform of a specific molecule. Genetic manipulations within the fruit fly and the mouse usually present an essential experimental link between gene merchandise, synaptic perform, and conduct. The trendy era of cellular plasticity research began within the Sixties when the classical conditioning paradigm of paired stimuli was utilized directly to a molluscan nervous system. The increase was termed heterosynaptic facilitation as a result of synaptic transmission at one set of synapses modified the useful standing of a second, independent set of synapses. By recording extracellularly from the hippocampus of anesthetized rabbits, it was discovered that a brief, excessive frequency stimulus to an afferent pathway resulted in an enhancement of the evoked potential that lasted for hours to days (Bliss and L�mo, 1973).

Order xenical 120 mg on lineIt also illustrates that drug use and its results on customers are influenced by many factors working collectively weight loss hypnosis app buy xenical 60 mg fast delivery. Most usually weight loss 4 texas buy xenical 60 mg without a prescription, the same criteria are utilized in describing the "symptoms" or criteria that represent a substance use disorder for all medication and drug courses that folks are most likely to weight loss pills that make you feel full xenical 60mg use for nonmedical reasons weight loss pills 20 pounds generic xenical 120 mg online. Criteria 1 by way of 9 focus on what traditionally has been referred to as "compulsive drug use," or drug addiction. Similarly, drug use persists despite the danger of incurring severe consequences by doing so. We have extra to say about them later on this chapter and in other chapters in this textual content. The substance is commonly taken in bigger quantities or over a longer period than was intended; 2. Users have a persistent need or unsuccessful efforts to reduce down or control use of the substance; 3. Recurrent use of the substance ends in a failure to fulfil major function obligations at work, faculty, or house; 6. Use of the substance is sustained despite having persistent or recurrent social or interpersonal issues brought on, or exacerbated, by the substance; 7. Use of the substance is recurrent so that necessary social, occupational, or recreational activities are given up or reduced; eight. Tolerance has developed, as defined by either of the following: (a) Need for markedly increased amounts of the substance to achieve intoxication or desired impact, or (b) Markedly diminished effect with continued use of the identical amount of the substance. Withdrawal is skilled, as manifested by either of the following: (a) the characteristic withdrawal syndrome for the substance, or (b) the identical (or intently related) substance is taken to relieve or keep away from withdrawal symptoms. Specify current severity: Mild, presence of two to three signs; Moderate, presence of 4 to 5 symptoms; Severe, presence of six or extra symptoms. Source: From the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition. Like many terms used in communicating about medication and their use, psychological dependence has had totally different meanings. In the Rinaldi study, psychological dependence was outlined as "the emotional state of craving a drug both for its optimistic effect or to avoid unfavorable effects associated with its abuse" (p. Not all medicine are associated with an identifiable withdrawal syndrome (also called abstinence syndrome). For any drug associated with withdrawal symptoms, the severity of those signs could change with the traits of the users and their historical past of use of that drug. Furthermore, psychological symptoms, such as anxiety, despair, and longing for medicine, are often part of withdrawal syndromes. These psychological signs strongly influence whether or not the person can cease utilizing medication for any length of time. Tolerance and withdrawal are addressed as part of any analysis or research of a drug. It is crucial to point out now, nevertheless, that tolerance and withdrawal have an result on drug-use patterns. For example, if tolerance to a drug develops, the individual must consume rising amounts of it to obtain a desired drug effect. Such a trend in use may have an result on how a lot time the particular person devotes each day to acquiring the drug and to utilizing it. Furthermore, with higher portions and frequencies of drug use, the person turns into more susceptible to experiencing varied unfavorable physical, social, or authorized penalties. Drug withdrawal additionally makes a person extra likely to proceed or resume the use of a drug after a period of abstaining. Many research have shown that aid from withdrawal is a strong motivator of drug use. In this regard, drug withdrawal could begin when the extent of drug in the blood drops. If the person takes more of the drug at this level, the withdrawal signs are relieved. Here the motivating force is the "turning off" of unpleasant withdrawal signs, which works to perpetuate a strong cycle of drug use�drug withdrawal�drug use. Withdrawal can be related to a better likelihood of resuming drug use following a period of abstinence because of realized reactions to cues in the environment. We want to emphasize here that the influences of tolerance and withdrawal are on the coronary heart of psychopharmacology-the incentives or motivators that drive human (and different animal) drug use. Chapter 5, on the ideas and strategies of psychopharmacology, addresses this topic in detail. You could have noticed from this discussion of drug tolerance, withdrawal, and drug-taking conduct that they could be instrumental within the development of what we Drug Tolerance, Withdrawal, and Drug-Taking Behavior tolerance Generally, increased amounts of a drug needed to obtain intoxication, or a diminished drug effect with continued use of the identical amount of a drug. Another factor that might be crucial to the development of addictive drug-use patterns is "sensitization" (Robinson & Berridge, 2003). The sensitization hypothesis is that one result of repeated use of a drug in interplay with environmental elements is changes within the mind neural pathways (Chapter 3) that may heighten (sensitize) the reward value of that drug. Critically, the brain adjustments ensuing from repeated drug use may be everlasting, which is one purpose why drug dependancy may be such an intractable drawback for many people, as we show later in this text. This dialogue exhibits that using a drug for a long time alters the patterns of use for that drug. Of course, dialogue of the consequences of tolerance and dependence on motivations for drug use addresses solely a small minority of the totally different causes that individuals use medicine, which takes us again to the ten methods that influence or are influenced by drug use that we mentioned initially of this chapter. In this regard, individuals give quite a few causes for "why" they use different medication, and different drugs could also be most strongly associated with different causes. The similar drug also may be used for various reasons in several times and locations. The complexity of human alcohol and drug use is also represented in the fashions of the causes of the substance use issues which are summarized in Chapter 15. Kennedy Overview of the Text You now are prepared for a quick overview of the remainder of this text, which is split into three main sections. The first part, which includes Chapters 1 via 5, offers you fundamental data on psychopharmacology and the historical past of legal guidelines and policy relating to drug use within the United States and other countries. You saw that this first chapter introduced you to necessary definitions of ideas and the epidemiology of drug use. Chapter 4 considerations pharmacology, as we evaluation the strategies scientists use to research medication and their results. Chapter 5 focuses on ideas and methods of psychopharmacology, which is the central matter of this textual content. Chapters 6 through 14 represent the second section of the text and concern individual drugs and drug courses. Our drug topics embrace cocaine and the amphetamines, nicotine, caffeine, alcohol, opiates, marijuana, hallucinogens, psychiatric medicines, and different prescription or over-the-counter medicine.
Syndromes - Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
- You need to plan to have a condom on hand when you have sex. However, female condoms may be placed up to 8 hours before intercourse. You may also make inserting the condom part of your lovemaking.
- Have not responded fully to antidepressant drugs
- Do not bundle a feverish child in blankets.
- Cytomegalovirus
- Multiple punctures to locate veins
- Name of product (as well as the ingredients and strength, if known)
- Weakness of an arm or leg
- Vomiting blood
Buy discount xenical 60mg lineAt their minus-ends weight loss pills recalled 120 mg xenical visa, the actin filaments in the filopodia are disassembled into monomeric globules weight loss pills that work over the counter generic xenical 60 mg free shipping, g-actin weight loss pills on tv buy 120mg xenical with amex, which may cycle up to weight loss pills while breastfeeding buy generic xenical 60 mg line the entrance and be integrated again into the plus-ends of filaments. The fast progress of a progress cone alongside a substrate relies on transmembrane receptors for adhesion molecules. With their extracellular domains, these receptors grip the substrate, and with their intracellular domains, they have interaction with rearward shifting actin filaments. The effect is to pull the whole development cone ahead just like the tread of a tank engaged with the ground (Mitchison and Kirschner, 1988). The disassembly of actin filaments at the minus-ends of the filopodia, breaks the connections between the substrate and the actin cables here. Meanwhile, new connections are fashioned between the substrate and the ever growing plusends. Indeed, when myosin perform in growth cones is blocked, ahead progress is slowed. The filopodia themselves, nonetheless, are inclined to lengthen as the drive that pulled them rearward into the main body progress cone, the place their minus-ends are disassembled, is attenuated (Lin et al. A schematic drawing exhibits leader axons and follower axons (blue and black) growing by way of the midline. The leading axon, being the primary, is completely exposed to the guidance cues in the surroundings. Its progress cone must sense all the constructive and negative midline cues and interpret them accordingly, which results in slow progress and complicated morphology of leader development cones at the midline where these cues are discovered. Time-lapse observations show that by growing along the chief, follower axons are less uncovered to midline cues, have more simply shaped growth cones, and develop sooner. Similarly, a single filopodium that makes contact with a extra adhesive substrate in tissue culture is in a position to steer the complete development cone by pulling it towards the attachment point (Letourneau, 1996). Conversely, in an experiment accomplished on vertebrate neurons, a single filopodium from a growth cone was detached from the surface of a culture dish using a fantastic glass needle; the expansion cone snapped into a model new direction that was consistent with the stress exerted by the remaining filopodia (Wessells and Nuttall, 1978). The importance of single filopodia in directing growth cones has even been demonstrated in vivo within the Ti1 pioneer axons of the grasshopper limb. The bulging central area and the skinny peripheral domain containing actin cables are seen. Here, microtubules additionally push ahead and carry cargo to and from the cell body along the axon shaft as they enter the growth cone and fan out towards the filopodia. Close-ups of assorted regions show a number of the molecular components of the cytoskeletal network which are localized within the development cone. If the expansion cones are handled with the actin-depolymerizing agent cytochalasin, the axon fails to navigate (bottom). When these axons are handled with cytochalasin, the axons fail to make the appropriate posterior flip, and most axons miss the tectum (bottom). Microtubules are the opposite major cytoskeletal components of the growth cone (Kahn and Baas, 2016). Pools of unassembled tubulin are concentrated in the growth cone, which is the most sensitive a part of the axon to the effects of microtubule depolymerizing brokers such as nocodozole (Brown et al. Natural microtubule stabilizing proteins, similar to Tau, are also extremely concentrated close to the expansion cone, suggesting that this is where unpolymerized tubulin is common into microtubules and stabilized. Like the actin filaments in the filopodia, the microtubules of the axons have a "plus" end the place polymerization takes place, and this is positioned in the course of the growing tip. Depolymerization of microtubules inhibits axon elongation utterly, displaying that in contrast to actin meeting, microtubule growth is completely essential for this course of (Marsh and Letourneau, 1984). Inside of the expansion cone, carboxyl terminal tyrosine is added to alpha-tubulin by the enzyme tubulin tyrosine ligase. This tyrosinated form of tubulin is sensitive to depolymerizing agents so the new microtubules inside the growth cone are very dynamic. In contrast, microtubules by which tubulin loses the tyrosine and turns into acetylated as an alternative, because it does in the axon shaft, turn out to be stabilized (Brown et al. This instability of nonacetylated microtubules is crucial for normal growth cone motility. A reagent like taxol which stabilizes microtubules, when applied to growth cones, causes them to advance relentlessly straight forward, and inhibits turning (Williamson et al. This is demonstrated in experiments where the microtubule stabilizing agent taxol was delivered simply on one side of a growth cone. The growth cone turns in that course, while if a depolymerizing agent similar to nocodazole is delivered to one side, the growth cone turns the other method (Buck and Zheng, 2002). The similarity of the results with actin and microtubule destabilizers means that actin bundles and microtubules interact in methods which are critical for correct progress cone navigation. The keys to making the growth cone cytoskeleton so dynamic are the numerous proteins that interact with actin filaments and microtubules. Chief among these are motor proteins, such as myosin that drives retrograde flow of actin (Schaefer et al. Wiring Up the Brain: Axon Navigation Chapter 5 131 but this effect is rescued if myosin exercise can be inhibited (Kahn and Baas, 2016). The other key microtubule-based motors are the kinesins that take cargo towards the rising plus-ends of microtubules. There are a large number of receptors on the growth cone floor that sense the substrates and guidance molecules that the expansion cone encounters in its journey and when activated, these receptors set in movement signaling cascades (see below) that regulate the exercise of all these cytoskeletal proteins as the expansion cone navigates. There are apparent mechanical options of the setting that affect progress cone navigation, similar to nerve sheathes and the outer surfaces of the brain, which kind impenetrable limitations and the presence of main pathways corresponding to tracts or commissures, which function bridges or major roadways from one area to another. Numerous filopodia and lamellipodia are prolonged and retracted rapidly on the floor of the growth cone. A particular mechanical feature of the nervous system to which growth cones attend is stiffness. The stiffness of tissues may be measured by atomic force microscopy (Franze, 2011, 2013; Franze et al. Brain tissue has barely any collagen so it is extremely soft-about the consistency of cream cheese. Muscle is an order of magnitude stiffer, and bone an extra two orders of magnitude stiffer. It may be shown by plating cells into tradition on substrates that differ solely in stiffness that this this mechanical function has dramatic effects on development cones and axon progress. Much of the work on progress cone cell biology has been carried out in tissue tradition, the place the plastic petri dishes on which the neurons grow are as hard as bone. Yet when grown on substrates as soft as brain, completely different neurons respond differently-spinal axons branch extra whereas sensory neurons of dorsal root ganglia develop shorter axons. On such stiff substrates the axons of retinal ganglion cells are inclined to grow straight and often fasciculate with each other. When grown as a substitute on substrates which would possibly be as delicate as brain tissue, these axons grow in a extra exploratory mode, altering directions frequently (Koser et al. When grown on gradients of stiffness that mimic these in the mind, retinal development cones are inclined to flip towards softer and away from more durable, and this matches the greatest way that they grow alongside gradients of stiffness within the embryonic brain. When these channels are blocked by mutation or a particular component of spider venom, development cones lose the flexibility to respond to tissue stiffness (Koser et al.
Order xenical 120 mg lineThe growth of the motion potential mechanism of amphibian neurons isolated in cell culture weight loss pills pure garcinia purchase xenical 60 mg without prescription. Spontaneous Ca2+ spikes and waves in embryonic neurons: signaling techniques for differentiation weight loss pills free trial trusted 60 mg xenical. Developmental up-regulation of the potassium-chloride cotransporter kind 2 in the rat lumbar spinal wire weight loss 8 months buy generic xenical 120 mg on line. Posttranslational regulation of Ca2+-activated K+ currents by a target-derived factor in developing parasympathetic neurons weight loss pills ukraine cheap xenical 60mg with amex. K+ and pH homeostasis within the growing rat spinal chord is impaired by early postnatal X-irradiation. Functional correlation of fetal and adult types of glycine receptors with developmental modifications in inhibitory synaptic receptor channels. Neurons born in the grownup dentate gyrus type useful synapses with target cells. Localization and focusing on of voltage-dependent ion channels in mammalian central neurons. Receptor tyrosine kinase specific for the skeletal muscle lineage: Expression in embryonic muscle, on the neuromuscular junction, and after harm. Postnatal growth of the hyperpolarization-activated excitatory current Ih in mouse hippocampal pyramidal neurons. A quantitative study of synapses on motor neuron dendritic growth cones in growing mouse spinal twine. Review: nice construction of synaptogenesis in the vertebrate central nervous system. Neurotrophins induce formation of practical excitatory and inhibitory synapses between cultured hippocampal neurons. Staurosporine inhibits agrin-induced acetylcholine receptor phosphorylation and aggregation. Electron microscopy of synaptic structures in olfactory cortex of early postnatal rats. Cadherin-9 regulates synapse-specific differentiation in the developing hippocampus. The discs-large tumor suppressor gene of Drosophila encodes a guanylate kinase homolog localized at septate junctions. Initial occasions within the formation of neuromuscular synapse: speedy induction of acetylcholine launch from embryonic neuron. Development of two kinds of calcium channels in cultured mammalian hippocampal neurons. Patterning of muscle acetylcholine receptor gene expression in the absence of motor innervation. Control of protein activity and cell destiny specification via light-mediated nuclear translocation. Synaptogenesis in layer I of the human cerebral cortex in the first half of gestation. Chapter 9 Refinement of Synaptic Connections Even as synaptogenesis proceeds, a process is ready in motion that leads to the elimination of some existing connections and the stabilization of others. As discussed under, developing synaptic connections can be altered permanently by experiences that have little to no impact during adulthood. Despite this difference, developmental plasticity and adult learning share a number of molecular mechanisms. Why are synapses being assembled and disbanded on the same time, notably when the molecular cues that help axon steerage, and target selection (see Chapters 5 and 6) result in such correct connections One possibility is that synapse addition and loss does improve the specificity of neural connections beyond that attained through molecular mechanisms. The right complement and strength of synaptic connections could optimize the computational properties of every neuron and, finally, enhance behavioral efficiency (see Chapter 10). In truth, the central nervous system is designed for steady modification, from delivery into maturity, and we discover the earliest iteration of this process in this chapter. In distinction, many cortical excitatory synapses type on dendritic spines the place they produce tiny postsynaptic potentials that have to be summed to produce a major depolarization. Two experimental approaches have been taken to determine whether or not a loss of synapses happens during growth. First, intracellular recordings show modifications within the number of functional afferents per postsynaptic neuron. Second, anatomical studies reveal that single axonal arbors become spatially restricted inside the target population. The lack of synaptic contacts is noticed all through the developing nervous system, from the nerve-muscle junction of invertebrates to the cerebral cortex of people. One imaginative strategy to this drawback makes use of intracellular recordings and electrical stimulation of the afferent pathway. While this may seem to be a trivial distance, if billions of neurons make immature projections of this type, then neural computations could be adversely affected. The ratio of innervating afferent axons per postsynaptic neuron, known as convergence, varies tremendously. Similarly, each cerebellar Purkinje cell is innervated by a single climbing fiber. A third immature pattern of innervation occurs when synapses initially kind Development of the Nervous System. However, practical estimates of synaptic convergence show that elimination occurs even in methods that remain multiply innervated in adulthood (Lichtman and Purves, 1980; Sanes, 1993; Kim and Kandler, 2003; Clause et al. An alternative strategy is to count all of the synaptic contacts in a set volume of tissue, and decide whether a web reduction occurs with age. For instance, a single afferent could initially make a hundred weak synapses, and progressively rework to make 50 robust contacts. Second, the processes of synapse addition and elimination overlap in time, and whole synapse quantity could enhance even whereas a fraction of synapses are being eradicated. If we assume that axons make synapses the place they arborize, then it must be possible to examine synapse elimination indirectly by measuring the territory occupied by individual axonal arbors. The most evident case happens when a projection is eradicated completely due to the dying of nerve cell bodies. Similarly, errant projections from the olfactory epithelium to the olfactory bulb are eradicated by neuron loss, but can persist into maturity when creating animals are disadvantaged of olfaction (Zou et al. This was demonstrated for commissural axons that project from one facet of the cerebral cortex to the other (Innocenti et al. However, the arbor initially extends to far, and some of its local branches are eliminated throughout improvement. The precise time course over which synapse elimination occurs, and the variety of connections which might be lost, varies significantly between areas of the nervous system, even within a single species. In the rat cerebellum, the elimination of climbing fiber synapses onto Purkinje cells happen through the second postnatal week (Mariani and Changeux, 1981). A stimulating electrode is placed on the afferent inhabitants whereas an intracellular recording is obtained from the postsynaptic cell. As the stimulation current is increased, the afferent inputs are recruited to turn into active.
Xenical: 120 mg, 60 mg

Purchase 120mg xenical with amexTogether weight loss in dogs buy xenical 60mg visa, these results recommend that dendrites are maximally delicate to synaptic exercise in periods of synapse refinement (Majewska and Sur weight loss percentage calculator discount 120mg xenical otc, 2003; Zuo et al weight loss 77080 purchase xenical 120 mg on-line. The effect of synaptic transmission on dendrite morphology could be examined by blocking glutamate receptors weight loss pills zotrim xenical 120mg otc. A comparable impact has been observed in frog optic tectal neurons and in spinal motor neurons. In hippocampal cultures, the variety of dendritic spines depends on glutamatergic synaptic exercise (Kossel et al. The results of excitatory transmission can change during improvement as new signaling systems are added to the cytoplasm. Spine morphology is managed by the cytoskeletal component, actin, which is extremely dynamic in growing methods (Star et al. In the primary, a backbone retracts (top), and within the second a backbone elongates (bottom). In the embryonic chick retina, dendritic retractions could be prevented by locally raising calcium levels within the process (Lohmann et al. A local rise in calcium could serve to stabilize actin filaments, maybe by activating gelsolin, the calcium-dependent actin-binding protein. However, sensory deprivation research suggest that the disuse of a synapse leads to its weakening or elimination, especially if competing synapses are energetic. At one degree, the purpose of synapse elimination appears clear: to create optimum connections between neurons based mostly upon their use. What is the optimal sample of connectivity for working, singing, perfect pitch, velocity reading, studying, and so forth This might be notably important for animals, such as people, that inhabit a variety of environments. However, the experimental manipulations which have been used to reveal an influence of setting or neural activity are probably to be rather extreme. Yet, we all know that creating humans do expertise many "excessive" rearing environments, such as blindness, deafness, malnutrition, and heaps of other challenges that outcome from genetic or epigenetic causes. Therefore, the clinical importance of understanding developmental plasticity is gigantic. Retinal waves coordinate patterned exercise all through the growing visual system. Development of particular person geniculocortical arbors in cat striate cortex and results of binocular impulse blockade. In vivo observations of pre- and postsynaptic adjustments during the transition from multiple to single innervation at developing neuromuscular junctions. Retrograde neurotrophin signaling through Tollo regulates synaptic progress in Drosophila. The formation of synapses in reinnervated and cross-reinnervated striated muscle during improvement. Synaptogenesis and improvement of pyramidal neuron dendritic morphology within the chimpanzee neocortex resembles people. Organization of ocular dominance and orientation columns within the striate cortex of neonatal macaque monkeys. Long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission within the dentate space of the anesthetized rabbit following stimulation of the perforant path. Experience-dependent plasticity in the inferior colliculus: a website for visual calibration of the neural illustration of auditory area in the barn owl. Morphological plasticity of motor axons in Drosophila mutants with altered excitability. Regulation of synapse construction and function by the Drosophila tumor suppressor gene dlg. Visual circuit development requires patterned exercise mediated by retinal acetylcholine receptors. Multiple forms of synaptic plasticity triggered by selective suppression of exercise in particular person neurons. Hebbian mechanisms revealed by electrical stimulation at growing rat neuromuscular junctions. Synapses shaped by identified retinogeniculate axons throughout segregation of eye enter. Dendritic translocation establishes the winner in cerebellar climbing fiber synapse elimination. Major role for neuronal dying throughout mind development: refinement of topographic connections. Long-term melancholy of synaptic inhibition is expressed postsynaptically within the creating auditory system. Emergence of lamina-specific retinal ganglion cell connectivity by axon arbor retraction and synapse elimination. The exact temporal sample of prehearing spontaneous activity is necessary for tonotopic map refinement. Spontaneous elimination of synapses on cat spinal motoneurons after start: do half of the synapses on the cell bodies disappear Afferent influences on mind stem auditory nuclei of the hen: time course and specificity of dendritic atrophy following deafferentation. Developmental loss of synchronous spontaneous activity in the mouse retina is impartial of visible experience. Long-term potentiation in an avian basal ganglia nucleus essential for vocal studying. Long-term potentiation and useful synapse induction in developing hippocampus. The effect of postsynaptic block on the development of the neuromuscular junction in postnatal rats. Homeostatic plasticity studied using in vivo hippocampal activity-blockade: synaptic scaling, intrinsic plasticity and age-dependence. Transitory corpus callosum axons projecting all through growing rat visible cortex revealed by Dil. Environmental complexity modulates development of granule cell dendrites in developing however not adult hippocampus of rats. Regional innervation of rabbit ciliary ganglion cells by the terminals of preganglionic axons. Bilateral cochlear ablation in postnatal rat disrupts development of banded sample of projections from the dorsal nucleus of the lateral lemniscus to the inferior colliculus. Repetitive motor learning induces coordinated formation of clustered dendritic spines in vivo. Development of afferent patterns in the inferior colliculus of the rat: projection from the dorsal nucleus of the lateral lemniscus. Persistence of experience-induced homeostatic synaptic plasticity through maturity in superficial layers of mouse visual cortex. Possible mechanisms determining synapses formation in creating skeletal muscle tissue of the chick. Effects of rearing complexity on dendritic branching in frontolateral and temporal cortex of the rat.
Cheap xenical 120mg with visaAt a low price weight loss without exercise buy xenical 60mg visa, G and T can interconvert to an enol kind lipo 6 weight loss pills side effects cheap xenical 120 mg amex, and A and C can change to an imino form weight loss pills like phentermine cheap xenical 120 mg visa. During replication weight loss pills hypothyroidism order xenical 60 mg otc, the daughter strand incorporates a guanine reverse this thymine, creating a base mismatch. Therefore, in the course of the second round of replication, an adenine base is discovered reverse this thymine. They can also be produced throughout certain forms of immune responses and by a variety of cleansing reactions within the cell. Colorful fruit and veggies, including grapes, blueberries, cranberries, citrus fruits, spinach, broccoli, beets, beans, pink peppers, carrots, and strawberries, are often high in antioxidants. Guanine bases are notably weak to oxidation, which can result in several totally different oxidized products. The time period refers to the phenomenon in which a repeated sequence of three nucleotides can readily improve in quantity from one generation to the next. In people and other species, sure genes and chromosomal areas include areas where trinucleotide sequences are repeated in tandem. These sequences are usually transmitted normally from father or mother to offspring with out mutation. This aggregation of proteins or protein fragments carrying glutamine repeats is correlated with the progression of the illness. However, recent proof means that the aggregated proteins might indirectly cause the disease symptoms. In the case of the 2 fragile X syndromes, the expansions produce CpG islands that turn out to be methylated. When the trinucleotide repeat sequence is abnormally long, such expansions could incessantly occur during gamete formation, and due to this fact offspring in successive generations might have trinucleotide repeat sequences which would possibly be even longer than those of their dad and mom. In this section, we turn our attention to induced mutations that are attributable to environmental agents. We usually hear in the news media that we should always keep away from these agents in our meals and living surroundings. For instance, we use products such as sunscreens to help us avoid the mutagenic results of ultraviolet (uV) gentle. In addition, as a result of new mutations may be deleterious, individuals need to avoid mutagens to forestall gene mutations that will have harmful effects on their future offspring. Base Modification Some chemical mutagens act by covalently modifying the construction of bases. Such brokers severely injury the skin, eyes, mucous membranes, lungs, and blood-forming organs. For example, acridine dyes similar to proflavin contain flat constructions that intercalate, or insert themselves, between adjacent base pairs, thereby distorting the helical structure. When integrated, these compounds tend to cause many mutations within the cells, resulting in the death of most cancers cells. Ionizing radiation can penetrate deeply into organic supplies, where it produces chemically reactive molecules generally known as free radicals. Nonionizing Radiation Nonionizing radiation, similar to uV gentle, has less vitality, and so it penetrates solely the floor of an organism, such because the pores and skin. This explains the higher incidence of skin cancer amongst individuals who have been exposed to large quantities of sunlight during their lifetime. Because of the recognized link between skin cancer and solar publicity, people now apply sunscreen to their skin to prevent the dangerous effects of uV light. Most sunscreens contain natural compounds, such as oxybenzone, which take up uV light, and/or opaque elements, similar to zinc oxide, that replicate uV mild. Concept Check: What is a standard cause of thymine dimer formation in folks, and in what cell type(s) is it most likely to happen The mutation rate is the chance that a gene will be altered by a new mutation. This rate is usually expressed because the variety of new mutations in a given gene per cell generation. The spontaneous mutation fee for a specific gene is usually in the vary from 1 in 100,000 to 1 in 1 billion, or 10�5 to 10 �9 per cell era. Given the human genome size of approximately three,200,000,000 bp, these numbers tell us that a mutation is a relatively rare event. The presence of sure environmental agents, corresponding to X-rays, can increase the rate of induced mutations to a much larger worth than the spontaneous mutation rate. In addition, mutation rates range considerably from species to species and even inside totally different strains of the same species. One clarification for this variation is that there are numerous different causes of mutations (refer back to Table 19. These strains include a point mutation inside a gene that encodes an enzyme required for histidine biosynthesis. However, a second mutation- a reversion-may happen that restores the flexibility to synthesize histidine. In different phrases, a second mutation could cause a reversion again to the wild-type condition. The Ames take a look at monitors the speed at which this second mutation occurs, thereby indicating whether or not an agent will increase the mutation price above the spontaneous price. A mutagen may require activation by mobile enzymes, which are supplied by the rat liver extract. This step improves the ability of the test to establish brokers that may trigger mutation in mammals. However, if a mutation has occurred that permits the pressure to synthesize histidine, it could develop on these plates to kind a visual bacterial colony. To estimate the mutation price, the colonies that develop on the media are counted and compared with the total number of bacterial cells that were originally streaked on the plate. For instance, if 10,000,000 micro organism were plated and 10 rising colonies were observed, the speed of mutation is 10 out of 10,000,000; this equals 1 in 106, or simply 10 �6. Researchers evaluate the mutation price in the presence and absence of the suspected mutagen. If statistical analysis reveals that the mutation rate in the experimental and control samples are significantly completely different, researchers might tentatively conclude that the agent could additionally be a mutagen. Many research have been conducted during which researchers used the Ames test to examine the urine from cigarette people who smoke to that from nonsmokers. This research has shown that the urine from people who smoke accommodates a lot larger ranges of mutagens. Control Suspected mutagen Salmonella pressure (requires histidine) Rat liver extract Rat liver extract Salmonella pressure (requires histidine) Plate the mixtures onto petri plates that lack histidine. Conduct a t-test to determine if suspected mutagen X is significantly affecting the mutation price. From your understanding of the topic, you may remember that the next number of colonies on the experimental plates could indicate that a substance is a mutagen. Analyze To start to remedy this downside, you first have to calculate the mutation price.
Epimedium violaceum (Epimedium). Xenical. - Are there safety concerns?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Impotence, ejaculation problems, sexual dysfunction, fatigue, memory loss, high blood pressure, heart disease, liver disease, bronchitis, joint pain, HIV/AIDS, osteoporosis, and other conditions.
- How does Horny Goat Weed work?
- Dosing considerations for Horny Goat Weed.
- What is Horny Goat Weed?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96686

Purchase 120mg xenical overnight deliveryAs a end result top 5 weight loss pills 2012 120mg xenical amex, these progenitors are sometimes referred to as "multipotent progenitors weight loss pills or shakes 120mg xenical with visa," or at occasions "neural stem cells weight loss gummies generic 120mg xenical with visa. We will revisit this concern on the end of the chapter in the discussion of grownup neurogenesis weight loss in face generic 120 mg xenical mastercard. By distinction, those cells that withdraw from the cycle and become postmitotic quickly after the 3H-thymidine was administered will stay closely labeled with the radioactive nucleotide. Thus the postmitotic neurons generated, or "born," within a day after the 3H-thymidine injection may have heavily labeled nuclei, and neurons generated later in growth might be more lightly labeled. Unlabeled cells are those who withdrew from the cell cycle earlier than the 3H-thymidine injection. More just lately, 3H-thymidine labeling has been replaced by bromo-deoxyuridine (BrdU), since this thymidine analog can additionally be included by S-phase cells and can be detected using an antibody and immunofluorescence, rather than the extra sophisticated autoradiography method. The 3H-thymidine birthdating method has been used extensively to observe the migration and birthdates of the completely different neuronal and glial populations in the nervous system. These studies revealed that the method of neurogenesis is remarkably nicely ordered. In many areas of the developing mind, there are spatial and temporal gradients of neuron production. In common, there are nicely conserved and orderly sequences of generation of several sorts of neurons and glia. For instance, in the cerebral cortex, the neurons are organized in layers or lamina. Often, the whole inhabitants of one sort of 58 Development of the Nervous System neuron, just like the spinal motor neurons, turns into postmitotic within a comparatively brief period of improvement. For instance, pyramidal cells turn into postmitotic earlier than granule cells within the hippocampus, cerebral cortex, and olfactory bulb, and in the cerebellum, the very large Purkinje cells are generated prior to the tiny granule cells (Jacobson, 1977). Interestingly, the patterns of neuronal technology are also according to the speculation that phylogenetically older components of the mind develop before more recently advanced constructions. The image of neurogenesis that has emerged from the thymidine birthdating studies and the retroviral lineage studies has led to many questions on the process: What controls the number of neurons and glia produced by the progenitors What controls the migration of the cells from the ventricular zone to their ultimate location within the mind The thymidine birthdating research and the retroviral lineage tracing studies described above provided a wealth of details about the migrations and cell varieties generated by the progenitors; however, additionally they supplied details about how cell numbers are regulated throughout development. Progenitor cells from the chick mind, for example, have an overall cell cycle time of 8 h on embryonic day three, however this will increase to 15 h by embryonic day 6. A comparable enhance in cell-cycle period occurs within the mammal, as rat cortical progenitor cells improve their cell-cycle time from 11 h on embryonic day 12 to 19 h at embryonic day 18. The improve within the cell-cycle interval is essentially due to increases in the G1 phase. The M and G2 phases of the cell cycle change little from embryonic day 10 to embryonic day 19 in mouse cerebral cortex progenitor cells; nonetheless, the G1 part almost triples in length. The lengthening of the G1 interval probably displays some regulatory course of that restricts or slows reentry of the progenitor cells into the S-phase from G1, possibly a limiting provide of a progress factor controls this step (see next section). Labeling individual progenitor cells with retroviruses at different stages of brain improvement has proven directly that the number of progeny generated by a ventricular zone cell declines over the period of neurogenesis. The most superficial layer, layer 1, incorporates solely the remnants of the preplate neurons (not shown). Simply counting the speed of overall enlargement of the nervous system over time has also led to insights into the process of neurogenesis. In the early embryonic cerebral cortex, for instance, the variety of cells doubles each day. During this early "expansion phase" of the progenitor cells, many of the cell divisions are symmetric, generating two further progenitor cells. As growth proceeds, and the cell-cycle time turns into progressively longer, the variety of new cells generated per day declines. Fewer cell divisions are symmetric and end in two progenitor cells at later stages of growth, in comparability with the early phases of embryogenesis. Instead, within the later stages of neurogenesis, a greater proportion of the progenitor cells differentiate into neurons and glia. By the top of neurogenesis, almost all the cells go away the cell cycle, and only a few remain to generate new neurons. From these outcomes then it seems that evidently the answer to the question of how cell numbers are regulated throughout development of the mind might be divisible into two subquestions: (1) What elements account for the gradual lengthening of the cell cycle during growth Many of the same molecular mechanisms that management the proliferation of progenitors within the nervous system are also necessary for the management of cell division in different tissues. Through the analysis of mutations in yeast cells that disrupt normal cell cycle, a variety of the parts of the molecular equipment controlling cell cycle have been recognized. An intricate sequence of protein interactions controls and coordinates the progress of a cell by way of the stages of cell replication. This molecular mechanism has been conserved over the millions of years of evolution from the best eukaryotic cells, like yeast, to more complicated animals and vegetation. Key elements of the cell cycle control course of are called Cyclins, a gaggle of proteins that show dramatic modifications of their expression ranges that correlate with specific stages of the cell cycle. The affiliation of Cyclins with one other class of proteins, called the Cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdk), causes the activation of those kinases and the next phosphorylation of substrate proteins necessary for progression to the subsequent part of the cell cycle. Molecules that promote cell proliferation are proven in green and those that inhibit the cell cycle are proven in red. However, there are "brakes" on S-phase entry, the Rb protein and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors, like p27kip. One of the important steps in the management of the cell cycle is on the transition from the G1 stage to the S-phase, and as famous above, CyclinD is a crucial regulator of this step. The CyclinD/Cdk4 complex causes cells to enter S-phase by phosphorylating a protein called retinoblastoma or Rb. This phosphorylation causes the Rb protein to launch one other transcription issue, E2F, and permits the E2F protein to activate many genes that push the cell into S-phase. The Rb protein obtained its name from a childhood tumor of the retina, retinoblastoma, since defects in this gene cause uncontrolled retinal progenitor proliferation. In fact, the Rb gene was the first of a class of genes called tumor suppressors to be identified. Children who inherit a mutant copy of 60 Development of the Nervous System the Rb gene develop retinoblastoma when the second allele of this gene is mutated in a progenitor cell within the retina. Thus the regulation of progenitor proliferation is important each for making a traditional retina and for preventing the uncontrolled cell proliferation that results in most cancers. The p27kip and p21 gene merchandise are therefore referred to as CdkIs (for Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors). Total cell output from the mitotic divisions of the cortical progenitors could be expressed as the P (or progenitor fraction) + Q (or the quit fraction). In the early embryonic cerebral cortex, the share of the total in the Q fraction is comparatively small, and those cells within the P fraction continue to divide and produce extra cells. However, as improvement proceeds, the share of cells in the Q fraction increases and the overall development rate of the cortex declines. On the opposite hand, the converse experiment of overexpressing p27kip results in a higher share of cells in the Q fraction, and a markedly thinner cortex.

Cheap 120mg xenical otcFurthermore weight loss kids cheap 120mg xenical overnight delivery, inside 15 s of contact weight loss pills on facebook 120mg xenical with mastercard, nerve-evoked synaptic transmission was great enough to elicit a postsynaptic action potential weight loss pills or powder safe xenical 60mg. In evaluating the development of synaptic structure and performance weight loss 80 20 rule buy xenical 120 mg amex, neurotransmission seems to evolve way more rapidly. In the chick ciliary ganglion, synaptic potentials may be recorded earlier than synapses are detected with an electron microscope (Landmesser and Pilar, 1972). When the neurons had been crammed with a calcium-sensitive dye (left), and the growth cone was imaged whereas a muscle cell was introduced into contact (right), intracellular free calcium increased in the progress cone (red). When the terminal is depolarized again, the vesicles once more fuse with the membrane and the dye is unloaded. Clearly, the emergence of synapse perform can proceed briskly, possibly due to events that precede contact corresponding to transmitter launch by development cones and neurotransmitter receptor expression by postsynaptic cells. Evidence for a target-derived stop signal comes from in vitro observations of pontine neurons coming into contact with their target, cerebellar granule cells (Baird et al. When granule cells are present, but not in touch with pontine neurons, the neurites grow at a standard price. Thus, development cone movement can be halted on the acceptable target by a contact-dependent mechanism. The preliminary dialogue between pre- and postsynaptic cells doubtless includes a rise of calcium in development cone filopodia (Dai and Peng, 1993; Zoran et al. When frog or snail motor neurons are filled with a calcium-sensitive indicator dye, their growth cones show an area increase of calcium inside seconds of contact with a muscle cell. To test this idea, progress cone calcium was elevated by exposure to an ionophore, a molecule that spontaneously inserts into a neuron membrane, allowing calcium to cross freely into the cell (Mattson and Kater, 1987). In reality, progress cones are likely to grew to become stationary in all but a restricted vary of calcium concentrations, from 200 to 300 nM (Lankford and Letourneau, 1991). During early growth, individual hippocampal astrocytes display many thin filopodial processes that overlap with one another (Bushong et al. Over the subsequent few weeks, astrocytes produce a meshwork of fantastic processes, producing a mature spongiform morphology. The dramatic proliferation of synapse formation in vivo is carefully associated with the birth and outgrowth of astrocytes. When astrocytes are eliminated in a small area of the developing spinal wire, sensory afferents form fewer excitatory synapses on motor neurons (Tsai et al. Retinal ganglion cells grown in isolation show little synaptic activity, but the addition of astrocytes from their target causes a dramatic improve in the quantity and energy of synaptic contacts (Ullian et al. Similarly, an astrocyte-derived soluble issue can increase hippocampal inhibitory synapses (Elmariah et al. Astrocytes additionally induce synapse formation via direct perisynaptic contact, and that is mediated by a family of cell adhesion molecules, the -protocadherins (Garrett and Weiner, 2009). The synapse-inducing exercise of astrocytes is dependent upon several molecular signals that change throughout mind areas (Bosworth and Allen, 2017; Buosi et al. However, particular person astrocytes envelop a couple of dendrite from a person neuron. These embody ldl cholesterol, a vital membrane constituent, thrombospondins, a household of huge extracellular matrix proteins, and glypicans, a family of heparin sulfate proteoglycans (Mauch et al. Thus, genetic deletion of two thrombospondins leads to a significant discount in cortical synapses in vivo (Christopherson et al. Astrocytes also launch a glycoprotein, known as hevin, into the synaptic clefts of retinal ganglion cell excitatory synapses, the place it enhances a synaptic adhesion between a presynaptic neurexin and a 238 Development of the Nervous System postsynaptic neuroligin, thereby facilitating synaptogenesis (Singh et al. When hevin is genetically eliminated in mice, fewer excitatory synapses type within the visual target regions (Kucukdereli et al. Finally, astrocytes can communicate with neurons by way of the synaptic neurexinneuroligin adhesion system, described under. When one sort of neuroligin is deleted from cortical astrocytes, excitatory synapse operate is decreased while inhibitory operate is enhanced (Stogsdill et al. This remark suggests that adhesion molecules mediate the initial formation of synaptic contacts. Synaptogenesis involves several forms of adhesion molecules, including the immunoglobulin superfamily and the cadherins, a big family of calcium-dependent cell adhesion molecules (Seong et al. There are about 20 classical cadherins expressed within the nervous system, as nicely as >80 members of the cadherin superfamily subgroup, generally identified as protocadherins. The variety of the cadherin superfamily implies that these molecules might mediate synaptic specificity (Inoue and Sanes, 1997; Togashi et al. In truth, the ability of cerebellar granule cells to induce pontine axons to cease and differentiate, discussed above, could be explained by cadherin-7. Both pre- and postsynaptic cells categorical cadherin-7, and lowering its expression in presynaptic pontine neurons in vivo disrupts connectivity (Kuwako et al. Deletion of the 22 member protocadherin gene cluster results in a dramatic reduction of spinal cord synapses (Weiner et al. Cadherins not only convey pre- and postsynaptic membranes in close apposition, but also bind to glutamate receptors and anchor them to newly shaped synapse (Saglietti et al. The intracellular tail binds to -catenin, and interacts with actin via -catenin and actin-binding proteins. Nectin is an immunoglobulin-like adhesion molecule, and afadin is an actin filament-binding protein that connects nectin to the actin cytoskeleton (bottom). The nectin-afadin system organizes adherens junctions cooperatively with the cadherin-catenin system. During growth, nectin-1 and -3 localize at each the puncta adherentia junctions. This changes during development such that nectin-afadin involves be localized across the synaptic active zone. The cadherin-catenin system could colocalize with the nectinafadin system at each stage. Finally, most of the intercellular signaling systems 240 Development of the Nervous System that induce synaptic differentiation are conveyed by cell adhesion molecules (see below). Therefore, progress cone collapse and adhesion to the postsynaptic cell are a basic step of the transformation from growth cone to presynaptic terminal. In reality, presynaptic release sites are preassembled and transported down the axon as a packet of proteins (Ahmari et al. In reality, preformed postsynaptic websites can apparently induce the conversion of a growth cone right into a presynaptic terminal (Gerrow et al. Thus, new synapses show rapid molecular improvement, and either pre- or postsynaptic membranes can provoke the process. Since pre- and postsynaptic construction differs, distinct inductive signals have to be delivered to the growth cone and the postsynaptic membranes. Two signaling techniques with this kind of asymmetry can recruit particular synaptic components to all sides of the synaptic contact.
Generic 120 mg xenical overnight deliveryHere Eph-B expressing axons of the ventral retina are drawn to weight loss dr oz buy xenical 120 mg on line Ephrin-Bs in the medial tectum weight loss pills amphetamine purchase xenical 120mg on line, and Ephrin-B expressing retinal ganglion cell axons of the dorsal retina are drawn to weight loss pills jessica simpson generic 60mg xenical visa Eph-B expressing cells in the lateral tectum via backward signaling from the receptor to the ligand weight loss pills for over 50 proven xenical 60 mg. In Xenopus, the prevention of all Ephrin-B/ Eph-B interactions causes dorsal axons to project medially somewhat than laterally (Mann et al. Responses to Ephrin-A2 membranes differ from complete outgrowth inhibition (at higher concentrations and more temporal positions) to severalfold outgrowth promotion (at lower concentrations and nasal positions). In Xenopus, Ephrin-B expressing retinal ganglion cells from the dorsal retina are interested in the excessive ranges of Eph-B in the lateral tectum through reverse signaling, whereas in chicks Eph-B expressing retinal ganglion cells are attracted by way of forward signaling to the excessive levels of Ephrin-B within the medial tectum. In chicks (bottom), retinal ganglion cells additionally express Wnt receptors Frizzled (Fz), mediating attraction, and Ryk, mediating repulsion, responding to graded Wnt3 expression along the tectal D-V axis. In the medial to lateral axis, there also wants to be countergradients that reinforce the motion of the Ephrin-B system. Indeed, the morphogen Wnt3 is expressed in a medial excessive to lateral low gradient within the tectum. Wnt3 repels retinal ganglion cell axons via the Wnt receptor Ryk, which is expressed in a ventral high to dorsal low gradient in the retina. Dorsal retinal ganglion cells axons, in distinction, express a special Wnt receptor, Frizzled, which causes them to be drawn to Wnt3 (Schmitt et al. The next question is whether or not the Ephs and Ephrins are also involved in establishing topographic projections in other regions of the nervous system. N, nasal; T, temporal; A, anterior; P, posterior; D, dorsal; V, ventral; L, lateral; M, medial. Innervating axons must due to this fact not solely map to their appropriate topographic place in two dimensions, however they have to also discover the suitable layer during which to synapse, making concentrating on a three-dimensional drawback. In many instances, a laminated goal is composed of layers of physiologically and molecularly distinct cell sorts, and the innervating axons should subsequently choose between completely different cell types, probably based on chemical differences. In some circumstances, the layers are composed of essentially comparable cells, but the innervating axons, by way of an activity-based competition, segregate them into layers. This latter case may be thought-about for instance of the refinement of synaptic connections and shall be discussed extra totally in Chapter 9. For instance, pain and temperature sensory fibers innervate neurons in the dorsal spinal twine, with axon terminals targeted to distinct dorsal laminae representing different sensory modalities. The results of this laminar arrangement by various sorts of input is that somatosensory modalities make a multilayered registered map, such that a column of cells within the spinal wire represents one area of the physique with different modalities at completely different depths. In the previous chapter, we described the varying sensitivities of different classes of neurons to the repulsive results of Sema3A, which is expressed within the ventral layers only. Additional cues likely work cooperatively with Sema3A to set up this principal dorsal-ventral divide in the spinal cord, since in mice by which sema3A has been knocked out the terminals of the pain and thermoreceptive afferents are still kept to their native dorsal laminae (Taniguchi et al. It might be defined, at least partially, by the truth that the proximodistal patterning of the limbs is regulated by the identical mechanisms that regulate rostrocaudal patterning in the spinal cord. Multimodal, layered maps are utilized in a quantity of locations within the nervous system, including the cerebral cortex, a highly laminated structure, composed of various cell varieties in several layers which would possibly be innervated by different inputs. In vitro 174 Development of the Nervous System research utilizing membrane fractions of cells from distinct layers counsel that the concentrating on cues are membrane-associated (Castellani and Bolz, 1997). Ephrin-A5 is probably certainly one of the few cortical cues studied to date, expressed on the membranes of cells in layer 4 but not layer 5 (Mann et al. Much better understood at this stage is laminar-selective development in the retino-tectal pathway. Just a couple of of those layers receive enter from retinal ganglion cells, whereas other laminae receive enter from different sensory modalities, including auditory and mechanosensory, making the tectum a web site for multisensory integration. The axon terminals of distinct retinal ganglion cell varieties converge to type totally different sublaminae. Each retinal ganglion cell kind parses specific visible info, so that the convergence within, in addition to the segregation between tectal sublaminae constitutes the anatomical architecture that permits visible characteristic computation in the tectum. How tectal sublaminae are specified and formed during growth remains to be elucidated. What is obvious though, is that the retinorecipient layers express distinct mixtures of cell floor recognition molecules. Several different cadherin molecules, such as N-cadherin, R-cadherin, and T-cadherin, are additionally expressed in numerous mixtures of the tectal laminae, with N-cadherin being selectively present within the retinorecipient layers. These studies suggest that different molecules regulate completely different features of laminar-specific innervation, including recognition, innervation, and branching (Inoue and Sanes, 1997; Sanes and Yamagata, 1999; Yamagata et al. The tectum integrates a number of sensory modalities and issues acceptable motor instructions. Each sublamina has dedicated neuronal circuitry for the processing of distinct types of visible info. To examine how this layered neuropil forms within the embryo, Randlett and colleagues used zebrafish and selectively eliminated every of those cell varieties individually and in combination, utilizing mutants, morpholinos, and pharmacological inhibitors. The results have been putting, showing that any one of the neuronal types is able to forming a layered synaptic neuropil structure, even within the absence of presynaptic or postsynaptic partners (Randlett et al. Such Semaphorin-Plexin-mediated patterning by repulsion is a extensively employed strategy, additionally used for synaptic lamination in the Drosophila mind (Xie et al. These cell adhesion molecules are a half of the Immunoglobin superfamily and mediate homophilic adhesion, which is thought to implement laminaspecific concentrating on of synaptic terminals. Indeed, ectopic expression of Sidekick-1 in Sidekick-negative cells redirects their processes to the Sidekick-1 constructive sublamina. That homophilic adhesion molecules bind axonal terminals to the dendritic processes of cells that are destined to synapse onto each other is smart. Indeed, during subsequent phases of synapse improvement Sidekick-2 is required to promote the development of applicable connections between partners, together with some essential for movement processing (Krishnaswamy et al. Each synaptic lamina has a singular mixture of homophilic cell adhesion molecules, encoded by associated genes of the Immunoglobulin Superfamily. Misexpression and knockdown experiments show that these cell adhesion molecules could be sufficient and necessary for concentrating on synaptic terminals to particular sublaminae. Dscam1 is currently the best studied gene answerable for mediating recognition of self. Splice variants of Dscam have the potential to produce greater than 38,000 distinct protein isoforms through alternative splicing. Isoform technology is stochastic, so that each neuron expresses a novel mixture of many various Dscam1 splice isoforms. The alternatively spliced exons four, 6, 9, and 17 encode the N-terminal half of Ig2 (red), the N-terminal half of Ig3 (blue), the whole Ig7 (green), and the transmembrane area (yellow), respectively (from Schmucker et al. As a neurite branches, every sister department expresses the identical set of Dscam1 isoforms. These isoforms bind homophilically and this transduces a sign to dissociate the receptor complex and provoke a repulsive response. Because the filopodia of a development cone or dendrites of a neuron will express the exact same mixture of splice isoforms, their binding to one another will result in repulsion, selling branching and selfavoidance. Because this mechanism prevents neurites from clumping together, such spreading of filopodia and neuronal processes is important for development cone exploration, for synaptic terminal branching, and spreading of dendritic arbors (Wang et al. Interestingly, in vertebrates, the process of neuronal self-recognition seems to have developed independently, mediated by the family of protocadherins (Pcdhs), yet operating along the same strategy of utilizing diverse splicing of IgSf proteins (Lefebvre et al. Remarkably, though the variety of Pcdh individual splice variants is far lower than for Drosophila Dscam1, Pcdh interactions are thought to function as tetrameric cis-complexes, thus introducing an additional level of combinatorial coding (Schreiner and Weiner, 2010).
Order xenical 60 mg overnight deliveryThe limbic system-associated membrane protein is an Ig superfamily member that mediates selective neuronal growth and axon concentrating on weight loss in face cheap 60 mg xenical amex. Signaling mechanisms underlying Slit2-induced collapse of Xenopus retinal progress cones weight loss pills without exercise generic 120mg xenical with amex. Endocytosisdependent desensitization and protein synthesis-dependent resensitization in retinal growth cone adaptation weight loss pills 7253 60mg xenical mastercard. Pathfinding in a big vertebrate axon tract: isotypic interactions guide retinotectal axons at multiple choice factors weight loss 45 year old woman purchase 60mg xenical with amex. The intricate relationship between microtubules and their related motor proteins throughout axon progress and upkeep. A quelle epoque aparaissent les expansions des cellule neurveuses de la moelle epinere du poulet. The oriented emergence of axons from retinal ganglion cells is directed by laminin contact in vivo. Response of retinal ganglion cell axons to striped linear gradients of repellent steerage molecules. A novel chemotaxis assay reveals the acute sensitivity of axons to molecular gradients. Response of mitochondrial traffic to axon willpower and differential department growth. Filopodia and actin arcs information the meeting and transport of two populations of microtubules with distinctive dynamic parameters in neuronal growth cones. Mutations affecting development cone guidance in Drosophila: genes needed for guidance towards or away from the midline. Semaphorin3A regulates neuronal polarization by suppressing axon formation and selling dendrite progress. Age-related modifications underlie switch in netrin-1 responsiveness as development cones advance alongside visual pathway. Change in chemoattractant responsiveness of growing axons at an intermediate goal. Postnatally induced formation of the corpus callosum in acallosal mice on glia-coated cellulose bridges. Conversion of neuronal development cone responses from repulsion to attraction by cyclic nucleotides. Polysialic acid regulates growth cone conduct during sorting of motor axons within the plexus region. The directed development of retinal axons towards surgically transposed tecta in Xenopus: an examination of homing behaviour by retinal ganglion cells. Slit proteins regulate distinct aspects of retinal ganglion cell axon steerage within dorsal and ventral retina. Distinct molecular interactions mediate neuronal process outgrowth on non-neuronal cell surfaces and extracellular matrices. Growth cone morphology and trajectory within the lumbosacral region of the chick embryo. Netrin1 produced by neural progenitors, not floor plate cells, is required for axon steering in the spinal twine. Plexin-A3 and plexin-A4 restrict the migration of sympathetic neurons but not their neural crest precursors. Neural cell adhesion molecules of the immunoglobulin superfamily: function in axon development and steerage. Essential function of heparan sulfates in axon navigation and concentrating on within the creating visual system. In vitro experiments on the elements determining the course of the outgrowing nerve fiber. Normal branching, induced branching, and steering of cultured parasympathetic motor neurons. Analysis of axon tract formation within the zebrafish brain: the role of territories of gene expression and their boundaries. The development of a easy scaffold of axon tracts within the mind of the embryonic zebrafish, Brachydanio rerio. Turning of nerve growth cones induced by localized will increase in intracellular calcium ions. EphB-ephrinB bidirectional endocytosis terminates adhesion allowing contact mediated repulsion. Sequence evaluation and neuronal expression of fasciclin I in grasshopper and Drosophila. Squeezing axons out of the grey matter: a job for slit and semaphorin proteins from midline and ventral spinal cord. Chapter 6 Target Selection As a progress cone nears the tip of its journey, it must find applicable goal cells with which to synapse. At the opposite, connections start out only roughly specified, however then kind themselves out through functional validation. When they enter the target space, they decelerate, and begin searching for their postsynaptic partners who may additionally be looking, via dendritic development, for the axons that will innervate them. Molecular limitations may also be erected across the borders of the goal space in order that the incoming axons are corralled till they discover probably the most appropriate companions. Having finally arrived at the correct location, the rising axons choose postsynaptic cells, depending on the diploma of genetically programmed specificity, perhaps specific dendrites or areas of these cells, and begin to make synapses. Almost all of the above phases of concentrating on and synapse formation can happen very accurately in the full absence of neural exercise. When action potentials are blocked from the earliest phases, retinal axons can still navigate to their appropriate topographic connections within the tectum and start to make synapses on tectal cells (Harris, 1984). Finally, the very specific connections that Drosophila photoreceptor axons make with their synaptic partners in the optic lobes of the mind kind usually at the ultrastructural stage in mutants that block the generation of electrical potentials, neurotransmitter launch, and vesicle endocytosis (Hiesinger et al. The last phase of goal choice, nonetheless, often entails the refinement of connections. This section is dependent on neural and synaptic exercise, for as synapses are formed, the nervous system can begin to function for the primary time. During this phase, the developing organism can start to take a look at out the wiring and if essential get rid of connections which would possibly be misplaced or poorly functioning. This functional verification is completed in order that the product of neural development, the mind, works as nicely as attainable when it faces the true world. Nerves, tracts, columns, bundles, and fasciculi typically travel past quite so much of potential targets. Bundling of axons into nerves and subsequent defasciculation of subbranches facilitates channeling growth cones into applicable target areas, delivering progress cones into the vicinity of their future companions. The neuromuscular system of the fruitfly larva, Drosophila, has been a robust experimental model for studying the specification of connectivity. Composed of 30 body wall muscle tissue per half phase, every is innervated by a specific motor neuron. How is that this point-to-point matching of 30 motor neuron-muscle pairs attained (there are 2. Motor neurons and musculature develop largely independently and are then matched up by successive axon pathfinding decisions (Broadie and Bate, 1993; Prokop et al.
References - Cahalan MK, Litt L, Botvinick EH, Schiller NB: Advances in noninvasive cardiovascular imaging: Implication for the anesthesiologist, Anesthesiology 66:356-372, 1987.
- Ferreiro JA. Immunohistochemistry of basal cell adenoma of the major salivary glands. Histopathology 1994;24: 539-542.
- Kfoury AG, Smith JC, Farhoud HH, et al. Adjuvant intrapleural amphotericin B therapy for pulmonary mucormycosis in a cardiac allograft recipient. Clin Transplant. 1997;11(6):608-612.
- Lechat P, Mas JL, Lascault G, et al: Prevalence of patent foramen ovale in patients with stroke, N Engl J Med 318:1148, 1988.
- Summers BK, Siegle RJ. Facial cutaneous reconstructive surgery: general aesthetic principles. J Am Acad Dermatol 1993;29:669-681.
|